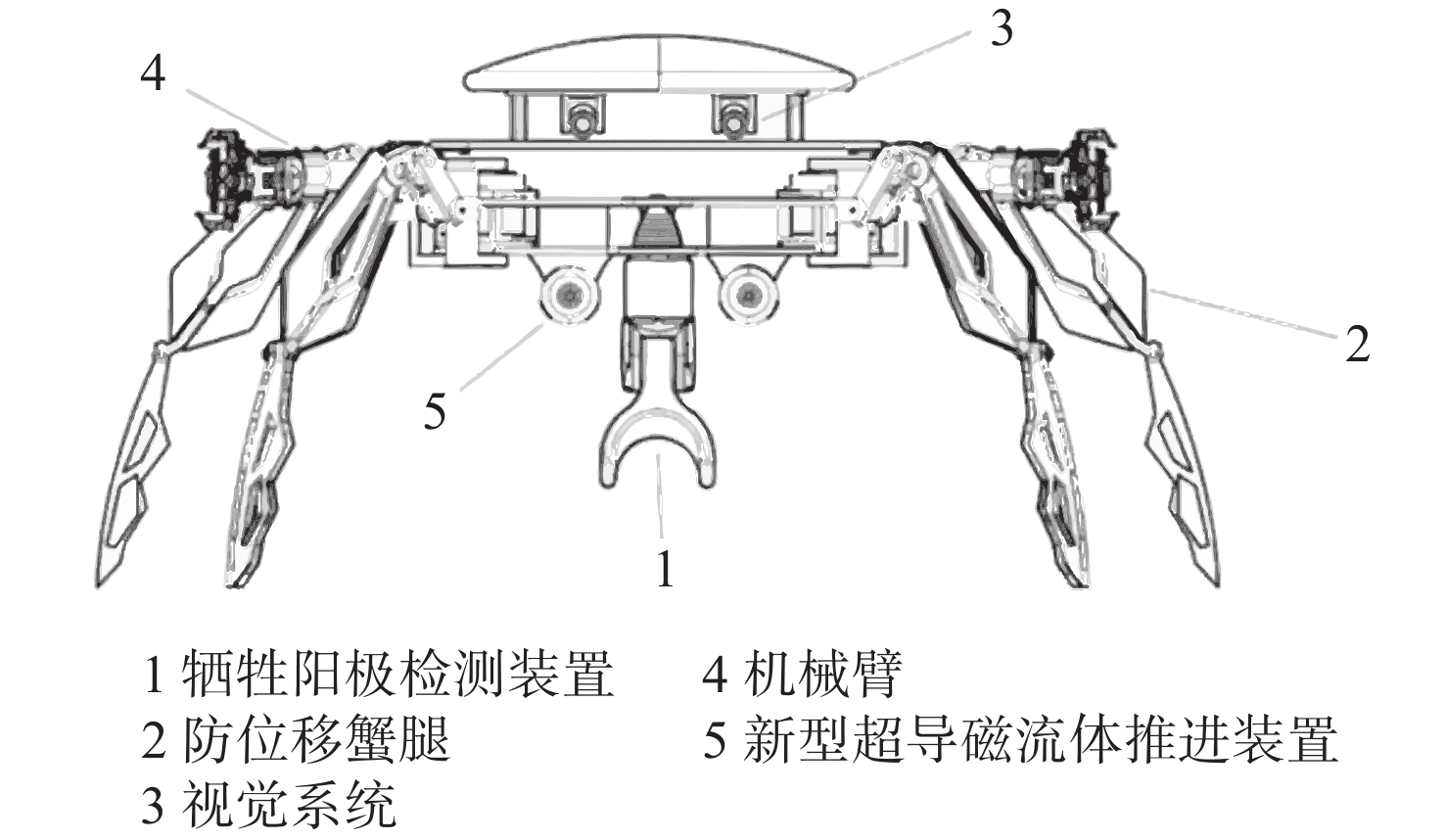
Design and Implementation of a Crab-Like Underwater Robot System
-
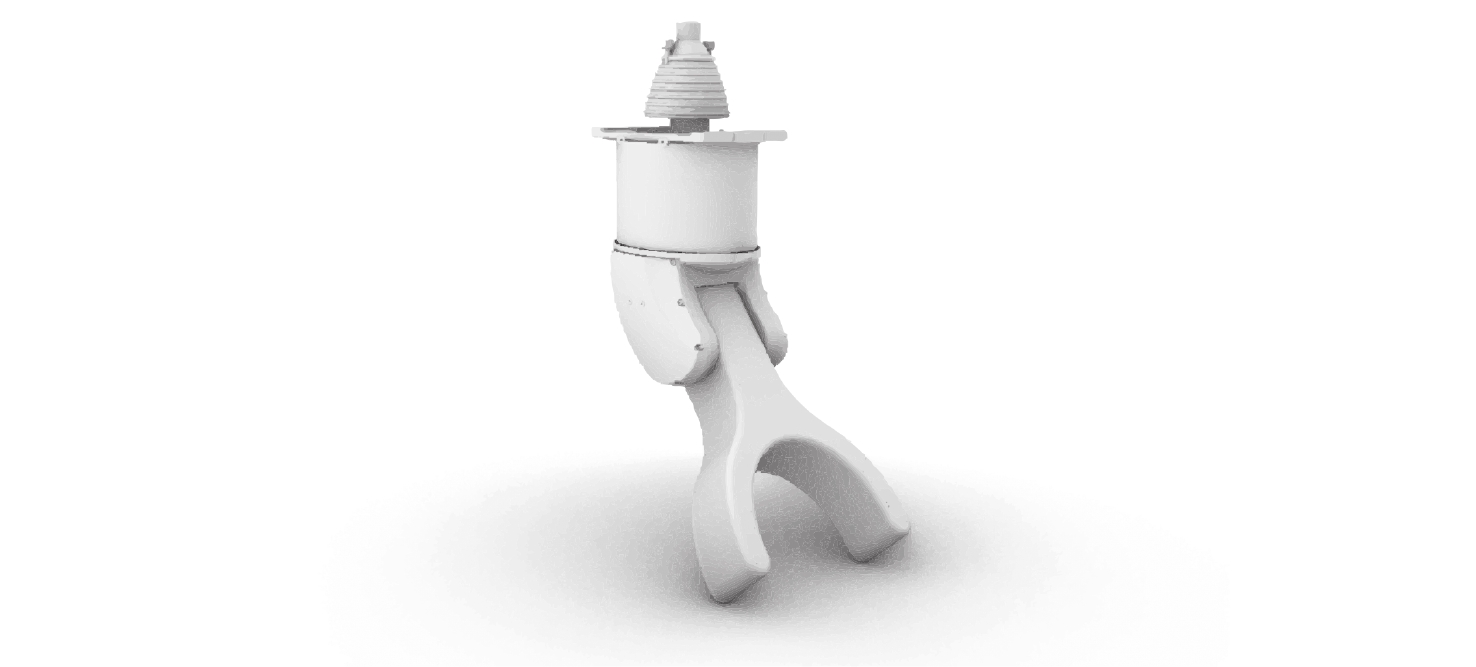
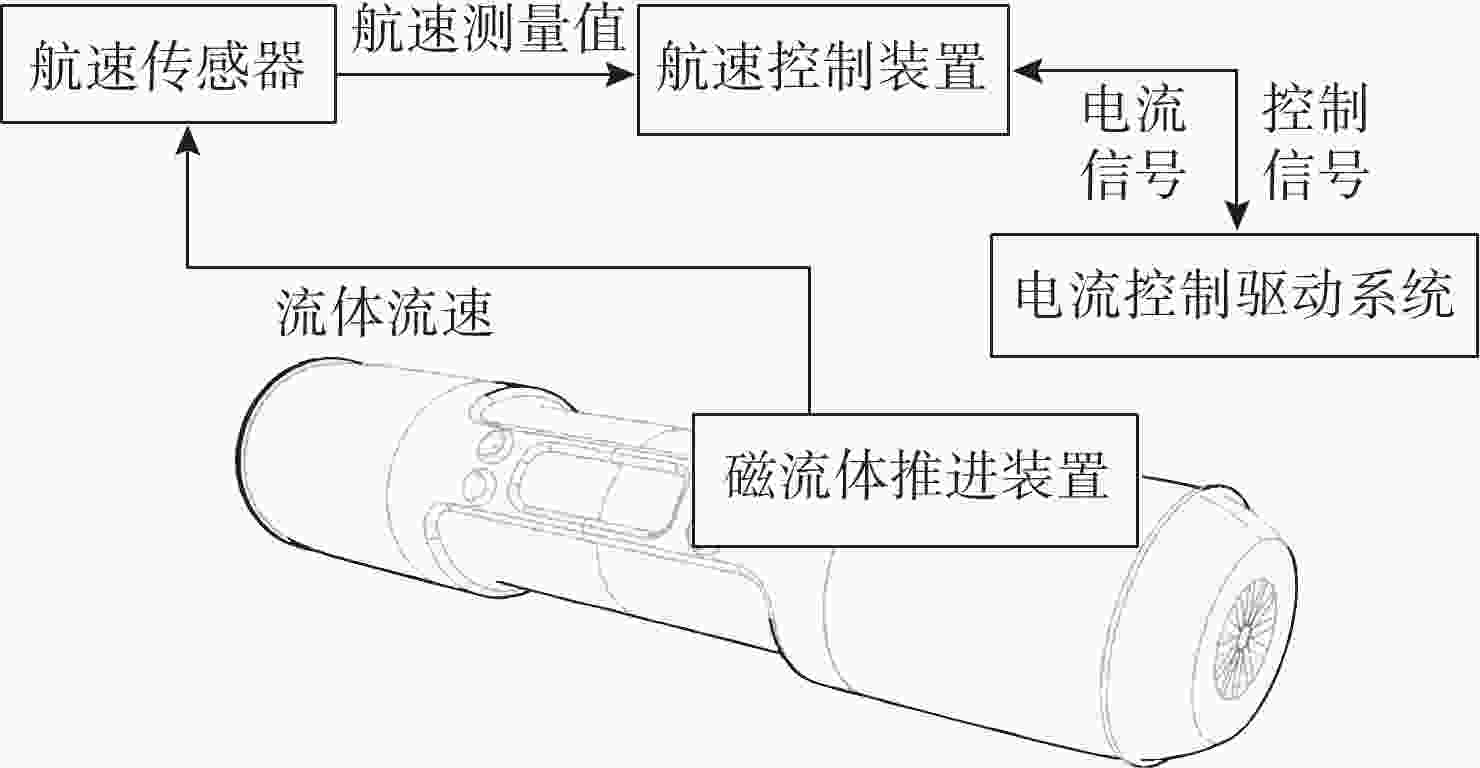
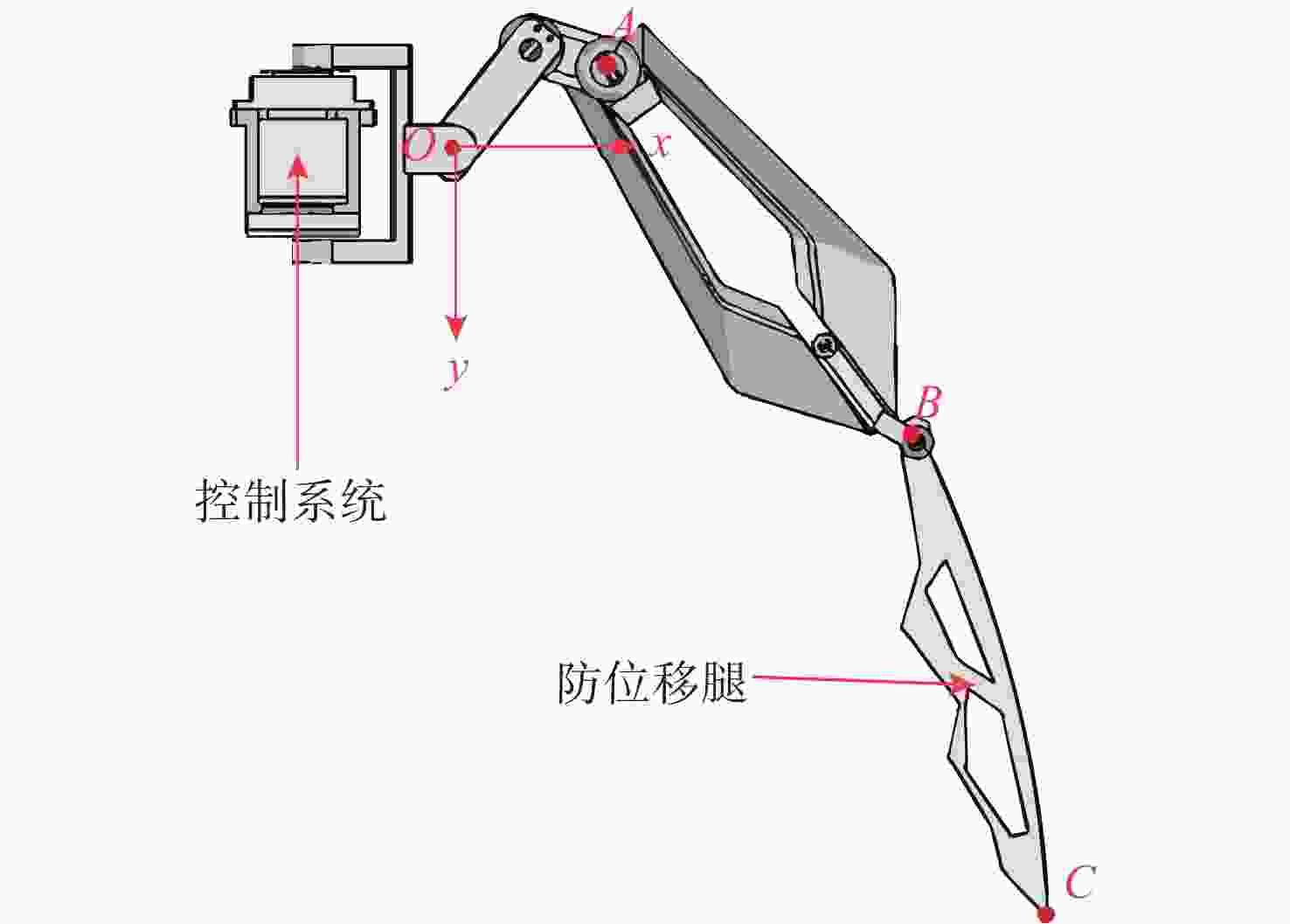
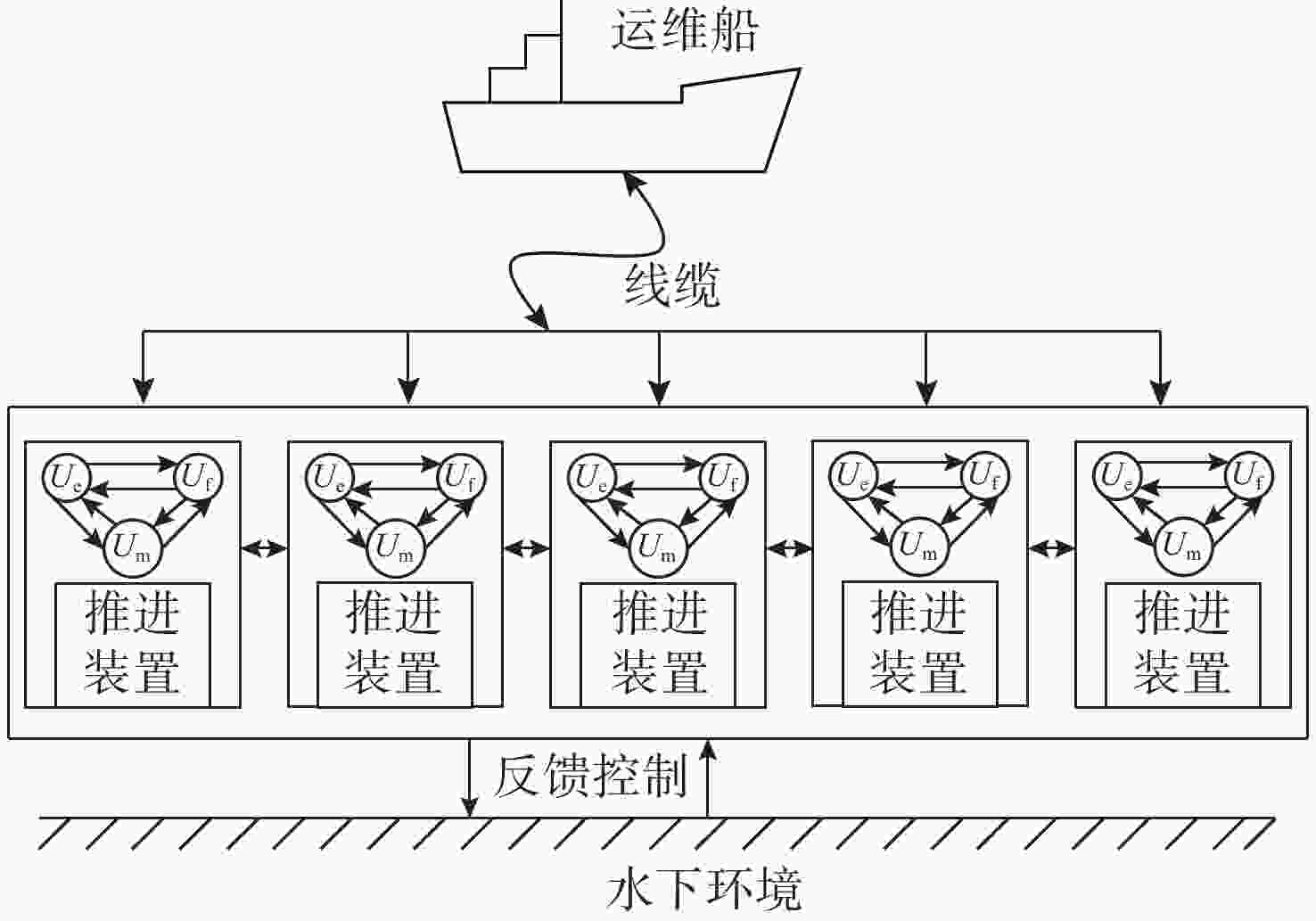
摘要: 针对水下机器人在复杂地形与强水流阻力环境下易受损、工作效率低等问题, 文中设计了一款仿螃蟹结构的水下机器人。该机器人采用仿生蟹型构型, 搭配防位移蟹腿装置, 集成磁流体推进和牺牲阳极检验装置,可降低水下作业成本并提高水下采样效率。文中设计旨在辅助油气开发的全周期提供技术支撑, 为油气管道铺设、巡检与维修提供指导建议。
-
关键词:
- 水下机器人 /
- 仿生设计 /
- 磁流体推进; 牺牲阳极检测
Abstract: To solve the problems of underwater robots being prone to damage and low work efficiency under complex terrains and strong water flow resistance environments, this paper designed an underwater robot with a crab-like structure. The robot adopted a bionic crab configuration and was equipped with anti-displacement crab leg devices. It integrated magnetohydrodynamic propulsion and sacrificial anode inspection devices. These features could reduce the cost of underwater operations and enhance underwater sampling efficiency. The design aims to provide technical support for the entire cycle of oil and gas development, provide guidance and suggestions for the laying, inspection, and maintenance of oil and gas pipelines. -
表 1 仿生水下机器人运动方式对比
Table 1. Comparison of bionic motion modes of underwater vehicles
名称 运动特性 蛇形机器人 采用蜿蜒、柔性运动, 具有高机动性,
可适应复杂环境且穿越狭隘空间。仿水母型机器人 能在水中移动, 能耗较低, 控制精度要求高 仿乌贼型机械手 模拟生物运动, 具有良好的抓取能力,
但结构设计复杂且维修难度大。仿螃蟹型防位移腿 稳定性强、适合复杂海底环境, 但足部
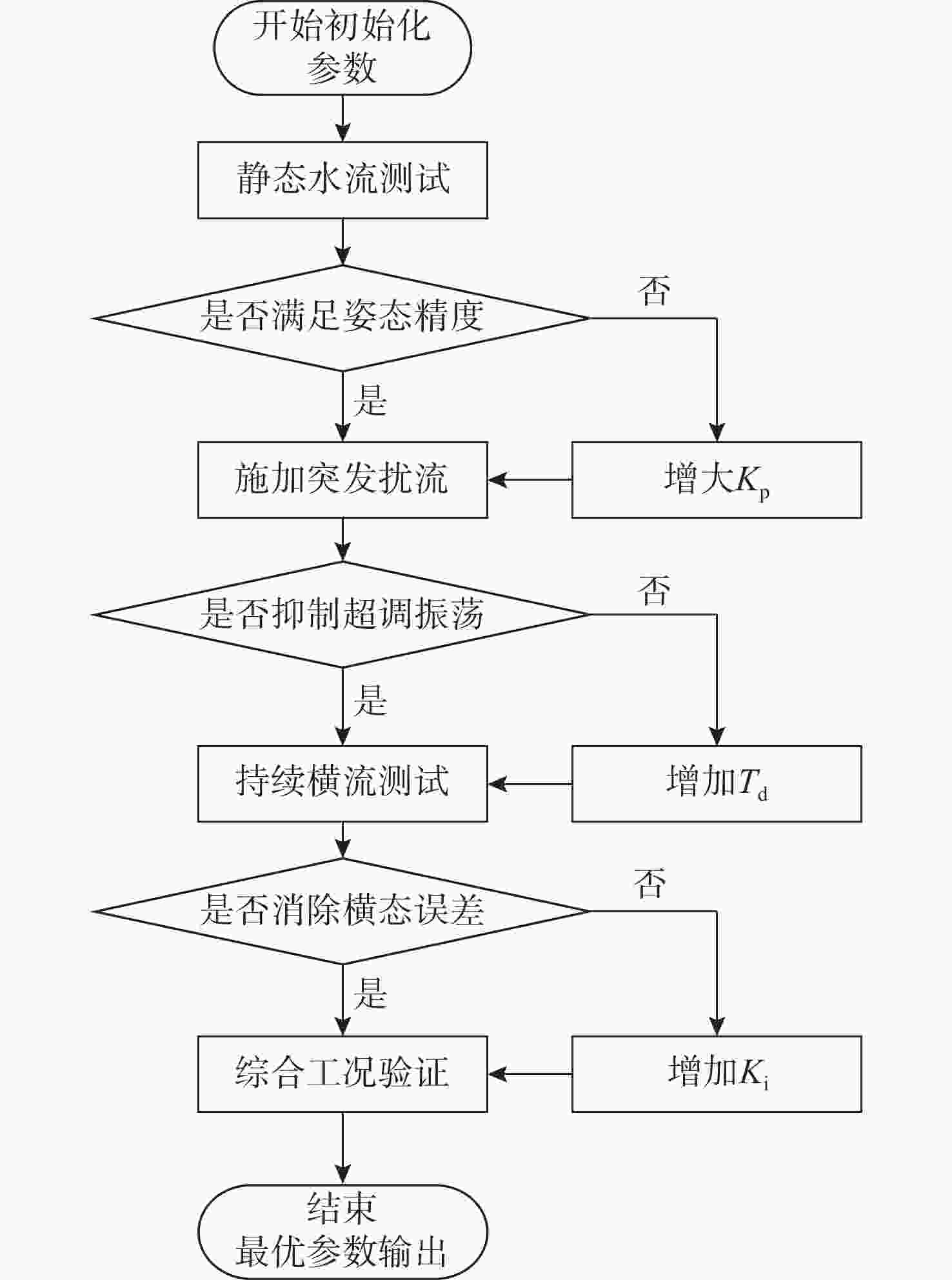
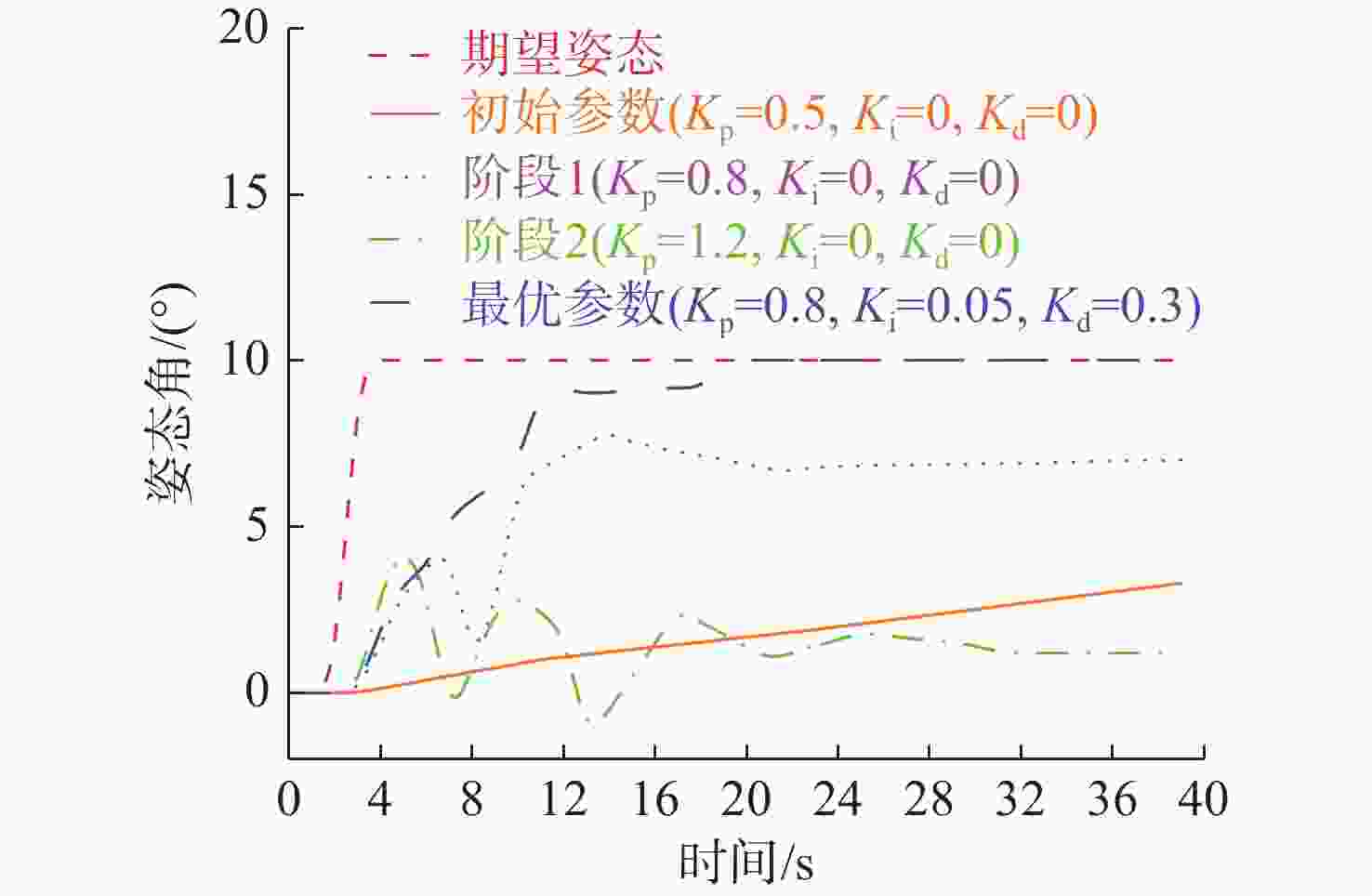
活动空间不足且运行速度较慢。表 2 PID参数调试过程
Table 2. Process of PID parameter debugging
调试阶段 参数组合
$ \left(K_{\mathrm{p}},K_{\mathrm{i}},T_{\mathrm{d}}\right) $测试现象 问题分析 初始值 $\left( {0.5,0,0} \right)$ 响应迟缓,
姿态偏差$ \gt 15^\circ $比例增益不足,
抗干扰能力弱阶段1 $\left( {1.2,0,0} \right)$ 超调量达$ 25%,\ $
剧烈振荡比例过强, 需微分
抑制振荡阶段2 $\left( {1.0,0.02,0.1} \right)$ 稳态误差$ 8^{\circ},\ $
恢复时间较长积分作用不足,
静差未消除最优参数 $\left( {0.8,0.05,0.3} \right)$ 超调$ < 5%,\ $
稳态误差$ \approx 0^\circ $响应快且平稳 表 3 PID最优参数
Table 3. Optimal PID parameters
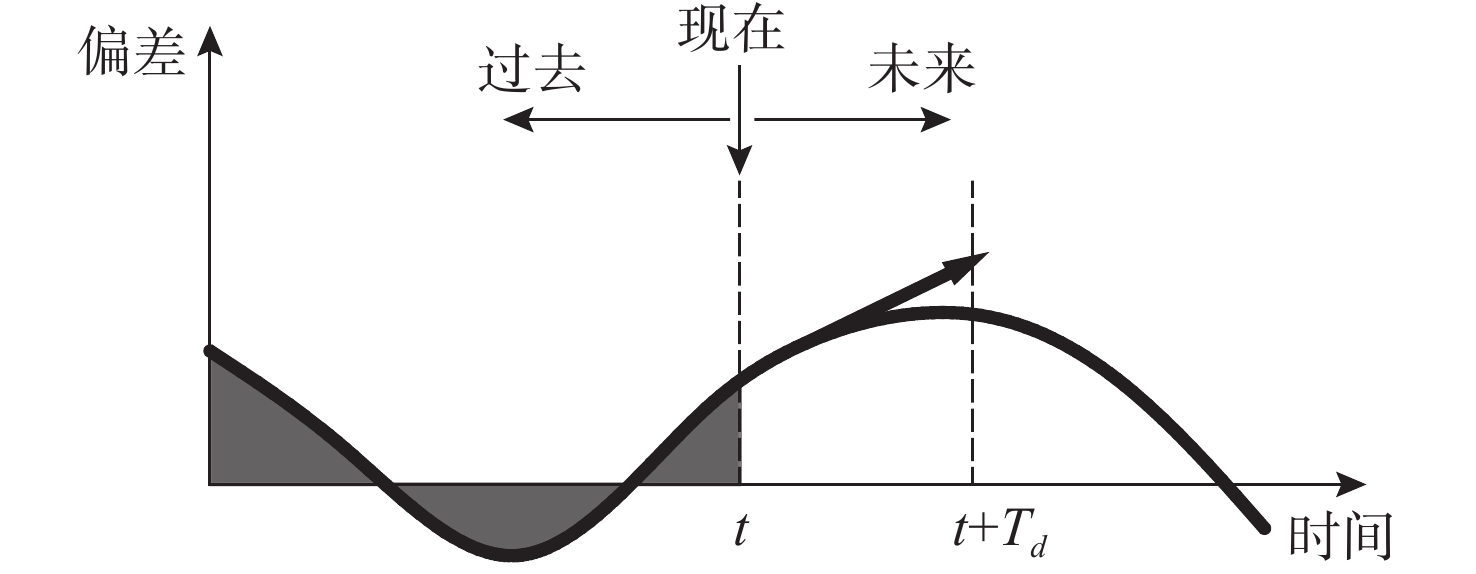
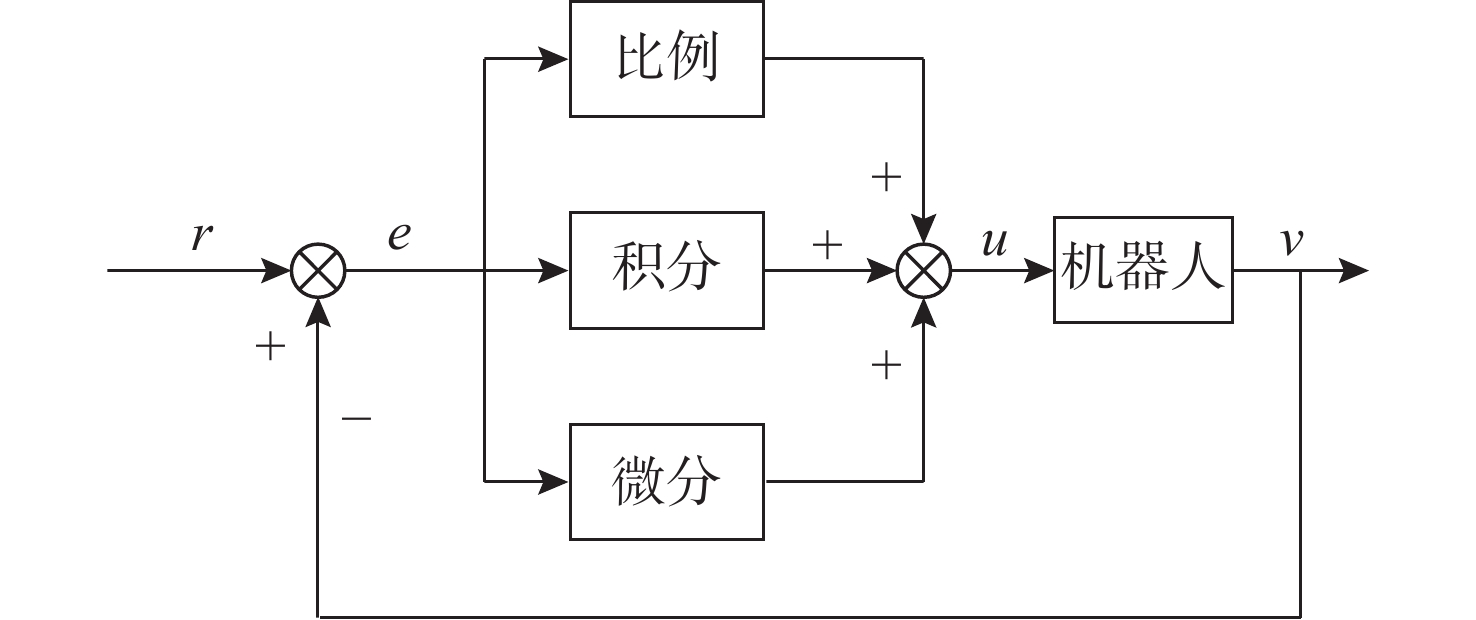
参数 数值 对系统的影响 ${K_{\mathrm{p}}}$ $ 0.80 $ 快速响应姿态偏移, 提供基础驱动力 ${K_{\mathrm{i}}}$ $0.05$ 消除静差, 抑制水流持续干扰 ${T_{\mathrm{d}}}$ $ 0.30 $ 预测运动趋势, 抑制机械振荡 表 4 腿部设计指标与验证结果
Table 4. Limb performance metrics and validation results
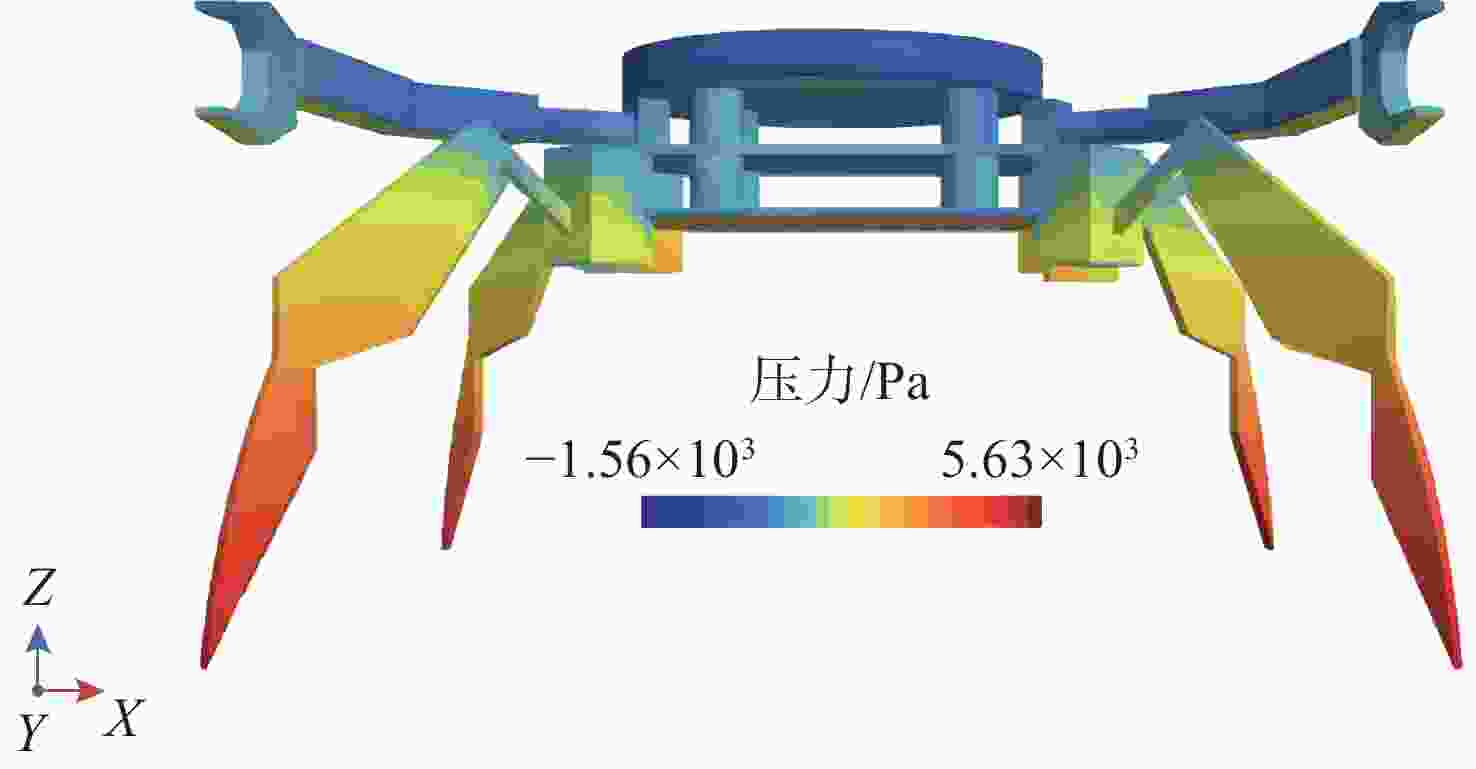
设计指标 目标值 验证方法 验证结果 髋关节弯曲范围 $ 0\sim120^{\circ} $ 三维模型与
关节设计达成 膝关节弯曲范围 $ 0\sim150^{\circ} $ 三维模型与
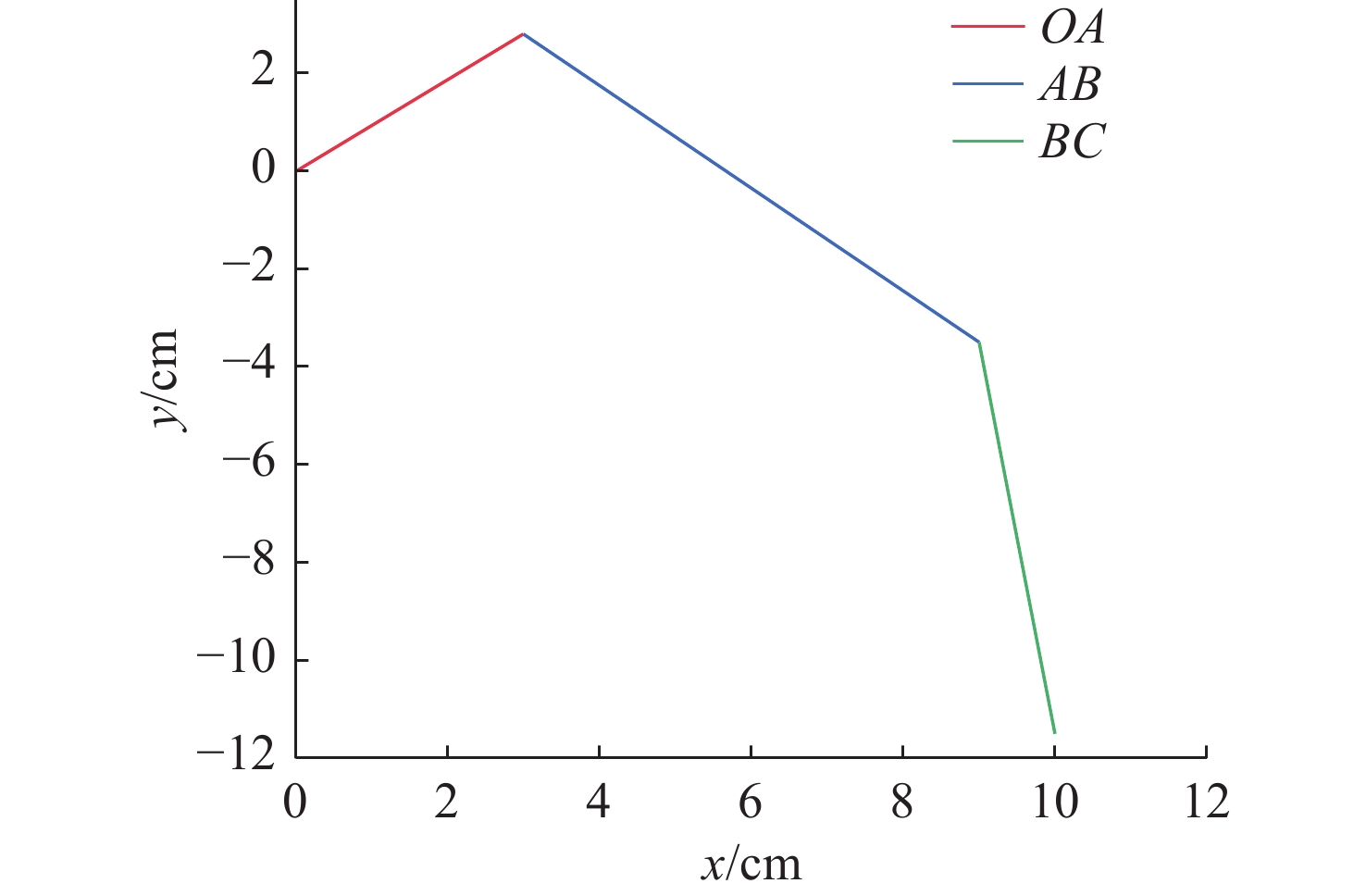
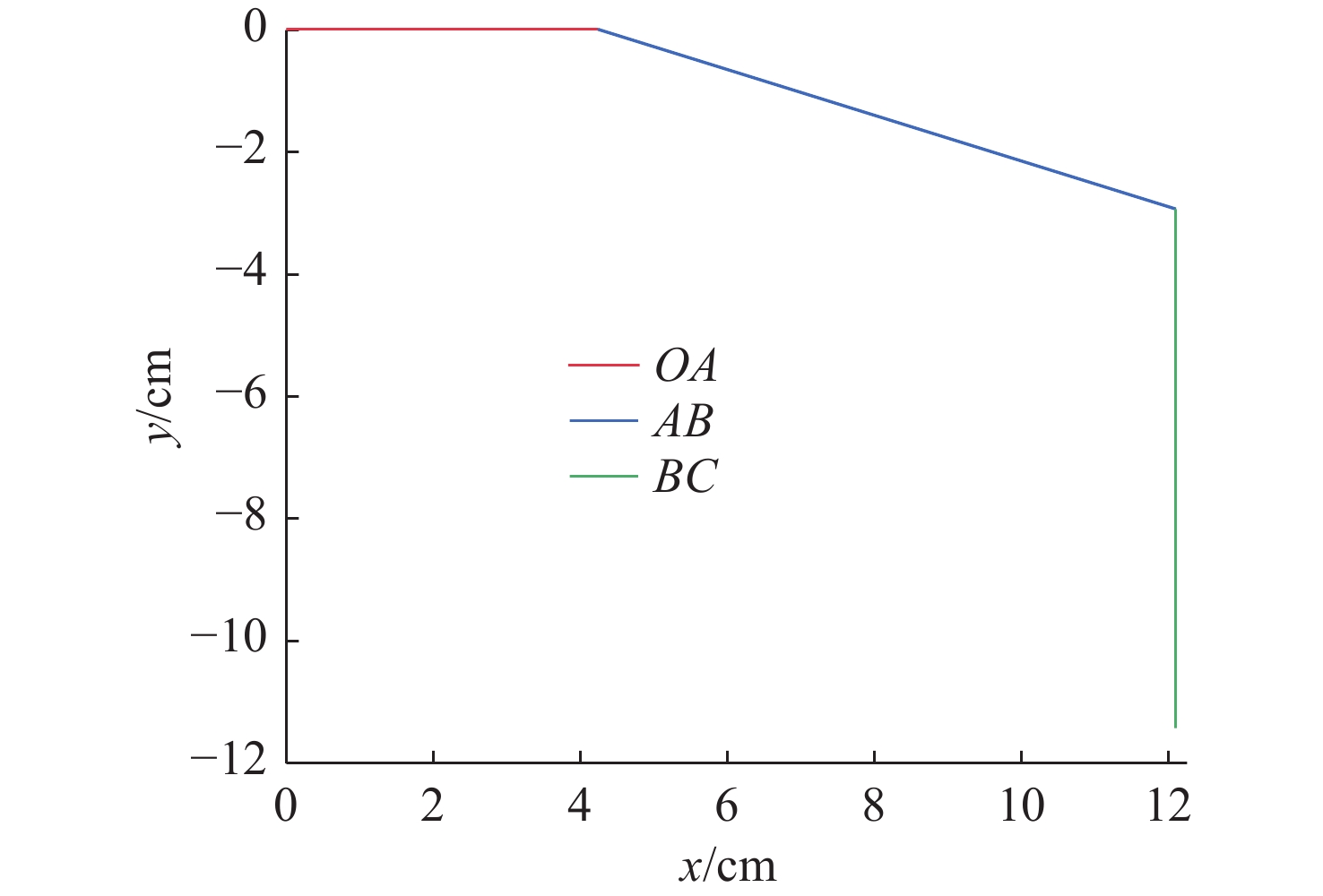
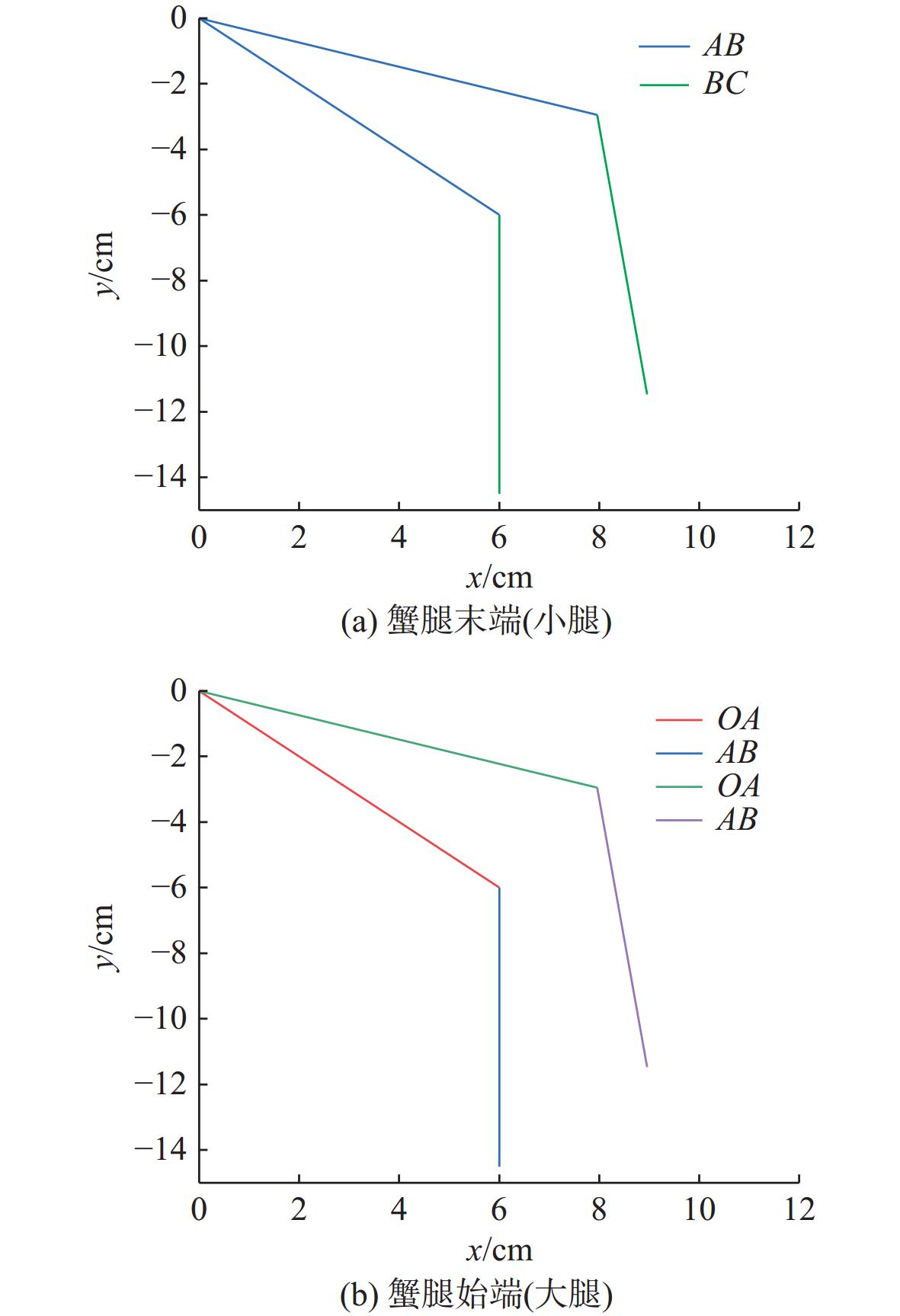
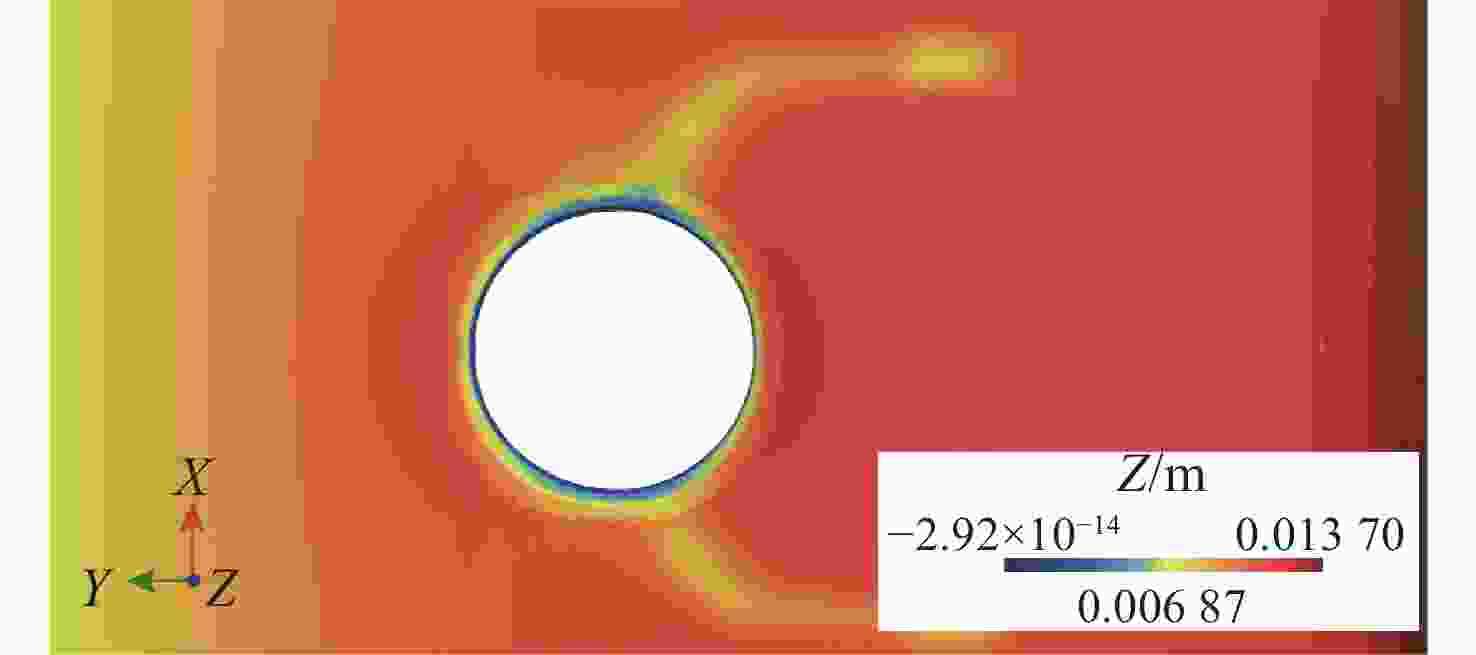
关节设计达成 末端吸附力 $ \geqslant 15\;{\mathrm{N}}$ 理论计算与选型 达成 管道适应范围 $ \mathit{\Phi}20\sim100\; \text{cm} $ 工作空间分析(图7) 可实现无死
角转向运动平稳性 — 运动学模型与
PID控制姿态误差$ \pm 2^\circ $ -
[1] 邱志明, 马焱, 孟祥尧, 等. 水下无人装备前沿发展趋势与关键技术分析[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(1): 1-9.QIU Z M, MA Y, MENG X Y, et al. Analysis on the development trend and key technologies of unmanned underwater equipment[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems. 2023, 31(1): 1-9. [2] 施先林, 张大朋, 严谨, 等. 固体力学的发展趋势、在各个领域中的应用及当前在我国存在的问题[J]. 科学咨询, 2024, 9: 122-125.SHI X L, ZHANG D P, YAN J, et al. Development trends, applications in various fields, and current issues in China of solid mechanics[J]. Scientific Consultation, 2024, 9: 122-125. [3] 王彪, 罗瑞龙, 王芳, 等. 深海无人装备控制系统研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2025, 33(3): 390-399.WANG B, LUO R L, WANG F, et al. Research status and development trends of control systems for deep-sea unmanned equipment[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2025, 33(3): 390-399. [4] 张军豪, 陈英龙, 杨昕宇, 等. 刚柔耦合水下蛇形机器人的建模与控制仿真[J]. 工程科学学报, 2023, 45(12): 2095-2107.ZHANG J H, CHEN Y L, YANG X Y, et al. Modeling and control simulation of a rigid-flexible coupled underwater snake-like robot[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2023, 45(12): 2095-2107. [5] 张学海, 杨泽慧, 王汝贵, 等. 仿乌贼水下采样机械手建模与仿真[J]. 机械传动, 2024, 48(6): 58-64.ZHANG X H, YANG Z H, WANG R G, et al. Modeling and simulation of a squid-inspired underwater sampling manipulator[J]. Journal of Mechanical Transmission, 2024, 48(6): 58-64. [6] 张冬冬, 江一行, 范云杰, 等. 基于仿生水母的水下机器人结构设计与试验研究[J]. 机电工程, 2024, 41(4): 739-746.ZHANG D D, JIANG Y H, FAN Y J, et al. Structural design and experimental research of an underwater robot based on bionic jellyfish[J]. Journal of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering, 2024, 41(4): 739-746. [7] CHEN L, HU Q, ZHANG H, et al. Research on underwater motion modeling and closed-loop control of bionic undulating fin robot[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 299: 11. [8] 曹勇, 陈刚, 李强. 基于仿生螳螂虾机器人的微型低成本沉浮系统设计与深度控制研究[J]. 海洋工程, 2025, 38(3): 251-224.CAO Y, CHEN G, LI Q. Design of a miniaturized low-cost sinking-floating system and depth control research based on a bionic mantis shrimp robot[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2025, 38(3): 251-224. [9] 陈国军, 林羊龙, 金俊, 等. 仿生机器蝠鲼动力学建模及试验研究[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(1): 40-47.CHEN G J, LIN Y L, JIN J, et al. Dynamic modeling and experimental study of a bionic manta ray robot[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(1): 40-47. [10] 李久岳. 自主水下管道巡检机器人的设计[D]. 大连: 大连交通大学, 2022. [11] Det Norsoke Veritas(DNV). Integrity management of submarine pipeline systems[S]. Oslo, Norway: DNV, 2009. [12] 中国造船工程学会发布2025年第二批团体标准[S]. 船舶标准化工程师, 2025, 58(4): 2. [13] 吴迅, 李纯清. 磁流体推进器优化设计及对比研究[J]. 船电技术, 2024, 44(8): 26-31, 37.WU X, LI C Q. Optimal design and comparative study of magnetohydrodynamic thrusters[J]. Marine Electric & Electronic Technology, 2024, 44(8): 26-31, 37. [14] 梁旭. 水下双模式管道巡检机器人的设计与实验分析[D]. 大连: 大连交通大学, 2025. [15] 葛倩倩, 葛亮, 汪耀明, 等. 离子交换膜的发展态势与应用展望[J]. 化工进展, 2016, 35(6): 1774-1785.GE Q Q, GE L, WANG Y M, et al. Development trends and application prospects of ion exchange membranes[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2016, 35(6): 1774-1785. [16] 齐侃侃, 董昊. 磁通门传感器探头测试分析[J]. 电子测试, 2020, 1: 41-44. [17] 申军伟, 程珩. 2自由度并联机构的运动轨迹规划优化[J]. 机械传动, 2021, 45(7): 110-115.SHEN J W, CHENG H. Optimization of motion trajectory planning for a 2-DOF parallel mechanism[J]. Journal of Mechanical Transmission, 2021, 45(7): 110-115. [18] 伍赛特. 船用磁流体推进技术应用前景展望[J]. 机电信息, 2020, 36: 74-75.WU S T. Prospects for the application of marine magnetohydrodynamic propulsion technology[J]. Mechanical and Electrical Information, 2020, 36: 74-75. [19] 辛旭. 磁流体推进技术应用及展望[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2022, 12(15): 186-189. [20] 冯一波, 石书强, 王建海, 等. 气水两相下降流中泡状流与段塞流转换边界研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2024, 31(2): 166-174. [21] FUKASAWA S ,KUMAGAI T ,OHMI T , et al. Effect of small rectangular channel height on bubble moving velocity in gas-liquid two-phase flow through sudden contraction[J]. Japanese Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2013, 27(2): 168-174.[J]. Japanese Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2013, 27(2): 168-174. doi: 10.3811/jjmf.27.168 [22] 马莉司. 油气管道中阴极保护技术的应用分析[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2025, 45(8): 148-150. [23] 罗文昊. 仿生六足机器人协同控制系统研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2024. [24] 南凯刚, 姜晟, 张进华, 等. 柔性胸鳍推进仿蝠鲼机器鱼CPG运动控制[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(2): 201-210.NAN K G, JIANG S, ZHANG J H, et al. CPG motion control of a robotic manta with flexible pectoral fin propulsion[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2023, 31(2): 201-210. [25] 李佩娟, 杨刚, 郭铁铮, 等. 水下蛇形机器人建模与运动控制[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(6): 1091-1099.LI P J, YANG G, GUO T Z, et al. Modeling and motion control of an underwater snake-like robot[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(6): 1091-1099. [26] 杜治宇, 吴政康, 丁强, 等. 基于中枢模式发生器的仿生机器鱼闭环控制方法[J]. 船舶工程, 2025, 47(4): 89-97.DU Z Y, WU Z K, DING Q, et al. A closed-loop control method for bionic robotic fish based on central pattern generator[J]. Ship Engineering, 2025, 47(4): 89-97. [27] 朱文亮, 刘敏杰, 王志鹏, 等. 水下机器人的PID控制系统设计[J]. 水上安全, 2024, 6: 1-3. [28] 陈振伟. 平衡机器人运动位姿PID控制优化仿真研究[J]. 河北北方学院学报(自然科学版), 2024, 40(7): 11-15. [29] 肖丽. 基于Matlab Simulink的系统建模与仿真技术分析[J]. 集成电路应用, 2024, 41(9): 108-109.XIAO L. Analysis of system modeling and simulation technology based on Matlab Simulink[J]. Application of IC, 2024, 41(9): 108-109. [30] 张帅杰, 钟国院, 臧春华, 等. 流程工业鲁棒性PID参数整定方法[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 2024, 52(11): 3273-3279, 3369.ZHANG S J, ZHONG G Y, ZANG C H, et al. A robust PID parameter tuning method for process industries[J]. Computer & Digital Engineering, 2024, 52(11): 3273-3279, 3369. [31] 郭进群. 基于几何代数的多环耦合机构自由度计算方法[D]. 杭州: 浙江理工大学, 2023. [32] 李宏强. 船舶交流超导磁流体推进技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2019. [33] ZHANG Y N, XIE Y F, ZHAO G, et al. The important role of fluid mechanics in the engineering field[J]. E3S Web of Conferences, 2024, 56: 1160. [34] 张大朋, 赵博文, 严谨, 等. 船体静水及波浪航行时在STAR-CCM+软件中仿真结果的有效性验证[J]. 水道港口, 2022, 43(1): 121-127. -




 下载:
下载: