Underwater Target Electric Field Positioning Method Based on Particle Swarm Optimization and Differential Evolution Hybrid Algorithm
-
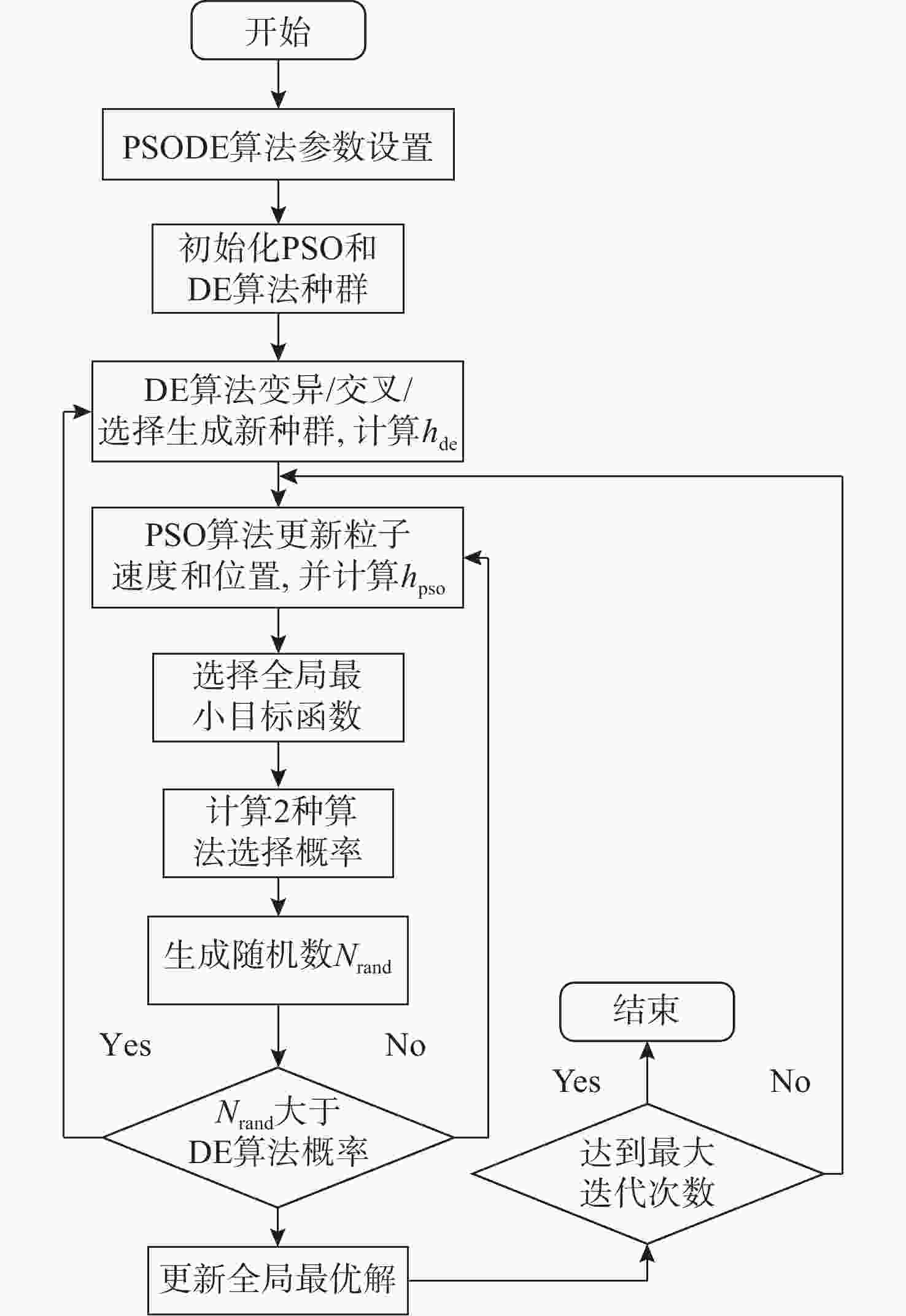
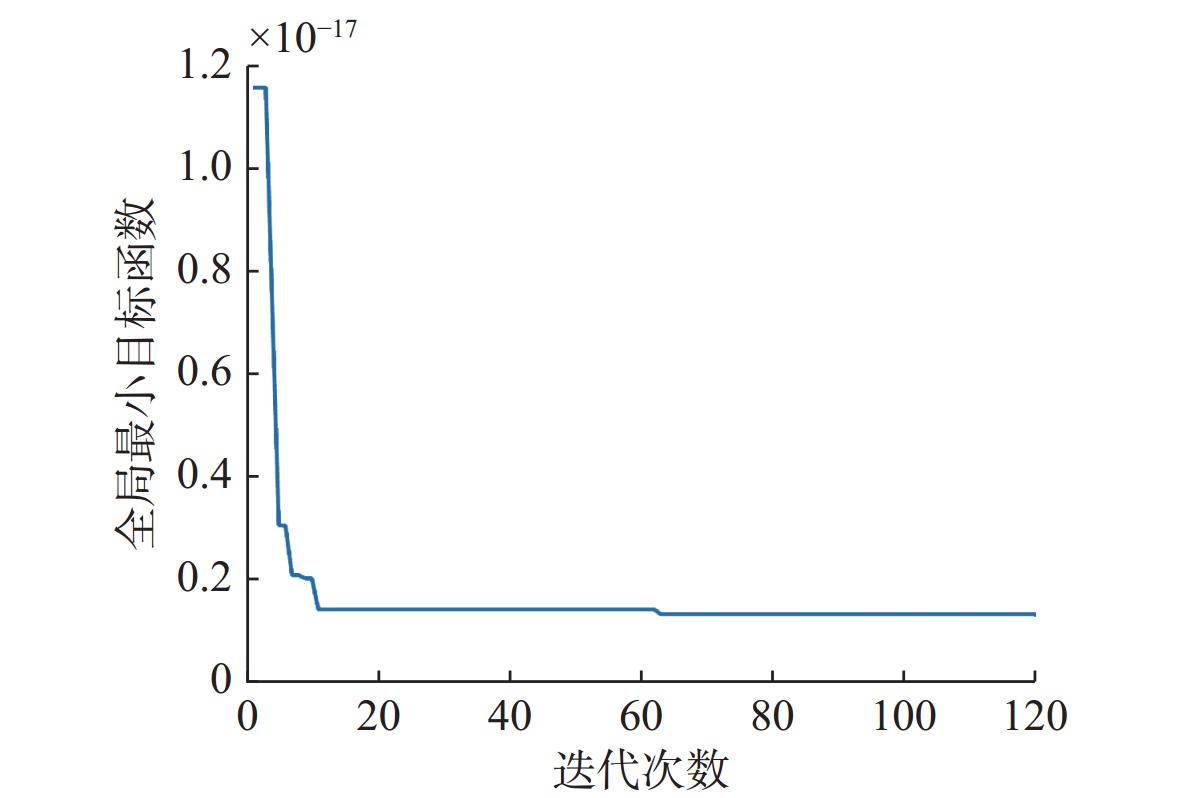
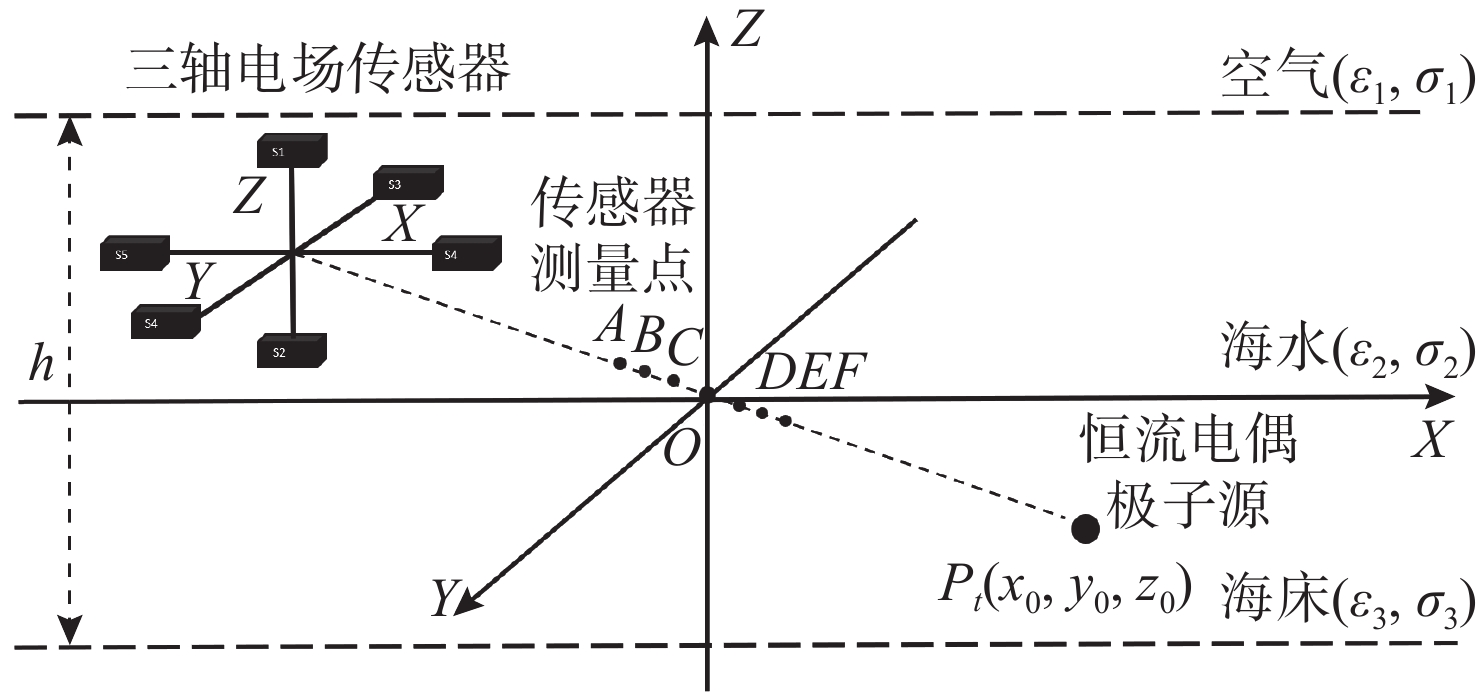
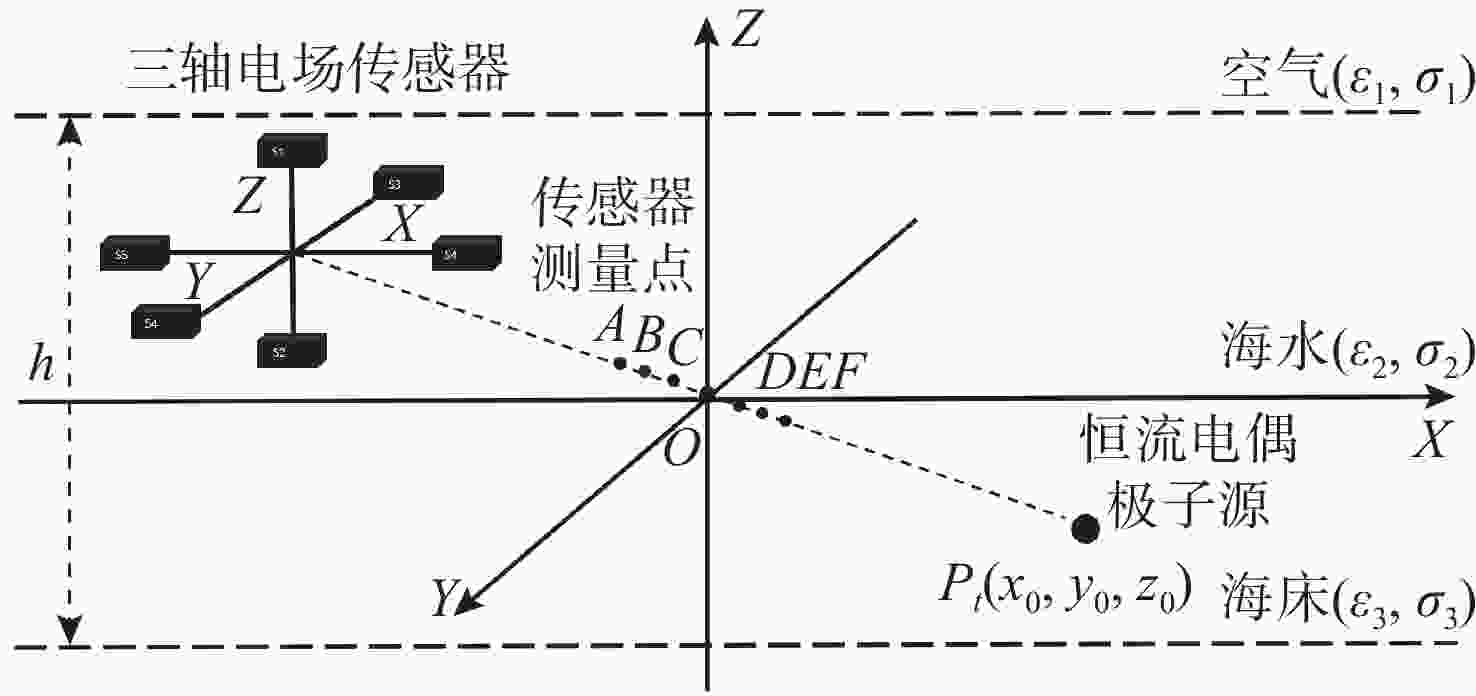
摘要: 为实现浅海环境下水下目标的远距离高精度定位, 提出一种基于粒子群差分进化混合算法(PSODE)的水下目标电场定位方法。从三层媒质电场辐射模型出发, 将水下目标等效为恒流电偶极子源, 利用非规则布放的三轴电场传感器阵列获取电场测量数据, 构建基于信噪比动态权重与鲁棒Huber损失的目标函数, 将定位问题转化为目标函数最小化问题。针对传统差分进化(DE)算法易早熟收敛、粒子群优化(PSO)算法局部搜索能力不足等问题, 提出一种协同优化机制。该机制通过DE变异交叉生成多样化解集, 并结合PSO的动态权重更新策略强化局部搜索能力, 同时引入自适应参数调整与概率选择机制, 在全局探索与局部开发之间实现更优平衡, 从而有效降低算法陷入局部最优解的风险。仿真实验结果表明, 所提方法具有初值不敏感、抗噪性强、收敛速度快等优势, 相比传统PSO和DE算法具有更高的定位精度, 为浅海环境下的水下目标高精度定位提供有效解决方案。Abstract: To achieve long-distance and high-precision positioning of underwater targets in shallow sea environments, a novel underwater target electric field positioning method based on the particle swarm optimization and differential evolution(PSODE) hybrid algorithm was proposed. Starting from the three-layer medium electric field radiation model, the underwater target was equivalent to a constant current electric dipole source. The electric field measurement data were obtained by using the irregularly arranged three-axis electric field sensor array, and a target function based on the dynamic weight of the signal-to-noise ratio and the robust Huber loss was constructed. The positioning problem was transformed into the minimization problem of the target function. To address the premature convergence of the traditional differential evolution(DE) algorithm and the insufficient local search ability of the particle swarm optimization(PSO) algorithm, a collaborative optimization mechanism was proposed. This mechanism generated diverse solution sets through DE mutation and crossover and combined the dynamic weight update strategy of PSO to enhance the local search ability. Meanwhile, an adaptive parameter adjustment and probability selection mechanism was introduced to achieve a better balance between global exploration and local exploitation, thereby effectively reducing the risk of the algorithm getting trapped in local optimal solutions. Simulation experiment results show that the proposed method has the advantages of being insensitive to initial values, strong anti-noise ability, and fast convergence speed. Compared with the traditional PSO and DE algorithms, it has higher positioning accuracy, providing an effective solution for high-precision positioning of underwater targets in shallow sea environments.
-
表 1 PSODE算法仿真结果
Table 1. Simulation results of the PSODE algorithm
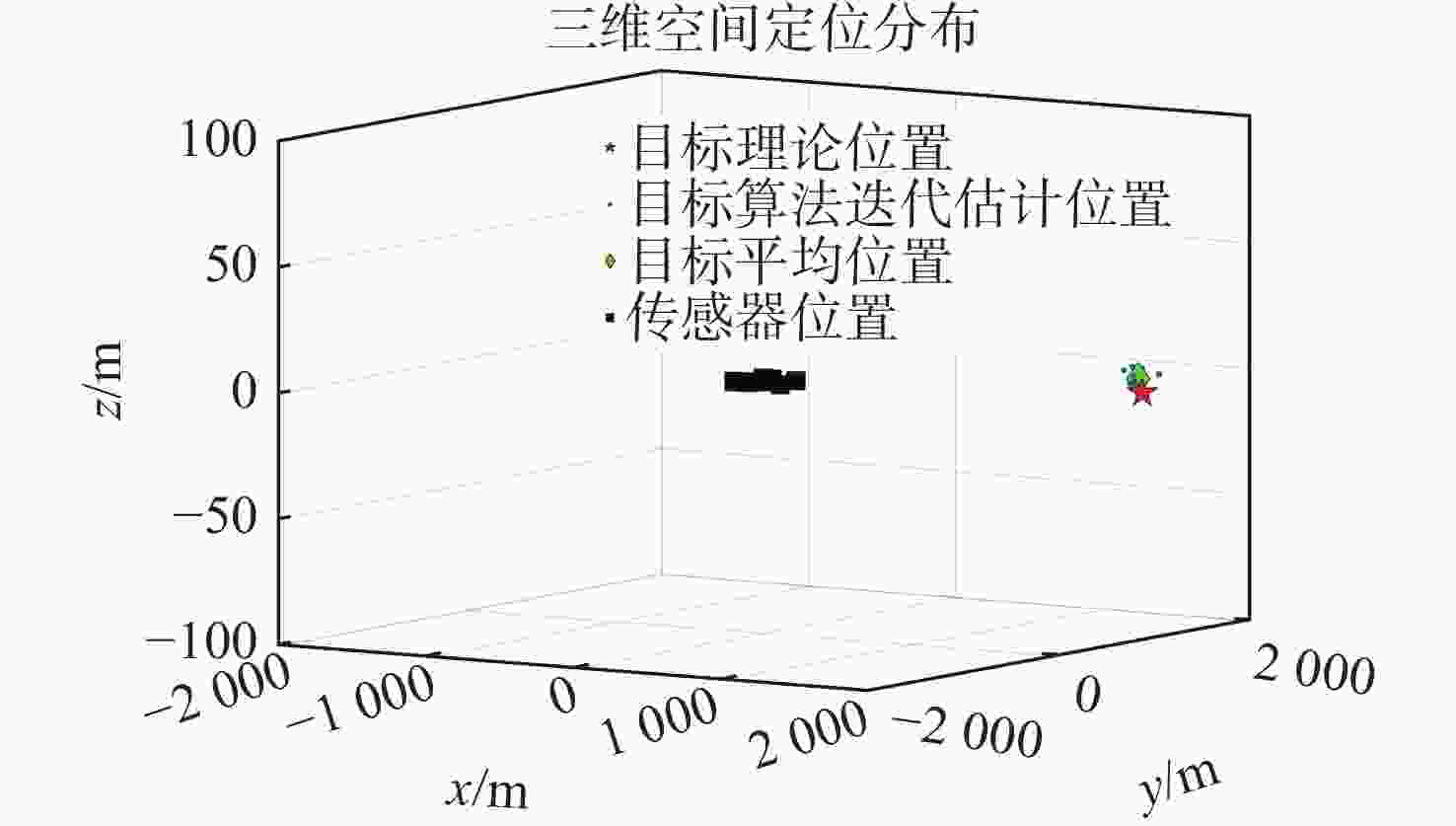
SNR/dB $ r\mathrm{_{avg}} $/m ${\delta _x}$/% ${\delta _y}$/% ${\delta _r}$/% 30 ( 1920.0 , 870.0, −1.2)3.03 3.33 3.08 20 ( 1874.0 ,1004.0 , 0.64)5.35 11.56 2.50 10 ( 1789.0 , 820.0, 0.18)9.65 8.89 9.50 表 2 不同定位算法误差比较
Table 2. Comparison of errors in different positioning algorithms
定位方法 ${\delta _x}$/% ${\delta _y}$/% ${\delta _{\textit{r}}}$/% PSO 14.8 18.2 15.31 DE 11.5 21.7 13.43 PSODE 1.5 5.32 4.63 -
[1] 赵爽, 王宏磊. 基于尾流空中辐射磁场的水下目标探测研究[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1-8. doi: 10.11990/jheu.202305037ZHAO S, WANG H L. Research on underwater target detection based on wake airborne radiation magnetic field[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2025, 45(6): 1-8. doi: 10.11990/jheu.202305037 [2] 丁文俊, 柴亚军, 杨宇贤, 等. 基于空海异构无人平台的水下目标搜索与跟踪[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(2): 237-249. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2024-0037DING W J, CHAI Y J, YANG Y X, et al. Underwater target search and tracking based on air-sea heterogeneous unmanned platform[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(2): 237-249. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2024-0037 [3] 韩博, 徐红丽, 邱少雄, 等. 基于边界约束粒子滤波的多UUV纯方位协同目标跟踪[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(2): 250-259.HAN B, XU H L, QIU S X, et al. Multi-UUV collaborative bearing-only target tracking based on boundary constrained particle filter[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(2): 250-259. [4] 陈聪, 吴旭, 孙嘉庆, 等. 基于改进差分进化算法的水下恒定电流元定位方法随电极数量的变化[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2025, 46(1): 173-180. doi: 10.11990/jheu.202301014CHEN C, WU X, SUN J Q, et al. Underwater steady current element positioning method based on improved differential evolution algorithm[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2025, 46(1): 173-180. doi: 10.11990/jheu.202301014 [5] HIROTA M, TERANISHI Y, NANAURA K. Study on underwater electric fields of a dipole moment in shallow water[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1996, 35(5): 2870-2878. [6] 包中华, 龚沈光, 孙剑英, 等. 使用双矢量传感器定位深海中水平直流电偶极子源[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2011, 23(3): 53-57.BAO Z H, GONG S G, SUN J Y, et al. Localization of a horizontal electric dipole source embedded in deep sea by using two vector-sensors[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2011, 23(3): 53-57. [7] 杜初阳, 陈聪, 黄高聪. 平行分层海域中电偶极子源的定位方法研究[J]. 电子学报, 2021, 49(9): 1761-1767.DU C Y, CHEN C, HUANG G C, et al. Research on localization method of electric dipole sources in parallel layered seas[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2021, 49(9): 1762-1767. [8] 李涛, 王向军, 嵇斗. 浅海中时谐水平电偶极子定位研究[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2015, 35(5): 142-146. [9] 张学峰, 李涛. 浅海中利用舰船轴频电场定位技术研究[J]. 河北省科学院学报, 2015, 32(2): 26-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9383.2015.02.006ZHANG X F, LI T. Research on positioning technology of the ship shaft-rate electric field in shallow sea[J]. Journal of the Hebei Academy of Sciences, 2015, 32(2): 26-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9383.2015.02.006 [10] ZHANG Y, CHEN C, SUN J, et al. An underwater passive electric field positioning method based on scalar potential[J]. Mathematics, 2024, 12(12): 1832. doi: 10.3390/math12121832 [11] KIM J, LEE I, KIM B, et al. Axis calibration method of underwater electric field measurement sensor for underwater robot[C]//2022 19th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots(Ur). Jeju, Republic of Korea: IEEE, 2022: 326-331. [12] KIM J, LEE I, LEE M, et al. Analysis of electrode configuration of underwater electric field sensor on electric-field-based localization for underwater robots[C]//2022 22nd International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems(ICCAS). Jeju, Republic of Korea: IEEE, 2022: 59-63. [13] 吴重庆, 赵爽. 电偶极子源定位问题的研究[J]. 物理学报, 2007, 56(9): 5180-5184. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2007.09.030WU C Q, ZHAO S. Study on the localization of the electric dipole sources[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2007, 56(9): 5180-5184. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2007.09.030 [14] WANG D, TAN D, LIU L. Particle swarm optimization algorithm: An overview[J]. Soft Computing, 2018, 22(2): 387-408. doi: 10.1007/s00500-016-2474-6 [15] GONG Y J, LI J J, ZHOU Y, et al. Genetic learning particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 46(10): 2277-2290. [16] ZHAN Z H, ZHANG J, LI Y, et al. Orthogonal learning particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2011, 15(6): 832-847. [17] DAS S, MANDAL A, MUKHERJEE R. An adaptive differential evolution algorithm for global optimization in dynamic environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 44(6): 966-978. [18] LI X T, MA S J, HU J H. Multi-search differential evolution algorithm[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2017, 47(1): 231-256. doi: 10.1007/s10489-016-0885-9 [19] WANG X, YANG Q, ZHAO Y. Research on hybrid PSODE with three populations based on multiple differential evolutionary models[C]//2010 International Conference on Electrical and Control Engineering. Wuhan, China: IEEE, 2010: 1692-1696. [20] 赖幸君, 唐鑫, 林磊, 等. 基于差分进化粒子群混合算法的多无人机协同区域搜索策略[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2024, 44(1): 89-97.LAI X J, TANG X, LIN L, et al. Multi-UAV collaborative area search strategy based on differential evolutionary particle swarm mixing algorithm[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2024, 44(1): 89-97. [21] SHANG W, XUE W, LI Y, et al. An improved underwater electric field-based target localization combining subspace scanning algorithm and meta-EP PSO algorithm[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2020, 8(4): 232. doi: 10.3390/jmse8040232 -




 下载:
下载: