Underwater Adaptive End Effector Based on Biomimetic Grasping Mechanism of Soft-Rigid Gripper
-
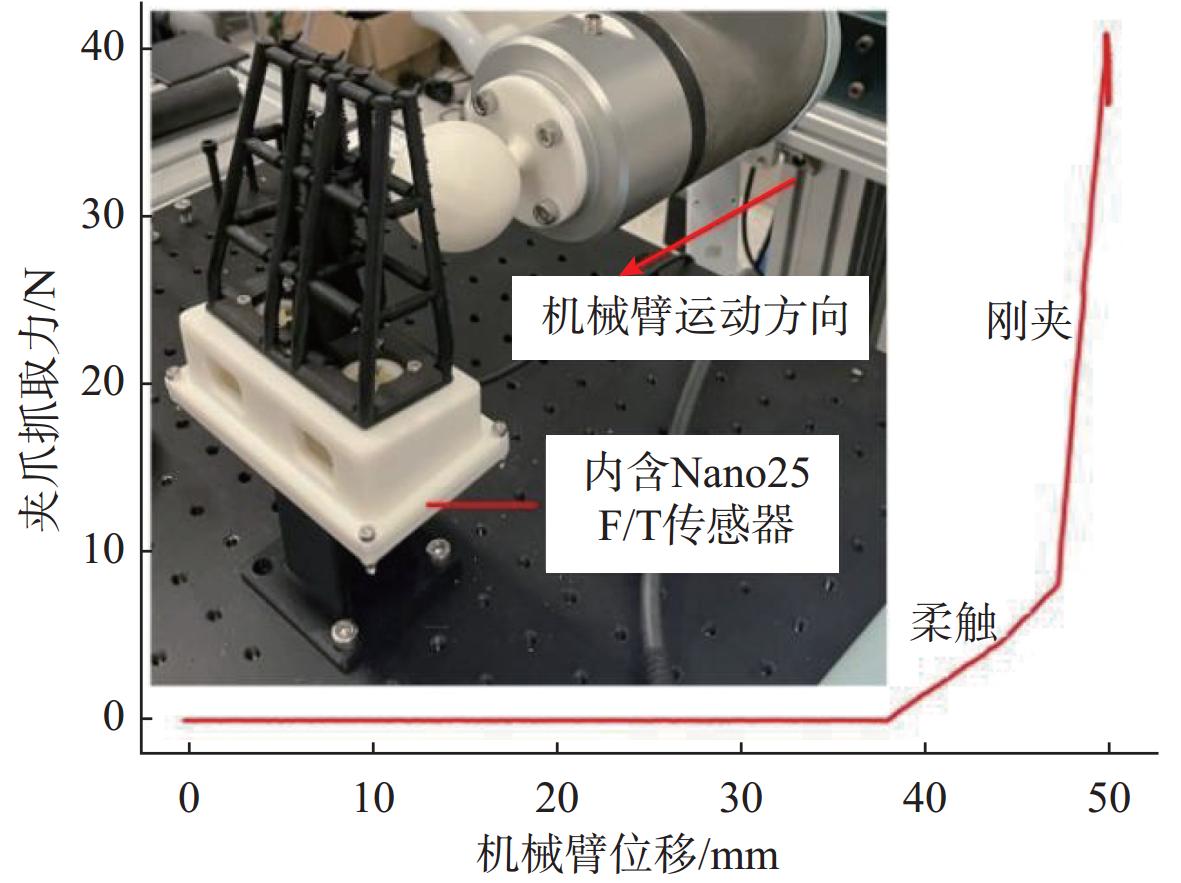
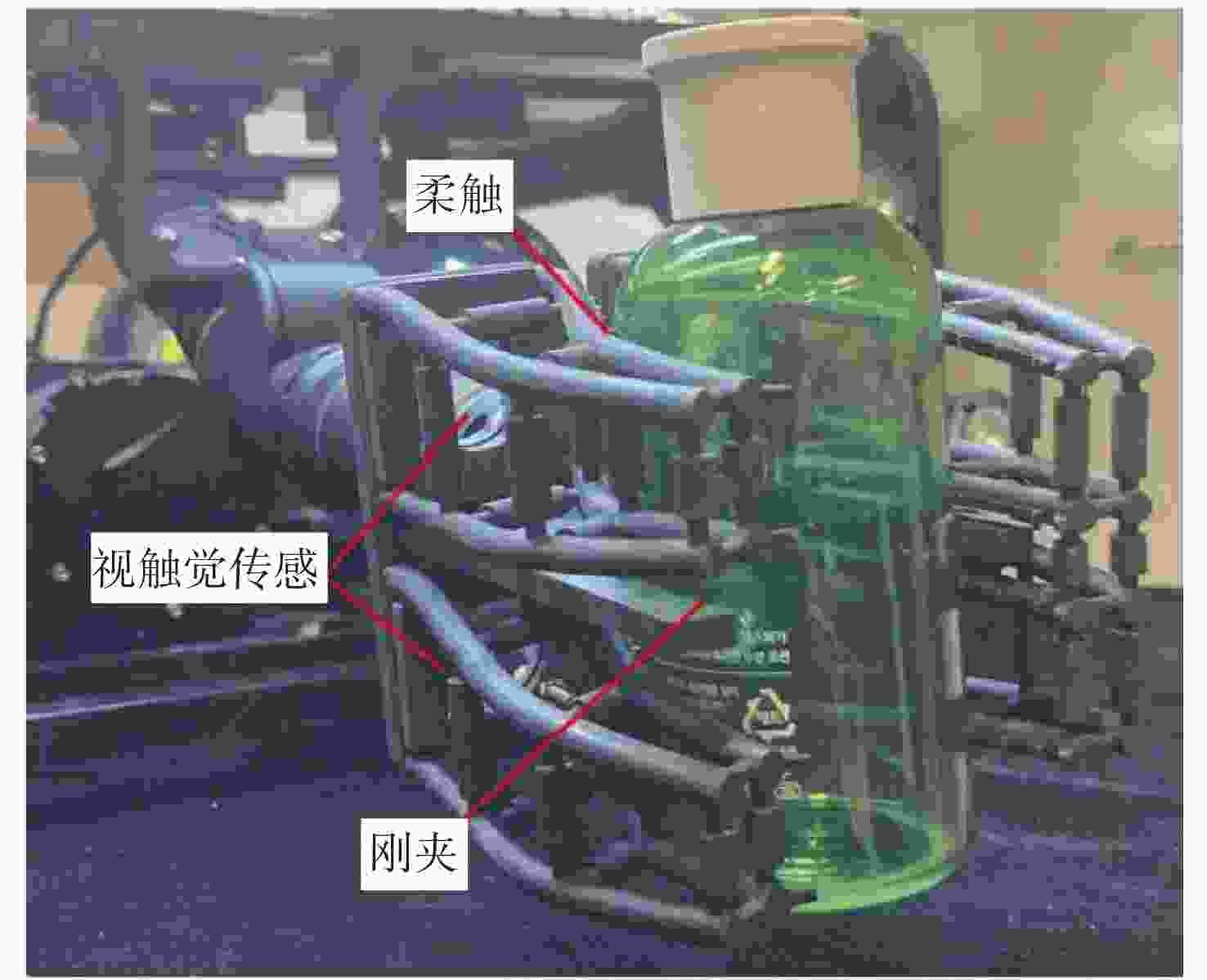
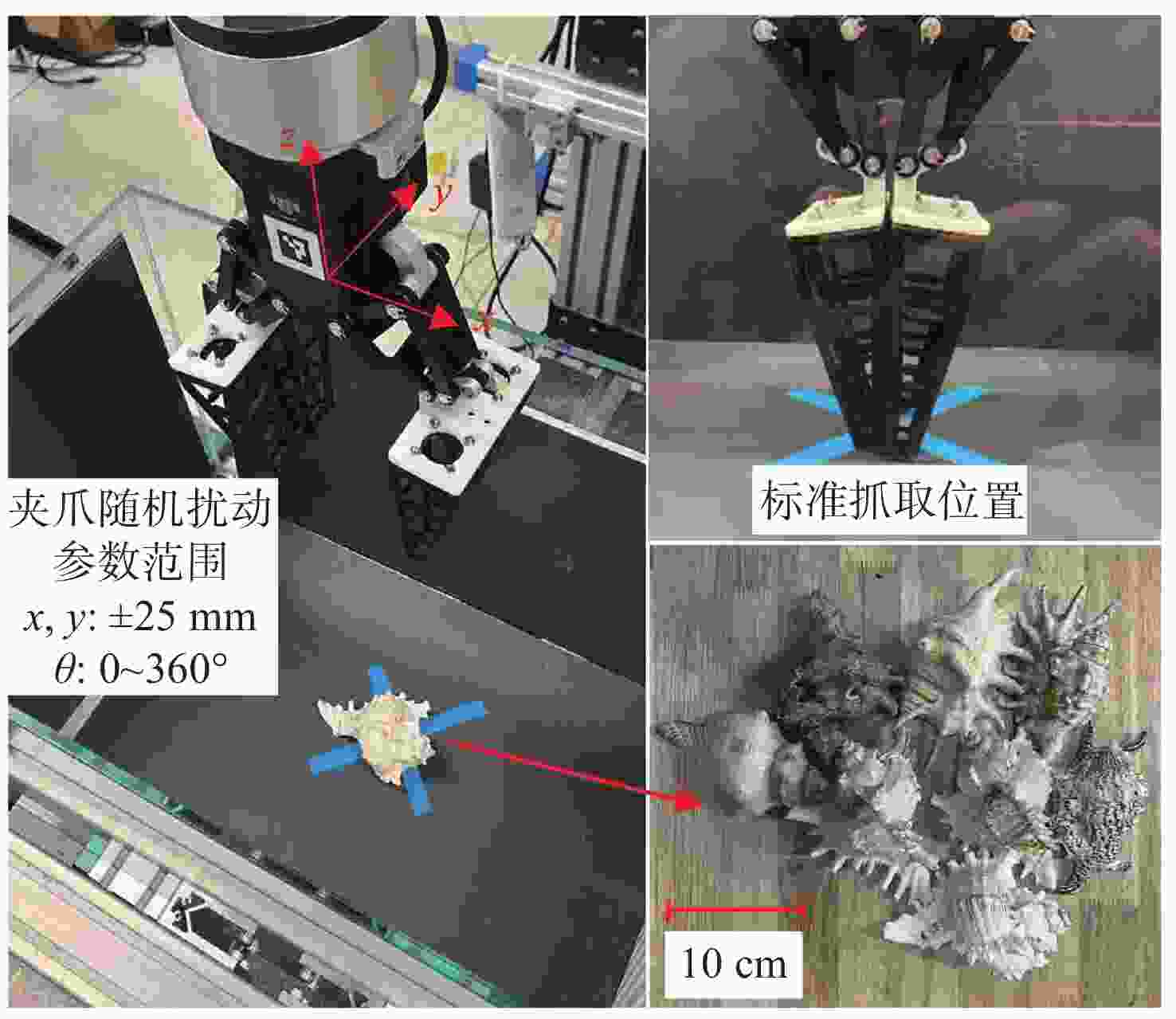
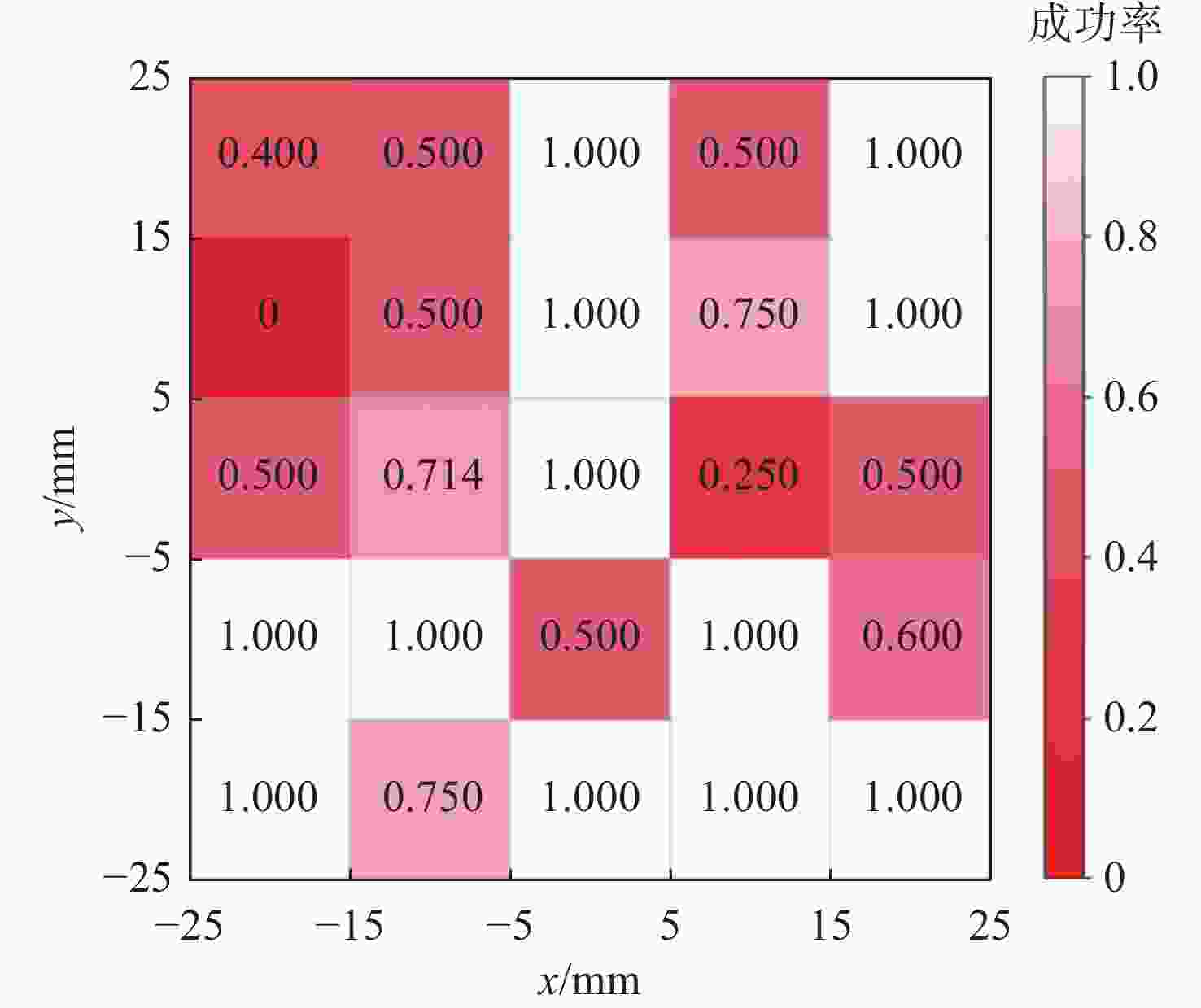
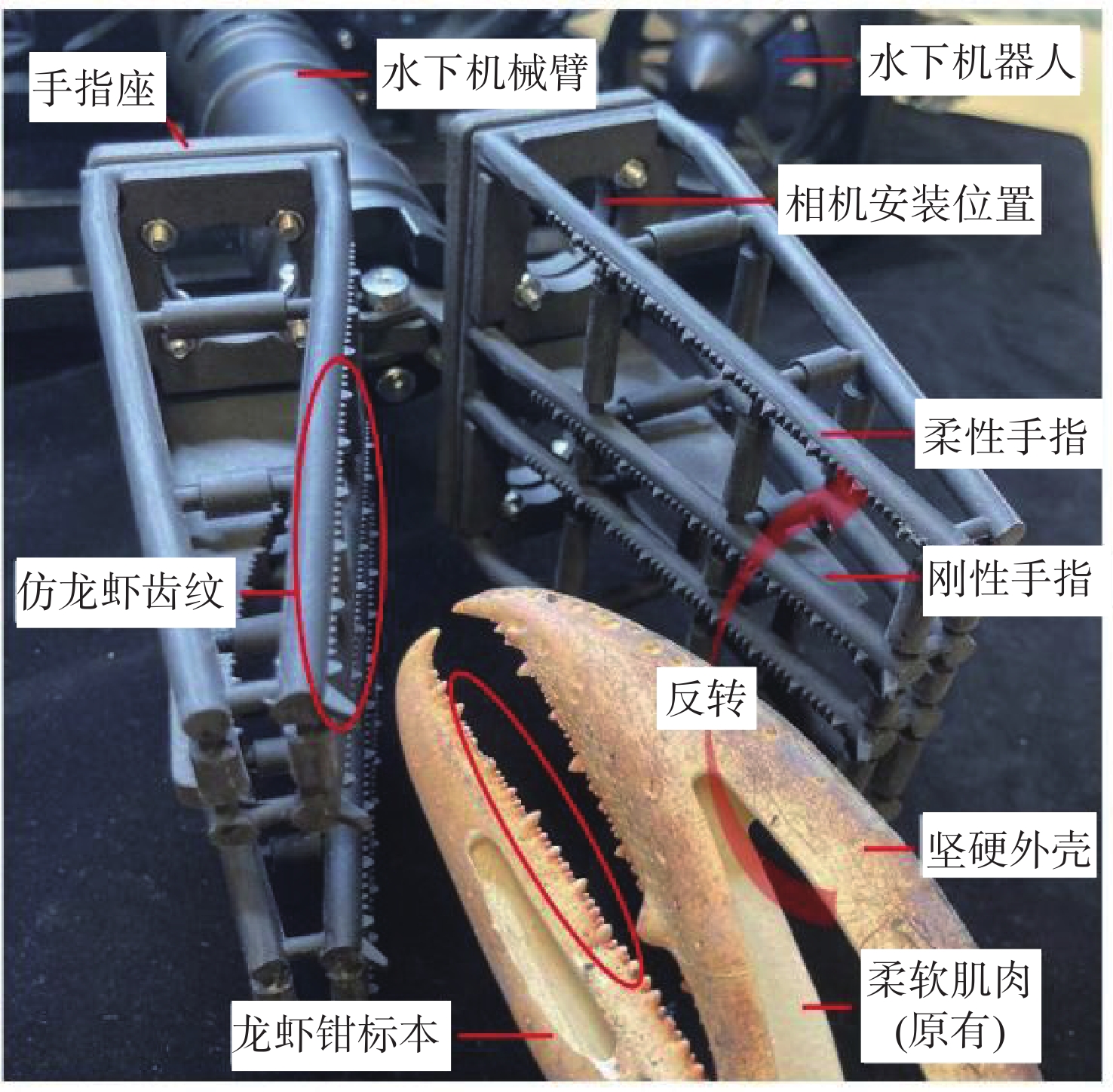
摘要: 水下夹爪作为水下无人装备的末端执行器,其性能直接决定任务执行效能。当前商业夹爪难以同时满足强负载与高适应性需求, 难以兼顾“无损抓取”与“强力持握”的双重要求。文中提出一种新型仿生刚柔耦合夹爪设计LobSTER Gripper, 灵感源自龙虾钳部生物结构。该夹爪采用“柔性指外覆刚性指”的仿生反转结构: 通过具有被动全向适应性的软体手指实现初始“柔触”包络, 再由内部刚性手指提供可靠“刚夹”持握, 无需复杂驱动控制即可分阶段完成刚度切换, 并可以在手指底部集成视触觉传感实现水下目标的精准感知与稳定抓取。实验验证显示, 该夹爪在位姿扰动场景下抓取成功率达100%, 显著优于传统刚性夹爪的80%。这一设计为水下自适应抓取提供了低成本、高可靠性的易迁移解决方案, 具备显著的工程应用价值与推广前景。Abstract: The underwater gripper serves as the end effector of underwater unmanned equipment, and its performance directly determines the effectiveness of the mission. Currently, commercial grippers are difficult to simultaneously meet the requirements of high load capacity and high adaptability, and it is hard to balance the dual demands of “non-destructive grasping” and “firm holding”. Inspired by lobster claws, this study proposed a novel biomimetic rigid-soft gripper, the “LobSTER Gripper”. It used a biomimetic reversed structure of soft fingers coated with rigid fingers: The soft fingers with passive compliance provided gentle initial contact, while internal rigid fingers ensured firm holding, enabling phased stiffness adaptation without complex drive control, it can also integrate visuo-tactile sensing at the base of the fingers to achieve precise perception and stable grasping of underwater targets. Experimental verification shows that the gripper achieves a 100% success rate in grasping in the pose disturbance scenario, significantly outperforming the traditional rigid gripper, which has an 80% success rate. The design offers a low-cost, reliable, and easily transferable solution for adaptive underwater grasping with significant engineering application value and promising promotion prospects.
-
Key words:
- underwater grasping /
- underwater gripper /
- biomimetic design /
- tactile sensing /
- soft-rigid gripper
-
表 1 近年水下夹爪及其触觉传感信息汇总
Table 1. Summary of recent years’ underwater gripper designs and tactile sensing information
文献 年份 刚柔
特性驱动方式 传感器类型 传感信息 [9] 2022 柔性 液压驱动 流量估计器 目标尺寸 [10] 2022 刚性 电机启动 摩擦电传感器 硬度 [11] 2023 柔性 液压驱动 霍尔传感器 力/硬度 [12] 2023 柔性 液压驱动 — — [13] 2023 柔性 形状记忆
合金驱动— — [14] 2024 柔性 液压驱动 — — [15]-[18] 2024 柔性 电机驱动 视触觉传感器 力/接触/
形状重建[19] 2024 刚柔
耦合电机驱动 立柱传感器 力 [20] 2025 刚柔
耦合伺服电机驱动 — — [21] 2025 柔性 气压驱动 — — [22]-[23] 2025 柔性 气压驱动 摩擦电
传感器目标形状/
硬度[24] 2025 刚柔
耦合气压驱动 — — -
[1] LIU Y, ZHANG J, XIANG X, et al. Design, implementation and verification of hardware-in-the-loop control system for work-class ROVs[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 313: 119605. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.119605 [2] MAZZEO A, AGUZZI J, CALISTI M, et al. Marine robotics for deep-sea specimen collection: A systematic review of underwater grippers[J]. Sensors 2022, 22(2): 648. [3] SIVČEV S, COLEMAN J, OMERDIĆ E, et al. Underwater manipulators: A review[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 163: 431-450. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.06.018 [4] ZHANG Y, KONG D, SHI Y, et al. Recent progress on underwater soft robots: Adhesion, grabbing, actuating, and sensing[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2023, 11: 1196922. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1196922 [5] STUART H S, WANG S, CUTKOSKY M R. Tunable contact conditions and grasp hydrodynamics using gentle fingertip suction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2019, 35(2): 295-306. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2018.2880094 [6] LICHT S, COLLINS E, MENDES M L, et al. Stronger at depth: Jamming grippers as deep sea sampling tools[J]. [J]. Soft Robotics, 2017, 4(4): 305-316. doi: 10.1089/soro.2017.0028 [7] SUN J, ZHANG Q, LU Y, et al. A review of touching-based underwater robotic perception and manipulation[J]. Machines, 2025, 13(1): 41. doi: 10.3390/machines13010041 [8] 李原正, 王天润, 关堂镇, 等. 基于液态金属型摩擦纳米发电的水下仿生触须传感器[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(5): 794-800.LI Y Z, WANG T R, GUAN T Z, et al. Underwater biomimetic whisker sensor based on liquid metal and triboelectric nanogenerator[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(5): 794-800. [9] WU M, ZHENG X, LIU R, et al. Glowing sucker octopus (stauroteuthis syrtensis)-inspired soft robotic gripper for underwater self-adaptive grasping and sensing[J]. [J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(17): 2104382. doi: 10.1002/advs.202104382 [10] XU P, LIU J, LIU X, et al. A bio-inspired and self-powered triboelectric tactile sensor for underwater vehicle perception[J]. npj Flexible Electronics, 2022, 6(1): 25. doi: 10.1038/s41528-022-00160-0 [11] LIU S, ZHANG D, FU X, et al. Tactile sensing for soft robotic manipulators in 50 MPa hydrostatic pressure environments[J]. Advanced Intelligent Systems, 2023, 5(12): 2300296. doi: 10.1002/aisy.202300296 [12] JI H, LAN Y, NIE S, et al. Development of an anthropomorphic soft manipulator with rigid-flexible coupling for underwater adaptive grasping[J]. Soft Robotics, 2023, 10(6): 1070-1082. doi: 10.1089/soro.2022.0215 [13] VAR S C, JOVANOVA J. Design of a soft underwater gripper with SMA actuation[C]//ASME 2023 Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems(ASME). Austin, Texas, USA: ASME, 2023: 111702. [14] WU M, AFRIDI W H, WU J, et al. Octopus-inspired underwater soft robotic gripper with crawling and swimming capabilities[J]. Research, 2024, 7: 456. doi: 10.34133/research.0456 [15] GUO N, HAN X D, ZHONG S Q, et al. Proprioceptive state estimation for amphibious tactile sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2024, 40: 4662-4676 . doi: 10.1109/TRO.2024.3463509 [16] GUO N, HAN X, LIU X, et al. Autoencoding a soft touch to learn grasping from on-land to underwater[J]. Advanced Intelligent Systems, 2024, 6(1): 2300382. doi: 10.1002/aisy.202300382 [17] LIU X, HAN X, HONG W, et al. Proprioceptive learning with soft polyhedral networks[J]. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2024, 43(12): 1916-1935. doi: 10.1177/02783649241238765 [18] WU T, DONG Y, LIU X, et al. Vision-based tactile intelligence with soft robotic metamaterial[J]. Materials & Design, 2024, 238: 112629. [19] GALLOWAY K C, BECKER K P, PHILLIPS B, et al. Soft robotic grippers for biological sampling on deep reefs[J]. Soft robotics, 2016, 3(1): 23-33. doi: 10.1089/soro.2015.0019 [20] SUO F, HUI X, HUA P, et al. A biomimetic rigid-soft hybrid underwater gripper with compliance, stability, precise control, and high load capacity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2025, 41: 3099-3112. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2025.3562458 [21] KIM M, OH J, SON D. Layer-jamming soft gripper for improved stiffness control and underwater adhesion[J]. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2025, 77: 102322. doi: 10.1016/j.eml.2025.102322 [22] CHEN H, LI Y, XU P, et al. Octopus-inspired soft gripper with embedded triboelectric tactile sensor for underwater target recognition and grasp[J]. Nano Energy, 2025, 140: 111007. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2025.111007 [23] QU J, YUAN Q, LI Z, et al. All-in-one strain-triboelectric sensors based on environment-friendly ionic hydrogel for wearable sensing and underwater soft robotic grasping[J]. Nano Energy, 2023, 111: 108387. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2023.108387 [24] SONG Z, WANG Z, LIU B, et al. A soft gripper based on PneuNets structure with stiffness-variable-enhanced load capacity for object grasping[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2025, 383: 116253. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2025.116253 [25] SUBAD R A S I, CROSS L B, PARK K. Soft robotic hands and tactile sensors for underwater robotics[J]. Applied Mechanics, 2021, 2(2): 356-382. doi: 10.3390/applmech2020021 [26] 常宗瑜, 张扬, 郑方圆, 等. 水下机器人-机械手系统研究进展: 结构、建模与控制[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(19): 53-69. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.19.053CHANG Z Y, ZHANG Y, ZHENG F Y, et al. Research progress of underwater vehicle-manipulator systems: Configuration, modeling and control[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(19): 53-69. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.19.053 [27] ZAREBIDOKI M, DHUPIA J S, LIAROKAPIS M, et al. A cable-driven underwater robotic system for delicate manipulation of marine biology samples[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2024, 41(8): 2615-2629. doi: 10.1002/rob.22381 [28] SAKAGAMI N, TAKEUCHI K, KOGANEZAWA K. Numerical and experimental testing of underwater gripper with adjustable stiffness joints[C]//2020 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration(SII). Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2020: 1118-1122. [29] TEOH Z E, PHILLIPS B T, BECKER K P, et al. Rotary-actuated folding polyhedrons for midwater investigation of delicate marine organisms[J]. Science Robotics, 2018, 20(3): 5276. [30] LI G, WONG T W, SHIH B, et al. Bioinspired soft robots for deep-sea exploration[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 7097. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42882-3 [31] SINATRA N R, TEEPLE C B, VOGT D M, et al. Ultragentle manipulation of delicate structures using a soft robotic gripper[J]. Science Robotics, 2019, 4(33): 5425. doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.aax5425 [32] 熊啸. 水下软体机器人仿生结构设计和研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2024. [33] STUART H, WANG S, KHATIB O, et al. The ocean one hands: An adaptive design for robust marine manipulation[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2017, 36(2): 150-166. doi: 10.1177/0278364917694723 [34] MUSCOLO G G, MORETTI G, CANNATA G. SUAS: A novel soft underwater artificial skin with capacitive transducers and hyperelastic membrane[J]. Robotica, 2019, 37(4): 756-777. doi: 10.1017/S0263574718001315 [35] ZHANG J, HAN P, LIU Q, et al. The design of underwater tactile force sensor with differential pressure structure and backpropagation neural network calibration[J]. Measurement and Control, 2024, 57(2): 124-138. doi: 10.1177/00202940231194116 [36] 郭力楠. 基于压电式仿海豹胡须传感器的水下目标尾流感知技术研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2024. [37] TIAN L, FU W Y, LEI C H, et al. Chapter 1-current status of anti-EGFR agents[M]//SHI H. Novel Sensitizing Agents for Therapeutic Anti-EGFR Antibodies, New York: Academic Press. 2023:1-12. [38] MERIBOUT M, ABULE T N, DEREGE O, et al. Tactile sensors: A review[J]. Measurement, 2024, 238: 115332. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2024.115332 [39] SUBAD R A, SAIKOT M M, PARK K. Soft multi-directional force sensor for underwater robotic application[J] . Sensors, 2022; 22(10): 3850. [40] KAMPMANN P, BÜSKENS C, WANG S, et al. Adaptive control for underwater gripping systems[M]. AI Technology for Underwater Robots. Berlin: Springer, 2019. [41] JIANG H, HAN X, JING Y, et al. Rigid-soft interactive design of a lobster-inspired finger surface for enhanced grasping underwater[J]. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 2021, 8: 78717. -





 下载:
下载: