Lightweight Multi-Scale CNN-Based Underwater Image Enhancement Algorithm and Edge Deployment
-
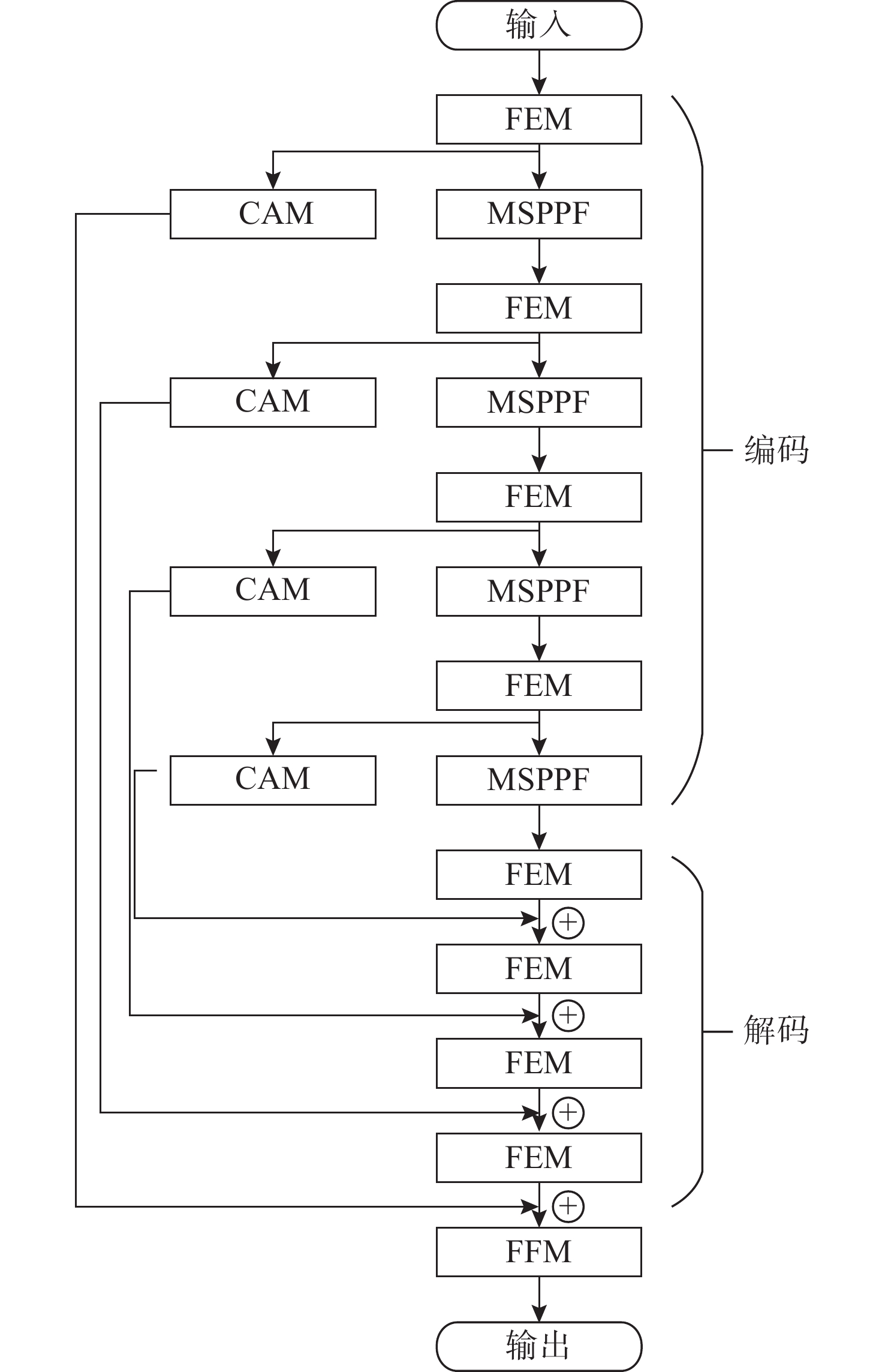
摘要: 针对水下可见光图像因水体散射、吸收导致的噪声干扰、纹理模糊、颜色失真问题, 以及传统增强算法计算量大且基本耗时长的缺陷, 文中提出一种基于轻量化多尺度卷积神经网络(CNN)的水下图像增强算法。该算法采用U-Net结构, 融合浅层纹理特征与深层语义特征, 有效恢复图像纹理细节与颜色信息; 引入轻量化特征提取模块, 在精简模型参数的同时加快网络收敛速度; 在主干网络中嵌入多尺度金字塔池化, 强化多尺度特征提取能力, 弥补传统算法细节恢复不足的短板; 采用L1损失与结构相似性损失联合优化, 提升图像亮度与对比度的恢复效果。为满足工程应用低延时需求, 算法经量化后部署于嵌入式平台, 通过调用嵌入式神经网络处理器资源加速推理, 在Atlas200IA2上的前向推理耗时仅28 ms。公开水下数据集的实验结果表明, 该算法在测试集上的水下图像质量度量与水下彩色图像质量评估指标分别达到4.33和0.63, 验证了其增强效果的有效性。Abstract: This paper proposed a lightweight multi-scale convolutional neural network(CNN)-based underwater image enhancement algorithm to address the problems of noise interference, texture blur, color distortion, and high computational complexity and long time consumption of traditional enhancement algorithms caused by water scattering and absorption in underwater visible light images. The U-Net structure was used, which combined shallow texture features with deep semantic features to effectively restore the texture and color information of the image. A lightweight feature extraction module was introduced, which not only simplified the model parameters but also accelerated the convergence speed of the network. A multi-scale pyramid pooling was embedded in the backbone network for extracting multi-scale features and compensating for the shortcomings of traditional algorithms in detail restoration. By combining L1 loss with structural similarity index loss for joint optimization, the restoration effect of image brightness and contrast was improved. To meet the low latency requirements of engineering applications, the algorithm was quantized and then deployed on an embedded platform. By calling the embedded neural processing unit resources to accelerate the inference process, the forward inference on the Atlas200IA2 took only 28 ms. Through experiments on publicly available underwater datasets, the algorithm proposed in this paper achieved an underwater image quality measure of 4.33 and the underwater color image quality evaluation index of 0.63, respectively, on the test set, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed enhancement algorithm.
-
表 1 网络参数配置表
Table 1. Network parameter configuration table
参数 值 输入尺寸 256×256 学习率 0.001 批大小 64 权重衰减 0.000 5 动量 0.937 表 2 不同平台推理耗时
Table 2. inference time on different platforms
平台 FP16/ms FP16&FP32/ms RK3588 42 58 Atlas 200I A2 28 31 表 3 不同算法测试指标
Table 3. Test indicators of different algorithms
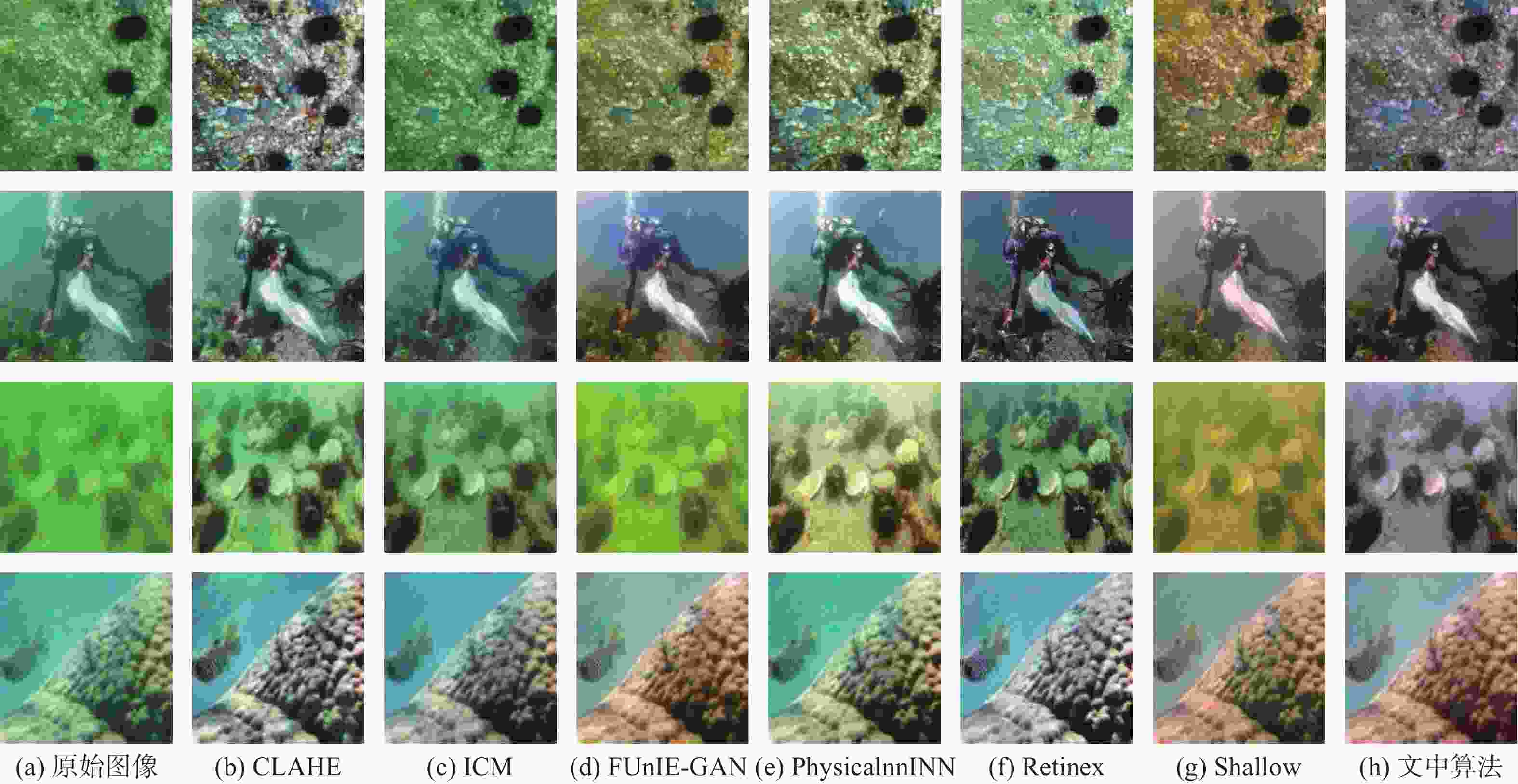
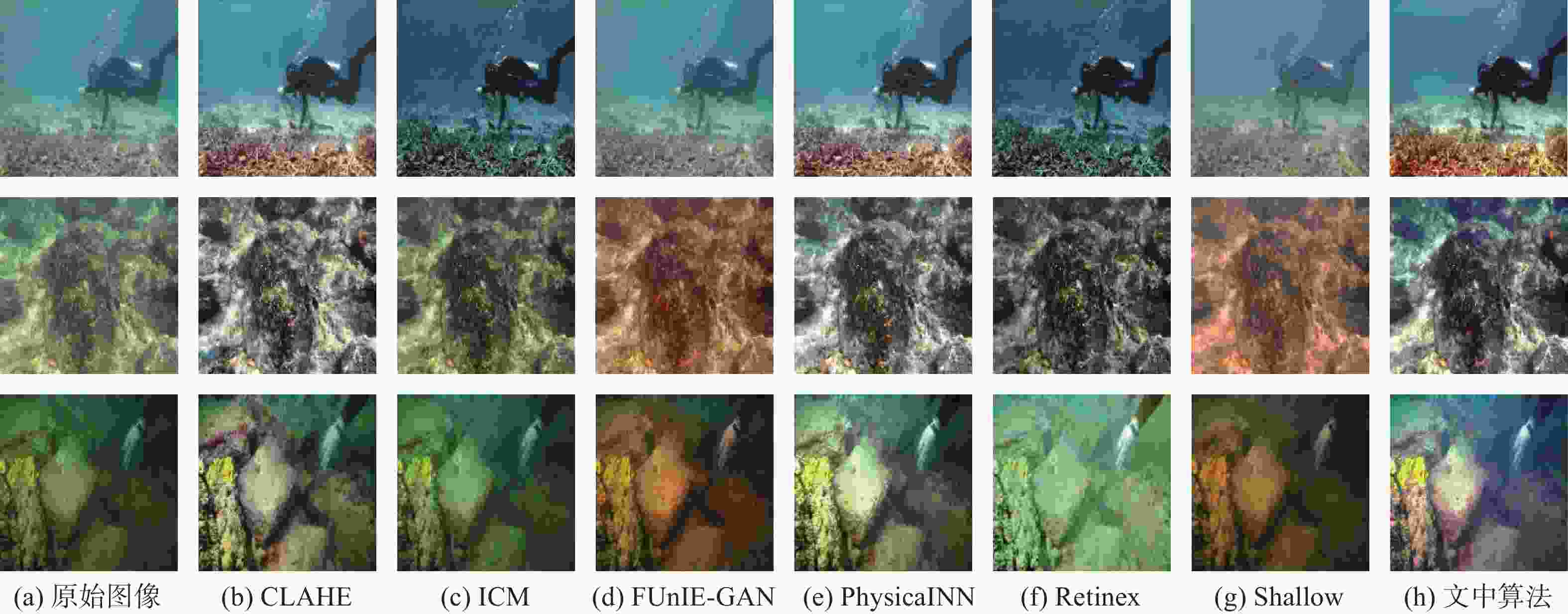
算法 UIQM UCIQE PSNR SSIM CLAHE 3.95 0.59 16.67 0.59 ICM 3.22 0.48 15.84 0.53 FUnIE-GAN 3.87 0.50 18.28 0.64 PhysicalNN 4.31 0.54 21.25 0.72 Retinex 4.08 0.53 19.75 0.61 Shallow 4.02 0.49 18.05 0.65 文中 4.33 0.63 25.84 0.87 -
[1] 王永鑫, 刁鸣, 韩闯. 基于同态滤波的水下图像增强与色彩校正模 型[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2018, 54(11): 30-34.WANG Y X, DIAO M, HAN C. Underwater image enhancement and color correction model based on homomorphic filtering[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2018, 54(11): 30-34. [2] 李黎, 王惠刚, 刘星. 基于改进暗原色先验和颜色校正的水下图像增强[J]. 光学学报, 2017, 37(12): 9.LI L, WANG H G, LIU X. Underwater image enhancement based on improved dark primary prior and color correction[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(12): 9. [3] 杨润, 刘增力, 赵宣植. 基于颜色校正和暗亮双通道先验的水下图像增强算法[J]. 红外技术, 2024, 46(9): 984-993.YANG R, LIU Z L, ZHAO X Z. Underwater image enhancement algorithm based on color correction and dual channel prior of brightness and darkness[J]. Infrared Technology, 2024, 46(9): 984-993. [4] 王燕, 张金峰, 王丽康, 等. 基于注意力机制与特征重建的水下图像增强[J]. 红外技术, 2024, 46(9): 1006-1014.WANG Y, ZHANG J F, WANG L K, et al. Underwater image enhancement based on attention mechanism and feature reconstruction[J]. Infrared Technology, 2024, 46(9): 1006-1014. [5] 程竹明, 李佳轩, 黄三傲, 等. 基于多分支残差注意力网络的水下图像增强[J]. 光学精密工程, 2025, 33(7): 1141-1151. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20253307.1141CHENG Z M, LI J X, HUANG S A, et al. Underwater image enhancement based on multi branch residual attention network[J]. Optical Precision Engineering, 2025, 33(7): 1141-1151. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20253307.1141 [6] 王树林, 杨建民, 卢昌宇, 等. 一种基于双通道的水下图像增强卷积神经网络[J]. 海洋工程, 2023, 41(6): 158-170.WANG S L, YANG J M, LU C Y, et al. A dual channel underwater image enhancement convolutional neural network[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 41(6): 158-170. [7] 严浙平, 曲思瑜, 邢文. 水下图像增强方法研究综述[J]. 智能系统学报, 2022, 17(5): 860-873.YAN Z P, QU S Y, XING W. A review of underwater image enhancement methods[J]. Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2022, 17(5): 860-873. [8] MAGGIORI E, TARABALKA Y, CHARPIAT G, et al. Convolutional neural networks for large-scale remote-sensing image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 55(2): 645-657. [9] WU Z, SHEN C, VAN DEN HENGEL A. Wider or deeper: Revisiting the resnet model for visual recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 90: 119-133. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.01.006 [10] CHEN R C. Automatic license plate recognition via sliding-window darknet-YOLO deep learning[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2019, 87: 47-56. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2019.04.007 [11] ZHAO C, CHEN M. YOLOv7-RFPCW of a lightweight target detection algorithm for benthic organisms underwater[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2024, 40(11): 168-177. [12] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904-1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [13] XU C, DU Y, ZHENG W, et al. Facial expression recognition based on YOLOv8 deep learning in complex scenes[J]. International Journal of Information and Communication Technology, 2025, 26(1): 89-101. doi: 10.1504/IJICT.2025.144013 [14] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017 : 7132-7141. [15] ZHAO D, LIU K, ZHANG Z, et al. Efficient stereo matching using attention mechanism and edge optimization[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2023, 32(5): 16. [16] 黄巧玲, 郑伯川, 丁梓成, 等. 融合监督注意力模块和跨阶段特征融合的图像修复改进网络[J]. 计算机应用, 2024, 44(2): 572-579.HUANG Q L, ZHENG B C, DING Z C, et al. Improved image restoration network integrating supervised attention module and cross stage feature fusion[J]. Computer Applications, 2024, 44(2): 572-579. [17] ZHANG W D, ZHUANG P X, SUN H H, et al. Underwater image enhancement via minimal color loss and locally adaptive contrast[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 3997-4010. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3177129 [18] SINGH N, BHAT A. A robust model for improving the quality of underwater images using enhancement techniques[J]. Multimedia tools and Applications, 2024(1): 83. [19] 朱恒军, 王天落, 马利浩. 水下图像的颜色校正及对比度增强算法研究[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2023, 43(8): 149-154.ZHU H J, WANG T L, MA L H. Research on color correction and contrast enhancement algorithms for underwater images[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2023, 43(8): 149-154. [20] KASHIF I, SALAM R A, AZAM O, et al. Underwater image enhancement using an integrated colour model[J]. Iaeng International Journal of Computer Science, 2007, 34(2): 239-244. [21] TSAI Y S, CHANG K W, LAN Y J. Advancing underwater image clarity: A GAN-based approach with residual blocks and linear blending[J]. Machine Vision and Applications, 2025, 36(4): 1-22. [22] 陈学磊, 张品, 权令伟, 等. 融合深度学习与成像模型的水下图像增强算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2022, 48(2): 243-249.CHEN X L, ZHANG P, QUAN L W, et al. Underwater image enhancement algorithm integrating deep learning and imaging models[J]. Computer Engineering, 2022, 48(2): 243-249. [23] ZHUANG P X, WU J M, PORIKL F, et al. Underwater image enhancement with Hyper-Laplacian reflectance priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 5442-5455. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3196546 [24] NAIK A, SWARNAKAR A, MITTAL K. Shallow-UWnet: Compressed model for underwater image enhancement(student abstract)[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, USA: AAAI, 2021, 35(18): 15853-15854. -




 下载:
下载: