Path Tracking Optimization for Unmanned Hydrofoil Vehicle Based on ILOS and IPID-GWO
-
摘要: 为解决新型无人水翼航行器的路径跟踪问题, 提出了一种基于视线制导法(LOS)并结合增量式比例-积分-微分控制器(IPID)的跟踪策略。首先, 建立了航行器的3自由度运动学和动力学模型, 并通过控制策略实现控制输入解耦; 结合可变前视距离与积分项改进了LOS制导法, 得到ILOS算法; IPID控制器使用ILOS算法得到的期望航向角进行跟踪过程的动态控制, 同时在算法中增加跟踪点切换时的补偿输入, 避免了因剧烈变化导致的系统失控; 分别使用灰狼优化算法(GWO)与遗传算法(GA)对IPID控制器的权重系数进行优化和对比。在Matlab中使用ILOS及IPID控制器对给定的直线-曲线混合路径在无干扰与有干扰时进行路径跟踪仿真, 通过分析跟踪效果和横向误差, 验证了ILOS和IPID-GWO算法结合的可行性和先进性。
-
关键词:
- 无人水翼航行器 /
- 路径跟踪 /
- 视线制导法 /
- 增量式比例-积分-微分控制器 /
- 灰狼优化算法
Abstract: In order to solve the path tracking problem of a new type of unmanned hydrofoil vehicle, a tracking strategy based on line of sight(LOS) guidance combined with an incremental proportional-integral-differential(IPID) controller was proposed. Firstly, the 3-DOF kinematic and dynamic models of the vehicle were established, and the control input was decoupled through the control strategy. The LOS guidance method was improved by combining the variable foresight distance and integral term, and the ILOS algorithm was obtained. The IPID controller used the desired heading angle obtained by the ILOS algorithm to dynamically control the tracking process. The compensation input when switching the tracking point was added to the algorithm to avoid the system’s out-of-control problem caused by excessive changes. The weight coefficients in the IPID controller were optimized and compared using the grey wolf optimizer(GWO) algorithm and genetic algorithm(GA). In Matlab, the ILOS and IPID controllers were used to track the given straight and curved mixed path in the absence and presence of interference. The tracking effect and lateral error were analyzed, and the feasibility and advancement of the combination of ILOS and IPID-GWO algorithms were verified. -
表 1 无人水翼航行器建模参数及公式
Table 1. Modeling parameters and formulas of unmanned hydrofoil vehicles
参数 取值/公式 参数 取值/公式 $ m $ 53.89 $ {x_g} $ 0 $ {X_{\dot u}} $ −2.29 $ {Y_{\dot v}} $ −13.71 $ {Y_{\dot r}} $ 2.23 $ {N_{\dot v}} $ 2.23 $ {I_{\textit{z}}} $ 8.71 $ {N_{\dot r}} $ 3.19 $ b $ 0.48 $ L $ 0.8 $ {d_{11}} $ $ 2.29 + 1.33\left| u \right| $ $ {d_{22}} $ $ 13.71 + 36.47\left| v \right| + 0.81\left| r \right| $ $ {d_{23}} $ $ - 2.23 + 0.85\left| v \right| - 0.13\left| r \right| $ $ {d_{32}} $ $ - 2.23 + 0.85\left| v \right| - 0.13\left| r \right| $ $ {d_{33}} $ $ - 3.19 - 0.08\left| v \right| + 0.75\left| r \right| $ 表 2 仿真结果数据
Table 2. Simulation result data
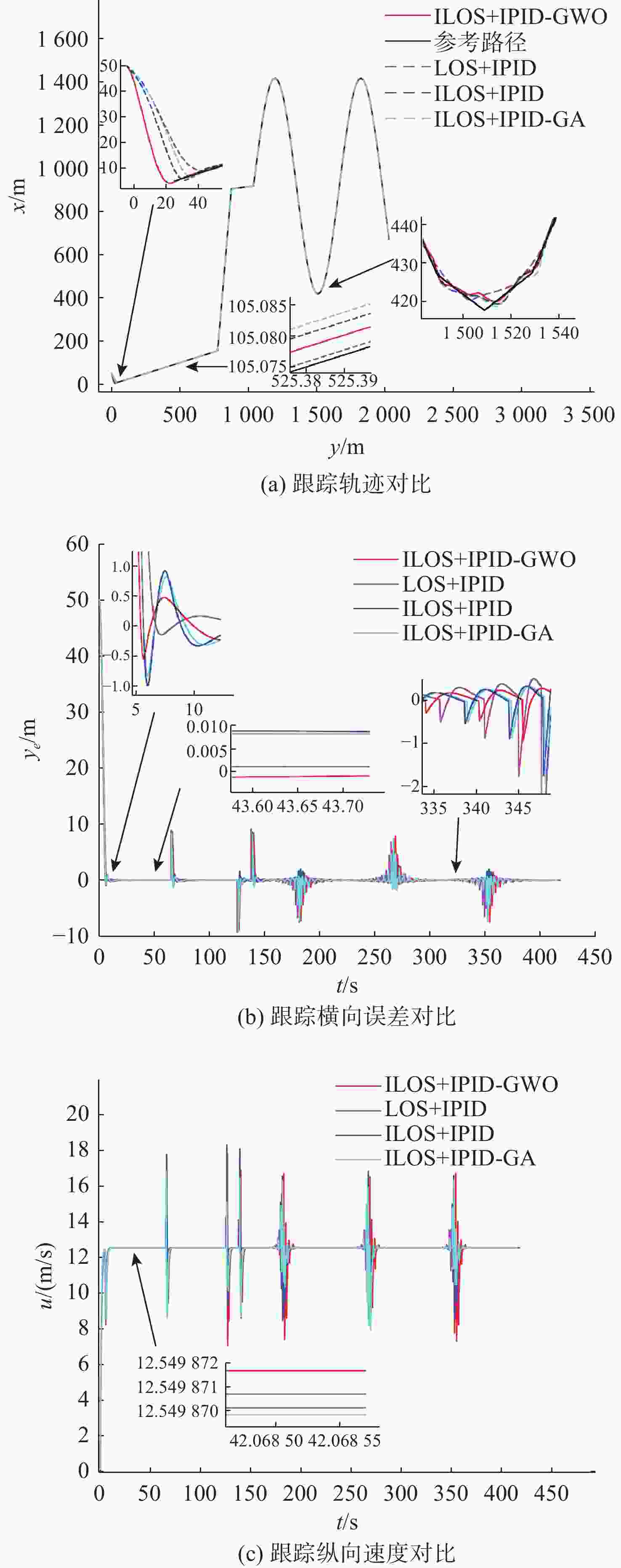
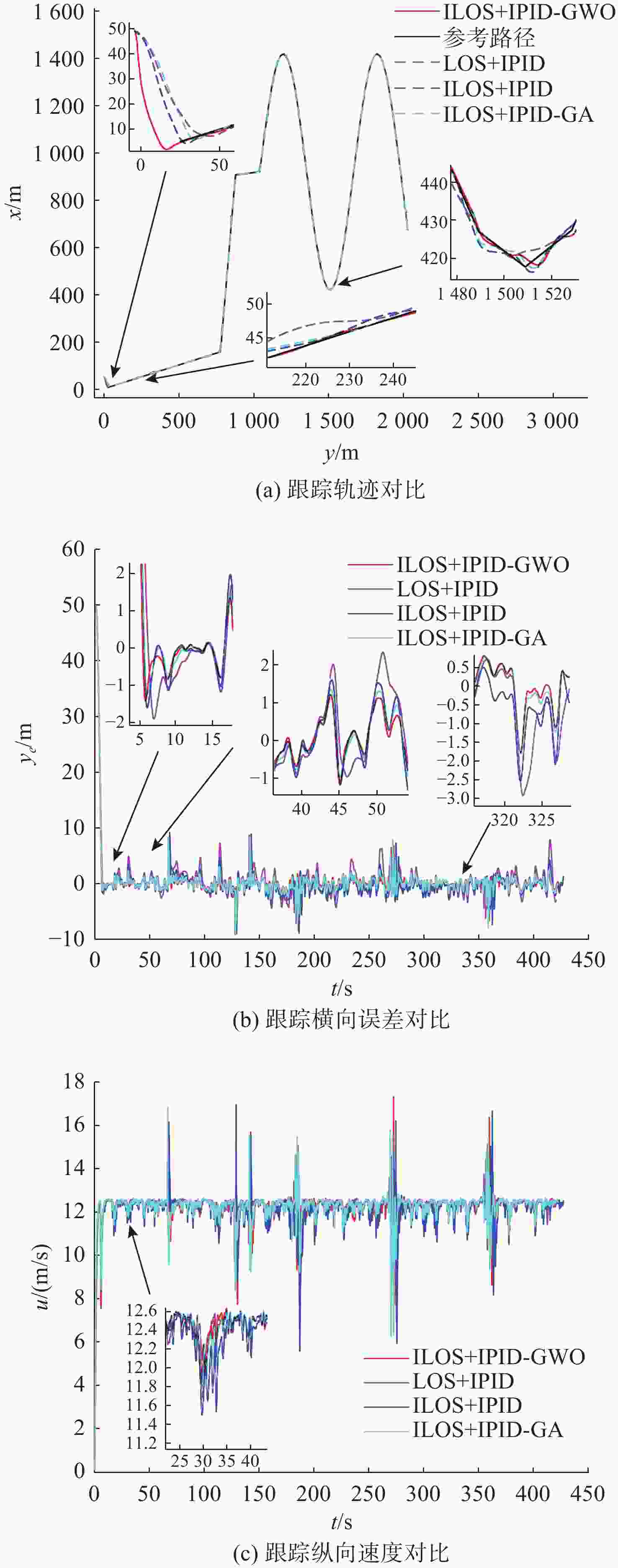
跟踪时间/s $ {y_e} $绝对值和 $ u $方差 无干扰 有干扰 无干扰 有干扰 部分直线-无干扰 部分直线-有干扰 部分直线-无干扰 部分直线-有干扰 LOS+IPID 400.5 407.9 2 746.4 7 583.1 10.914 4 563.794 7 0.002 058 0.034 333 ILOS+IPID 404.2 415.0 2 694.0 5 903.0 30.240 5 397.614 7 0.012 211 0.092 868 ILOS+IPID-GA 403.8 410.2 2 685.4 4 826.3 30.520 6 308.041 4 0.008 972 0.044 648 ILOS+IPID-GWO 406.3 408.6 2 536.5 3 760.9 25.458 2 197.470 7 0.003 199 0.018 585 -
[1] 孙佳宇, 段富海. 基于AKF的无人水翼航行器纵向姿态控制研究[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2023, 44(2): 108-112.SUN J Y, DUAN F H. Research on longitudinal attitude control of unmanned hydrofoil vehicles based on AKF[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2023, 44(2): 108-112. [2] 王宁, 贾薇, 吴浩峻. 欠驱动无人船路径跟踪: 一种有限时间正切漂角视线制导方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2025, 40(1): 187-195.WANG N, JIA W, WU H J. Path following of underactuated marine vehicles: A finite-time sideslip-tangent LOS guidance approach[J]. Control and Decision, 2025, 40(1): 187-195. [3] 马天珩, 宁杨阳. 基于非线性模型预测控制的无人船航迹跟踪控制方法[J]. 船舶工程, 2023, 45(2): 123-130, 166.MA T H, NING Y Y. Trajectory tracking control method of unmanned surface vehicles based on nonlinear model predictive control[J]. Ship Engineering, 2023, 45(2): 123-130,166. [4] LIU Z, SONG S, YUAN S, et al. ALOS-Based USV path-following control with obstacle avoidance strategy[J]. Journal of Marine Science & Engineering, 2022, 10(9): 1203. [5] FAN Z, XU Y, FU M. Finite-time command filtered backstepping control for USV path following[C]//OCEANS 2023-Limerick. Limerick, Ireland: IEEE, 2023: 1-6. [6] MIRJALILI S, MIRJALILI S M, LEWIS A. Grey wolf optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 69(3): 46-61. [7] 王泽文. 水面无人驾驶的动力学建模与路径跟踪控制算法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021. [8] 任帅. 固定双桨推进无人船的自抗扰运动控制研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2019. [9] 林孝工, 丁福光, 赵大威. 无人船状态估计和路径跟踪控制[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2022. [10] SHAMSUDDIN P N F B M, MANSOR M A B. Motion control algorithm for path following and trajectory tracking for unmanned surface vehicle: A review paper[C]//2018 3rd International Conference on Control, Robotics and Cybernetics. Penang, Malaysia: IEEE, 2018. [11] FOSSEN T I, BREIVIK M, SKJETNE R. Line-of-sight path following of underactuated marine craft[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2003, 36(21): 211-216. doi: 10.1016/S1474-6670(17)37809-6 [12] 韩鹏, 刘志林, 周泽才, 等. 基于LOS法的自航模航迹跟踪控制算法实现[J]. 应用科技, 2018, 45(3): 5. doi: 10.11991/yykj.201706005HAN P, LIU Z L, ZHOU Z C, et al. Path tracking control algorithm based on LOS method for surface selfpropulsion vessel[J]. Applied Science and Technology, 2018, 45(3): 5. doi: 10.11991/yykj.201706005 [13] 裴志远, 戴永寿, 李立刚, 等. 无人船运动控制方法综述[J]. 海洋科学, 2020, 44(3): 153-162.PEI Z Y, DAI Y S, LI L G, et al. Overview of unmanned surface vehicle motion control methods[J]. Marine Sciences, 2020, 44(3): 153-162. [14] 陈霄, 刘忠, 罗亚松, 等. 海洋环境下欠驱动无人艇航迹跟踪控制算法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2018, 50(10): 8.CHEN X, LIU Z, LUO Y S, et al. Path tracking control algorithm for the underactuated USV in the marine environment[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018, 50(10): 8. [15] LIU S, XU C, ZHANG L. Hierarchical robust path following control of fully submerged hydrofoil vessels[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 21472-21487. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2756852 [16] 黄凤娇, 杨雪, 许祥威. 改进增量式PID算法在物料分拣流水线中的应用[J]. 兵工自动化, 2020, 39(9): 4.HUANG F J, YANG X, XU X W. Application of improved incremental PID algorithm in material sorting pipeline[J]. Ordnance Industry Automation, 2020, 39(9): 4. [17] JIANG W X. Enhancing the application of the grey wolf optimizer algorithm in USV path planning: A research study[C]//Third International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communication Engineering. Changsha, China: SPIE, 2024: 130730N.1-130730N.7. -





 下载:
下载: