Ship Radiated Noise Recognition Based on Dual Low-Rank Adaptation Training
-
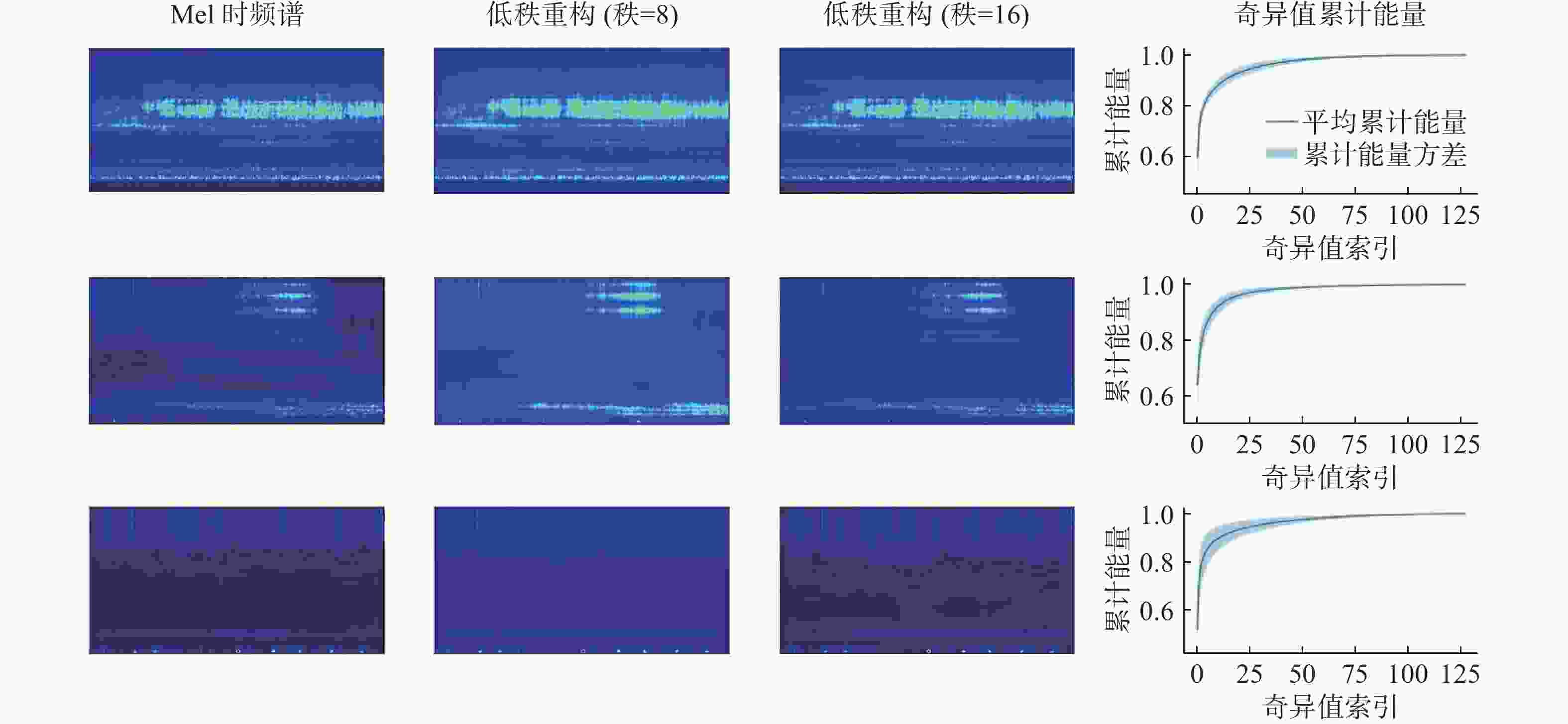
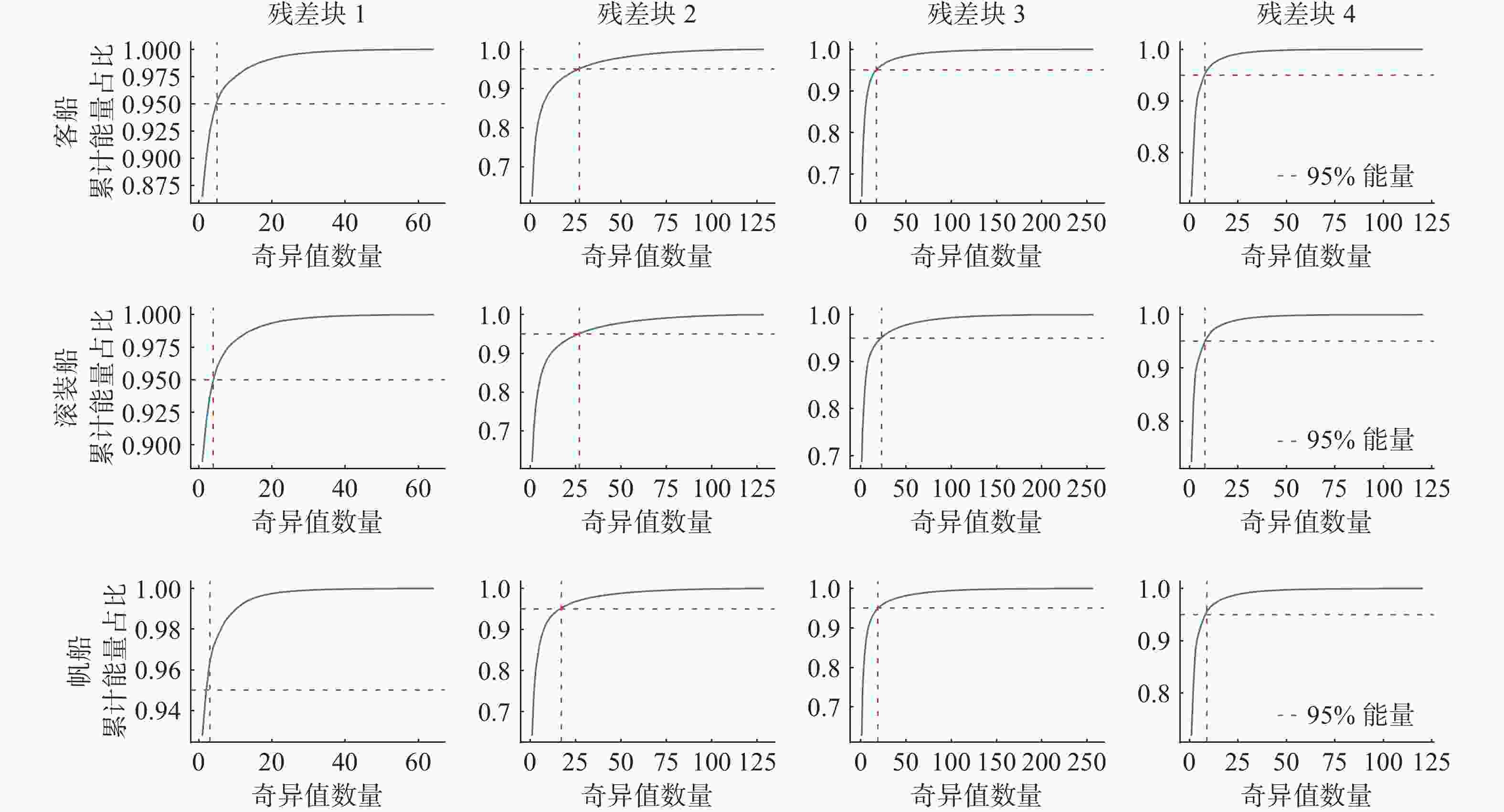
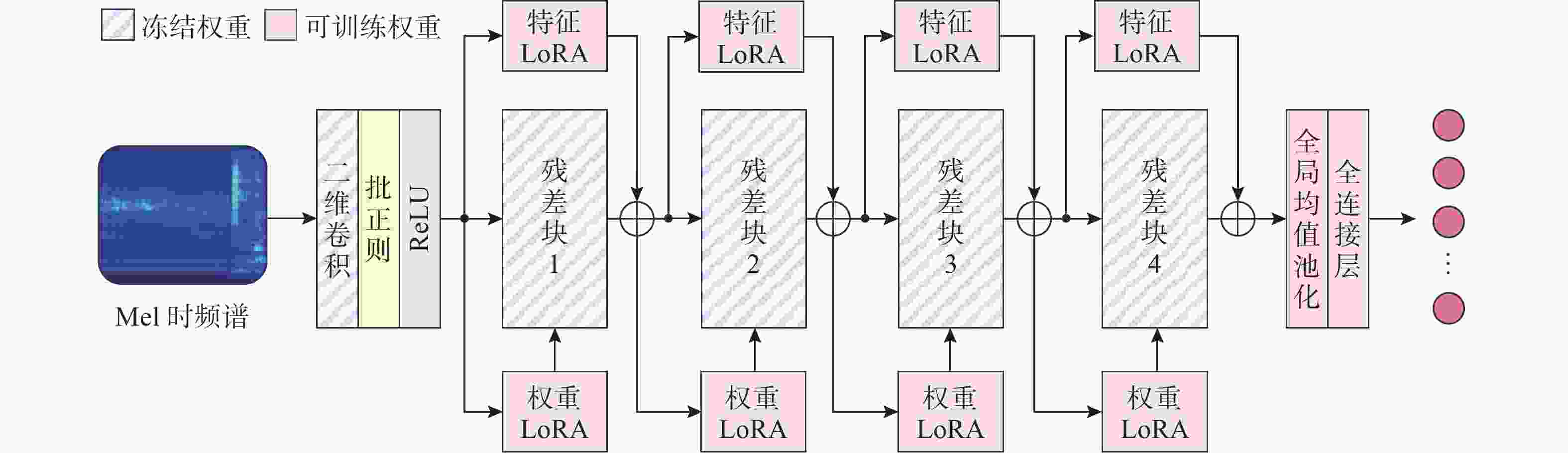
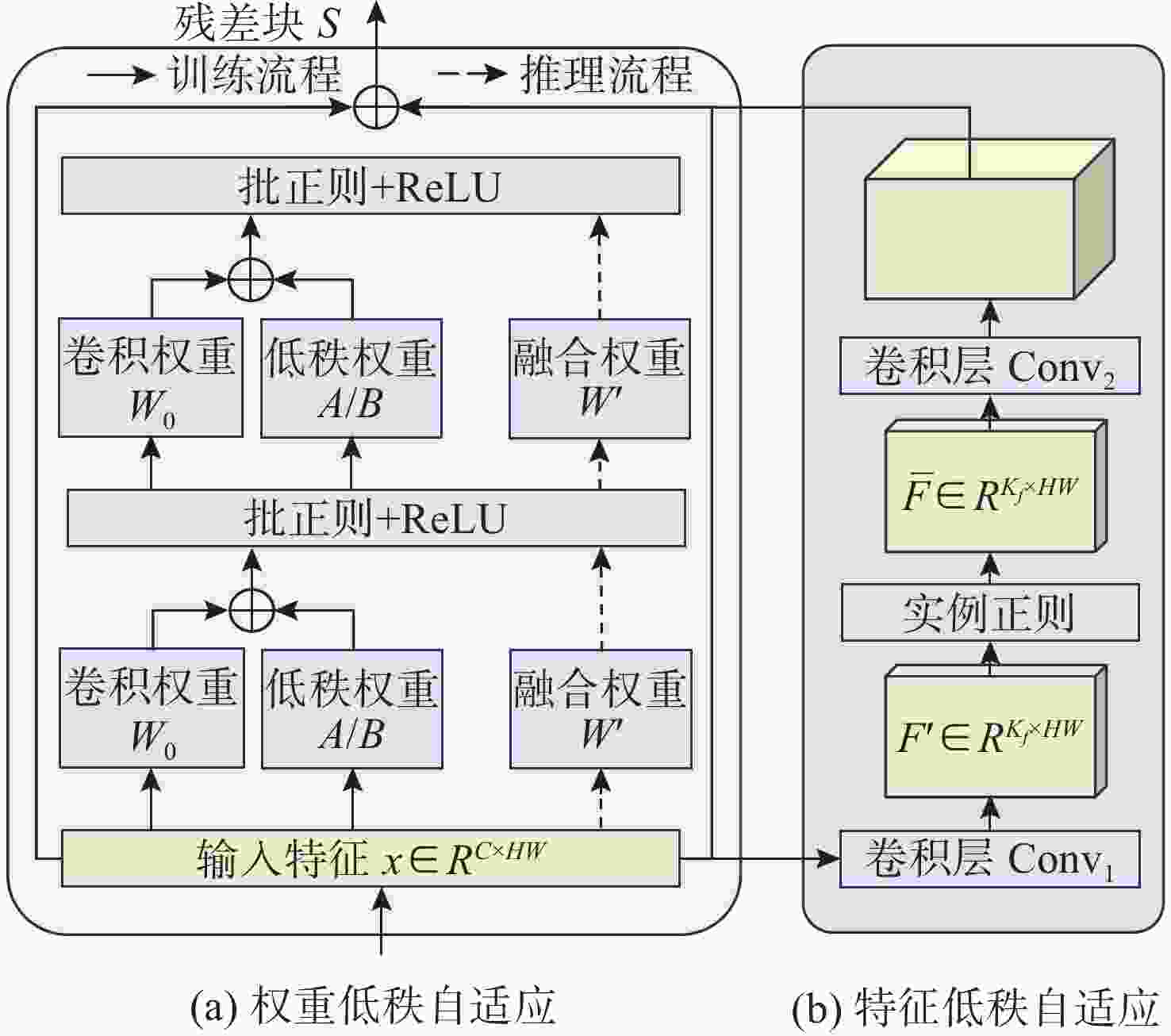
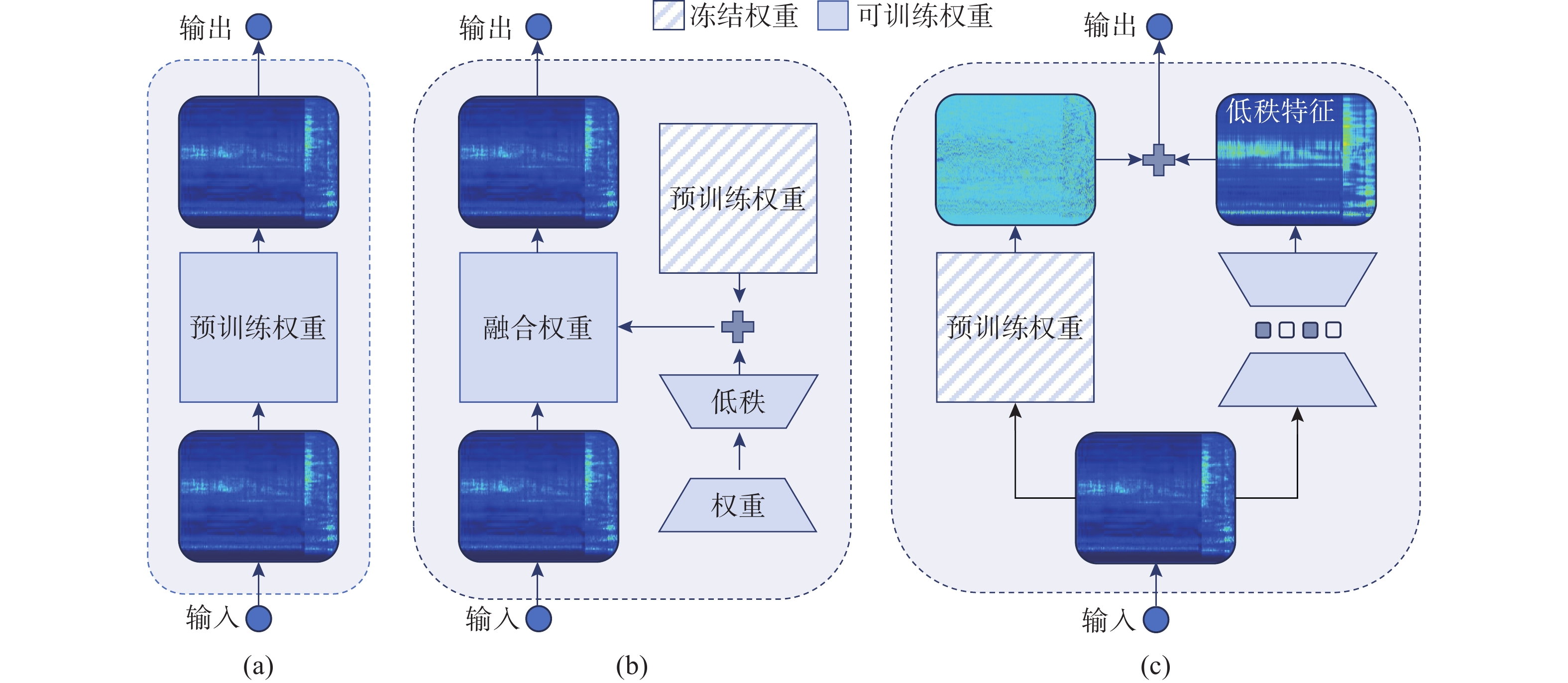
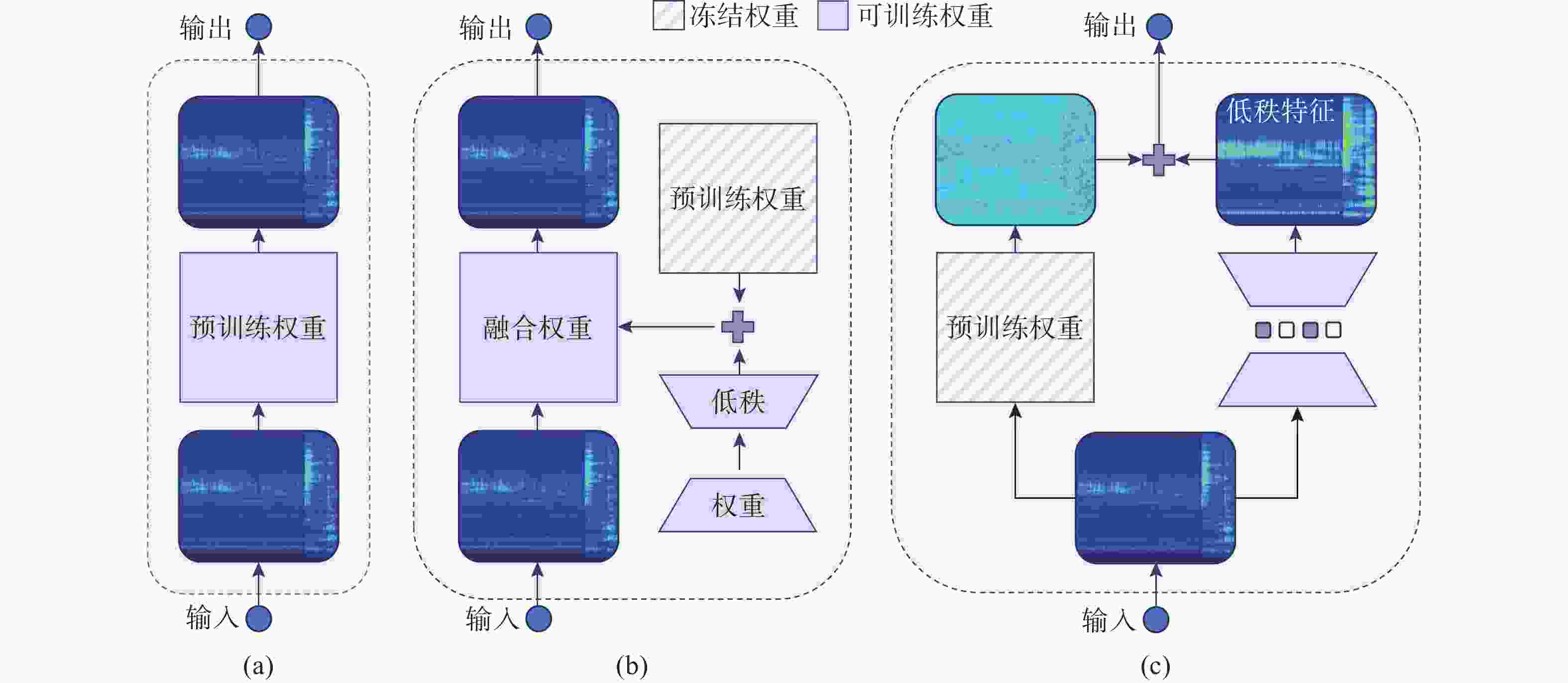
摘要: 针对深度学习模型在船舶辐射噪声识别中由数据短缺导致的泛化能力受限问题, 文中提出了权重-特征双低秩迁移学习框架。该框架从模型权重和特征表达两个维度协同展开低秩优化: 在权重空间, 冻结预训练权重, 通过轻量化低秩权重调整(WLoRA)模块构建可学习低秩权重更新, 以较少参数量完成权重微调, 从而降低过拟合风险; 在特征空间, 基于船舶辐射噪声Mel时频谱的内在低秩结构, 通过低秩特征调整(FLoRA)模块对特征进行压缩和重构, 从而显式约束模型学习低秩特征。该框架充分考虑了Mel时频谱的固有低秩结构, 深入挖掘预训练模型潜力, 有效提升了迁移学习性能。通过ShipsEar和Deepship两个公开数据集的实验证明, 相对于直接微调预训练模型, 所提出方法能够有效提升迁移学习在船舶辐射嗓声分类模型中的性能。进一步的消融实验验证了两个低秩模块的有效性。Abstract: To address the limited generalization capability of deep learning models in ship-radiated noise recognition, this paper proposes a dual low-rank transfer learning framework that simultaneously optimizes both model weights and feature representations. Specifically, in the weight space, the pretrained weights are frozen, and a lightweight low-rank weight adjustment(WLoRA) module is introduced to construct learnable low-rank increments. This strategy enables efficient fine-tuning with significantly fewer trainable parameters, thereby mitigating the risk of overfitting. In the feature space, considering the inherent low-rank properties of Mel spectrograms derived from ship-radiated noise, a low-rank feature adjustment(FLoRA) module is designed to compress and reconstruct the extracted features. This explicit low-rank constraint encourages the model to learn compact and discriminative representations that better capture the essential structures of ship-radiated noise. By jointly exploiting low-rank optimization in both the weight and feature dimensions, the framework maximizes the potential of pretrained models and improves transfer learning performance. The experimental results on two publicly available underwater acoustic datasets, ShipsEar and Deepship, demonstrate that the proposed method significantly enhances the performance of transfer learning in the classification model of ship-radiated noise compared to direct fine-tuning of pre-trained models. Furthermore, ablation studies validate the effectiveness of the two low-rank modules.
-
Key words:
- ship radiated noise /
- low rank analysis /
- transfer learning /
- LoRA training
-
表 1 数据集划分
Table 1. Division of datasets.
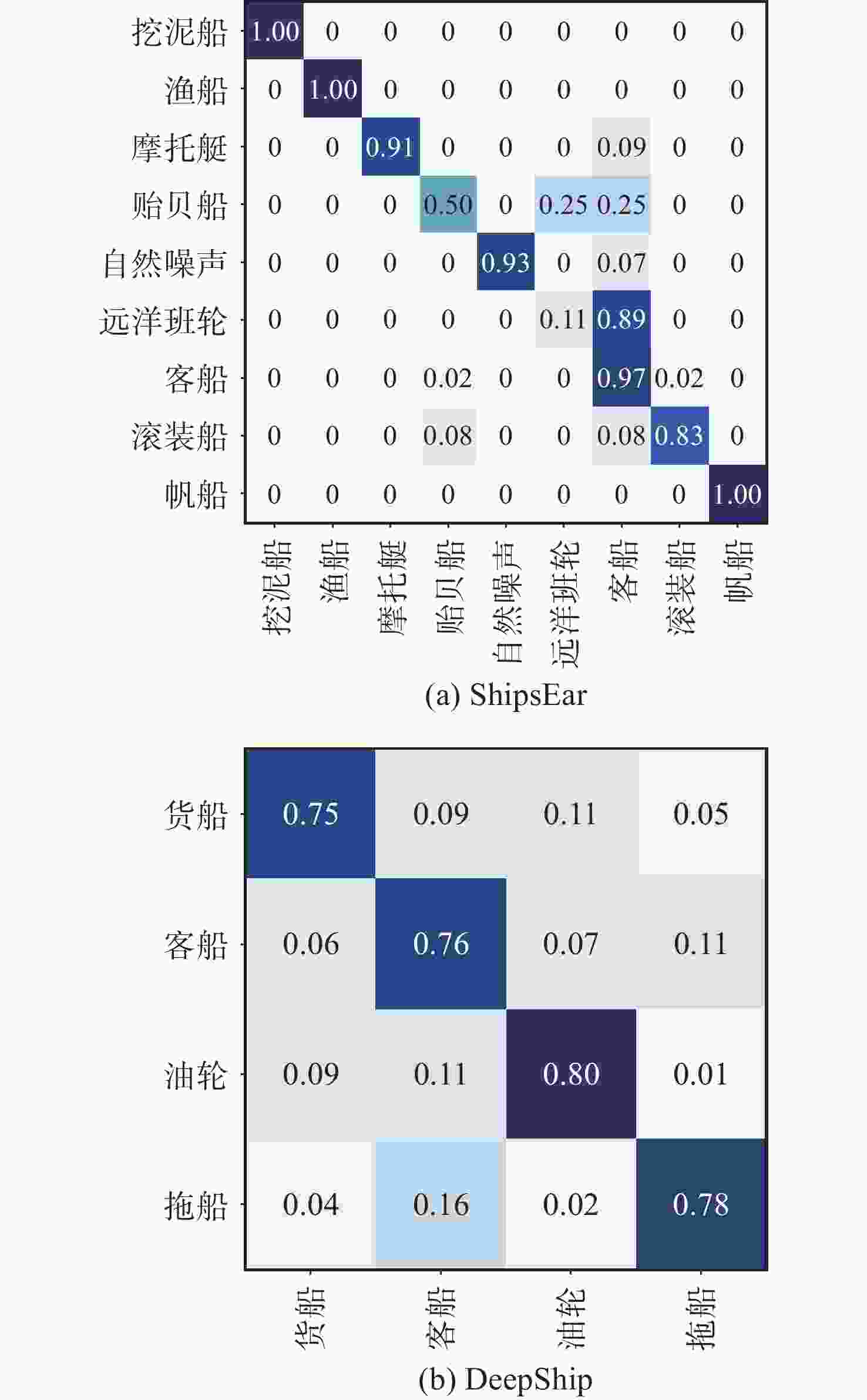
数据集 训练音频 测试音频 训练样本 测试样本 ShipsEar 64 21 470 117 DeepShip 403 137 7 650 2 516 表 2 ShipsEar数据集上对比实验结果
Table 2. Results of experiments on ShipsEar dataset.
方法 特征 OA/% Params/M 时间/s FLOPs/G ResNet18 Mel 79.5 11.179 768 4.40 SIR&LMR Mel 83.8 11.841 1 733 13.40 CMoE STFT 85.5 11.191 2 102 55.62 所提方法 Mel 86.3 11.241 824 4.43 表 3 DeepShip数据集上对比实验结果
Table 3. Results of experiments on DeepShip dataset.
方法 特征 OA/% Params/M 时间/s FLOPs/G ResNet18 Mel 74.8 11.179 768 4.40 SIR&LMR Mel 77.1 11.841 1 733 17.70 CMoE STFT 76.8 11.191 2 102 16.90 所提方法 Mel 77.2 11.241 824 4.43 表 4 模块消融实验结果
Table 4. Results of ablation experiments
方法 OA Params ResNet 77.7% 11.179M ResNet-pre 79.5% 11.179M WLoRA 83.8% 11.179M FLoRA 85.5% 11.241M Full 86.3% 11.241M 表 5
$ \alpha $ 参数敏感性实验Table 5. Results of
$ \boldsymbol{\alpha } $ sensitivity analysis$ \alpha $取值 OA/% Params/M 0.0 82.1 11.241 0.1 83.5 11.241 0.2 86.3 11.241 0.3 85.5 11.241 0.4 82.1 11.241 0.5 80.3 11.241 表 6
$ {K}_{w} $ 参数敏感性实验Table 6. Results of
$ {\boldsymbol{K}}_{\boldsymbol{w}} $ sensitivity analysis方法 OA/% Params/M 4 82.1 11.241 8 83.8 11.241 16 85.5 11.241 32 86.3 11.241 64 86.3 11.241 表 7 单独使用WLoRA的
$ {\boldsymbol{K}}_{\boldsymbol{w}} $ 参数敏感性实验Table 7. Results of
$ {\boldsymbol{K}}_{\boldsymbol{w}} $ sensitivity analysis without FLoRA Module方法 OA/% Params/M 4 77.7 11.179 8 80.3 11.179 16 82.1 11.179 32 82.1 11.179 64 83.8 11.179 表 8
$ {\boldsymbol{K}}_{\boldsymbol{f}} $ 参数敏感性实验Table 8. Results of
$ {\boldsymbol{K}}_{\boldsymbol{f}} $ sensitivity analysis方法 OA/% Params/M 4 83.8 11.187 8 82.1 11.195 16 84.6 11.201 32 86.3 11.241 64 85.5 11.302 -
[1] BROOKER A, HUMPHREY V. Measurement of radiated underwater noise from a small research vessel in shallow water[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2016, 120: 182-189. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2015.09.048 [2] FILLINGER L, DE THEIJE P, ZAMPOLLI M, et al. Towards a passive acoustic underwater system for protecting harbours against intruders[C]//2010 International WaterSide Security Conference. Carrara, Italy: IEEE, 2010: 1-7. [3] 王培兵, 彭圆. 深度学习在水声目标识别中的应用研究[J]. 数字海洋与水下攻防, 2020, 3(1): 11-17.WANG P B, PENG Y. Research on application of deep learning in underwater acoustic target recognition[J]. Digital Ocean & Underwater Warfare, 2020, 3(1): 11-17. [4] 张奇, 笪良龙, 王超, 等. 基于深度学习的水声被动目标识别研究综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(11): 4190-4202.ZHANG Q, DA L L, WANG C, et al. An overview on underwater acoustic passive target recognition based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(11): 4190-4202. [5] 刘嘉尉. 基于改进型ResNet模型的水声目标识别方法研究[D]. 延吉: 延边大学, 2024. [6] 薛灵芝, 曾向阳. 动态水声环境中SE_ResNet模型目标识别方法[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2023, 44(6): 939-946.XUE L Z, ZENG X Y. Target recognition method of SE_ResNet model in dynamic underwater acoustic environment[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2023, 44(6): 939-946. [7] XU Y C, CAI Z M, KONG X P. Improved pitch shifting data augmentation for ship-radiated noise classification[J]. Applied acoustics, 2023, 211: 109468. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2023.109468 [8] 李理, 李向欣, 殷敬伟. 基于生成对抗网络的船舶辐射噪声分类方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(6): 1974-1983.LI L, LI X X, YIN J W. Research on classification algorithm of ship radiated noise data based on generative adversarial network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(6): 1974-1983. [9] JIANG Z, ZHAO C, WANG H Y. Classification of underwater target based on S-ResNet and modified DCGAN models[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(6): 2293. doi: 10.3390/s22062293 [10] XU J, XIE Y, WANG W C. Underwater acoustic target recognition based on smoothness-inducing regularization and spectrogram-based data augmentation[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 281: 114926. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114926 [11] CUI X D, HE Z F, XUE Y T, et al. Few-shot underwater acoustic target recognition using domain adaptation and knowledge distillation[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2025, 50(2): 637-653. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2025.3532036 [12] LI Z Y, XIANG S C, YU T, et al. Oceanship: A large-scale dataset for underwater audio target recognition[C]//International Conference on Intelligent Computing. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2024: 475-486. [13] GONG Y, CHUNG Y A, GLASS J. PSLA: Improving audio tagging with pretraining, sampling, labeling, and aggregation[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2021, 29: 3292-3306. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2021.3120633 [14] HU E, SHEN Y L, WALLIS P, et al. LoRA: Low-rank adaptation of large language models[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations. Online: ICLR, 2021: 1-26. [15] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. [16] ZHANG H Y, CISSÉ M, DAUPHIN Y, et al. Mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations. Online: ICLR, 2017: 1-11. [17] SANTOS-DOMÍNGUEZ D, TORRES-GUIJARRO S, CARDENAL-LÓPEZ A, et al. ShipsEar: An underwater vessel noise database[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2016, 113: 64-69. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2016.06.008 [18] IRFAN M, ZHANG J B, ALI S, et al. DeepShip: An underwater acoustic benchmark dataset and a separable convolution based autoencoder for classification[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 183: 115270. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115270 [19] XIE Y, REN J W, XU J. Unraveling complex data diversity in underwater acoustic target recognition through convolution-based mixture of experts[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 249: 123431. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.123431 -




 下载:
下载: