Application of Ensemble Learning Algorithms on Ship Radiation Noise Prediction
-
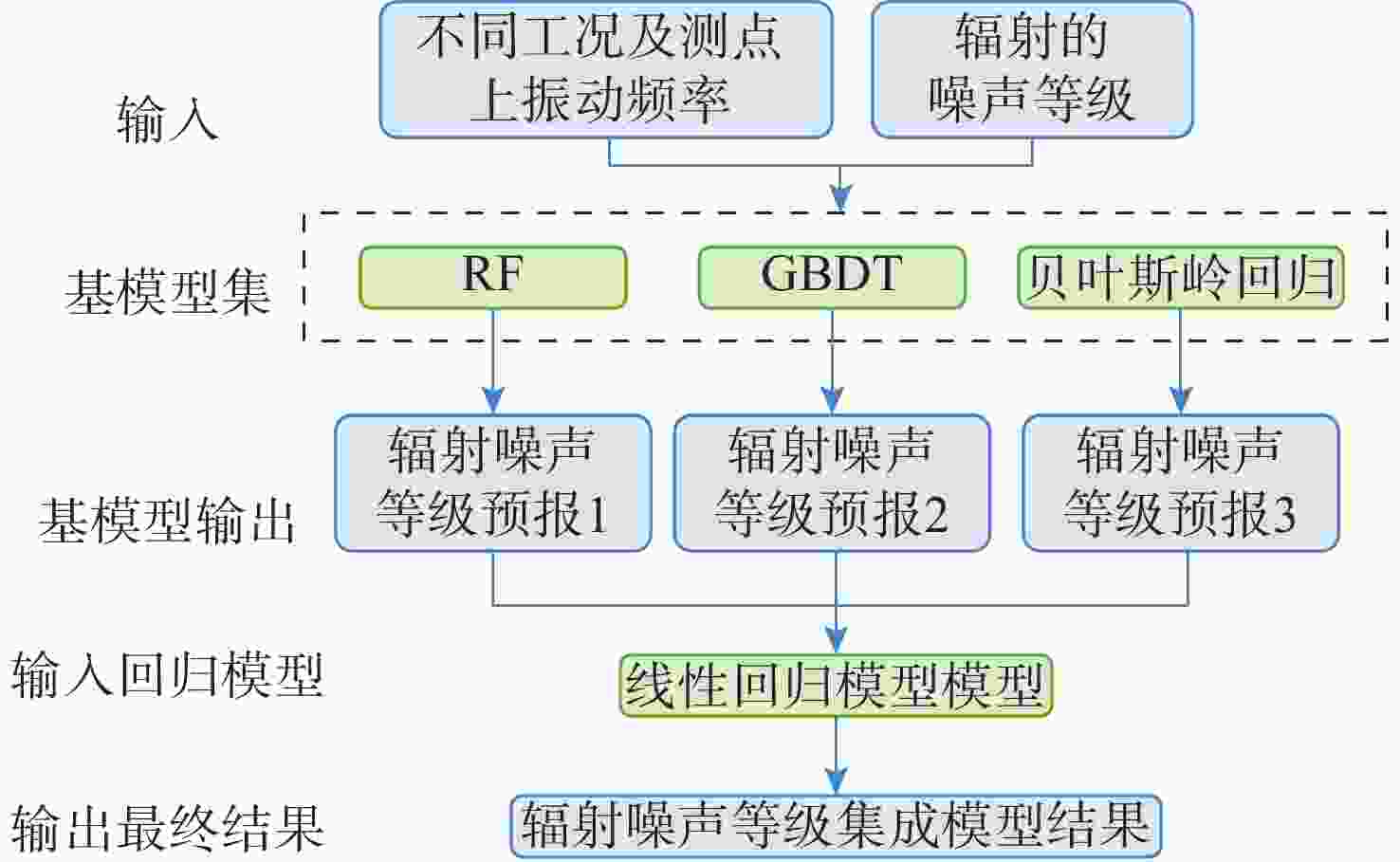
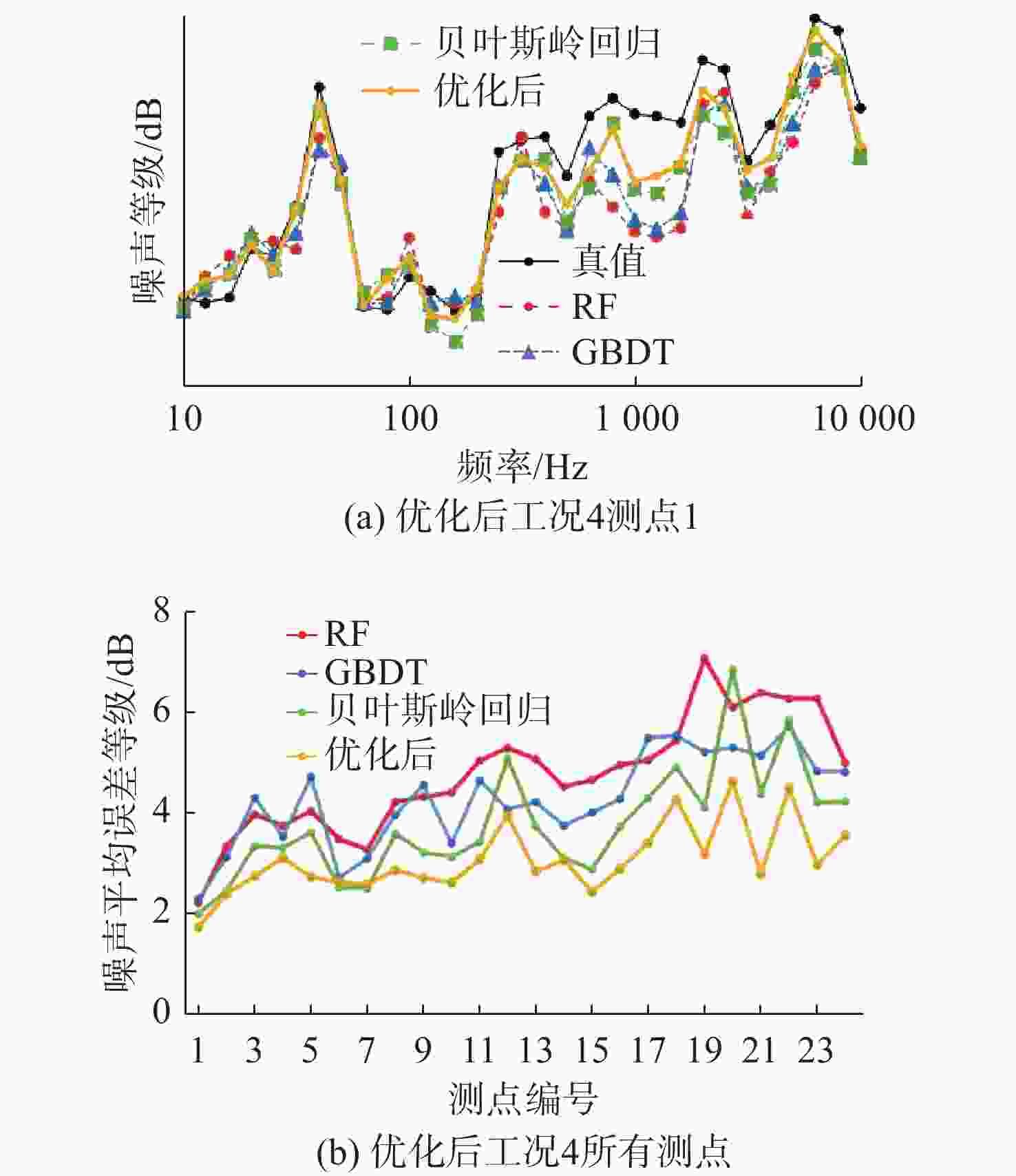
摘要: 船舶多振动源产生的辐射噪声会严重影响其舒适性与隐身性。准确预测其辐射噪声水平与分布, 可为船舶设计阶段的减振降噪优化提供关键支撑。针对船舶振动源数量多以及噪声辐射机制复杂的问题, 文中首先采用集成学习算法中的随机森林与梯度提升树算法, 对不同工况、不同测点的1/3倍频程噪声声压级开展快速预报, 并与贝叶斯岭回归模型的预报效果进行对比验证。4种测试工况的验证结果显示, 集成学习算法在3种工况下的预报效果优于贝叶斯岭回归, 平均绝对误差均小于5 dB; 进一步对上述模型进行优化, 通过在不同层次构建集成学习算法与线性算法的基础单元并组合, 形成辐射噪声联合预报方案, 其精度较单一集成学习算法提升1.5 dB。文中所提集成学习算法及联合预报方案可为船舶辐射噪声的快速精准分析提供有效技术工具。Abstract: The radiation noise generated by multiple vibration sources on ships can seriously affect their comfort and stealth performance. Accurately predicting the radiation noise level and distribution can provide crucial support for the vibration and noise reduction optimization during the ship design stage. In response to the problem of numerous vibration sources in ships and the complex noise radiation mechanism, this paper first employed the random forest and gradient boosting tree algorithms from the ensemble learning algorithms to conduct rapid prediction of the 1/3 octave band noise sound pressure level under different operating conditions and at different measurement points. The prediction results were then compared and verified with those of the Bayesian ridge regression model. The verification results of the four test conditions show that the ensemble learning algorithm outperforms the Bayesian ridge regression in all three conditions, with an average absolute error of less than 5 dB. Further optimization of the above model is conducted by constructing the basic units of the ensemble learning algorithm and the linear algorithm at different levels and combining them to form a joint radiation noise prediction scheme. Its accuracy is improved by 1.5 dB compared to the single ensemble learning algorithm. The ensemble learning algorithm and the joint prediction scheme proposed in this paper can provide effective technical tools for the rapid and accurate analysis of ship radiation noise.
-
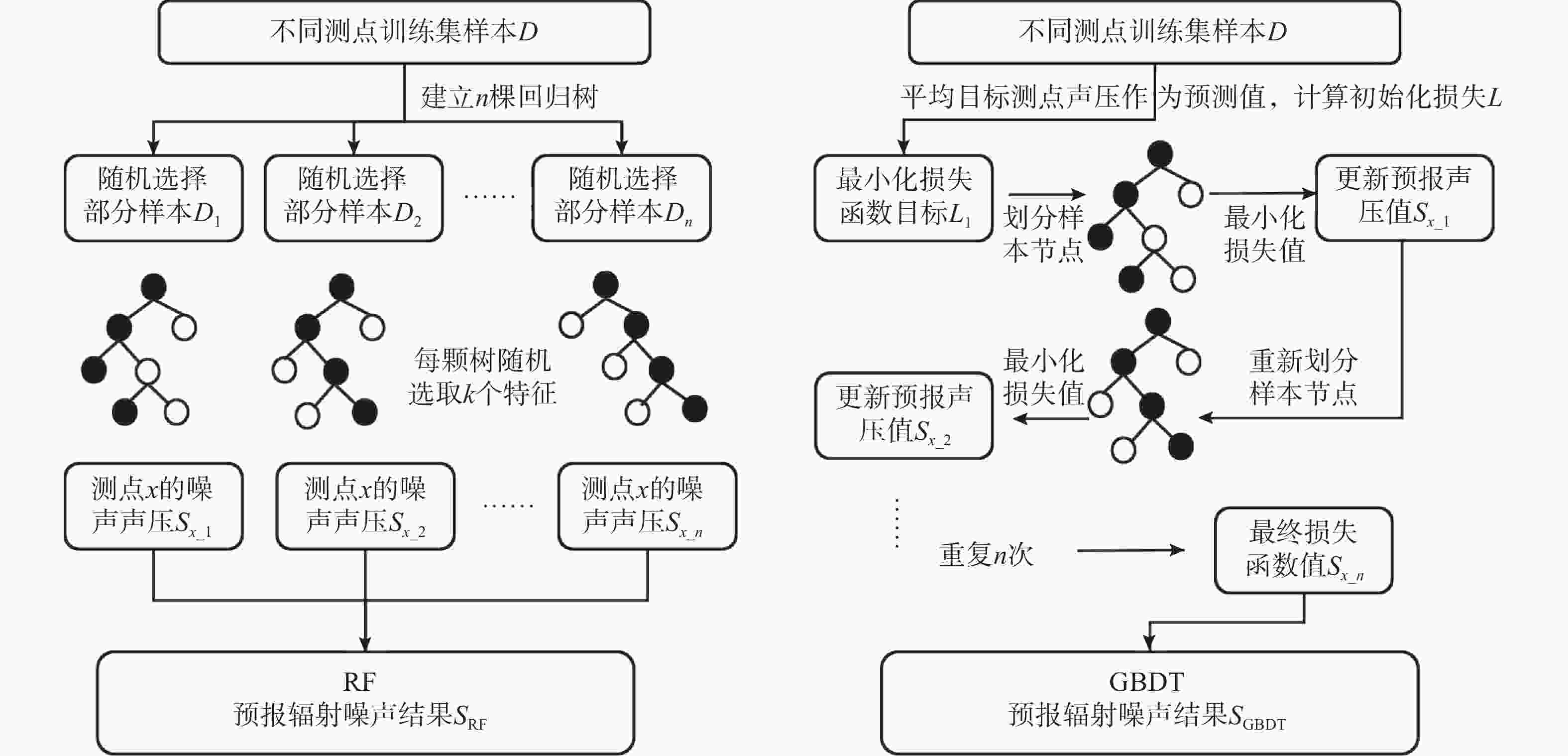
表 1 集成模型超参数列表
Table 1. List of integration model superparameters
模型名称 模型超参数 RF回归 CART数量、袋外评分、最大特征数及最大深度等 GBDT回归 CART数量、学习率、阿尔法系数、子样本比例及最大特征数等 表 2 不同频率区模型预报误差对比
Table 2. Comparison of model prediction errors in different frequency regions
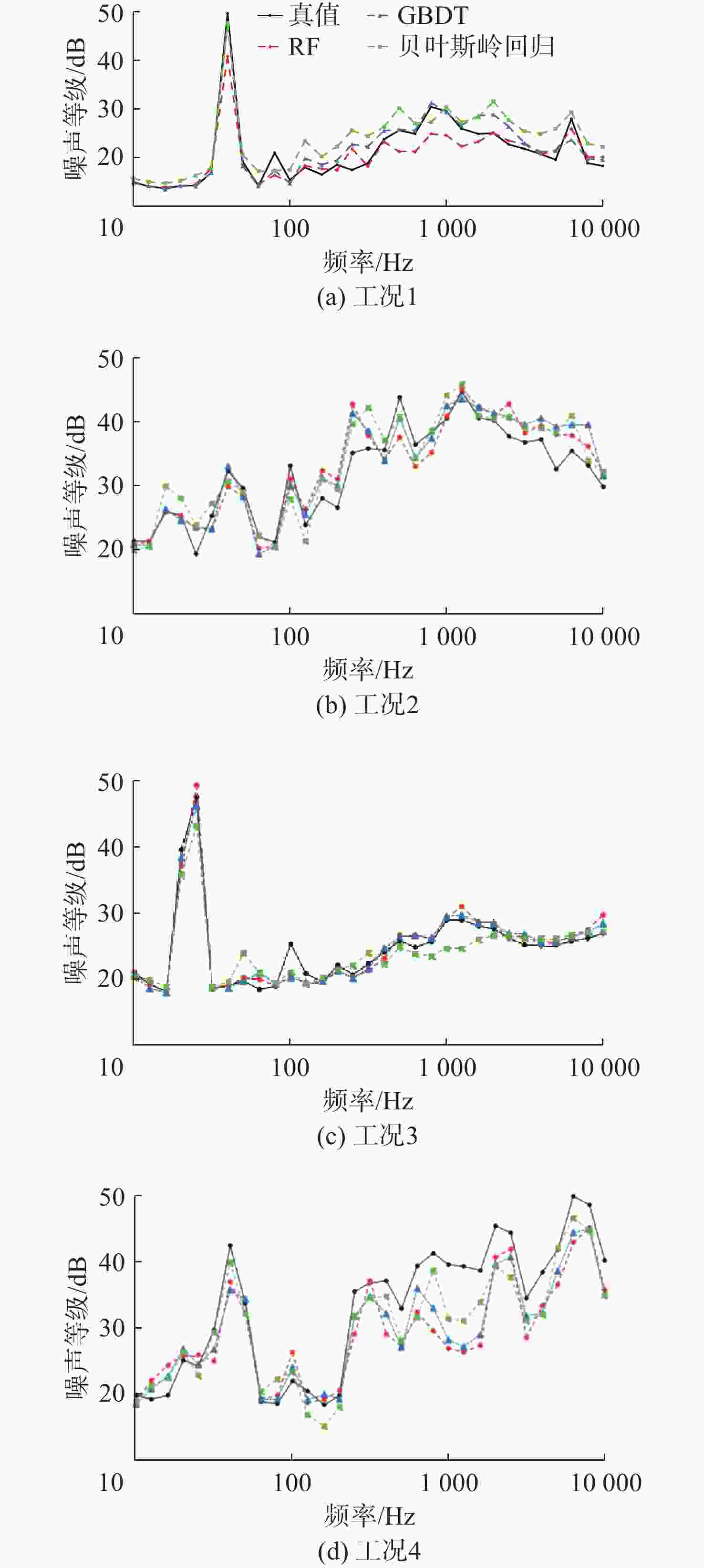
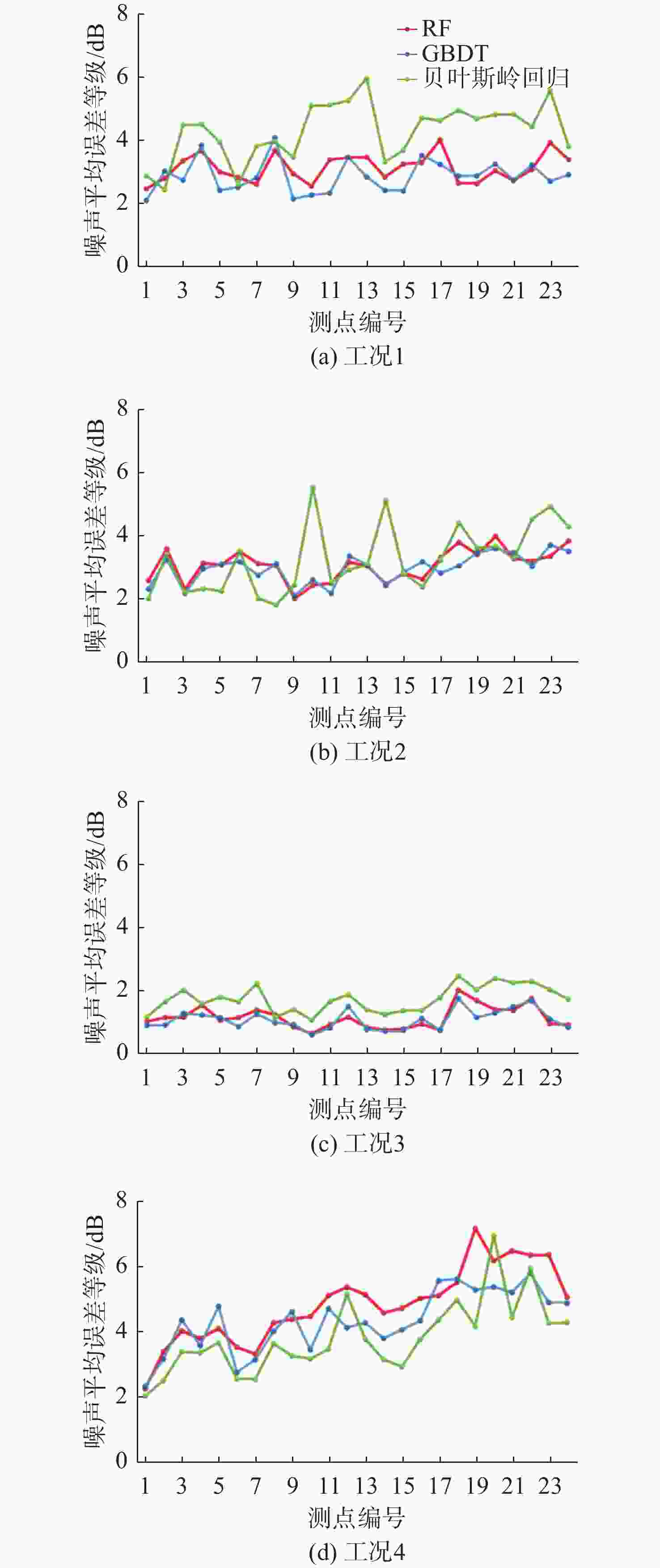
频域/ Hz RF GBDT 贝叶斯岭回归 10 ~100 2.49 2.21 2.56 100 ~ 1 000 2.83 2.53 2.76 1 000~10 000 2.12 2.31 3.33 表 3 不同工况下模型预报误差对比
Table 3. Comparison of model prediction errors under different working conditions
MAE/dB RMSE /dB 工况1 工况2 工况3 工况4 工况1 工况2 工况3 工况4 RF 3.2 3.0 1.2 4.8 3.2 3.1 1.2 4.9 GBDT 2.9 2.9 1.1 4.3 2.9 3.0 1.1 4.4 贝叶斯岭回归 4.3 3.2 1.7 3.8 4.4 3.4 1.8 3.9 -
[1] HODGES C H, WOODHOUSE J. Theories of noise and vibration transmission in complex structures[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 1986, 49(2): 107-170. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/49/2/001 [2] 庞业珍, 裴雨晴. 基于船上振动噪声监测的水下辐射噪声实时预报研究进展[J]. 隐身技术, 2023(1): 1-10.PANG Y Z, PEI Y Q. Research progress on real-time prediction of underwater radiated noise based on shipboard vibration and noise monitoring[J]. Stealth Technology, 2023(1): 1-10. [3] 王学杰, 单衍贺, 秦新华, 等. 舰船水下辐射噪声快速预报方法[J]. 噪声与振动控制, 2018, 38(3): 1-5.WANG X J, SHAN Y H, QIN X H, et al. Rapid prediction method of ship underwater radiated noise[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2018, 38(3): 1-5 . [4] 庞业珍, 俞孟萨. 基于多距离声阵实测回归传播损失的浅水域水下辐射噪声源级测量方法[J]. 船舶力学, 2023, 27(4): 598-606. [5] CINTOSUN E, GILROY L. Estimating ship underwater radiated noise from onboard vibrations[C]//SNAME Maritime Convention. Sname, Italy: 2021: 1-15. [6] ZHANG B, XIANG Y, HE P, et al. Study on prediction methods and characteristics of ship underwater radiated noise within full frequency[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 174: 61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.01.028 [7] GUO J, WANG M, KANG Y, et al. Prediction of ship cabin noise based on RBF neural network[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2019: 1-12. [8] 徐源超, 蔡志明, 孔晓鹏, 等. 船舶辐射噪声分类卷积神经网络的可视化分析和卷积核剪枝[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(1): 1-9. [9] SHIKI T. Estimation of prediction error by using K-fold cross-validation[J]. Statistics and Computing, 2011, 21(2): 137-146. doi: 10.1007/s11222-009-9153-8 [10] DIETTERICH T G. Ensemble learning[J]. The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks, 2002, 2(1): 110-125. [11] DONG X, YU Z, CAO W, et al. A survey on ensemble learning[J]. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2020, 14(2): 241-258. doi: 10.1007/s11704-019-8208-z [12] WEBB G I, ZHENG Z. Multistrategy ensemble learning: Reducing error by combining ensemble learning techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2004, 16(8): 980-991. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2004.29 [13] BREIMAN L. Bagging predictors[J]. Machine Learning, 1996, 24(2): 123-140. doi: 10.1023/A:1018054314350 [14] SCORNET E, BIAU G. A random forest guided tour[J]. Test, 2016, 25(2): 197-227. doi: 10.1007/s11749-016-0481-7 [15] SCHAPIRE R E. The strength of weak learnability[J]. Machine Learning, 1990, 5(2): 197-227. doi: 10.1023/A:1022648800760 [16] FRIEDMAN J, HASTIE T, TIBSHIRANI R. The elements of statistical learning[M]. Beijing: World Publishing Corporation, 2009. [17] 杨欢, 吴震, 张鹏, 等. 侧信道多层感知机攻击中基于贝叶斯优化的超参数寻优[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2021, 38(5): 323-330. [18] RASMUSSEN C E, WILLIAMS C K I. Gaussian processes for machine learning[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2006. [19] BERGSTRA J, YAMINS D, BENGIO Y. Practical Bayesian optimization of machine learning algorithms[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2012, 13(1): 2951-2981. -




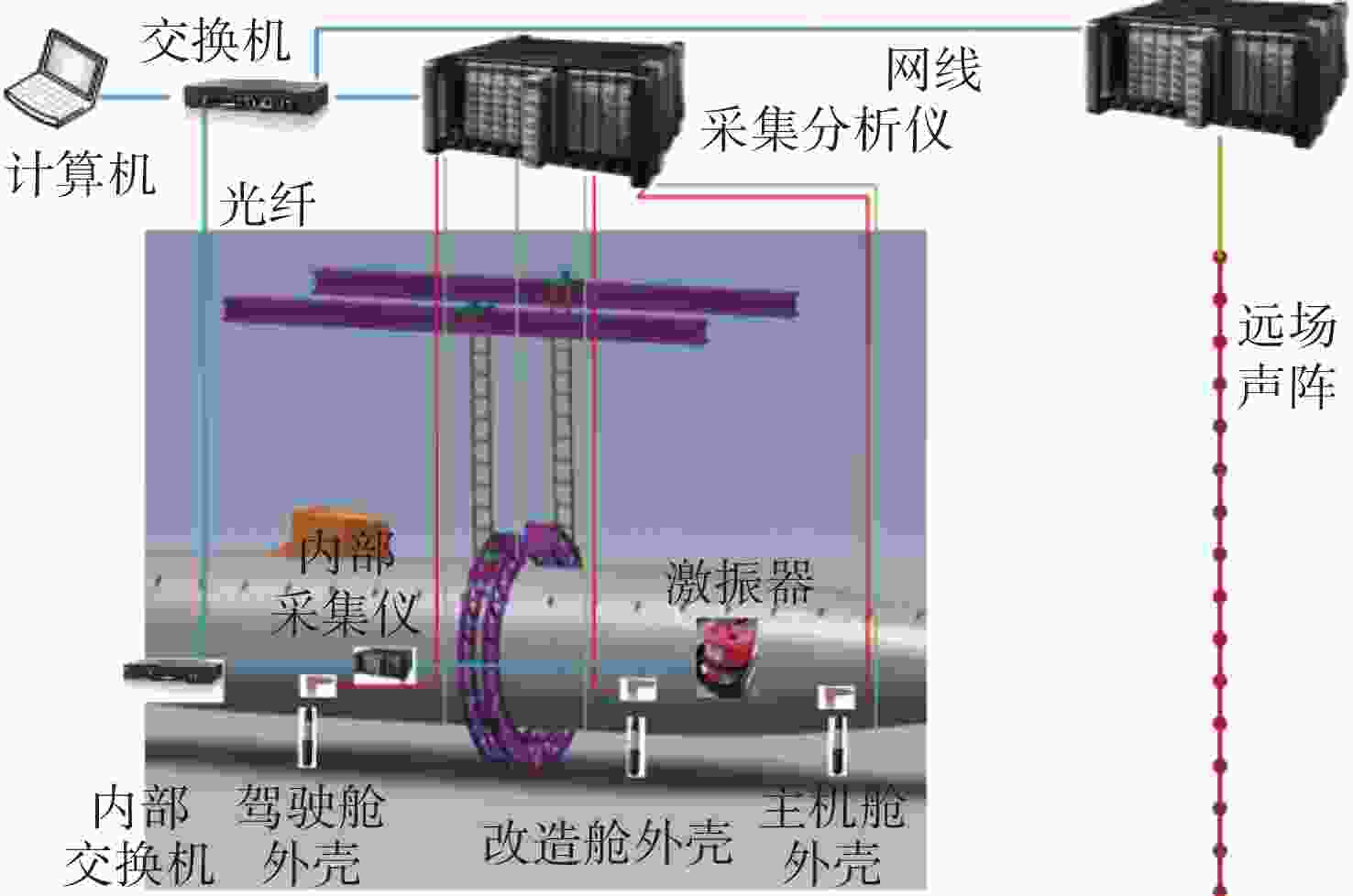
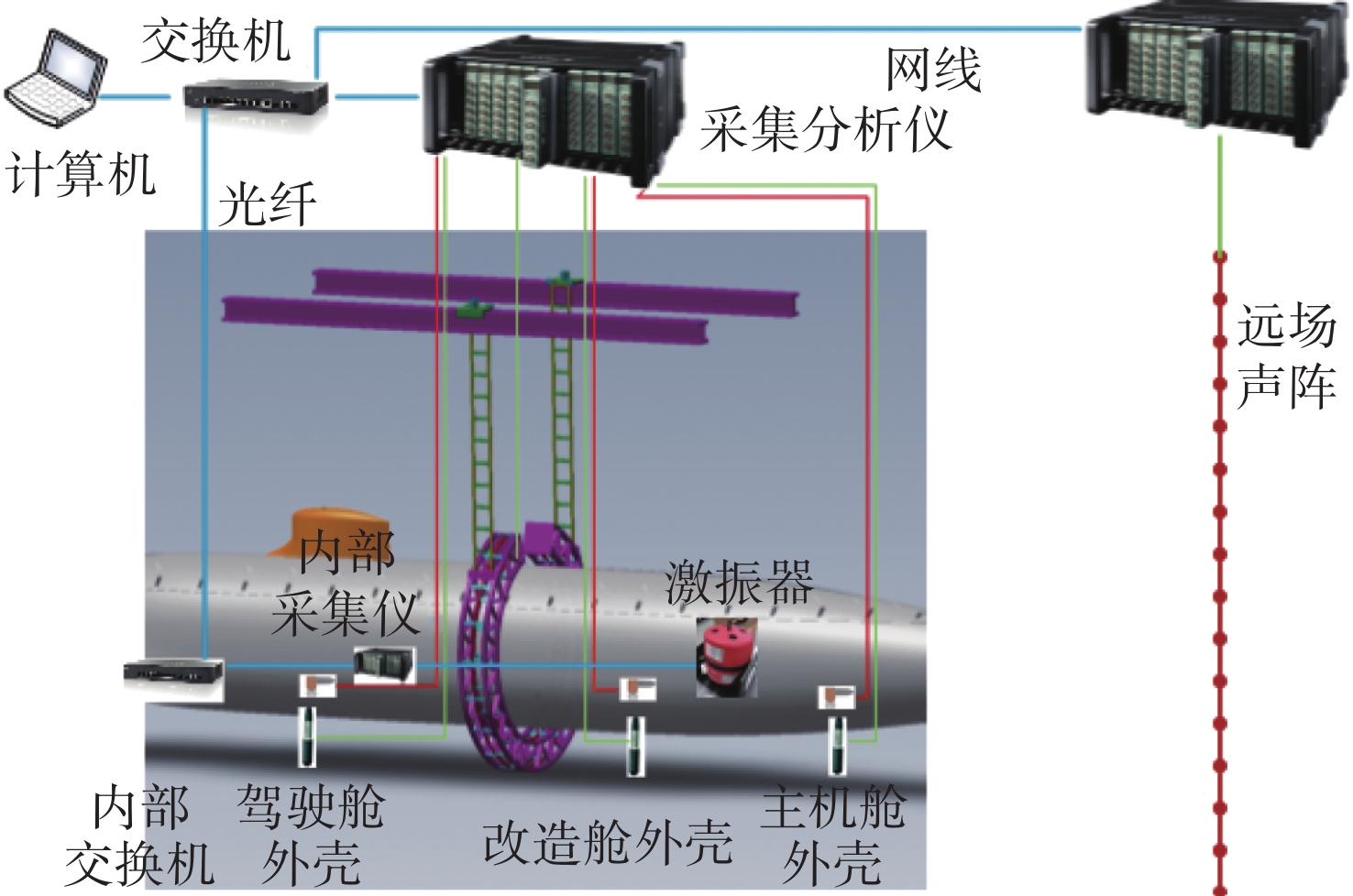
 下载:
下载: