Research Status and Development Trends of Deep-sea Unmanned Equipment Control System
-
摘要: 深海无人装备作为国家海洋科技实力的战略体现, 已广泛应用于资源探测、海洋科学研究、军事安全及经济开发等核心领域。其控制系统作为实现复杂水下作业的神经中枢, 直接决定装备的任务执行效能。文章系统梳理了深海无人装备的控制理论体系, 包括传统比例-积分-微分控制、基于模型的控制、数据驱动的智能控制及多智能体控制等技术路径, 深入剖析了集中式、分层式、分布式及混合式控制架构的技术特性与工程适用性。通过对比分析导航定位、通信传输和能源供给等关键技术的研究现状, 揭示了模型不确定性、鲁棒控制性能以及多装备协同机制等行业共性挑战。研究表明, 未来控制系统将朝着人工智能深度赋能、集群化协同作业、新型通信与能源技术融合以及跨学科融合的方向发展, 为深海装备智能化转型提供理论与技术支撑。Abstract: Deep-sea unmanned equipment, as a strategic reflection of a nation’s marine scientific and technological strength, has been widely integrated into core fields such as resource exploration, marine scientific research, military security, and economic development. The control system, serving as the neural center for complex underwater operations, directly determines the mission execution efficiency of the equipment. This paper systematically combed the control theory system of deep-sea unmanned equipment, including technical paths such as traditional proportional-integral-derivative (PID) control, model-based control, data-driven intelligent control, and multi-agent control. It deeply analyzed the technical characteristics and engineering applicability of centralized, hierarchical, distributed, and hybrid control architectures. By comparing and analyzing the research status of key technologies such as navigation and positioning, communication transmission, and energy supply, the paper revealed common challenges in the industry, including model uncertainty, robust control performance, and multi-equipment collaboration mechanisms. The study shows that future control systems will develop towards deep empowerment of artificial intelligence, clustered collaborative operations, integration of new communication and energy technologies, and interdisciplinary innovation, providing theoretical and technical support for the intelligent transformation of deep-sea equipment.
-
Key words:
- deep-sea unmanned equipment /
- control theory /
- control architecture /
- key technology
-
表 1 不同控制理论特点对比
Table 1. Characteristics comparison of different control theories
类别 控制方法 优势 劣势 典型应用 传统控制 PID控制 简单稳定, 易于工程实现 无法处理非线性、时变或强扰动环境 底层运动控制 ADRC 抗强扰动, 强鲁棒性 扩张状态观测器增加计算量, 对测量噪声敏感 底层运动控制 SMC 结构简单, 强鲁棒性 存在抖振 悬停控制与轨迹跟踪 MPC 显式处理约束, 动态优化能力强 计算复杂度高, 实时性受限 轨迹跟踪与避障 自适应控制 动态适应环境变化, 鲁棒性较强 参数调整算法复杂, 暂态不稳 动态调参 智能控制 模糊控制 无需精确模型, 适合非线性系统 需先验知识, 高维系统调试困难 轨迹跟踪与避障 深度学习 端到端优化, 数据驱动 需大量标注数据, 可解释性差 图像增强与目标识别 强化学习 无需环境模型, 支持多目标优化 训练效率低, 需大量交互数据 路径规划与编组控制 表 2 不同动力电池性能对比
Table 2. Performance comparison of different power batteries
电池类型 质量能量密度/(Wh/kg) 体积能量密度/(Wh/L) 循环寿命 /次 特点 代表性装备(国别) 铅酸电池 25~45 40~80 300 稳定, 低成本, 有气体析出 Nautile(法) 银锌电池 80~110 180~200 30 稳定, 大电流放电, 高成本 Shinkai 6500(日) 锂离子电池 120~270 320~750 >500 相对稳定, 高能量密度 “思源号”(中) 固态电池 220~550 450~ 1200 > 1000 高能量密度, 技术尚未成熟 “探索一号”(中) 燃料电池 500~700 1000 ~1200 需解决深海燃料存储问题 Hugin(挪) -
[1] 梁波, 赵宏宇, 王楠. 水下机器人在中国的早期发展[J]. 科学, 2022(3): 53-56. [2] NAKAMURA M, KOTERAYAMA W, YAMAMOTO I, et al. Control of heading angle of launcher of deep sea exploration unmanned underwater vehicle “KAIKO”[C]//Proceedings of The Sixteenth 2006 International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference. San Francisco, CA, USA: ISOPE, 2006: 213-220. [3] FENUCCI D, FANELLI F, CONSENSI A, et al. A multi-platform guidance, navigation and control system for the autosub family of autonomous underwater vehicles[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2024, 146: 105902. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2024.105902 [4] ALLEN B, STOKEY R, AUSTIN T, et al. REMUS: A small, low cost AUV; system description, field trials and performance results[C]//Oceans' 97. MTS/IEEE Conference Proceedings. Halifax, NS, Canada: IEEE, 1997: 994-1000. [5] WHITCOMB L L, JAKUBA M V, KINSEY J C, et al. Navigation and control of the Nereus hybrid underwater vehicle for global ocean science to 10903 m depth: Preliminary results[C]//2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Anchorage, Alaska, USA: IEEE, 2010: 594-600. [6] 任峰, 张莹, 张丽婷, 等. “海龙Ⅲ”号ROV系统深海试验与应用研究[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2019, 38(2): 30-35.REN F, ZHANG Y, ZHANG L T, et al. Research on the deep-sea test and application of the "Hailong Ⅲ" ROV system[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2019, 38(2): 30-35. [7] 梁一飞, 李永龙, 王皓冉, 等. 基于降阶扩张状态观测器的水下机器人自抗扰运动控制[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2024, 43(8): 141-145.LIANG Y F, LI Y L, WANG H R, et al. Active disturbance rejection motion control of ROV based on reduced order extended state observer[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2024, 43(8): 141-145. [8] 黄陶俊, 石凯, 乌云嘎, 等. 基于自抗扰控制的AUV抗洋流对接研究[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2024, 46(14): 89-96.HUANG T J, SHI K, WU Y G, et al. Research on AUV docking of anti ocean current based on active disturbance rejection control[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2024, 46(14): 89-96. [9] JING A, WANG J, GAO J, et al. Self-tuning adaptive active disturbance rejection pitch control of a manta-ray-like underwater glider[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 254: 111364. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.111364 [10] 王翻, 武建国, 王晓鸣, 等. 改进型自抗扰在ROV位姿控制中的应用[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2024, 46(14): 91-98.WANG F, WU J G, WANG X M, et al. Application of improved active disturbance rejection in ROV pose control[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2024, 46(14): 91-98. [11] 褚悦, 石泽林, 王孟军, 等. 水下航行器有限时间滑模控制[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(6): 878-884. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2022-0060CHU Y, SHI Z L, WANG M J, et al. Finite-time sliding mode control for undersea vehicles[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2023, 31(6): 878-884. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2022-0060 [12] JOE H, KIM M, YU S C. Second-order sliding-mode controller for autonomous underwater vehicle in the presence of unknown disturbances[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2014, 78(1): 183-196. doi: 10.1007/s11071-014-1431-0 [13] TAHERI E, FERDOWSI M H, DANESH M. Design boundary layer thickness and switching gain in SMC algorithm for AUV motion control[J]. Robotica, 2019(10): 1-19. [14] 孙旭瑶. 基于高阶滑模控制的水下机器人轨迹跟踪算法研究[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2023. [15] DENG S Y, HAO L Y, SHEN C. Autonomous underwater vehicle(AUV) motion design: Integrated path planning and trajectory tracking based on model predictive control(MPC)[J]. Journal of Marine Science & Engineering, 2024, 12(9): 1655. [16] XIN G, ZHOU M, YANG B, et al. Energy optimization control algorithm of underwater vehicle based on model predictive control[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2020, 103(SI): 830-834. [17] LIU Z, ZHU D, LIU C, et al. A novel path planning algorithm of AUV with model predictive control[J]. International Journal of Robotics and Automation, 2022, 37(6): 460-467. [18] ZHANG W, WANG Q, WU W, et al. Event-trigger NMPC for 3-D trajectory tracking of UUV with external disturbances[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 283: 115050. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.115050 [19] BIAN Y, ZHANG J, HU M, et al. Self-triggered distributed model predictive control for cooperative diving of multi-AUV system[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 267: 113262. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.113262 [20] TABATABA’I-NASAB F S, KEYMASI KHALAJI A, MOOSAVIAN S A A. Adaptive nonlinear control of an autonomous underwater vehicle[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2019, 41(11): 3121-3131. doi: 10.1177/0142331218823869 [21] ZHENG X, TIAN Q, ZHANG Q. Development and control of an innovative underwater vehicle manipulator system[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2023, 11(3): 548. doi: 10.3390/jmse11030548 [22] LI J, WANG Y, LI H, et al. Sliding mode control with adaptive-reaching-law-based fault-tolerant control for AUV sensors and thrusters[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2023, 11(11): 2170. doi: 10.3390/jmse11112170 [23] LU D, XIONG C, ZENG Z, et al. Adaptive dynamic surface control for a hybrid aerial underwater vehicle with parametric dynamics and uncertainties[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2019, 45(3): 740-758. [24] 熊保星, 甘文洋, 陈铭治, 等. 基于模糊线性自抗扰的水下机器人定深控制[J]. 控制工程, 2024: 1-9.XIONG B X, GAN W Y, CHEN M Z, et al. Depth control of underwater vehicle based on fuzzy linear active disturbance rejection[J]. Control Engineering, 2024: 1-9. [25] JI D, ZHOU S, REN J, et al. A prototype of newly dynamic underwater vehicle using fuzzy PID control[C]//2019 IEEE 28th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics(ISIE). Vancouver, BC, Canada: IEEE, 2019: 1121-1126. [26] CHENG C, SHA Q, HE B, et al. Path planning and obstacle avoidance for AUV: A review[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 235: 109355. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.109355 [27] LONDHE P S, SANTHAKUMAR M, PATRE B M, et al. Task space control of an autonomous underwater vehicle manipulator system by robust single-input fuzzy logic control scheme[J]. IEEE Journal of oceanic engineering, 2016, 42(1): 13-28. [28] HINTON G E, SALAKHUTDINOV R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks[J]. Science, 2006, 313(5786): 504-507. doi: 10.1126/science.1127647 [29] 郑雨帆, 王银涛, 孙琦. 基于轻量化深度网络的水下声呐目标识别方法[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2025: 1-10.ZHENG Y F, WANG Y T, SUN Q. Underwater sonar target recognition method based on lightweight deep network [J]. Command Control & Simulation, 2025: 1-10. [30] 李培坤, 李锋, 葛忠显, 等. 基于改进YOLOv8n的水下目标检测算法[J]. 电子测量技术, 2025, 48(3): 172-179.LI P K, LI F, GE Z X, et al. Underwater target detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv8n[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2025, 48(3): 172-179. [31] WANG N, CHEN T, LIU S, et al. Deep learning-based visual detection of marine organisms: A survey[J]. Neurocomputing, 2023, 532: 1-32. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.02.018 [32] 张天驰, 刘宇轩. 深度学习驱动的水下图像处理研究进展[J]. 计算机科学, 2024, 51(z1): 271-282. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.230400107ZHANG T C, LIU Y X. Research progress of underwater image processing based on deep learning[J]. Computer Science, 2024, 51(z1): 271-282. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.230400107 [33] ANWAR S, LI C. Diving deeper into underwater image enhancement: A survey[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2020, 89: 115978. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2020.115978 [34] XIA S, ZHOU X, SHI H, et al. A fault diagnosis method based on attention mechanism with application in Qianlong-2 autonomous underwater vehicle[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 233: 109049. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.109049 [35] 潘云伟, 李敏, 曾祥光, 等. 基于人工势场和改进强化学习的自主式水下潜航器避障和航迹规划[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(4): 72-83.PAN Y W, LI M, ZENG X G, et al. AUV obstacle avoidance and path planning based on artificial potential field and improved reinforcement learning[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(4): 72-83. [36] 孙玉山, 冉祥瑞, 张国成, 等. 智能水下机器人路径规划研究现状与展望[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2020, 41(8): 1111-1116. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201906048SUN Y S, RAN X R, ZHANG G C, et al. Research status and prospect of path planning for autonomous underwater vehicles[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2020, 41(8): 1111-1116. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201906048 [37] WANG Y, GAO J. Reinforcement-learning-based visual servoing of underwater vehicle dual-manipulator system[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2024, 12(6): 940. doi: 10.3390/jmse12060940 [38] 闫敬, 徐龙, 曹文强, 等. 基于深度强化学习的多潜器编队控制算法设计[J]. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(5): 1457-1463. [39] SONG D, GAN W, YAO P, et al. Guidance and control of autonomous surface underwater vehicles for target tracking in ocean environment by deep reinforcement learning[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 250: 110947. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.110947 [40] 谢伟, 陶浩, 龚俊斌, 等. 海上无人系统集群发展现状及关键技术研究进展[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2021, 16(1): 7-17, 31. [41] 赵蕊, 许建, 向先波, 等. 多自主式水下机器人的路径规划和控制技术研究综述[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2018, 13(6): 58-65. [42] HASAN M W, ABBAS N H. An adaptive neural network with nonlinear FOPID design of underwater robotic vehicle in the presence of disturbances, uncertainty, and obstacles[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 279: 114451. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114451 [43] JI D, ZHOU S, REN J, et al. A prototype of newly dynamic underwater vehicle using fuzzy PID control[C]//2019 IEEE 28th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics(ISIE). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2019: 1121-1126. [44] WANG Y, HOU Y, LAI Z, et al. An adaptive PID controller for path following of autonomous underwater vehicle based on Soft Actor-Critic[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 307: 118171. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.118171 [45] VON BENZON M, SØRENSEN F F, UTH E, et al. An open-source benchmark simulator: Control of a bluerov2 underwater robot[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2022, 10(12): 1898. doi: 10.3390/jmse10121898 [46] VALAVANIS K P, GRACANIN D, MATIJASEVIC M, et al. Control architectures for autonomous underwater vehicles[J]. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 1997, 17(6): 48-64. doi: 10.1109/37.642974 [47] PHILLIPS A B, TEMPLETON R, ROPER D, et al. Autosub long range 1500: A continuous 2000 km field trial[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 280: 114626 [48] JAFFRE F, LITTLEFIELD R, GRUND M, et al. Development of a new version of the Remus 6000 autonomous underwater vehicle[C]//OCEANS 2019-Marseille. Marseille, France: IEEE, 2019: 1-7. [49] GOLDBERG D. Huxley: A flexible robot control architecture for autonomous underwater vehicles[C]//OCEANS 2011 IEEE-Spain. Santander, Spain: IEEE, 2011: 1-10. [50] WANG J, TANG Y, LI S, et al. The Haidou-1 hybrid underwater vehicle for the Mariana Trench science exploration to 10, 908 m depth[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2024, 41(4): 1054-1079. doi: 10.1002/rob.22307 [51] XU J, DU Z, HUANG X, et al. Design and development of 10, 000-meter class autonomous underwater vehicle[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2024, 12(11): 2097. doi: 10.3390/jmse12112097 [52] LIU H, WANG Y, LEWIS F L. Robust distributed formation controller design for a group of unmanned underwater vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 51(2): 1215-1223. [53] 赵万龙, 刘功亮, 张敏, 等, 水下多源融合定位与导航技术[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2023. [54] 邢奥成, 李海兵, 阚宝玺, 等. 海洋地磁导航关键技术及发展趋势[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2025, 12(2): 1-14.XING A C, LI H B, KAN B X, et al. Review of key technologies and development trends in marine geomagnetic navigation[J]. Navigation Positioning and Timing, 2025, 12(2): 1-14. [55] 兰天, 李鼎, 娄琪欣, 等. 水下地形辅助导航算法综述[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2025, 12(1): 14-28. [56] ZHANG S, ZHAO S, AN D, et al. Visual SLAM for underwater vehicles: A survey[J]. Computer Science Review, 2022, 46: 100510. doi: 10.1016/j.cosrev.2022.100510 [57] YANG H, XU Z, JIA B. An underwater positioning system for UUVs based on LiDAR camera and inertial measurement unit[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(14): 5418. doi: 10.3390/s22145418 [58] 杨健敏, 王佳惠, 乔钢, 等. 水声通信及网络技术综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(1): 1-21. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230424 [59] FARR N, WARE J, PONTBRIAND C, et al. Optical communication system expands CORK seafloor observatory's bandwidth[C]//OCEANS 2010 MTS/IEEE SEATTLE. Seattle, Washington, USA: IEEE, 2010: 1-6. [60] 韩笑天. 水下长距离无线光通信若干关键技术研究 [D]. 西安: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所), 2024. [61] BOWEN A D, YOERGER D R, TAYLOR C, et al. The Nereus hybrid underwater robotic vehicle for global ocean science operations to 11, 000 m depth[C]//OCEANS 2008. Quebec City, QC, Canada: IEEE, 2008. [62] 李围, 杨创, 赵胜. 基于CAN总线的全海深锂离子电池组监测系统设计[J]. 船电技术, 2022, 42(10): 80-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4862.2022.10.020 [63] 苑志祥, 张浩, 张雪, 等. 深潜器用蓄电池的研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2023, 51(11): 2868-2875. [64] KWON L, KANG J G, BAIK K D, et al. Advancement and applications of PEMFC energy systems for large-class unmanned underwater vehicles: A review[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 79: 277-294. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.07.016 -




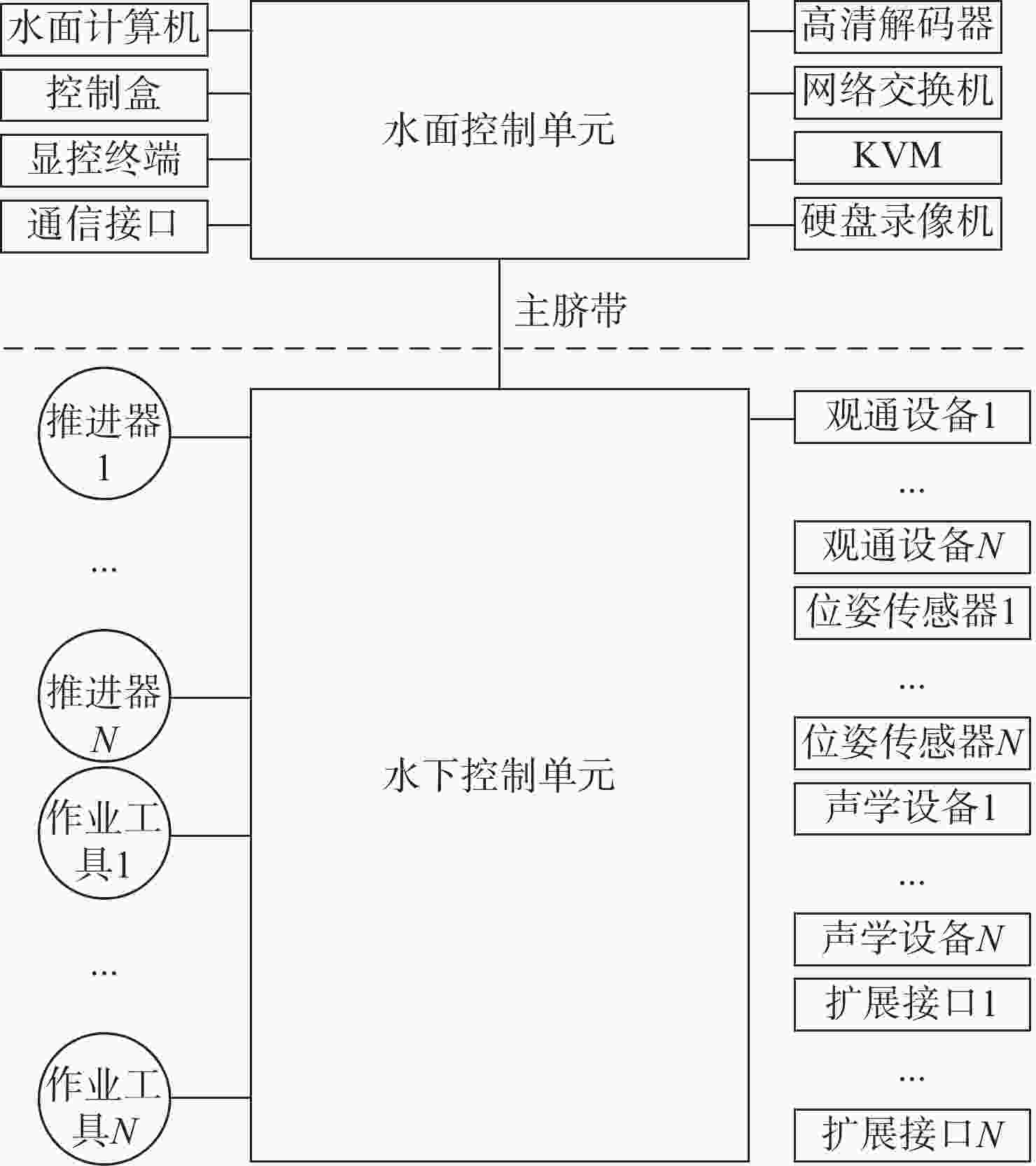
 下载:
下载: