Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Based on One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network with Attention Mechanism
-
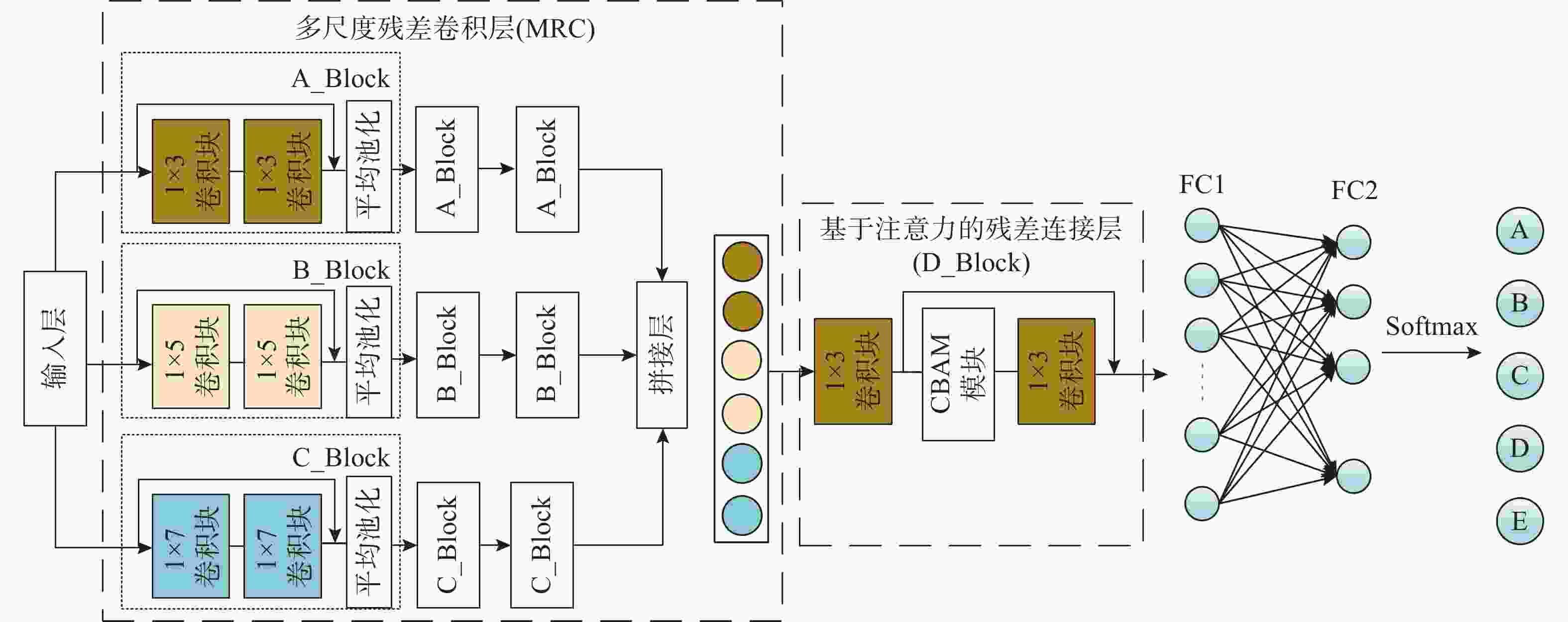
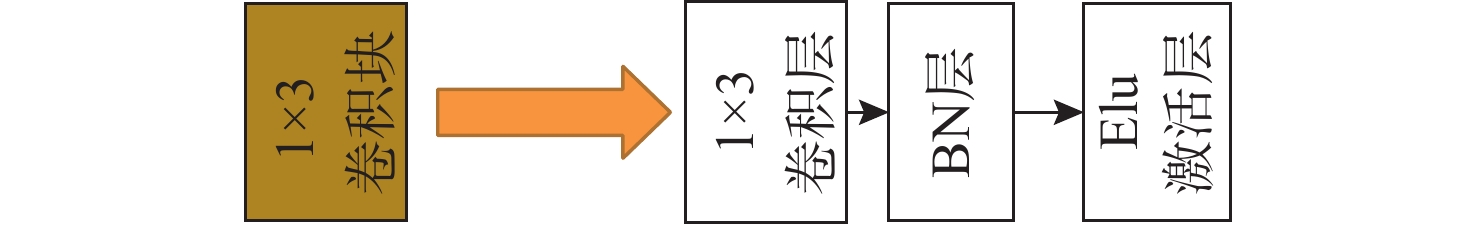
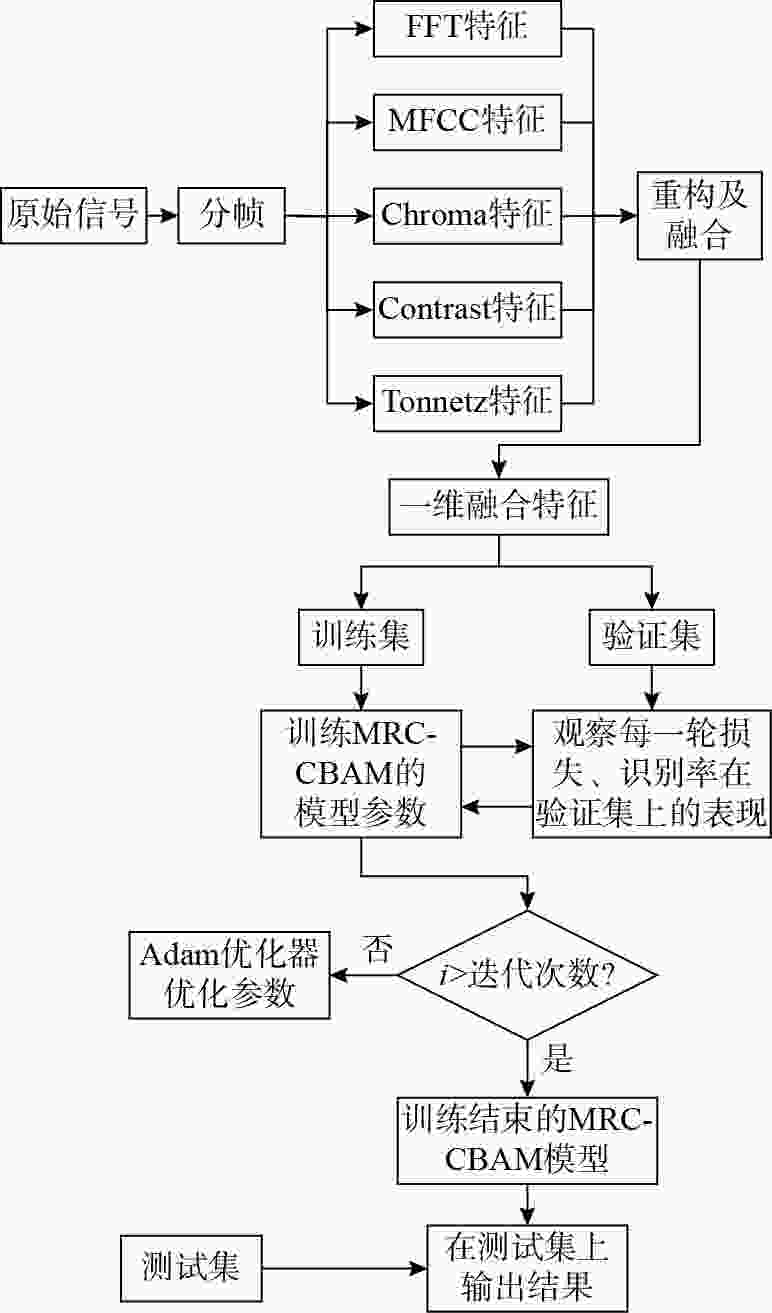
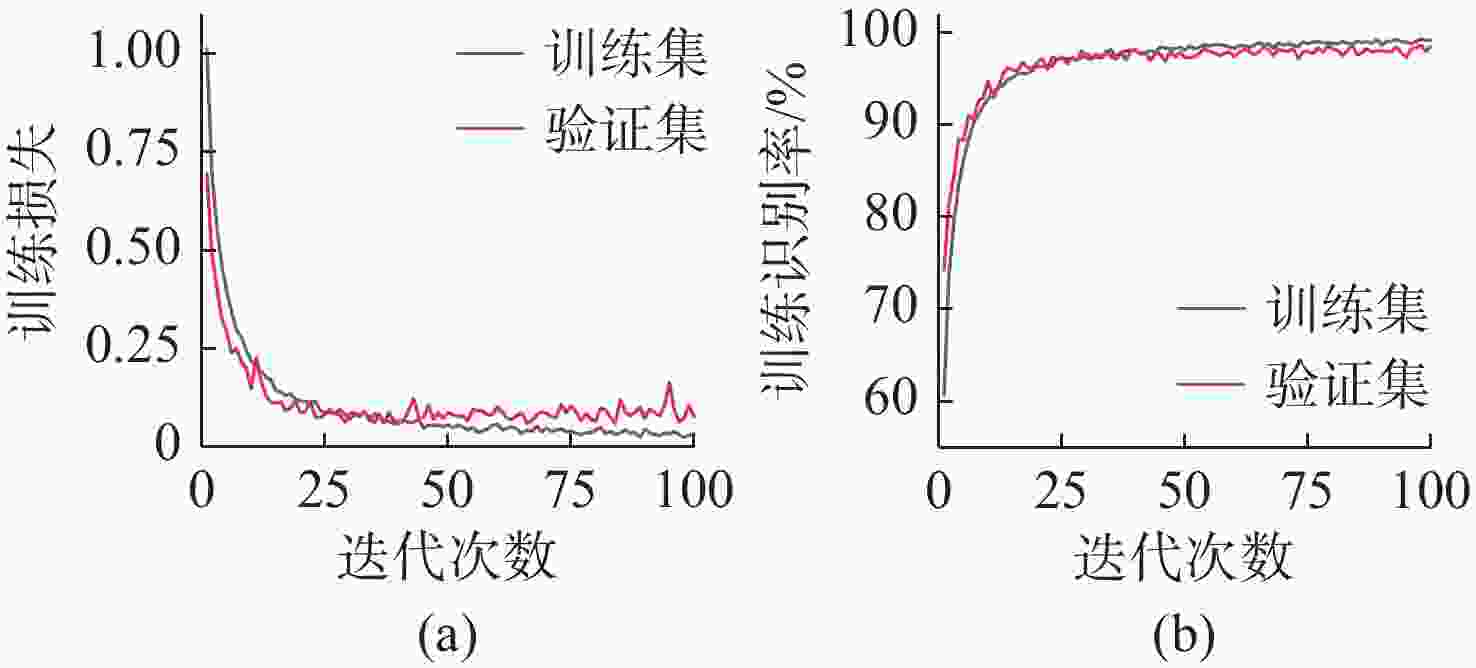
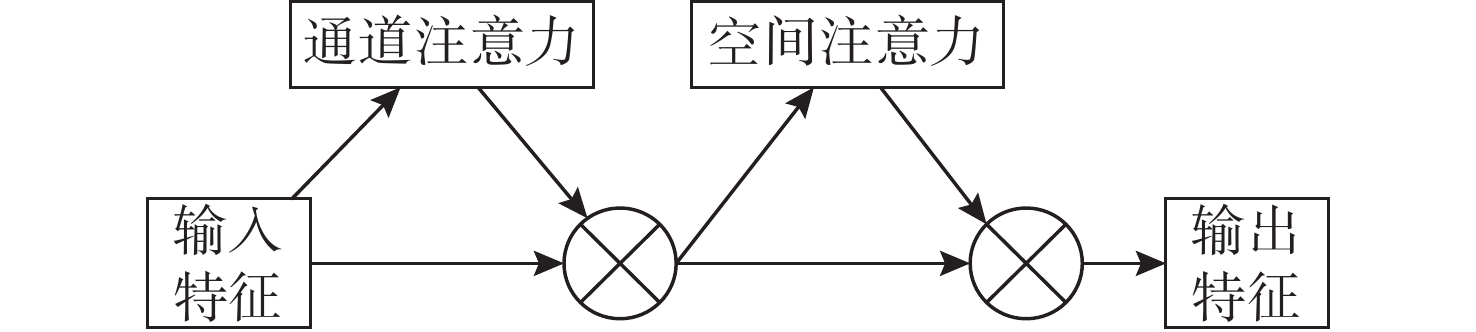
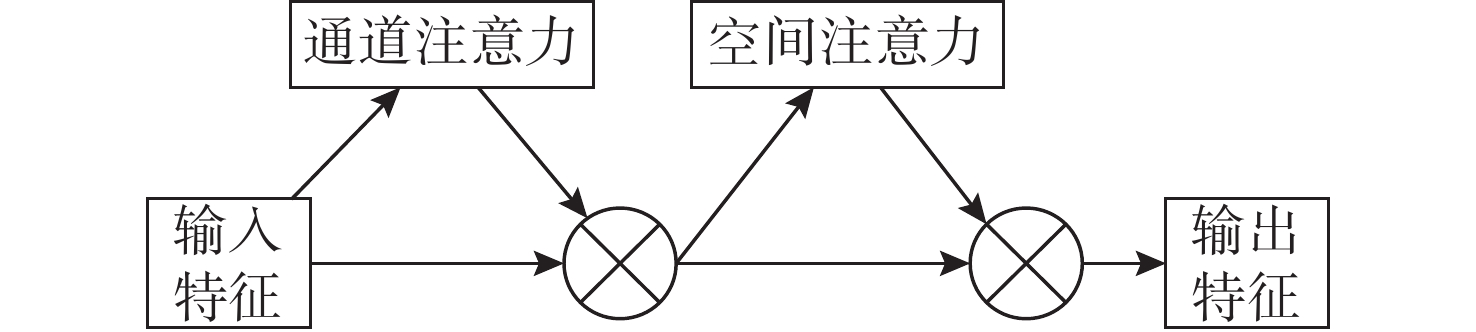
摘要: 针对基于深度学习的水声目标识别模型存在网络参数复杂、计算成本高等问题, 提出一种轻量级一维注意力机制卷积神经网络水声目标识别模型。首先, 在特征提取阶段, 选择频谱、梅尔谱、色度、谱对比度和色调特征, 将其重构并融合为一维混合特征; 之后, 通过多尺度残差卷积(MRC)以增强混合特征在不同尺度上的特征表达能力; 同时, 引入卷积注意力模块(CBAM), 通过通道注意力和空间注意力模块自适应地调整特征权重, 提升模型对关键区域的关注。实验结果表明, 该模型在ShipsEar数据集上的平均识别率达到98.58%, 表现出良好的分类效果, 且运算量大大减少。Abstract: To address the issues of complex network parameters and high computational costs in deep learning-based underwater acoustic target recognition models, this study proposed a lightweight one-dimensional convolutional neural network with an attention mechanism for underwater acoustic target recognition. First, during the feature extraction stage, spectral, Mel-spectrogram, chroma, spectral contrast, and tonal features were selected and reconstructed into a fused one-dimensional hybrid feature. Next, the hybrid feature was processed by a multi-scale residual convolution(MRC) module to enhance feature representation across different scales. Simultaneously, a convolutional block attention module(CBAM) was introduced to adaptively adjust feature weights through channel and spatial attention modules, improving the model’s focus on critical regions. Experimental results show that the proposed model achieves an average recognition accuracy of 98.58% on the ShipsEar dataset, demonstrating excellent classification performance and significantly reducing computational complexity.
-
表 1 各模块输出大小及运算量
Table 1. Output size and computational volumes of each module
模块 输入大小 输出大小 运算量 A_Block (1, 1, 2 000) (1, 16, 500) 2.5×103 B_Block (1, 1, 2 000) (1, 16, 500) 4.1×103 C_Block (1, 1, 2 000) (1, 16, 500) 5.7×103 拼接层 (1, 16, 31) (1, 48, 31) 12.3×103 D_Block (1, 48, 31) (1, 16, 31) 4.3×103 FC1 (1, 16, 31) (1, 1, 256) 127×103 FC2 (1, 1, 256) (1, 1, 16) 54.1×103 表 2 ShipsEar数据集样本分类
Table 2. Sample classification of the ShipsEar dataset
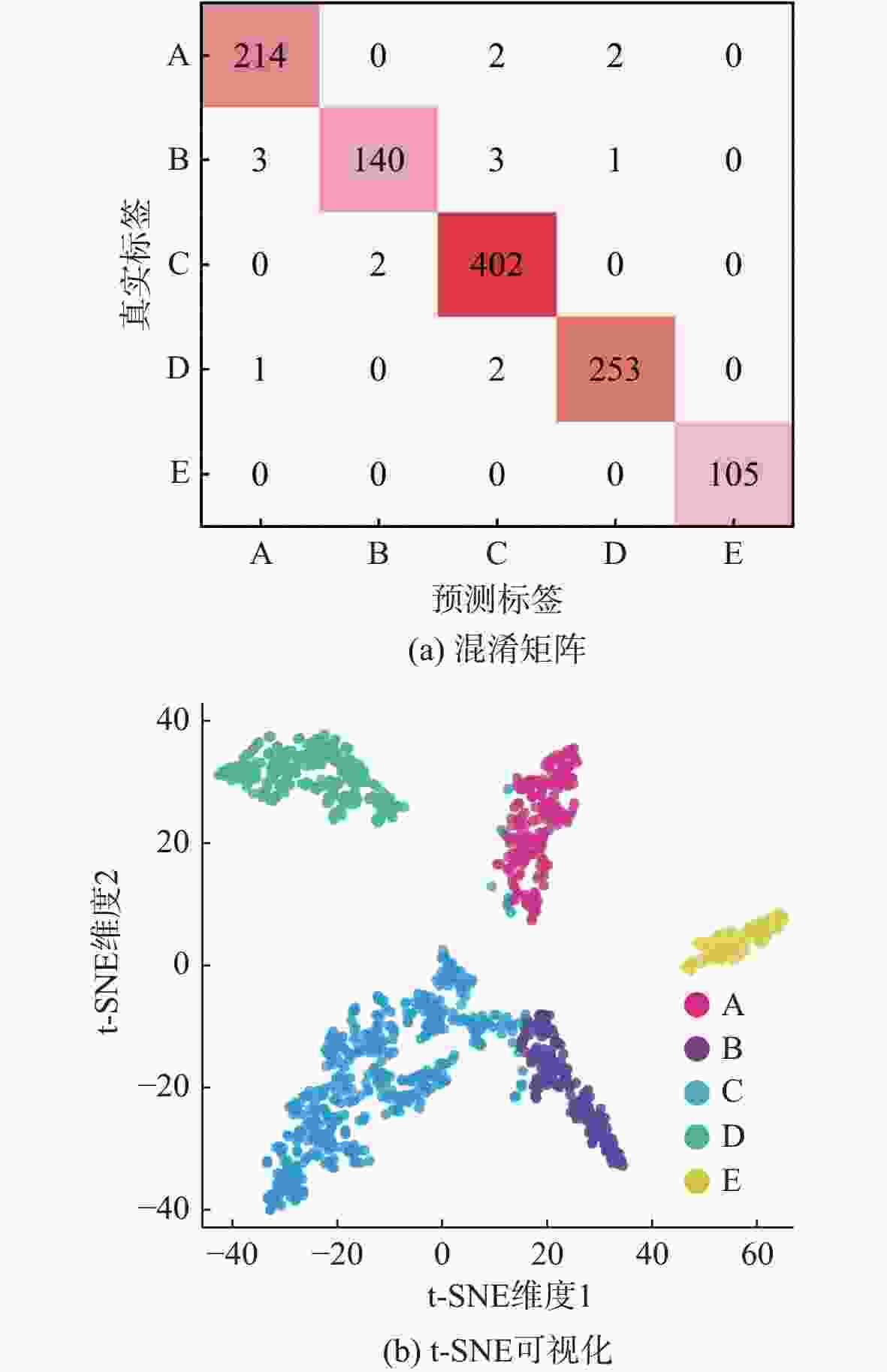
分类 船只种类 样本数 A 挖泥船/渔船/贻贝船/拖网渔船/拖船 1 875 B 摩托艇/引航船/帆船 1 560 C 客船 4 270 D 邮轮/滚装船 2 455 E 自然噪声 1 140 表 3 不同特征重构前后维度大小
Table 3. Dimensional sizes of features before and after reconstruction
特征 原始大小 重构后大小 FFT 1×1 000 1×1 000 MFCC 25×20 1×500 Chorma 12×20 1×240 Contrast 6×20 1×120 Tonnetz 6×20 1×120 表 4 模型参数设置
Table 4. Parameterization of the model
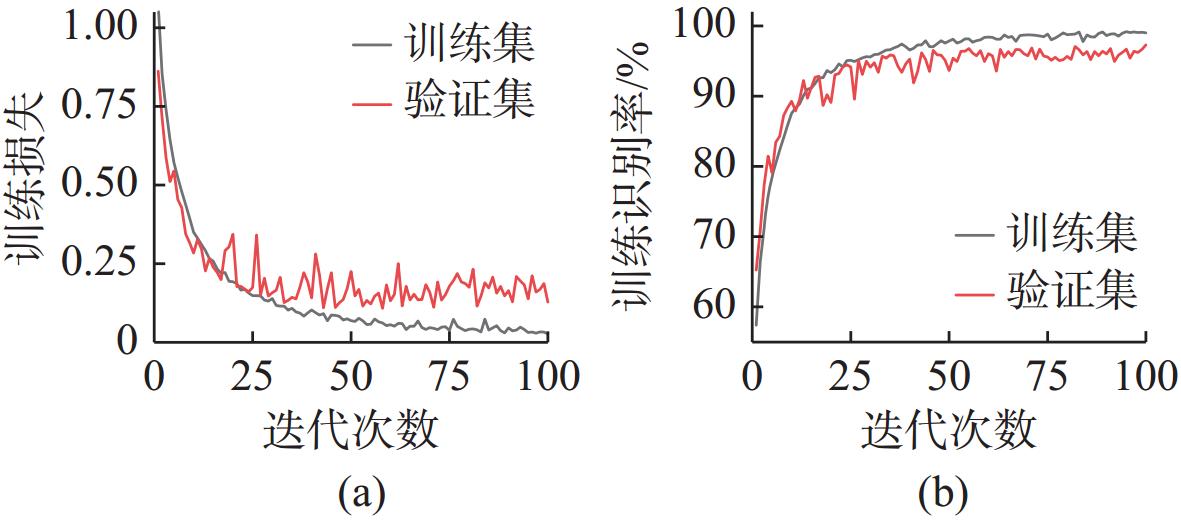
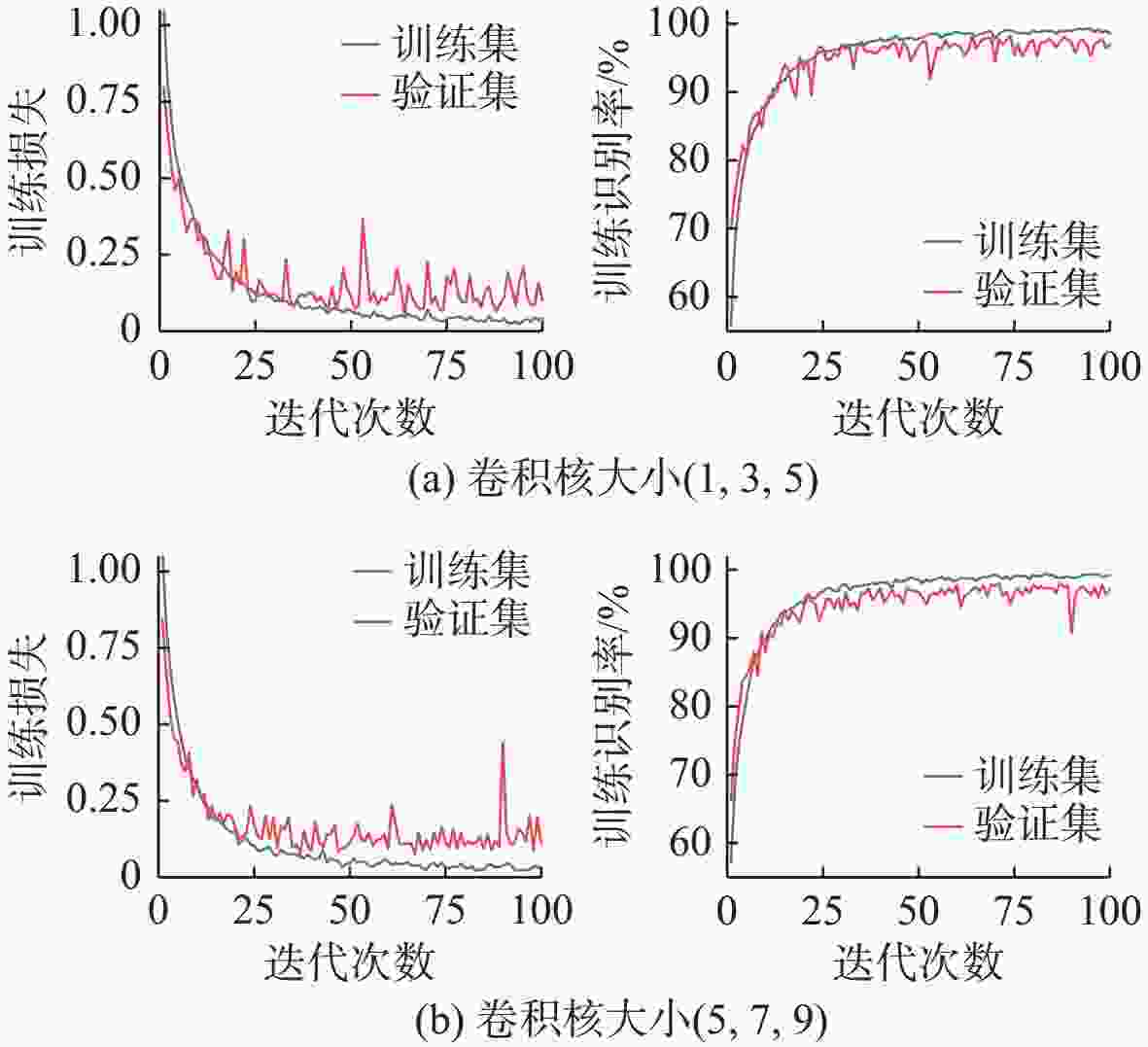
参数选择 参数设置 学习率 10−3 迭代次数 100 优化器 Adam 损失函数 交叉熵损失函数 训练批次 64 表 5 不同信噪比下模型识别率
Table 5. Recognition rates of the model under different signal-to-noise ratios
信噪比/dB 识别率/% A B C D E 5 97.01 95.88 97.28 99.18 100 0 93.40 93.03 95.62 98.74 97.87 −5 96.39 90.41 93.03 94.67 94.06 −10 88.06 77.70 85.45 95.45 93.85 −15 77.90 70.80 78.99 82.37 87.00 −20 64.24 52.94 74.07 66.80 80.86 表 6 不同输入特征下模型识别率
Table 6. Model recognition rates with different input features
输入特征 识别率/% FFT 97.32 MFCC 97.43 FFT+MFCC 98.32 FMCCT 98.58 -
[1] 徐及, 黄兆琼, 李琛, 等. 深度学习在水下目标被动识别中的应用进展[J]. 信号处理, 2019, 35(9): 1460-1475.XU J, HUANG Z Q, LI C, et al. Advances in applications of deep learning in passive underwater target recognition[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 35(9): 1460-1475. [2] 蔡悦斌, 张明之, 史习智, 等. 舰船噪声波形结构特征提取及分类研究[J]. 电子学报, 1999(6): 129-130. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1999.06.030CAI Y B, ZHANG M Z, SHI X Z, et al. Research on extraction and classification of structural features of ship-radiated noise waveform[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 1999(6): 129-130. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1999.06.030 [3] 葛轶洲, 姚泽, 张歆, 等. 水声目标的MFCC特征提取与分类识别[J]. 计算机仿真, 2024, 41(2): 13-16, 33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2024.02.003GE Y Z, YAO Z, ZHANG X, et al. MFCC feature extraction and classification recognition of underwater acoustic targets[J]. Computer Simulation, 2024, 41(2): 13-16, 33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2024.02.003 [4] 谢东日. 水声目标非线性特征提取研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2020. [5] 倪俊帅, 赵梅, 胡长青. 基于深度学习的舰船辐射噪声多特征融合分类[J]. 声学技术, 2020, 39(3): 366-371.NI J S, ZHAO M, HU C Q. Multi-feature fusion classification of ship-radiated noise based on deep learning[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2020, 39(3): 366-371. [6] 梁喆, 侯朋, 夏春艳, 等. 融合时频域特征的舰船识别方法及实验研究[J]. 声学技术, 2021, 40(5): 607-613.LIANG Z, HOU P, XIA C Y, et al. Ship recognition method and experimental study based on fusion of time-frequency domain features[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2021, 40(5): 607-613. [7] 刘承伟, 洪峰, 冯海泓, 等. 结合多尺度卷积网络和双端注意力机制的水声目标识别[J]. 声学技术, 2023, 42(2): 161-167.LIU C W, HONG F, FENG H H, et al. Underwater acoustic target recognition combining multi-scale convolutional networks and dual attention mechanism[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2023, 42(2): 161-167. [8] 杨基睿, 鄢社锋, 曾迪, 等. 改进通道注意力机制的时域水声信号识别网络[J]. 信号处理, 2023, 39(6): 1025-1035.YANG J R, YAN S F, ZENG D, et al. Time-domain underwater acoustic signal recognition network with improved channel attention mechanism[J]. Signal Processing, 2023, 39(6): 1025-1035. [9] LIU Y X, ZHANG B Q, KONG F T, et al. Underwater acoustic classification using wavelet scattering transform and convolutional neural network with limited dataset[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2025, 232: 110564. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2025.110564 [10] LYU C G, HU X Y, NIU Z H, et al. A light-weight neural network for marine acoustic signal recognition suitable for fiber-optic hydrophones[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 235: 121235. [11] 杨路飞, 章新华, 吴秉坤, 等. 基于MFCC特征的被动水声目标深度学习分类方法[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2020, 42(19): 129-133. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2020.10.025YANG L F, ZHANG X H, WU B K, et al. Passive underwater acoustic target classification method based on MFCC features and deep learning[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2020, 42(19): 129-133. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2020.10.025 [12] ZHANG S K, TIAN D Y, WANG C, et al. Intelligent recognition of underwater acoustic target noise on underwater glider platform[C]//2018 Chinese Automation Congress(CAC). Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2018: 4189-4193. [13] 任晨曦, 王黎明, 韩星程, 等. 基于联合神经网络的水声目标识别方法[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2022, 44(1): 136-141. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2022.01.026REN C X, WANG L M, HAN X C, et al. Underwater acoustic target recognition method based on joint neural network[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2022, 44(1): 136-141. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2022.01.026 [14] YANG K, WANG B, FANG Z, et al. An end-to-end underwater acoustic target recognition model based on one-dimensional convolution and transformer[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(10): 1793. [15] LIU D Y, YANG H Y, HOU W M, et al. A novel underwater acoustic target recognition method based on MFCC and RACNN[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(1): 273. doi: 10.3390/s24010273 [16] YÜCESOY E. Gender recognition based on the stacking of different acoustic features[J]. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(15): 6564. doi: 10.3390/app14156564 [17] ZHANG S, GAO Y, CAI J, et al. A novel bird sound recognition method based on multi-feature fusion and a transformer encoder[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(19): 8099. doi: 10.3390/s23198099 [18] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[J]. European Conference on Computer Vision, 2018, 1: 3-19. [19] DAVID S D, TORRES G S, ANTONIO C L, et al. ShipsEar: An underwater vessel noise database[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2016, 113: 64-69. [20] YANG S, JIN A, ZENG X, et al. Underwater acoustic target recognition based on sub-band concatenated Mel spectrogram and multidomain attention mechanism[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2024, 133: 107983. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2024.107983 [21] NI J, JI F, LU S, et al. Underwater target recognition method based on singular spectrum analysis and channel attention convolutional neural network[J]. Sensors, 2025, 25: 2573. doi: 10.3390/s25082573 [22] WANG B, ZHANG W, ZHU Y, et al. An underwater acoustic target recognition method based on AMNet[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 1-5. [23] WANG J Y, QIAN P, CHEN Y X, et al. Adaptive underwater acoustic target recognition based on multi-scale residual and attention mechanism[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2025, 163: 105193. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2025.105193 [24] NI J, JI F, LU S, et al. An auditory convolutional neural network for underwater acoustic target timbre feature extraction and recognition[J]. Remote Sens, 2024, 16: 3074. -




 下载:
下载: