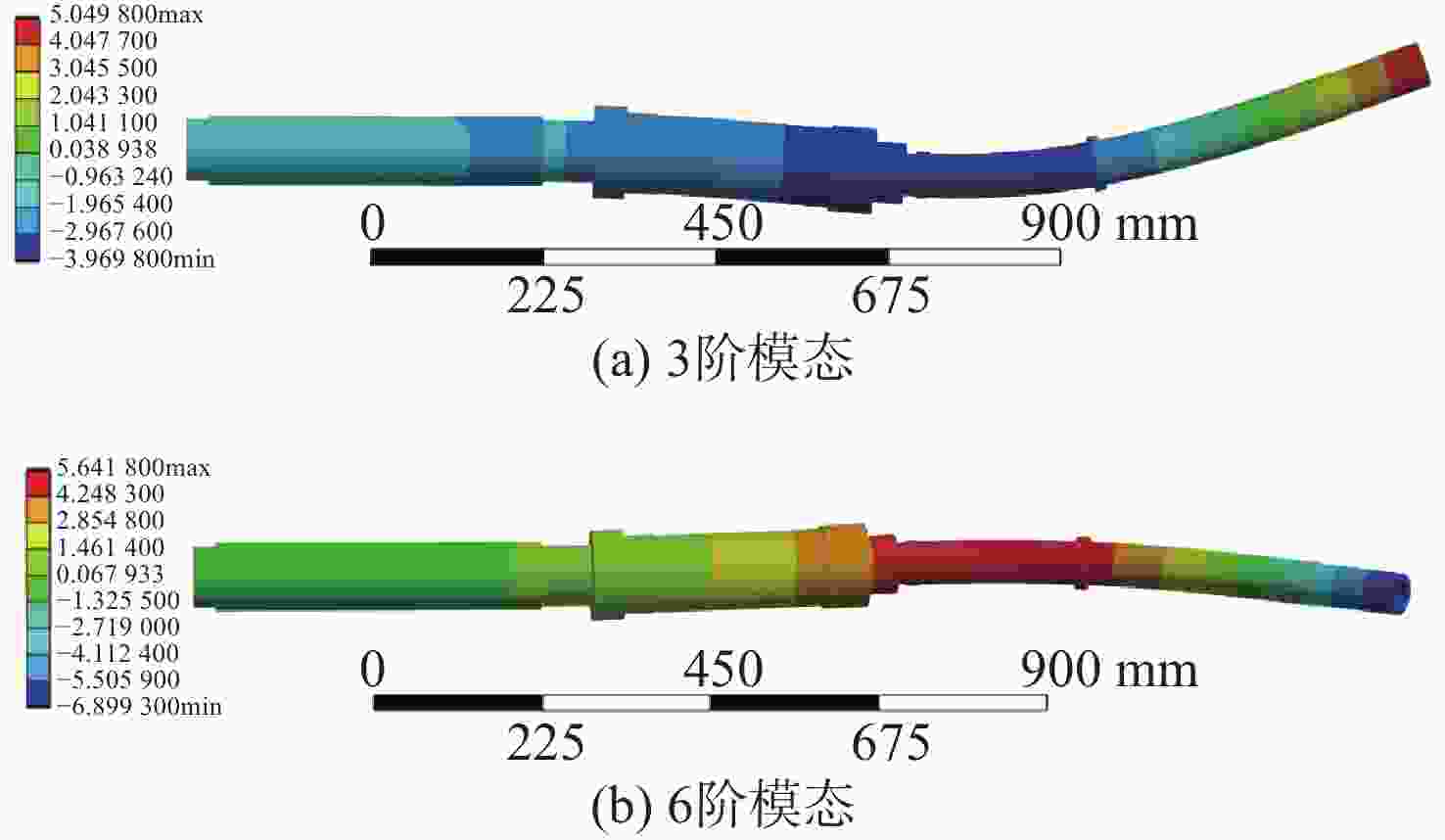
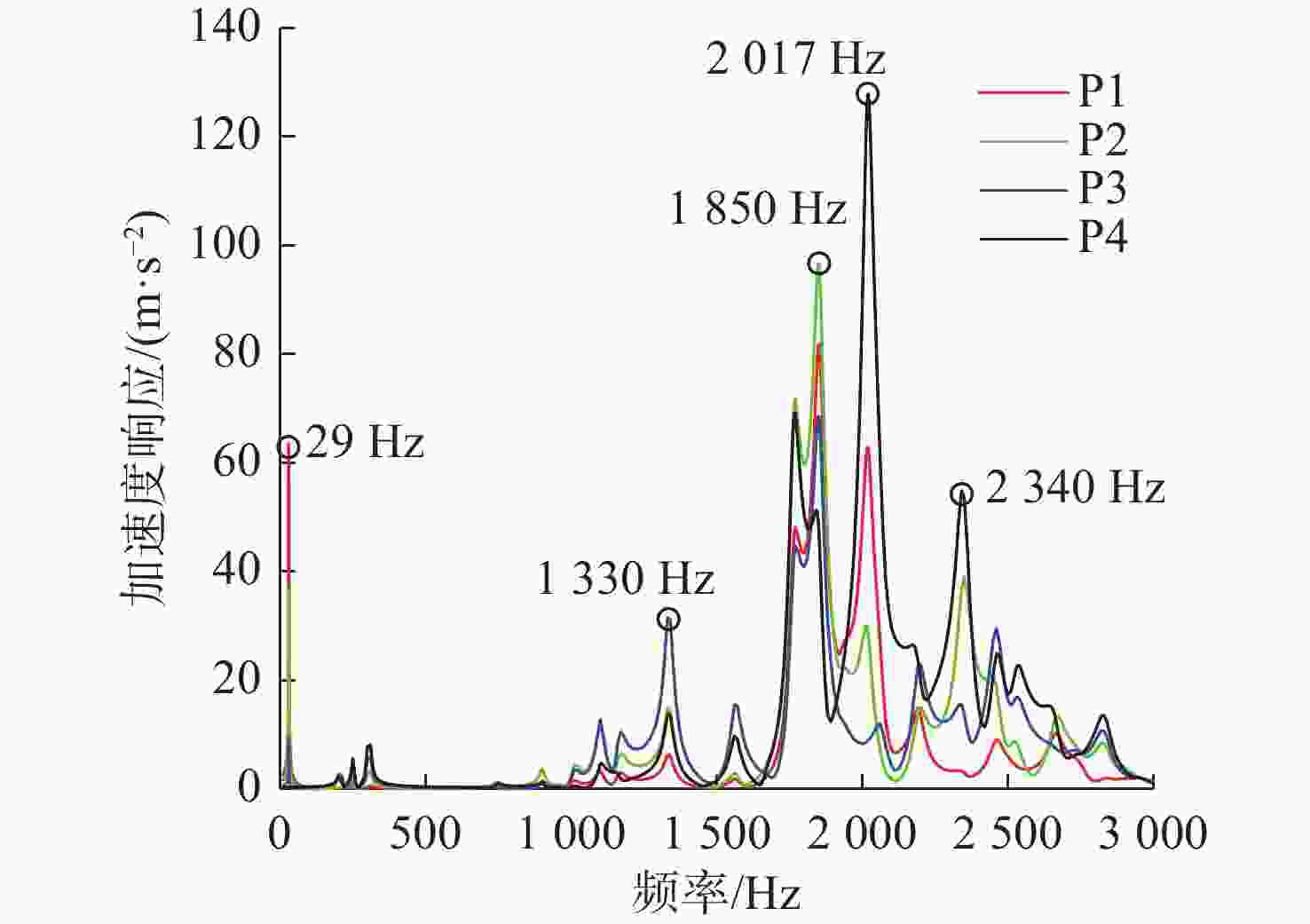
Research on Overall Matching Optimization Design of Supporting Parameters of the Power Propulsion System for Underwater Vehicles
-
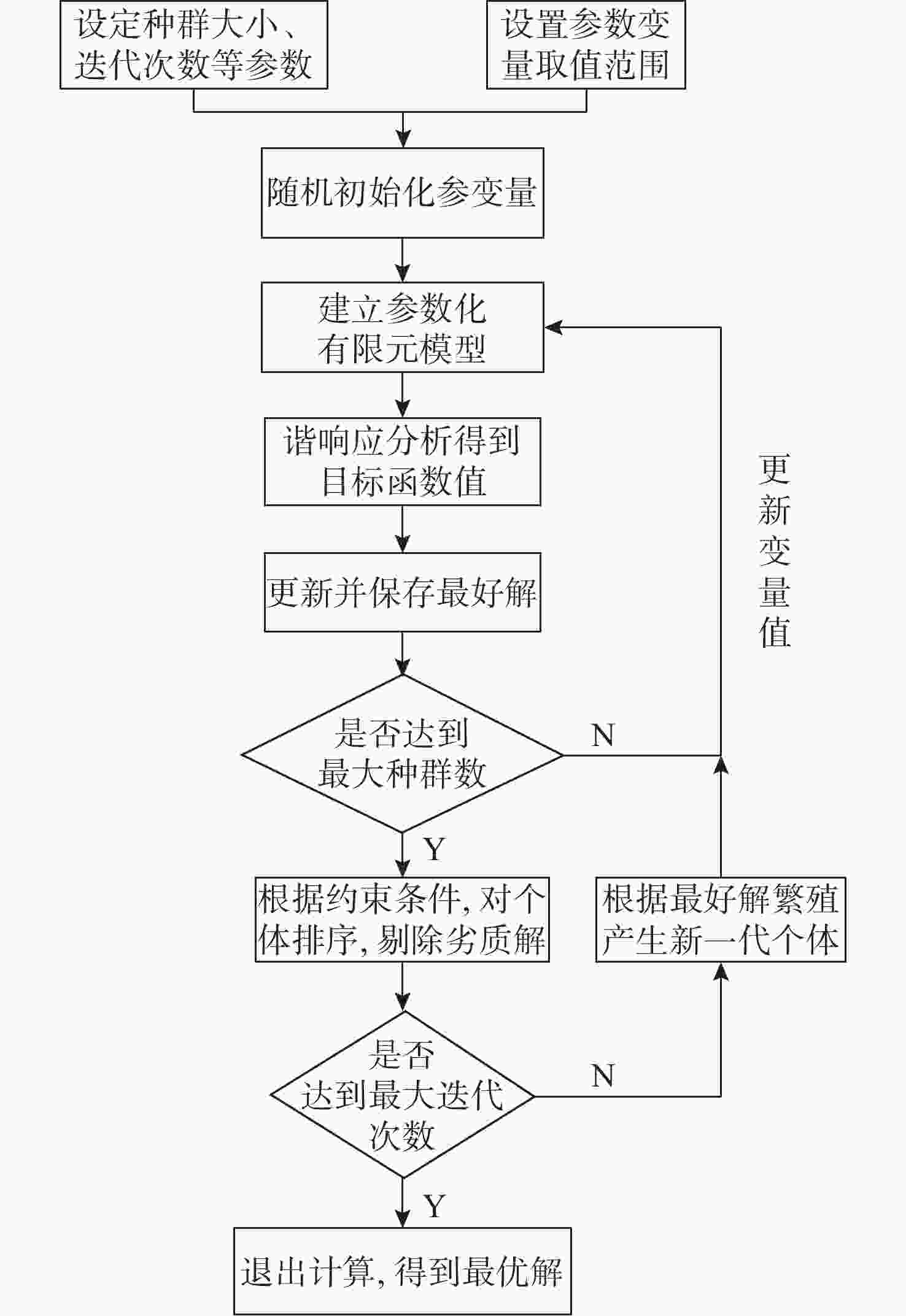
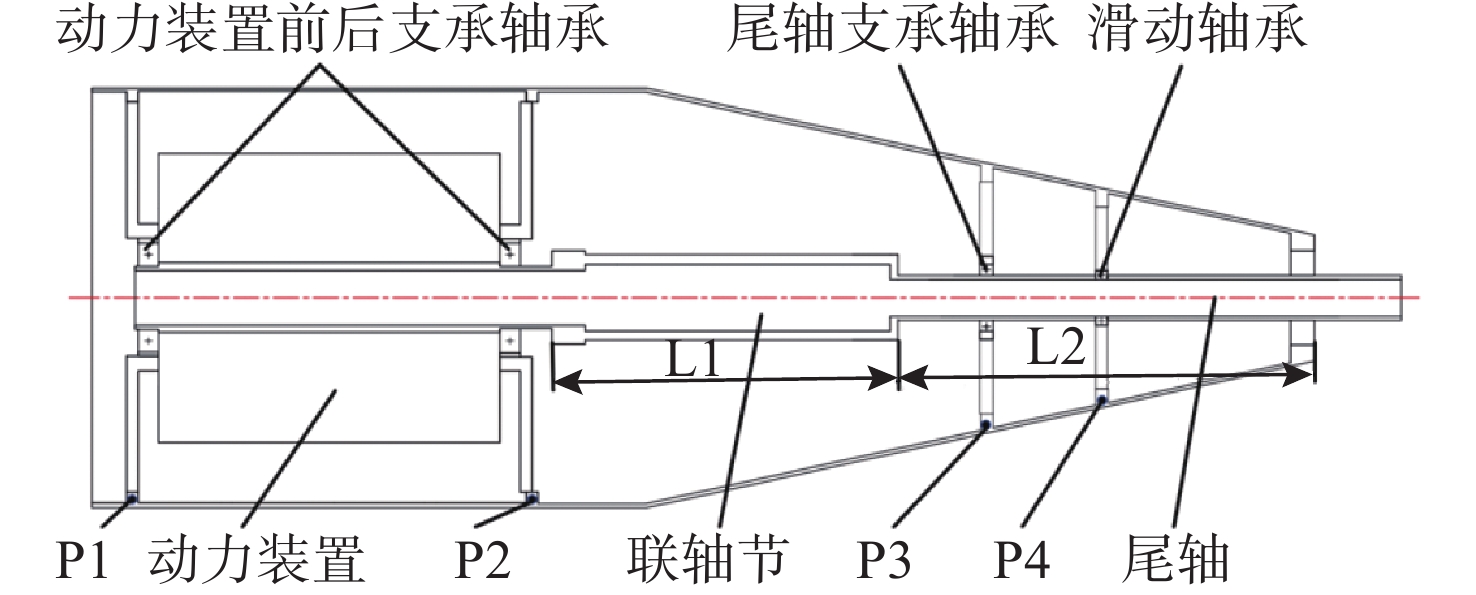
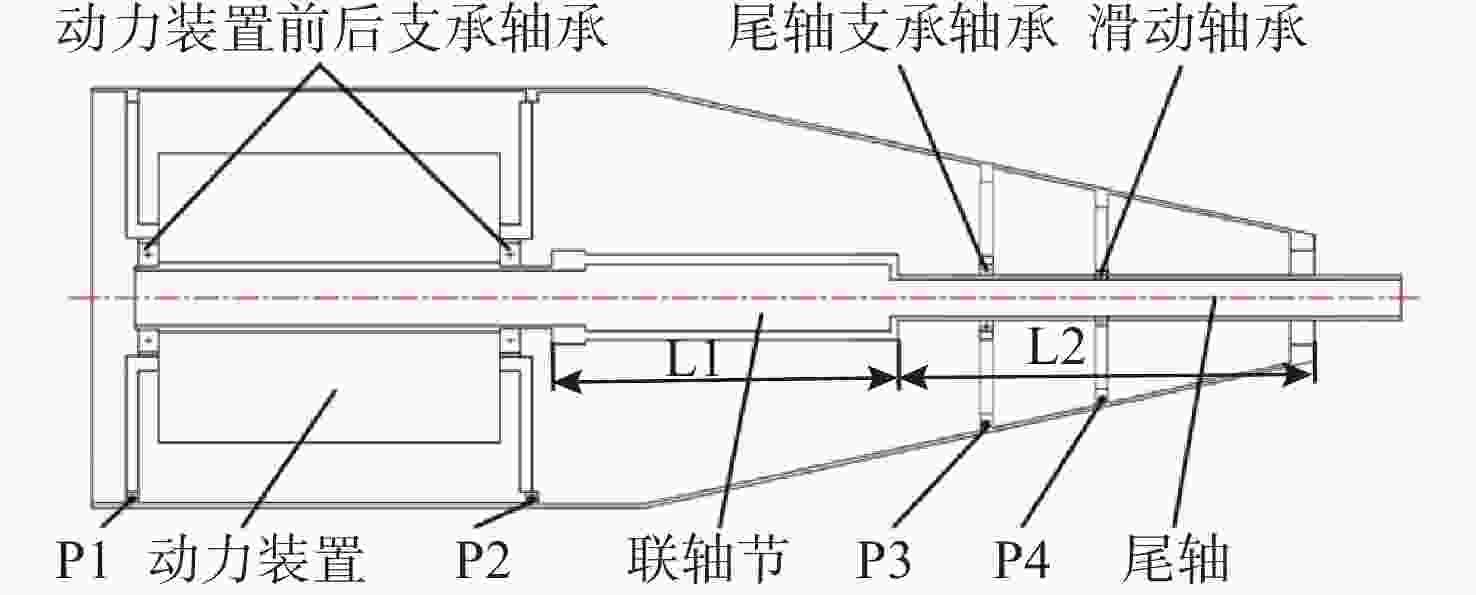
摘要: 为验证整体匹配优化设计效果, 以某典型水下航行器动力推进系统仿真模型为例, 通过建立其有限元简化模型, 基于多目标遗传算法(Multi Objective Genetic Algorithm, MOGA), 选取联轴节与尾轴长度比、尾轴支承位置以及支承刚度作为参数变量, 以壳体上四处关键位置的振动能级作为目标函数, 分别进行参数变量单独优化与整体匹配优化。结果表明, 可通过调整联轴节与尾轴长度比、改变尾轴支承位置和支承刚度等措施来优化系统振动响应, 其中联轴节与尾轴长度比优化后的减振效果可达5.2 dB, 而整体匹配优化相比各参变量单独优化效果更为显著, 其振动能级落差可达9.2 dB。最终得出结论在动力推进系统支承参数优化过程中, 各参数之间可通过多目标遗传算法进行匹配优化, 可最大程度降低系统整体振动响应水平。整体匹配优化方法可为水下航行器动力推进系统的减振优化设计提供新的优化思路。Abstract: To verify the effect of the overall matching optimization design, this study takes the simulation model of a typical underwater vehicle Power Propulsion System (PPS) as an example. By establishing its finite element simplified model and based on the Multi Objective Genetic Algorithm (MOGA), the length ratio of the coupling to the tail shaft, the support position of the tail shaft, and the support stiffness are selected as parameter variables. The vibration levels at four key positions on the shell are used as the objective functions to carry out separate optimization of parameter variables and overall matching optimization respectively. The results show that the vibration response of the system can be optimized by adjusting the length ratio of the coupling to the tail shaft, changing the support position and support stiffness of the tail shaft, etc. Among them, the vibration reduction effect after optimizing the length ratio of the coupling to the tail shaft can reach 5.2 dB, while the overall matching optimization is more significant than the separate optimization of each parameter, with the vibration level drop reaching 9.2 dB. Finally, the conclusion is drawn that in the process of optimizing the support parameters of the power propulsion system, each parameter can be matched and optimized through a multi-objective genetic algorithm to minimize the overall vibration response level of the system. The overall matching optimization method can provide a new optimization idea for the vibration reduction optimization design of the power propulsion system of underwater vehicles.
-
Key words:
- MOGA /
- power propulsion systems /
- support layout /
- stiffness optimization.
-
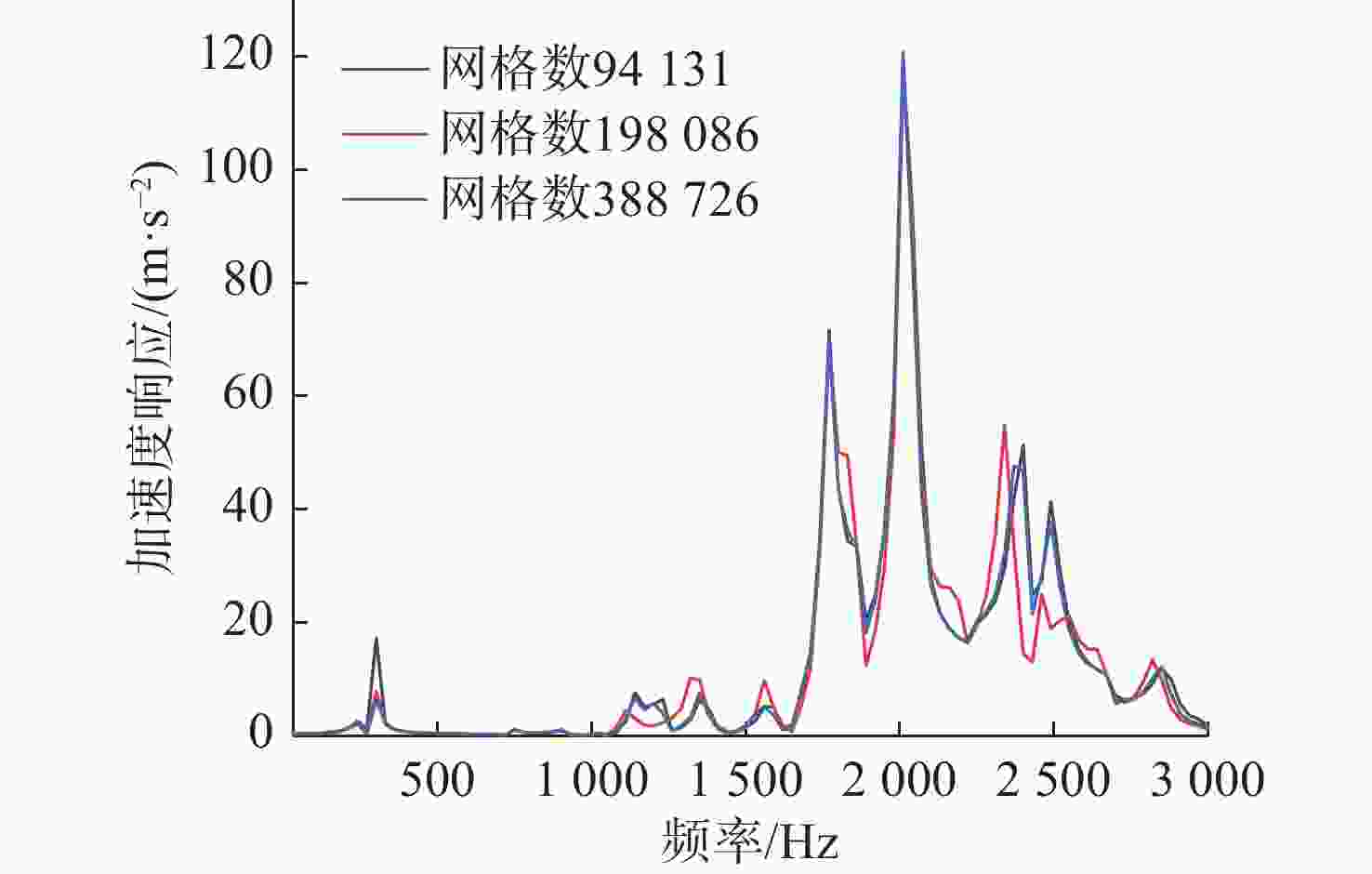
表 1 网格收敛性验证
Table 1. Mesh convergence verification
网格单元数 均方根/(m·s−2) 误差/% 94 131 23.92 — 198 086 23.37 2.33 388 726 23.39 0.10 表 2 联轴节与尾轴长度比优化结果
Table 2. Optimization results of the coulpling-tail shaft length ratio
Lc/Ls V1/dB V2/dB V3/dB V4/dB 优化前 0.8 119.3 120.1 116.2 122.5 优化后 0.7 114.2 114.9 115.6 118.3 衰减量 5.1 5.2 0.6 4.2 表 3 尾轴支承位置优化结果
Table 3. Optimization results of the tail shaft support position
L1/mm L2/mm V1/dB V2/dB V3/dB V4/dB 优化前 20 220 119.3 120.1 116.2 122.5 优化后 50 260 118.8 117.5 113.9 119.7 衰减量 0.5 2.6 2.3 2.8 表 4 支承刚度优化结果
Table 4. Optimization results of the support stiffness
k1/(N/m) k2/(N/m) k3/(N/m) k4/(N/m) V1/dB V2/dB V3/dB V4/dB 优化前 2.5×108 2.5×108 2.5×108 2.0×108 119.3 120.1 116.2 122.5 优化后 2.5×108 3.0×108 3.5×108 2.5×108 117.8 116.6 112.7 117.9 衰减量 1.5 3.5 3.5 4.6 表 5 整体匹配优化结果
Table 5. Optimization results of the overall matching
Lc/Ls L1/mm L2/mm k1/(N/m) k2/(N/m) k3/(N/m) k4/(N/m) V1/dB V2/dB V3/dB V4/dB 优化前 0.8 20 220 2.5×108 2.5×108 2.5×108 2.0×108 119.3 120.1 116.2 122.5 优化后 0.75 130 360 2.0×108 3.0×108 3.0×108 3.0×108 111.0 112.3 109.6 113.3 衰减量 8.3 7.8 6.6 9.2 -
[1] 尹韶平. 鱼雷减振降噪技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2016. [2] 史小锋, 党建军, 梁跃, 等. 水下攻防武器能源动力技术发展现状及趋势[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2021, 29(6): 634-647. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2021.06.001SHI X F, DANG J J, LIANG Y, et al. Development status and trend of energy and power technology for underwater attack and defensive weapon[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2021, 29(6): 634-647. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2021.06.001 [3] 张凯, 尹韶平, 曹小娟, 等. 鱼雷动力及推进系统简化建模与振动分析[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2019, 27(2): 217-224. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2019.02.015ZHANG K, YIN S P, CAO X J, et al. Simplified modeling and vibration analysis of power and propulsion system for torpedo[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2019, 27(2): 217-224. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2019.02.015 [4] 段勇, 刘瑞杰, 马琳. 金属橡胶在鱼雷推进轴系振动控制中的应用[J]. 船舶力学, 2020, 24(9): 1187-1195.DUAN Y, LIU R J, MA L. Application of metal rubber to the vibration control of torpedo propulsion shafting[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2020, 24(9): 1187-1195. [5] 曹浩, 张伟伟, 文立华, 等. 鱼雷动力系统振动控制技术及应用研究[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2019, 27(5): 595-600. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2019.05.017CAO H, ZHANG W W, WEN L H, et al. Research on Vibration Control Technologies of Torpedo Power System and Its Application[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2019, 27(5): 595-600. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2019.05.017 [6] 李海峰, 朱石坚, 翁雪涛. 轴承刚度及间距对水下结构声振特性影响研究[J]. 船舶工程, 2016, 38(9): 57-61. doi: 10.13788/j.cnki.cbgc.2016.09.057LI H F, ZHU S J, WENG X T. Research on Effects of Shaft Bearing Stiffness and Spacing on Vibra-acoustic Radiation of Underwater Structure[J]. Ship Engineering, 2016, 38(9): 57-61. doi: 10.13788/j.cnki.cbgc.2016.09.057 [7] 黄修长, 苏智伟, 倪臻, 等. 基于频响函数综合的推进轴系动力学建模与支撑结构参数优化分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(4): 33-39. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2019.04.006HUANG X C, SU Z W, NI Z, et al. Dynamic modeling and optimization of the supporting structure of a propulsion shaft system by an FRF-based substructuring method[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2019, 38(4): 33-39. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2019.04.006 [8] 田金鑫. 潜航器中浮筏隔振系统的设计与应用研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2020. [9] TANG C K, JIANG Y H, LIU J. Optimization method of bearing support positions in a high-speed flexi-ble rotor system[J]. Journal of Donghua University(English Edition), 2020, 37(6): 504-511. [10] LIU J, TANG C K. A method for predicting the influences of bearing support stiffness and position on the vibrations of a flexible rotor system[J]. International Journal of Acoustics and Vibrations, 2021, 26(4): 287-295. doi: 10.20855/ijav.2021.26.41798 [11] AN Y C, LIU J, YANG C Y, et al. Vibration characteristic analysis and optimization of the propulsion shaft in the underwater vehicle[C]// Proceedings of the 11th IFToMM International Conference on Rotordynamics. Beijing, China: IFToMM, 2023: 439-451. [12] 安宇晨, 刘静, 潘光. 支撑刚度对水下航行器电机-推进轴系振动特性的影响规律分析及优化[J]. 推进技术, 2024, 45(11): 198-209. doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.2311055AN Y C, LIU J, PAN G. Influences and optimization of support stiffness on vibrations of motor propulsion shaft system in an unmanned underwater vehicle[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2024, 45(11): 198-209. doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.2311055 [13] 黄晶晶. 基于振动控制的柔性转子系统多目标优化技术研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2016. [14] 张聪, 疏炳南, 张江涛, 等. 基于响应面法-遗传算法的船舶推进轴系多目标优化设计[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2025, 59(4): 466-475. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2023.318ZHANG C, SHU B N, ZHANG J T, et al. Multi-Objective Optimization Design of Ship Propulsion Shafting Based on Response Surface Methodology and Genetic Algorithm[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2025, 59(4): 466-475. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2023.318 [15] 代丽华, 张志敏. 基于MOGA的船舶推进轴系校中优化方法[J]. 船舶工程, 2022, 44(2): 65-68,139. doi: 10.13788/j.cnki.cbgc.2022.02.11DAI L H, ZHANG Z M. Optimization method of ship propulsion shafting alignment based on MOGA[J]. Ship Engineering, 2022, 44(2): 65-68,139. doi: 10.13788/j.cnki.cbgc.2022.02.11 [16] 丁鸿昌, 李家成, 李茂源, 等. 高速角接触球轴承刚度计算及影响因素分析[J]. 轴承, 2019(11): 1-7. doi: 10.19533/j.issn1000-3762.2019.11.001DING H C, LI J C, LI M Y, et al. Calculation and influencing factor analysis of stiffness of high speed angular contact ball bearings[J]. Bearing, 2019(11): 1-7. doi: 10.19533/j.issn1000-3762.2019.11.001 [17] 孙旭阳, 周景军, 王谦, 等. 基于声学超材料的鱼雷动力舱段减振方法[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(6): 1072-1081. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2024-0063SUN X Y, ZHOU J J, WANG Q, et al. Vibration Reduction Method for Power Cabin of Torpedoes Based on Acoustic Metamaterials[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(6): 1072-1081. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2024-0063 -




 下载:
下载: