Human Factors Engineering Analysis for Underwater Carriers
-
摘要: 人因工程学是优化人机交互效能、提升系统作业安全性与效率的核心支撑, 将其融入水下运载器设计与操控对拓展装备应用场景、保障作业可靠性具有重要现实意义。文中基于人因工程学理论, 针对潜水员操控水下运载器时的重心分布、潜水装具类型以及疲劳度等3个人因工程因素, 以某水下运载器为试验载体, 开展理论研究与试验分析。研究结果表明, 合理的重心布局、适配的潜水装具及可控的作业疲劳度可显著提升水下运载器的航速稳定性与航向精准度。文中总结的水下运载器人因工程优化方向为未来水下运载器的人性化设计与操控规范制定提供新的研究思路。Abstract: Human factors engineering is a core support for optimizing human-machine interaction efficiency and improving system operational safety and efficiency. Integrating it into the design and operation of underwater carriers is of great practical significance for expanding equipment application scenarios and ensuring operational reliability. This paper, grounded in human factors engineering theory, examined three key human factors, namely center of gravity distribution, diving equipment type, and fatigue levels, when divers operate these vehicles. Using an underwater carrier as a test case, the study conducted theoretical research and experimental analysis. The research results show that reasonable center of gravity layout, suitable diving equipment, and controllable operational fatigue can significantly improve the speed stability and heading accuracy of underwater carries. The human factors engineering optimization directions summarized in the article provide new research ideas for the future design of underwater carriers and the formulation of operation specifications.
-
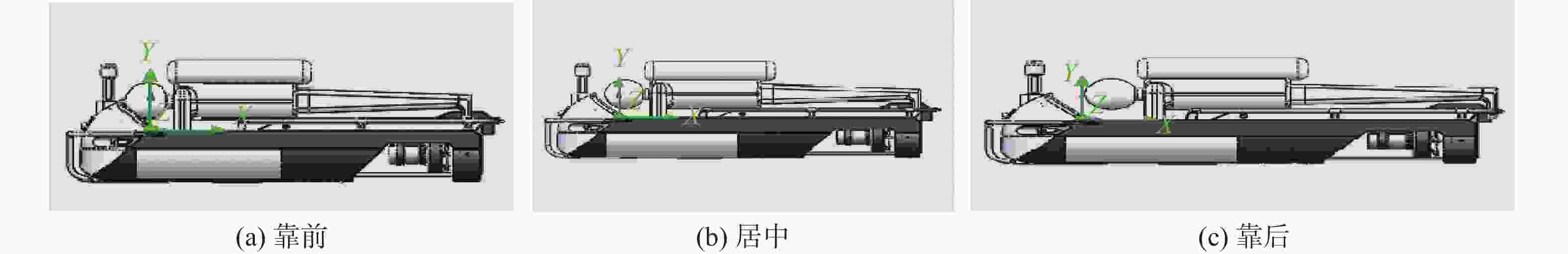
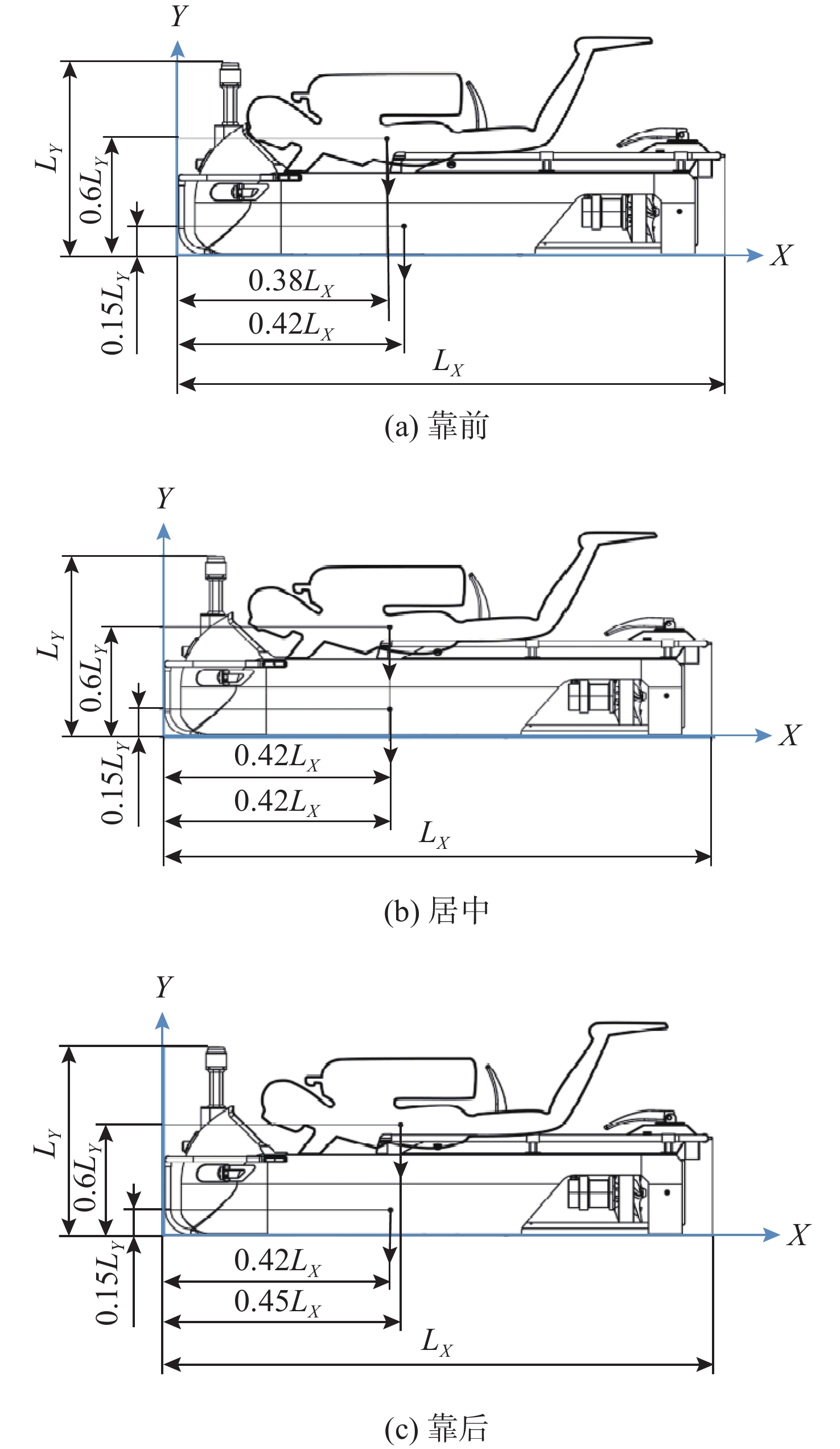
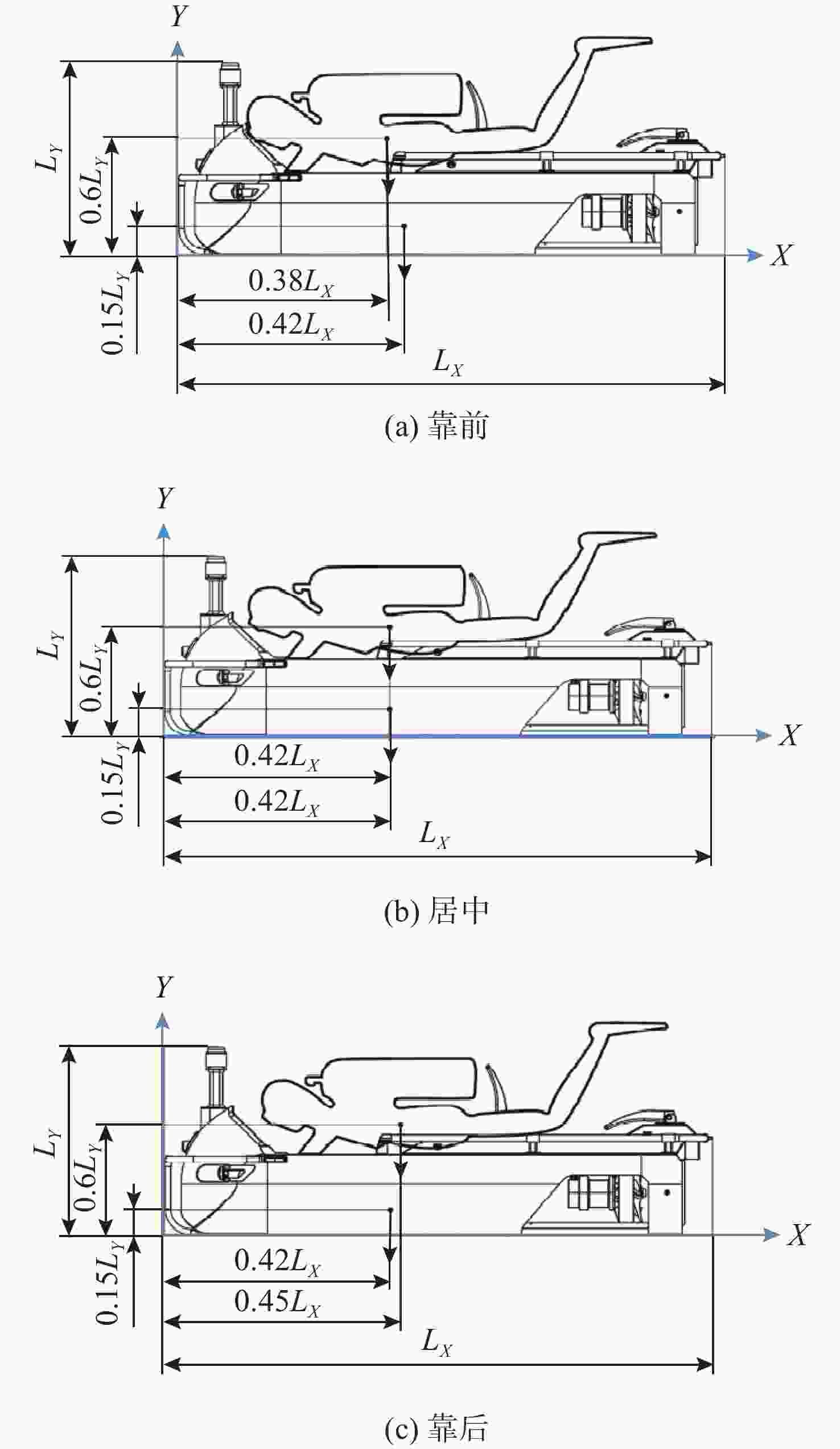
表 1 水下运载器、潜水员及整机重心浮心位置表
Table 1. Center of gravity and buoyancy position for underwater carrier, diver and overall unit
项目 运载器 潜水员 整机 重心 浮心 重心 浮心 重心 浮心 靠前 (0.42$ {L_X} $, 0.15$ {L_Y} $) (0.42$ {L_X} $, 0.27$ {L_Y} $) (0.38$ {L_X} $, 0.6$ {L_Y} $) (0.38$ {L_X} $, 0.6$ {L_Y} $) (0.398$ {L_X} $, 0.395$ {L_Y} $) (0.398$ {L_X} $, 0.453$ {L_Y} $) 居中 (0.42$ {L_X} $, 0.15$ {L_Y} $) (0.42$ {L_X} $, 0.27$ {L_Y} $) (0.42$ {L_X} $, 0.6$ {L_Y} $) (0.42$ {L_X} $, 0.6$ {L_Y} $) (0.42$ {L_X} $, 0.395$ {L_Y} $) (0.42$ {L_X} $, 0.453$ {L_Y} $) 靠后 (0.42$ {L_X} $, 0.15$ {L_Y} $) (0.42$ {L_X} $, 0.27$ {L_Y} $) (0.45$ {L_X} $, 0.6$ {L_Y} $) (0.45$ {L_X} $, 0.6$ {L_Y} $) (0.436$ {L_X} $, 0.395$ {L_Y} $) (0.436$ {L_X} $, 0.453$ {L_Y} $) 表 2 潜水员操控水下运载器疲劳度等级统计表
Table 2. Statistics of fatigue degree of divers operating underwater carriers
序号 疲劳度等级 T1 T2 T3 T4 潜水员1 2 4 6 10 潜水员2 1 2 6 9 潜水员3 1 2 5 9 潜水员4 1 3 5 8 潜水员5 2 2 5 8 潜水员6 2 3 5 9 潜水员7 2 2 6 9 潜水员8 1 4 5 10 表 3 潜水员相对重心位置试验数据
Table 3. Test data of diver’s relative center of gravity position
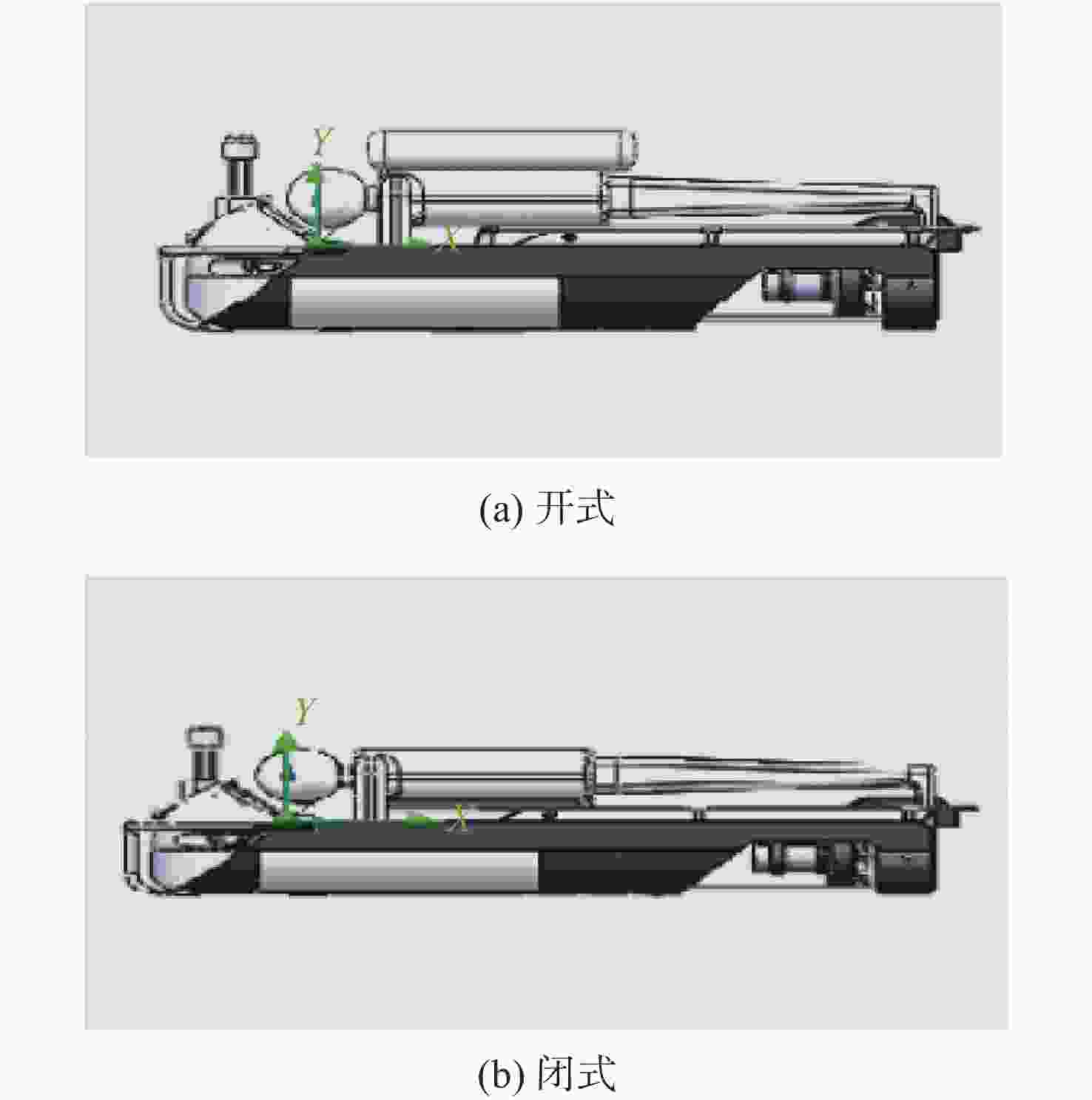
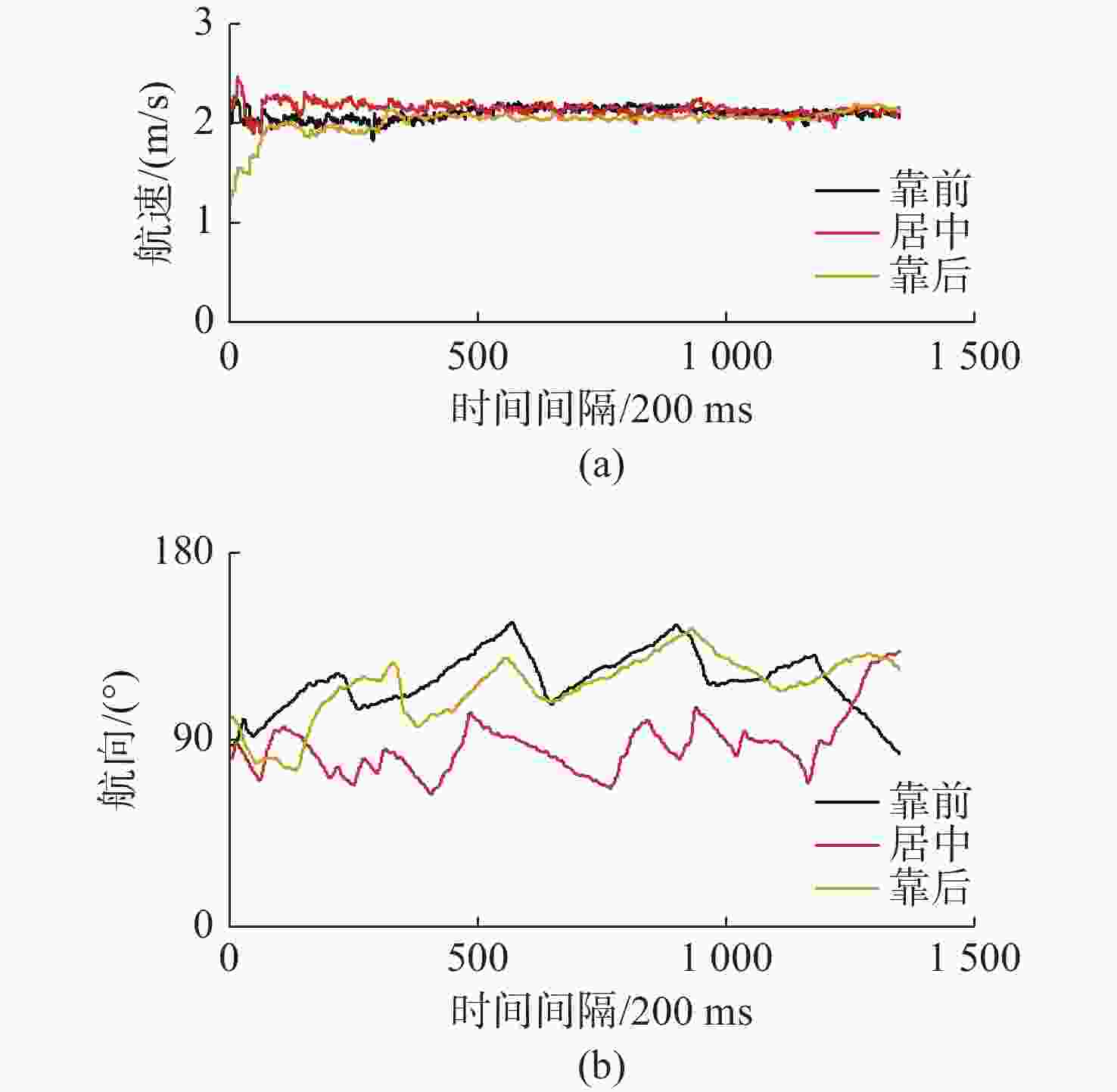
重心位置 平均航速/(m/s) 平均航向/(°) 标准值航向偏差/(°) 靠前 2.09 118.24 +28.24 居中 2.14 89.90 −0.10 靠后 2.03 114.45 +24.45 表 4 不同潜水装具操控水下运载器试验数据
Table 4. Test data of underwater carriers operated by different diving equipment
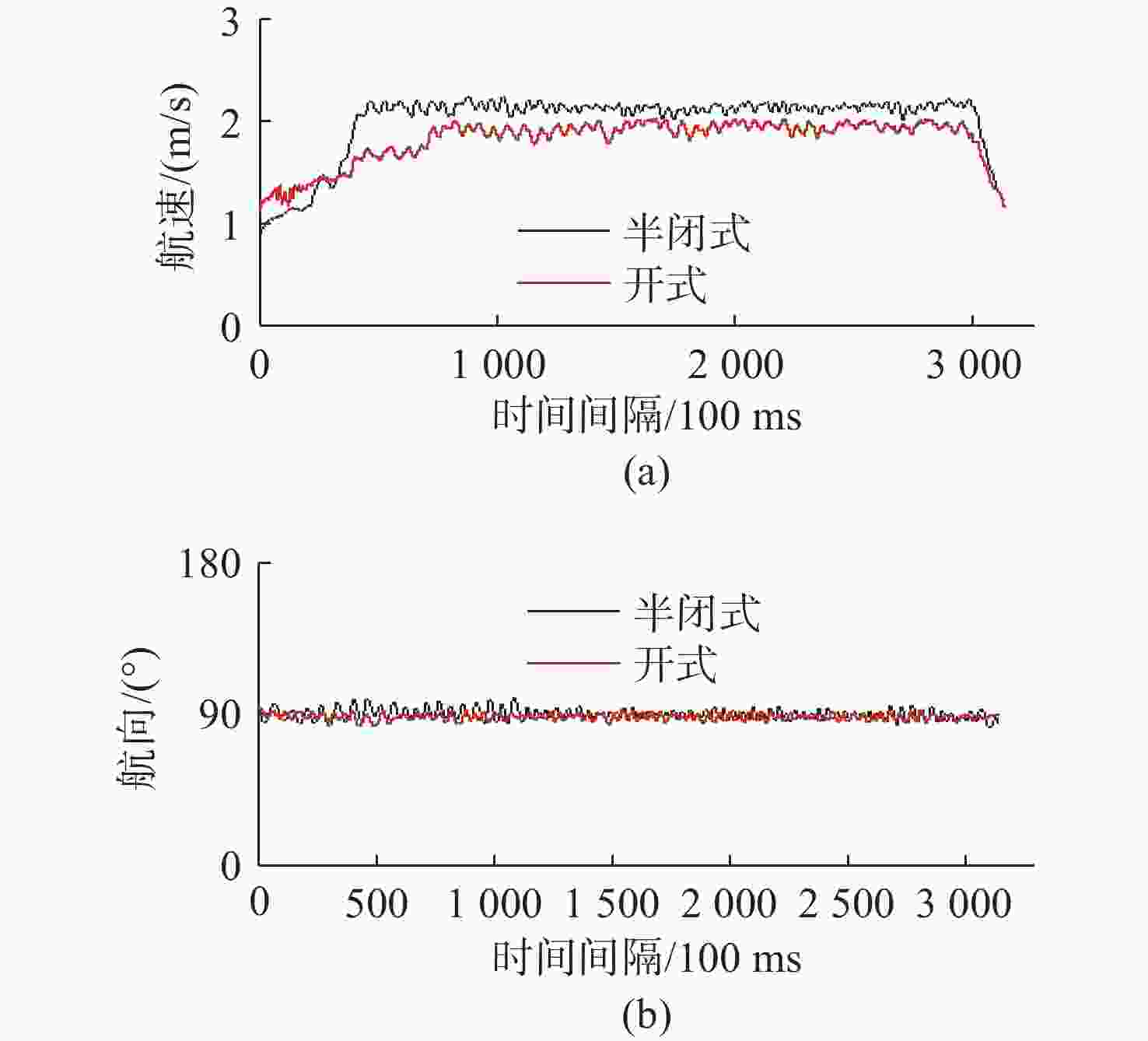
装具类型 平均航速/(m/s) 平均航向/(°) 标准值航向偏差/(°) 开式 1.81 88.29 −1.71 半闭式 2.00 90.03 +0.03 表 5 潜水员操控水下运载器疲劳度试验数据均值
Table 5. Mean values of fatigue test data of divers operating underwater carriers
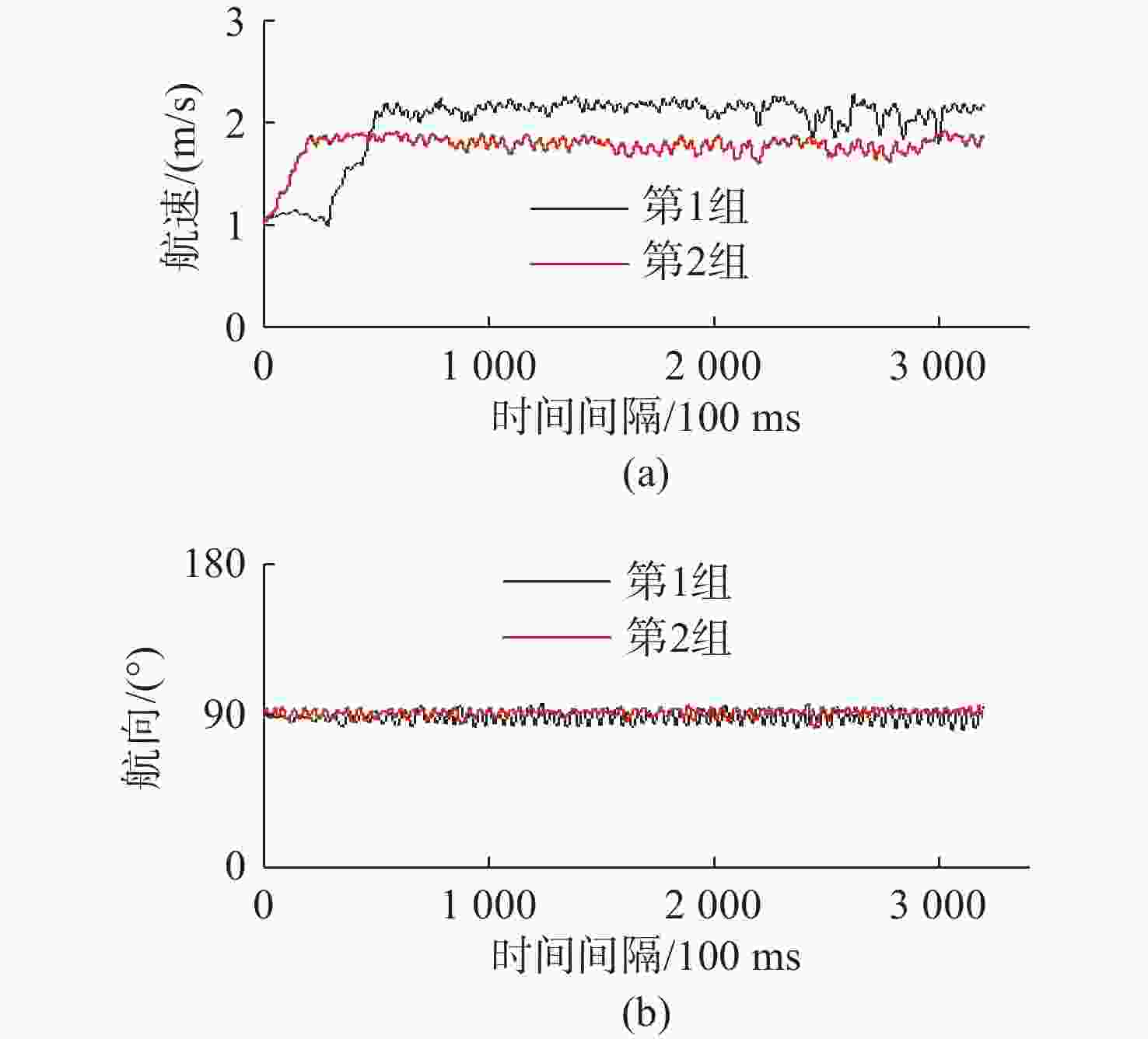
疲劳度测试 平均航速/(m/s) 平均航向/(°) 标准值航向偏差/(°) 第1组 1.99 89.13 −0.87 第2组 1.77 91.70 +1.70 -
[1] 刘宁, 李珊, 茶文丽. 蛙人装备研究现状及发展展望[J]. 中国造船, 2018, 59(4): 212-222LIU N, LI S, CHA W L. Research status and development prospects of amphibious equipment[J]. China Shipbuilding, 2018, 59(4): 212-222. [2] STIDD. Diver propulsion device(DPD)[EB/OL]. [2025-06-10]. https://stiddmil.com/diver-propulsion-device-dpd/. [3] ROTINOR. DIVEJET RD2 High-performance diving scooter[EB/OL]. [2025-06-10]. https://rotinor.com/divejet/. [4] SUEX. SUEX submarine exploration[EB/OL]. [2025-06-10]. https://www.suex.it/pdf/. [5] 钟多就. 蛙人运载器导航与控制系统关键技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2011. [6] 李玉阳, 李锐, 李遥. 某型蛙人运载器辐射噪声测量与特征分析[J]. 声学技术, 2023, 42(6): 726-732. [7] 王帅. 水下运载器总体优化与自平衡控制技术研究[D]. 无锡: 中国船舶科学研究中心, 2012. [8] 王君贤. 基于Cortex-A9的蛙人运载器图像声呐显示系统设计[D]. 昆明: 云南大学, 2017. [9] 李晗生. 蛙人推进器的水下航行数值模拟及实验研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2020. [10] 付学志, 石建飞, 江源. 蛙人水下作战系统装备发展现状及趋势[J]. 电声技术, 2019, 43(12): 11-17. [11] 周超, 钟宏伟, 陈迎亮, 等. 国外蛙人水下输送平台技术发展综述[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2022, 30(6): 680-695.ZHOU C, ZHONG H W, CHEN Y L, et al. A review of underwater transport platform technology development for diving robots in foreign countries[J]. Journal of Underwater Unmanned Systems, 2022, 30(6): 680-695. [12] 张志伟, 方泽江, 和润民, 等. 美军水下特种作战装备的发展现状及趋势分析[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(5): 962-970ZHANG Z W, FANG Z J, HE R M, et al. Analysis of the current status and development trends of U. S. underwater special operations equipment[J]. Journal of Underwater Unmanned Systems, 2024, 32(5): 962-970. [13] 陈善广, 李志忠, 葛列众, 等. 人因工程研究进展及发展建议[J]. 中国科学基金, 2021, 35(2): 203-212. [14] 王锡东. 水下机器人重心测量及误差分析技术研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2015. [15] 俞旭华, 徐佳骏, 刘文武, 等. 闭式呼吸人因工程设计思考[J]. 海军医学杂志, 2023, 44(11): 1107-1109. [16] 鲁刚, 金忠贤. 国内外潜水装具现状及发展趋势[J]. 海军医学杂志, 2006, 27(3): 260-262. [17] 何金良. 人体疲劳评价标准综述[J]. 西藏医药杂志, 2013, 34(2): 29-32. [18] 王春蕾. 基于人因工程学的油壶组装作业疲劳评估与应用研究[D]. 青岛: 山东科技大学, 2020. [19] 付国举, 陈余祥, 钟朝廷, 等. 模拟480m氦氧饱和潜水不同深度下潜水员作业效率的变化[J]. 海军医学杂志, 2015, 36(4): 289-295. [20] 黄育敏, 张明月, 陈锐勇, 等. 心率与自觉疲劳分级在氦氧饱和潜水中潜水员机体疲劳监测中的应用[J]. 第二军医大学学报, 2015, 36(9): 978-982. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1008.2015.00978 -




 下载:
下载: