Ocean sound separation algorithm based on time-frequency interleaved attention
-
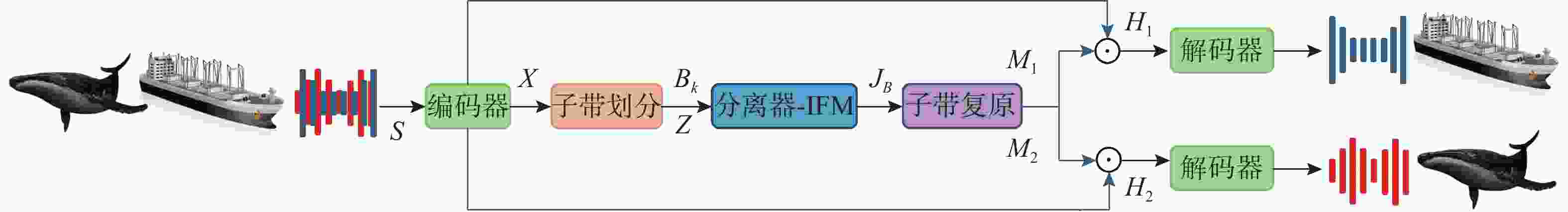
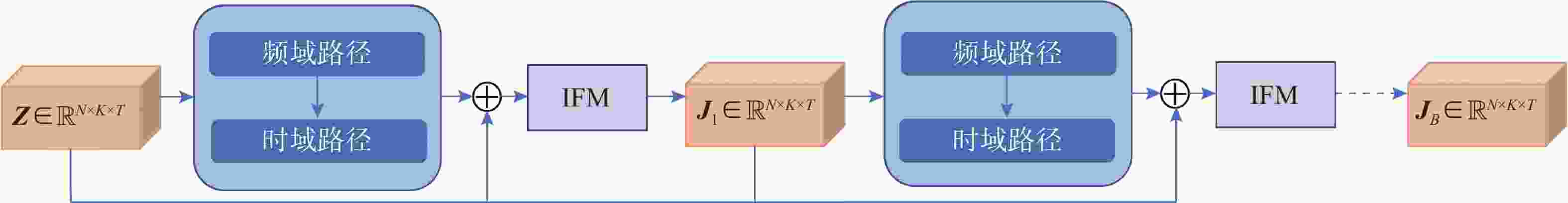
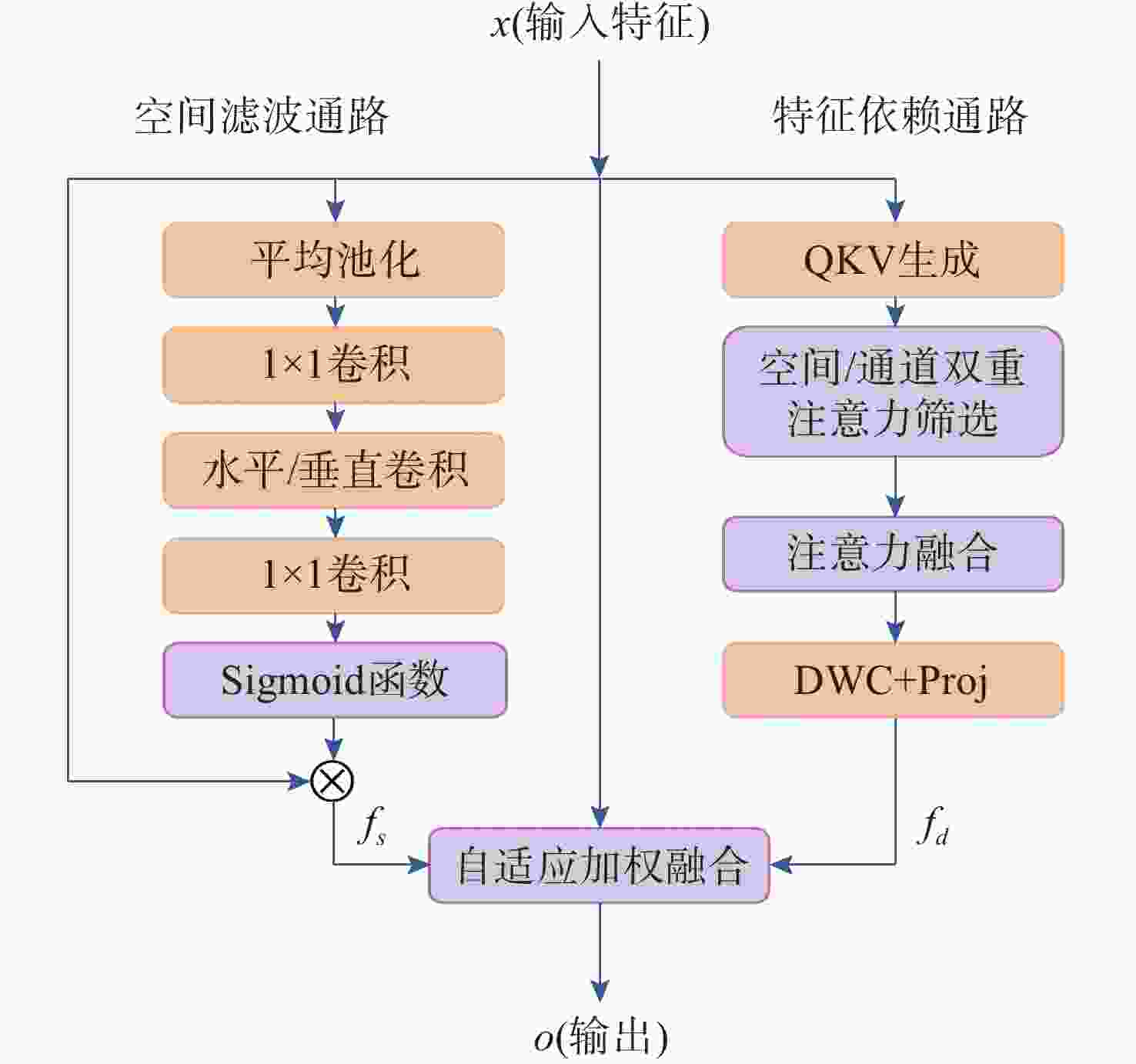
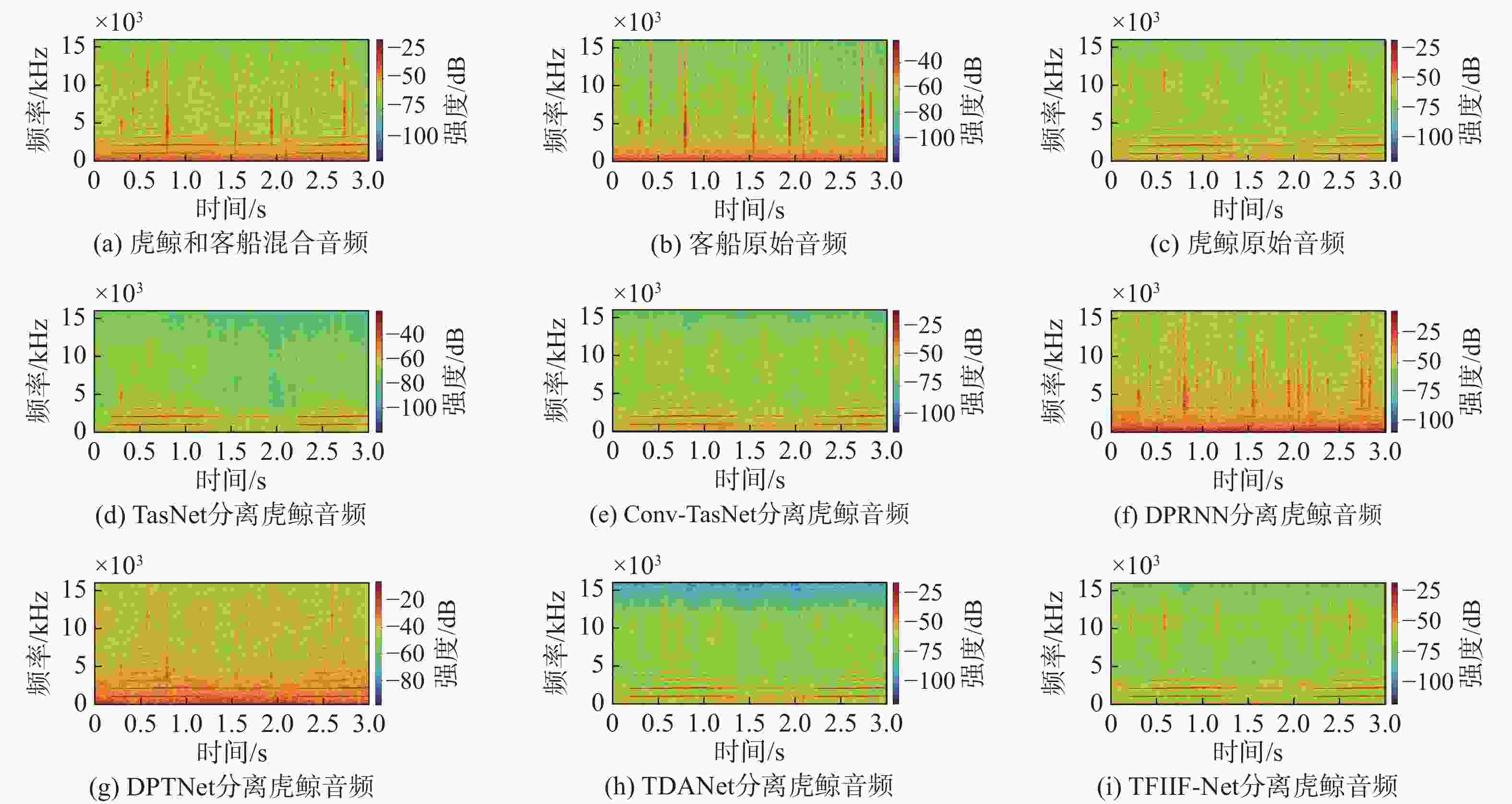
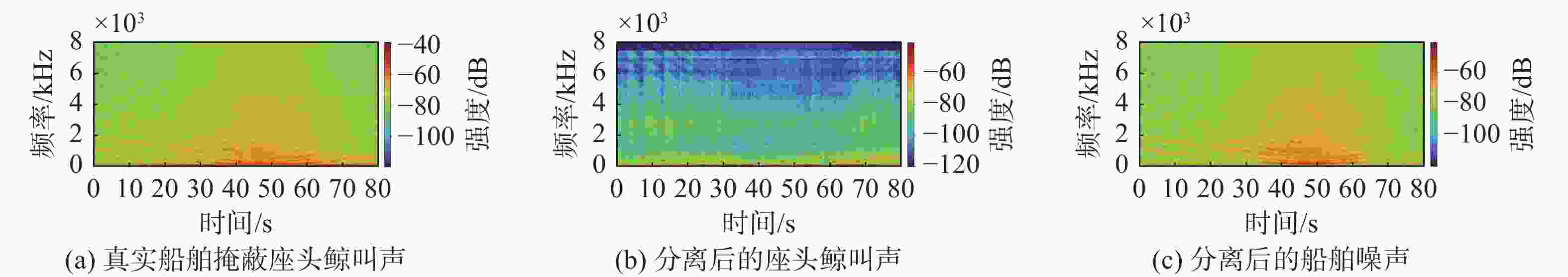
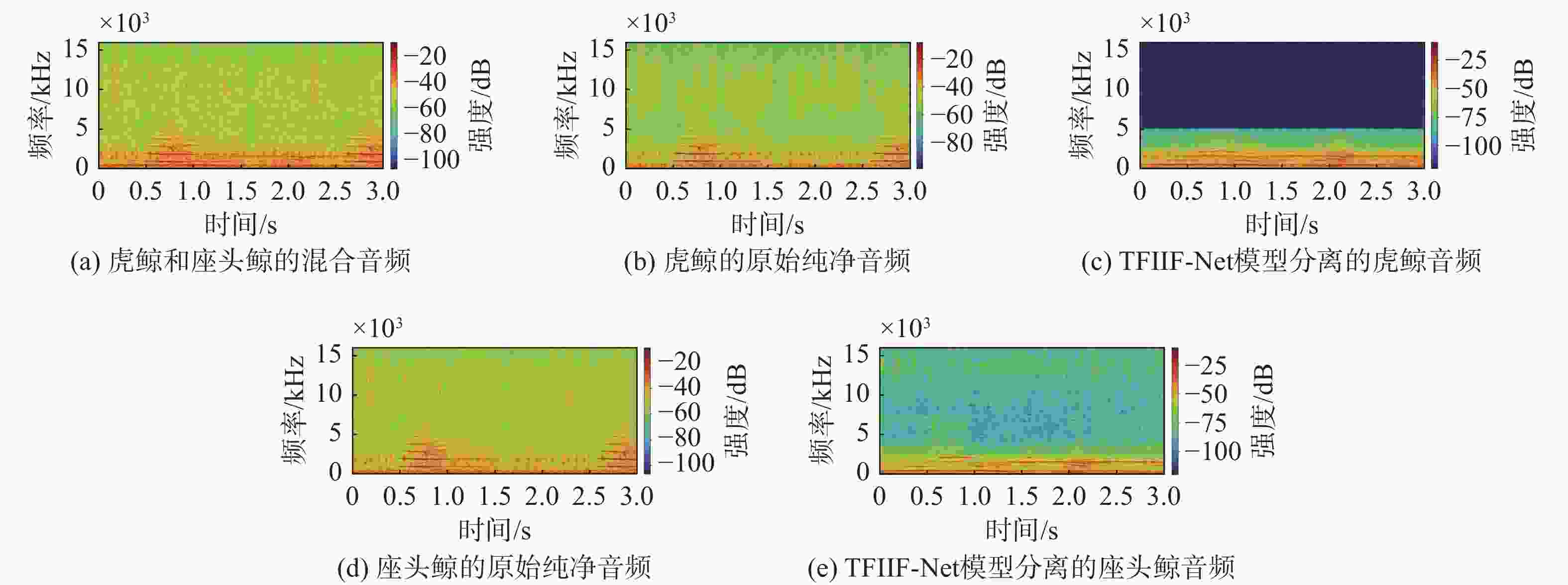
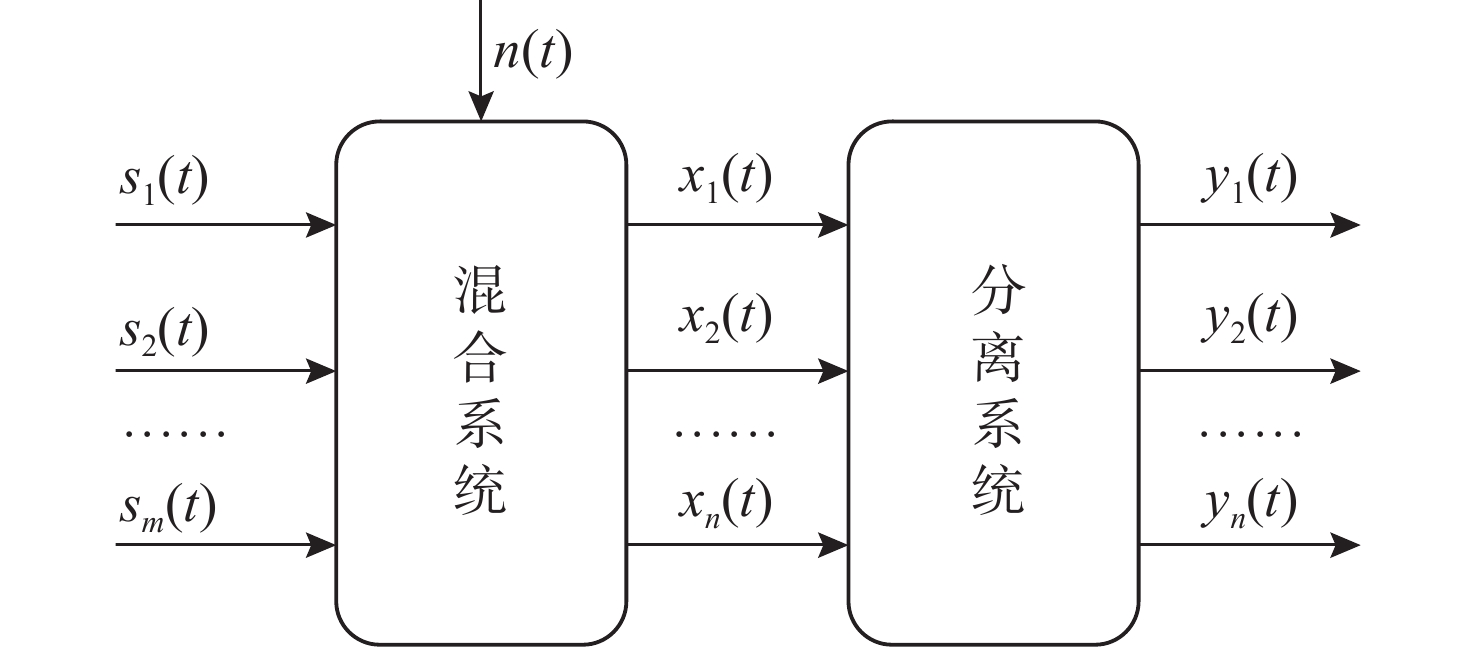
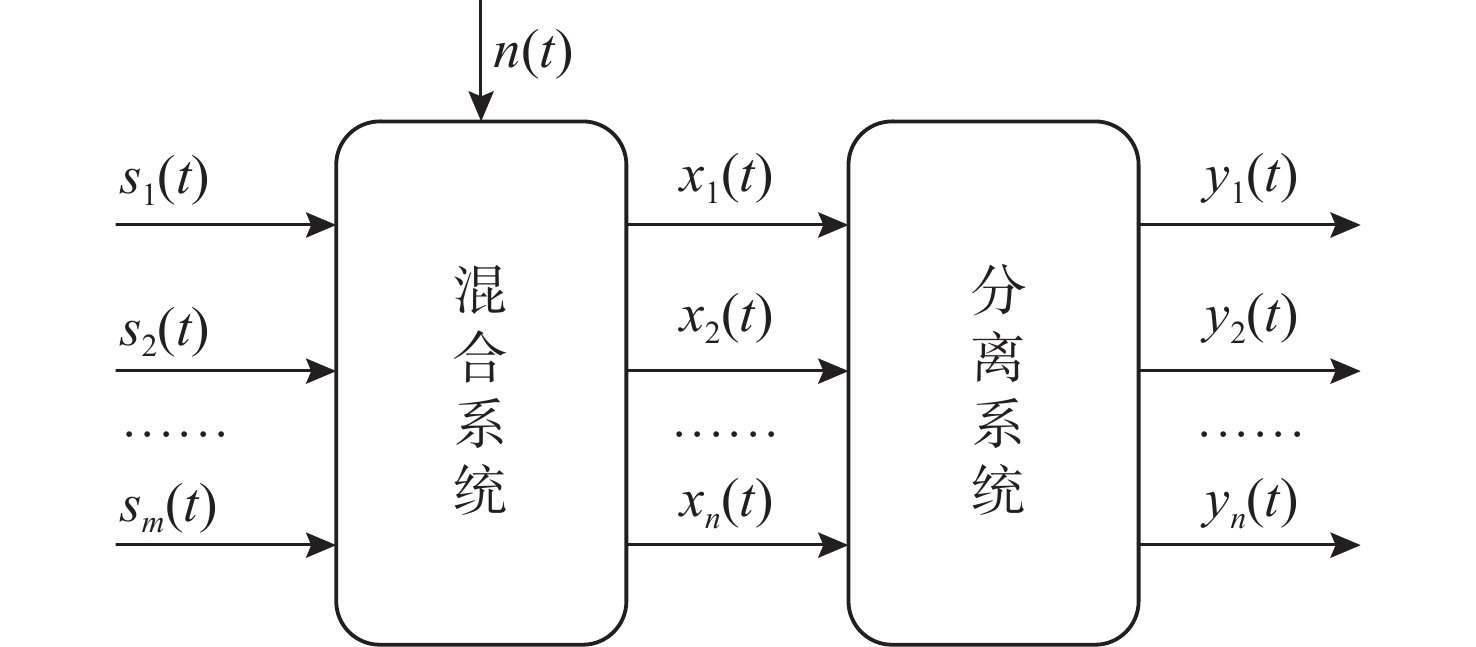
摘要: 海洋声音蕴含着丰富信息, 而复杂海洋声学环境与水下目标信号多变的特性, 给水下声音特征精细化感知与分辨能力带来了严峻挑战。为真实还原水下感兴趣目标的声音, 文中提出基于集成滤波模块(IFM)的海洋声源分离算法。采用频带划分策略, 使用编码器将混合音频转换至时频谱, 利用多尺度注意力机制交叉提取时频增益, 并通过IFM提高水下声音分离能力。其中, IFM采用自适应加权机制, 将多尺度卷积空间滤波通路与自注意力特征依赖通路所提取的特征与原始特征进行高效融合, 并将融合后的特征输入解码器以重建高质量的纯净目标音频, 在增强目标信号细节的同时有效滤除背景噪声和干扰。在海洋典型声音数据集上的实验结果表明, 文中所提算法能够显著提升感兴趣目标音频分离性能, 在座头鲸与客船、虎鲸与客船的音频分离实验中, 源失真比改善量(SDRi)分别达到8.56 dB和10.74 dB, 在其他多种指标上也优于现有的基线模型。Abstract: Ocean sound contains rich information, but the complex ocean acoustic environment and the variable characteristics of underwater target signals pose a serious challenge to the ability of fine perception and discrimination of underwater sound features. In order to truly restore the underwater target sound of interest, the paper proposes a marine sound source separation algorithm based on integrated filtration module(IFM). The model adopts a frequency band segmentation strategy, uses an encoder to convert the mixed audio to the time-frequency spectrum, cross extracts the time-frequency gain using a multi-scale attention mechanism, and improves the separation capability of the underwater sound by the IFM proposed in the paper. Among them, the IFM employs an adaptive weighting mechanism to efficiently fuse the features extracted from the multiscale convolutional spatial filtering pathway and the self-attention feature-dependent pathway with the original features, and inputs the fused features into a decoder to reconstruct high-quality pure target audio, which enhances the details of the target signals while efficiently filtering out the background noises and interferences. Experimental results on marine typical sound datasets show that the proposed algorithm can significantly improve the audio separation performance of the target of interest, and the SDRi reaches 8.56dB and 10.74dB in the audio separation experiments between humpback whales and passenger ships, and killer whales and passenger ships, respectively, and also outperforms the existing baseline model in a variety of other metrics.
-
表 1 音频分离模型的性能指标对比实验
Table 1. Comparison of performance metrics of audio separation models experiment
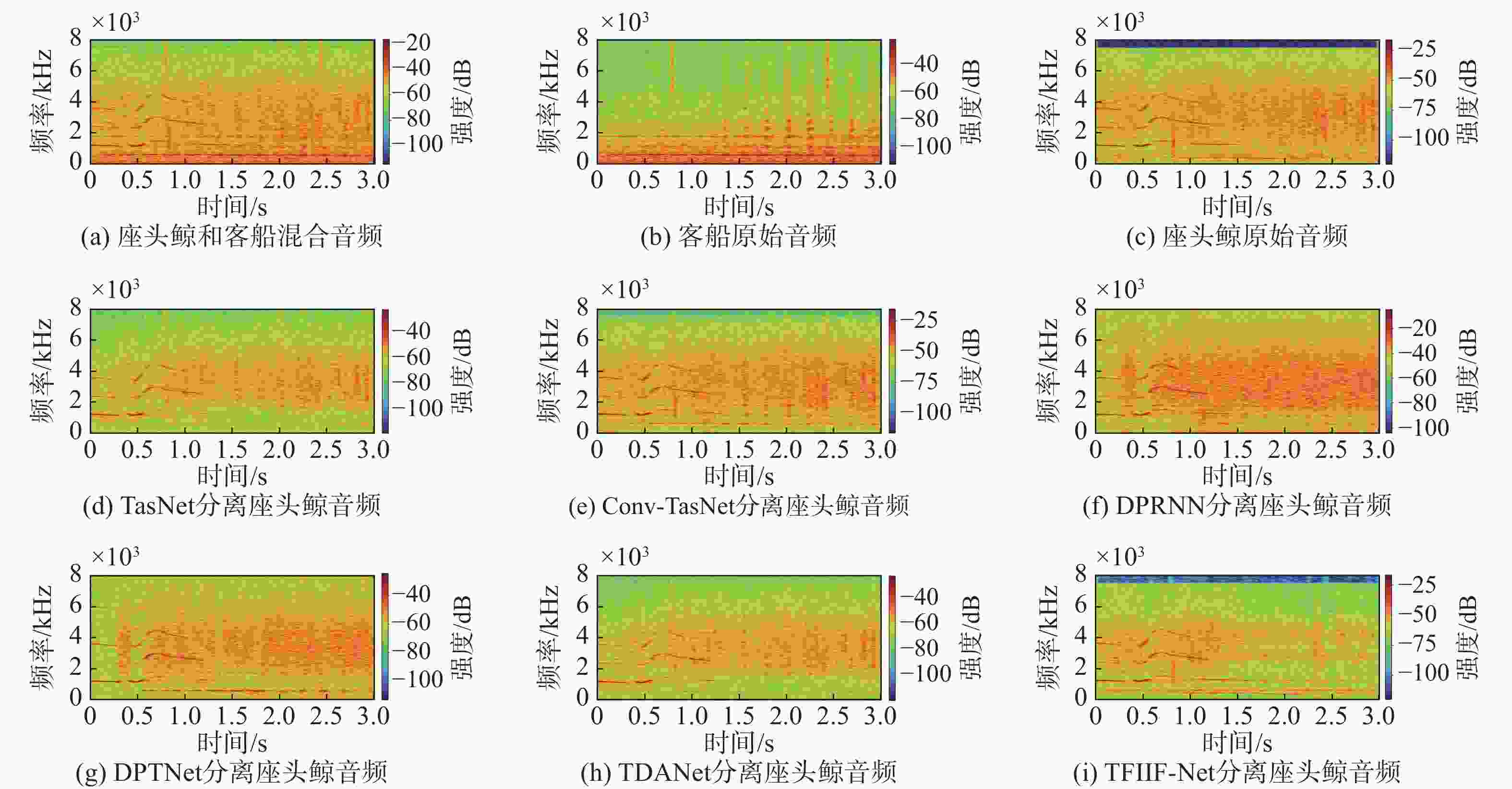
实验类别 处理方法 SAR/dB SIR/dB SDR/dB SDRi/dB 实验1 Tas-Net 10.09 10.68 6.71 6.17 Conv-TasNet 11.34 11.84 7.96 7.42 DPRNN 11.33 12.76 8.32 7.78 DPTNet 11.43 11.03 7.63 7.09 TDANet 10.98 11.60 7.71 7.17 TFIIF-Net 11.98 13.32 9.10 8.56 实验2 TasNet 10.09 11.31 7.11 7.01 Conv-TasNet 11.63 13.58 9.04 8.94 DPRNN 11.04 13.44 8.59 8.49 DPTNet 7.11 6.10 2.28 2.18 TDANet 10.99 12.49 8.08 7.98 TFIIF-Net 12.80 16.21 10.84 10.74 表 2 消融实验
Table 2. Ablation experiment
Methods SAR/dB SIR/dB SDR/dB SDRi/dB Base 11.83 13.18 8.97 8.43 Spatial 11.95 13.30 9.06 8.52 Feature 11.93 12.83 8.84 8.30 Equalweight 12.68 11.55 8.67 8.13 TFIIF-Net 11.98 13.32 9.10 8.56 -
[1] BAYRAKCI G, KLINGELHOEFER F. An introduction to the ocean soundscape[M]. Noisy Oceans: Monitoring Seismic and Acoustic Signals in the Marine Environment. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2024. [2] DUARTE C M, CHAPUIS L, COLLIN S P, et al. The soundscape of the Anthropocene ocean[J]. Science, 2021, 371(6529): eaba4658. doi: 10.1126/science.aba4658 [3] LI D, WU M, YU L, et al. Single-channel blind source separation of underwater acoustic signals using improved NMF and FastICA[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2023, 9: 1097003. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.1097003 [4] 谢加武. 基于深度学习的水下声源分离技术研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2019. [5] WANG M, ZHANG W, SHAO M, et al. Separation and extraction of compound-fault signal based on multi-constraint non-negative Matrix factorization[J]. Entropy, 2024, 26(7): 583. doi: 10.3390/e26070583 [6] SCHULZE F K, RICHARD G, KELLEY L, et al. Unsupervised music source separation using differentiable parametric source models[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2023, 31: 1276-1289. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2023.3252272 [7] ANSARI S, ALATRANY A S, ALNAJJAR K A, et al. A survey of artificial intelligence approaches in blind source separation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2023, 561: 126895. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.126895 [8] CHANDNA P, CUESTA H, PETERMANN D, et al. A deep-learning based framework for source separation, analysis, and synthesis of choral ensembles[J]. Frontiers in Signal Processing, 2022, 2: 808594. doi: 10.3389/frsip.2022.808594 [9] LUO Y, MESGARANI N. Tasnet: time-domain audio separation network for real-time, single-channel speech separation[C]//2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP). Calgary, AB, Canada: IEEE, 2018: 696-700. [10] LUO Y, MESGARANI N. Conv-tasnet: Surpassing ideal time–frequency magnitude masking for speech separation[J]. IEEE/ACM transactions on audio, speech, and language processing, 2019, 27(8): 1256-1266. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2019.2915167 [11] LUO Y, CHEN Z, YOSHIOKA T. Dual-path rnn: efficient long sequence modeling for time-domain single-channel speech separation[C]//ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP). Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2020: 46-50. [12] CHEN J, MAO Q, LIU D. Dual-path transformer network: Direct context-aware modeling for end-to-end monaural speech separation[EB/OL]. [2025-11-25] https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.13975. [13] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017(30): 5998-6008. [14] ZHANG W, LI X, ZHOU A, et al. Underwater acoustic source separation with deep Bi-LSTM networks[C]//2021 4th International Conference on Information Communication and Signal Processing (ICICSP). Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2021: 254-258. [15] HE Q, WANG H, ZENG X, et al. Ship-radiated noise separation in underwater acoustic environments using a deep time-domain network[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2024, 12(6): 885. doi: 10.3390/jmse12060885 [16] LIU Y, JIANG L. Passive underwater acoustic signal separation based on feature decoupling dual-path network[EB/OL]. [2025-09-25] https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.08371 [17] XU M, LI K, CHEN G, et al. Tiger: Time-frequency interleaved gain extraction and reconstruction for efficient speech separation[EB/OL]. [2025-09-25] https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.01469 [18] SAYIGH L, DAHER M A, ALLEN J, et al. The Watkins marine mammal sound database: an online, freely accessible resource[C]//Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics. Acoustical Society of America. Dublin, Ireland: POMA, 2016: 040013. [19] SANTOS-DOMÍNGUEZ D, TORRES-GUIJARRO S, CARDENAL-LÓPEZ A, et al. ShipsEar: An underwater vessel noise database[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2016, 113: 64-69. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2016.06.008 [20] YUREN B. Research on music source separation technology based on deep learning[J]. Computer Science and Application, 2022, 12: 2788. doi: 10.12677/CSA.2022.1212283 -




 下载:
下载: