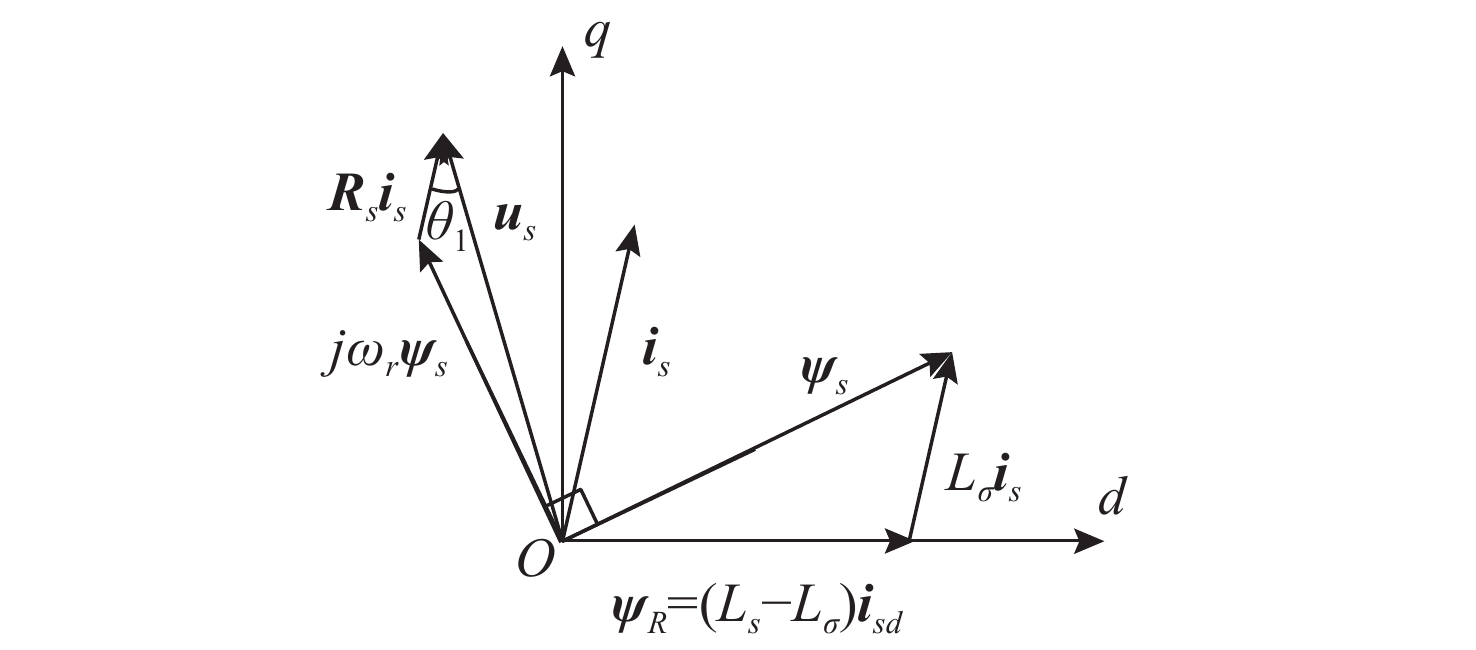
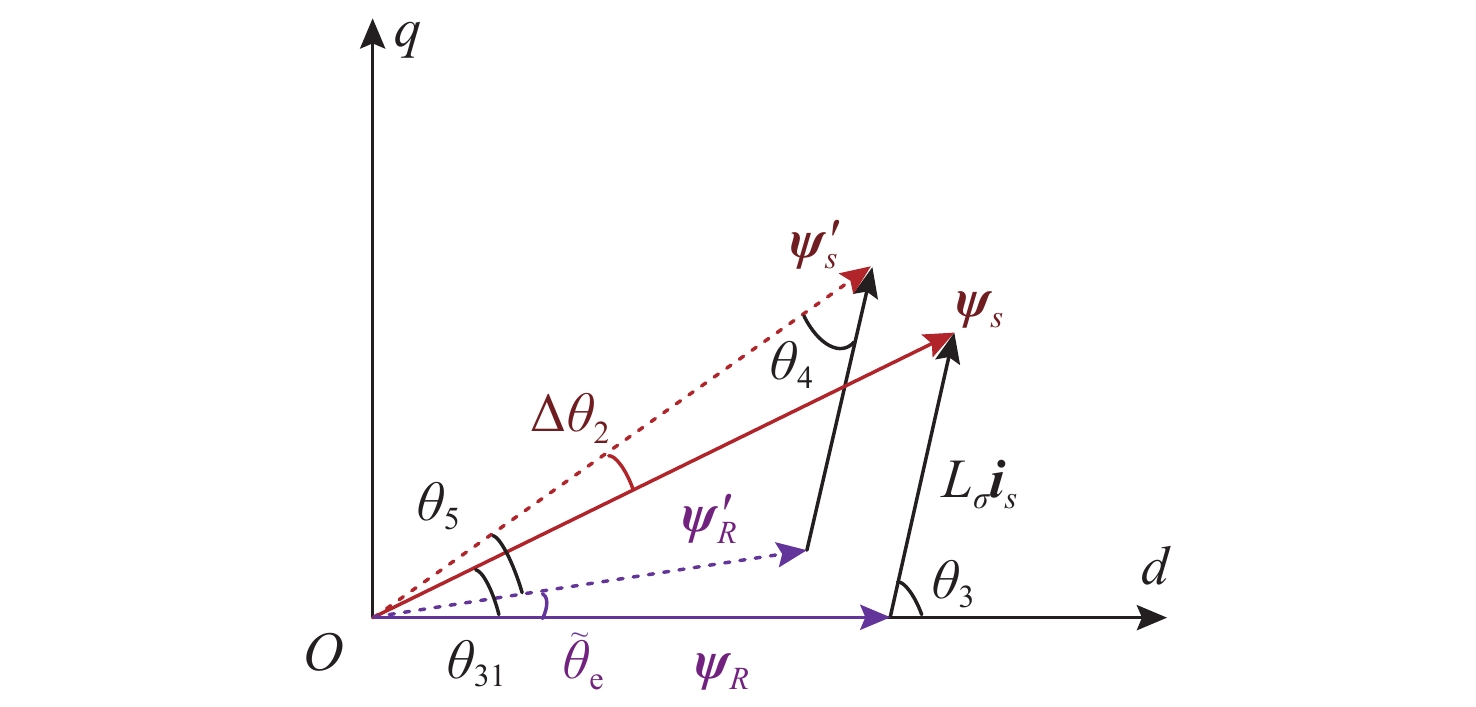
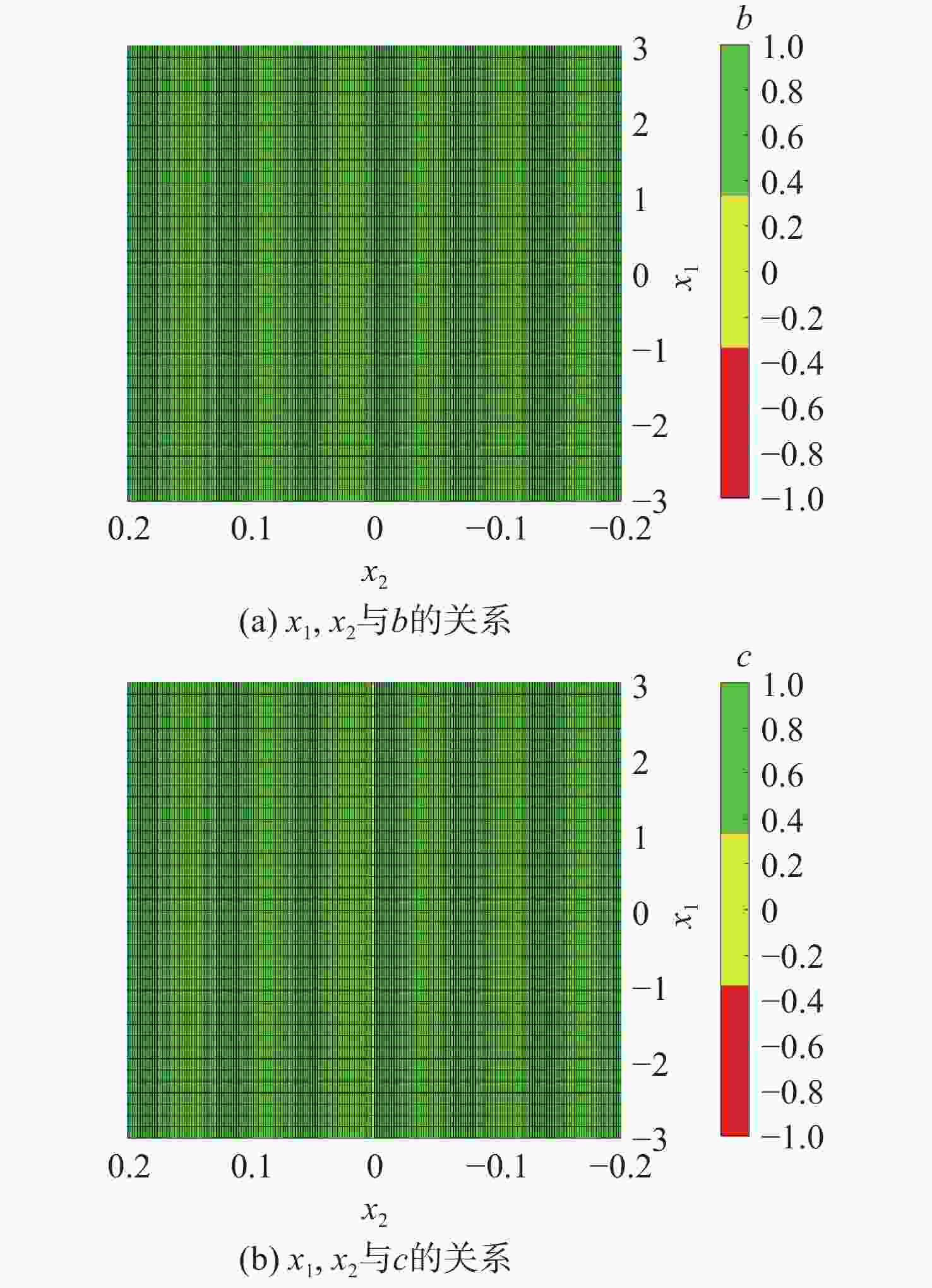
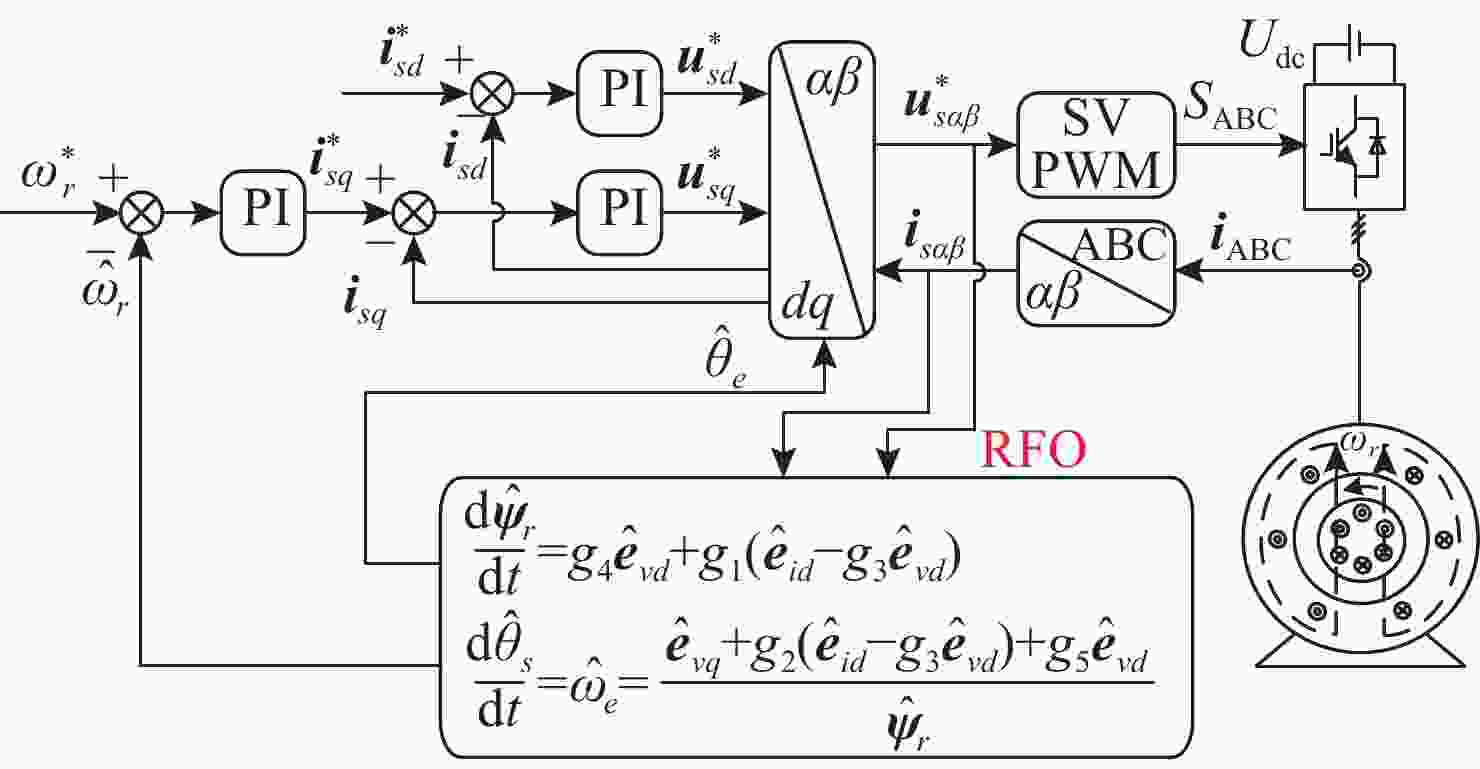
Sensorless Speed Control of Induction Motors Using Reduced-Order Flux Linkage Observers with Strong Robustness to Stator Resistance
-
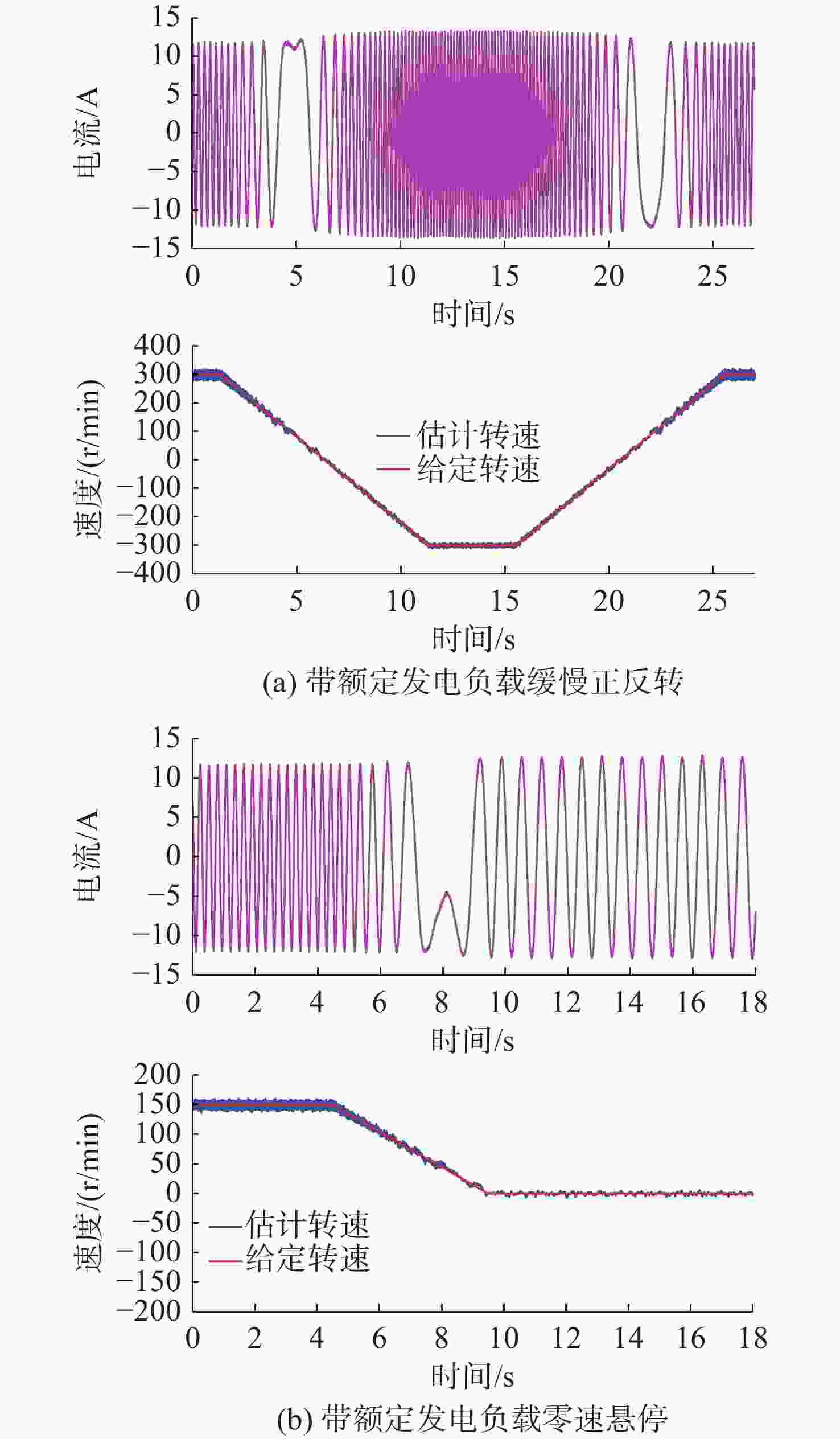
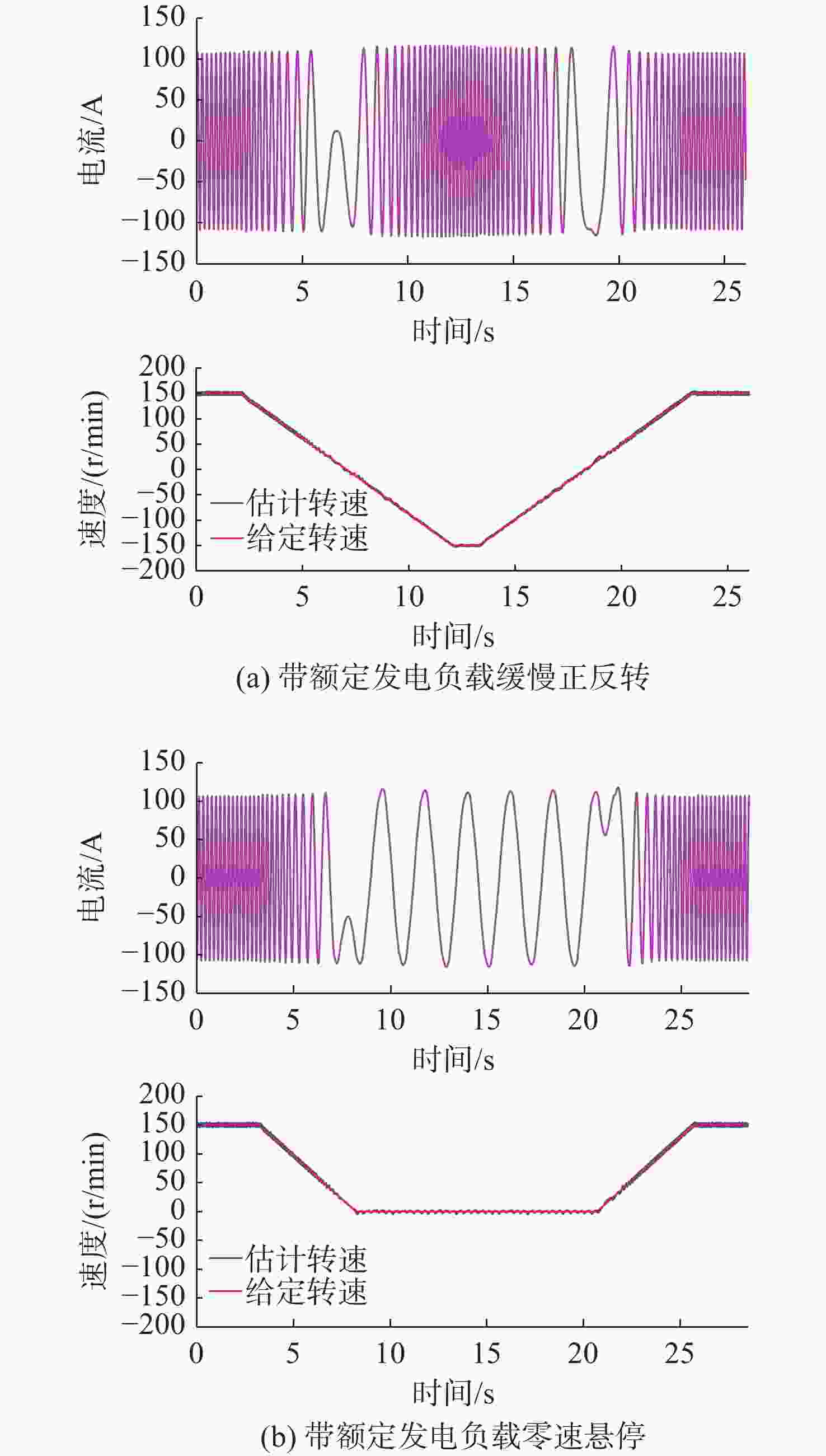
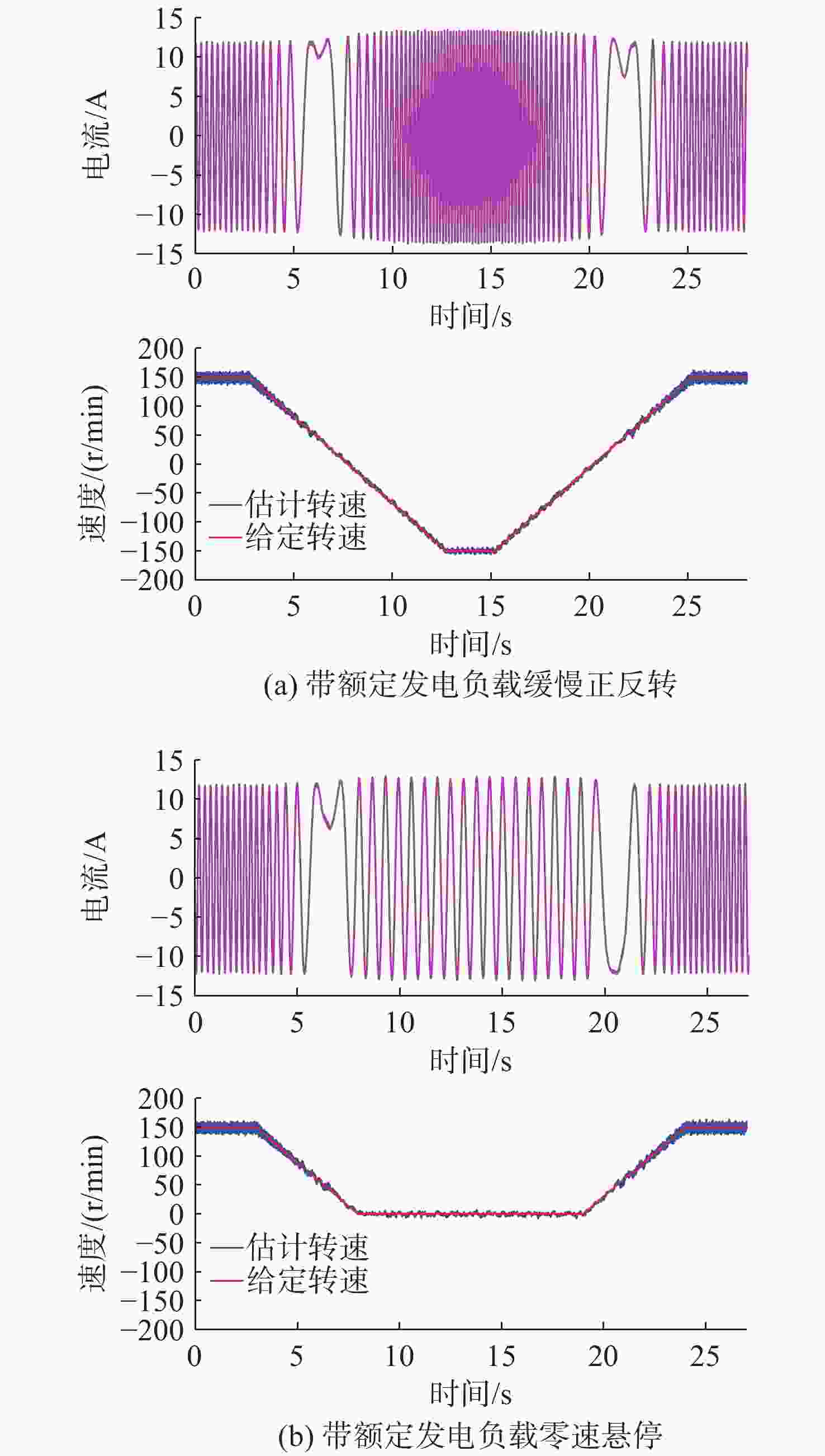
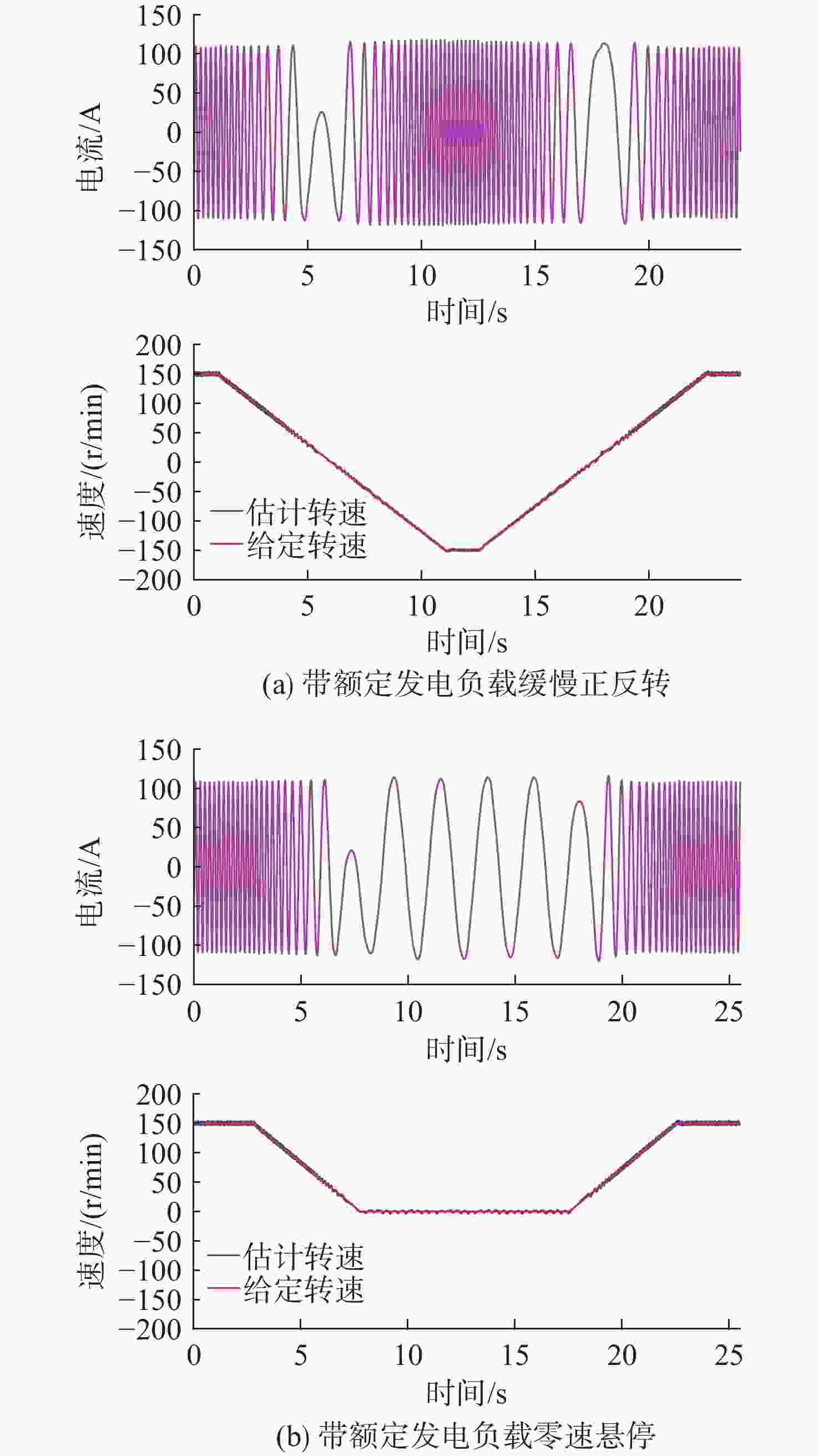
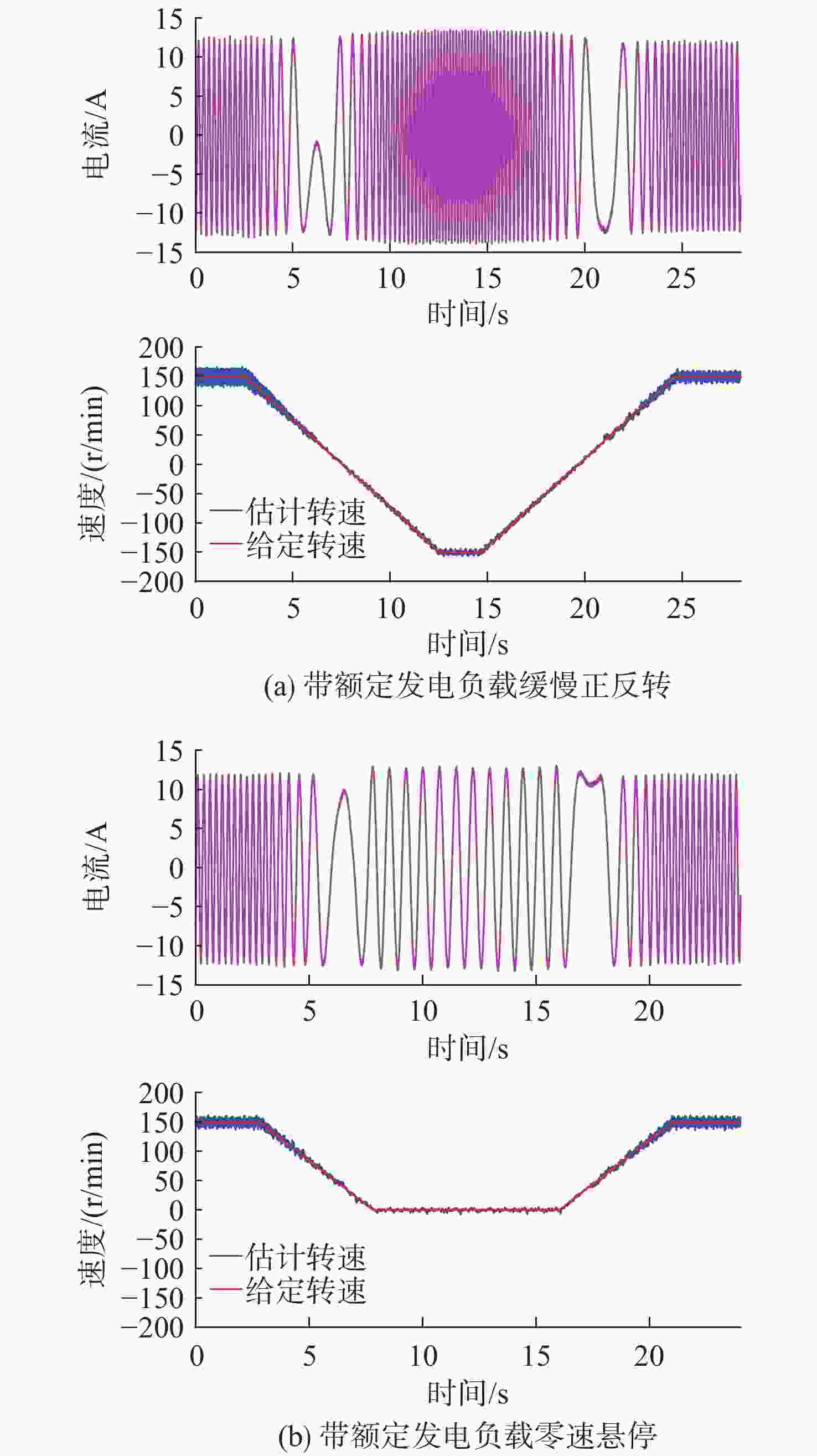
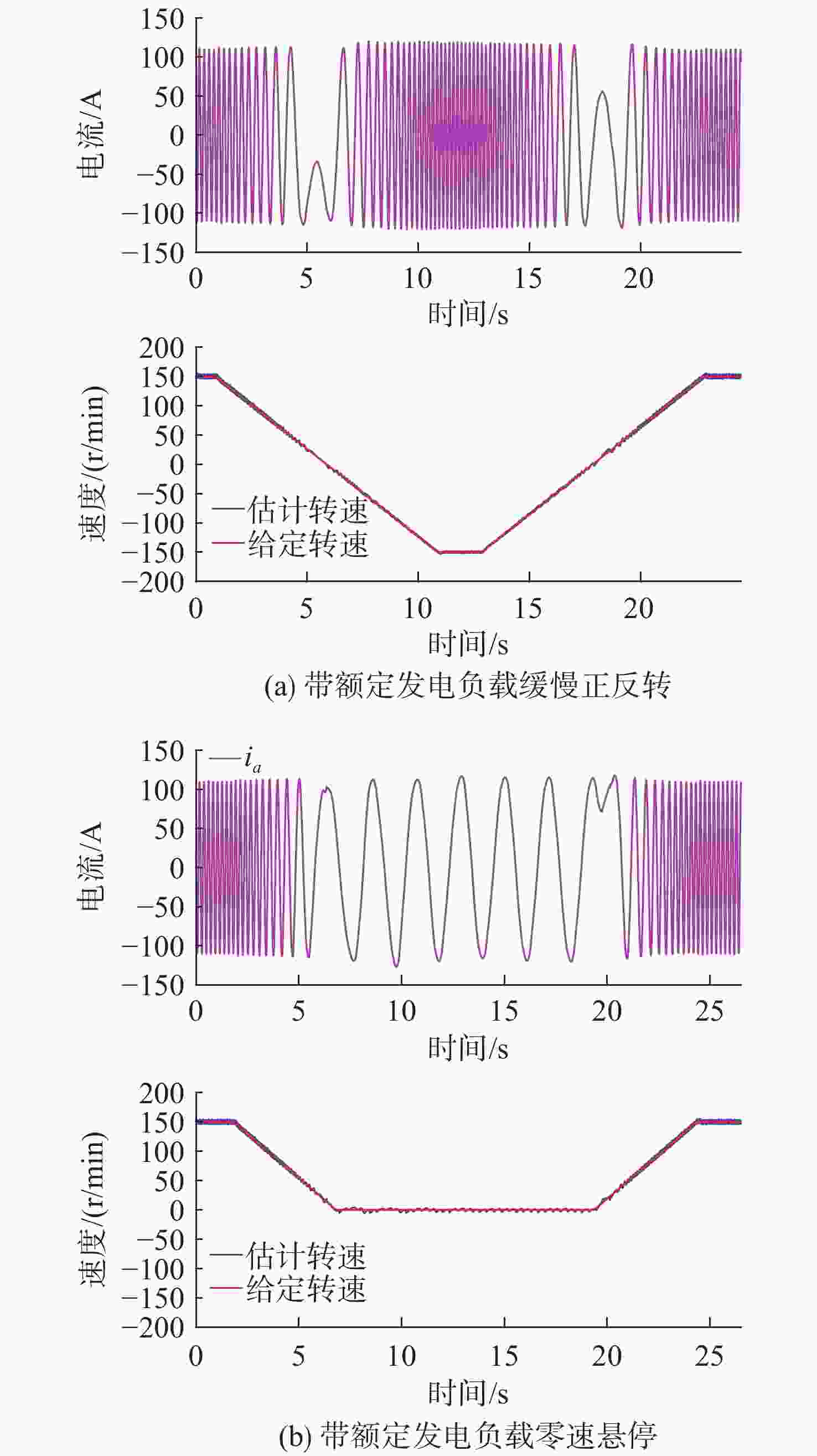
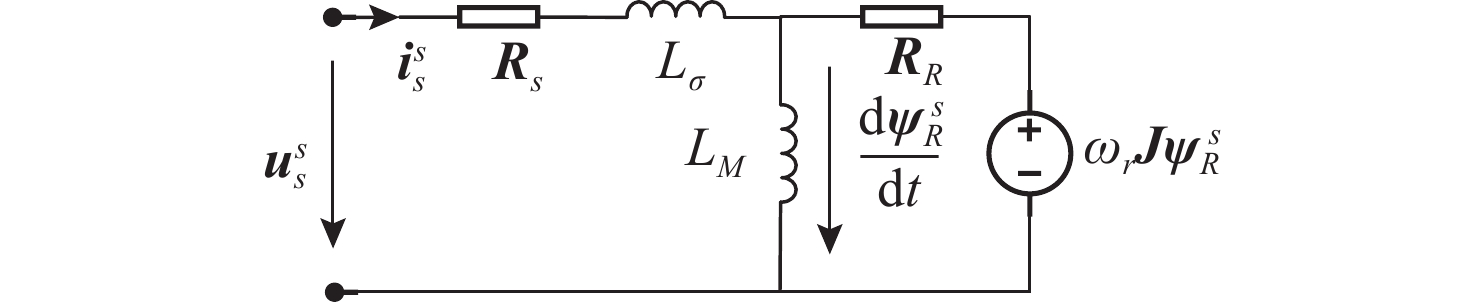
摘要: 感应电机无速度传感器控制技术能够减低系统成本和体积、优化硬件结构、可靠性高且易于维护, 已成为现代工业自动化、机器人控制和电动汽车驱动等领域的重要技术手段。然而, 该技术在低速发电区域内仍存在关键问题:系统在低速运行时可能会出现不稳定现象, 且低速控制性能易受定子电阻变化的影响。针对这些问题, 文中对感应电机降阶磁链观测器的增益设计进行优化, 在不添加额外的定子电阻自适应或在线辨识环节的前提下, 实现了降阶磁链观测器在低速发电区域的稳定运行和对定子电阻变化的强鲁棒性。为了充分验证所提方法的有效性和通用性, 在不同功率等级电机和不同定子电阻误差条件下开展了全低速范围带载实验。实验结果表明, 优化后的降阶磁链观测器在整个低速区域内表现出优异的稳定性和定子电阻鲁棒性, 系统控制性能显著提升。Abstract: Sensorless speed control technology for induction motors has become an important technical approach in fields including modern industrial automation, robot control, and electric vehicle drives, due to its advantages of reduced system cost and volume, optimized hardware structure, high reliability, and ease of maintenance. However, this technology still faces critical challenges in the low-speed generating region. Specifically, the system may experience instability during low-speed operation, and the control performance is susceptible to variations in stator resistance. In response to these issues, this paper proposed an optimized gain design for the reduced-order flux linkage observer. This method ensured stable operation in low-speed generating regions and strong robustness against stator resistance variations without introducing additional stator resistance adaptation or online identification processes. In order to thoroughly verify the effectiveness and general applicability of the proposed method, load experiments were conducted across the entire low-speed range under different motor power levels and stator resistance error conditions. The experimental results demonstrate that the optimized reduced-order flux linkage observer exhibits excellent stability and robustness to stator resistance in the entire low-speed region, significantly enhancing system control performance.
-
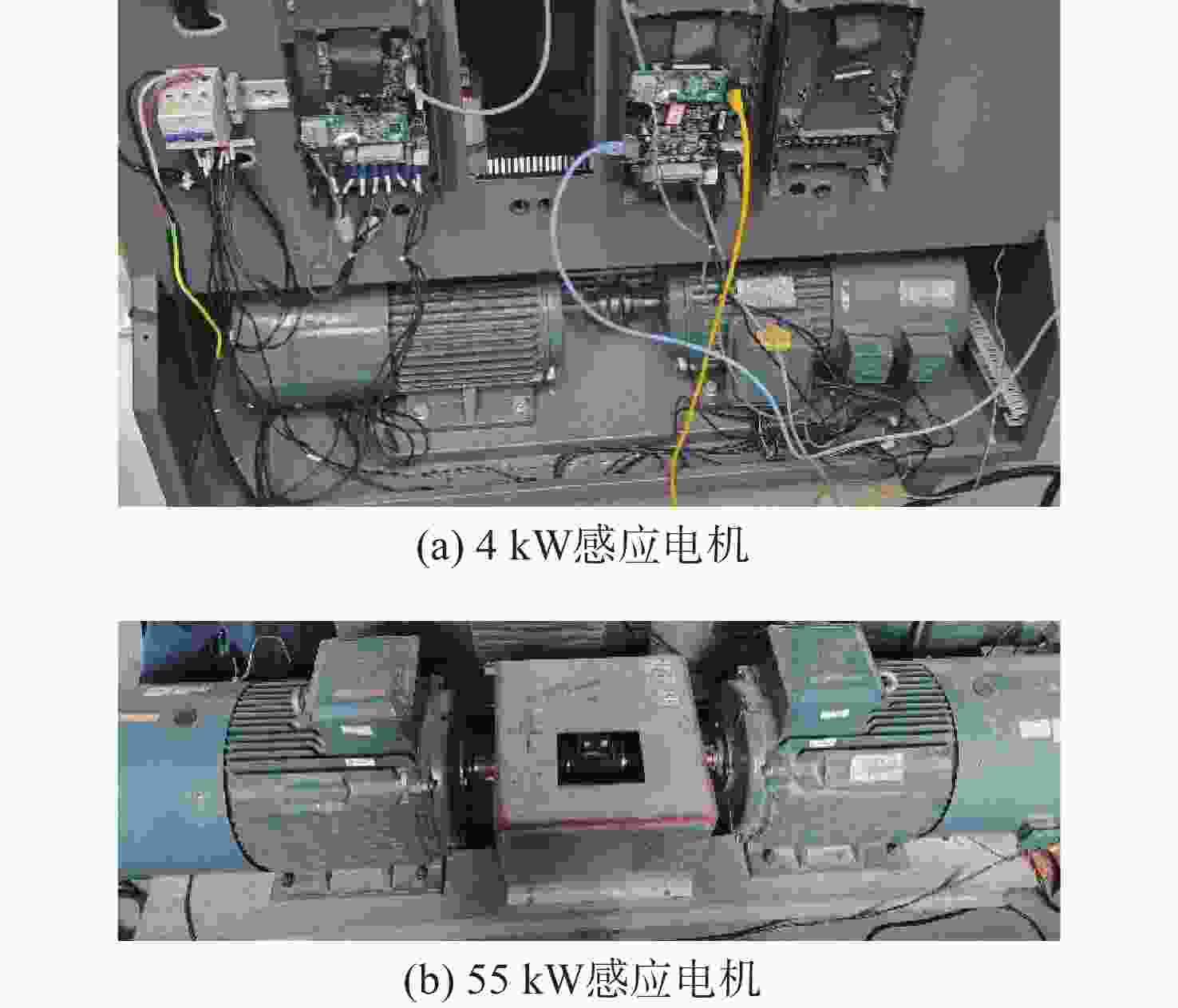
表 1 感应电机参数
Table 1. Parameters of induction motors
参数 数值 4 kW 55 kW 额定功率/kW 4 55 额定电压/V 380 380 额定电流/A 8.8 103 额定频率/Hz 50 50 额定转速/(r/min) 1 440 1 440 极对数 2 2 定子电阻/Ω 1.12 0.046 转子电阻/Ω 0.833 0.032 互感/mH 149.5 21.4 定子电感/mH 153.9 22 转子电感/mH 153.9 22 -
[1] ODHANO S A, PESCETTO P, AWAN H A A, et al. Parameter identification and self-commissioning in ac motor drives: A technology status review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2019, 34(4): 3603-3614. [2] ZERDALI E, BARUT M. The comparisons of optimized extended kalman filters for speed-sensorless control of induction motors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(6): 4340-4351. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2674579 [3] MONTERO E R, VOGELSBERGER M, WOLBANK T. Sensorless saliency-based control of dual induction machines under dynamic load imbalances using three current sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(12): 12093-12101. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3241394 [4] HOLTZ J. Sensorless control of induction machines—with or without signal injection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2006, 53(1): 7-30. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2005.862324 [5] GAO Q, ASHER G, SUMNER M. Sensorless position and speed control of induction motors using high-frequency injection and without offline precommissioning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2007, 54(5): 2474-2481. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2007.900364 [6] METWALY M K, ELKALASHY N I, ZAKY M S, et al. Slotting saliency extraction for sensorless torque control of standard induction machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2018, 33(1): 68-77. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2017.2726998 [7] ORLOWSKA-KOWALSKA T, KORZONEK M, TARCHALA G. Stability improvement methods of the adaptive full-order observer for sensorless induction motor drive-comparative study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(11): 6114-6126. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2930465 [8] AMBROZIC V, NEDELJKOVIĆ D, NASTRAN J. Sensorless control of induction machine with parameter adaptation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics. Bled, Slovenia: IEEE, 1999. [9] SANGWONGWANICH S, NITTAYATAREEKUL U, MAGYAR P. Direct speed estimation based on back-EMF of induction motors-Its equivalent MRAS representation and stability analysis[C]//EPE2003. Toulouse, France: IEEE, 2003. [10] HINKKANEN M, HARNEFORS L, LUOMI J. Reduced-order flux observers with stator-resistance adaptation for speed-sensorless induction motor drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2010, 25(5): 1173-1183. [11] TARCHALA G, ORLOWSKA-KOWALSKA T. Equivalent-signal-based sliding mode speed mras-type estimator for induction motor drive stable in the regenerating mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(9): 6936-6947. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2795518 [12] MOAVENI B, MASOUMI Z, RAHMANI P. Introducing improved iterated extended Kalman filter(IIEKF) to estimate the rotor rotational speed, rotor and stator resistances of induction motors[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 17584-17593. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3244830 [13] TIR Z, ORLOWSKA-KOWALSKA T, AHMED H, et al. Adaptive high gain observer based MRAS for sensorless induction motor drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(1): 271-281. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3243271 [14] MAKSOUD H A, SHAABAN S M, ZAKY M S, et al. Performance and stability improvement of AFO for sensorless IM drives in low speeds regenerating mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2019, 34(8): 7812-7825. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2018.2879759 [15] WANG T, WANG B, YU Y, et al. High-order sliding-mode observer with adaptive gain for sensorless induction motor drives in the wide-speed range[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(11): 11055-11066. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3227272 [16] 李筱筠, 杨淑英, 曹朋朋, 等. 低速运行时异步驱动转速自适应观测器稳定性分析与设计[J]. 电工技术学报, 2018, 33(23): 5391-5401.LI X Y, YANG S Y, CAO P P, et al. Stability analysis and design of asynchronous drive speed adaptive observer during low-speed operation[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2018, 33(23): 5391-5401. [17] LI R, YANG K, LUO C, et al. Phase compensation factor-based low frequency crossing for sensorless induction motor drives with changing loads[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2023, 38(9): 10680-10691. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2023.3280486 [18] SUN W, YU Y, WANG G, et al. Design method of adaptive full order observer with or without estimated flux error in speed estimation algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2016, 31(3): 2609-2626. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2015.2440373 [19] CHEN J, HUANG J, SUN Y. Resistances and speed estimation in sensorless induction motor drives using a model with known regressors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(4): 2659-2667. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2849964 [20] SAEJIA M, SANGWONGWANICH S. Averaging analysis approach for stability analysis of speed-sensorless induction motor drives with stator resistance estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2006, 53(1): 162-177. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2005.862301 [21] SUN W, GAO J, YU Y, et al. Robustness improvement of speed estimation in speed-sensorless induction motor drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2016, 52(3): 2525-2536. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2015.2512531 [22] LUO C, LI R, YANG K, et al. Graphical multiple-error feedback matrix design for stability and robustness enhancement of speed-sensorless induction motor drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(4): 3537-3548. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3176269 [23] SUN W, WANG Z, XU D, et al. Robust stability improvement for speed sensorless induction motor drive at low speed range by virtual voltage injection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(4): 2642-2654. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2910039 [24] NURETTIN A, İNANÇ N. Sensorless vector control for induction motor drive at very low and zero speeds based on an adaptive-gain super-twisting sliding mode observer[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2023, 11(4): 4332-4339. doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2023.3265352 [25] LIU H. Sensorless control with adaptive speed observer using power winding information for dual-stator winding induction starter/generator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(2): 1388-1398. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3253965 [26] CHEN J, YANG G, YUAN X, et al. Experimental validation of a minimum-order sensorless induction motor control method[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2024, 12(4): 3715-3728. doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2024.3404227 [27] SLEMON G R. Modelling of induction machines for electric drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 1989, 25(6): 1126-1131. doi: 10.1109/28.44251 [28] BOLDEA I, PAICU M C, ANDREESCU G D. Active flux concept for motion-sensorless unified AC drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2008, 23(5): 2612-2618. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2008.2002394 -




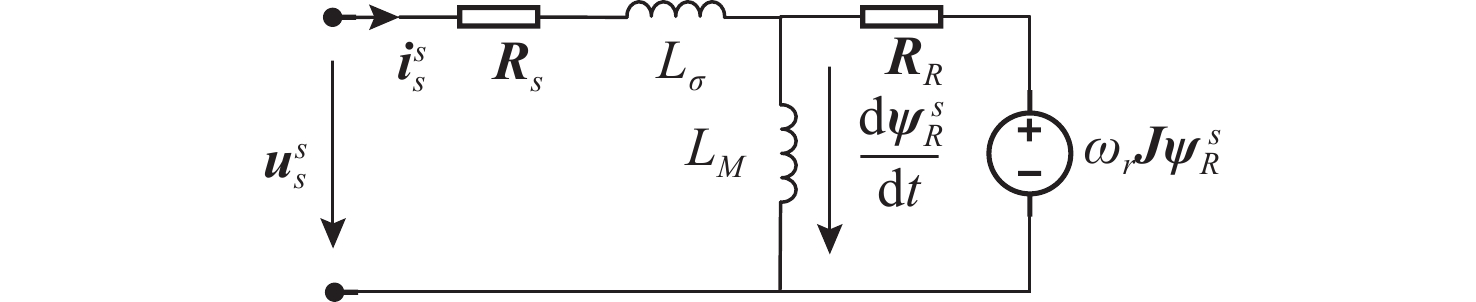


 下载:
下载: