Style Transfer-Based Augmentation for Side-Scan Sonar Images
-
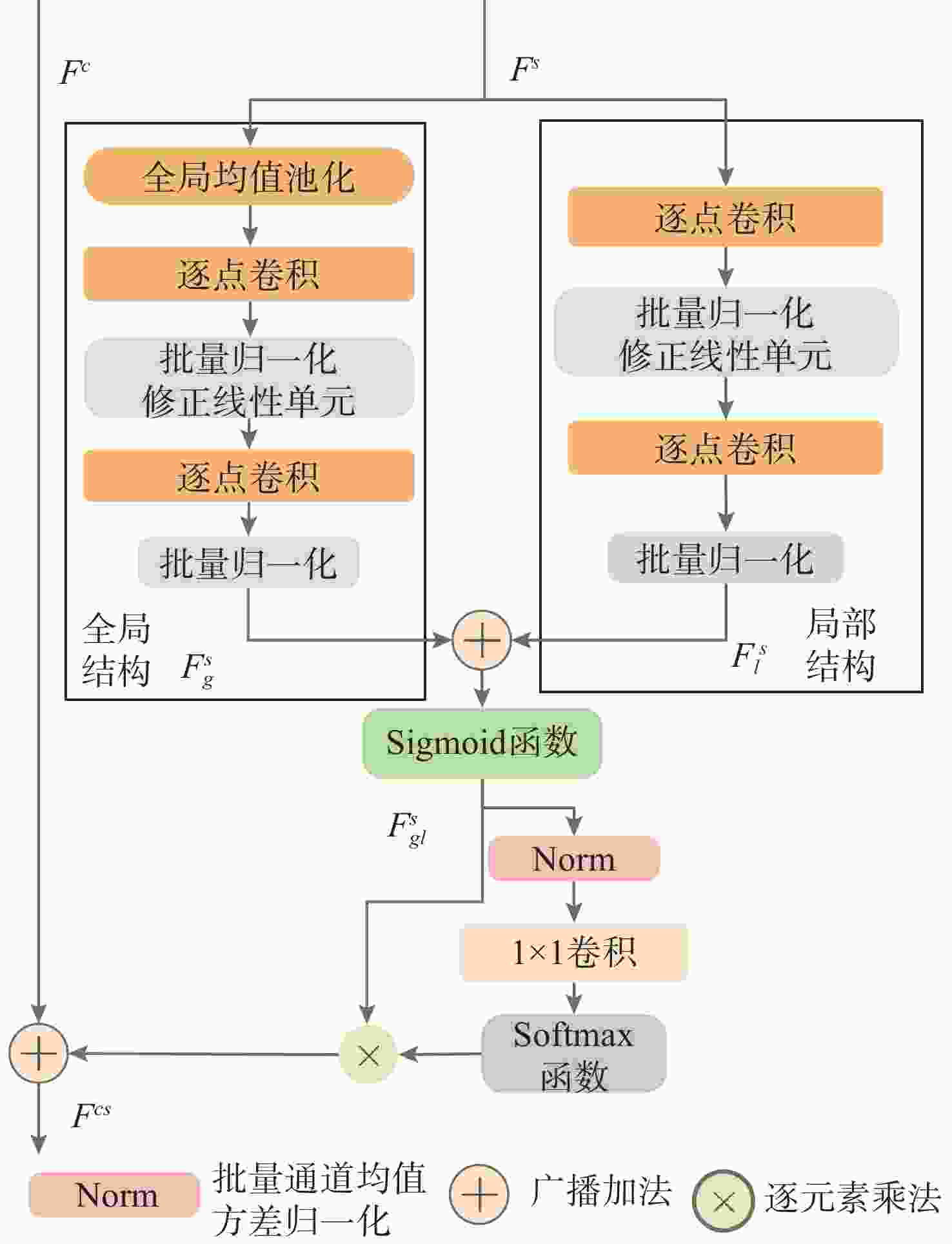
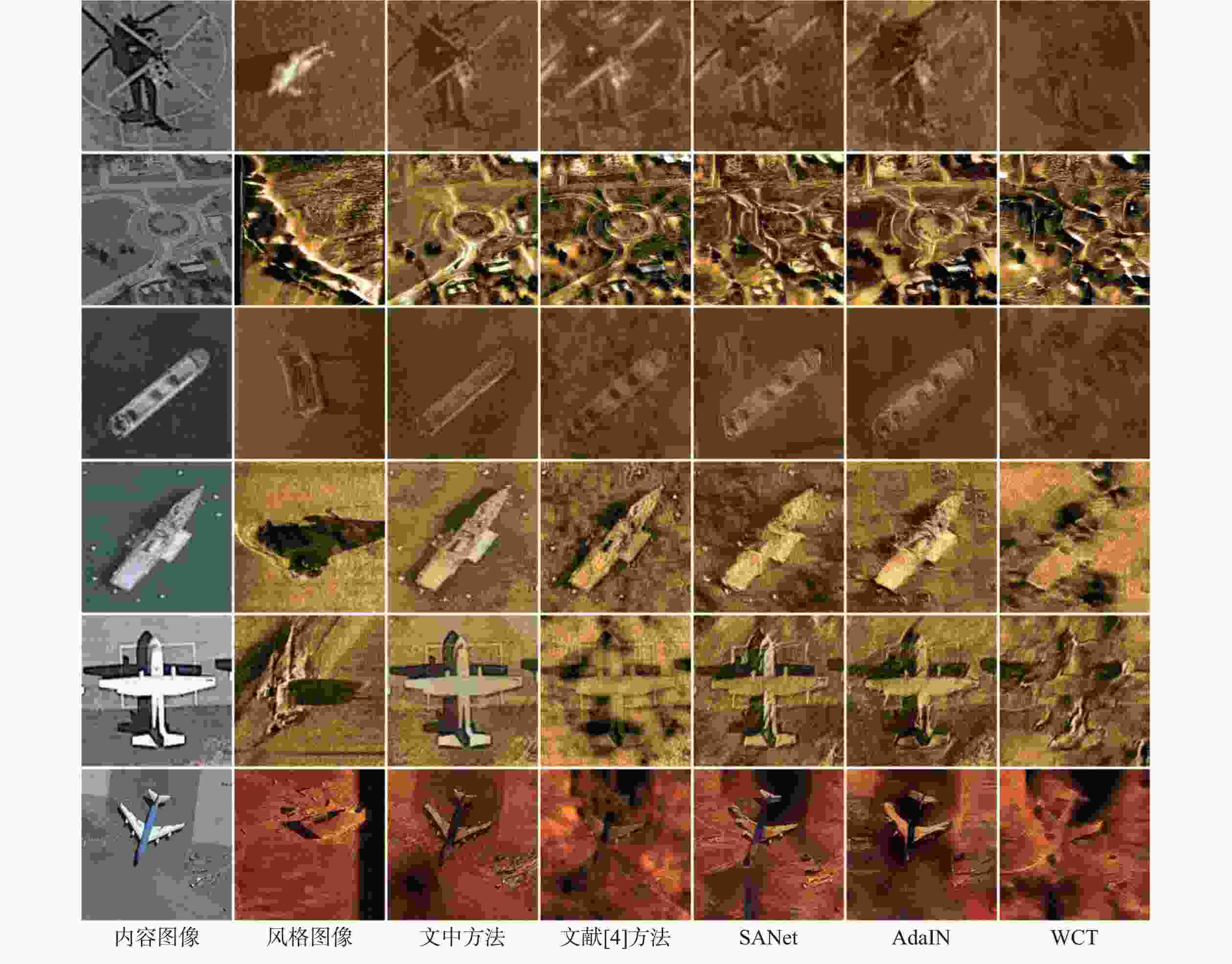
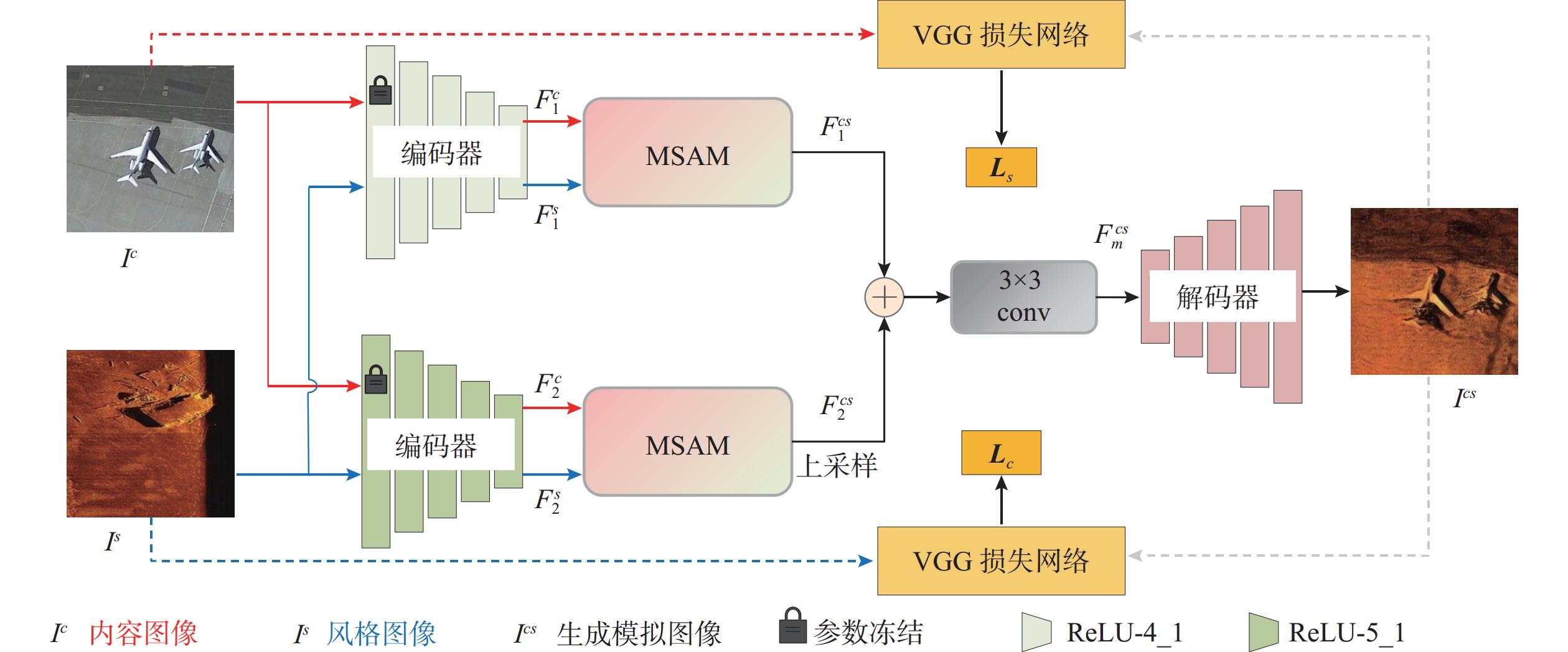
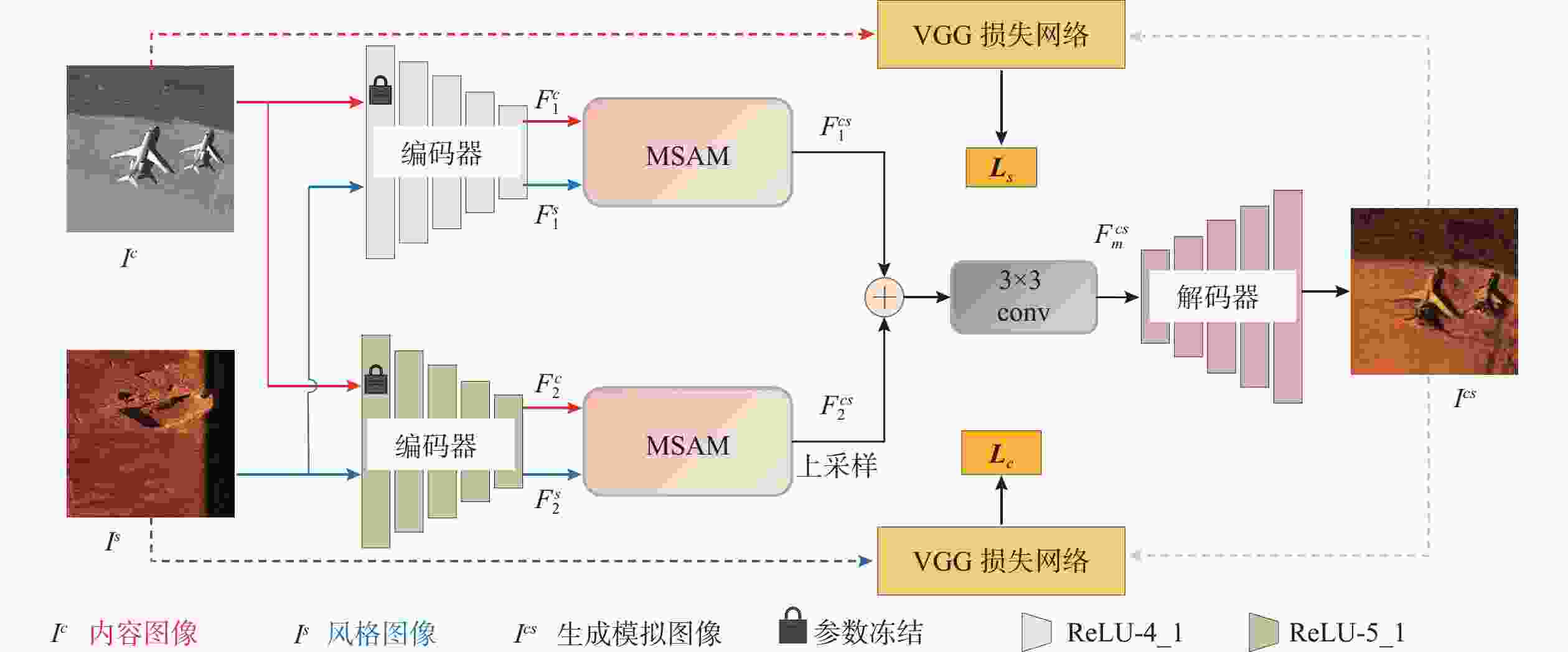
摘要: 侧扫声呐(SSS)因其在自主水下航行器(AUV)上的稳定性与高效性, 在海洋探测领域得到了广泛应用。然而, SSS图像获取难度大、样本数量稀少, 严重限制了基于深度神经网络(DNN)的SSS图像分类性能。针对这一问题, 文中提出了一种多尺度注意力融合网络(MSANet), 利用光学-声学图像进行数据扩充来提升SSS图像分类模型的泛化能力。首先, 通过编码器不同层提取输入图像的浅层与深层特征, 以充分捕捉内容与风格信息。随后, 引入多尺度注意力模块(MSAM), 提取风格图像在通道维度上的局部与全局上下文信息, 并与光学特征进行高效融合, 使光学特征在不同空间位置精准匹配相应的声学特征。最终, 将不同层融合后的特征进行尺度对齐, 并输入到解码器生成高质量的模拟SSS图像样本, 用于训练SSS图像分类网络。在真实SSS图像数据集上的实验结果表明, 提出的风格迁移方法能够有效生成高质量模拟SSS图像样本, 进而提高基于DNN的SSS图像分类性能。Abstract: Side-scan sonar(SSS) has been extensively adopted in ocean exploration because of its stability and efficiency when deployed on autonomous undersea vehicles(AUVs). Nevertheless, the difficulty in acquiring SSS images and the limited availability of training samples severely constrain the performance of the deep neural network(DNN)-based SSS image classification. To mitigate this limitation, this paper proposed a multi-scale attention network(MSANet) that utilized optical-acoustic image pairs for data augmentation to enhance the generalization capacity of SSS image classification models. First, shallow and deep features were extracted from multiple encoder layers to comprehensively capture both content and style information. Next, a multi-scale attention module(MSAM) was introduced to extract both local and global contextual information of style features along the channel dimension. These style features were then effectively fused with optical features to achieve precise spatial alignment of optical and acoustic features. Finally, the fused multi-scale features were aligned and input to a decoder to generate high-fidelity SSS images that were subsequently used to train the classification network. Extensive experiments on real-world SSS datasets demonstrate that the proposed style transfer-based augmentation strategy can effectively generate high-quality simulated SSS image samples, thereby improving the performance of SSS image classification based on DNN.
-
表 1 不同图像扩充方法的SSS图像分类实验结果
Table 1. Experimental results of SSS image classification with different image augmentation methods
表 2 不同方法合成图像训练分类器的分类实验结果
Table 2. Classification experimental results of classifiers trained with synthetic images using different methods
表 3 不同分类器对真实SSS图像的分类实验结果
Table 3. Classification experimental results of real SSS images by different classifiers
方法 图像张数 识别精度/% 飞机 沉船 VGG-19 21 209 83.94 ResNet-152 23 218 87.96 ViT-B/32 23 213 86.13 EfficientNet-v2s 25 215 87.59 -
[1] 郝紫霄, 王琦. 基于声呐图像的水下目标检测研究综述[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(2): 339-348.HAO Z X, WANG Q. Underwater target detection based on sonar image[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2023, 31(2): 339-348. [2] 朱兆彤, 付学志, 胡友峰. 一种利用迁移学习训练卷积神经网络的声呐图像识别方法[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2020, 28(1): 89-96.ZHU Z T, FU X Z, HU Y F. A sonar image recognition method based on convolutional neural network trained through transfer learning[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2020, 28(1): 89-96. [3] ZHU B, WANG X, CHU Z, et al. Active learning for recognition of shipwreck target in side-scan sonar image[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(3): 243. doi: 10.3390/rs11030243 [4] LI C, YE X, CAO D, et al. Zero shot objects classification method of side scan sonar image based on synthesis of pseudo samples[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2021, 173: 107691. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2020.107691 [5] NAYAK N, NARA M, GAMBIN T, et al. Machine learning techniques for AUV side-scan sonar data feature extraction as applied to intelligent search for underwater archaeological sites[C]//Field and Service Robotics: Results of the 12th International Conference. Singapore: Springer, 2021: 219-233. [6] JIANG Y, KU B, KIM W, et al. Side-scan sonar image synthesis based on generative adversarial network for images in multiple frequencies[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 18(9): 1505-1509. [7] HUANG C, ZHAO J, YU Y, et al. Comprehensive sample augmentation by fully considering SSS imaging mechanism and environment for shipwreck detection under zero real samples[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 1-14. [8] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2015-04-10)[2025-03-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556. [9] DAI Y, GIESEKE F, OEHMCKE S, et al. Attentional feature fusion[C]//2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision(WACV). Waikoloa, USA: WACV, 2021: 3559-3568. [10] CAO Y, XU J, LIN S, et al. GCNET: Non-local networks meet squeeze-excitation networks and beyond[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop(ICCVW). Seoul, Korea(South): ICCVW, 2019: 1971-1980. [11] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA: CVPR, 2016: 770-778. [12] PARK D Y, LEE K H. Arbitrary style transfer with style-attentional networks[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR). Long Beach, CA, USA: CVPR, 2019: 5873-5881. [13] NOMAN M, STANKOVIC V, TAWFIK A. Object detection techniques: Overview and performance comparison[C]//2019 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology(ISSPIT). Ajman, United Arab Emirates: ISSPIT, 2019: 1-5. [14] PHILLIPS F, MACKINTOSH B. Wiki Art Gallery, inc.: A case for critical thinking[J]. Issues in Accounting Education, 2011, 26(3): 593-608. doi: 10.2308/iace-50038 [15] LI Y, FANG C, YANG J, et al. Universal style transfer via feature transforms[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 386-396. [16] HUANG X, BELONGIE S. Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision(ICCV). Venice, Italy: ICCV, 2017: 1510-1519. [17] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[EB/OL]. (2021-06-03) [2025-03-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929. [18] TAN M, LE Q. Efficientnetv2: Smaller models and faster training[EB/OL]. (2021-06-23) [2025-03-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.00298. -




 下载:
下载: