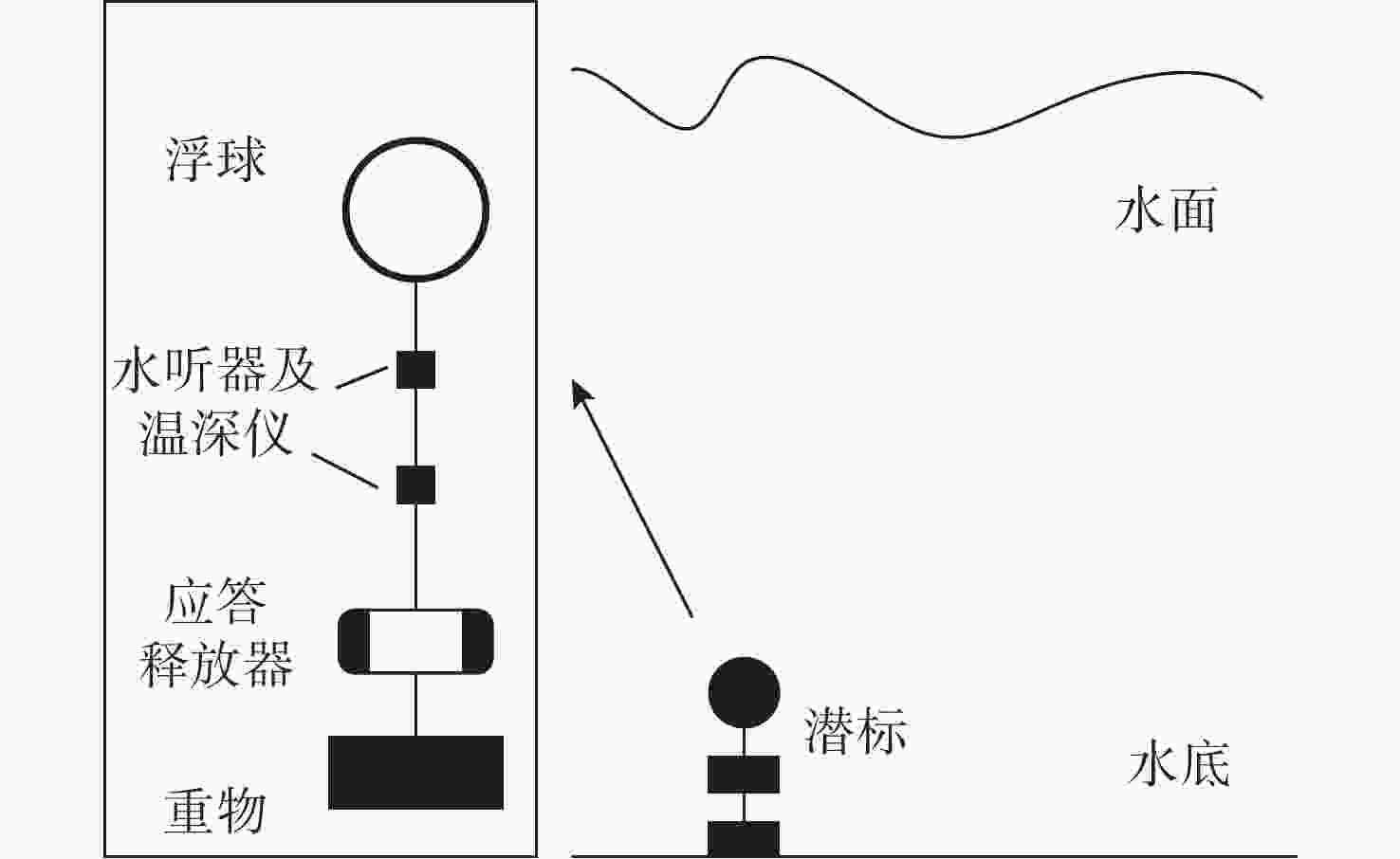
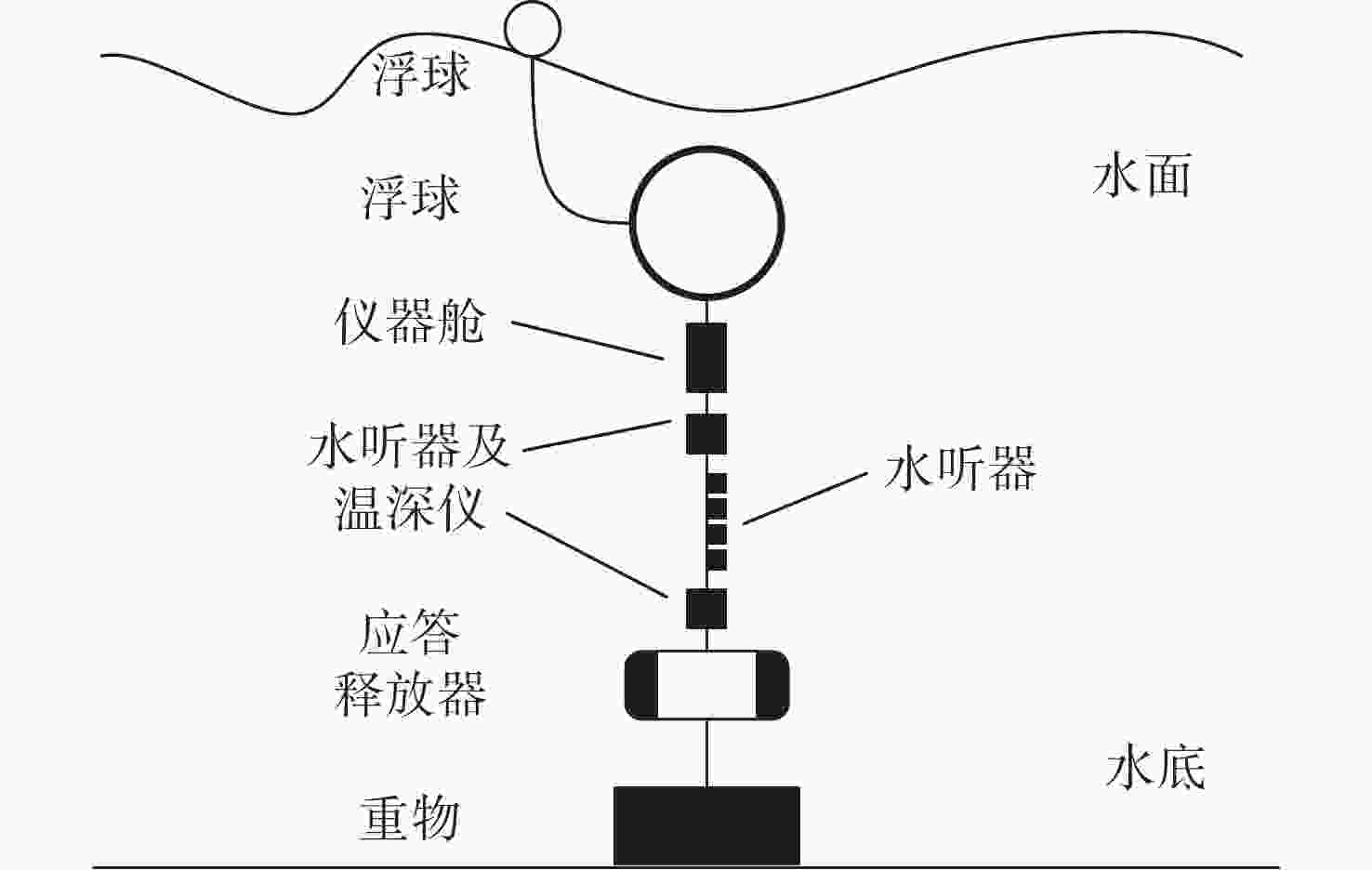
Blind Source Separation of Single-Channel Ship Radiated Noise Based on VMD-FastICA
-
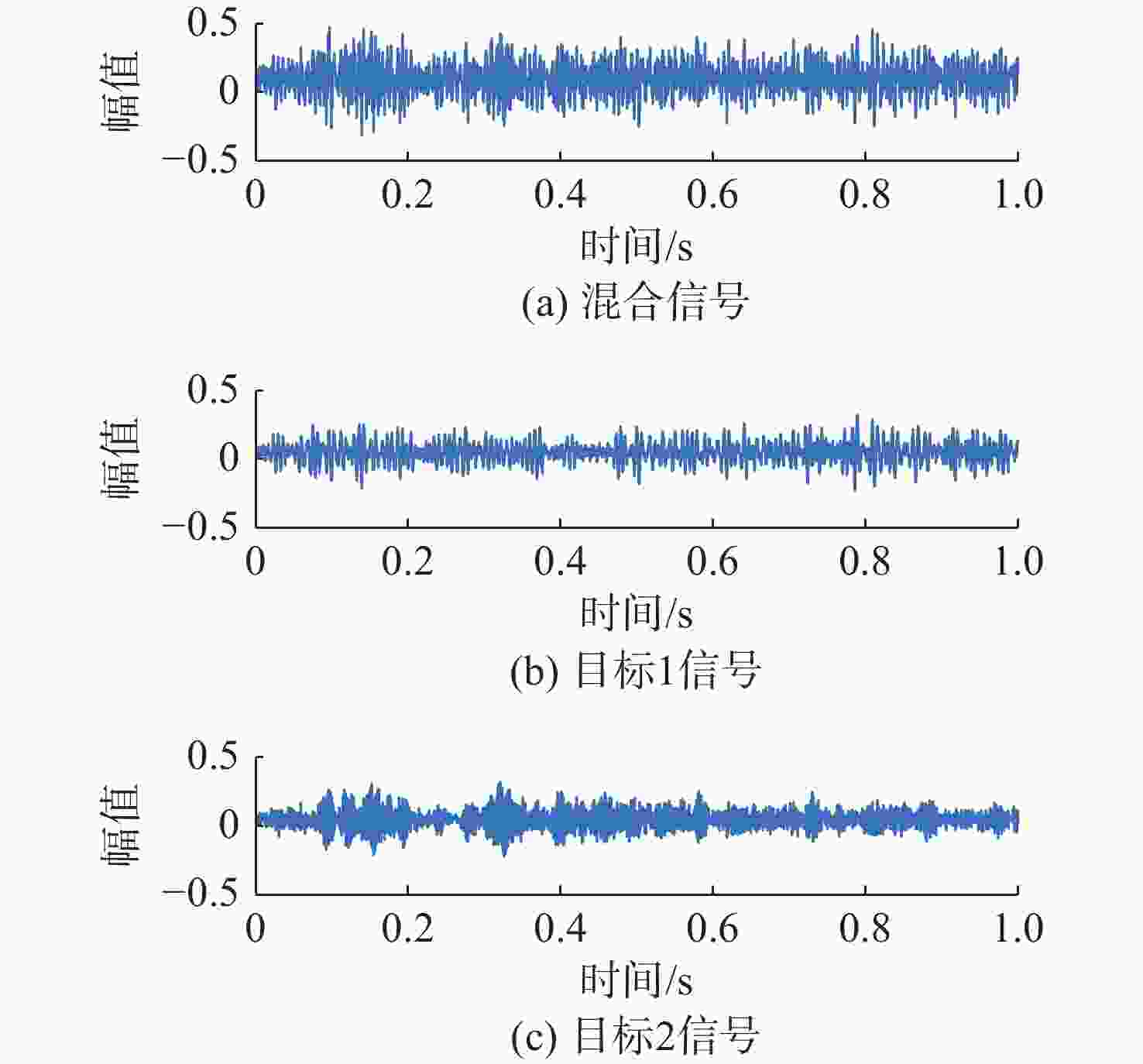
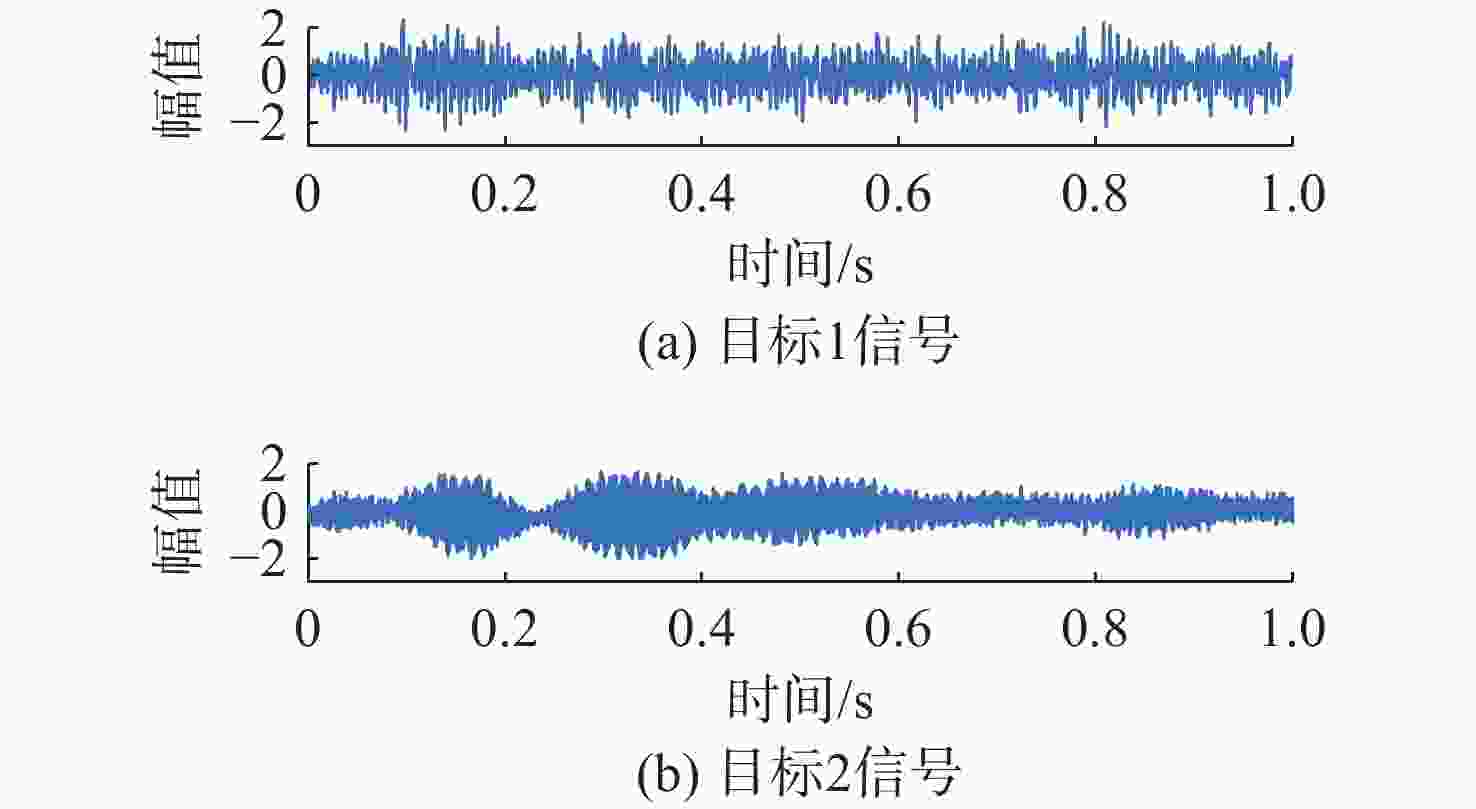
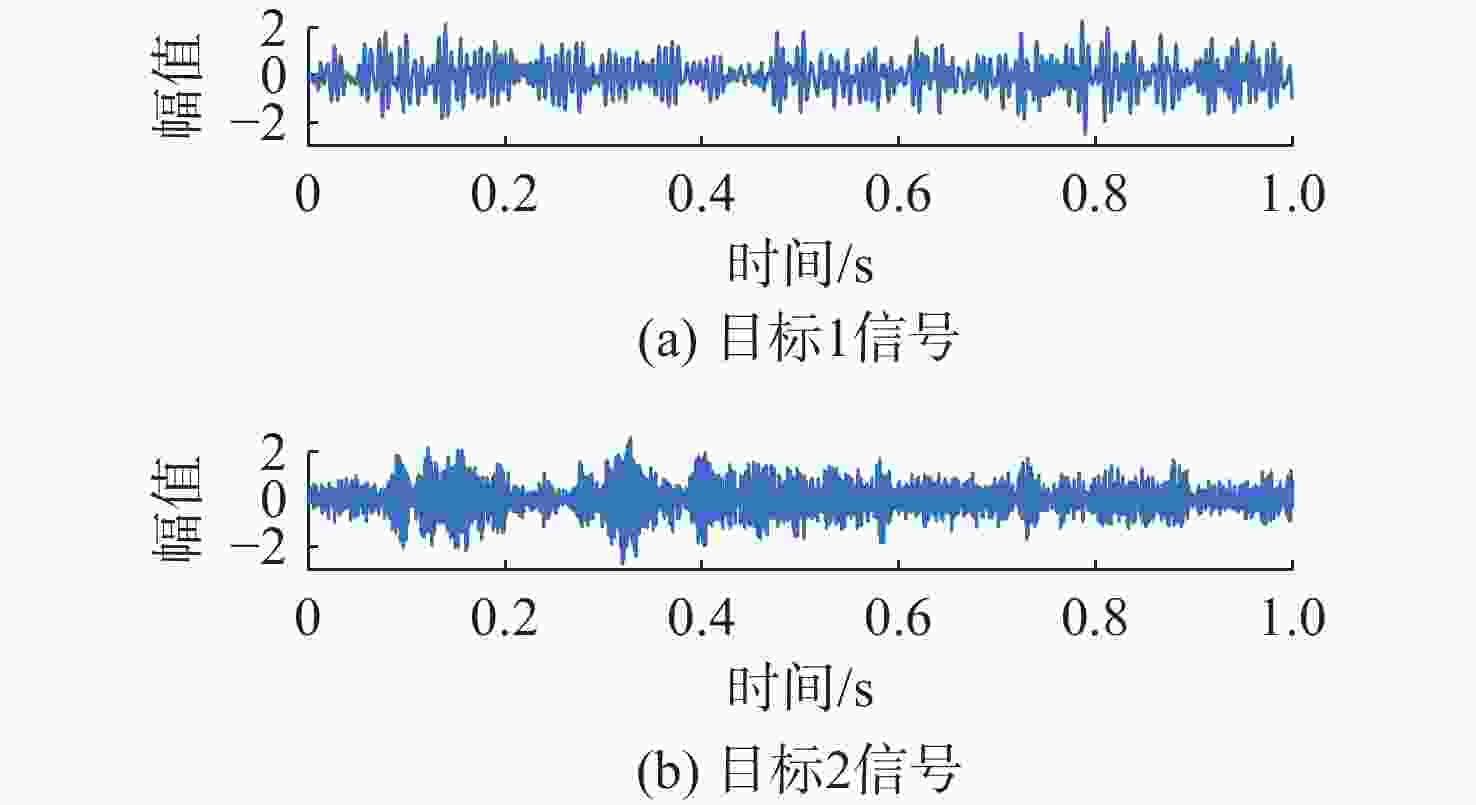
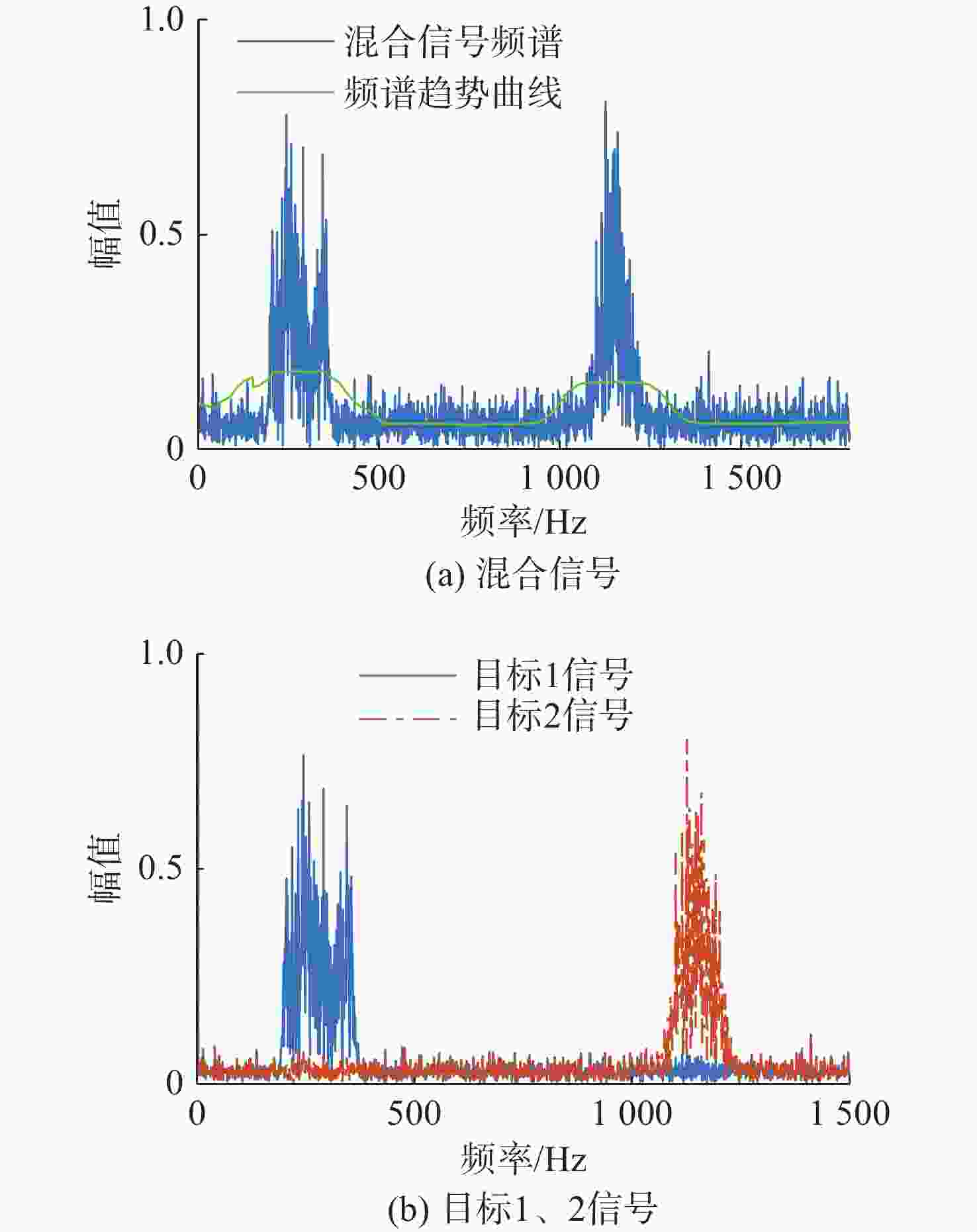
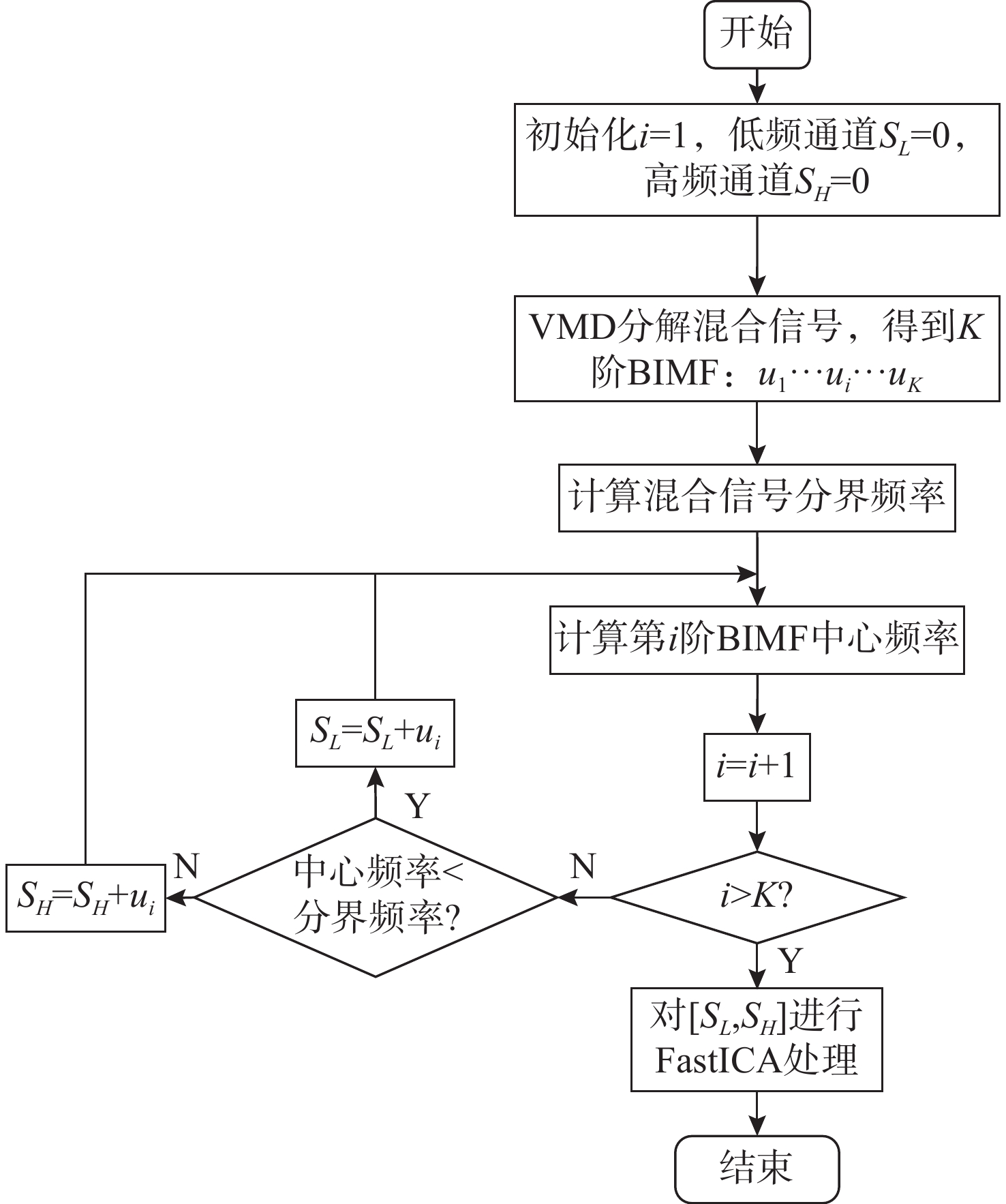
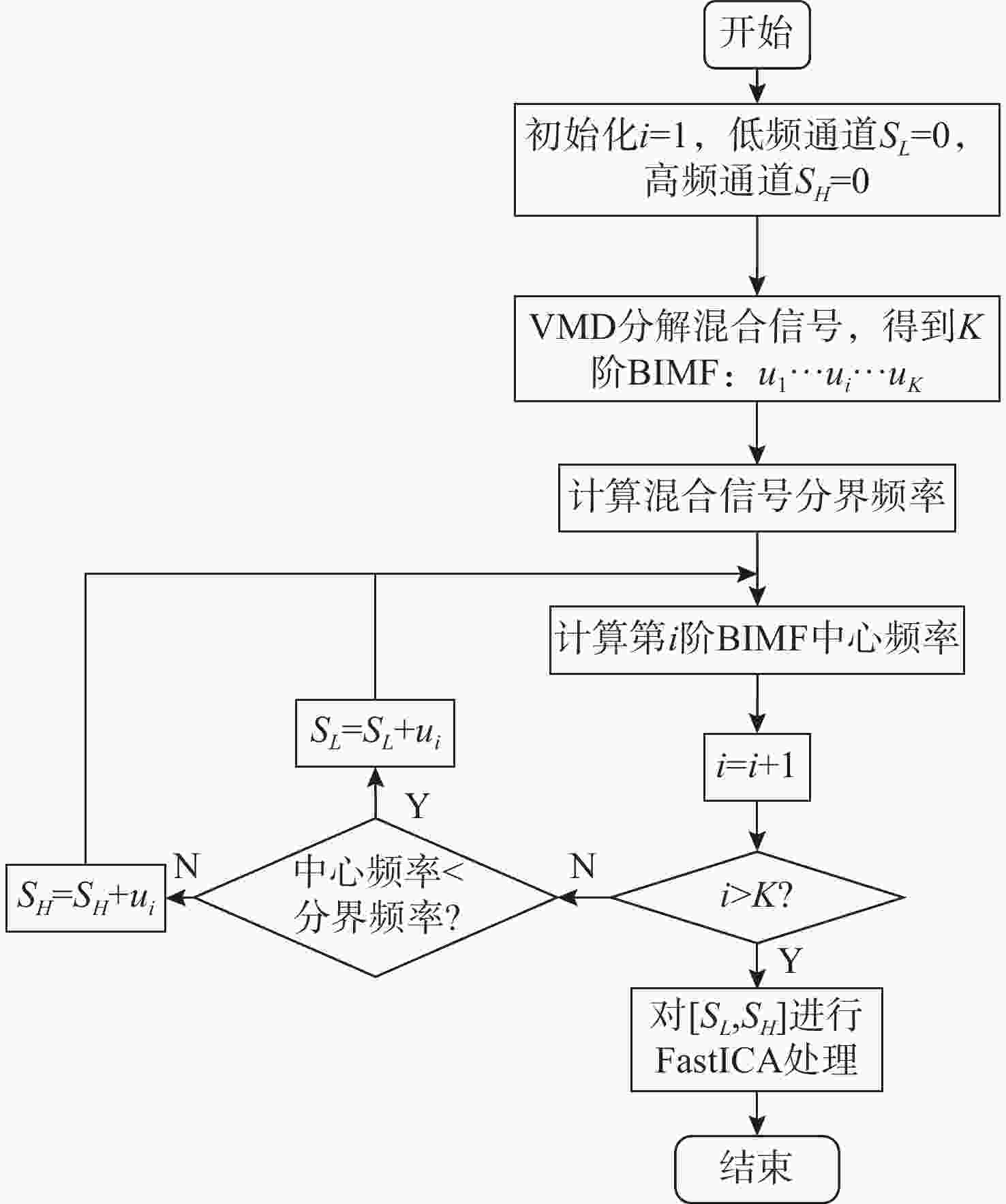
摘要: 针对在仅有单通道信号可用的极端条件下, 难以从混合信号中分离出不同目标舰船辐射噪声信号的问题, 开展单通道盲源分离算法研究。提出一种基于变分模态分解(VMD)-改进快速独立成分分析(FastICA)的舰船辐射噪声盲源分离算法。在单通道条件下, 首先通过VMD将单通道信号分解为频率成分相对独立的多阶模态, 初步实现独立频率成分的分离; 而后将各阶模态组合为虚拟多通道信号, 解决FastICA无法处理单通道信号的问题; 最后通过FastICA对虚拟多通道信号进行处理, 进一步分离独立信号成分, 从而实现单通道舰船辐射噪声盲源分离。仿真与试验数据分析结果显示, VMD-FastICA算法分离的目标信号与原目标信号的相似度, 较奇异谱分析-独立成分分析(SSA-ICA)算法均有提升, 表明其在单通道舰船辐射噪声信号盲源分离中效果良好, 能够实现单通道条件下不同目标舰船辐射噪声信号的有效分离。Abstract: To address the challenge of separating different target ship radiated noise signals from mixed signals under extreme conditions where only a single-channel signal is available, a blind source separation algorithm under single-channel conditions was researched. A ship radiated noise blind source separation algorithm based on the improved fast independent component analysis(Fast-ICA) using variational mode decomposition(VMD) was proposed. Under single-channel conditions, the single-channel signal was first decomposed into multiple modes featuring relatively independent frequency components through VMD, initially achieving the separation of independent frequency components. Then, these modes were combined into virtual multi-channel signals to solve the issue that Fast-ICA cannot process a single-channel signal. Finally, the virtual multi-channel signals were processed using Fast-ICA to further separate independent signal components, thereby achieving blind source separation of single-channel ship radiated noises. Simulation and experimental data analysis results show that the similarity between the target signals separated by the proposed VMD-FastICA algorithm and the original target signals is improved compared to the singular spectrum analysis-independent component analysis(SSA-ICA) algorithm. This demonstrates that the VMD-FastICA algorithm has good performance for separating bind sources of single-channel ship radiated noise signals and can achieve effective separation of different target ship radiated noise signals under single-channel conditions.
-
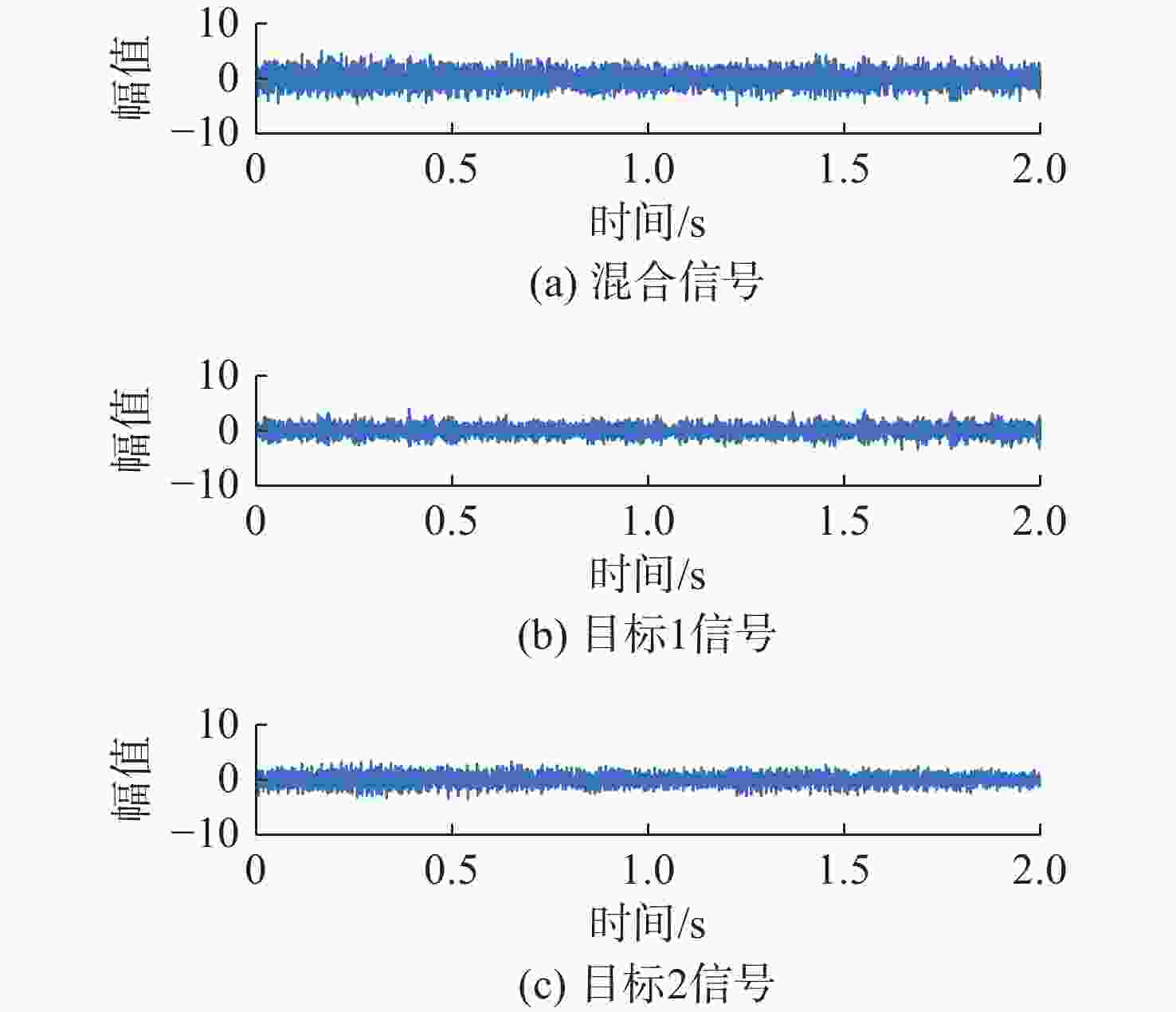
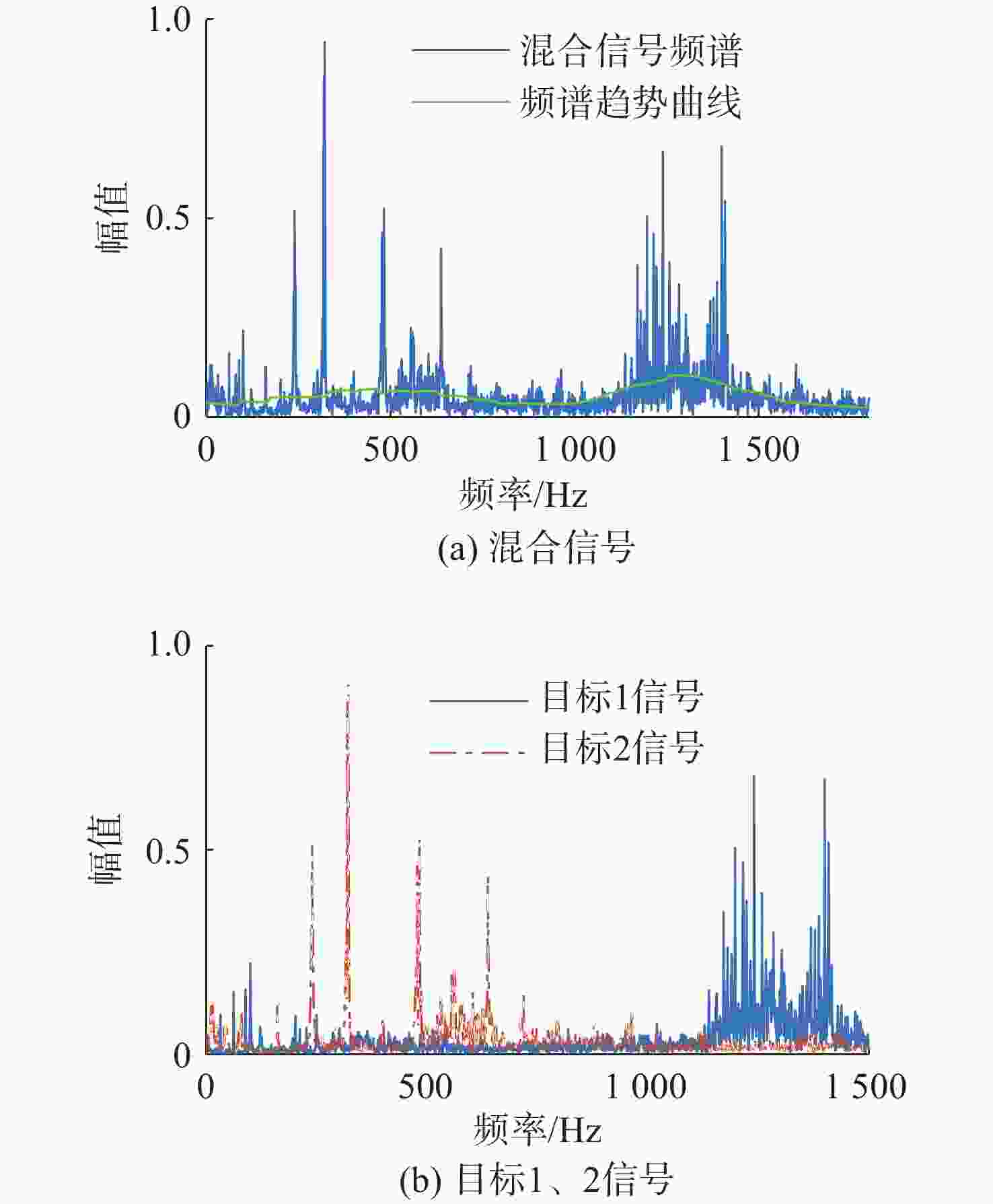
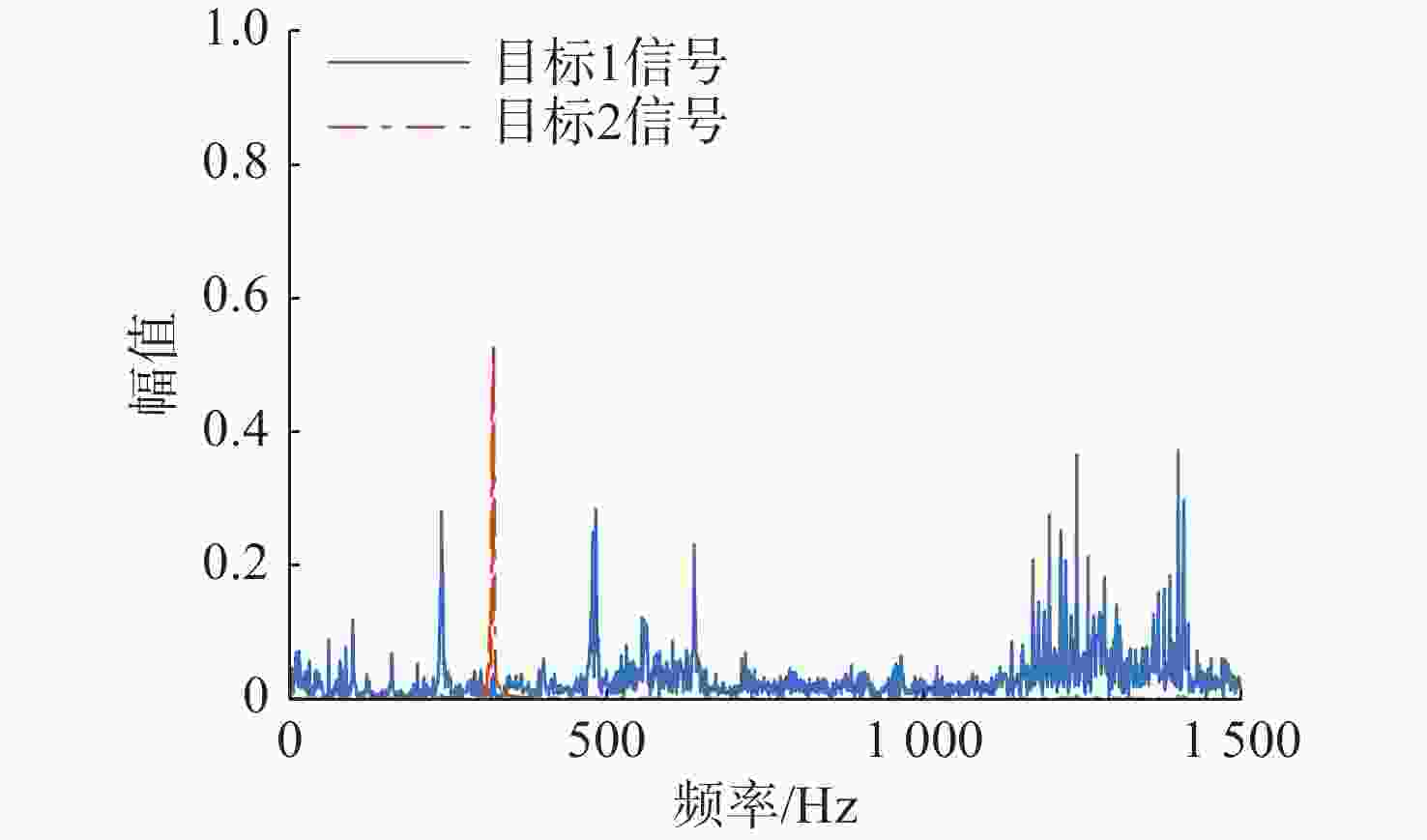
表 1 仿真信号相关系数绝对值
Table 1. Absolute values of correlation coefficients for simulation signals
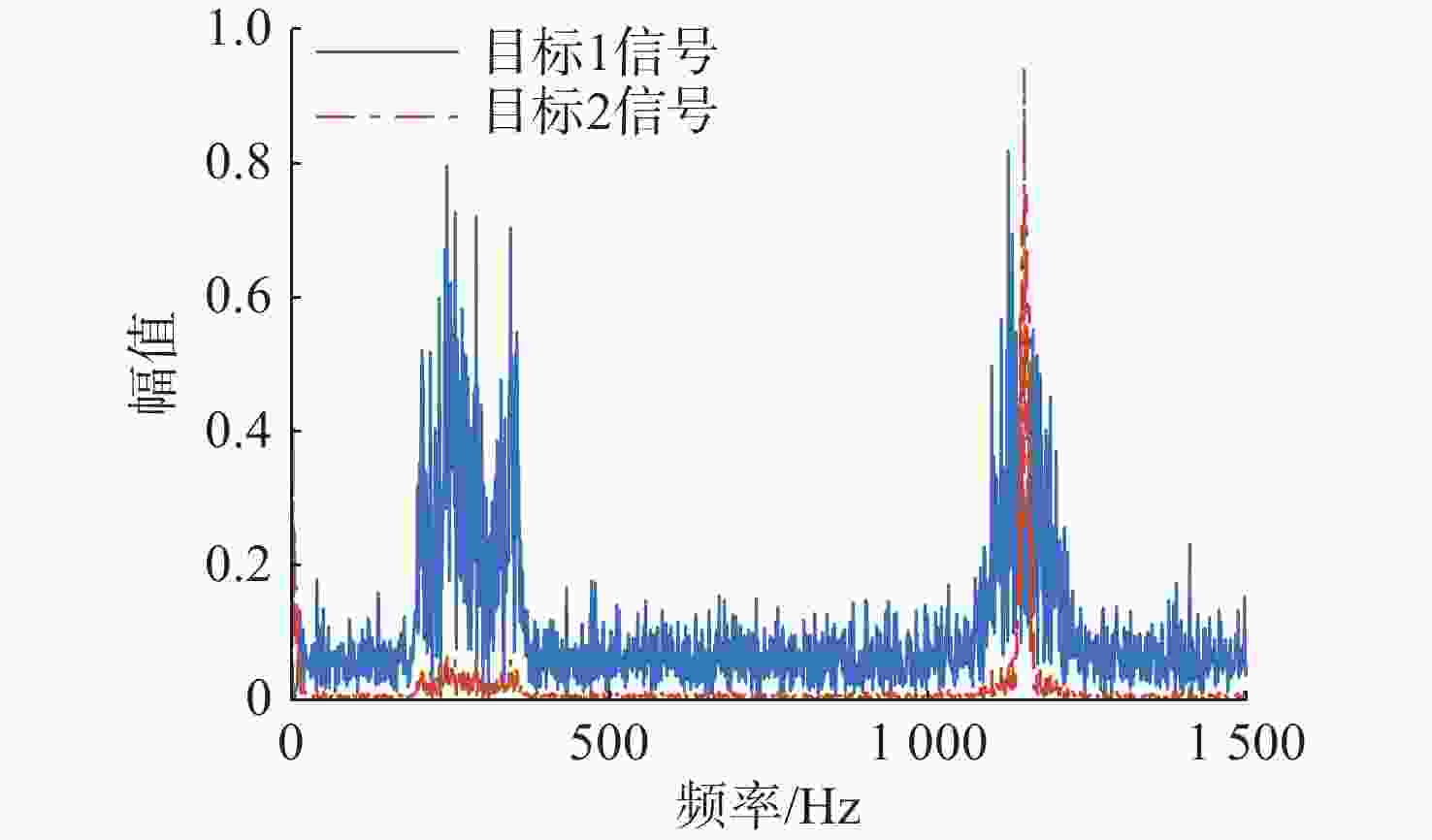
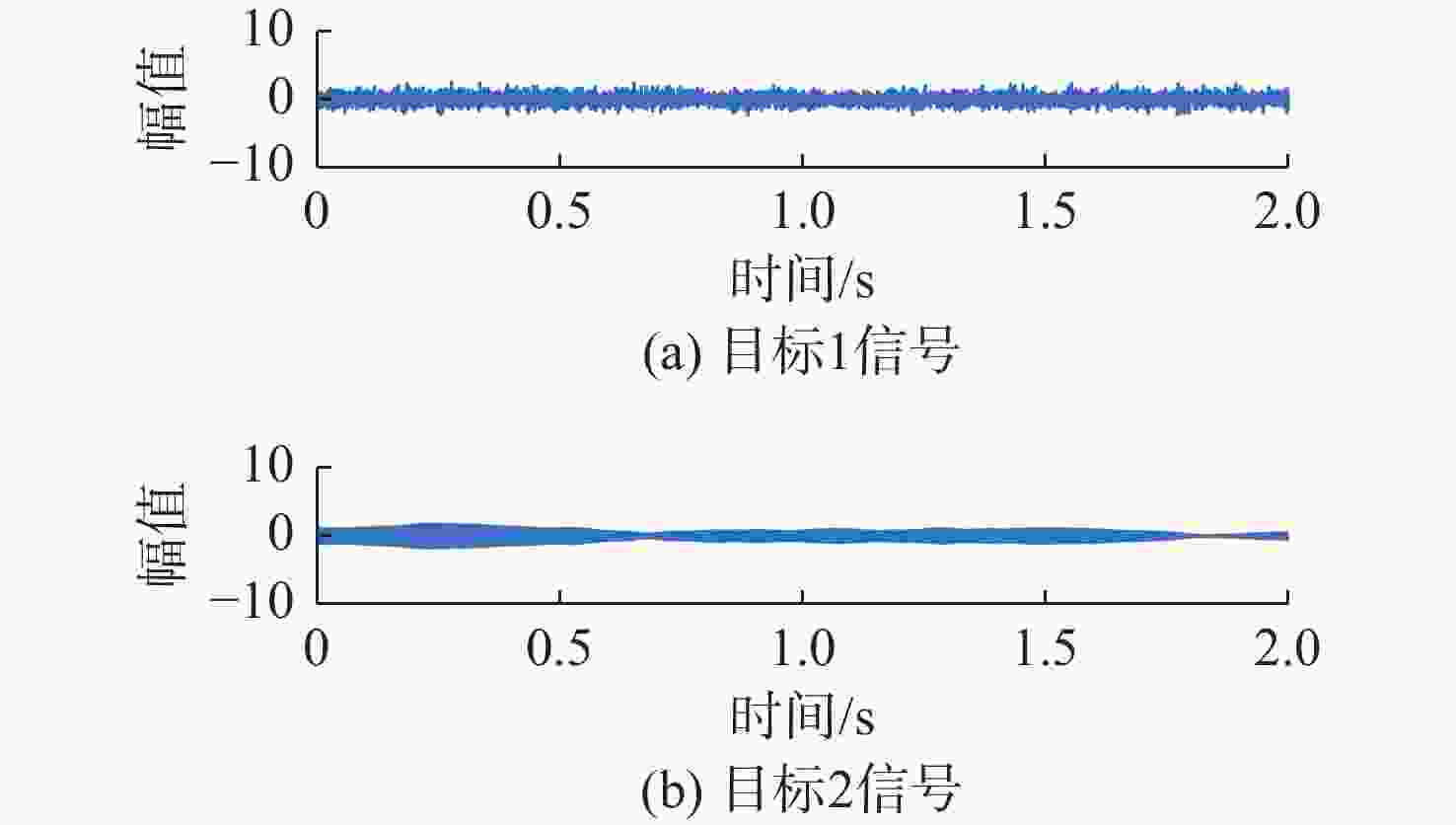
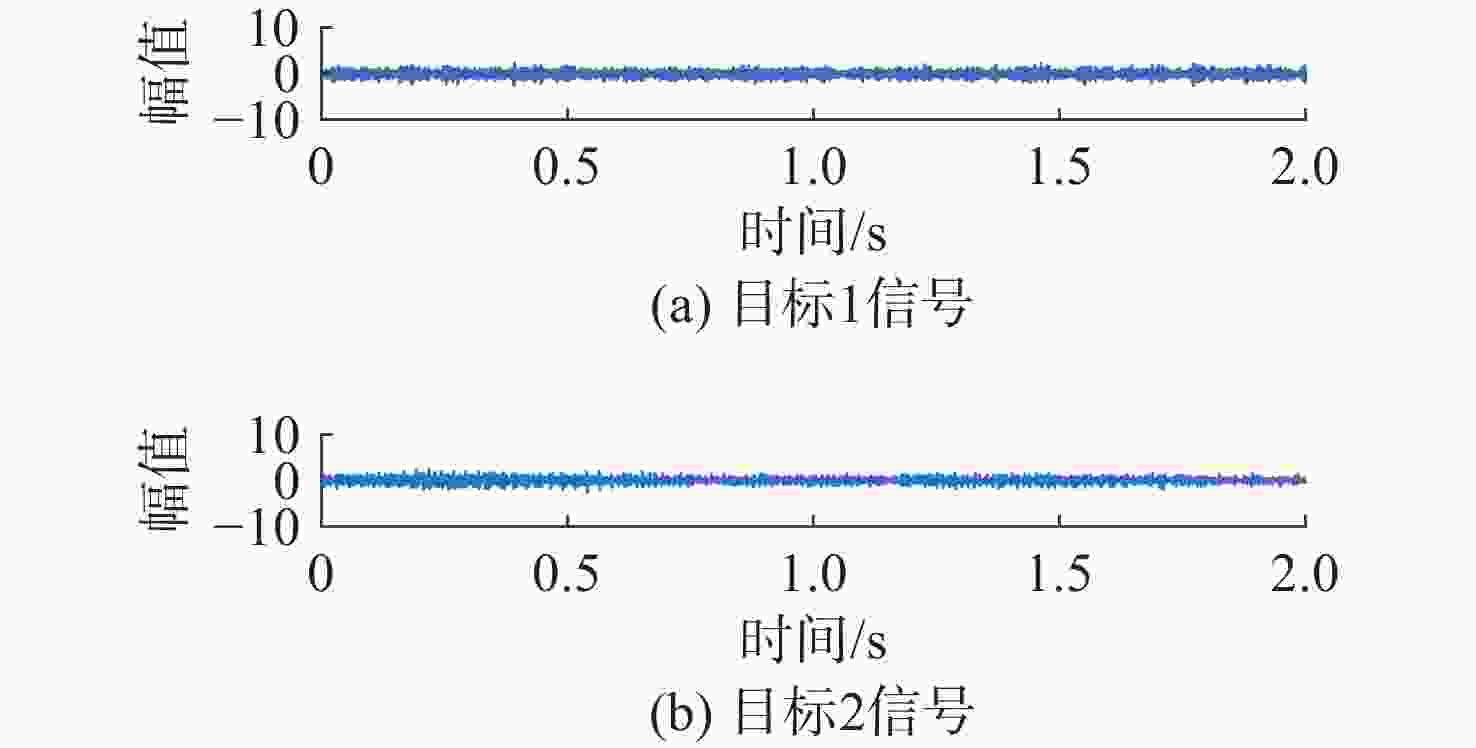
处理方法 目标1信号 目标2信号 混合信号 0.7852 0.7263 SSA-ICA 0.8416 0.3881 VMD-FastICA 0.9607 0.9488 表 2 试验1信号相关系数绝对值
Table 2. Absolute values of correlation coefficients for signals in experiment 1
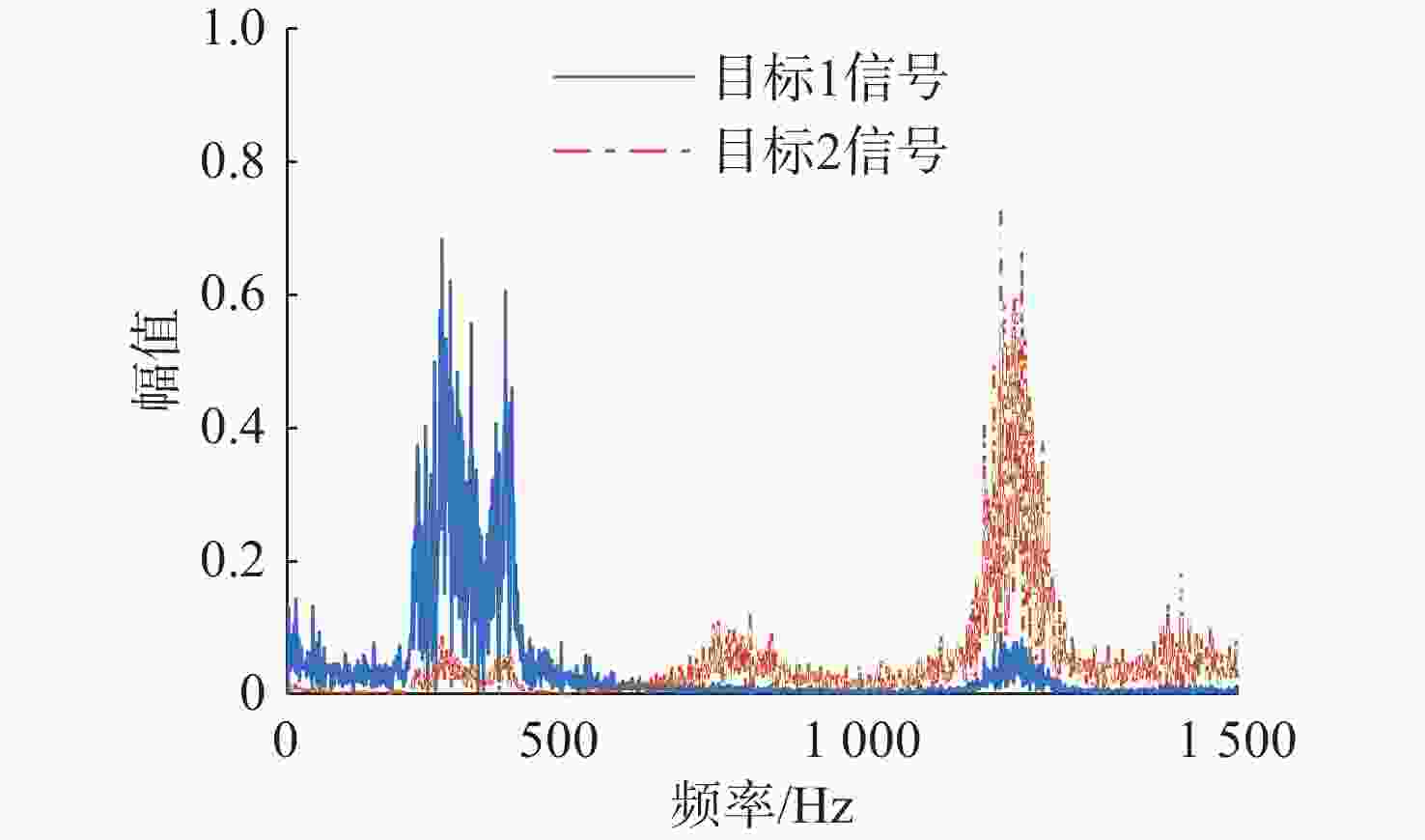
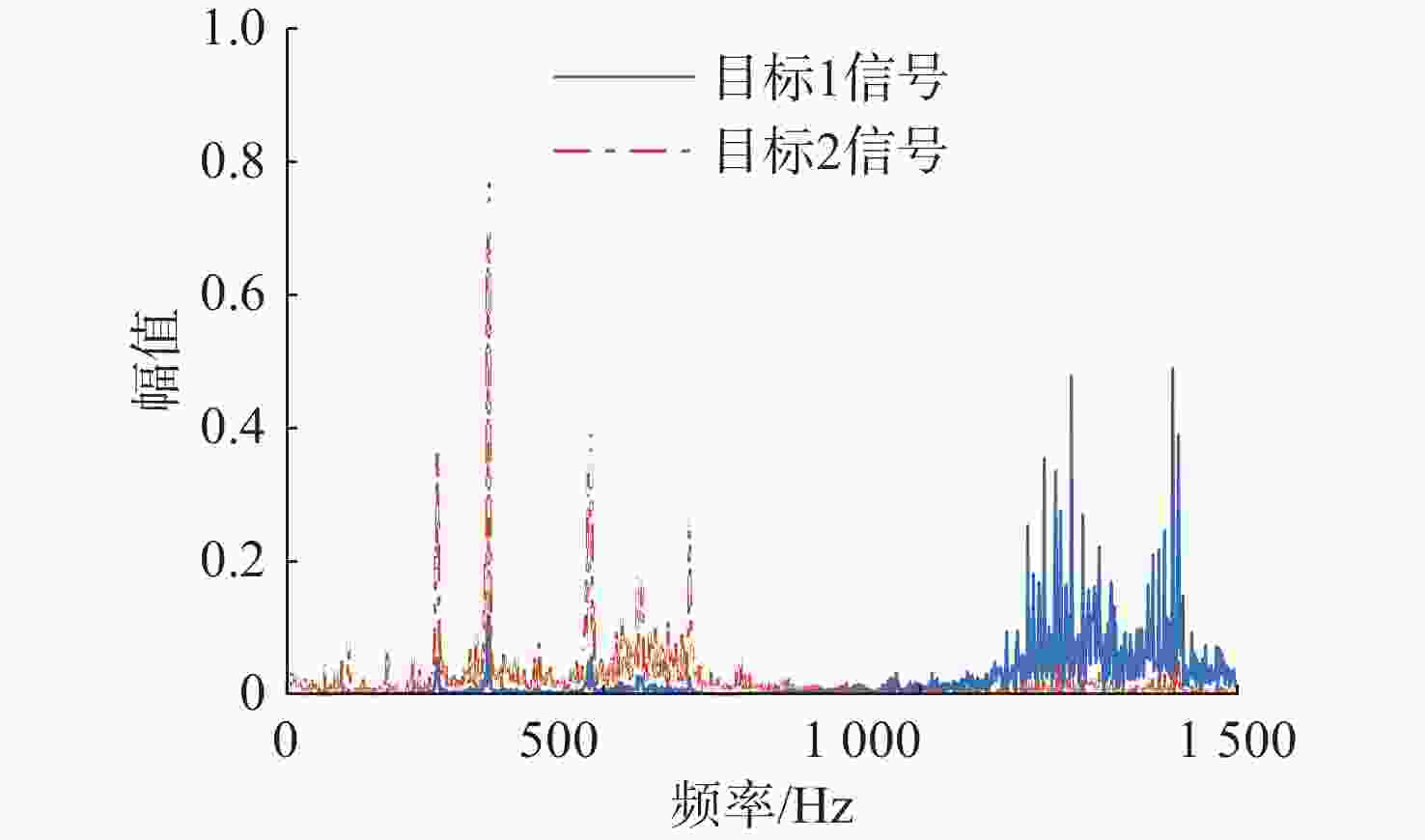
处理方法 目标1信号 目标2信号 混合信号 0.7110 0.7110 SSA-ICA 0.7806 0.5706 VMD-FastICA 0.8860 0.8863 表 3 混合信号、分离后信号与原信号相关系数绝对值
Table 3. Absolute correlation coefficients among mixed signal, separated signal and original signal
处理方法 目标1信号 目标2信号 混合信号 0.7160 0.7160 SSA-ICA 0.7533 0.4590 VMD-FastICA 0.7593 0.7538 表 4 加入环境噪声后试验信号相关系数绝对值
Table 4. Absolute values of correlation coefficients for experiment signals with environmental noise
试验类别 处理方法 目标1信号 目标2信号 试验1 混合信号 0.5871 0.5776 SSA-ICA 0.6385 0.5362 VMD-FastICA 0.7906 0.6760 试验2 混合信号 0.6047 0.5488 SSA-ICA 0.4238 0.5892 VMD-FastICA 0.6654 0.6249 表 5 VMD-FastICA分离试验信号与原信号相关系数绝对值
Table 5. Absolute values of correlation coefficients between VMD-FastICA separated experiment signals and original signals
试验
类别α 信号
类别K=5 K=6 K=7 K=8 K=9 试验1 1450 目标1 0.880 5 0.889 6 0.889 8 0.885 8 0.865 9 目标2 0.885 4 0.885 0 0.886 3 0.886 7 0.798 2 1500 目标1 0.880 0 0.889 6 0.890 0 0.886 0 0.865 8 目标2 0.884 9 0.884 6 0.885 9 0.886 3 0.797 8 1550 目标1 0.880 5 0.889 6 0.889 8 0.885 8 0.865 9 目标2 0.885 4 0.885 0 0.886 3 0.886 7 0.798 2 试验2 1450 目标1 0.651 9 0.751 6 0.759 9 0.759 9 0.745 1 目标2 0.767 9 0.754 0 0.753 3 0.754 0 0.726 9 1500 目标1 0.651 0 0.750 8 0.759 2 0.759 3 0.744 2 目标2 0.767 1 0.753 7 0.753 0 0.753 8 0.726 6 1550 目标1 0.650 3 0.749 9 0.758 6 0.758 8 0.743 2 目标2 0.766 3 0.753 4 0.752 8 0.753 6 0.726 4 表 6 VMD-FastICA分离试验信号与原信号相关系数绝对值(含环境噪声)
Table 6. Absolute values of correlation coefficients between VMD-FastICA separated experiment signals and original signals with environmental noise
试验
类别α 信号
类别K=5 K=6 K=7 K=8 K=9 试验1 1450 目标1 0.776 0 0.775 6 0.799 4 0.790 3 0.790 0 目标2 0.672 2 0.675 1 0.676 3 0.675 4 0.655 3 1500 目标1 0.775 3 0.775 1 0.790 4 0.790 6 0.790 4 目标2 0.672 1 0.675 0 0.655 7 0.676 0 0.655 7 1550 目标1 0.774 7 0.774 5 0.800 2 0.790 9 0.790 8 目标2 0.672 0 0.674 9 0.677 3 0.676 5 0.656 1 试验2 1450 目标1 0.607 8 0.595 6 0.623 4 0.665 6 0.628 9 目标2 0.523 8 0.477 3 0.665 7 0.625 2 0.644 4 1500 目标1 0.606 9 0.592 0 0.623 0 0.665 4 0.628 8 目标2 0.523 4 0.470 1 0.665 5 0.624 9 0.644 1 1550 目标1 0.606 0 0.588 1 0.622 8 0.665 2 0.628 6 目标2 0.523 0 0.462 6 0.665 3 0.624 6 0.643 8 -
[1] 倪晋平, 马远良, 孙超, 等. 用独立成份分析算法实现水声信号盲分离[J]. 声学学报, 2002, 27(4): 321-326.NI J P, MA Y L, SUN C, et al. Blind separation of underwater acoustic signals via independent component analysis algorithms[J]. Acta Acustica, 2002, 27(4): 321-326. [2] 张安清, 章新华. 基于信息理论的舰船噪声盲分离算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2002(1): 38-40, 51.ZHANG A Q, ZHANG X H. Blind separation algorithm for ship noise based on information theory[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2002(1): 38-40, 51. [3] 姜卫东, 高明生, 陆佶人. 基于两个频点的水声信号盲源分离[J]. 声学技术, 2004(4): 197-200.JIANG W D, GAO M S, LU J R. Blind source separation for underwater signals using only two frequency bins[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2004(4): 197-200. [4] 单志超, 林春生, 向前. 基于二阶非平稳统计量的船舶噪声信号的盲分离[J]. 信号处理, 2009, 25(6): 973-976.SHAN Z C, LIN C S, XIANG Q. The separation of ship noise signal based on second order nonstationary statistic[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2009, 25(6): 973-976. [5] 刘佳, 杨士莪, 朴胜春, 等. 单观测通道船舶辐射噪声盲源分离[J]. 声学学报, 2011, 36(3): 265-270.LIU J, YANG S E, PIAO S C, et al. Blind source separation of ship-radiated noise using single observing channel[J]. Acta Acustica, 2011, 36(3): 265-270. [6] 何会会, 李钢虎, 要庆生, 等. 用慢特征分析算法实现水声信号盲分离[J]. 声学技术, 2014, 33(3): 270-274.HE H H, LI G H, YAO Q S, et al. Blind source separation of underwater acoustic signals by using slowness feature analysis[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2014, 33(3): 270-274. [7] 康春玉, 李文哲, 夏志军, 等. 盲重构频域阵列信号的压缩感知水声目标方位估计[J]. 声学学报, 2019, 44(6): 951-960.KANG C Y, LI W Z, XIA Z J, et al. Direction of arrival estimation for underwater acoustic target based on compressed sensing after blind reconstruction of array signal in frequency domain[J]. Acta Acustica, 2019, 44(6): 951-960. [8] 郑艳艳, 朱永利, 高佳程. 基于SSA与ICA的变压器局部放电混合信号分离[J]. 电测与仪表, 2020, 57(22): 84-90.ZHENG Y Y, ZHU Y L, GAO J C. Hybrid signal separation of transformer partial discharge based on SSA and ICA[J]. Electrical Measurement and Instrumentation, 2020, 57(22): 84-90. [9] MOHEBBIAN R M, ALAM W M, WAHID A K, et al. Single channel high noise level ECG deconvolution using optimized blind adaptive filtering and fixed-point convolution kernel compensation[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2020, 57: 101673. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101673 [10] 付卫红, 周雨菲, 张鑫钰, 等. 基于参数估计和Kalman滤波的单通道盲源分离算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46(8): 2850-2856.FU W H, ZHOU Y F, ZHANG X Y, et al. Single-channel blind source separation algorithm based on parameter estimation and Kalman filter[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(8): 2850-2856. [11] DRAGOMIRETSKIY K, ZOSSO D. Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(3): 531-544. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675 [12] HYVARINEN A. Fast and robust fixed-point algorithms for independent component analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1999, 10(3): 626-634. doi: 10.1109/72.761722 [13] 姚小俊, 孙守鹏, 王强, 等. 变分模态分解与时间序列模型相结合的结构损伤识别方法研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2025, 44(5): 131-139, 217.YAO X J, SUN S P, WANG Q, et al. Structural damage identification method combining VMD and ARIMA model[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2025, 44(5): 131-139, 217. [14] SARMADI H, ENTEZAMI A, KHORRAM D M. Energy-based damage localization under ambient vibration and non-stationary signals by ensemble empirical mode decomposition and Mahalanobis-squared distance[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2019, 26(11-12): 1012-1027. [15] 李威霖, 蒋扬名, 张众杰, 等. 基于VMD与FastICA的电动汽车减速器噪声测试分离技术研究[J]. 机械传动, 2024, 48(11): 162-168.LI W L, JIANG Y M, ZHANG Z J, et al. Research on background noise separation of reducers based on VMD and FastICA[J]. Journal of Mechanical Transmission, 2024, 48(11): 162-168. [16] 刘佳, 杨士莪, 朴胜春. 多途环境下的单通道水声信号盲源分离[J]. 振动与冲击, 2012, 31(6): 15-18.LIU J, YANG S E, PIAO S C. Single channel blind source separation for underwater acoustic signal under multipath condition[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2012, 31(6): 15-18. -




 下载:
下载: