Numerical Analysis of Effect of Stern Flap on Hydrodynamic Performance of Amphibious Vehicles
-
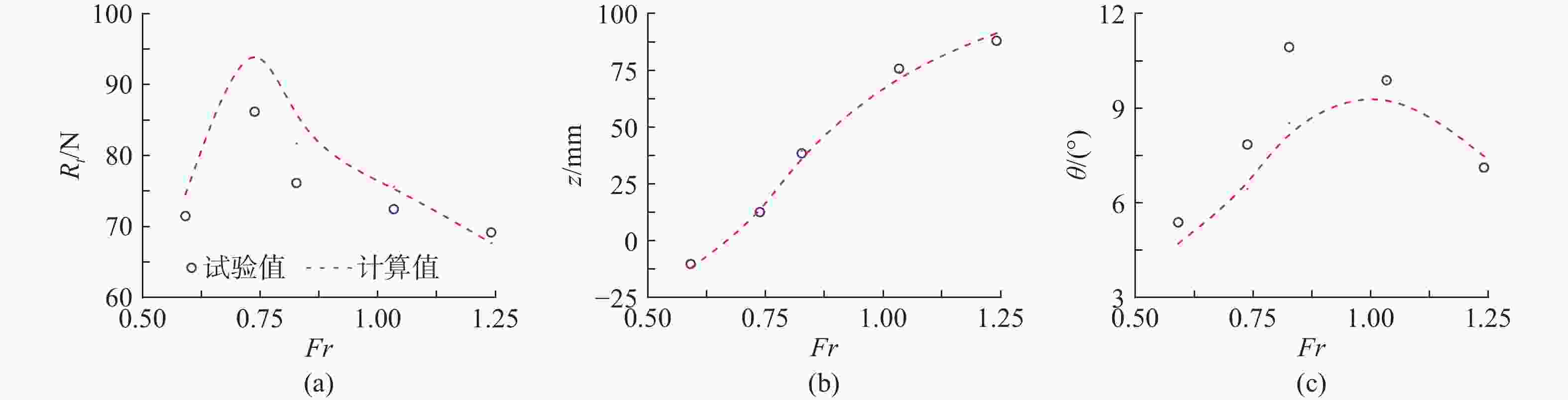
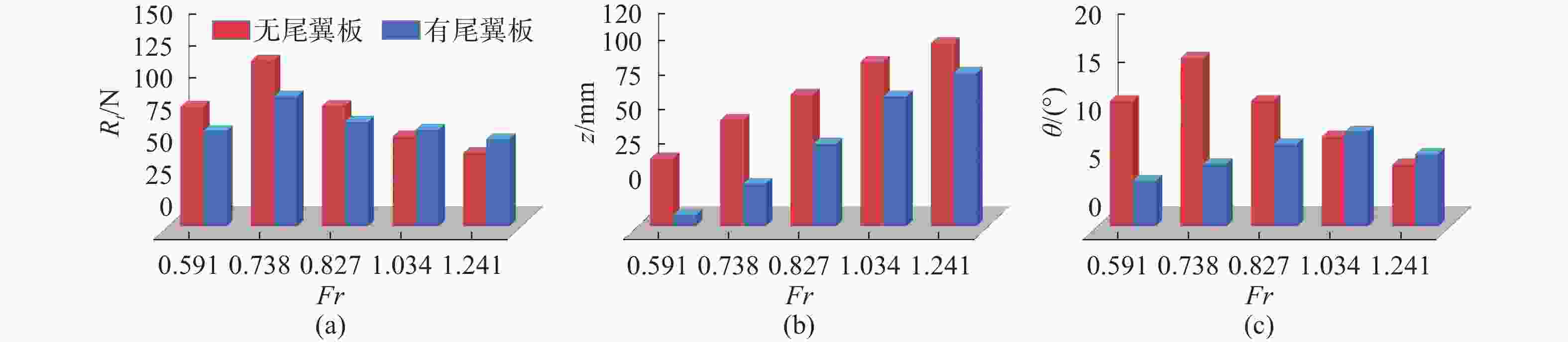
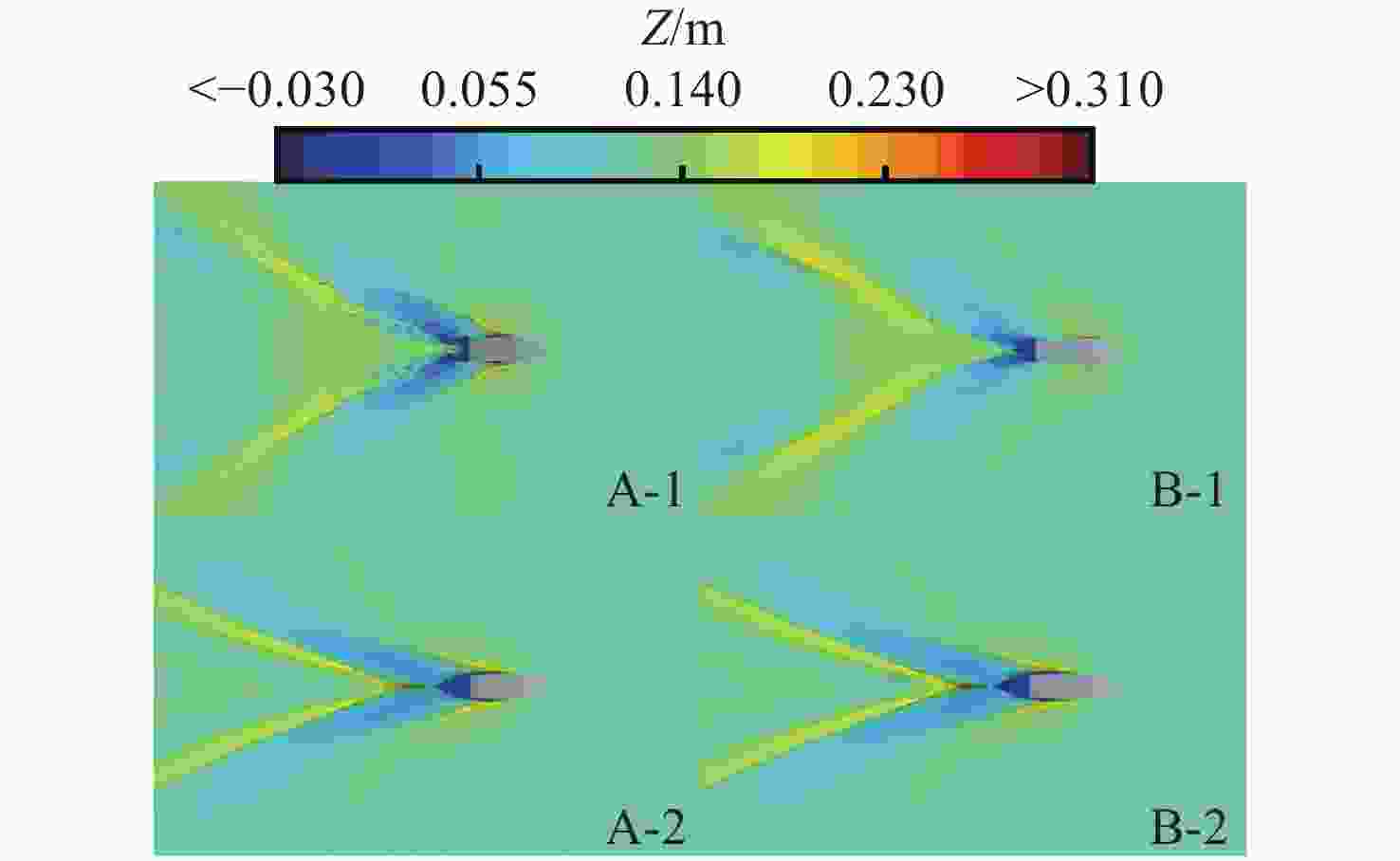
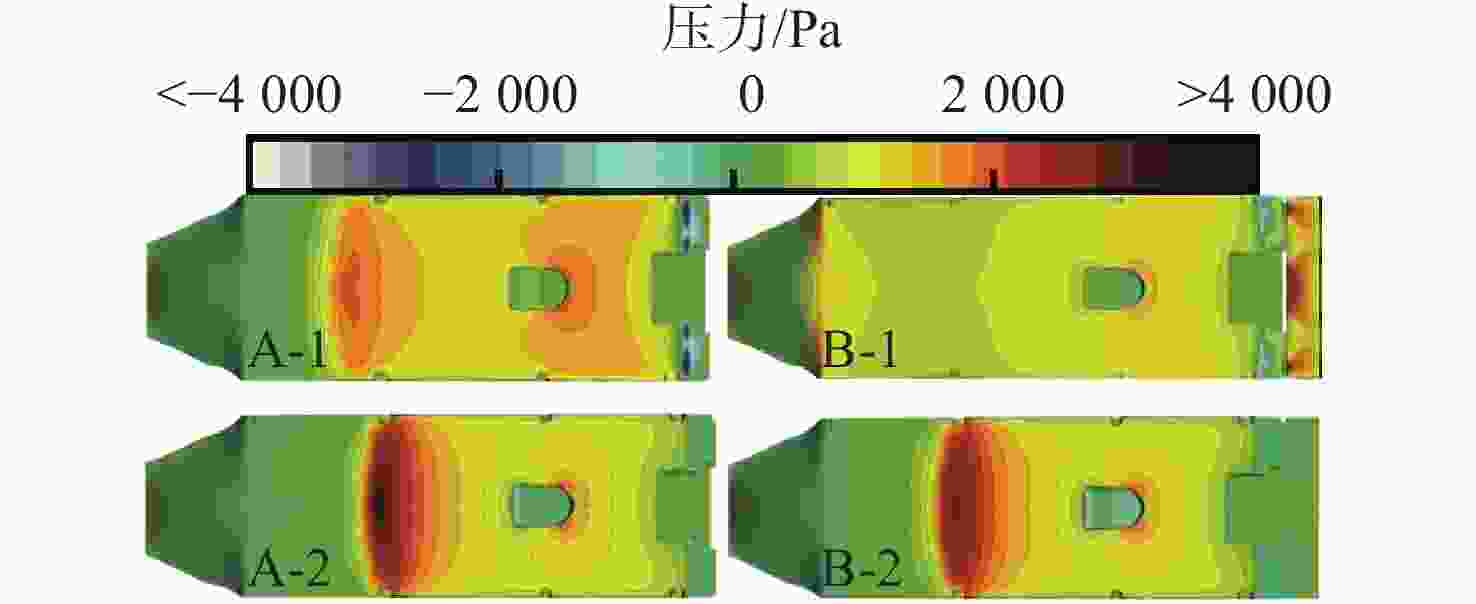
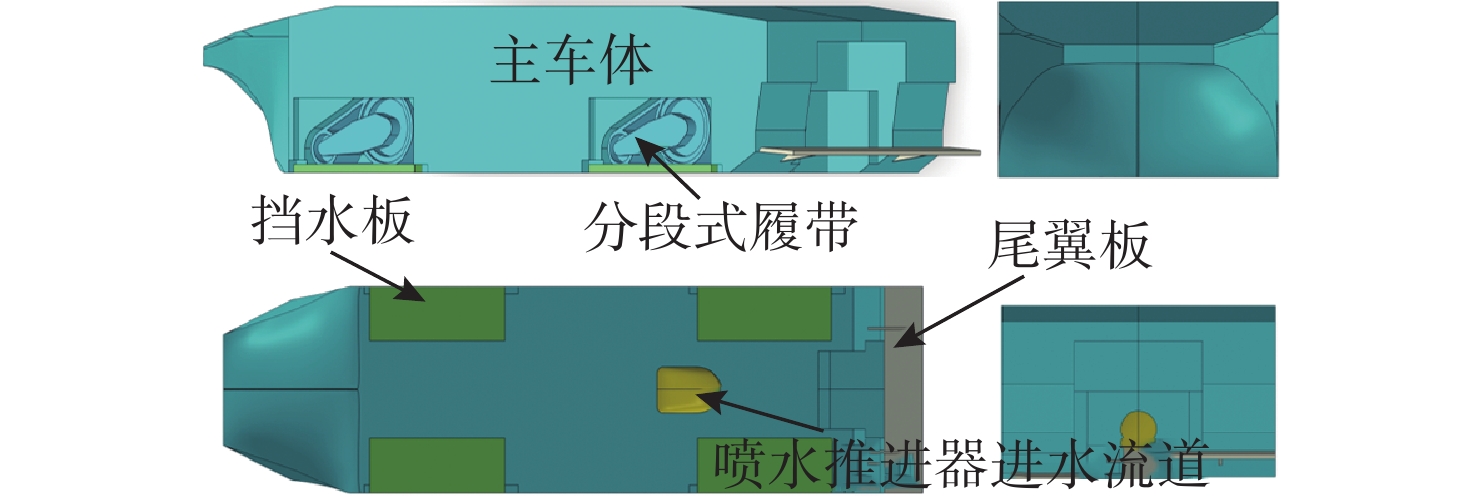
摘要: 为揭示尾翼板对水陆两栖车水动力性能的影响机制, 结合静水拖曳试验与数值仿真方法, 基于STAR-CCM+数值计算对比分析了加装尾翼板前后两栖车在不同航速下的运动参数、自由液面波形及车身压力分布特性。研究结果表明: 尾翼板可显著改变水陆两栖车水动力特性, 其作用效果具有明显的速度依赖性。运动参数方面, 尾翼板使航行阻力呈先降后增趋势, 在弗劳德数为0.738时减阻率达21.6%; 同时, 其对航行姿态的调控作用突出, 纵摇角度峰值差异达63.3%, 且有效抑制计算航速域内的垂荡运动。在流场特性方面, 尾翼板通过改变车体纵摇角度和垂荡幅值, 重构了两栖车周围流场波形和车身压力分布特征, 低速时改善艉部流场分离, 高速时需防范过度埋首引发的气蚀风险。文中研究为水陆两栖车的水动力优化设计提供了理论依据。Abstract: To explore the effect mechanism of the stern flap on the hydrodynamic performance of amphibious vehicles, still water towing tests and numerical simulation methods were combined to comparatively analyze the motion parameters, free surface waveforms and pressure distribution of the vehicle at different speeds before and after the installation of the stern flap based on STAR-CCM+. The results show that the stern flap significantly alters the hydrodynamic characteristics of the amphibious vehicle, with a significant speed dependence in the effect. In terms of motion parameters, the stern flap gets the resistance lower and then higher, with a resistance reduction rate of 21.6% at Fr=0.738. The regulation effect on sailing attitude is prominent, with a peak difference in pitch angle reaching 63.3% at the same time, effectively suppressing the heave motion within the speed range. In terms of flow field characteristics, by changing the pitch angle and heave amplitude, the stern flap significantly reconstructs the waveform of the flow field around the amphibious vehicle and the pressure distribution characteristics of vehicle. At a low speed, the flow field separation of the stern can be improved. At a high speed, the risk of cavitation caused by over plough-in should be prevented. The study provides a theoretical basis for the hydrodynamic optimization design of amphibious vehicles.
-
Key words:
- amphibious vehicle /
- stern flap /
- towing test /
- sailing attitude /
- hydrodynamic performance
-
表 1 模型主尺度参数
Table 1. Main scale parameters of the model
名称/单位 符号 数值 质量/kg m 29.110 长度/m LOA 1.290 宽度/m B 0.383 深度/m D 0.241 平均吃水深度/m d 0.122 船艏吃水深度/m dF 0.071 船艉吃水深度/m dA 0.118 排水量/m3 $ \nabla $ 0.029 绕Y轴转动质量/(kg·m2) Iyy 10.371 尾翼板宽度/m b 0.071 表 2 网格细节计算结果(Fr=0.827)
Table 2. Calculation results of mesh details
网格编号 网格单元数 Rt/N M01 2 613 217 93.962 M02 1 531 197 94.076 M03 864 187 95.322 表 3 水动力系数计算结果(Fr=0.827)
Table 3. Calculation results of hydrodynamic coefficient
系数名称 符号 数值 网格收敛比 Rg 0.091 精确度估计阶数 PRE 13.12 网格误差估计值 δRE/% 0.0104 修正系数 Cg 22.582 不确定度 Ug/% 0.459 -
[1] SHIHUA J, LIEM R, LI Y. An improved experimental framework of amphibious marine vehicle hull hydrodynamics[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2024, 49(1): 80-91. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2023.3303956 [2] SUN C L, XU X J, ZOU T A, et al. Investigation on trim control of semi-planning amphibious cargo truck using experimental and numerical approaches[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2022, 236(3): 1322-1333. doi: 10.1177/09544062211021445 [3] LEE D, KO S, PARK J, et al. An experimental analysis of active pitch control for an assault amphibious vehicle considering waterjet-hydrofoil interaction effect[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9(8): 894. doi: 10.3390/jmse9080894 [4] ZHANG G Q, FENG Y K, XU X J. Effect of waterjet propulsion on the hydrodynamic performance of caterpillar track amphibious vehicle[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 309: 118505. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.118505 [5] SONG K W, GUO C Y, WANG C, et al. Numerical analysis of the effects of stern flaps on ship resistance and propulsion performance[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 193: 106621(1-19). [6] 刘健, 周广礼, 彭嘉澍, 等. 双壳体混合驱动水下滑翔机结构原理及水动力性能研究[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(1): 25-31. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2023-0150LIU J, ZHOU G L, PENG J S, et al. Research on structural principle and hydrodynamic performance of double-hull hybrid powered underwater glider[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(1): 25-31. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2023-0150 [7] WANG X Z, LIU L W, ZHANG Z G, et al. Numerical study of the stern flap effect on catamaran’s seakeeping characteristic in regular head waves[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020(206): 107172. [8] 潘柏衡, 高霄鹏. 尾插板对滑行艇阻力及纵向稳定性影响试验分析[J]. 船海工程, 2018, 47: 26-28. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-7953.2018.01.006 [9] 彭锟, 刘影. 尾翼板对轮式两栖车航行阻力特性影响的研究[J]. 车辆与动力技术, 2014, 4: 15-19.PENG K, LIU Y. Influence of empennage on resistance characteristics of a wheeled amphibious vehicle[J]. Vehicle & Power Technology, 2014, 4: 15-19. [10] GUAN G, TIAN Y, LIANG G P. Multi-objective optimization of a fishery administration vessel’s stern flap design based on surrogate model[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2025, 337: 121912. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2025.121912 [11] 孙承亮, 徐小军, 唐源江, 等. 分段履带式水陆两栖车减阻增速试验及数值仿真[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2022, 44(5): 201-208. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202205022SUN C L, XU X J, TANG Y J, et al. Experimental and numerical simulation of reducing resistance an increasing speed for a segmented-track amphibious vehicle[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2022, 44(5): 201-208. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202205022 [12] 王丽丽, 张家旭, 刘涛, 等. 压浪板对两栖车辆水动力特性影响的数值分析[J]. 系统仿真技术, 2018, 14(2): 113-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1964.2018.02.007WANG L L, ZHANG J X, LIU T, et al. Numerical analysis on effect of wave suppression plate on hydrodynamical characteristics of amphibious vehicle[J]. System Simulation Technology, 2018, 14(2): 113-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1964.2018.02.007 [13] 郑义, 董文才, 姚朝帮, 等. 排水型深V船系列模型尾板减阻试验研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2011, 45(4): 475-480. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2011.04.007ZHENG Y, DONG W C, YAO C B, et al. Experimental study on resistance reduction of displacement type deep-V hull model using stern flap[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao tong University, 2011, 45(4): 475-480. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2011.04.007 [14] SONG K W, GUO C Y, GONG J, et al. Influence of interceptors, stern flaps, and their combinations on the hydrodynamic performance of a deep-vee ship[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018(170): 306-320. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.10.048 [15] ZHANG G Q, WANG J C, FENG Y K, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on the hydrodynamic performance of an amphibious vehicle under the interaction of traveling mechanism mudguard and waterjet propulsor duct[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2025(340): 122426. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2025.122426 [16] SUN C L, XU X J, WANG L H, et al. Research on hydrodynamic performance of a blended wheel-track amphibious truck using experimental and simulation approaches[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021(228): 108969. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.108969 [17] BI X S, SHEN H L, ZHOU J, et al. Numerical analysis of the influence of fixed hydrofoil installation position on seakeeping of the planing craft[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2019(90): 101863. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2019.101863 [18] FENG Y K, ZHANG G Q, WANG J C, et al. Numerical investigation of the hydrodynamic characteristics of a light high-speed amphibious vehicle in still water under oblique inflow conditions[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2025, 37(4): 047150 doi: 10.1063/5.0271256 [19] 冯亿坤. 尾鳍与胸鳍联合推进的仿生鱼自主游动数值模拟研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2021. [20] 毕明琪. 多船体编队航行水动力性能数值与试验研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2024. -




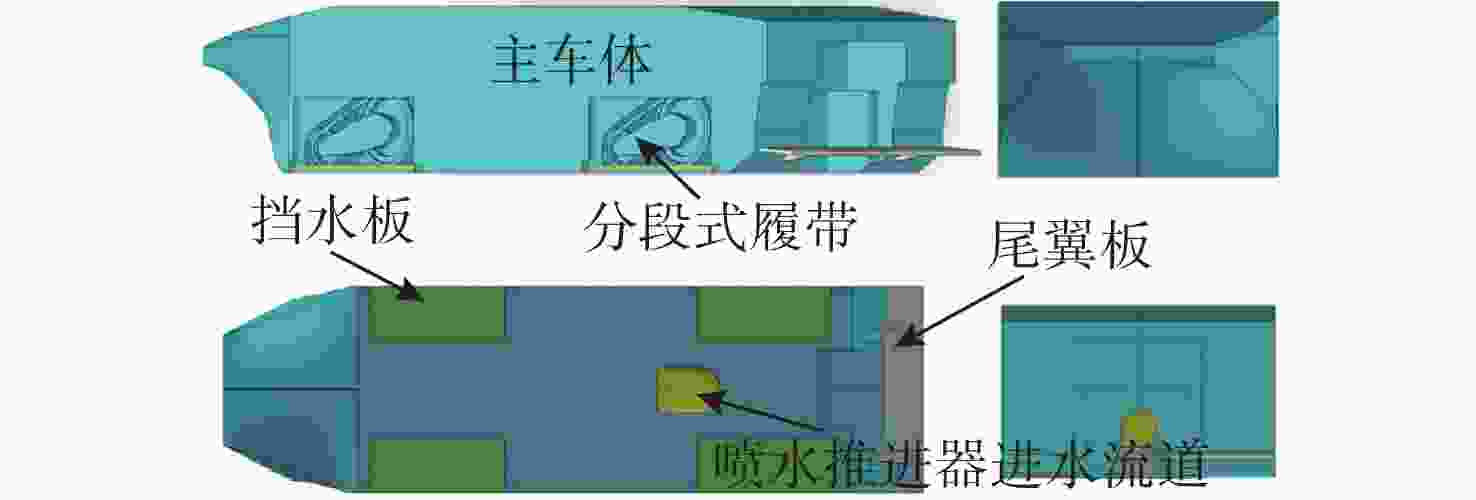
 下载:
下载: