Research Progress on AI-Driven Decision and Control of Maritime Unmanned Systems
-
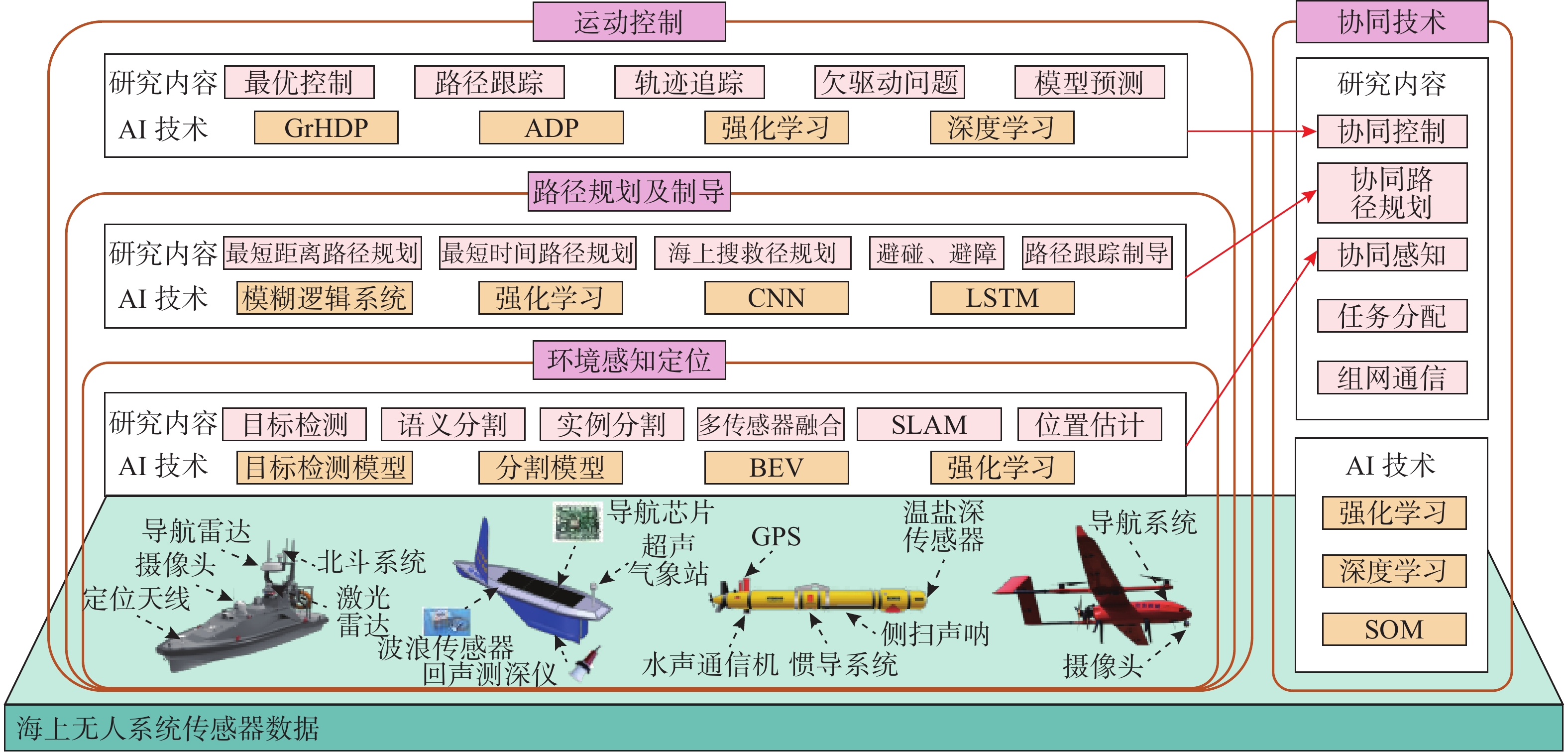
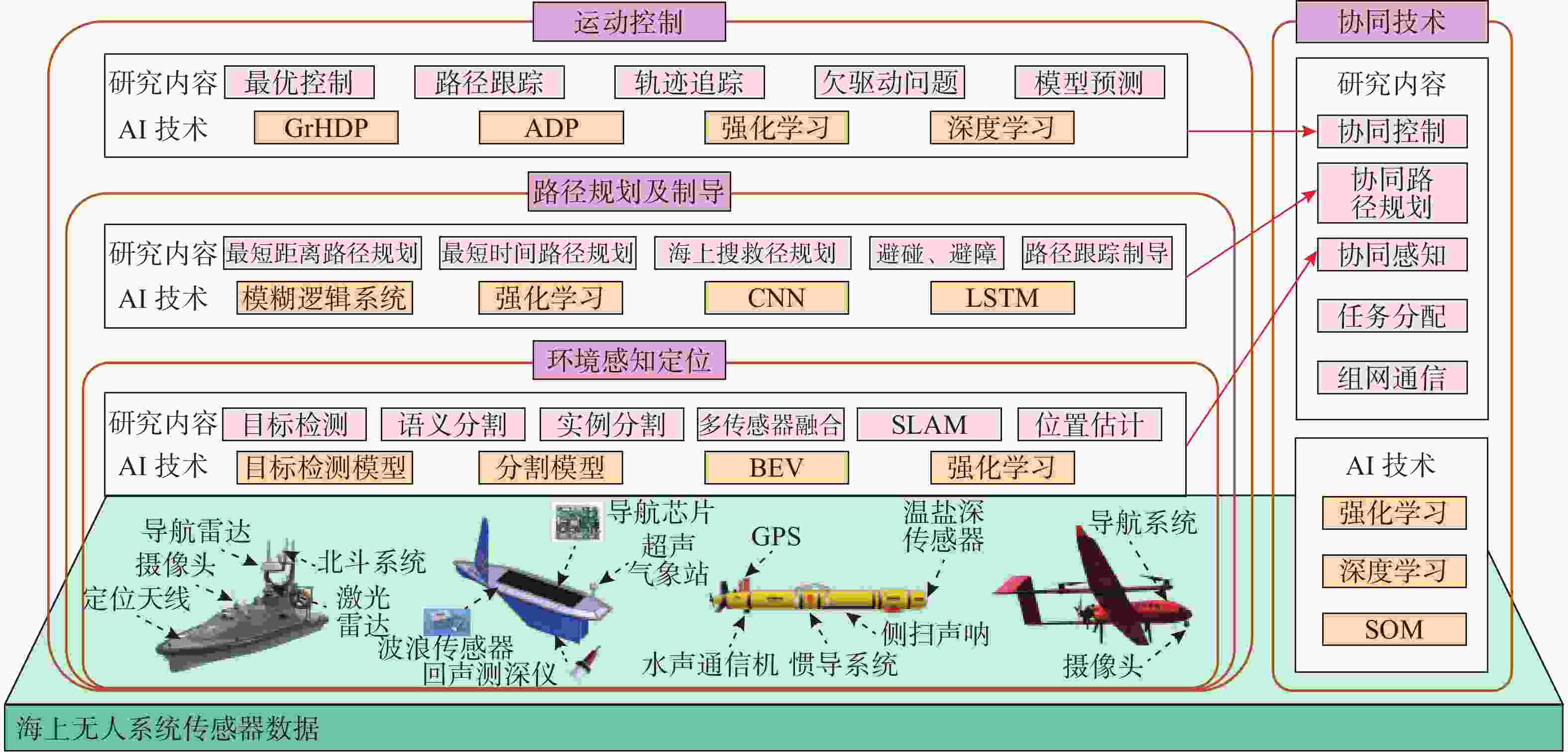
摘要: 海上无人系统是指具有自主作业能力的智能化水面、水下以及空中无人平台, 采用人工智能(AI)技术提升其决策与控制水平是未来的必然发展趋势。尽管AI技术已经取得了长足发展, 其应用于海上无人系统仍受到环境干扰和系统特性的诸多制约。文中首先阐述了海上无人系统决策与控制基本架构, 剖析了传统基于数学建模和固定规则的方法在非平稳海洋环境、多约束任务及异构集群协同中的固有缺陷。其次, 综述了各国在AI驱动海上无人系统领域的发展现状, 梳理总结了AI在环境感知与定位、路径规划与制导、运动控制以及多系统协同等关键技术上的研究进展及存在的问题。进而, 揭示了当前研究面临的数据依赖性强、模型可解释性不足以及非平稳环境下学习困难等挑战。最后, 从数据集构建、算法优化、可解释性增强、人机协同及大模型与通用人工智能(AGI)融合等方面, 提出了针对性解决方案与未来发展路径, 为 AI 技术与海上无人系统的深度融合提供理论参考与技术支撑。Abstract: Maritime unmanned systems refer to intelligent unmanned platforms on the water surface, underwater, and in the air with autonomous operation capabilities. Adopting artificial intelligence(AI) technology to improve the decision-making and control level of maritime unmanned systems is an inevitable development trend in the future. Although AI technology has made considerable progress, its application in maritime unmanned systems is still restricted by many factors such as environmental interference and system characteristics. First, this paper elaborates on the basic framework of decision-making and control for maritime unmanned systems and analyzes the inherent defects of traditional methods based on mathematical modeling and fixed rules in unsteady marine environments, multi-constrained tasks, and heterogeneous cluster collaboration. Second, it reviews the development status of AI-driven maritime unmanned systems in various countries, and combs through the research progress and existing problems in key AI technologies including environmental perception and localization, path planning and guidance, motion control, and multi-system collaboration. Furthermore, it reveals the current challenges in research, such as strong data dependence, insufficient model interpretability, and difficulty in learning under unsteady environments. Finally, targeted solutions and future development paths are proposed from aspects of dataset construction, algorithm optimization, interpretability enhancement, human-machine collaboration, and the integration of large models with artificial general intelligence(AGI), providing theoretical references and technical support for the in-depth integration of AI technology and maritime unmanned systems.
-
表 1 AI与AGI应用于海上无人系统能力维度对比
Table 1. Capability comparison between AI and AGI for maritime unmanned systems
对比维度 传统AI驱动海上无人系统 AGI驱动海上无人系统 跨模态感知能力 依赖单一模态或简单数据拼接, 恶劣海况下易失效, 无法互补修正 基于Transformer等架构实现视觉、激光点云、声呐等多模态深度关联, 强光/遮挡场景下可自主调整融合权重, 鲁棒性较高 群体行为预测能力 基于预设规则, 无法预判群体内冲突(如UAV交汇), 对突发干扰时响应滞后 通过图神经网络构建全局交互模型, 实时整合设备状态与环境数据, 提前预测冲突风险, 生成避让策略 任务推理能力 按固定流程执行(如预设巡逻路线), 突发状况下需人工干预, 无法自主切换任务优先级 结合知识图谱与强化学习, 动态规划备选方案, 可实现分层决策及任务自组织学习 环境适应能力 仅适配训练场景, 新场景需重新标注数据、训练模型, 适应周期长 通过元学习快速迁移知识, 新场景下仅需少量数据即可适配, 适应周期短 故障容错能力 单设备故障时(如传感器失效)整体系统性能骤降, 需人工排查故障点, 恢复时间较长 多模态数据交叉验证(如视觉失效时用雷达补位), 自主定位故障源并切换备用方案, 恢复时间短 -
[1] 闫敬, 张诗杭, 关新平, 等. 水下无人系统跨域协同控制: 研究进展与挑战[J]. 控制与决策, 2025, 40(1): 7-27. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2024.0283YAN J, ZHANG S H, GUAN X P, et al. Cross domain cooperative control of underwater unmanned systems: Research progresses and challenges[J]. Control and Decision, 2025, 40(1): 7-27. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2024.0283 [2] 闫敬, 关新平. 海上无人系统跨域集群发展现状及其关键技术[J]. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(4): 744-761.YAN J, GUAN X P, Development status and key techniques for cross domain swarm of maritime unmanned systems[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(4): 744-761. [3] 徐国平, 张显库. 船舶自动舵研究综述[J]. 中国造船, 2013, 54(2): 191-200.XU G P, ZHANG X K, An overview of ship autopilot research[J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2013, 54(2): 191-200. [4] 王少博. 海上自主航行船舶智能避碰决策技术研究 [D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2023. [5] RUSSELL S. Artifical intelligence: A modern approach[J]. Plant Cell Tissue & Organ Culture, 1995, 43(1): 59-65. [6] DUAN Y, EDWARDS J S, DWIVEDI Y K. Artificial intelligence for decision making in the era of big data – evolution, challenges and research agenda[J]. International Journal of Information Management, 2019, 48: 63-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.01.021 [7] 张俊, 徐箭, 许沛东, 等. 人工智能大模型在电力系统运行控制中的应用综述及展望[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2023, 56(11): 1368-1379. doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2023-11-008ZHANG J, XU J, XU P D, et al. Overview and prospect of application of artificial intelligence large model in power system operation control[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2023, 56(11): 1368-1379. doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2023-11-008 [8] 严新平, 刘佳仑, 胡欣珏, 等. 新一代航运系统的未来船舶技术展望[J]. 船海工程, 2024, 53(5): 1-4. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-7953.2024.05.001YAN X P, LIU J L, HU X Y, et al. Prospects for future ship technologies in the new generation shipping system[J]. Ship & Ocean Engineering, 2024, 53(5): 1-4. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-7953.2024.05.001 [9] 马勇, 王雯琦, 严新平. 水域无人系统平台自主航行及协同控制研究进展[J]. 无人系统技术, 2022, 5(1): 1-16.MA Y, WANG W Q, YAN X P, Research progress on autonomous navigation and cooperative control of water area unmanned system platform[J]. Unmanned Systems Technology, 2022, 5(1): 1-16. [10] 俞建成, 孙朝阳, 张艾群. 无人帆船研究现状与展望[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(24): 98-110.YU J C, SUN Z Y, ZHANG A Q, Research status and prospect of autonomous sailboats[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(24): 98-110. [11] 邱志明, 孟祥尧, 马焱, 等. 海上无人系统发展及关键技术研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2023, 25(3): 74-83. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2023.03.005QIU Z M, MENG X Y, MA Y, et al. Development and key technologies of maritime unmanned systems[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2023, 25(3): 74-83. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2023.03.005 [12] 孙海文, 于邵祯, 孟祥尧, 等. 海上无人机及蜂群作战指挥控制系统发展[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2022, 44(5): 19-23.SUN H W, YU S Z, MENG X Y, et al. Development of command and control system for unmanned aerial vehicle and swarm warfare at sea[J]. Command Control & Simulation, 2022, 44(5): 19-23. [13] LIU Z Y, ZHANG Q, XIANG X B, et al. Intelligent decision and planning for unmanned surface vehicle: A review of machine learning techniques[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2025, 327: 120968. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2025.120968 [14] TRINH L, MERCELIS S, ANWAR A. A comprehensive review of datasets and deep learning techniques for vision in unmanned surface vehicles[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2025, 334: 121501. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2025.121501 [15] ER M J, MA C, LIU T H, et al. Intelligent motion control of unmanned surface vehicles: A critical review[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 280: 114562. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114562 [16] GAO K Z, GAO M L, ZHOU M C, et al. Artificial intelligence algorithms in unmanned surface vessel task assignment and path planning: A survey[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2024, 86: 101505. doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2024.101505 [17] 郝紫霄, 王琦. 基于声呐图像的水下目标检测研究综述[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(2): 339-348.HAO Z X, WANG Q, Underwater target detection based on sonar image[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2023, 31(2): 339-348. [18] 侯玉立, 王宁, 邱赤东, 等. 无人艇集群路径规划研究综述: 深度强化学习[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2025, 33(2): 194-203. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2025-0034HOU Y L, WANG N, QIU C D, et al. A review of research on path planning of unmanned surface vessel swarm: Deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2025, 33(2): 194-203. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2025-0034 [19] KIM H, PARK J, JIN C, et al. Real-time inverse estimation of multi-directional random waves from vessel-motion sensors using Kalman filter[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 280: 114501. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114501 [20] 王宁, 张雪峰, 李洁龙, 等. 面向港口环境精细感知的无人船多传感器融合SLAM系统[J]. 船舶工程, 2024, 46(7): 81-89.WANG N, ZHANG X F, LI J L, et al, Multi-sensor fusion SLAM system of an unmanned surface vehicle for fine sensing in port environment[J]. Ship Engineering, 2024, 46(7): 81-89. [21] YAN J, GUAN X, YANG X, et al. A survey on integration design of localization, communication, and control for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(6): 6300-6324. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2025.3525482 [22] 廖勇, 朱俊豪. 人工智能辅助的深海运载器探测技术研究进展[J]. 河北大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 45(3): 299-308.LIAO J, ZHU J H. Research progress on artificial intelligence-assisted deep-sea vehicle exploration technology[J]. Journal of Hebei University(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 45(3): 299-308. [23] LIANG C, ZHANG X, WATANABE Y, et al. Autonomous collision avoidance of unmanned surface vehicles based on improved a star and minimum course alteration algorithms[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2021, 113: 102755. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2021.102755 [24] TAN G, ZHUANG J, ZOU J, et al. Adaptive adjustable fast marching square method based path planning for the swarm of heterogeneous unmanned surface vehicles (USVs)[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 268: 113432. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.113432 [25] CUI R, LI Y, YAN W. Mutual information-based multi-AUV path planning for scalar field sampling using multidimensional RRT*[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2016, 46(7): 993-1004. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2015.2500027 [26] ZHAO J, MA X, YANG B, et al. Global path planning of unmanned vehicle based on fusion of A* algorithm and Voronoi field[J]. Journal of Intelligent and Connected Vehicles, 2022, 5(3): 250-259. doi: 10.1108/JICV-01-2022-0001 [27] SHEN Z, DING W, LIU Y, et al. Path planning optimization for unmanned sailboat in complex marine environment[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 269: 113475. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.113475 [28] GAN L, LI X, YAN T, et al. Intelligent ship path planning based on improved artificial potential field in narrow inland waterways[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2025, 317: 119928. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.119928 [29] GAO X, JIA D, LIU X, et al. AUV path planning based on the flow field method and dynamic window approach[J]. IEEE Access, 2025, 13: 88484-88498. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3570790 [30] ZHANG G, SHANG X, LIU J, et al. Improved iterative learning path-following control for USV via the potential-based DVS guidance[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 280: 114543. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114543 [31] DENG Y, ZHANG X, ZHANG G. Line-of-sight-based guidance and adaptive neural path-following control for sailboats[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2020, 45(4): 1177-1189. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2019.2923502 [32] DENG Y, ZHANG X, ZHANG G, et al. Parallel guidance and event-triggered robust fuzzy control for path following of autonomous wing-sailed catamaran[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 190: 106442. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106442 [33] ÖZTURK Ü, AKDAG M, AYABAKAN T. A review of path planning algorithms in maritime autonomous surface ships: Navigation safety perspective[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 251: 111010. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.111010 [34] DENG Y, NI T, ZHANG Z, et al. Path-following and collision-avoidance guidance of unmanned sailboats based on beetle antennae search optimization[J]. Robotica, 2023, 41(7): 2105-2121. doi: 10.1017/S0263574723000346 [35] 罗阳, 陶建国, 邓立平, 等. 水下焊接机器人变质心补偿控制[J]. 机器人, 2020, 42(3): 289-300.LUO Y, TAO J G, DENG L P, et al, Centroid variability compensation control of underwater welding vehicle[J]. Robot, 2020, 42(3): 289-300. [36] 代波, 何玉庆, 谷丰, 等. 基于加速度反馈增强的旋翼无人机抗风扰控制[J]. 机器人, 2020, 42(1): 79-88.DAI B, HE Y Q, GU F, et al. Acceleration feedback enhanced controller for wind disturbance rejection of rotor unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Robot, 2020, 42(1): 79-88. [37] PENG Z, CUI K, LI H, et al. Model-free antidisturbance autopilot design for autonomous surface vehicles with hardware-in-the-loop experiments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(2): 2387-2396. doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3288217 [38] PENG Z, WANG D, WANG J. Data-driven adaptive disturbance observers for model-free trajectory tracking control of maritime autonomous surface ships[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(12): 5584-5594. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3093330 [39] HOU Z, ZHU Y. Controller-dynamic-linearization-based model free adaptive control for discrete-time nonlinear systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(4): 2301-2309. doi: 10.1109/TII.2013.2257806 [40] ZHANG G, ZHANG X. Concise robust adaptive path-following control of underactuated ships using DSC and MLP[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2014, 39(4): 685-694. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2013.2280822 [41] YANG X, YAN J, HUA C, et al. Trajectory tracking control of autonomous underwater vehicle with unknown parameters and external disturbances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(2): 1054-1063. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2894171 [42] DENG Y, ZHANG Z, GONG M, et al. Event-triggered asymptotic tracking control of underactuated ships with prescribed performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(1): 645-656. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3216808 [43] DENG Y J, ZHANG X K, REN N H, et al. Model-based event-triggered tracking control of underactuated surface vessels with minimum learning parameters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(10): 4001-4014. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2951709 [44] DENG Y, ZHANG X. Event-Triggered composite adaptive fuzzy output-feedback control for path Following of autonomous surface vessels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2021, 29(9): 2701-2713. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3006562 [45] DENG Y, ZHANG X, ZHAO B, et al. Event-triggered compound learning tracking control of autonomous surface vessels in the measurement network[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 228: 108817. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.108817 [46] 邢博闻, 张昭夷, 王世明, 等. 基于深度强化学习的多无人艇协同目标搜索算法[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2023, 44(11): 118-125. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2023.11.015XING B W, ZHANG Z Y, WANG S M, et al. Multi-USV cooperative target search algorithm based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2023, 44(11): 118-125. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2023.11.015 [47] GUO X, CUI R, YAN W. Pursuit-evasion games of marine surface vessels using neural network-based control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2025, 55(1): 18-27. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3347044 [48] CUI Z, GUAN W, ZHANG X. USV formation navigation decision-making through hybrid deep reinforcement learning using self-attention mechanism[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 256: 124906. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.124906 [49] GU N, PENG Z, WANG D, et al. Path-guided containment maneuvering of mobile robots: Theory and experiments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(8): 7178-7187. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3000120 [50] HUNG N T, REGO F F C, PASCOAL A M. Cooperative distributed estimation and control of multiple autonomous vehicles for range-based underwater target localization and pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2022, 30(4): 1433-1447. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2021.3107346 [51] 潘书阳. 第三次抵消战略视阈下美国人工智能的军事运用[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2019. [52] LI Y, GUO J, GUO X, et al. A novel target detection method of the unmanned surface vehicle under all-weather conditions with an improved YOLOV3[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(17): 4885. doi: 10.3390/s20174885 [53] HE G W, WANG W L, SHI B W, et al. An improved YOLO-v4 algorithm-based object detection method for maritime vessels[J]. International Journal of Science and Engineering Applications, 2022, 11(4): 50-55. doi: 10.7753/ijsea1104.1001 [54] KIM J H, KIM N, PARK Y W, et al. Object detection and classification based on YOLO-v5 with improved maritime dataset[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2022, 10(3): 377. doi: 10.3390/jmse10030377 [55] NING Y, ZHAO L, ZHANG C, et al. STD-YOLO-v5: A ship-type detection model based on improved Yolo-v5[J]. Ships and Offshore Structures, 2024, 19(1): 66-75. doi: 10.1080/17445302.2022.2142362 [56] 李江川, 韩彦岭, 董传胜, 等. YOLO-U: 基于结构重参数化和双重注意力机制的水下目标检测算法[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2025, 34(3): 696-706. doi: 10.12024/jsou.20240404474LI J C, HAN Y L, DONG C S, et al. YOLO-U: Underwater object detection algorithm based on structural re-parameterization and dual attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2025, 34(3): 696-706. doi: 10.12024/jsou.20240404474 [57] 孙鹏麒, 胡家祯, 黄小华, 等. 基于YOLO的养殖鱼群全向声呐实时监测方法研究与应用[J]. 中国水产科学, 2025, 32(3): 409-419.SUN P Q, HU J Z, HUANG X H, et al. Research and application of real-time monitoring method for aquaculture fish schools using omnidirectional sonar based on YOLO[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2025, 32(3): 409-419. [58] MIAO T, ZENG H, WANG H, et al. Inshore ship detection in SAR images via an improved SSD model with wavelet decomposition[C]//2021 7th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar(APSAR). Bali, Indonesia: IEEE, 2021: 1-5. [59] 强伟, 贺昱曜, 郭玉锦, 等. 基于改进SSD的水下目标检测算法研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2020, 38(4): 747-754. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210761QIANG W, HE Y Y, GUO Y J, et al. Exploring underwater target detection algorithm based on improved SSD[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2020, 38(4): 747-754. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210761 [60] YANG Y, CHEN P, DING K, et al. Object detection of inland waterway ships based on improved SSD model[J]. Ships and Offshore Structures, 2023, 18(8): 1192-1200. doi: 10.1080/17445302.2022.2110406 [61] CHEN B, YU C, ZHAO S, et al. An anchor-free method based on transformers and adaptive features for arbitrarily oriented ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 2012-2028. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3325573 [62] 徐昌贵, 张波, 高建威, 等. FCOSR: 一种无锚框的SAR图像任意朝向船舶目标检测网络[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(3): 335-346. doi: 10.12000/JR21204XU C G, ZHANG B, GAO J W, et al. FCOSR: An anchor-free method for arbitrary-oriented ship detection in SAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(3): 335-346. doi: 10.12000/JR21204 [63] CHEN M, SUN J, AIDA K, et al. Weather-aware object detection method for maritime surveillance systems[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2024, 151: 111-123. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2023.09.030 [64] CHEN Z, GAO X. An improved algorithm for ship target detection in SAR images based on Faster R-CNN[C]//2018 Ninth International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing(ICICIP). Wanzhou, China: IEEE, 2018: 39-43. [65] LIU J, LIU S, XU S, et al. Two-stage underwater object detection network using swin transformer[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 117235-117247. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3219592 [66] JAIN R, ZAWARE S, KACHOLIA N, et al. Advancing underwater trash detection: Harnessing mask R-CNN, YOLOv8, efficientDet-D0 and YOLACT[C]//2024 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Smart Systems(ICSCSS). Coimbatore, India: IEEE, 2024: 1314-1325. [67] HOU T, LI J. Application of mask R-CNN for building detection in UAV remote sensing images[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(19): 38141. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38141 [68] DONG H, LI Y, LIU R. A detection algorithm based on improved cascade R-CNN for UAV aerial images[C]// 2023 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronic Technology, Communication and Information(ICETCI). Changchun, China: IEEE, 2023: 700-704. [69] YU N, REN H, DENG T, et al. A lightweight radar ship detection framework with hybrid attentions[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(11): 2743. doi: 10.3390/rs15112743 [70] STECCANELLA L, BLOISI D D, CASTELLINI A, et al. Waterline and obstacle detection in images from low-cost autonomous boats for environmental monitoring[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2020, 124: 103346. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2019.103346 [71] ZHOU G C, CHENG C, CHEN Y Z. Efficient multi-branch segmentation network for situation awareness in autonomous navigation[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 302: 117741. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.117741 [72] HANSEN K F, YAO L, REN K, et al. Image segmentation in marine environments using convolutional LSTM for temporal context[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2023, 139: 103709. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2023.103709 [73] SHARMA R, SAQIB M, LIN C T, et al. MASSNet: Multiscale attention for single-stage ship instance segmentation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2024, 594: 127830. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2024.127830 [74] ZHANG W, HE X, LI W, et al. An integrated ship segmentation method based on discriminator and extractor[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2020, 93: 103824. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2019.11.002 [75] ZHANG Y, LI C, SHANG S, et al. SwinSeg: Swin transformer and MLP hybrid network for ship segmentation in maritime surveillance system[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 281: 114885. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114885 [76] HELGESEN Ø K, STAHL A, BREKKE E F. Maritime tracking with georeferenced multi-camera fusion[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 30340-30359. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3261556 [77] JIN J, LIU D, LI F, et al. Wide baseline stereovision based obstacle detection for unmanned surface vehicles[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2024, 18(5): 4605-4614. doi: 10.1007/s11760-024-03098-0 [78] HONG B, ZHOU Y, QIN H, et al. Few-shot object detection using multimodal sensor systems of unmanned surface vehicles[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(4): 1511. doi: 10.3390/s22041511 [79] 吴文静, 王中训, 但波, 等. 多模态信息融合舰船目标识别研究进展[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2024, 46(2): 1-12.WU W J, WANG Z X, DAN B, et al. A review of ship target recognition based on multi-modal information fusion[J]. Journal of Detection & Control, 2024, 46(2): 1-12. [80] XU H, ZHANG X, HE J, et al. Real-time volumetric perception for unmanned surface vehicles through fusion of radar and camera[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 1-12. doi: 10.1109/tim.2024.3381690 [81] DOE J, SMITH S, WANG L. Deep-learning-based vessel trajectory prediction model with clustering-enhanced phased destination recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(3):2890-2899. [82] ZHANG J, MENG Z, LIU S, et al. A novel trajectory prediction method for UAV air combat based on QCNet-3D[J]. Defence Technology, 2025, 54: 151-165. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2025.07.007 [83] GONG Z, LI C, JIANG F. A machine learning-based approach for auto-detection and localization of targets in underwater acoustic array networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(12): 15857-15866. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3036350 [84] YAN J, LI X, YANG X, et al. Integrated localization and tracking for AUV with model uncertainties via scalable sampling-based reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(11): 6952-6967. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3129534 [85] YAN J, YI M, YANG X, et al. Broad-learning-based localization for underwater sensor networks with stratification compensation[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(15): 13123-13137. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3260192 [86] SILVA JUNIOR A G D, SANTOS D H D, NEGREIROS A P F D, et al. High-level path planning for an autonomous sailboat robot using Q-learning[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(6): 1550. doi: 10.3390/s20061550 [87] 荆纬, 李浩, 咸琳涛, 等. 基于强化学习的自动帆船路径规划算法研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 51(8): 79-87. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20190069JING W, LI H, XIAN L T, et al. Research on path planning of automatic sailboat based on reinforcement learning[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2021, 51(8): 79-87. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20190069 [88] YU L, CHEN Z, WU H, et al. Soft actor-critic combining potential field for global path planning of autonomous mobile robot[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(5): 7114-7123. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3521508 [89] WU J, CHENG L, CHU S, et al. An autonomous coverage path planning algorithm for maritime search and rescue of persons-in-water based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 291: 116403. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.116403 [90] CHU Z, WANG F, LEI T, et al. Path planning based on deep reinforcement learning for autonomous underwater vehicles under ocean current disturbance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2023, 8(1): 108-120. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2022.3153352 [91] SONG W, CHEN Z, SUN M, et al. A COLREGs-based path-planning method for collision avoidance considering path cost through reinforcement learning[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2025, 325: 120746. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2025.120746 [92] XIAO H, FU L, SHANG C, et al. Multi objective cooperative path planning of uncrewed surface vehicle based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(8): 9743-9758. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3509521 [93] WALTZ M, PAULIG N, OKHRIN O. 2-level reinforcement learning for ships on inland waterways: Path planning and following[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2025, 274: 126933. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2025.126933 [94] SONNTAG V, PERRUSQUIA A, TSOURDOS A, et al. A COLREGs compliance reinforcement learning approach for USV manoeuvring in track-following and collision avoidance problems[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2025, 316: 119907. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.119907 [95] 关巍, 罗文哲, 崔哲闻. 基于深度强化学习的无人驾驶船舶避碰行为决策方法[J]. 大连海事大学学报, 2024, 50(1): 11-19.GUAN W, LUO W Z, CUI Z W, Collision avoidance behavior decision-making of unmanned ship based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2024, 50(1): 11-19. [96] WANG C, ZHANG X, GAO H, et al. COLERGs-constrained safe reinforcement learning for realising MASS’s risk-informed collision avoidance decision making[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2024, 300: 112205. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2024.112205 [97] GAO W, HAN M, WANG Z, et al. Research on method of collision avoidance planning for UUV based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2023, 11(12): 2245. doi: 10.3390/jmse11122245 [98] ZHANG A, WANG W, BI W, et al. A path planning method based on deep reinforcement learning for AUV in complex marine environment[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 313: 119354. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.119354 [99] KIM D, HUH K. Neural motion planning for autonomous parking[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2023, 21(4): 1309-1318. doi: 10.1007/s12555-022-0082-z [100] YOON Y, JO A. Obstacle avoidance planning for autonomous vehicles based on neural network-centric path sampling[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2025, 23(1): 126-136. doi: 10.1007/s12555-024-0697-3 [101] WANG J, JIA X, ZHANG T, et al. Deep neural network enhanced sampling-based path planning in 3D space[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(4): 3434-3443. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2021.3121408 [102] HU L, WEI C, YIN L. Fuzzy A* quantum multi-stage Q-learning artificial potential field for path planning of mobile robots[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2025, 141: 109866. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2024.109866 [103] SAMADI GHARAJEH M, JOND H B. An intelligent approach for autonomous mobile robots path planning based on adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system[J]. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 2022, 13(1): 101491. doi: 10.1016/j.asej.2021.05.005 [104] DENG Y, ZHANG S, XU Y, et al. Event-triggered optimal trajectory tracking control of underactuated ships based on goal representation heuristic dynamic programming[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 308: 118251. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.118251 [105] CHEN L, DAI S L, DONG C. Adaptive optimal tracking control of an underactuated surface vessel using actor–critic reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(6): 7520-7533. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3214681 [106] ZHANG G, YIN S, LI J, et al. Game-based event-triggered control for unmanned surface vehicle: Algorithm design and harbor experiment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2025, 55(6): 2729-2741. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2025.3556042 [107] DENG Y, LIU T, ZHAO D. Event-triggered output-feedback adaptive tracking control of autonomous underwater vehicles using reinforcement learning[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2021, 113: 102676. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2021.102676 [108] ZHANG G, LI Z, LI J, et al. Prescribed performance path-following control for rotor-assisted vehicles via an improved reinforcement learning mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2025, 36(9): 17395-17405. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2025.3562245 [109] BAI W, CHEN D, ZHAO B, et al. Reinforcement learning control for a class of discrete-time non-strict feedback multi-agent systems and application to multi-marine vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2025, 10(5): 3613-3625. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2024.3458894 [110] FAN Y, DONG H, ZHAO X, et al. Path-following control of unmanned underwater vehicle based on an improved TD3 deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2024, 32(5): 1904-1919. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2024.3377876 [111] XIA J, ZHU X, LIU Z, et al. LSTM-DPPO based deep reinforcement learning controller for path following optimization of unmanned surface vehicle[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 34(5): 1343-1358. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2023.000113 [112] JIANG P, SONG S, HUANG G. Attention-based meta-reinforcement learning for tracking control of AUV with time-varying dynamics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(11): 6388-6401. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3079148 [113] JIANG Y, ZHANG K, ZHAO M, et al. Adaptive meta-reinforcement learning for AUVs 3D guidance and control under unknown ocean currents[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 309: 118498. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.118498 [114] ZHANG Q, PAN W, REPPA V. Model-reference reinforcement learning for collision-free tracking control of autonomous surface vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(7): 8770-8781. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3086033 [115] PENG Z, XIA F, LIU L, et al. Online deep learning control of an autonomous surface vehicle using learned dynamics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2024, 9(2): 3283-3292. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2023.3333437 [116] LIU T, ZHAO J, HUANG J, et al. Research on model predictive control of autonomous underwater vehicle based on physics informed neural network modeling[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 304: 117844. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.117844 [117] XU P F, HAN C B, CHENG H X, et al. A physics-informed neural network for the prediction of unmanned surface vehicle dynamics[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2022, 10(2): 148. doi: 10.3390/jmse10020148 [118] WANG S, YU W, WU C, et al. Self-supervised learning with high-stable guidance law and label generation for USV trajectory tracking control[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2025, 329: 121079. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2025.121079 [119] 段续庭, 吴思凡, 王奇, 等. 车机协同智能无人系统关键技术研究与展望[J]. 无人系统技术, 2025, 8(2): 1-18.DUAN X T, WU S F, WANG Q, et al, Key technology research and prospect of truck-drone cooperative intelligent unmanned systems[J]. Unmanned Systems Technology, 2025, 8(2): 1-18. [120] CUI Z, GUAN W, HAO S, et al. Gated communication attention-based MADDPG algorithm for multiple USVs collaborative hunting decision-making strategy[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2025, 334: 121510. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2025.121510 [121] WANG Z, DU J, JIANG C, et al. Task scheduling for distributed AUV network target hunting and searching: An energy-efficient AOI-aware DMAPPO approach[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(9): 8271-8285. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3230916 [122] LIU Y, SONG R, BUCKNALL R, et al. Intelligent multi-task allocation and planning for multiple unmanned surface vehicles(USVs) using self-organising maps and fast marching method[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 496: 180-197. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.05.029 [123] MA S, GUO W, SONG R, et al. Unsupervised learning based coordinated multi-task allocation for unmanned surface vehicles[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 420: 227-245. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.09.031 [124] TAN G, ZHUANG J, ZOU J, et al. Multi-type task allocation for multiple heterogeneous unmanned surface vehicles(USVs) based on the self-organizing map[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2022, 126: 103262. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2022.103262 [125] LIU Z, LIU C, QU W, et al. Deep reinforcement learning-based multi-AUV task allocation algorithm in underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2025, 25(2): 3909-3922. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3507796 [126] ZHAO Z, LIU C, GUANG X, et al. A transmission-reliable topology control framework based on deep reinforcement learning for UWSNs[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(15): 13317-13332. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3262690 [127] LI J, YI P, DUAN T, et al. Centroid-guided target-driven topology control method for UAV Ad-Hoc networks based on tiny deep reinforcement learning algorithm[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(12): 21083-21091. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3376647 [128] YAN J, CAO W, YANG X, et al. Communication-efficient and collision-free motion planning of underwater vehicles via integral reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(6): 8306-8320. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3226776 [129] LIU D, ZHANG J, CUI J, et al. Deep learning aided routing for space-air-ground integrated networks relying on real satellite, flight, and shipping data[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2022, 29(2): 177-184. doi: 10.1109/MWC.003.2100393 [130] TARIF M, HOMAEI M, MOSAVI A. An enhanced fuzzy routing protocol for energy optimization in the underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Computers, Materials and Continua, 2025, 83(2): 1791-1820. doi: 10.32604/cmc.2025.063962 [131] ULLAH KHAN S, ULLAH KHAN Z, ALKHOWAITER M, et al. Energy-efficient routing protocols for UWSNs: A comprehensive review of taxonomy, challenges, opportunities, future research directions, and machine learning perspectives[J]. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 2024, 36(7): 102128. doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2024.102128 [132] YAN J, ZHOU X, YANG X, et al. Joint design of channel estimation and flocking control for multi-AUV-based maritime transportation systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(12): 14520-14535. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3292967 [133] JING L, WANG Q, HE C, et al. A learned denoising-based sparse adaptive channel estimation for OTFS underwater acoustic communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2024, 13(4): 969-973. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2024.3354280 [134] SHAO S, PENG Y, HE C, et al. Efficient path planning for UAV formation via comprehensively improved particle swarm optimization[J]. ISA Transactions, 2020, 97: 415-430. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2019.08.018 [135] SHORAKAEI H, VAHDANI M, IMANI B, et al. Optimal cooperative path planning of unmanned aerial vehicles by a parallel genetic algorithm[J]. Robotica, 2016, 34(4): 823-836. doi: 10.1017/S0263574714001878 [136] 于月平, 袁莞迈, 段海滨. 仿鹰-欧椋鸟智能行为的无人机集群追逃控制[J]. 指挥与控制学报, 2022, 8(4): 422-433.YU Y P, YUAN W M, DUAN H B, Pursuit-evasion control for uav swarm imitating the intelligent behavior in hawks-starlings[J]. Journal of Command and Control, 2022, 8(4): 422-433. [137] JIN W, TIAN X, SHI B, et al. Enhanced UAV pursuit-evasion using boids modelling: A synergistic integration of bird swarm intelligence and DRL[J]. Computers, Materials and Continua, 2024, 80(3): 3523-3553. doi: 10.32604/cmc.2024.055125 [138] ISMAIL A H, SONG X, OUELHADJ D, et al. Unmanned surface vessel routing and unmanned aerial vehicle swarm scheduling for off-shore wind turbine blade inspection[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2025, 284: 127534. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2025.127534 [139] 苏昊, 董豪, 印薇, 等. 海上装备群体博弈方法研究综述[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2025, 1-24.SU H, DONG H, YIN W, et al. Group gaming approaches for maritime equipment: A survey[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2025, 1-24. [140] WEN J, LI Z, XI M, et al. A LLM-assisted auv 3D path planning scheme under ocean current interference via reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(19): 39185-39196. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2025.3540820 [141] XU C, CHU Y, GAO Q, et al. Autonomous unmanned surface vehicle docking using large language model guide reinforcement learning[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2025, 323: 120608. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2025.120608 [142] KU J, KIM S, LEE E, et al. Enhancing autonomous ship communication: a cost-effective and high-accuracy LLM framework using decision trees and RAG[C]//2025 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication(ICAIIC). Fukuoka, Japan: IEEE, 2025: 420-426. -




 下载:
下载: