Research on USV path planning for assisted multi-AUVs navigation
-
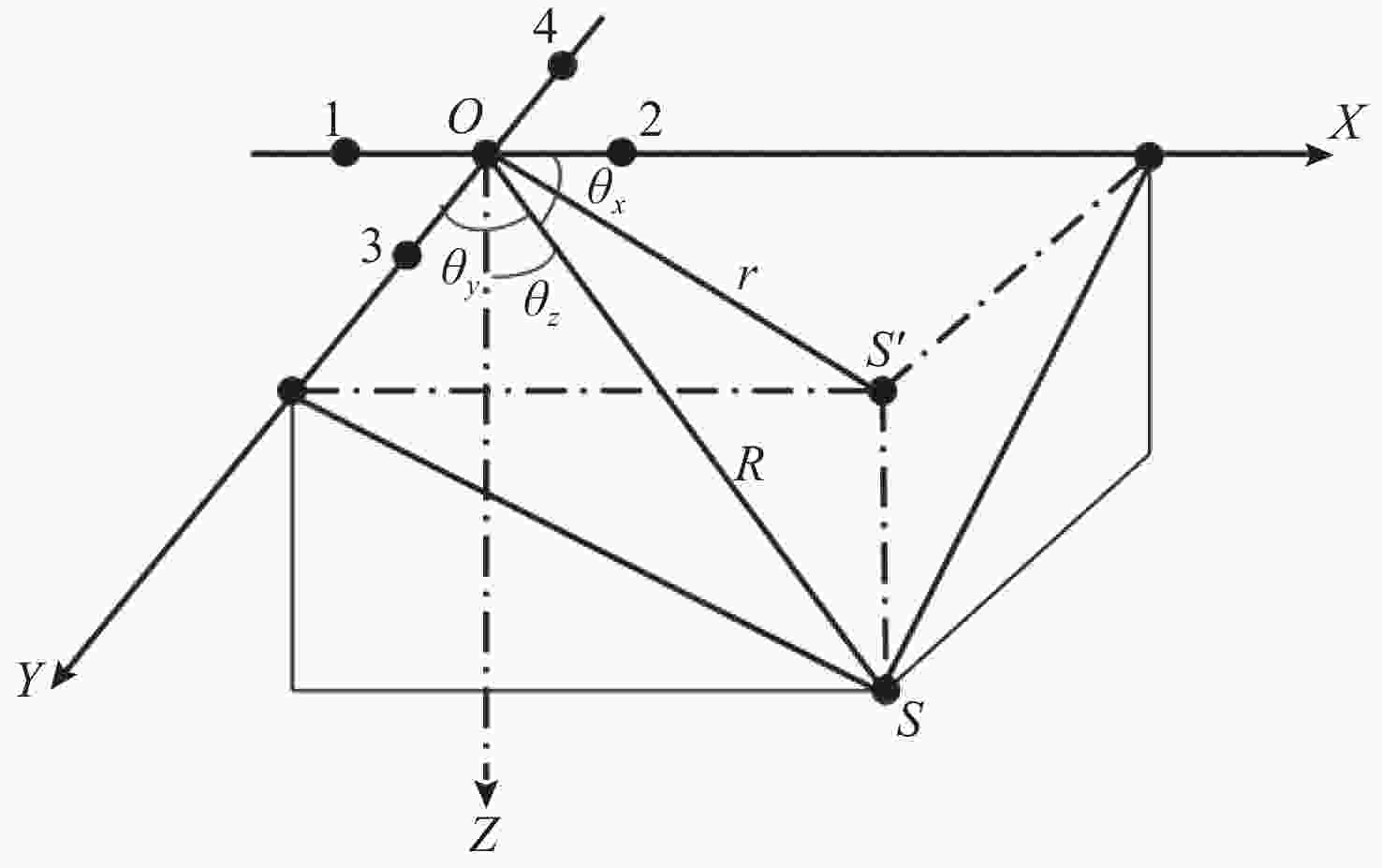
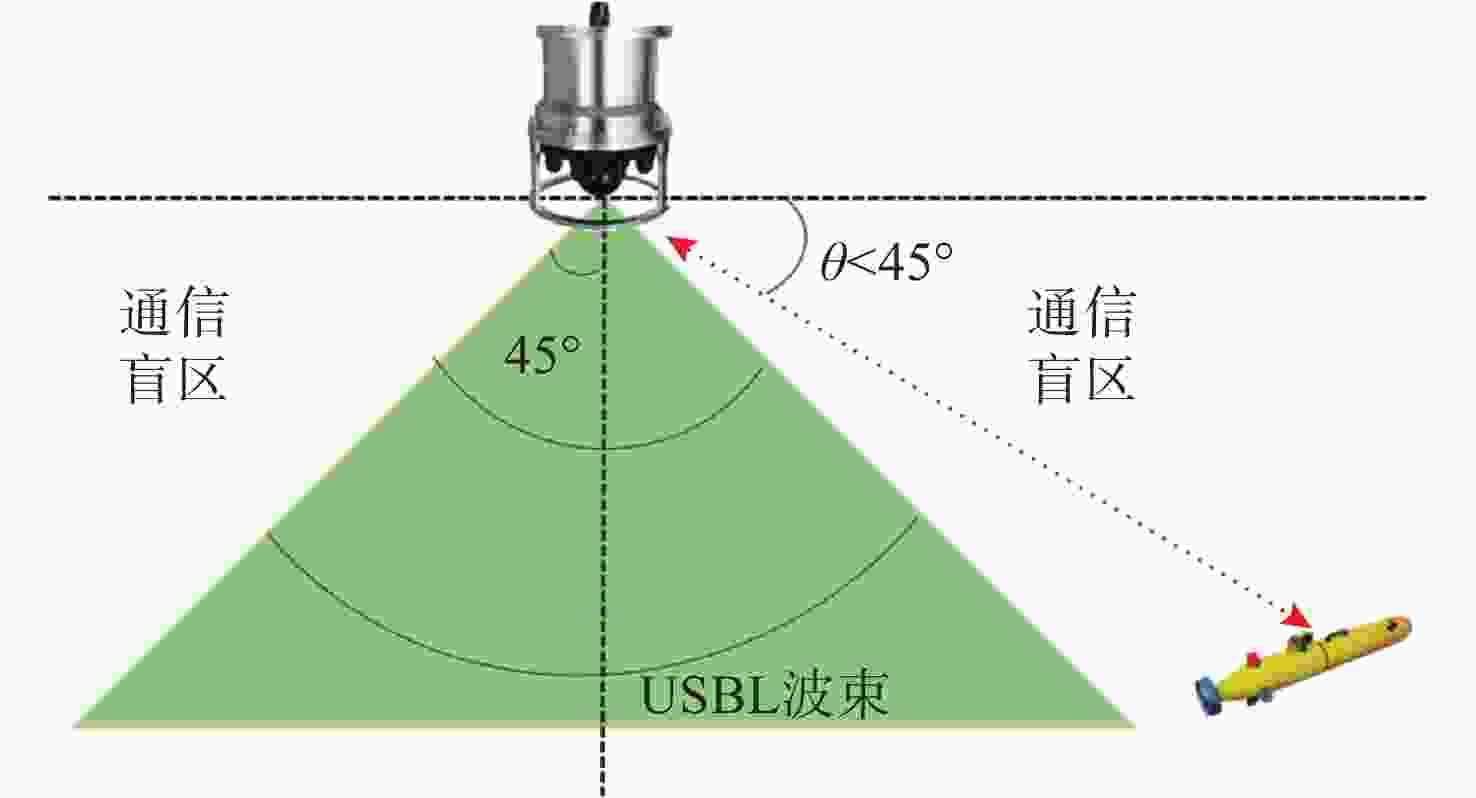
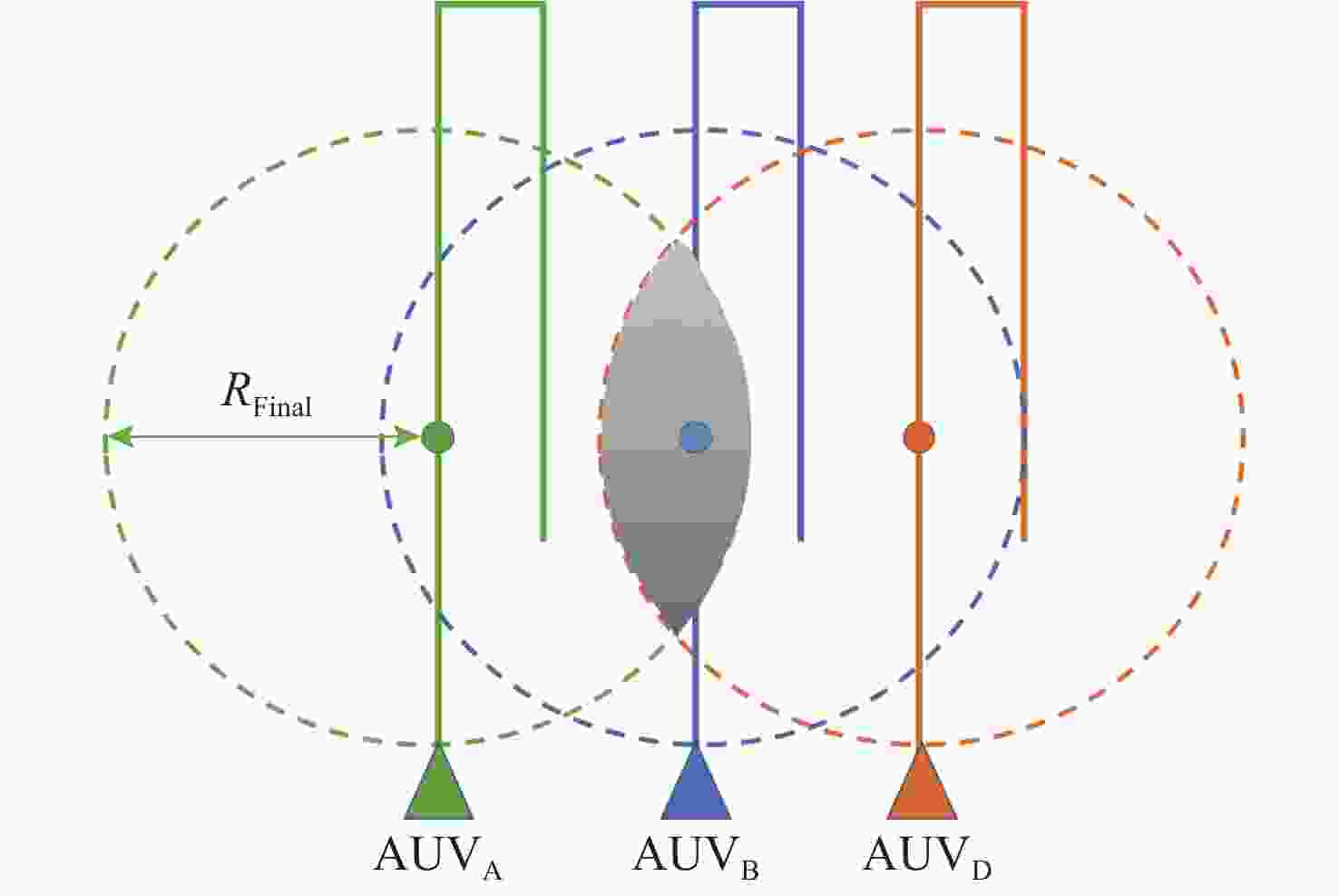
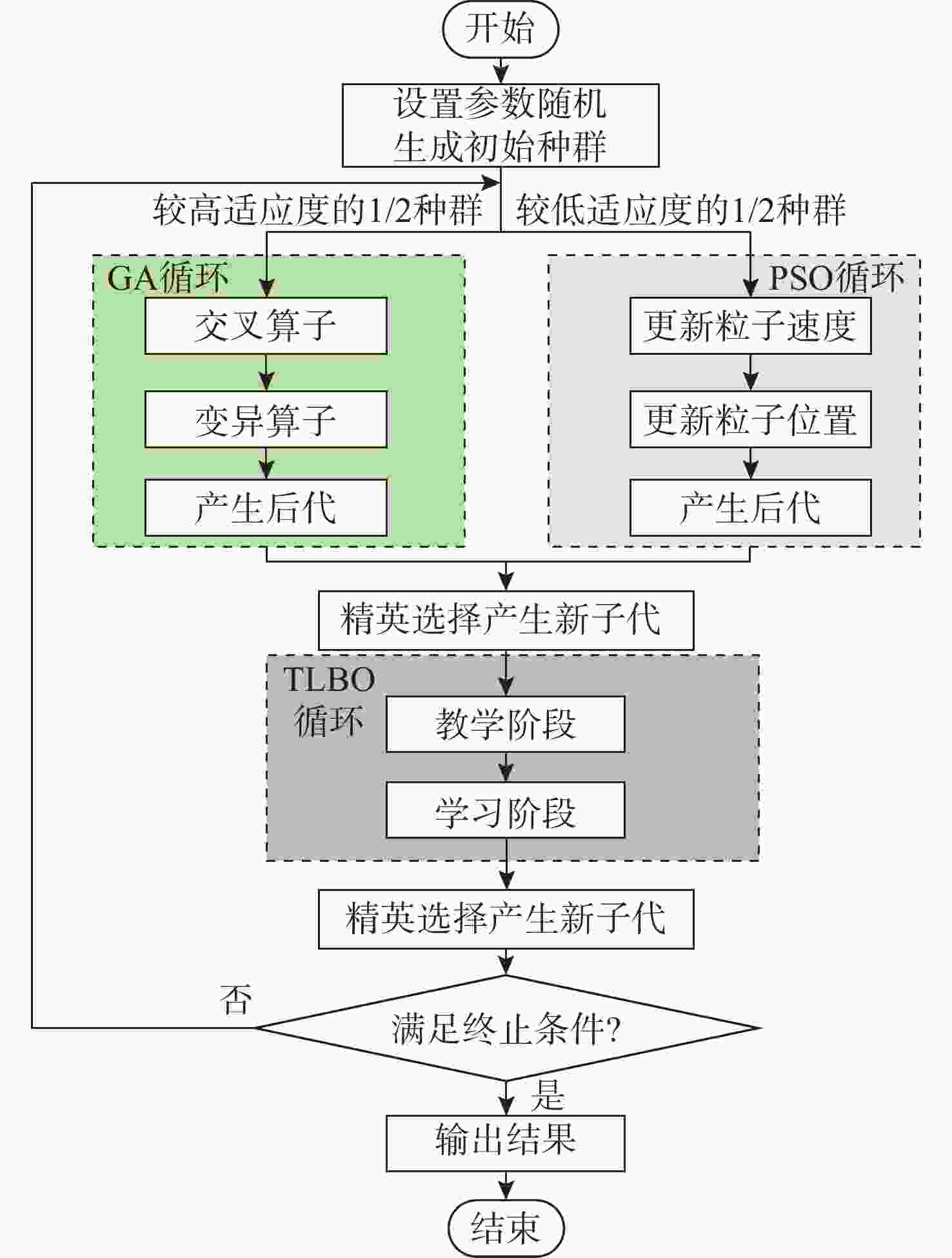
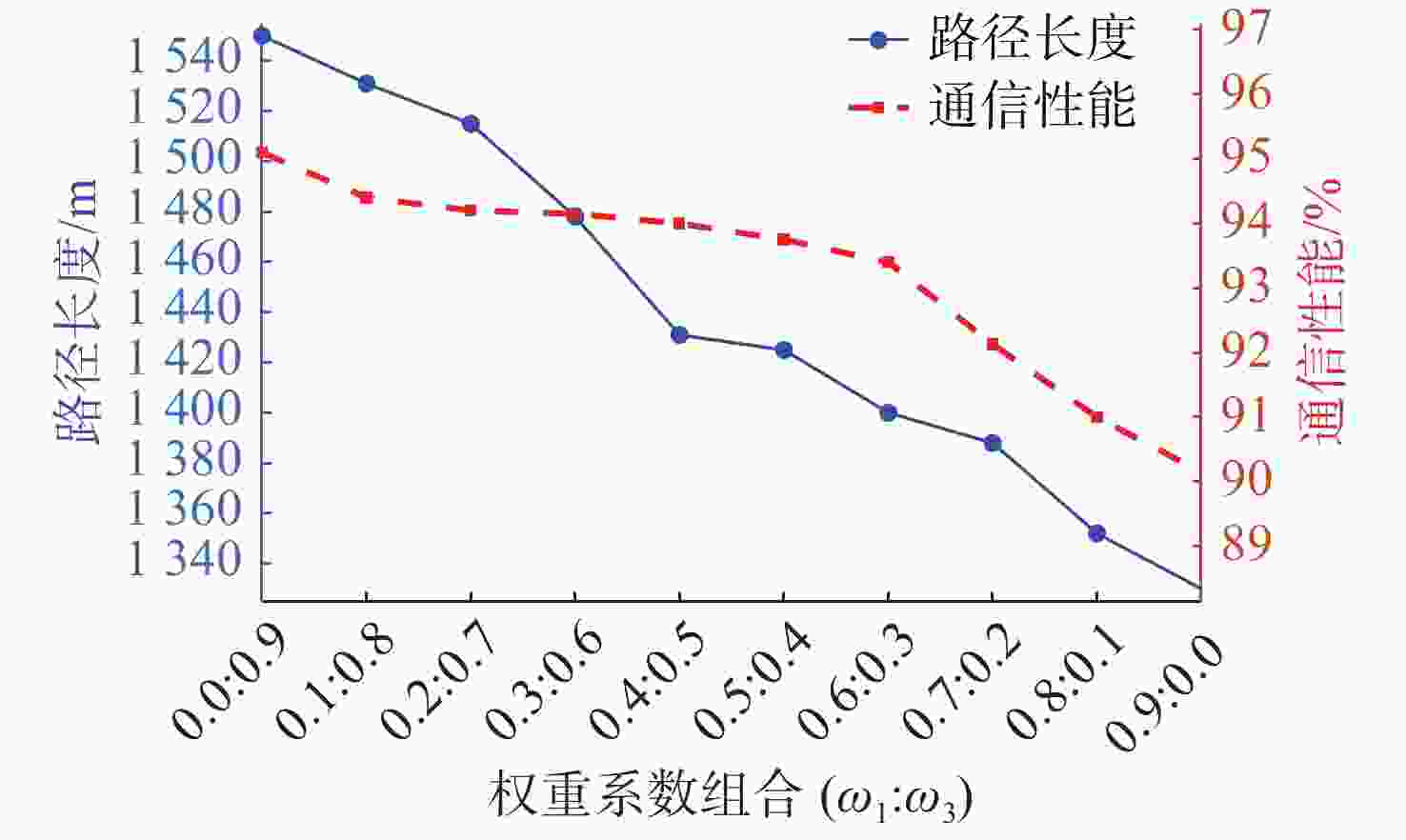
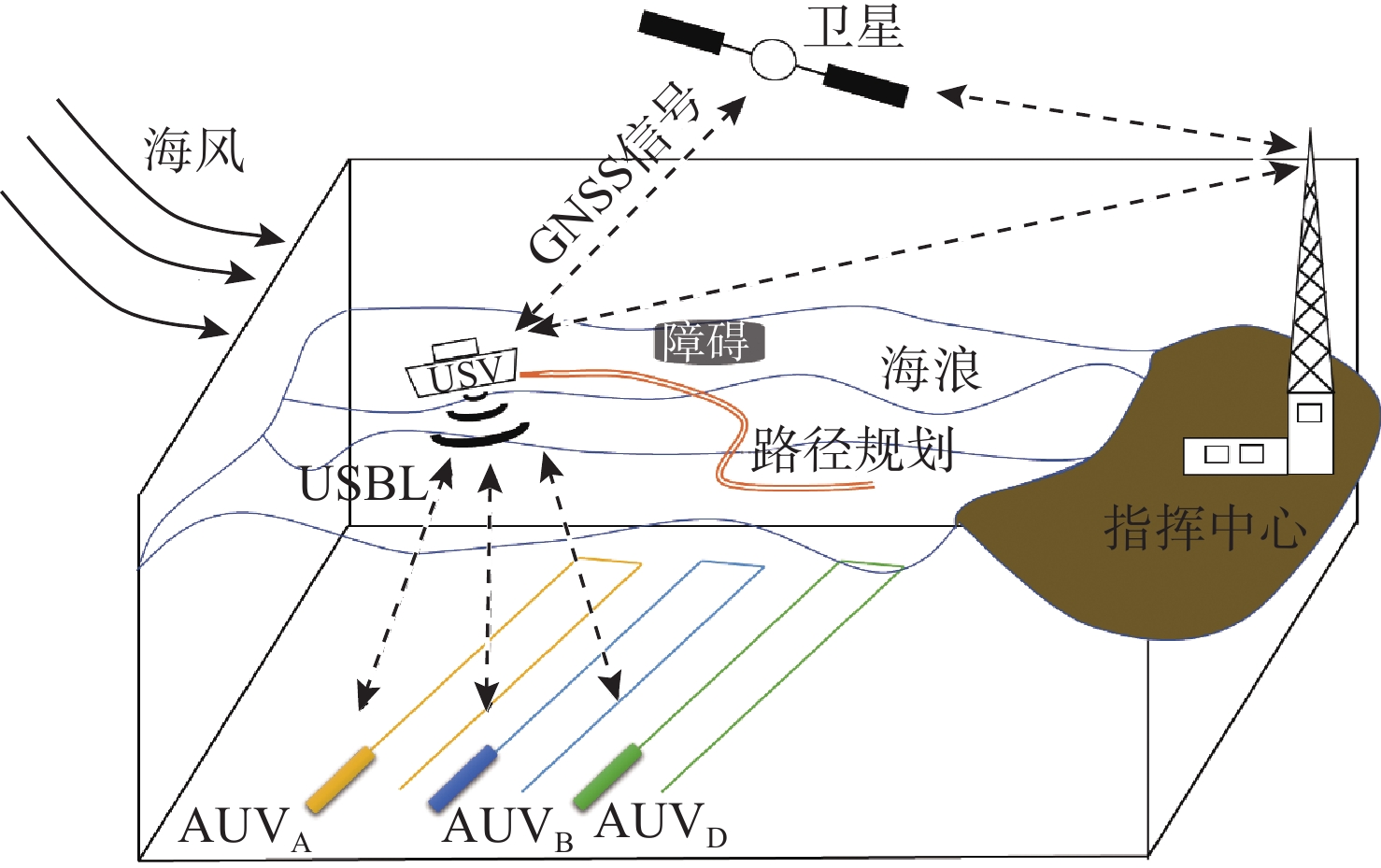
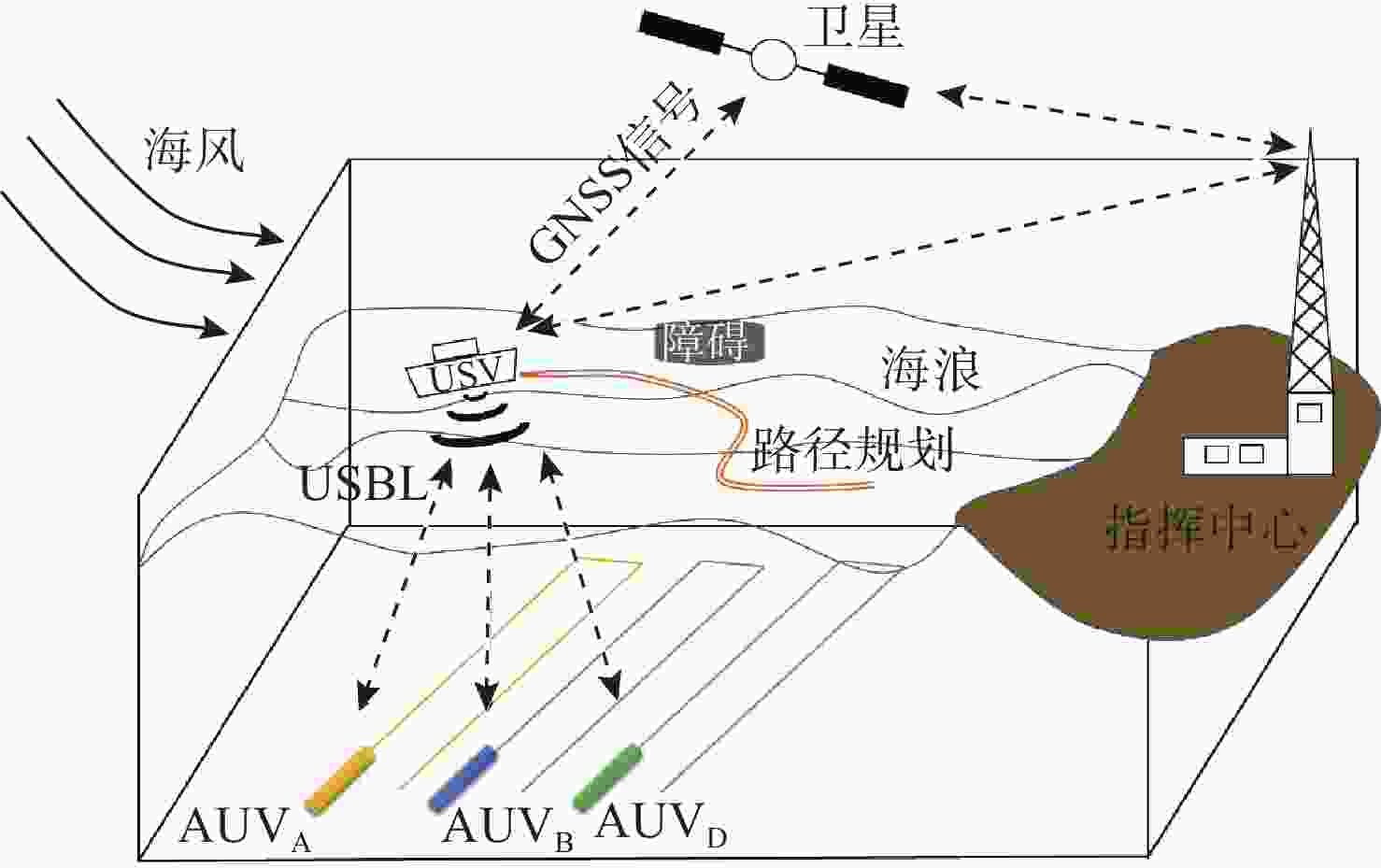
摘要: 面向无人水面艇(USV)辅助多自主水下航行器(AUV)作业应用背景, 提出一种基于超短基线定位系统(USBL)的USV-AUV多目标协同路径规划方法。通过分析USBL工作原理, 结合海洋水声信号传播特性, 由USBL信号的有效区、射线声学理论定义的声线传播边界及根据声呐方程计算出的最大作用距离共同构成协同作业的稳定通信范围。在确保USV-AUV保持在水声通信有效范围内的同时, 进一步优化路径长度、路径平滑度和USV-AUV的通信性能, 建立了USV-AUV协同路径规划的多目标优化模型, 利用改进遗传算法求解, 探究通信距离、AUV作业深度等参数对USV规划路径影响的仿真实验, 结果表明, 所提方法在满足USBL通信约束的前提下, 能够有效提升USV与AUV协同工作的稳定性, 为多AUV执行复杂海洋任务提供可靠保障。
-
关键词:
- 无人水面艇-自主水下航行器协同 /
- 超短基线定位系统 /
- 路径规划
Abstract: In the context of USV-assisted multi-AUVs operations, this paper proposes a multi-objective collaborative path planning method for USV-AUVs systems based on the Ultra-Short Baseline Locating System (USBL). The working principle of the USBL is analysed, and combined with the acoustic signal propagation characteristics in marine environments, the stable communication range for collaborative operations is defined by the effective zone of the USBL signal, the acoustic ray propagation boundary defined by ray acoustics theory, and the maximum effective range calculated using the sonar equation. While ensuring that the USV and AUV remain within the effective range of acoustic communication, the method further optimises path length, path smoothness, and communication performance between the USV and AUV. A multi-objective optimisation model for USV-AUVs collaborative path planning is established, and an improved genetic algorithm is used to solve it. Simulation experiments are conducted to investigate the influence of parameters such as communication distance and AUV operational depth on the USV planning path. The results indicate that the proposed method can effectively enhance the stability of USV-AUVs collaborative operations while satisfying USBL communication constraints, providing a reliable foundation for multiple AUVs to execute complex marine missions. -
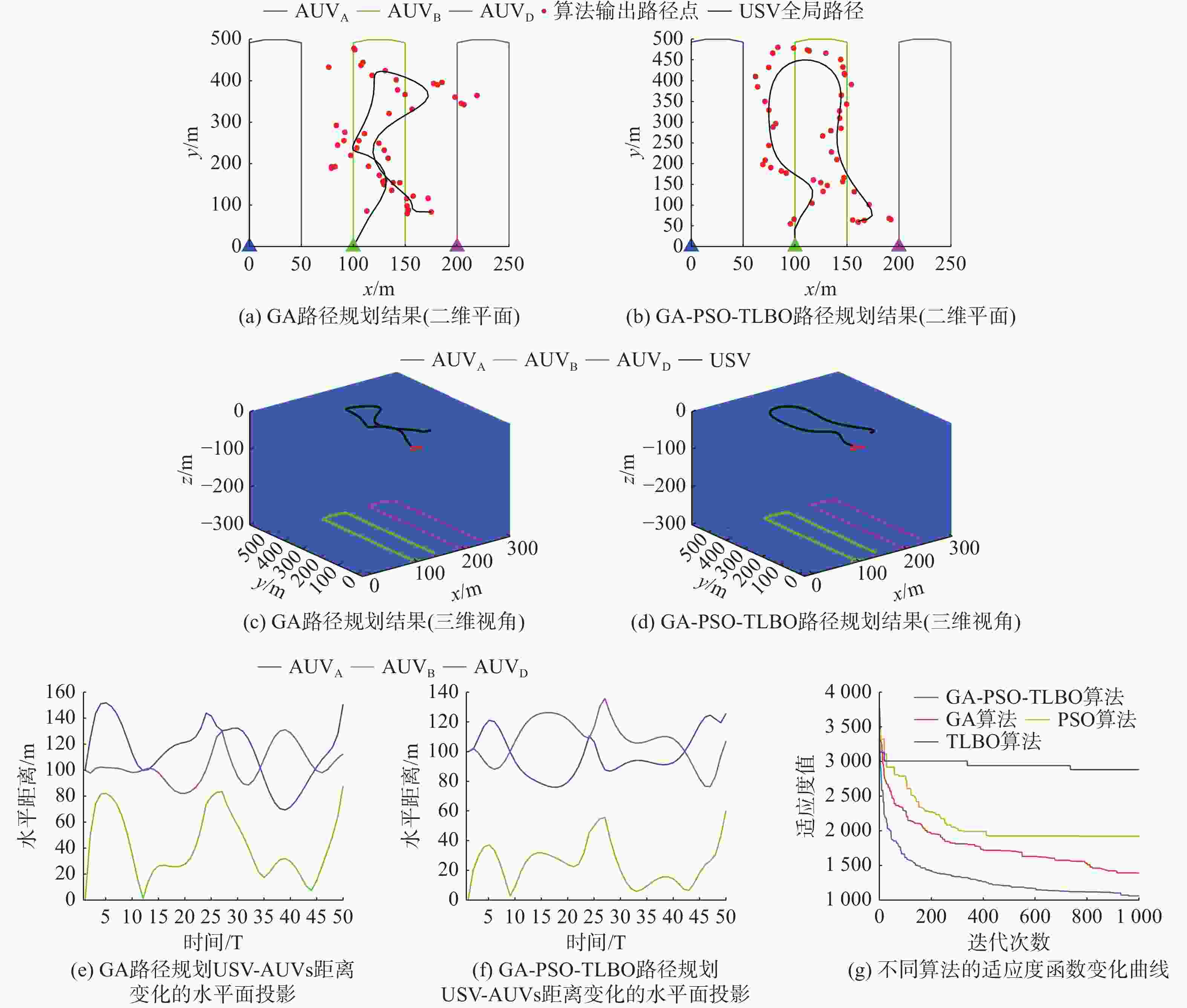
表 1 不同高度差的路径规划结果
Table 1. Path planning results under different height differences
USV-AUV
高度差/mGA GA-PSO-TLBO 路径
长度/m通信性
能评估/%USV
最大转
角/(°)路径
长度/m通信性
能评估/%USV
最大转
角/(°)100 1052 97.33 40.16 1052 97.33 40.40 150 1279 96.00 75.37 1130 96.67 75.20 200 1280 95.34 92.56 1203 96.33 66.07 250 1311 95.33 93.81 1211 95.50 103.60 300 1562 94.10 107.84 1431 94.40 103.53 表 2 不同稳定通信距离的路径规划结果
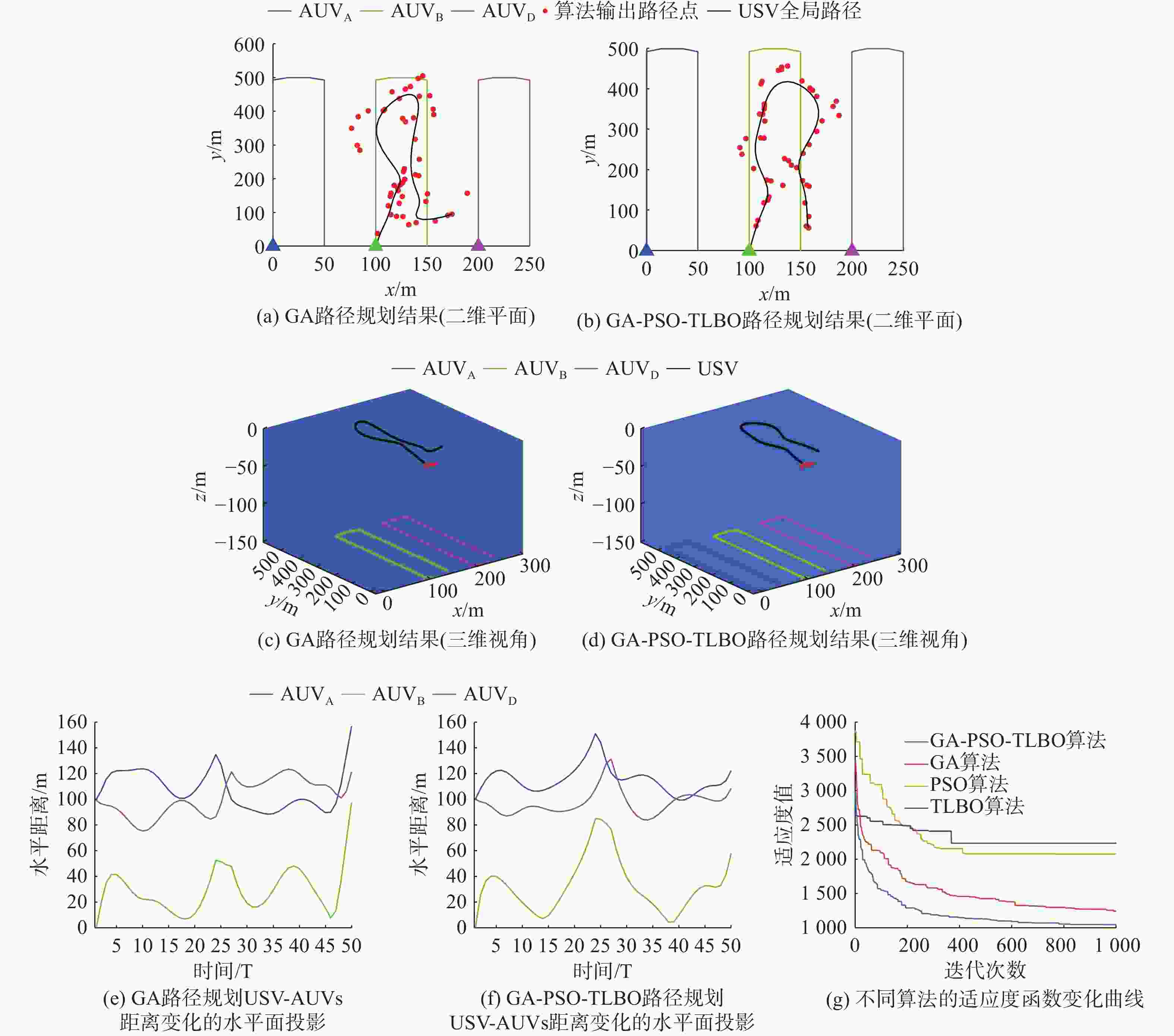
Table 2. Path planning results for different stable communication distances
稳定通
信距离/mGA GA-PSO-TLBO 路径
长度/m通信
性能
评估/%USV
最大
转角/(°)路径
长度/m通信
性能
评估/100%USV
最大
转角/(°)100 1050 79.74 40.24 1050 79.74 40.70 150 1280 82.98 72.79 1170 84.50 72.77 200 1280 89.29 93.44 1250 90.33 84.35 250 1310 93.13 90.98 1200 95.50 100.80 300 1660 94.99 111.10 1474 97.00 106.77 -
[1] BERTRAM V. Unmanned surface vehicles-a survey[J]. Skibsteknisk Selskab, 2008, 1: 1-14. [2] 焦慧峰, 叶琛, 王文初, 等. 基于移动长基线和导航误差修正的USV/UUV协同导航算法[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(5): 864-873. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2024-0005JIAO H F, YE C, WANG W C, et al. USV/UUV cooperative navigation algorithm based on moving long baseline and navigation error correction[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(5): 864-873. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2024-0005 [3] 冯业, 杜民. 基于无人机平台的水下通信中继技术研究[J]. 电脑与信息技术, 2025, 33(2): 61-63,90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1228.2025.02.013FENG Y, DU M. Research on underwater communication relay technology based on UAV platform[J]. Computer and Information Technology, 2025, 33(2): 61-63,90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1228.2025.02.013 [4] YUAN X, WANG J, TONG C, et al. Integrated path planning for AUV communication efficiency and obstacle avoidance based on ant colony optimization and three-dimensional dynamic window algorithm[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2025, 156: 104465. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2025.104465 [5] 王洋, 沈同圣, 汪涛, 等. 融合多特征的水声通信信号调制识别方法[J]. 声学学报, 2025, 50(5): 1338-1348. doi: 10.12395/0371-0025.2023246WANG Y, SHEN T S, WANG T, et al. Modulation classification method based on multi-feature fusion for underwater acoustic communication signals[J]. Acta Acustica, 2025, 50(5): 1338-1348. doi: 10.12395/0371-0025.2023246 [6] FAN Y, QIAO S, WANG G, et al. A modified adaptive Kalman filtering method for maneuvering target tracking of unmanned surface vehicles[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 266: 112890. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112890 [7] 谢志华, 蒋丞, 吴俊超, 等. 水下目标多平台协同定位和跟踪方法[J]. 声学学报, 2021, 46(6): 1028-1038.XIE Z H, JIANG C, WU J C, et al. Method of multi-platform cooperative localization and tracking for underwater targets[J]. Acta Acustica, 2021, 46(6): 1028-1038. [8] SANG H, YOU Y, SUN X, et al. The hybrid path planning algorithm based on improved A* and artificial potential field for unmanned surface vehicle formations[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 223: 108709. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.108709 [9] GUO X, JI M, ZHAO Z, et al. Global path planning and multi-objective path control for unmanned surface vehicle based on modified particle swarm optimization(PSO) algorithm[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 216: 107693. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107693 [10] XIN J, ZHONG J, YANG F, et al. An improved genetic algorithm for path-planning of unmanned surface vehicle[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(11): 2640. doi: 10.3390/s19112640 [11] 孙硕, 杨少龙, 向先波, 等. 基于动态领域势场法的船舶避碰路径规划[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(5): 679-686. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2022-0058SUN S, YANG S L, XIANG X B, et al. Ship collision avoidance path planning based on dynamic domain potential field[J]. Journal of Unmanned Underwater Systems, 2023, 31(5): 679-686. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2022-0058 [12] 宋俊辉, 刘宇庭, 郭世杰. 动态环境下AIP-RRT*与DGF-APF融合的机器人路径规划[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2025, 46(3): 51-64. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2413268SONG J H, LIU Y T, GUO S J. Robot path planning by fusion of AIP-RRT* and DGF-APF in dynamic environments[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2025, 46(3): 51-64. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2413268 [13] 庞舟岐, 郝程鹏, 林晓波, 等. 基于深度强化学习的水下无人航行器高速目标捕获路径规划[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2025, 42(10): 1968-1980. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2025.40272PANG Z Q, HAO C P, LIN X B, et al. High speed target acquisition path planning for underwater unmanned vehicles based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2025, 42(10): 1968-1980. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2025.40272 [14] XUE J, HE M, CHEN J, et al. Improved DDPG based on enhancing decision evaluation for path planning in high-density environments[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2025: 127378. [15] VERMA D, VERMA H, TIWARI P K. A hybrid approach for MRI brain image segmentation using KIFECM-IPSO algorithm[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2025, 268: 126239. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.126239 [16] LIU N, HU Z, WEI M, et al. Improved A* algorithm incorporating RRT* thought: A path planning algorithm for AGV in digitalised workshops[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2025: 106993. [17] XU B, ZHU H, GUO Y. A robust iterative algorithm for SINS/USBL integrated navigation based on dual hydrophone differential model[J]. Measurement, 2025, 242: 115854. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2024.115854 [18] 杨士莪. 水声传播原理[M]. 哈尔滨工程大学出版社, 2007. [19] LI X, ZHANG W. Application of Snell's law in reflection raytracing using the multistage fast marching method[J]. Earthquake Research Advances, 2021, 1(1): 100009. doi: 10.1016/j.eqrea.2021.100009 [20] LIU Y, CHEN Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Research on reconstruction of the global sound speed profile combining partial underwater prior information[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 2024, 200: 102516. doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2024.102516 [21] SUN T, JIN J, YANG Y, et al. A multi-order Fractional Fourier domain feature union method for active sonar target classification[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2023, 205: 109257. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2023.109257 [22] AN L, HUANG X, YANG P, et al. Adaptive bézier curve-based path following control for autonomous driving robots[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2025, 189: 104969. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2025.104969 [23] 卢俊, 张群飞, 史文涛. 水下探测通信一体化关键技术分析[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2018, 26(5): 470-479. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2018.05.015LU J, ZHANG Q F, SHI W T. Analysis on the key technology of integrated underwater detection and communication[J]. Journal of Unmanned Underwater Systems, 2018, 26(5): 470-479. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2018.05.015 [24] YUN Y, GEN M, ERDENE T N. Applying GA-PSO-TLBO approach to engineering optimization problems[J]. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering, 2023, 20(1): 552-571. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2023025 -




 下载:
下载: