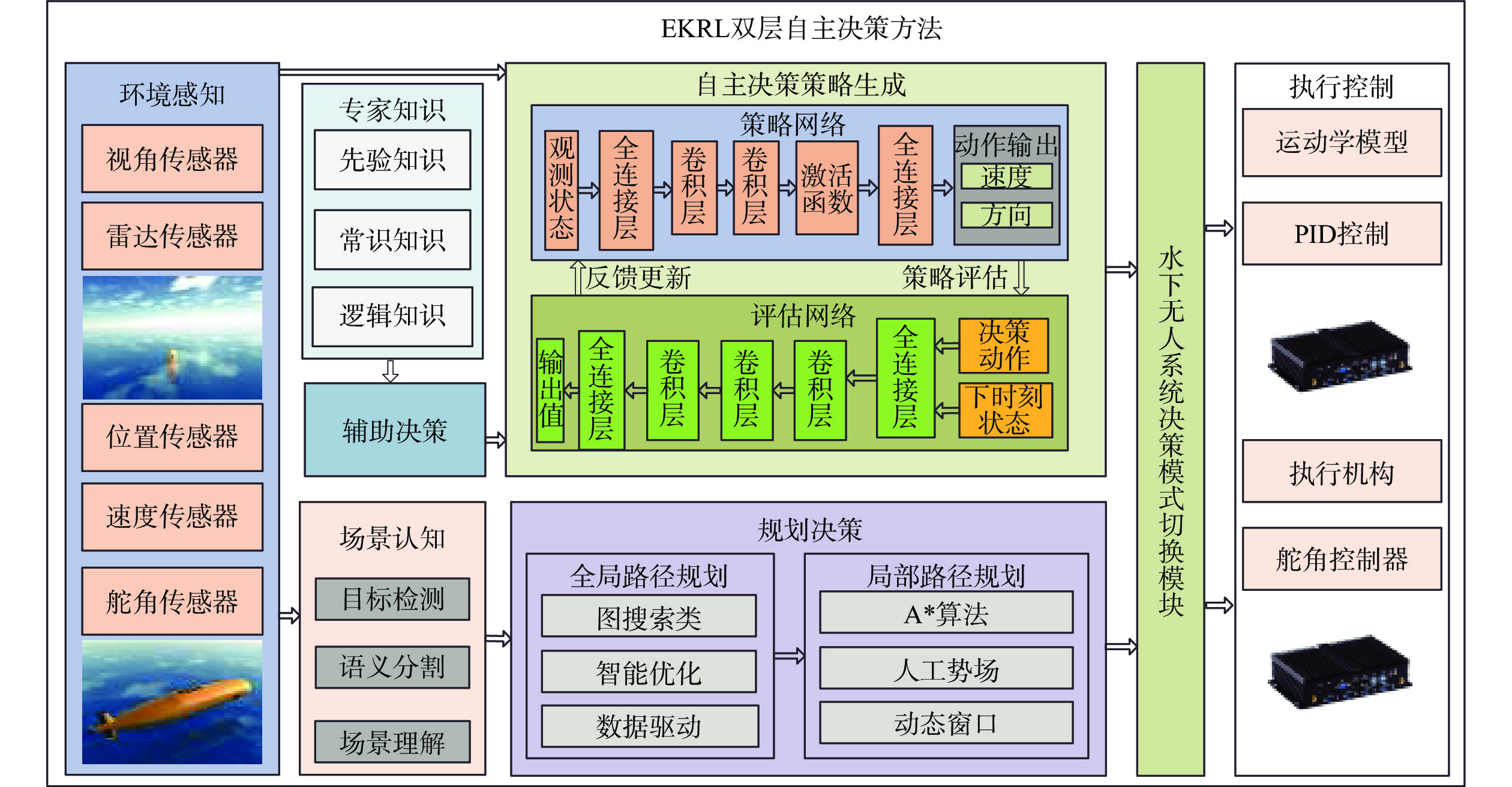
A Double-Layer Autonomous Decision-Making Method Based on Expert Knowledge and Deep Reinforcement Learning
-
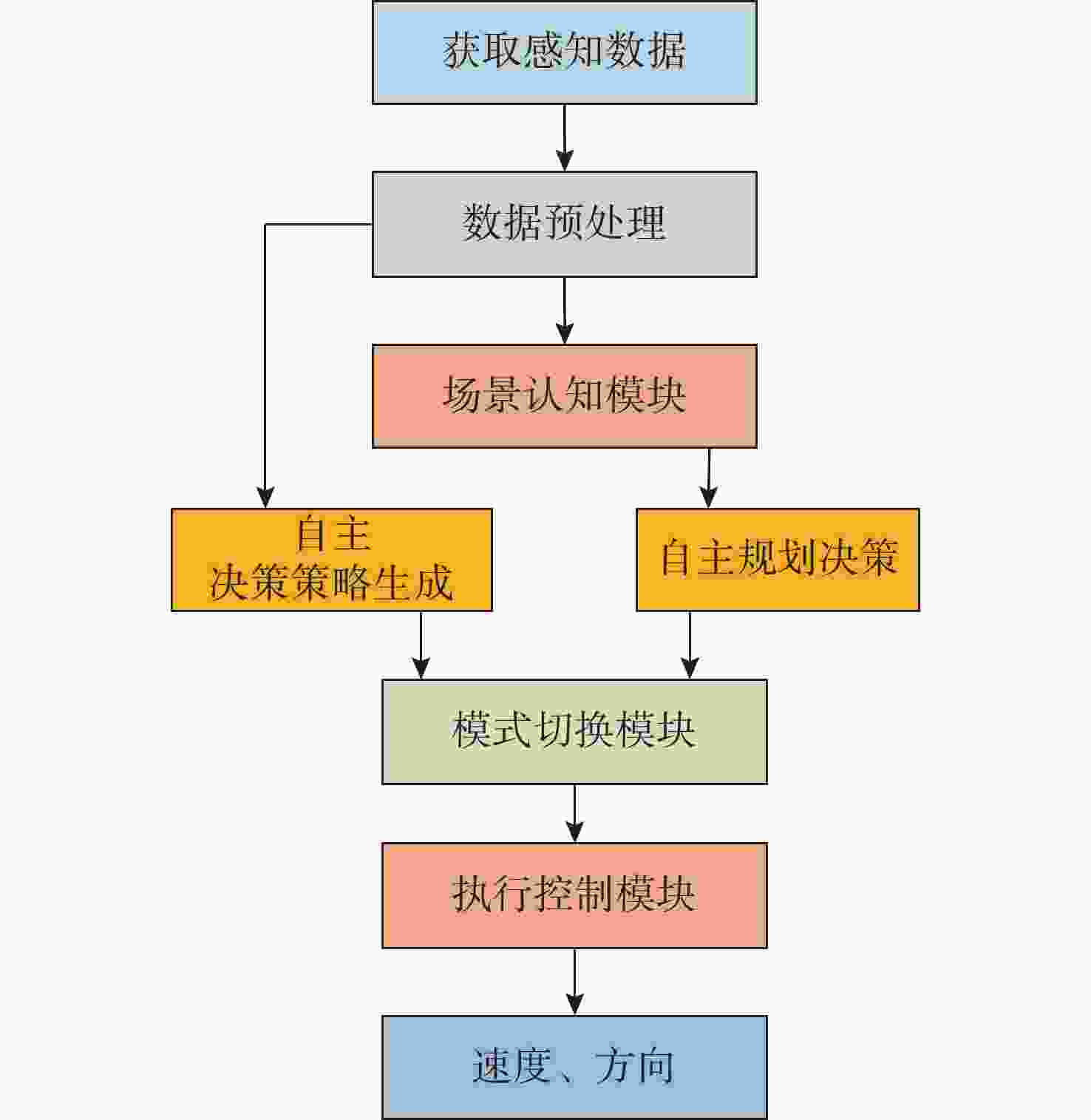
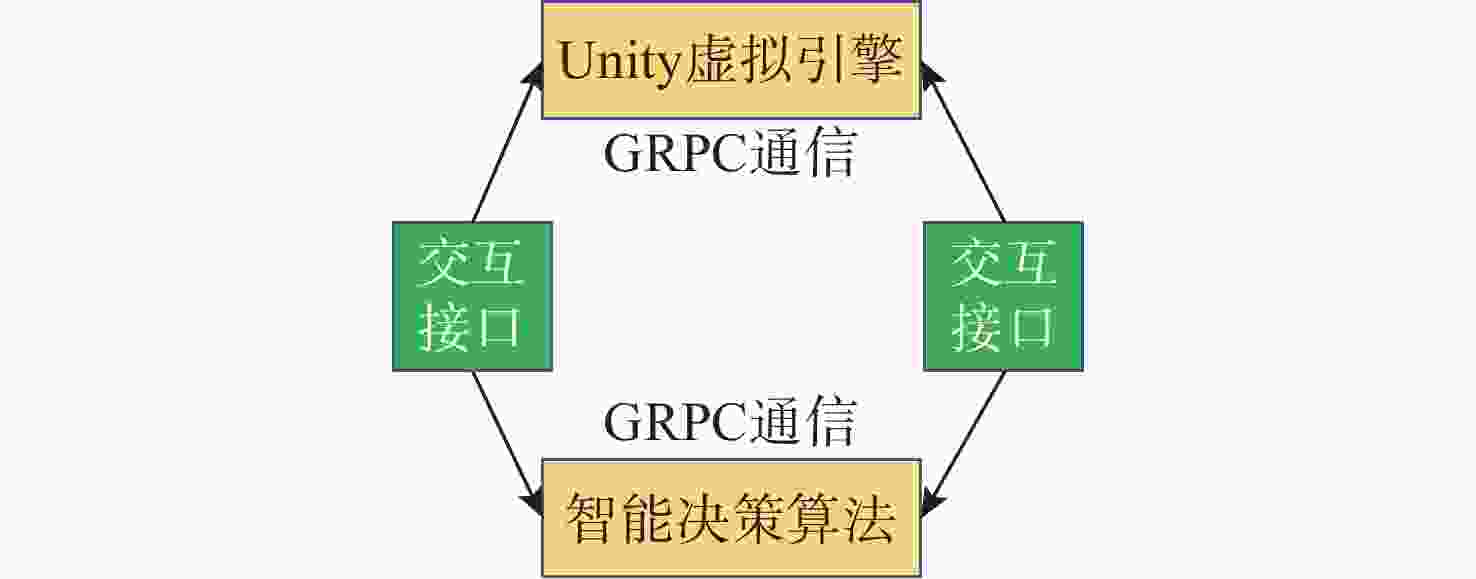
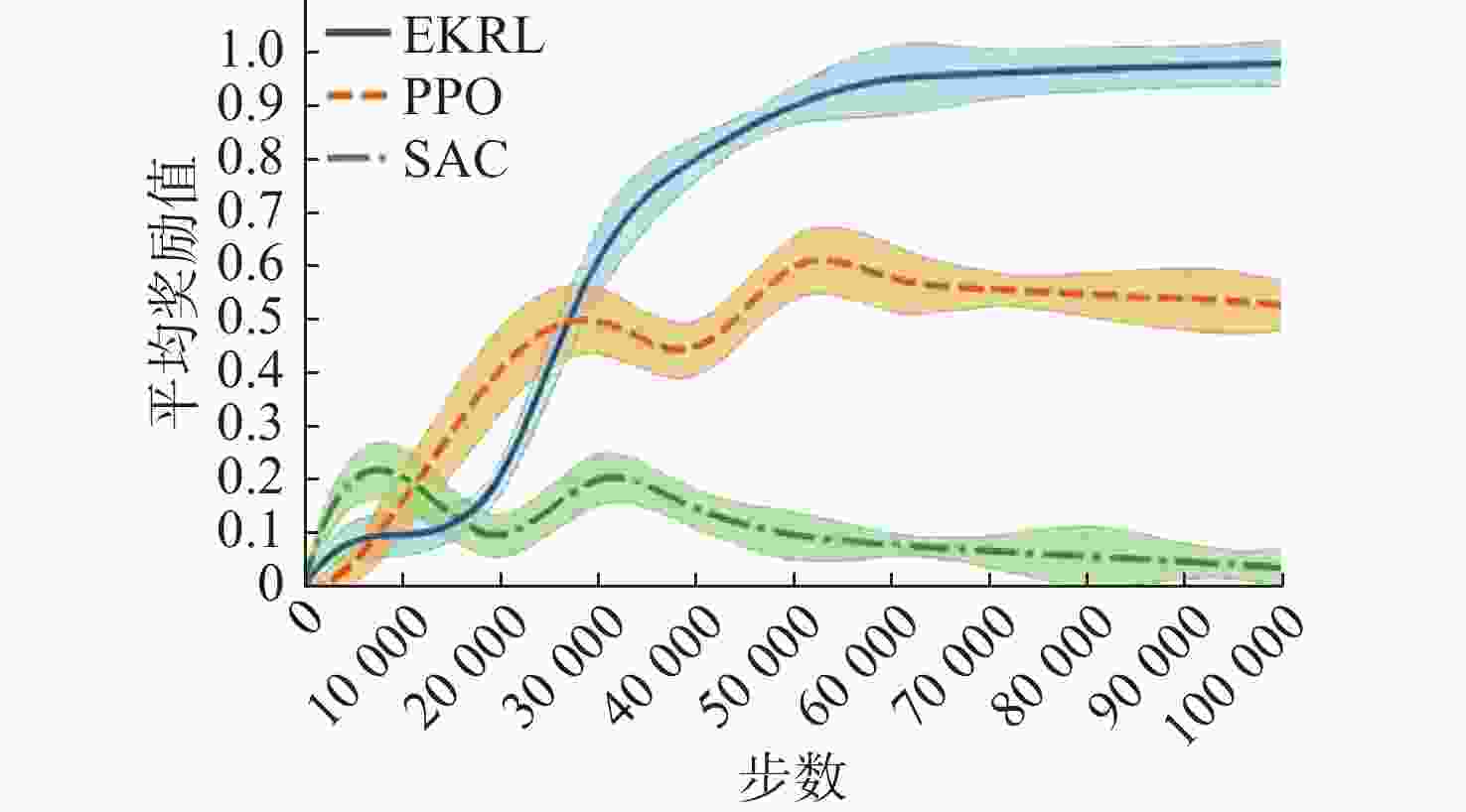
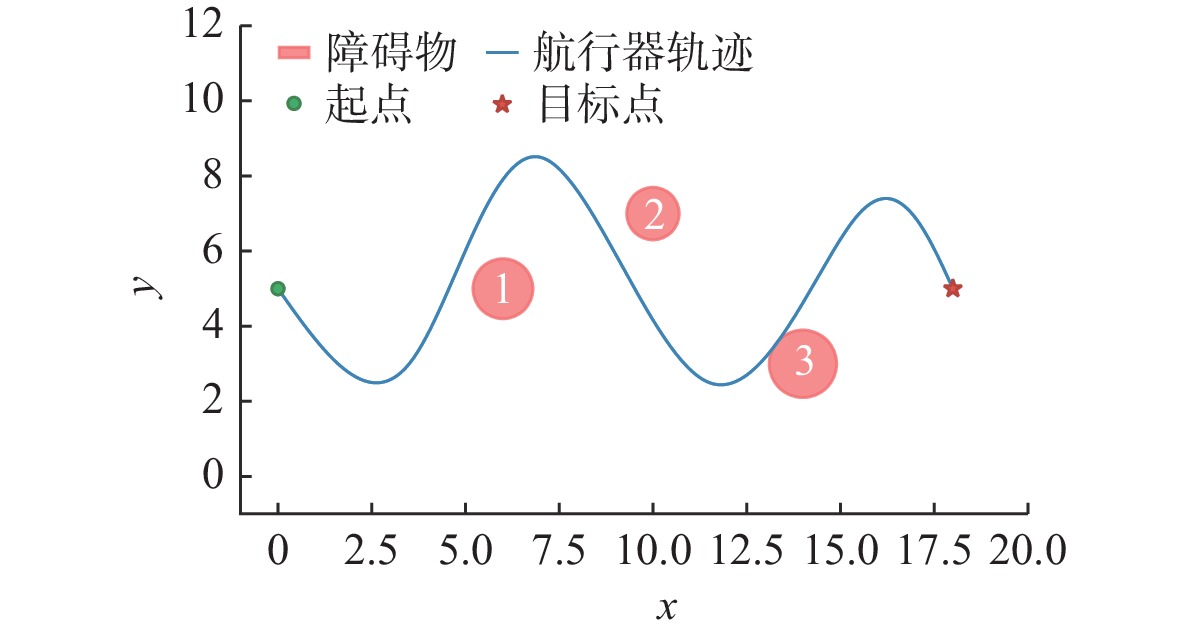
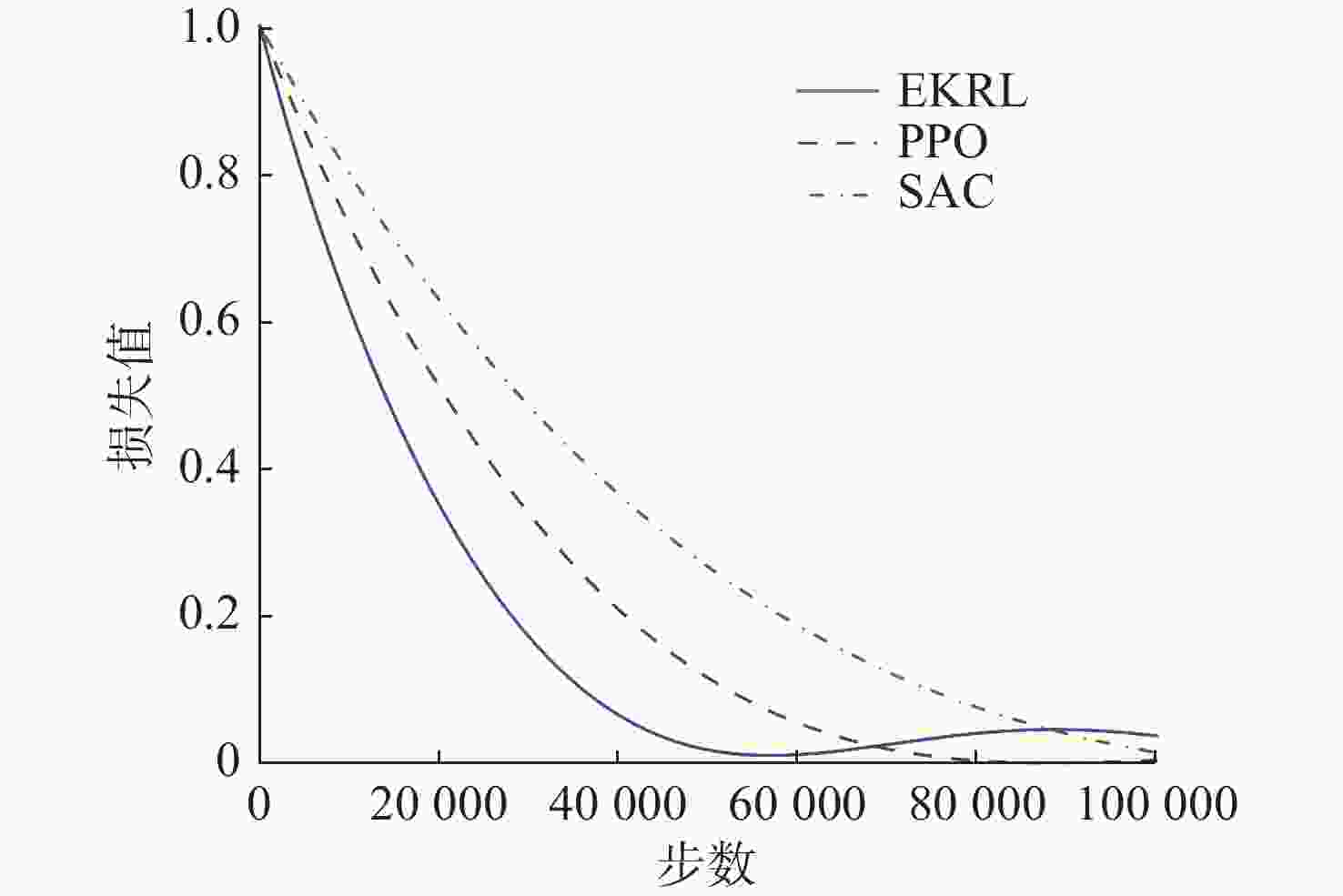
摘要: 水下环境复杂多变, 水下无人系统面临感知信息不完备与环境不确定性的双重挑战, 传统决策方法依赖完备的感知数据与地图信息, 在动态复杂场景中自适应能力不足, 难以高效完成自主导航、避障等任务。针对此, 文中提出一种基于专家知识与深度强化学习的双层自主决策方法, 旨在提升水下无人系统的智能决策自适应能力与任务执行效率。具体而言, 首先设计包含七大功能模块的双层自主决策架构, 通过强化系统鲁棒性切实保障航行安全; 然后, 提出融合专家知识与深度强化学习的自主决策策略生成方法, 提升水下无人系统在未知场景中的自适应能力; 最后, 提出多模块设计方法实现各功能模块的解耦, 有效提升水下无人系统的研发效率。以水下无人系统为研究对象, 在Unity虚拟仿真平台开展自主导航与避障实验, 结果表明, 文中所提方法的任务成功率与平均奖励值收敛速度均优于近端策略优化、软演员-评论家等基准方法, 为真实场景下的自主决策优化研究提供了坚实的理论支撑。Abstract: The underwater environment is complex and volatile, where underwater unmanned systems face the dual challenges of incomplete perceptual information and environmental uncertainty. Traditional decision-making methods highly rely on complete perceptual data and map information, resulting in insufficient adaptability in dynamically complex scenarios and difficulty in efficiently completing tasks such as autonomous navigation and obstacle avoidance. To address the above challenges, this paper proposed a double-layer autonomous decision-making method based on expert knowledge and deep reinforcement learning, aiming to enhance the adaptive capacity of unmanned systems in underwater intelligent decision-making and significantly improve the efficiency of task execution. Specifically, a double-layer autonomous decision-making architecture consisting of seven functional modules was first designed to effectively ensure navigation safety by strengthening system robustness. Secondly, an autonomous decision-making strategy generation method integrating expert knowledge and deep reinforcement learning was proposed to improve the adaptability of underwater unmanned systems in unknown scenarios. Finally, a multi-module design method was proposed to achieve the decoupling of each functional module, effectively improving the research and development efficiency of unmanned undersea systems. By taking unmanned undersea systems as the research object, experiments on autonomous navigation and obstacle avoidance were conducted on the Unity virtual simulation platform. The results show that the success rate and the convergence speed of the average reward value of the proposed method are superior to those of benchmark methods such as proximal policy optimization and soft actor-critic, providing solid theoretical support for autonomous decision-making in real-world scenarios.
-
表 1 模型训练参数
Table 1. Model training parameters
超参数 值 学习率 0.000 3 批量大小 512 折扣因子 0.99 隐藏层 512 缓存池 120 00 最大步数 500 000 0 回合长度/步 300 表 2 算法性能比较
Table 2. Comparison among algorithms’ performance
算法 障碍物数量 成功率/% 碰撞次数/次 回合长度/步 PPO 3 静态 70 80 312 1 动态 67 86 351 3静态+1动态 61 95 373 SAC 3静态 65 60 432 1动态 59 71 459 3 静态+1动态 43 106 531 EKRL 3静态 92 22 216 1动态 81 35 267 3静态+1动态 68 54 312 表 3 蒸馏实验性能对比
Table 3. Performance comparison of distillation experiment
算法 成功率/% 碰撞次数/次 回合长度/步 EKRL-RL 70 150 240 EKRL-TC 72 30 238 EKRL 91 20 216 -
[1] 曹迟, 史文涛, 王百合, 等. 无人水下航行器反潜作战模型仿真[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2025, 33(1): 156-163.CAO C, SHI W T, WANG B H, et al. Simulation of anti-submarine warfare model for unmanned underwater vehicles[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2025, 33(1): 156-163. [2] 陈昭, 丁一杰, 张治强. 无人潜航器发展历程及运用优势研究[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2024, 46(23): 98-102. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2024.23.016CHEN Z, DING Y J, ZHANG Z Q. Development history and application advantages of unmanned underwater vehicles[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2024, 46(23): 98-102. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2024.23.016 [3] 张龙伟, 李中政, 董黄伟. 基于UUV的海洋环境测量系统设计[J]. 船电技术, 2023, 43(8): 38-41. [4] 王旭, 李金明, 毛昭勇, 等. 基于组合赋权TOPSIS的智能UUV目标识别与反对抗效能评估[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(5): 779-786.WANG X, LI J M, MAO Z Y, et al. Intelligent UUV target recognition and anti-countermeasure effectiveness evaluation based on combined weighting TOPSIS[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(5): 779-786. [5] 郑康洁, 张新宇, 王伟菘, 等. DQN与规则结合的智能船舶动态自主避障决策[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2025, 47(6): 1994-2001. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.06.27 [6] 李磊, 杜度, 陈科. 基于改进生物启发模型的UUV在线避障方法[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2019, 27(3): 266-271. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2019.03.005LI L, DU D, CHEN K. UUV online obstacle avoidance method based on improved bio-inspired model[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2019, 27(3): 266-271. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2019.03.005 [7] 杨长兵, 张海华, 刘焕牢. 基于深度强化学习的船舶路径规划方法研究[J]. 信息技术, 2024(10): 128-135. doi: 10.13274/j.cnki.hdzj.2024.10.019 [8] 詹天碧, 冯辉, 徐海祥, 等. 基于噪声DQN的智能船舶全局路径规划方法[J]. 大连海事大学学报, 2025, 51(1): 43-53. doi: 10.16411/j.cnki.issn1006-7736.2025.01.005ZHAN T B, FENG H, XU H X, et al. Global path planning method for intelligent ships based on noisy DQN[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2025, 51(1): 43-53. doi: 10.16411/j.cnki.issn1006-7736.2025.01.005 [9] 欧昌奎, 谢磊, 查天奇, 等. 基于深度强化学习和历史轨迹的船舶路径规划[J]. 中国航海, 2024, 47(1): 36-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2024.01.005 [10] 徐江鹏, 王俊雷, 唐怡. AUV全向运动轨迹跟踪控制方法[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(6): 1018-1028.XU J P, WANG J L, TANG Y. AUV omnidirectional motion trajectory tracking control method[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(6): 1018-1028. [11] 刘清河, 聂文鹏, 乔应, 等. 基于强化学习的无人船路径跟踪控制方法[C]//第三十一届中国汽车工程学会年会论文集(1). 威海: 中国汽车工程学会, 2024: 158-164. [12] 谭靖, 杨丽刚, 李潇睿, 等. 深度强化学习及其在工业场景的应用与展望[J]. 工程科学学报, 2025, 47(4): 768-779. doi: 10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2024.10.29.006TAN J, YANG L G, LI X R, et al. Deep reinforcement learning and its applications and prospects in industrial scenarios[J]. Journal of Engineering Sciences, 2025, 47(4): 768-779. doi: 10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2024.10.29.006 [13] 赵经纬, 熊华乔, 崔峰, 等. 无人水下航行器智能运动控制方法研究[J]. 运输经理世界, 2024(34): 58-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3681.2024.34.020 [14] 温志文, 蔡卫军, 杨春武. UUV自主航行路径规划方法[J]. 制造业自动化, 2016, 38(11): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0134.2016.11.001 [15] 严浙平, 姜玲, 王晓娟, 等. 基于双目视觉的UUV避障半实物仿真系统[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2012, 20(2): 143-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1948.2012.02.014YAN Z P, JIANG L, WANG X J, et al. Semi-physical simulation system for UUV obstacle avoidance based on binocular vision[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2012, 20(2): 143-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1948.2012.02.014 [16] 李康斌, 朱齐丹, 牟进友, 等. 基于改进DDQN船舶自动靠泊路径规划方法[J]. 智能系统学报, 2025, 20(1): 73-80. doi: 10.11992/tis.202401005LI K B, ZHU Q D, MU J Y, et al. Automatic berthing path planning method for ships based on improved DDQN[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2025, 20(1): 73-80. doi: 10.11992/tis.202401005 [17] ZHU X, HOU X. Quantum architecture search via truly proximal policy optimization[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): 5157. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32349-2 [18] 徐红丽, 贾本卿, 栾阔. 基于改进人工势场的多UUV编队避障方法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(11): 1547-1556. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2024.11.004XU H L, JIA B Q, LUAN K. Multi-UUV formation obstacle avoidance method based on improved artificial potential field[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2024, 45(11): 1547-1556. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2024.11.004 [19] 程建华, 李鹏程, 管行, 等. 基于改进A*算法的UUV冰下避障航迹规划算法[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2021, 8(6): 13-18. doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2021.06.002CHENG J H, LI P C, GUAN X, et al. UUV under-ice obstacle avoidance trajectory planning algorithm based on improved a algorithm[J]. Navigation Positioning and Timing, 2021, 8(6): 13-18. doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2021.06.002 [20] 周畅, 于特, 刘佳鹏, 等. 基于快速随机搜索树*与凸优化的船舶路径规划与跟踪算法[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2025, 20(1): 147-161. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.03837ZHOU C, YU T, LIU J P, et al. Ship path planning and tracking algorithm based on rapidly-exploring random tree and convex optimization[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2025, 20(1): 147-161. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.03837 [21] 滕建平, 梁霄, 陶浩, 等. 无人水下航行器全局路径规划及有限时间跟踪控制[J]. 上海海事大学学报, 2022, 43(1): 1-7. doi: 10.13340/j.jsmu.2022.01.001TENG J P, LIANG X, TAO H, et al. Global path planning and finite-time tracking control for unmanned underwater vehicles[J]. Journal of Shanghai Maritime University, 2022, 43(1): 1-7. doi: 10.13340/j.jsmu.2022.01.001 [22] 马焱, 肖玉杰, 陈轶, 等. 基于改进烟花-蚁群算法的海流环境下水下无人潜航器的避障路径规划[J]. 导航与控制, 2019, 18(1): 51-59.MA Y, XIAO Y J, CHEN Y, et al. Obstacle avoidance path planning for underwater unmanned vehicles in ocean current environments based on improved fireworks-ant colony algorithm[J]. Navigation and Control, 2019, 18(1): 51-59. [23] 张宏瀚, 王亚博, 李娟, 等. 近海复杂环境下UUV动态路径规划方法研究[J]. 智能系统学报, 2024, 19(1): 114-121. doi: 10.11992/tis.202302028ZHANG H H, WANG Y B, LI J, et al. Dynamic path planning method for UUVs in complex coastal environments[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2024, 19(1): 114-121. doi: 10.11992/tis.202302028 [24] 王景楠, 薛晨阳, 齐向东, 等. 基于RBF神经网络PID的UUV轨迹跟踪控制[J]. 中北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(6): 843-851.WANG J N, XUE C Y, QI X D, et al. UUV trajectory tracking control based on RBF neural network PID[J]. Journal of North University of China (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 45(6): 843-851. [25] 野汶博, 方洋旺, 洪瑞阳, 等. 基于控制障碍函数的欠驱动无人水下航行器椭圆障碍物避障制导[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(5): 362-374. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2024.0404YE W B, FANG Y W, HONG R Y, et al. Elliptical obstacle avoidance guidance for underactuated unmanned underwater vehicles based on control barrier functions[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(5): 362-374. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2024.0404 [26] 何喆, 刘峰, 马子飞. 一种基于膨胀算法的多UUV队形生成与避障策略[J]. 中国新通信, 2022, 24(7): 40-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4866.2022.07.015 -




 下载:
下载: