Research Status and Development of Intelligent Optimization Methods for Mission Schemes
-
摘要: 针对任务环境愈发复杂, 任务节奏明显加快的问题, 传统的人工决策已无法满足需求, 亟需先进的辅助决策系统辅助决策者进行临机任务指挥, 为推动任务方案人工智能推荐方法的深入研究, 文章分析了近年来国内外该方向相关研究成果, 将智能推荐方法分为智能分析、智能匹配和智能学习三类, 详细阐述了各类方法的核心原理、技术路径及典型应用, 同时梳理分析了三类方法的优缺点, 明确了现有方法在动态适应性、自主决策能力、数据依赖以及可信度方面的不足, 最后展望了未来的发展方向, 为该领域后续研究提供了有价值参考。Abstract: The mission environment has become more and more complex, and the tempo has obviously accelerated. As a result, the traditional manual decision-making can no longer meet the requirements. There is a strong need for an advanced decision-making system to assist decision makers in carrying out on-the-spot mission command. To better carry out the research on artificial intelligent recommendation methods for mission schemes, this paper collated the research articles in this direction in China and abroad in recent years and divided the intelligent recommendation methods into three categories, namely intelligent analysis, intelligent matching, and intelligent learning. It elaborated on the core principles, technical paths, and typical applications of various methods and simultaneously analyzed the advantages and disadvantages of the three types of methods. It identified the deficiencies of the existing methods in terms of dynamic adaptability, autonomous decision-making ability, data dependence, and credibility. Finally, the future development direction was prospected, providing valuable references for subsequent research in this field.
-
Key words:
- artificial intelligence /
- decision-making aid /
- scheme recommendation
-
表 1 SVM方法对比
Table 1. Comparison of support vector machine methods
方法 优点 缺点 线性SVM 高维空间表现出色, 适用于高维特征数据; 对数据中的噪声和离群点具有一定的鲁棒性; 参数配置合适时能够产生较好泛化能力 处理非线性关系的数据时表现有限 非线性SVM 通过引入核函数, 可处理非线性关系, 模型灵活性强; 能够学习更为复杂的决策边界, 适用于各种复杂的分类问题 核函数的引入增加了模型复杂度, 可能导致过拟合, 训练和预测的计算开销相对较大, 特别是对于大规模数据集和复杂的核函数 多类别SVM 能够直接处理多类别分类问题, 不需要将问题转化为多个二分类问题, 对于大规模多类别问题, 支持向量机仍然可以有效地处理 针对多类别问题, 可能需要构建多个二分类器, 导致计算开销增加 SVM回归 能够处理非线性关系的回归问题, 通过调整核函数和超参数进行适应, 对于一些异常值具有一定的鲁棒性, 不会过度受到其影响 训练和预测的计算开销相对较大, 特别是对于大规模数据集和复杂的核函数; 需要仔细选择和调整正则化参数、核函数参数等超参数, 以获得最佳性能 表 2 智能模型优缺点对比
Table 2. Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of intelligent models
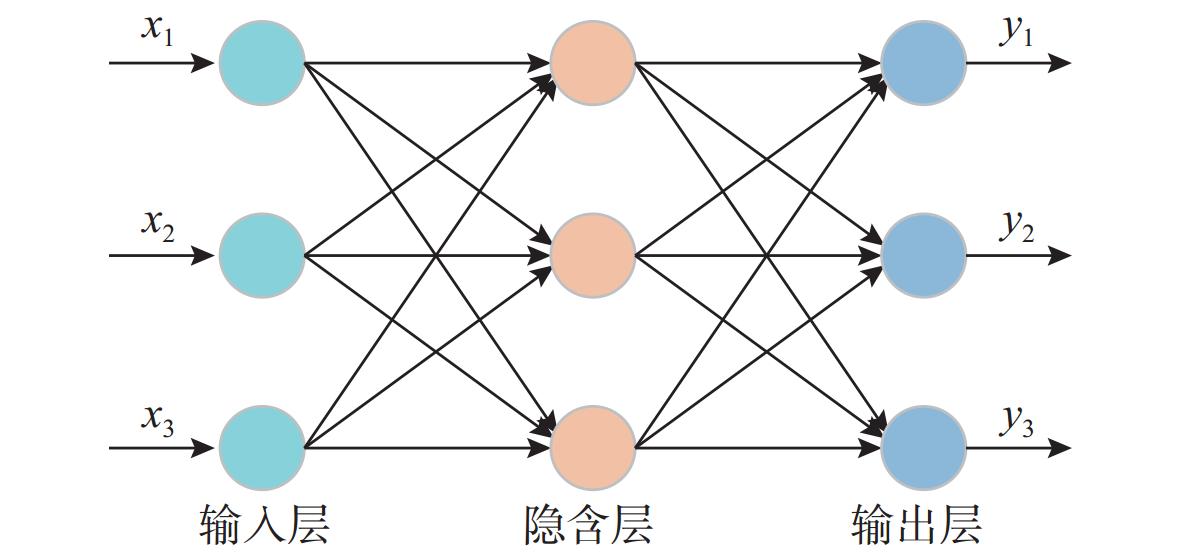
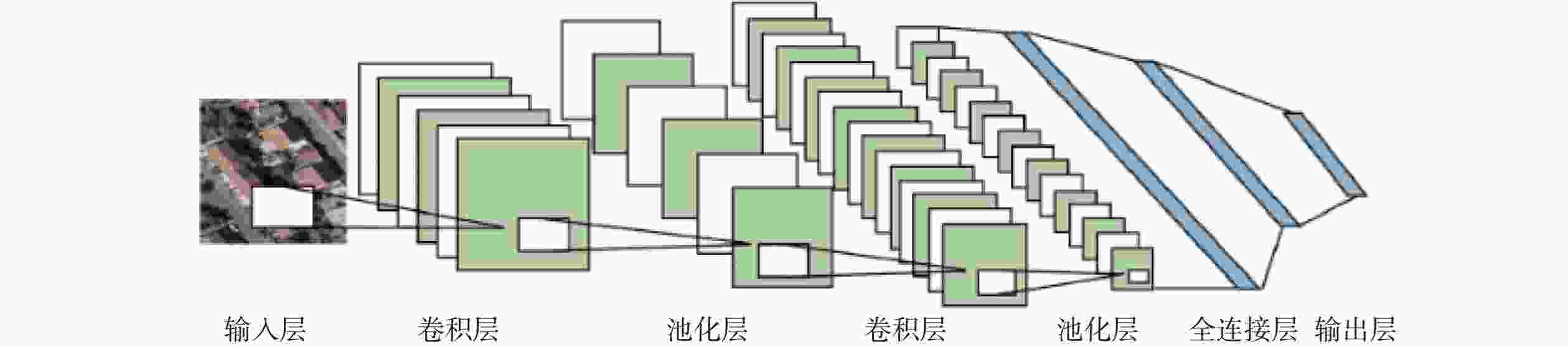
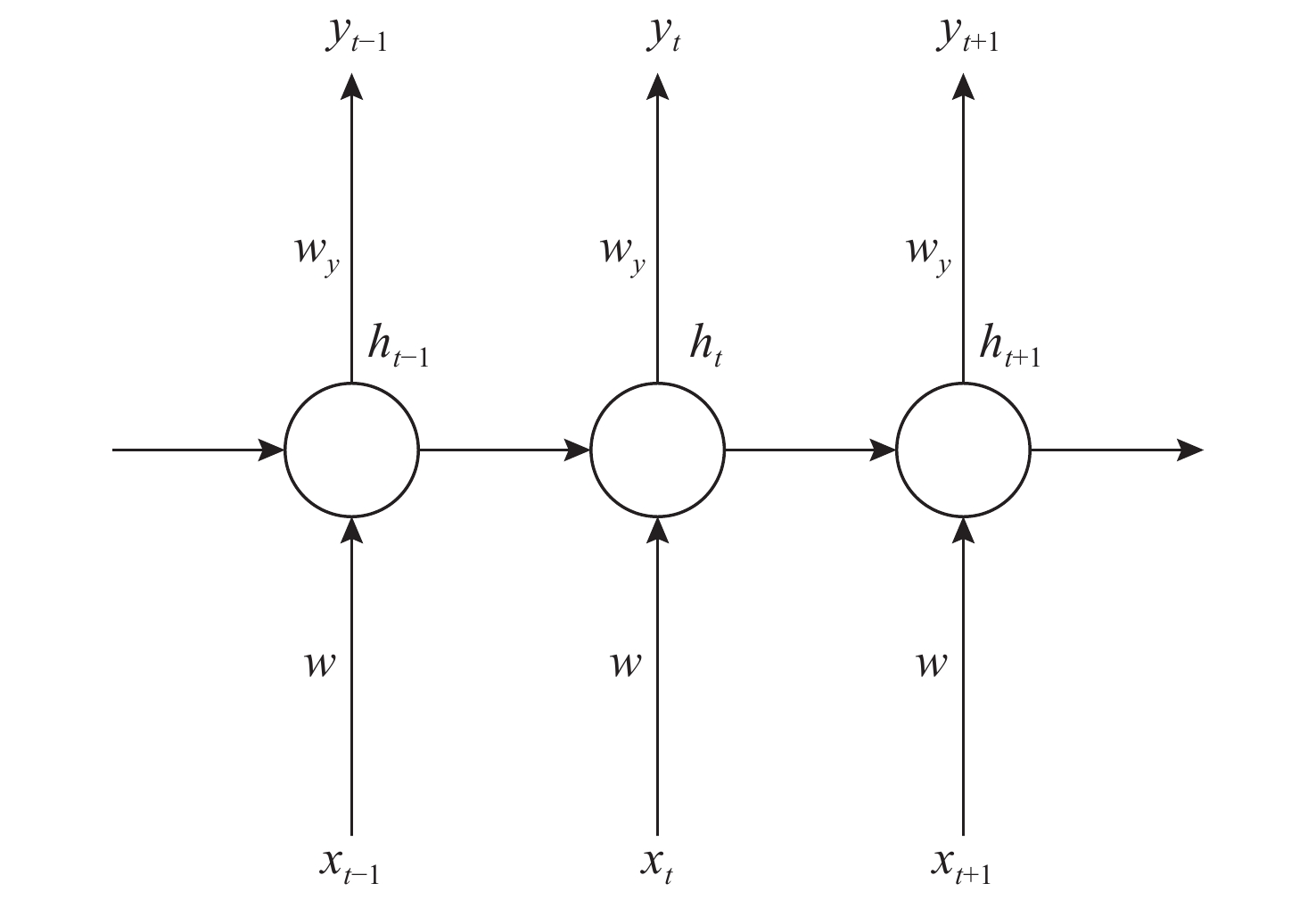
神经网络类型 优点 缺点 BPNN 具有良好的非线性映射和自学习能力; 具有一定泛化和容错能力 需根据应用场景设定网络结构, 收敛速度慢; 易陷入局部极小值点 CNN 模型参数量小, 计算复杂度低; 对图形变换具有一定不变性 易出现过拟合, 需正则化操作; 在高维数据下训练时间较长 RNN 可记忆上一时间的输入信息; 处理任意长度输入; 权重随时间共享 计算速度慢; 难以获取很久以前的信息; 会出现梯度消失和爆炸现象 表 3 不同大模型优缺点对比
Table 3. Comparison of Advantages and Disadvantages of Large Models
大模型 优点 缺点 GPT-4 具备强大的知识信息整合能力和高效的逻辑推理能力; 支持多模态数据处理, 基于海量案例库可提出非传统解决方案[61] 存在信息准确性风险; 对预训练数据依赖度高; API调用成本高与训练使用成本较高 Claude 3 超长文本处理能力优异; 准确性高与幻觉率低; 具有严格的事实核查机制[62] 多模态能力不足; 中文支持与本土化适配能力差; 保守性设计导致其创新性与灵活性受限 Deepseek r1 内置垂直领域结构化知识库; 专业性和合规性显著优于通用模型; 幻觉率低; 中文理解能力强; 推理高效且部署成本低[63] 多模态能力差, 仅支持文本输入; 多语言支持能力较差; 复杂逻辑推理能力局限, 在多跳推理(如“需求分析→技术选型→风险评估→应急预案”链式生成)中易出现步骤跳跃或因果倒置 文心ERNIE 4.0 中文场景深度适配; 支持多模态生成; 成本极低 复杂逻辑推理能力差; 动态数据整合能力不足; 无法接入实时API; 因合规限制, 创新性与开放性不足 表 4 决策方法对比
Table 4. Comparison of decision methods
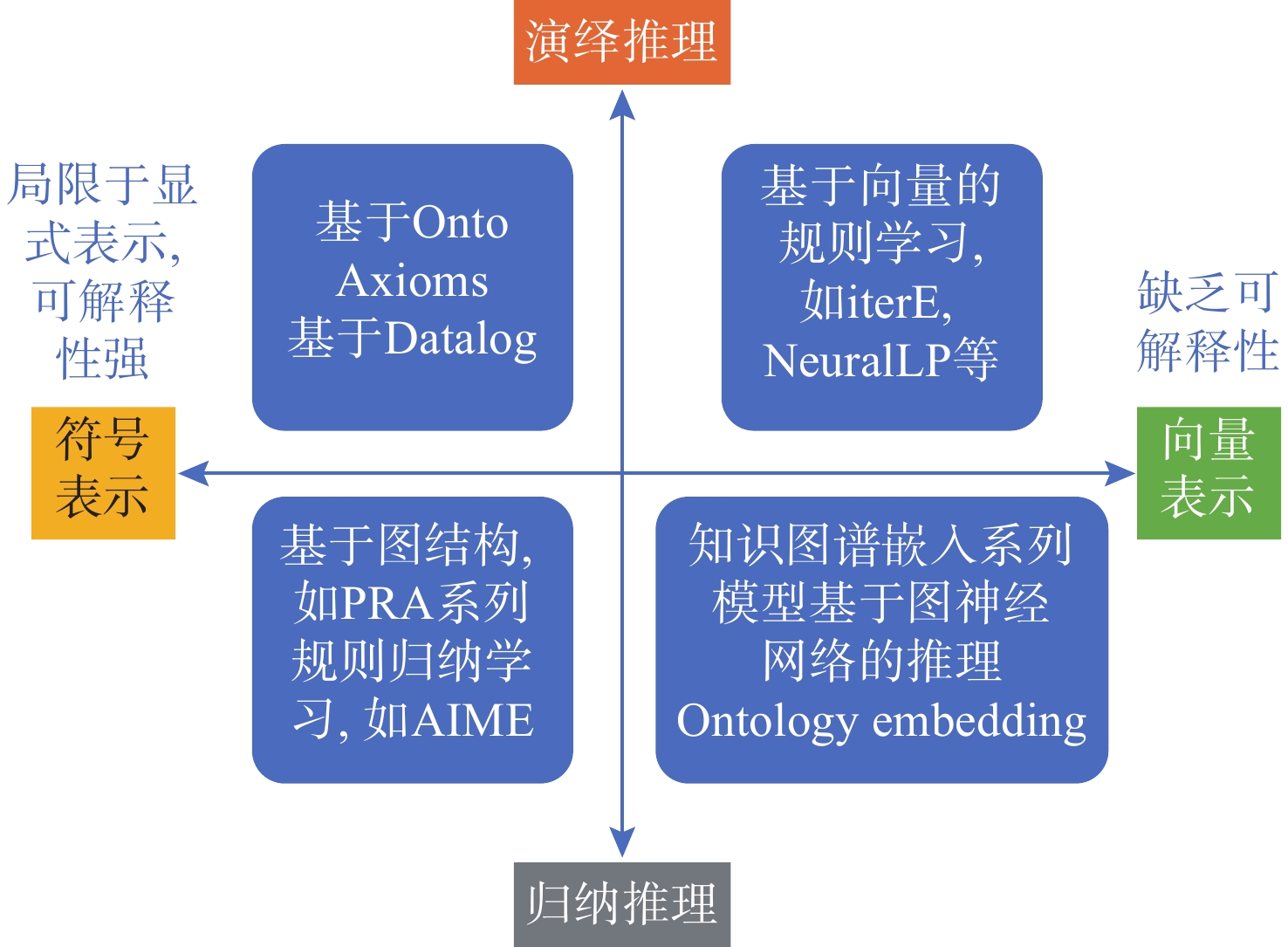
方法 优点 缺点 适用场景 人工决策 易实现, 灵活性与适应性强; 可结合决策者自身经验与直觉综合考量多种因素; 数学解析法可一定程度降低决策主观性 主观性强, 受情绪及心理影响大; 存在认知局限; 决策速度慢、效率低 数据匮乏场景、高风险、需严格遵循行业标准或法规的场景 智能分析方法 灵活性强, 可依据预设的算法和模型, 按照客观规律分析; 可通过数据挖掘等技术分析要素关联信息 需大量样本数据; 样本不足时性能受限 模式识别需求场景; 动态场景建模; 多维度决策支持场景 智能匹配方法 可根据场景需求精确匹配方案; 响应速度快 过度依赖资源库; 资源不足时存在局限; 缺乏主观性; 复杂环境适应性差 知识库依赖场景; 实时响应需求场景; 多目标约束优化场景 智能学习方法 灵活性强, 发展到一定程度可真实模拟人脑决策; 决策效率高; 可应对动态场景 训练资源依赖度高; 需要大量人力物力准备; 对载体要求高, 性能水平高度依赖算力 复杂非线性问题; 动态环境适应场景; 高维数据处理场景; 探索性场景 -
[1] 焦鹏博, 罗志浩, 范长俊, 等. 作战方案智能推荐方法综述[EB/OL]. [2025-1-12]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2422.TN.20241010.0913.002.JIAO P B, LUO Z H, FAN C J, et al. Review on intelligent recommendation methods for combat plans[EB/OL]. [2025-11-12]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2422.TN.20241010.0913.002. [2] 陈东林, 赵利佳, 赵岳, 等. 基于深度神经网络的作战方案辅助生成研究[C]//第十届中国指挥控制大会论文集(上册). 北京, 中国: 中国指挥与控制学会, 2022: 249-253. [3] GIN C R, SHEA D E, BRUNTON S L, et al. DeepGreen: Deep learning of Green’s functions for non-linear boundary value problems[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 21614. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00773-x [4] 李皓, 常国岑, 孙鹏, 等. 基于Agent的作战方案自动生成系统研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2009, 31(1): 134-136.LI H, CHANG G C, SUN P, et al. Research on agent-based automatic generation system for combat plans[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(1): 134-136. [5] 徐任杰, 宫琳, 朱明仁, 等. 不确定信息下考虑相关性与多样性的作战方案推荐方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(10): 3115-3123.XU R J, GONG L, ZHU M R, et al. A method for recommending combat plans considering correlation and diversity under uncertain information[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(10): 3115-3123. [6] ZHAO Y, DU K. A matching scheme from supply and demand sides of electronic health records based on blockchain[C]//2022 7th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing(ICSP). Xi’an, China: IEEE, 2022: 1089-1092. [7] QU Z T, HE P. Interactive intelligent analysis method: An application of criminal investigation[C]//2009 International Symposium on Intelligent Ubiquitous Computing and Education. Chengdu, China: IEEE, 2009: 152-155. [8] 谢炜, 黄建业, 程斌, 等. 基于大语言模型的知识图谱复杂逻辑推理方法[C]//第39次全国计算机安全学术交流会论文集. 西安, 中国: 中国计算机学会, 2024: 175-180. [9] HARB H, NADER D, SABEH K, et al. Real-time approach for decision making in IoT-based applications[C]//International Conference on Sensor Networks. On Line: HAL, 2022: 223-230. [10] 徐涛. 基于知识图谱的数据关联融合技术研究[J]. 软件, 2024, 45(10): 96-98.XU T. Research on data association and fusion technology based on knowledge graph[J]. Software, 2024, 45(10): 96-98. [11] 邱天搏, 张东, 李冠宇, 等. MSIM: 融合注意力机制的多阶段推理知识图谱问答模型[EB/OL]. [2024-11-29]. https://read.cnki.net/web/Journal/Article/JSGG20241127008.html. [12] 刘将. 基于深度学习的知识图谱关系推理算法优化及系统实现[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2023. [13] GENG D Q, DENG J. Knowledge graph embedding model based on multi-hop adaptive graph attention net-work[C]// 2024 36th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC). Xi’an, China: IEEE, 2024: 3086-3091. [14] 殷泽恒, 余敦辉, 邓怡辰, 等. 融合逻辑规则和推理路径嵌入的知识图谱推理[J]. 微电子学与计算机, 2025, 42(9): 134-144. doi: 10.19304/J.ISSN1000-7180.2024.0640YIN Z H, YU D H, DENG Y C, et al. Knowledge graph reasoning based on the integration of logical rules and embedding of inference paths[J]. Microelectronics and Computer, 2025, 42(9): 134-144. doi: 10.19304/J.ISSN1000-7180.2024.0640 [15] 吴冰涛. 基于扩展置信规则库的规则推理网络模型[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄铁道大学, 2024 [16] 宋晨烨, 贺筱媛, 郭圣明, 等. 基于时序知识图谱的智能任务推断方法[J]. 系统仿真技术, 2024, 20(3): 275-281, 306.SONG C Y, HE X Y, GUO S M, et al. Intelligent task inference method based on temporal knowledge graph[J]. System Simulation Technology, 2024, 20(3): 275-281, 306. [17] 胡诗, 毛杰. 海上编队协同作战规则推理技术研究[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2017, 37(5): 109-113.HU S, MAO J. Research on reasoning technology for rules of sea battle group’s cooperative operations[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2017, 37(5): 109-113. [18] SAID A M, MAROT M, BOUCETTA C, et al. Reinforcement learning vs rule-based dynamic movement strategies in UAV assisted networks[R]. Vehicular Communications, 2024, 48: 100788. [19] 胡诗. 作战方案全要素仿真推演技术研究[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2019, 39(12): 11-17.HU S. Research on full-element simulation and drift evaluation technology for combat plans[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2019, 39(12): 11-17. [20] YANG Z L, BONSALL S, WANG J. Fuzzy rule-based bayesian reasoning approach for prioritization of failures in FMEA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2008, 57(3): 517-528. doi: 10.1109/TR.2008.928208 [21] 周攀, 黄江涛, 章胜, 等. 基于深度强化学习的智能空战决策与仿真[J]. 航空学报, 2023, 44(4): 99-112.ZHOU P, HUANG J T, ZHANG S, et al. Intelligent air combat decision-making and simulation based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(4): 99-112. [22] 邱少明, 王雪珂, 杜秀丽, 等. 基于优化BP神经网络的气象环境下军事通信效能评估[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2022, 47(3): 89-96.QIU S M, WANG X K, DU X L, et al. Evaluation of military communication effectiveness under meteorological environments based on optimized BP neural network[J]. Firepower and Command and Control, 2022, 47(3): 89-96. [23] 陈强, 陈长兴, 陈婷, 等. 基于灰色层次分析法-BP神经网络的数据链系统效能评估[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2016, 36(3): 109-113, 116.CHEN Q, CHEN C X, CHEN T, et al. Data link system effectiveness evaluation based on grey analytic hierarchy process-BP neural network[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2016, 36(3): 109-113, 116. [24] 唐永果. 基于APSO-BP神经网络的末敏弹作战效能评估方法[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2024, 45(10): 100-106.TANG Y G. Evaluation method for the operational effectiveness of terminal munitions based on APSO-BP neural network[J]. Journal of Armament and Equipment Engineering, 2024, 45(10): 100-106. [25] 勾起跃, 邓满琪, 呼凯凯, 等. 基于灰色-粗糙集的雷达阵地工程建设风险评价指标体系构建[J]. 项目管理技术, 2024, 22(11): 102-107.GOU Q Y, DENG M Q, HU K K, et al. Construction risk evaluation index system for radar positioning facilities based on grey-rough set[J]. Project Management Technology, 2024, 22(11): 102-107. [26] 韩斌, 苏奎峰. 改进型RBF神经网络下目标威胁评估[J]. 价值工程, 2015, 34(6): 306-307. doi: 10.14018/j.cnki.cn13-1085/n.2015.06.170HAN B, SU K F. Target threat assessment based on improved RBF neural network[J]. Engineering Economics, 2015, 34(6): 306-307. doi: 10.14018/j.cnki.cn13-1085/n.2015.06.170 [27] 冯卉, 宋宝军, 邢清华, 等. 基于直觉模糊VIKOR决策的反导作战预案评估方法[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2022, 47(6): 17-21, 27.FENG H, SONG B J, XING Q H, et al. Evaluation method for anti-missile combat plans based on intuitionistic fuzzy VIKOR decision-making[J]. Firepower and Command and Control, 2022, 47(6): 17-21, 27. [28] 欧一鸣, 苏雍贺, 靳健, 等. 基于知识图谱的分布式光伏运维方案匹配方法[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2021(7): 1860-1870. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2021.07.002OU Y M, SU Y H, JIN J, et al. A method for matching distributed photovoltaic operation and mainte-nance schemes based on knowledge graph[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2021(7): 1860-1870. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2021.07.002 [29] DING C, LIU J, WANG D Y, et al. A knowledge graph-based muti-agent learning method for dynamic scheduling of flexible job shop[C]//2023 China Automation Congress(CAC). Chongqing, China: IEEE, 2023: 2832-2836. [30] MITRA D, GUPTA S. Plant disease identification and its solution using machine learning[C]//2022 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Engineering and Management(ICIEM). London, United Kingdom: IEEE, 2022: 152-157. [31] LIU Z J. Fully automated CFD simulation system research based on design scheme tree[EB/OL]. [2025-02-07]. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-83582-2 [32] STAVRAKOUDIS D G, THEOCHARIS J B. Employing effective feature selection in genetic fuzzy rule-based classification systems[C]//2010 4th International Workshop on Genetic and Evolutionary Fuzzy Systems(GEFS). Mieres, Spain: IEEE, 2010: 21-26. [33] 刘嘉, 黄馨漪, 和志成, 等. 基于统计规则匹配的防火墙优化方案设计[J]. 电子设计工程, 2019, 27(23): 135-138, 143. doi: 10.14022/j.issn1674-6236.2019.23.028LIU J, HUANG X Y, HE Z C, et al. Design of fire-wall optimization scheme based on statistical rule matching[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2019, 27(23): 135-138, 143. doi: 10.14022/j.issn1674-6236.2019.23.028 [34] ZHANG X, TAO X H, KONG P, et al. Automatic generation and optimization of power grid operation modes based on production simulation calculation results[C]// 2024 7th International Conference on Energy, Electrical and Power Engineering(CEEPE). Yangzhou, China: IEEE, 2024: 771-777. [35] 何占豪, 杨君刚. 基于事件图谱的作战指挥控制系统构建研究[C]//第十一届中国指挥控制大会论文集. 北京, 中国: 中国指挥与控制学会, 2023: 590-595. [36] 张子伟, 郭齐胜, 董志明, 等. 体系作战效能评估与优化方法综述[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2022, 34(2): 303-313. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.21-0225ZHANG Z W, GUO Q S, DONG Z M, et al. Review on evaluation and optimization methods for system combat effectiveness[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2022, 34(2): 303-313. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.21-0225 [37] 郭健, 王磊, 张常龙, 等. 基于仿真推演的航天侦察体系效能评估[J]. 信息工程大学学报, 2023, 24(3): 364-369.GUO J, WANG L, ZHANG C L, et al. Evaluation of the effectiveness of space reconnaissance system based on simulation analysis[J]. Journal of Information Engineering University, 2023, 24(3): 364-369. [38] 王兴众, 王敏, 罗威, 等. 基于SAC算法的作战仿真推演智能决策技术[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2021, 16(6): 99-108. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.02099WANG X Z, WANG M, LUO W, et al. Intelligent decision-making technology for combat simulation and scenario-based analysis based on SAC algorithm[J]. China Ship Research, 2021, 16(6): 99-108. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.02099 [39] 熊伟, 于小岚, 刘亚丽, 等. 基于贝叶斯网络的作战效能分析方法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2023, 23(17): 7428-7435.XIONG W, YU X L, LIU Y L, et al. Analysis method of combat effectiveness based on Bayesian network[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2023, 23(17): 7428-7435. [40] SIVAKUMAR P, JANSON P, RAJASEGARAN J, et al. FewShotNeRF: Meta-learning-based novel view synthesis for rapid scene-specific adaptation[EB/OL]. [2024-08-09]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2408.04803. [41] 张涛. 面向装备作战效能评估的多源数据融合方法研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2022 [42] 杨文卓. 基于改进鲸鱼算法优化的支持向量机分类器的研究与应用[D]. 武汉: 武汉轻工大学, 2024 [43] 汪迪. 基于改进布谷鸟算法优化支持向量机的轴承故障识别研究[D]. 大连: 大连交通大学, 2023 [44] CAI Y H, ZHOU Z Y, LI Z H. Optimization study of BP neural network based on genetic algorithm[C]//2023 IEEE International Conference on Electrical, Automation and Computer Engineering(ICEACE). Changchun, China: IEEE, 2023: 1555-1560. [45] 曹同宇, 乔栋, 郭子瑜, 等. 基于改进蜣螂优化算法优化BP神经网络[J]. 无线互联科技, 2024, 21(22): 109-114.CAO T Y, QIAO D, GUO Z Y, et al. Optimization of BP neural network based on improved antlion optimization algorithm[J]. Wireless Internet Technology, 2024, 21(22): 109-114. [46] PAULOSKI J G, ZHANG Z, HUANG L, et al. Convolutional neural network training with distributed K-FAC[EB/OL]. [2020-07-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.00784. [47] BARRIGA N A, STANESCU M, BESOAIN F. Improving RTS game AI by supervised policy learning, tactical search, and deep reinforcement learning[J]. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers(IEEE), 2019, 14(3): 8-18. [48] 张成苗. 基于强化学习的智能抗干扰决策方案[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2022. [49] 潘长鹏, 王中发, 王海涛, 等. 基于BP神经网络的舰载机对陆打击作战效能评估[J]. 兵工自动化, 2022, 41(12): 9-12.PAN C P, WANG Z F, WANG H T, et al. Evaluation of the combat effectiveness of carrier-based air-craft for ground attack based on BP neural network[J]. Automation of Military Industry, 2022, 41(12): 9-12. [50] BARRIGA N A, STANESCU M, BESOAIN F. Improving RTS game AI by supervised policy learning, tactical search, and deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 2019, 14(3): 8-18. doi: 10.1109/MCI.2019.2919363 [51] 丁沛灏. 基于深度学习的长时间序列预测方法研究与应用[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2024. [52] 孙志鹏. 基于网约车行程时间预测的多方式协同出行方案推荐及优化[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2021. [53] 张尧. 激活函数导向的RNN算法优化[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017. [54] 张尧, 沈海斌. 非饱和区扩展的RNN算法优化[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2018, 37(3): 41-43. doi: 10.13873/j.1000-9787(2018)03-0041-03ZHANG Y, SHEN H B. Optimization of RNN algorithm for non-saturated zone expansion[J]. Sensors and Microsystems, 2018, 37(3): 41-43. doi: 10.13873/j.1000-9787(2018)03-0041-03 [55] 袁琳娜, 杨良斌. 基于APSO的LSTM神经网络模型优化方法研究[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2024, 47(8): 103-111.YUAN L N, YANG L B. Research on optimization method of LSTM neural network model based on APSO[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2024, 47(8): 103-111. [56] 孙怡峰, 李智, 吴疆, 等. 作战方案驱动的可学习兵棋推演智能体研究[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2024, 36(7): 1525-1535. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.23-0477SUN Y F, LI Z, WU J, et al. Research on learning-based intelligent agents for war gaming driven by combat plans[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2024, 36(7): 1525-1535. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.23-0477 [57] COUSSEMENT K, ABEDIN M Z, KRAUS M, et al. Explainable AI for enhanced decision-making[J]. Decision Support Systems, 2024, 184: 114276. doi: 10.1016/j.dss.2024.114276 [58] JIN W Q, DU H Y, ZHAO B. A comprehensive survey on multi-agent cooperative decision-making: Scenarios, approaches, challenges and perspectives[EB/OL]. [2025-03-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.13415. [59] YU C Y, MAO Z Y, WU Y L, et al. BA-GPT: Battlefield awareness interactive Q&A system based on RAG[C]// Proceedings of 4th 2024 International Conference on Autonomous Unmanned Systems(4th ICAUS 2024). Hangzhou, China: Chinese Academy of Engineering, 2024. [60] PAMUNGKAS R F, UTAMA I B K Y, HINDRIYANDHITO K, et al. A hybrid approach of Con-vLSTMBNN-DT and GPT-4 for real-time anomaly detection decision support in edge-cloud[J]. ICT Express, 2024, 10(5): 1026-1033. doi: 10.1016/j.icte.2024.07.007 [61] WU H Y, LI S Y, WU D R. TMMM: Transformer in multimodal sentiment analysis under missing modalities[C]// 2024 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Yokohama, Japan: IEEE, 2024: 1-8. [62] HU M. Planning with a model: AlphaZero[M]. Berkeley, CA, USA: Springer Nature, 2023: 245-280. [63] GOECKS V G, WAYTOWICH N. COA-GPT: Generative pre-trained transformers for accelerated course of action development in military operations[C]//2024 International Conference on Military Communication and Information Systems(ICMCIS). Koblenz, Germany: IEEE, 2024. -




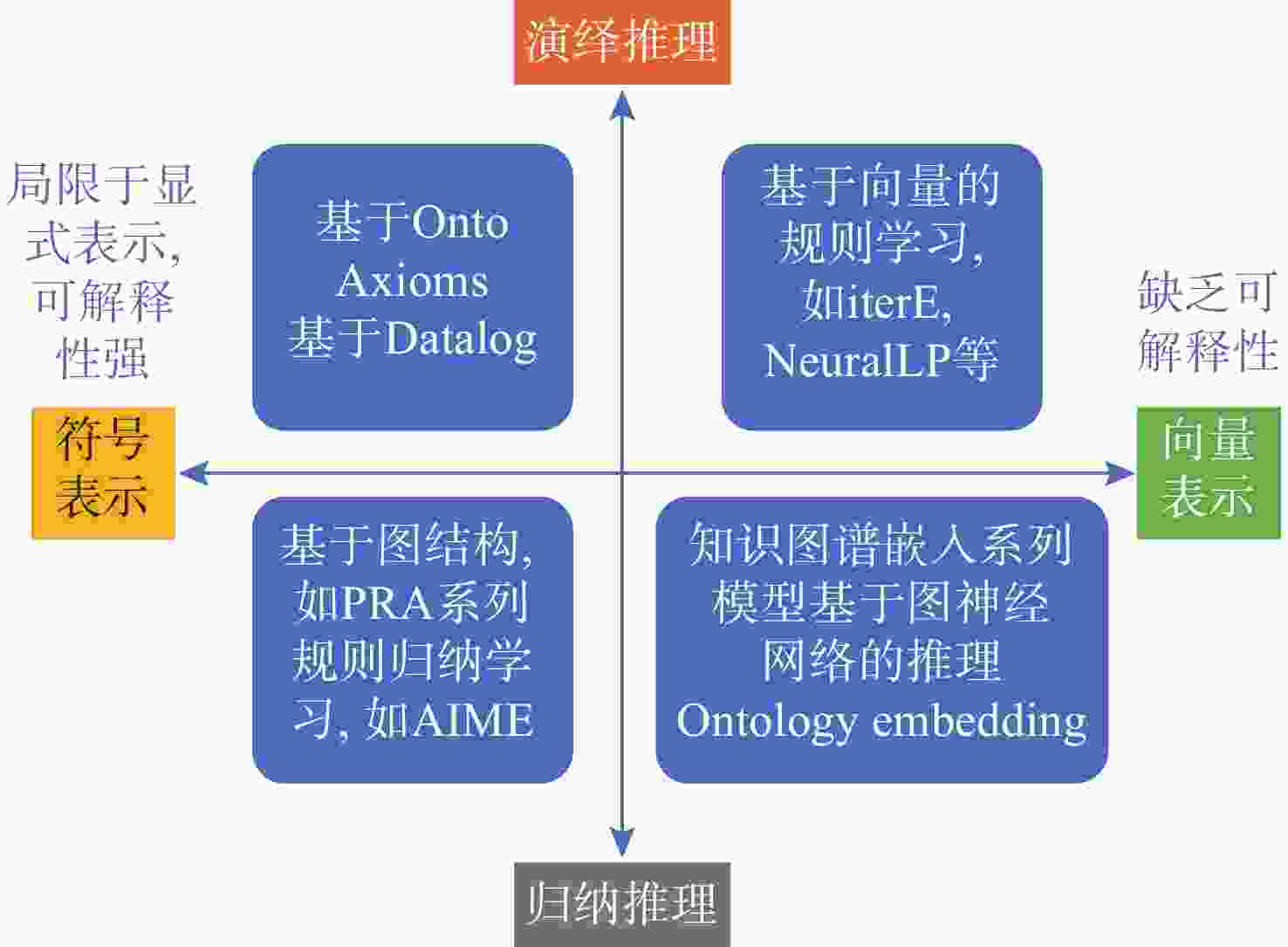
 下载:
下载: