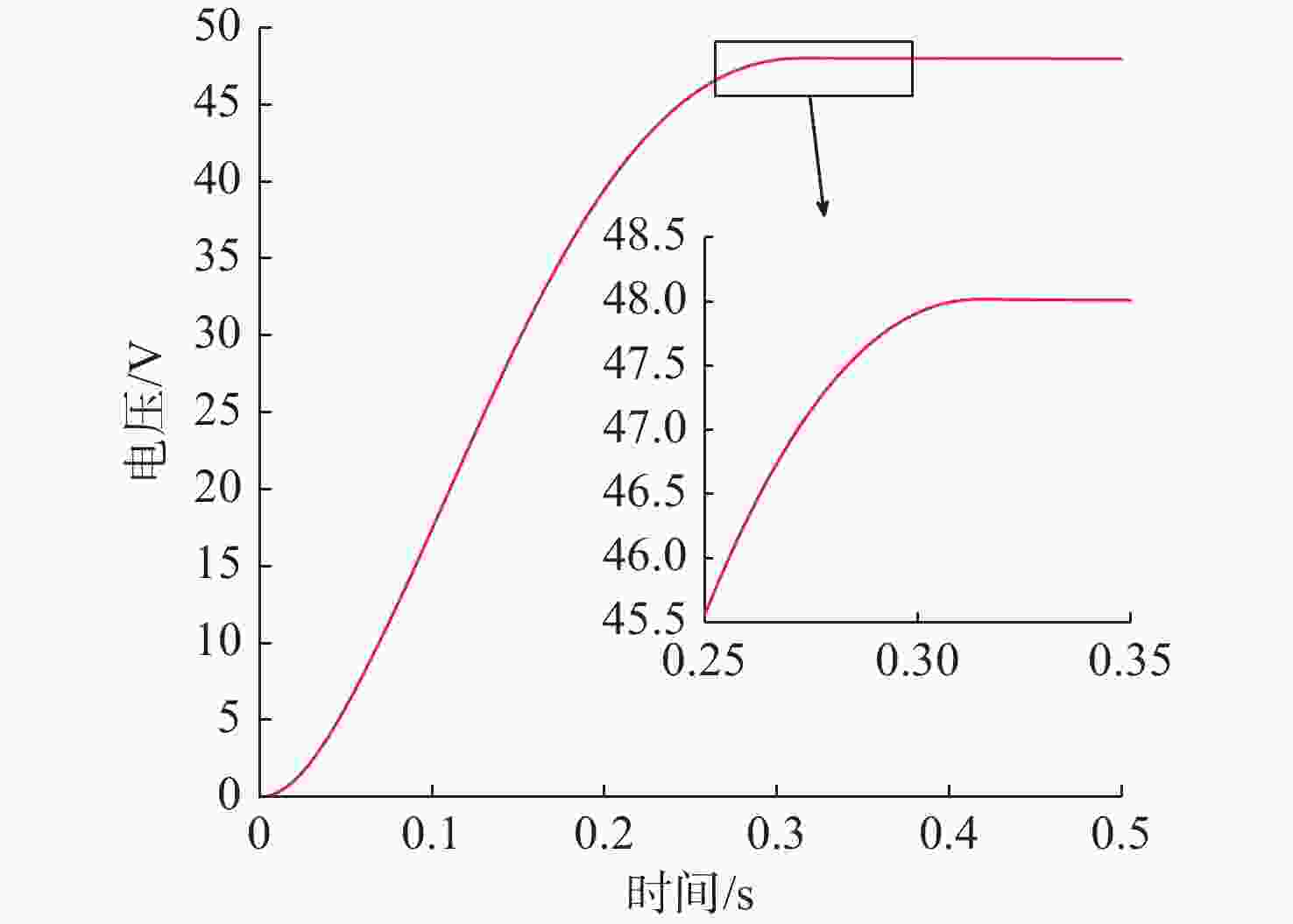
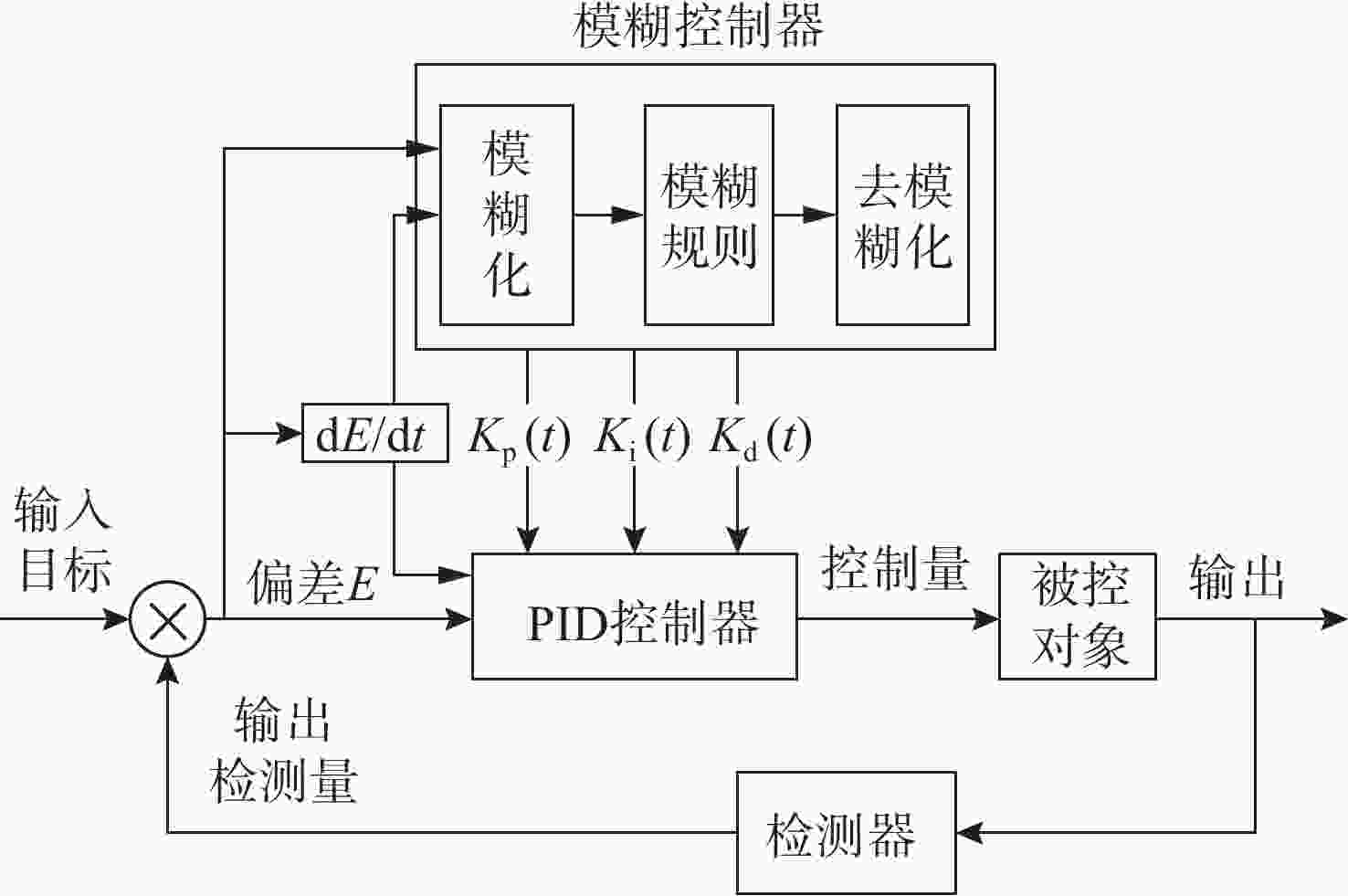
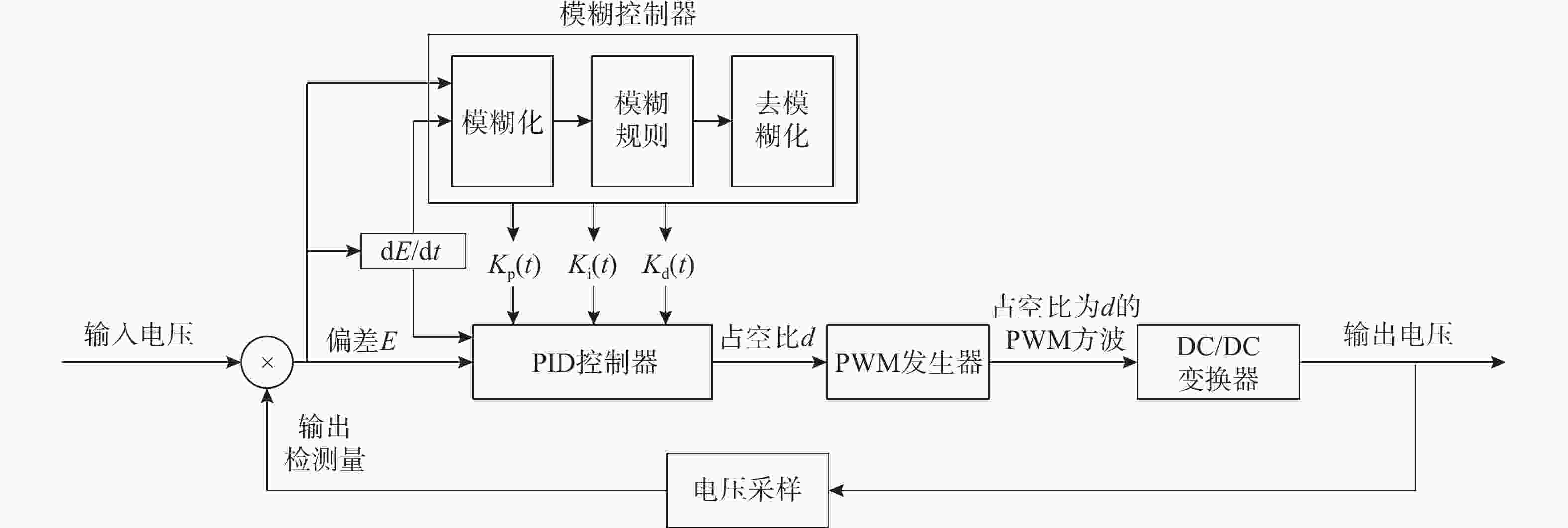
Simulation of PEMFC Voltage Stabilization System for Underwater Unmanned Power Platform Based on Fuzzy Control
-
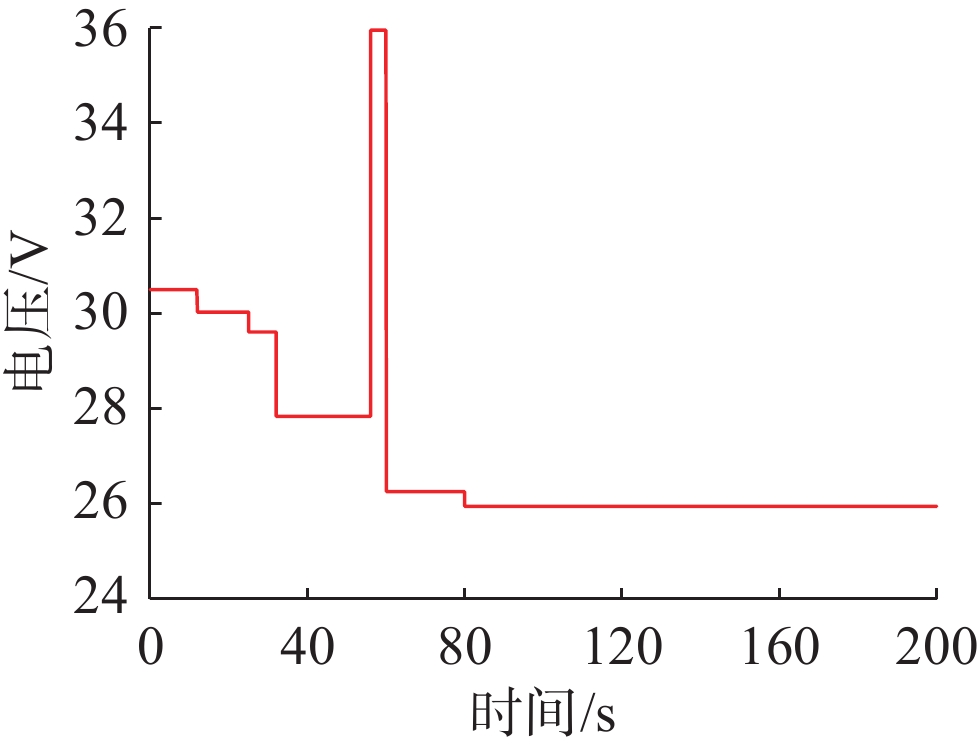
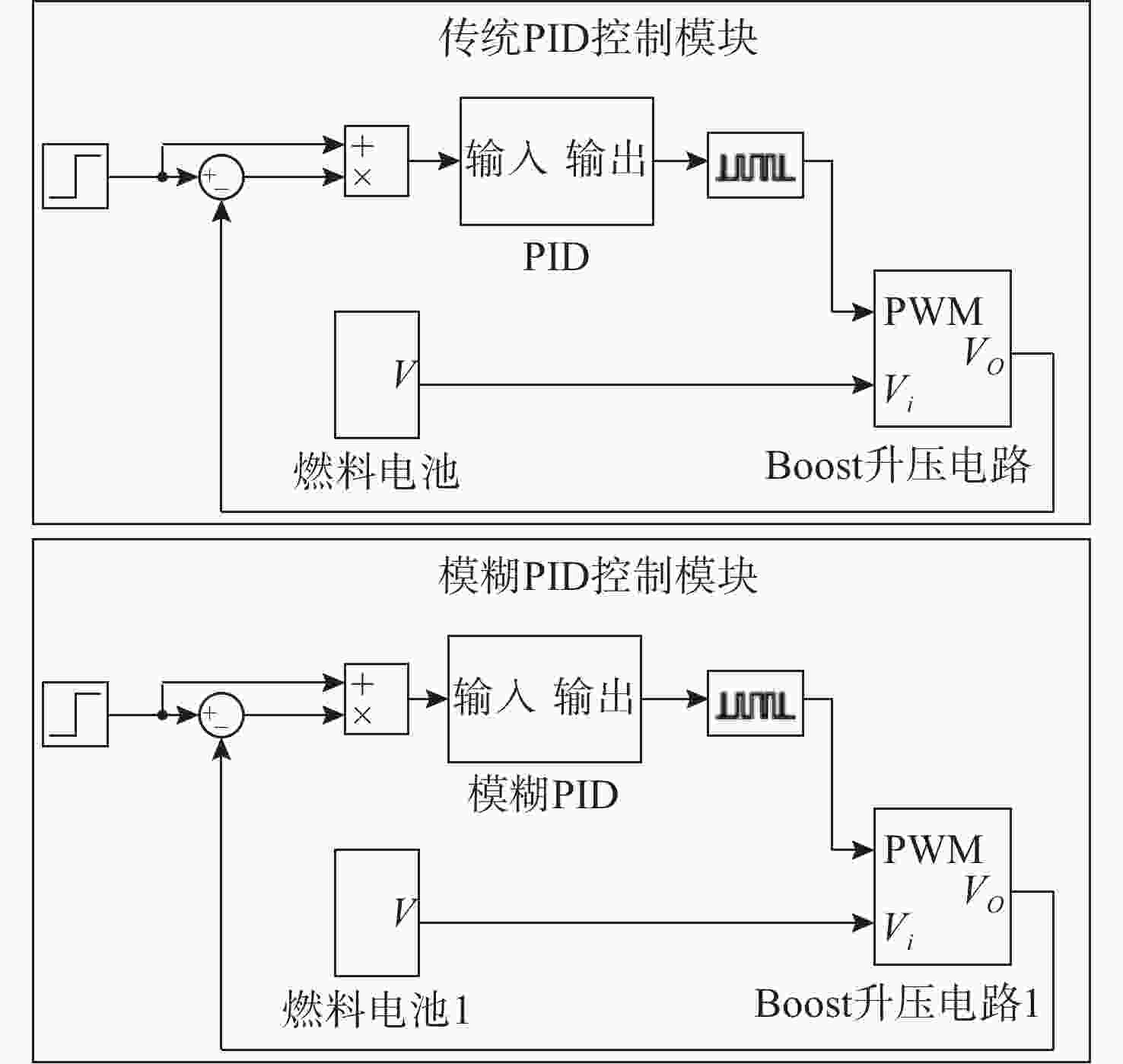
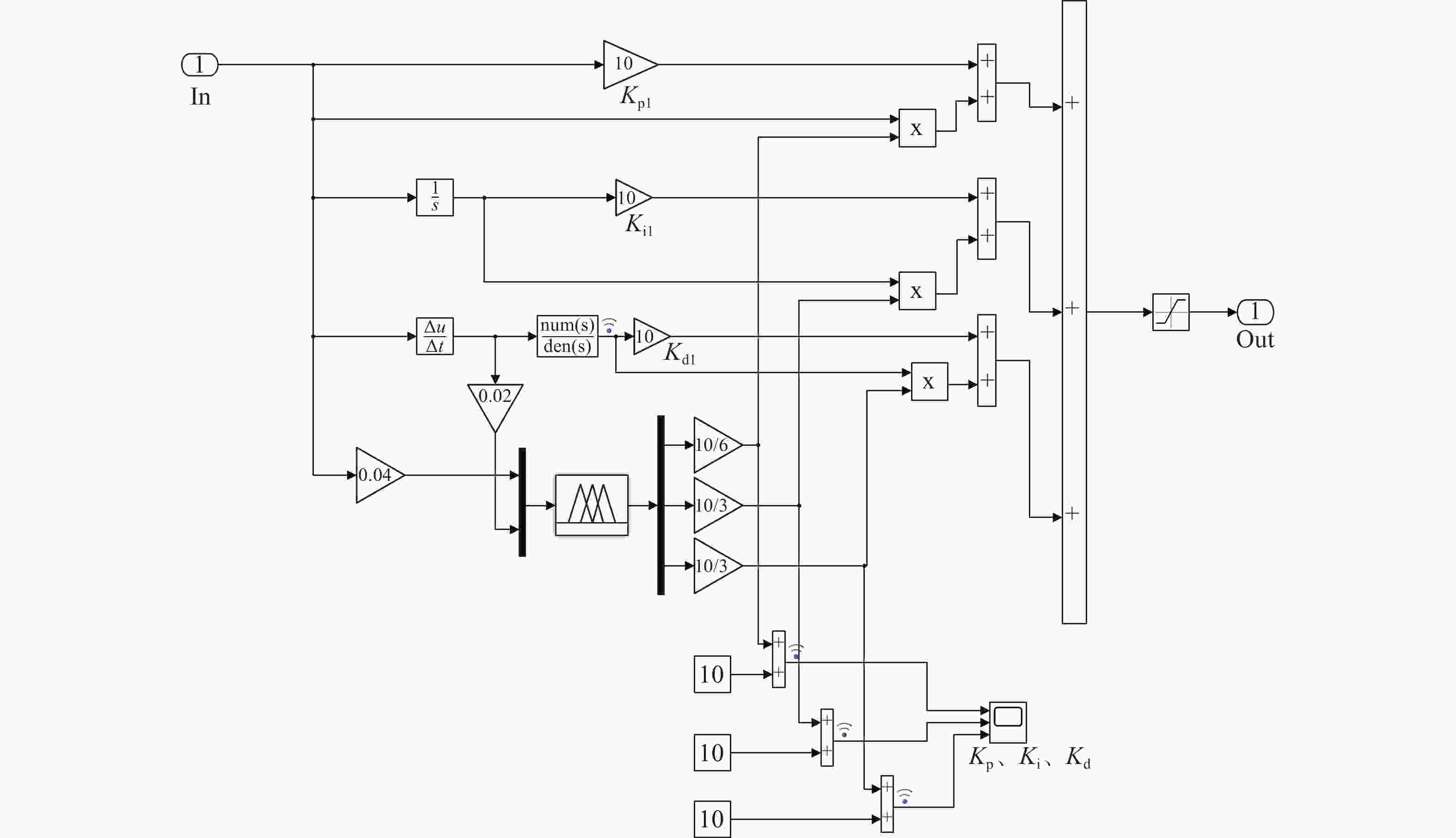
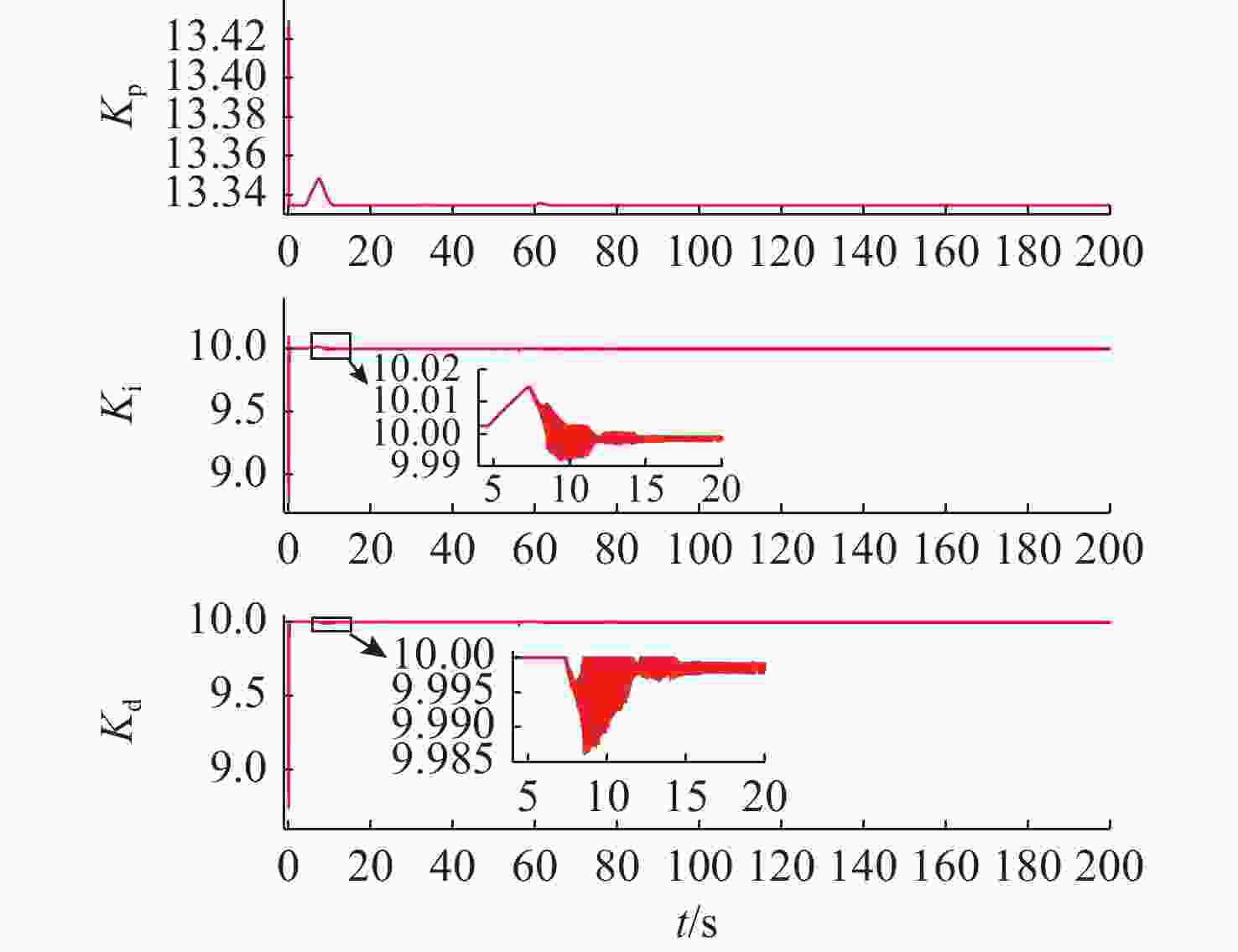
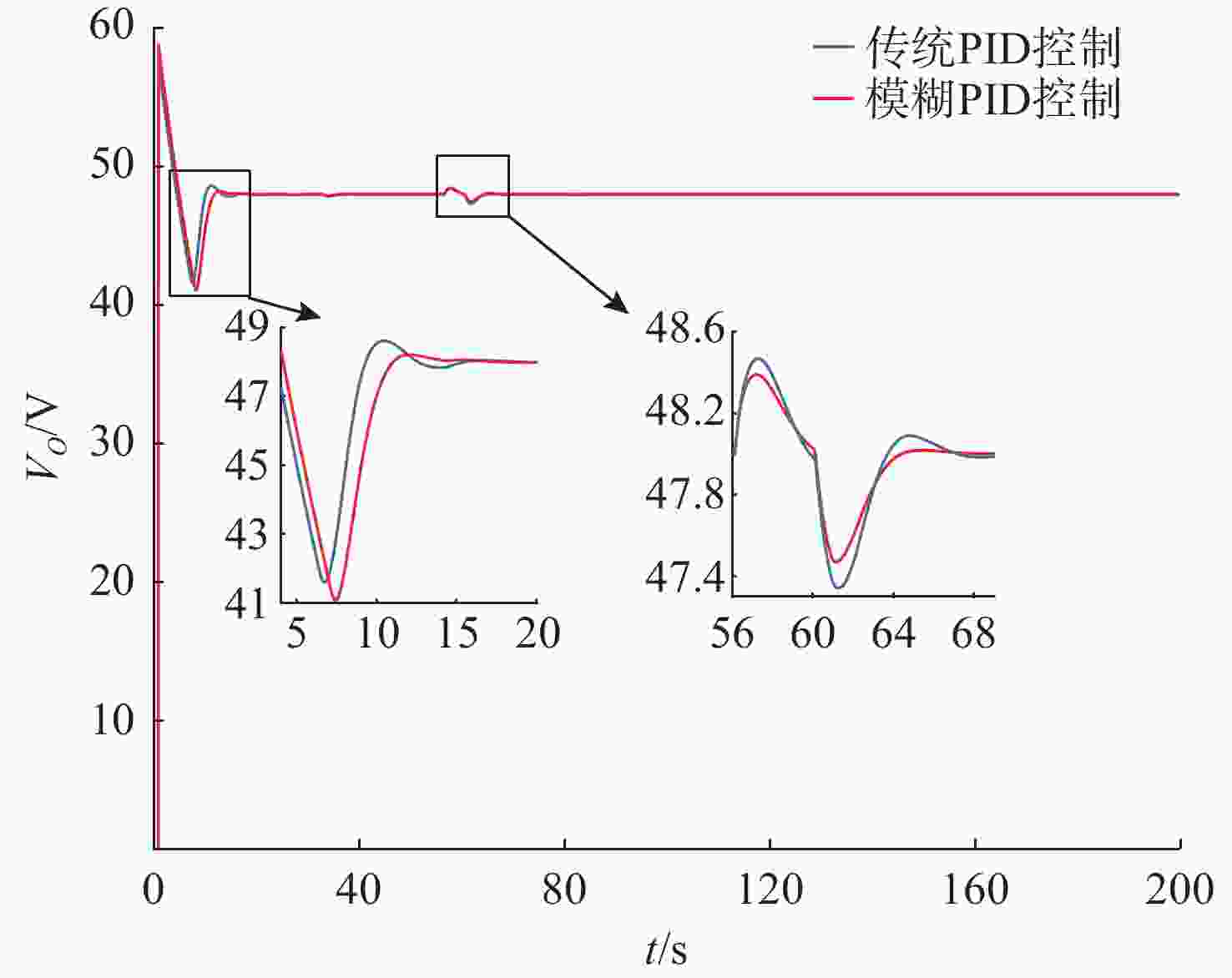
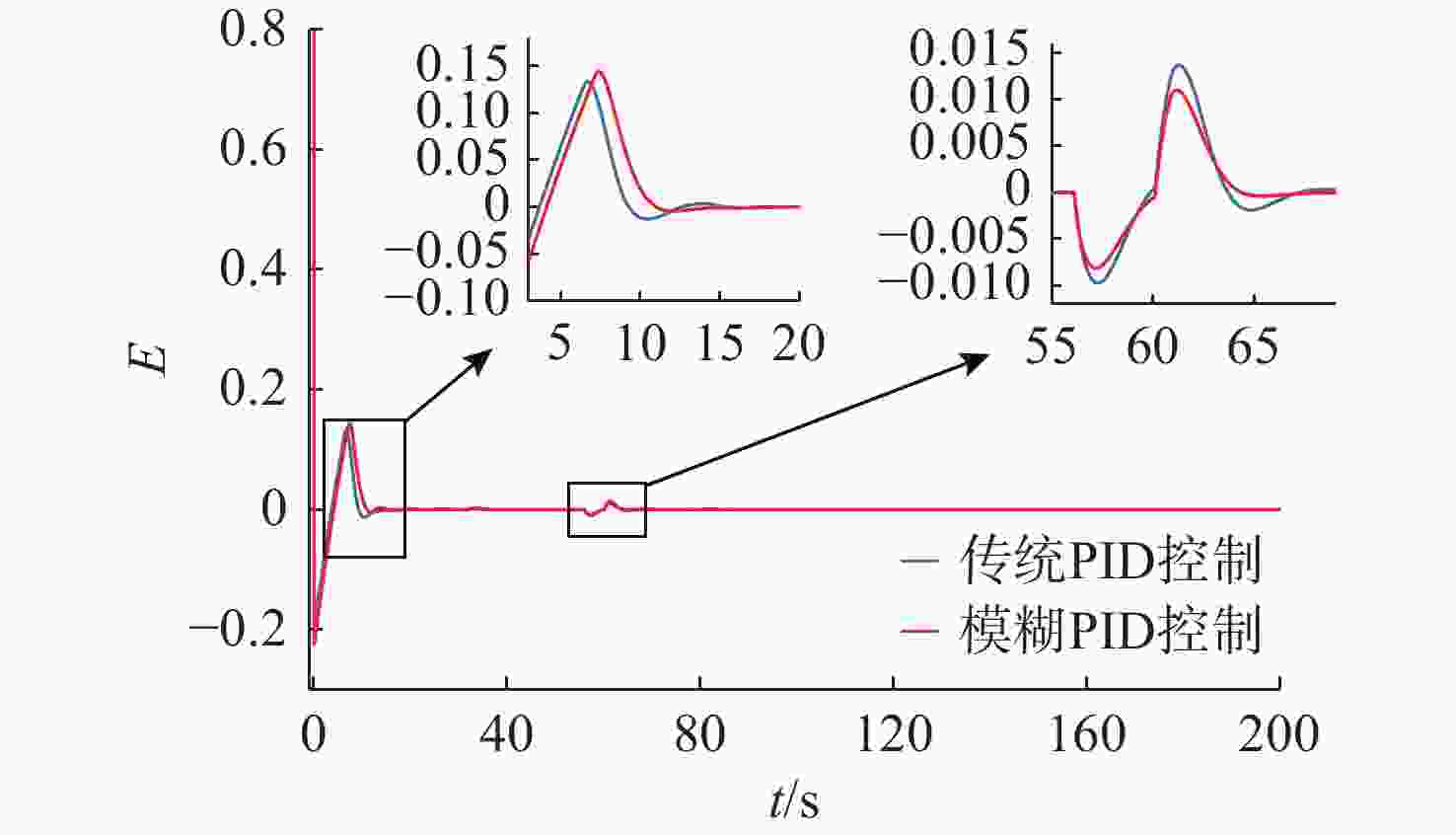
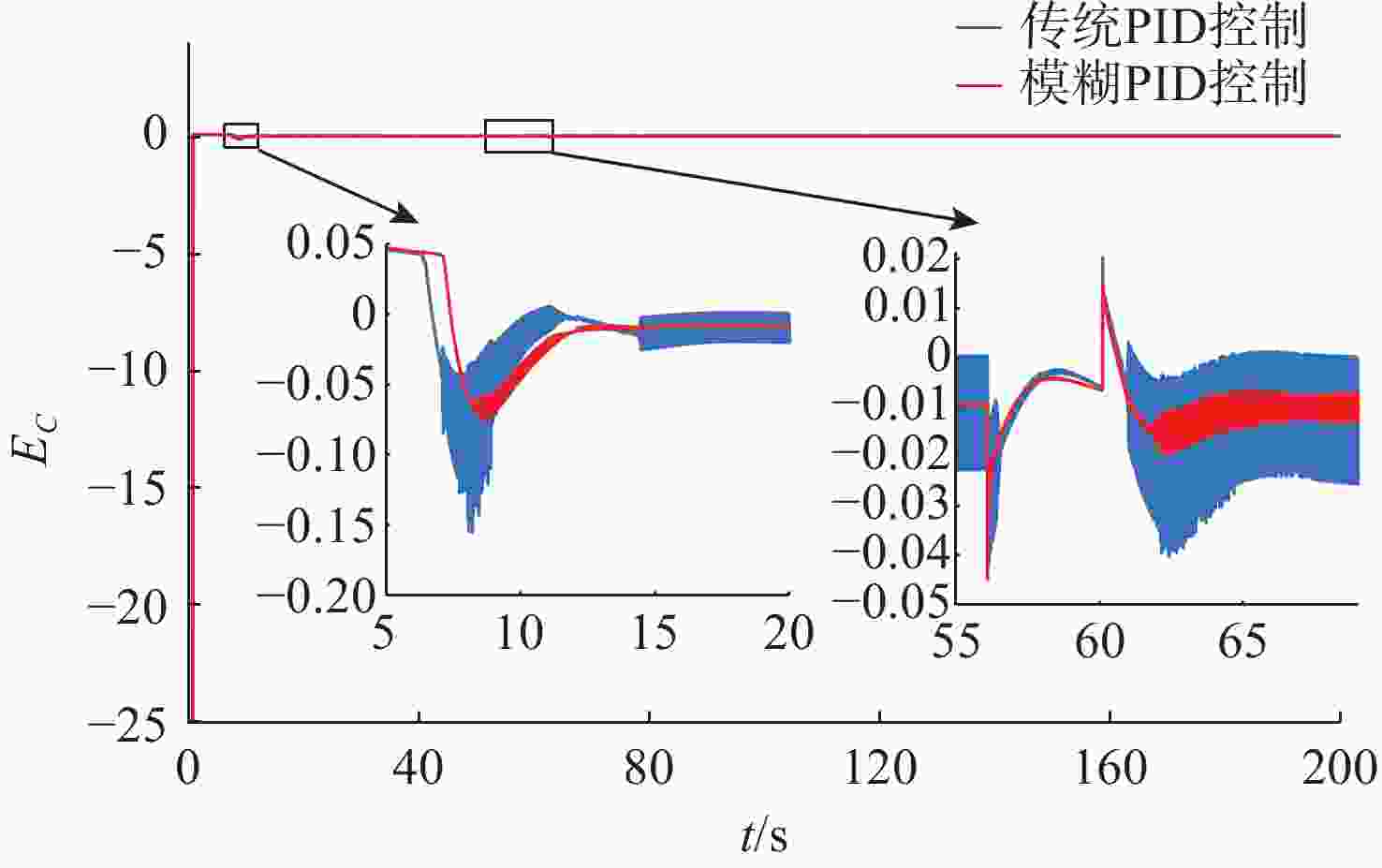
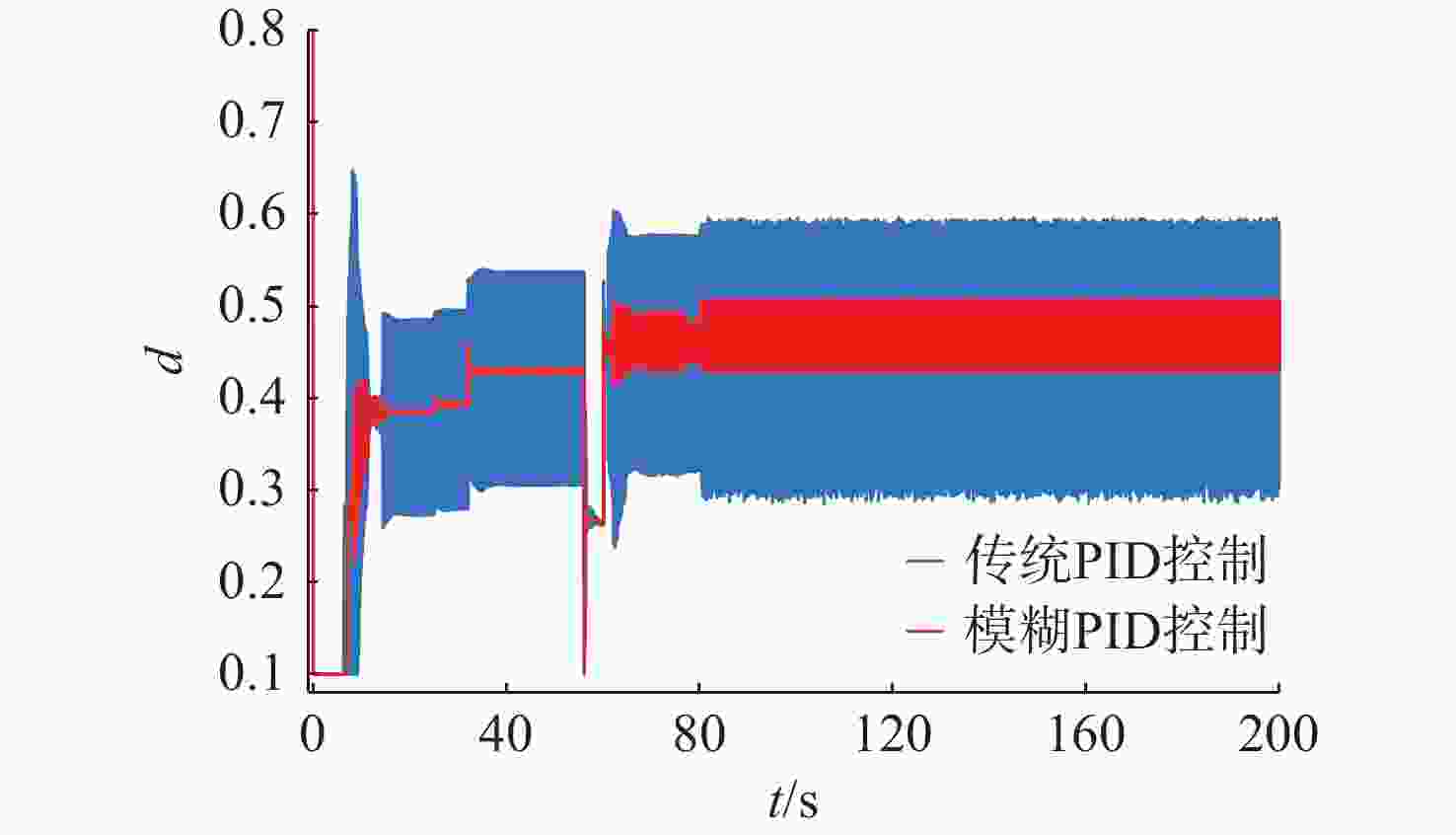
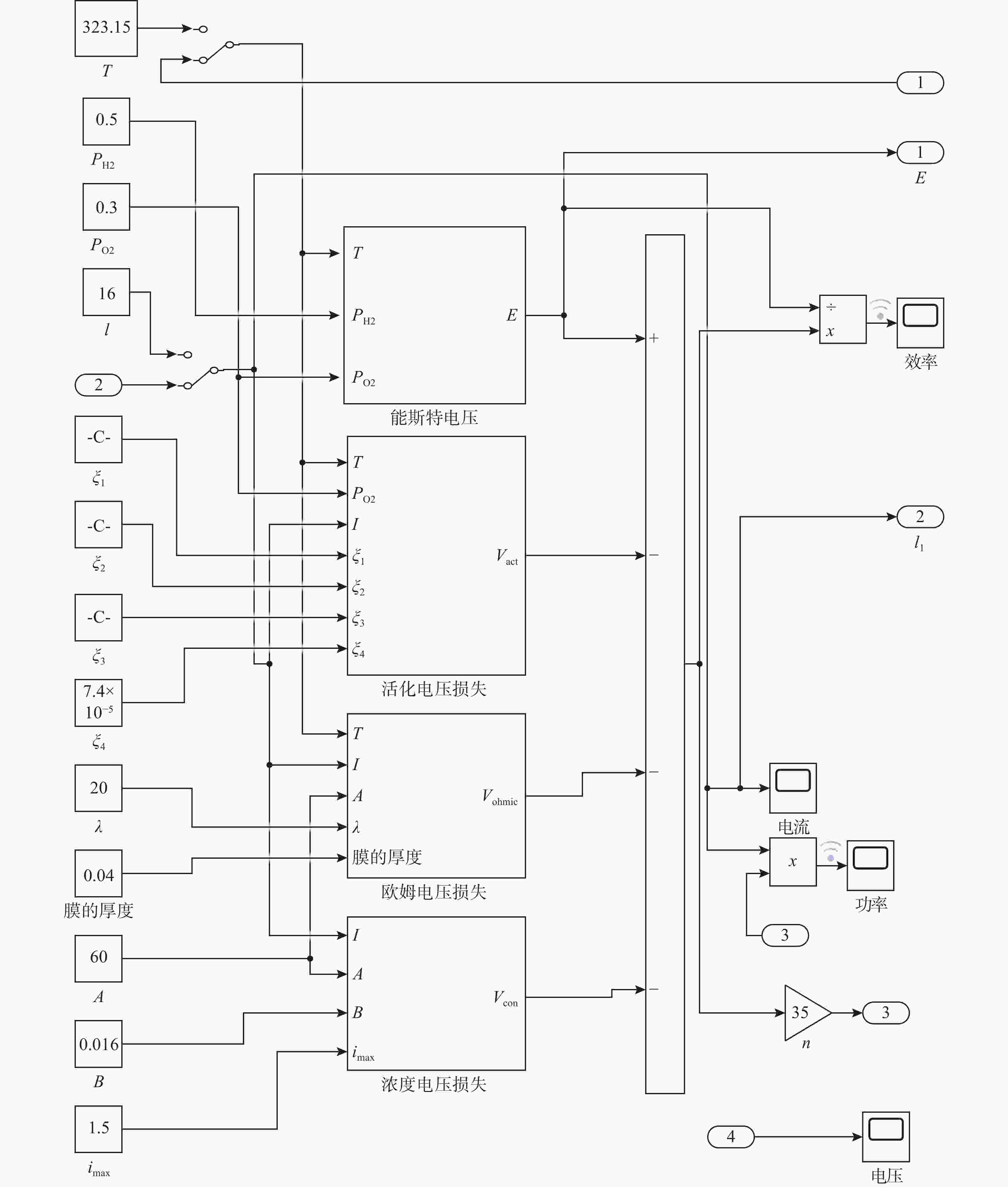
摘要: 针对水下无人动力平台对高效、稳定能源系统的需求, 文中聚焦质子交换膜燃料电池(PEMFC)输出电压强非线性、易波动的难题, 提出一种基于模糊比例-积分-微分(PID)自适应控制的DC-DC变换器稳压策略。PEMFC输出电压因强非线性特性且易波动, 传统控制方法在动态响应与鲁棒性方面存在局限。为此, 建立了含能斯特电压及活化、欧姆、浓差损失的PEMFC数学模型, 以及Boost升压电路模型, 剖析其电压波动机理; 设计了一种模糊PID控制器, 其规则库深度耦合PID控制原理与PEMFC非线性特性, 实现了PID参数的在线动态自整定, 从而实时优化DC-DC变换器占空比。仿真结果表明: 相较于传统PID控制, 模糊PID控制可缩短系统调节时间, 使稳态误差趋近于零, 在电流突变工况下输出电压波动范围缩小至±0.5 V以内, 且占空比响应更精准。该模糊PID自适应策略显著增强了系统的动态响应速度与鲁棒性, 为水下无人平台能源系统的高效、稳定运行提供了可靠的理论支撑与解决方案。Abstract: Aiming at the demand of underwater unmanned power platform for an efficient and stable energy system, this paper focused on the problem of strong nonlinearity and easy fluctuation of the output voltage of proton exchange membrane fuel cell(PEMFC) and proposed a DC-DC converter voltage stabilization strategy based on the fuzzy proportional-integral-derivative(PID) adaptive control. Due to the strong nonlinear characteristics of the output voltage of the PEMFC and its fluctuation trend, the traditional control methods have limitations in the dynamic response and robustness. Therefore, a mathematical model of PEMFC, including Nernst voltage and activation, ohmic, and concentration loss and a Boost boost circuit model were established to analyze the voltage fluctuation mechanism. A fuzzy PID controller was designed, with a rule base that deeply coupled the PID control principle with the nonlinear characteristics of PEMFC, which realized the online dynamic self-tuning of PID parameters to optimize the duty cycle of the DC-DC converter in real time. The simulation results show that compared with the traditional PID control, the fuzzy PID control can shorten the system regulation time, and the steady-state error tends to be close to zero; the output voltage fluctuation range is narrowed to within ±0.5 V under the sudden current change condition, and the duty cycle response is more accurate. The fuzzy PID adaptive strategy significantly enhances the dynamic response speed and robustness of the system, providing a reliable theoretical cornerstone and solution for the efficient and stable operation of the energy system of the underwater unmanned platform.
-
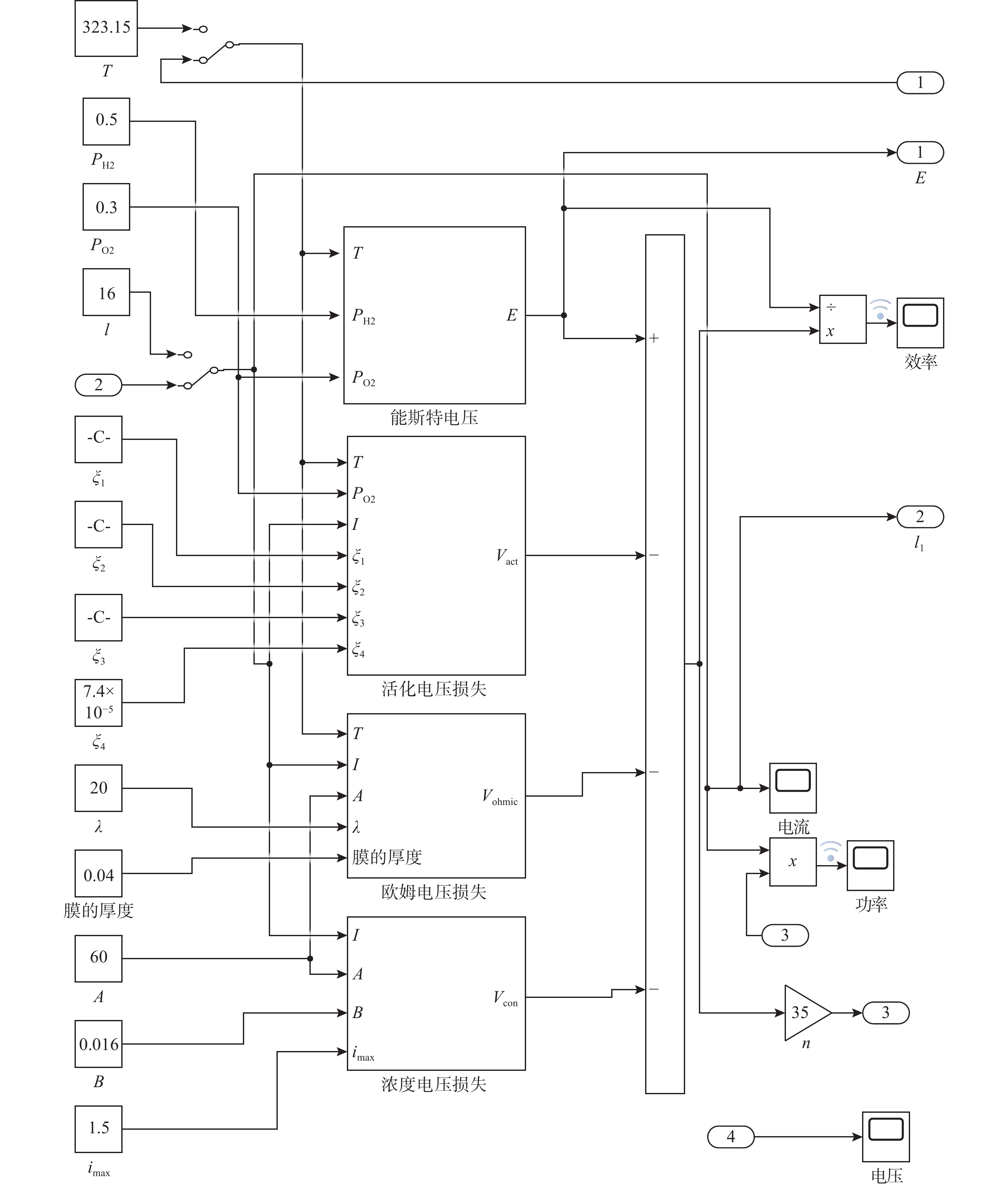
表 1 PEMFC主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of PEMFC
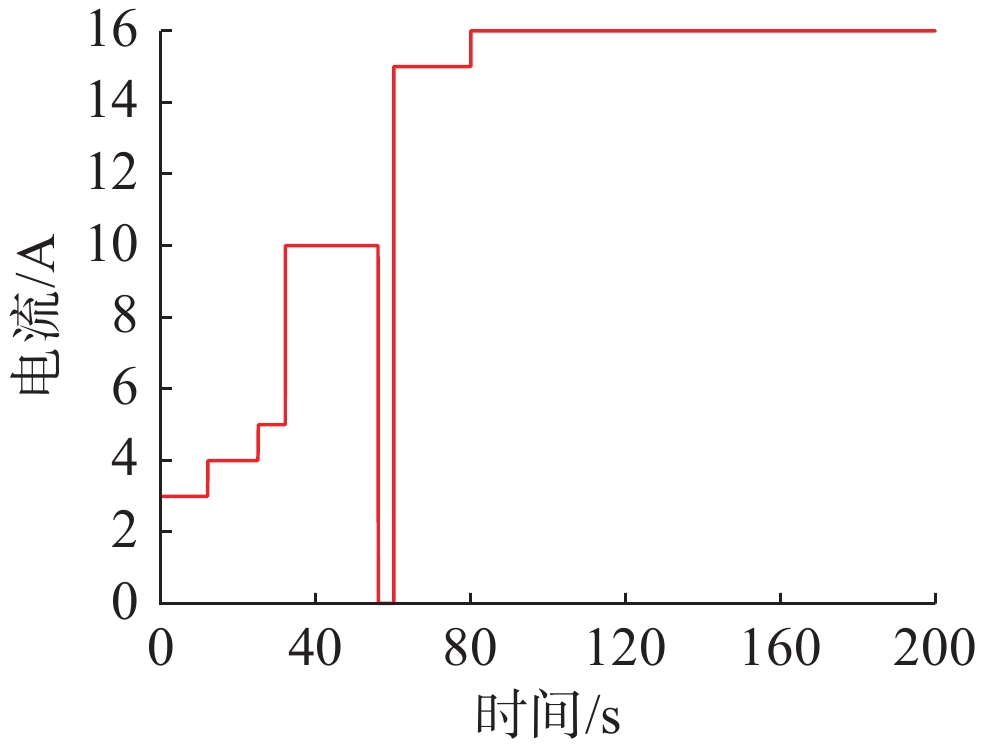
参数 值 参数 值 n/个 35 l/cm 0.04 T/K 323 A/cm2 60 PH2/atm 0.5 λ 20 PO2/atm 0.3 B 0.016 I/A 16 imax/ (A/cm2) 1.5 尺寸/mm3 104×67×120 Cst/[kJ/(kg·K)] 0.71 Mst/kg 1.08 理想工作温度/K 318.15~327.15 注: Mst为PEMFC的质量; Cst为PEMFC的比热容。 表 2 输入电流数据
Table 2. Input current data
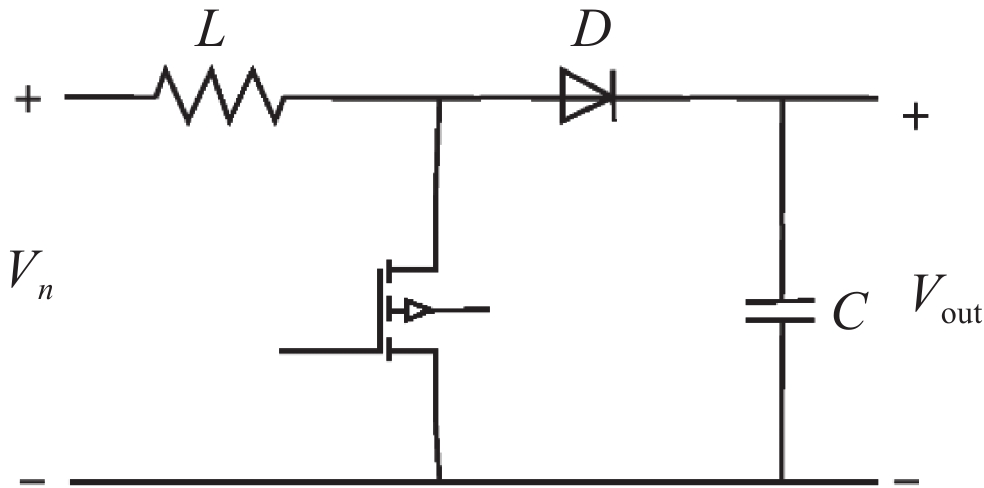
时间/s 电流/A 时间/s 电流/A 0 3 56 0 12 4 60 15 25 5 80 16 32 10 200 16 表 3 Boost升压电路参数
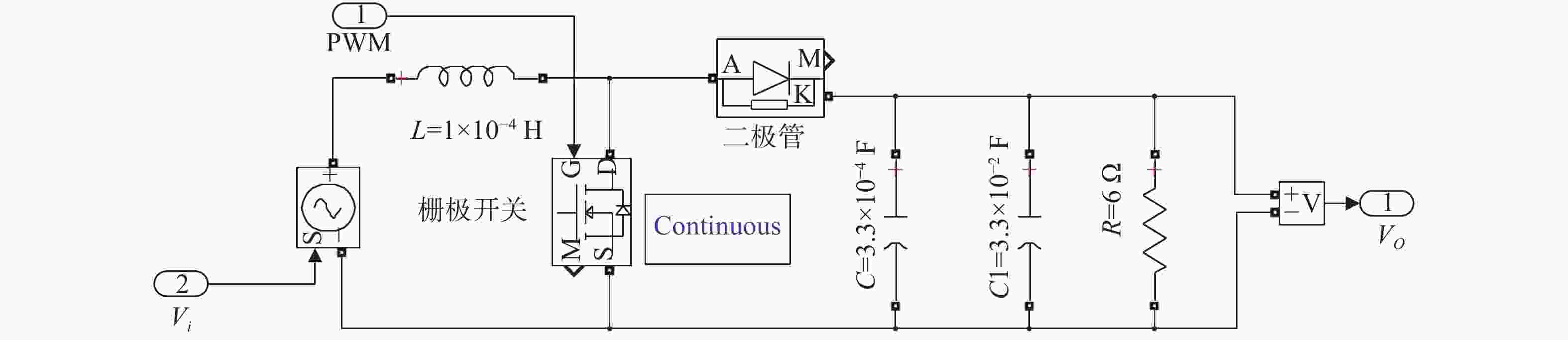
Table 3. Parameters of Boost converter
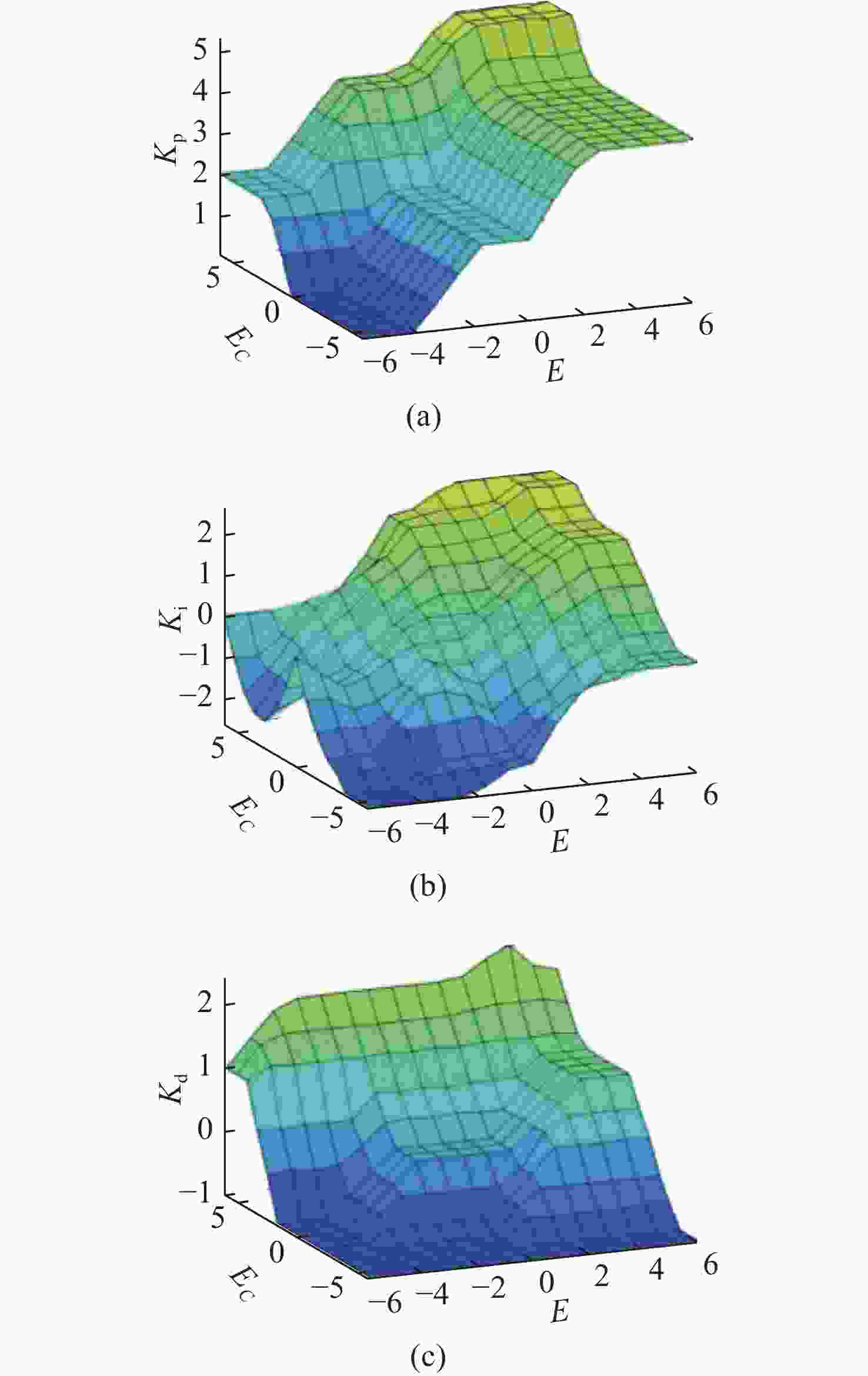
参数 值 参数 值 η 1(仿真时) d 0.46 P/W 416 L/μH 100 Fs/Hz 25 000 C/μF 330 表 4 Kp模糊规则表
Table 4. Table of fuzzy rule for Kp
E EC NB NM NS Z PS PM PB NB Z Z Z Z PS PS PS NM Z Z Z Z PS PS PS NS PS PS PS PS PS PM PM Z PS PS PS PS PS PM PM PS PM PM PM PM PM PB PB PM PM PM PM PM PM PB PB PB PM PM PM PM PM PB PB 表 5 Ki模糊规则表
Table 5. Table of fuzzy rules for Ki
E EC NB NM NS Z PS PM PB NB NB NB NM Z NM NM Z NM NB NB NM NS NS Z Z NS NB NM Z Z Z PS Z Z NM NM NS Z PS PM PM PS Z NS Z PS PS PM PB PM Z Z PS PM PM PB PB PB Z Z PS PM PM PB PB 表 6 Kd模糊规则表
Table 6. Table of fuzzy rules for Kd
E EC NB NM NS Z PS PM PB NB NS NS NS NS NS PS PS NM NS NS NS NS NS PS PM NS NS NS NS Z Z PS PM Z NS NS NS Z Z PS PM PS NS NS Z Z Z PS PM PM NS NS Z PS PS PS PB PB NS NS Z PS PS PS PM -
[1] 张庚, 刘国金. 质子交换膜燃料电池输出电压稳定控制技术[J]. 电源学报, 2022, 20(1): 134-140. [2] MADHESWARAN K D, THANGAMUTHU M, GNANASEKARAN S, et al. Powering the future: Progress and hurdles in developing proton exchange membrane fuel cell components to achieve department of energy goals—A systematic review[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(22): 15923. [3] 戚志东, 裴进, 胡迪. 基于分数阶 PID 控制的质子交换膜燃料电池前级功率变换器[J]. 电工技术学报, 2019, 34(S1): 235-243. [4] 廉洁, 陈雨. 直接甲醇燃料电池模糊PID控制研究[J]. 河南科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012, 31(5): 584-588.LIAN J, CHEN Y. Research on fuzzy PID control of direct methanol fuel cell[J]. Journal of Henan University of Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2012, 31(5): 584-588. [5] LI S, FAIRBANK M, JOHNSON C, et al. Artificial neural networks for control of a grid-connected rectifier/inverter under disturbance, dynamic and power converter switching conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 25(4): 738-750. [6] YANG B, LIANG B, QIAN Y, et al. Parameter identification of PEMFC via feedforward neural network-pelican optimization algorithm[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 361: 122857. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.122857 [7] CHEN X, GU B, FENG W, et al. Research on control strategy of PEMFC air supply system for power and efficiency improvement[J]. Energy, 2024, 304: 132100. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2024.132100 [8] CHEN J H, HE P, CAI S J, et al. Modeling and temperature control of a water-cooled PEMFC system using intelligent algorithms[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 372: 123790. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.123790 [9] 王京阳. 光-氢-储直流系统变流器控制与功率协调策略研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2023. [10] JIA J, LI Q, WANG Y, et al. Modeling and dynamic characteristic simulation of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2009, 24(1): 283-291. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2008.2011837 [11] 韩爱国, 宋福豪, 田韶鹏, 等. 燃料电池系统建模与供气系统控制方法[J]. 江苏大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(2): 147-153. [12] 兰洪星. 氢燃料电池系统建模与控制策略研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020. [13] BAROUD Z, BENMILOUD M, BENALIA A. Fuzzy selftuning PID controller for air supply on a PEM fuel cell system[C]//Internation Conference on Electrical Engineering. Piscataway, USA: IEEE, 2016: 361-366. [14] ZHANG Z, JIA L, HE H, et al. Modeling dynamic behaviors of a single cell proton exchange membrane fuel cell under different operating conditions[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2010, 41(6): 689-698. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2010.02.003 [15] 裴尧旺, 陈凤祥, 胡哲, 等. 基于自适应LQR控制的质子交换膜燃料电池热管理系统温度控制[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(9): 2014-2024. [16] 皇甫宜耿, 石麒, 李玉忍. 质子交换膜燃料电池系统建模仿真与控制[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2015, 33(4): 682-687.HUANGFU Y G, SHI Q, LI Y R. Modeling simulation and control of proton exchange membrane fuel cell system[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2015, 33(4): 682-687. [17] 刘佳, 李秀亮, 沈晔晔, 等. 燃料电池DC-DC变换器的设计与数字控制[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2016, 50(6): 910-916.LIU J, LI X L, SHEN Y Y, et al. Design and digital control of DC-DC converter for fuel cell[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2016, 50(6): 910-916. [18] MARIO M, CAMILLO V. New DC-DC converter for energy storage system interfacing in fuel cell hybrid electric vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2007, 22(1): 301-308. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2006.886650 [19] 黄宬, 黄亮, 卢叶, 等. 燃料电池 Buck 变换器的动态演化控制仿真[J]. 机电工程, 2014, 31(11): 1490-1494. [20] 胡鹏, 刘波, 石瑛, 等. 质子交换膜燃料电池前级直流变换器的仿真研究[J]. 电源技术, 2016, 40(3): 561-564,708. [21] 吴宇, 皇甫宜耿, 张琳, 等. 大扰动 Buck-Boost 变换器的鲁棒高阶滑模控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35(7): 1740-1748. [22] 魏成伟. 模糊—神经—PID融合的控制策略的工程应用[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2008. [23] 苏明, 陈伦军, 林浩. 模糊PID控制及其MATLAB仿真[J]. 现代机械, 2004(4): 51-55. [24] 李智辉, 杨曦, 肖刚, 等. 基于模糊PID控制的燃料电池稳压技术研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2024, 46(1): 138-143. -




 下载:
下载: