Method for Obstacle Avoidance Path Planning of Unmanned Surface Vessel Based on Improved Artificial Potential Field Method
-
摘要: 针对无人艇避障局部路径规划问题, 依托人工势场架构, 提出了一种基于经纬度坐标水面态势动态构建的避障局部路径规划方法。首先梳理了经纬度坐标系中的基本运算, 进而推导了传统势函数法的引力及斥力函数形式, 阐述了传统势函数法及其改进方法在工程中存在的虚拟目标点确定困难、被控对象轨迹无法准确预测等问题, 设计了依托水面态势动态构建的改进势函数局部路径规划算法。最后对所设计的方法进行了仿真验证及海上试验, 结果表明, 所提出的避障路径规划工程方法能够引导无人艇完成避障任务, 具有较强的可靠性和鲁棒性。Abstract: To solve the problem of local path planning for obstacle avoidance of unmanned surface vessels, an artificial potential field framework was proposed, and a local path planning method for obstacle avoidance based on the dynamic construction of the water surface situation in longitude and latitude coordinates was proposed. Initially, the basic operations in the longitude and latitude coordinate system were sorted out and organized, and then the gravitational and repulsive force functions of the traditional potential function method were derived. The problems existing in the traditional potential function method and its improved methods, such as the difficulty in determining the virtual target point in the project and the inability to accurately predict the trajectory of the controlled object, were expounded. An improved potential function local path planning algorithm relying on the dynamic construction of the water surface situation was designed. Finally, the designed method was verified by simulation and sea trials. The results show that the proposed engineering method for obstacle avoidance path planning can guide the unmanned surface vessel to complete the obstacle avoidance task and has strong reliability and robustness.
-
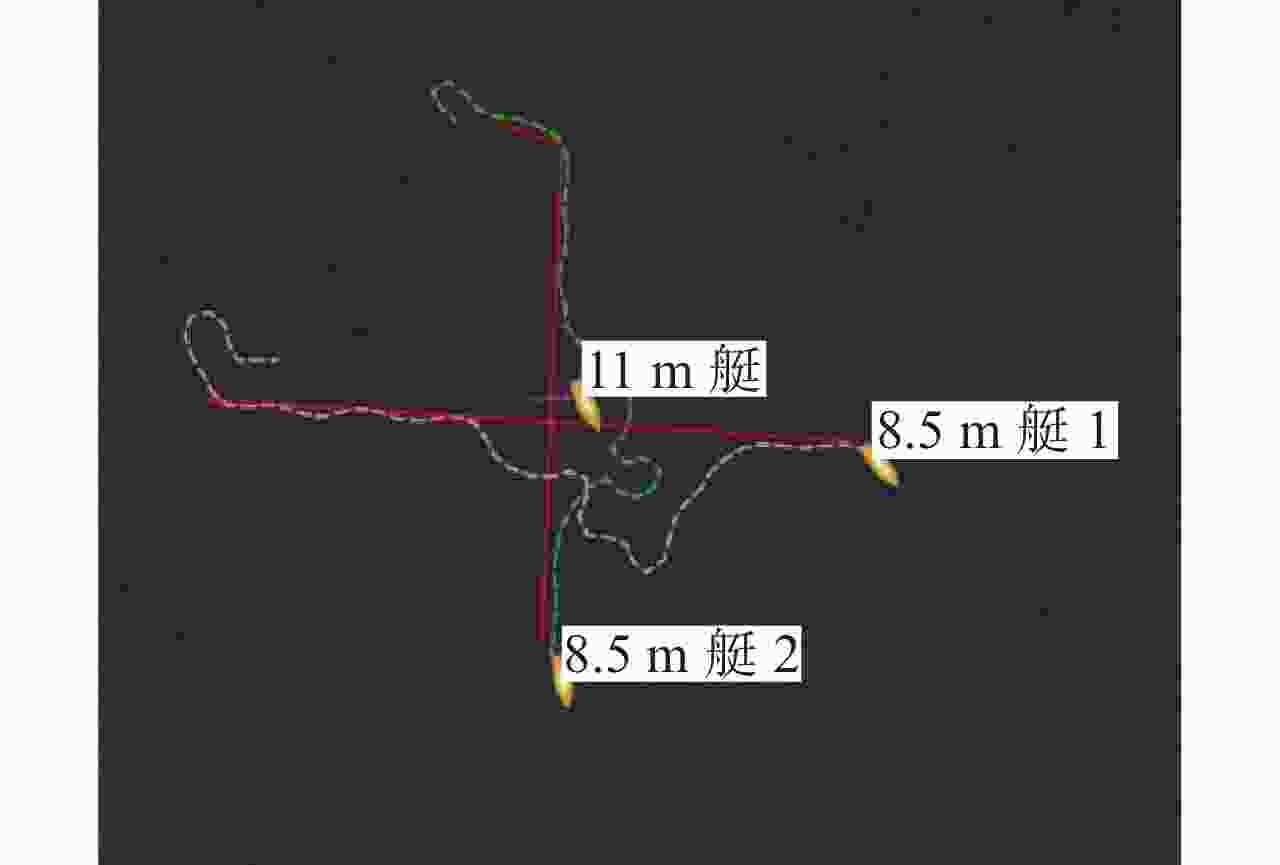
表 1 无人艇状态信息
Table 1. State information of unmanned surface vessel
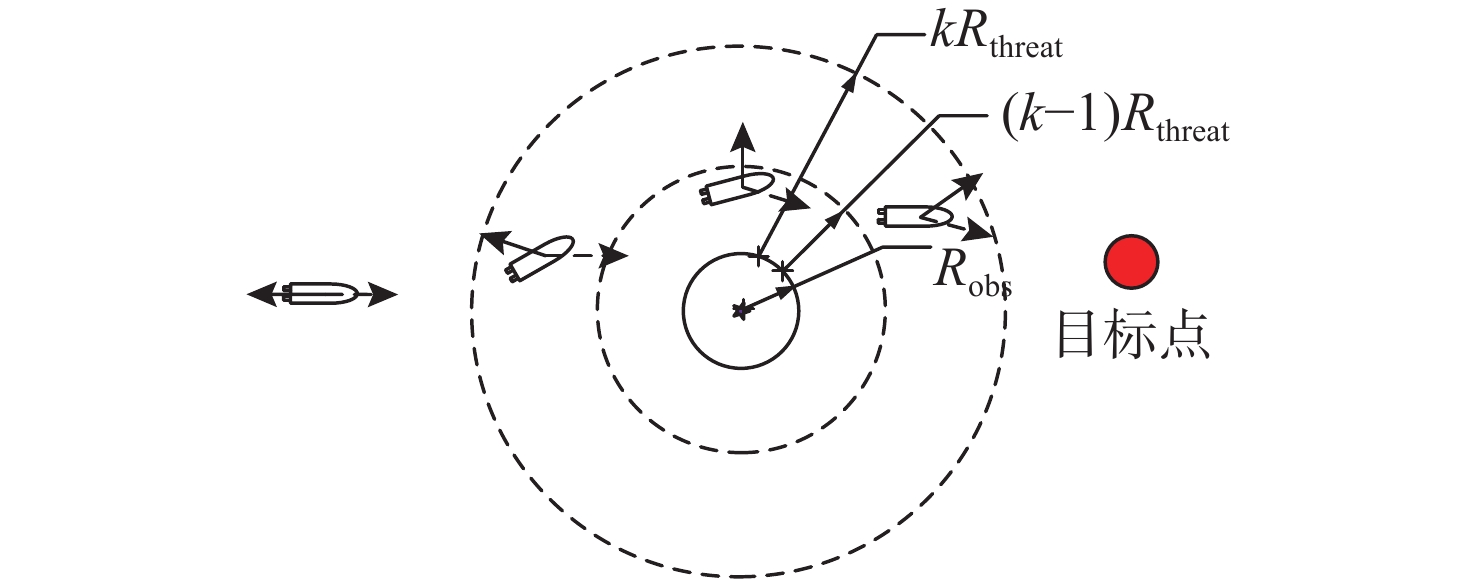
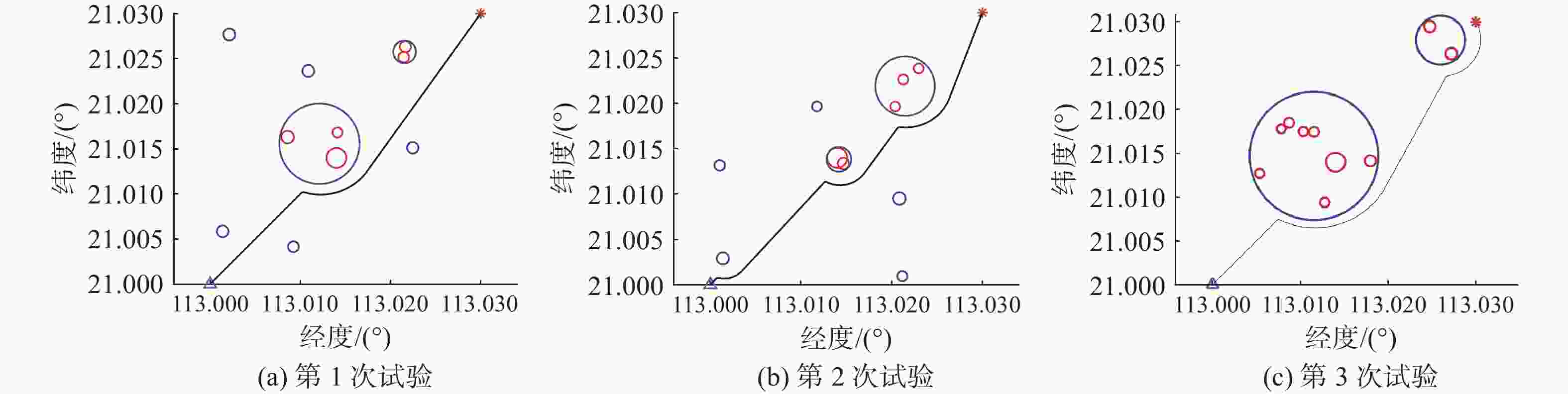
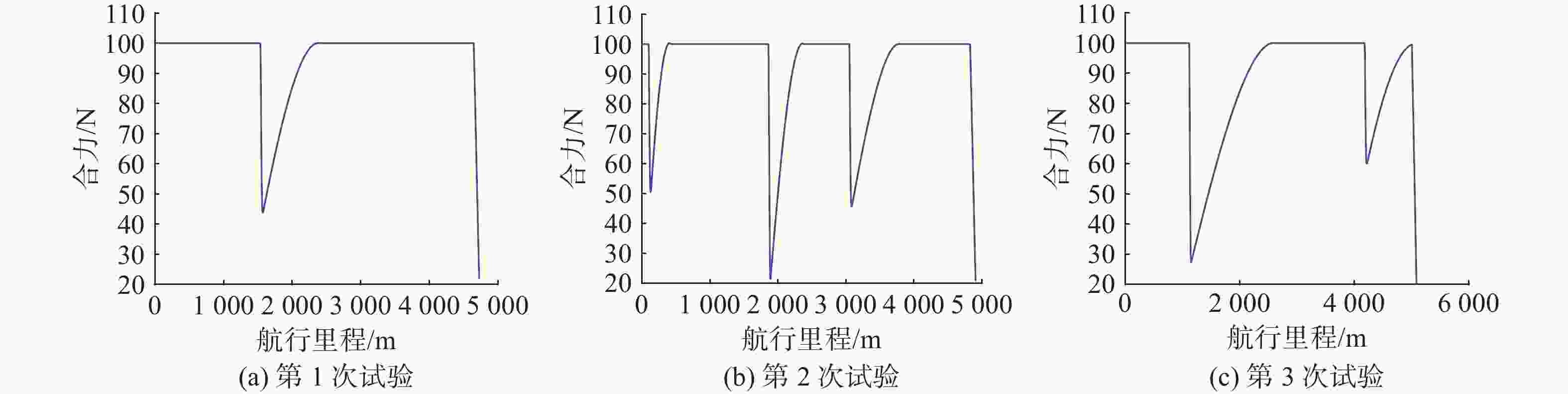
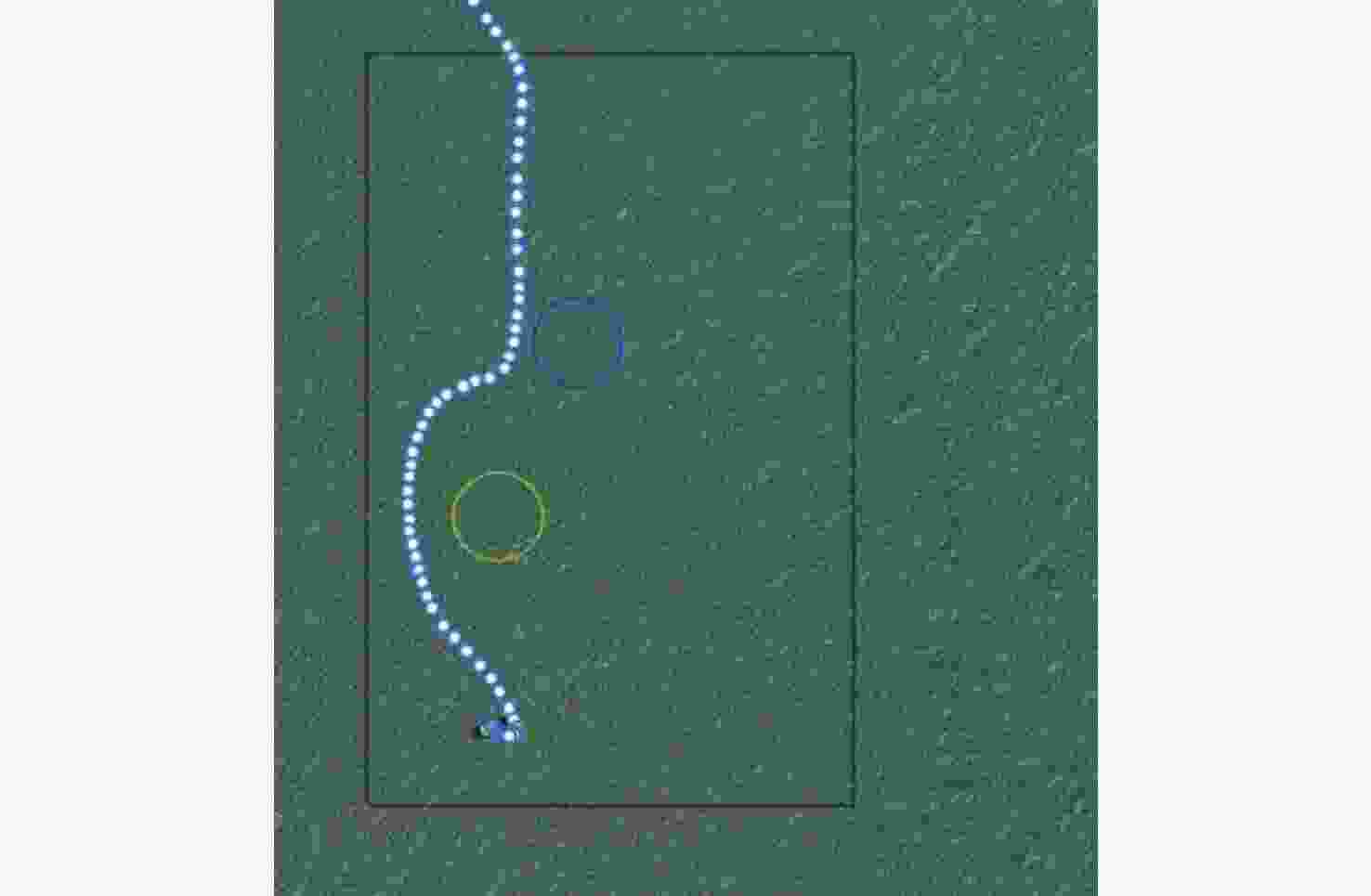
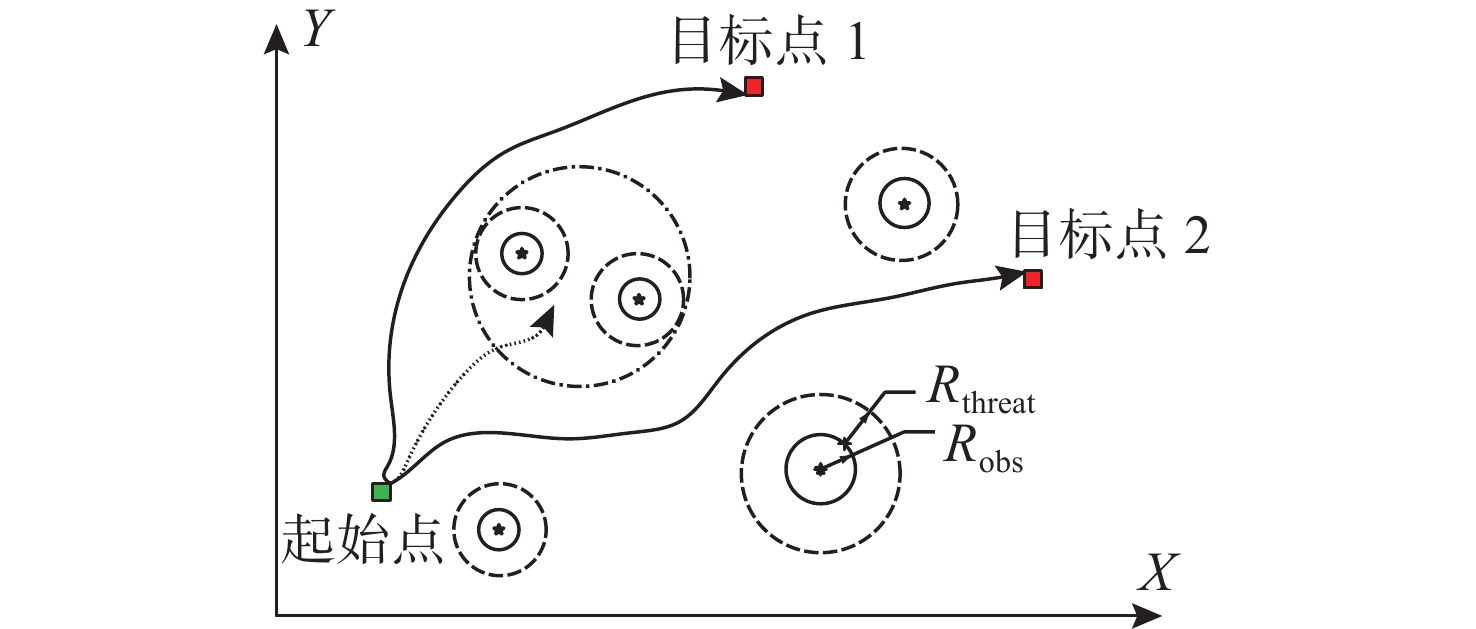
初始位置 期望位置 $ {R_{{\text{threat}}}} $/m $ {R_{{\text{turn}}}} $/m $ k $ [113.000 00, 21.000 00] [113.030 00, 113.030 00] 50 30 4 表 2 原始障碍物信息
Table 2. Information of original obstacles
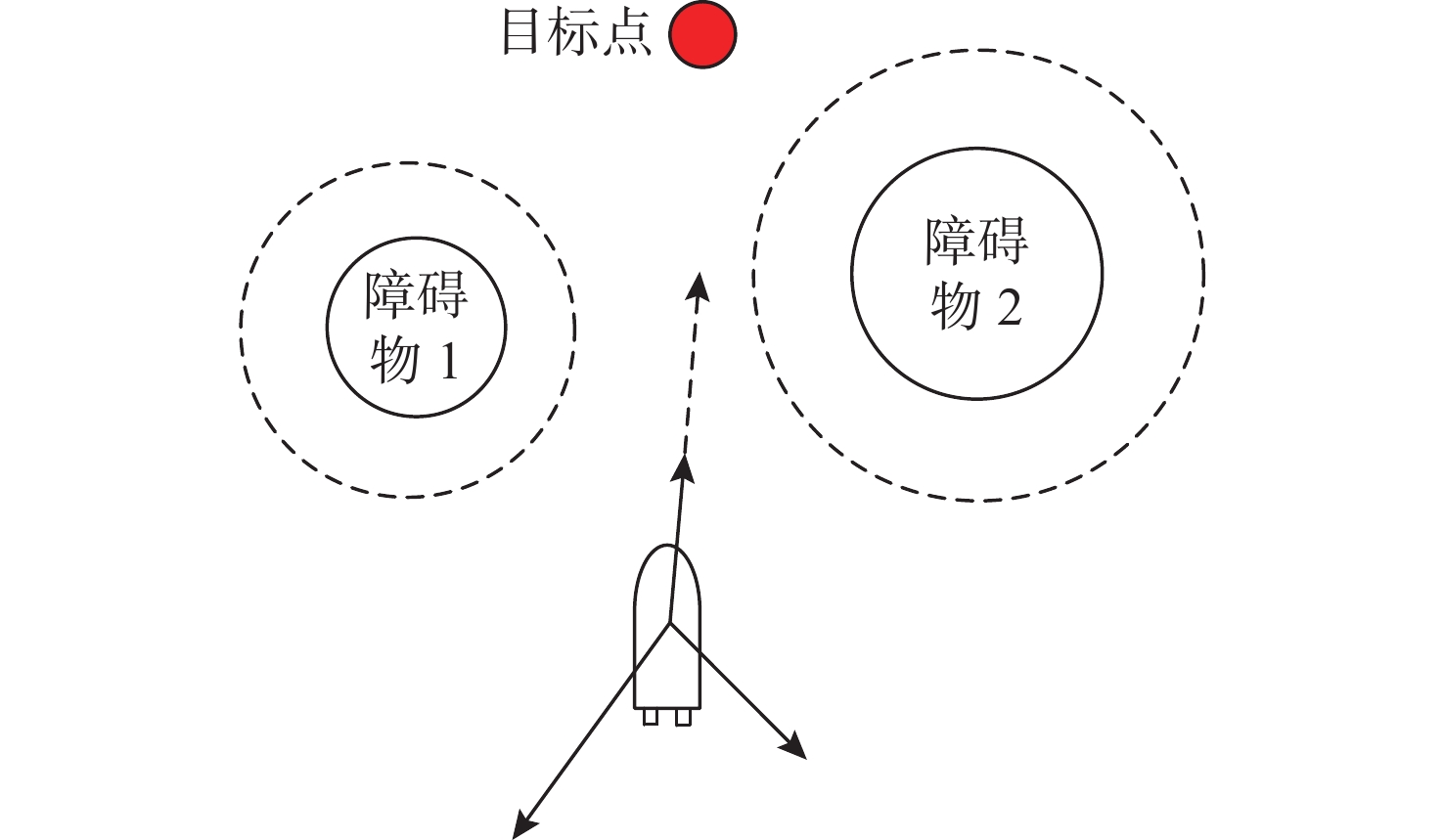
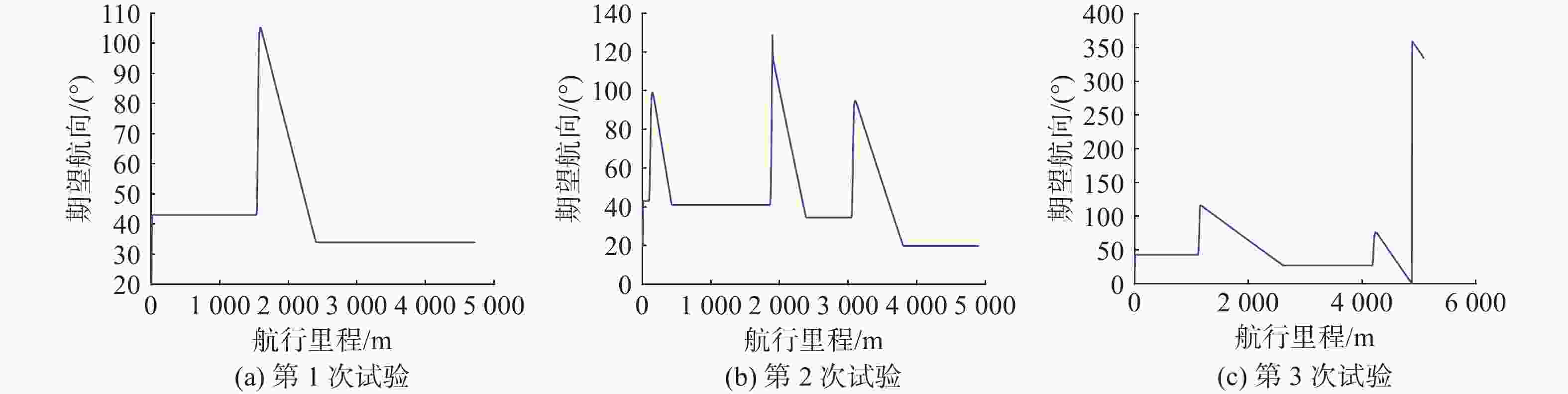
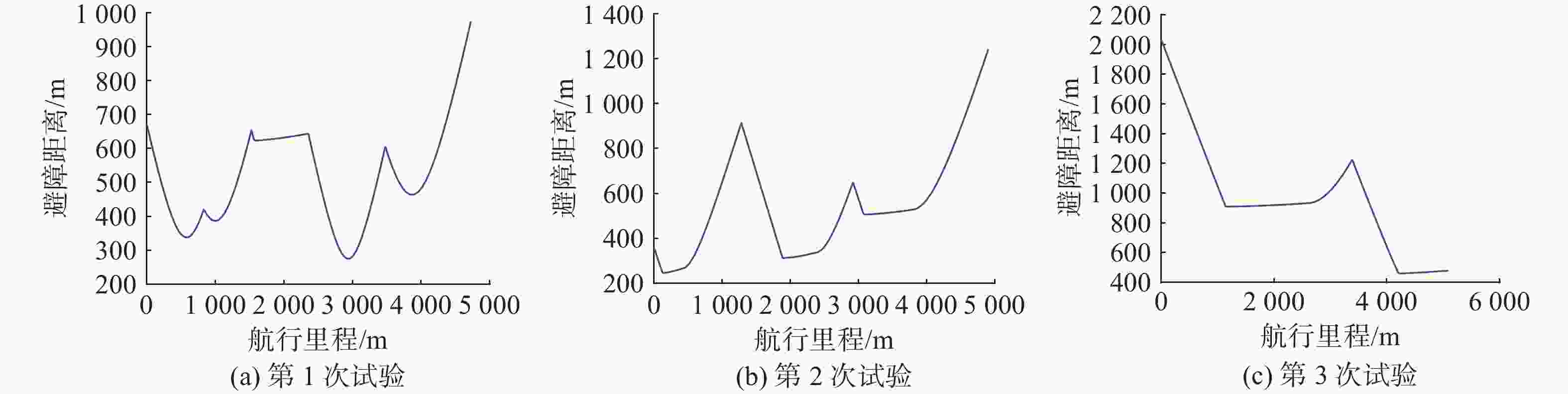
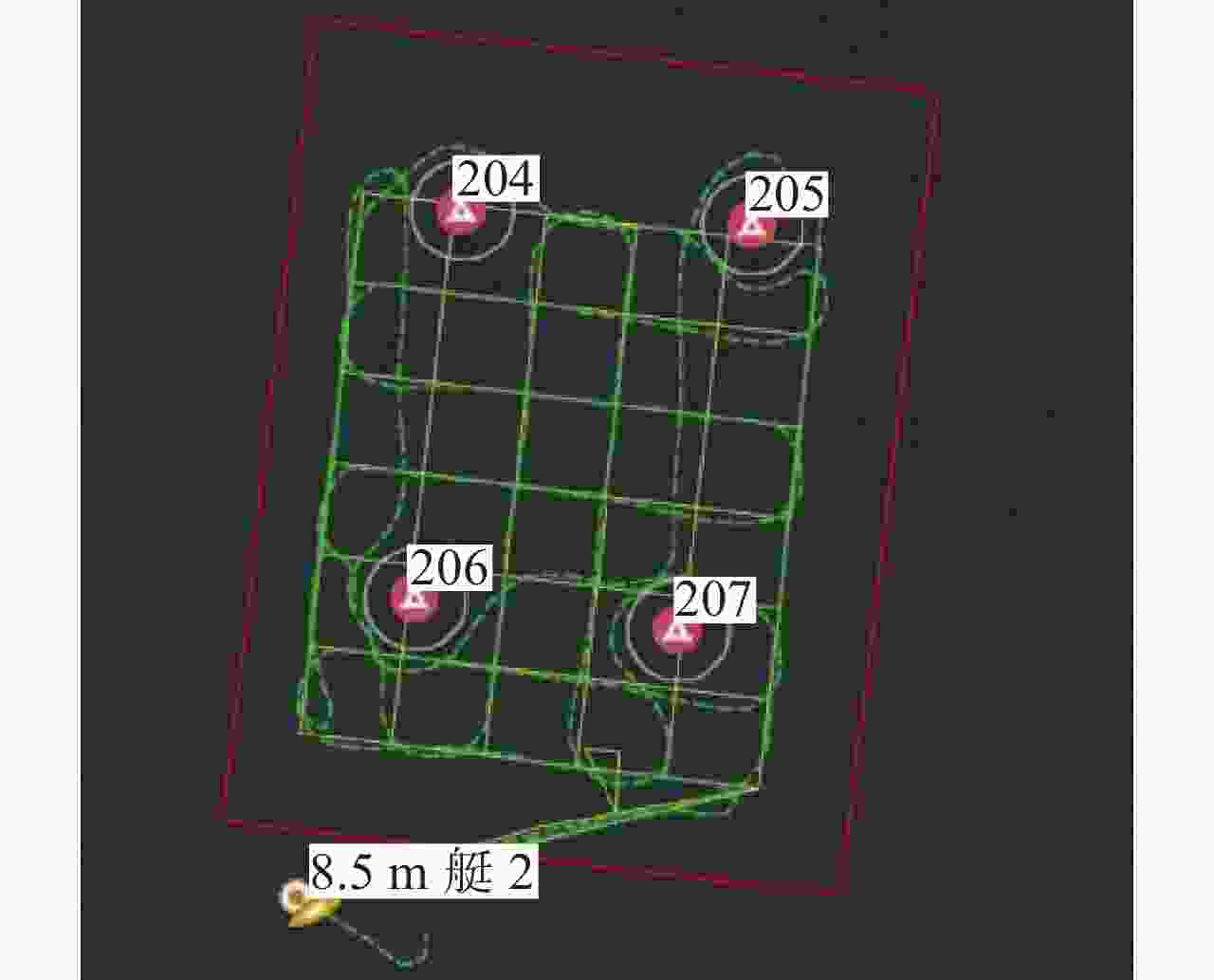
试验 经度/(°) 纬度/(°) 尺寸/m 试验 经度/(°) 纬度/(°) 尺寸/m 试验 经度/(°) 纬度/(°) 尺寸/m 第1次 113.001 38 21.005 86 64.40 第2次 113.011 76 21.019 66 53.42 第3次 113.011 53 21.017 48 55.03 113.021 65 21.026 33 61.64 113.021 18 21.000 95 55.53 113.008 71 21.018 51 55.30 113.002 12 21.027 68 66.00 113.001 38 21.002 91 66.46 113.024 73 21.029 47 64.60 113.008 57 21.016 30 69.69 113.020 84 21.009 51 69.00 113.010 31 21.017 52 52.15 113.021 47 21.025 16 58.66 113.001 03 21.013 16 57.63 113.027 18 21.026 38 66.35 113.014 11 21.016 82 55.38 113.022 96 21.023 85 53.73 113.007 82 21.017 83 50.45 113.022 47 21.015 11 62.93 113.014 69 21.013 36 62.92 113.012 75 21.009 38 53.22 113.009 23 21.004 16 59.51 113.021 28 21.022 64 55.52 113.005 36 21.012 68 51.88 113.010 87 21.023 64 65.60 113.020 39 21.019 65 53.25 113.017 95 21.014 12 63.91 113.014 00 21.014 00 110.00 113.014 00 21.014 00 110.00 113.014 00 21.014 00 110.00 表 3 归并后的障碍物信息
Table 3. Information of merged obstacles
试验 经度/(°) 纬度/(°) 尺寸/m 试验 经度/(°) 纬度/(°) 尺寸/m 试验 经度/(°) 纬度/(°) 尺寸/m 第1次 113.009 23 21.004 161 59.51 第2次 113.021 47 21.021 90 327.97 第3次 113.011 54 21.014 71 733.24 113.010 87 21.023 64 65.60 113.014 18 21.013 83 136.75 113.025 97 21.027 92 279.46 113.001 38 21.005 86 64.40 113.011 77 21.019 66 53.42 113.021 56 21.025 76 125.60 113.021 18 21.000 95 55.53 113.002 12 21.027 68 66.00 113.001 39 21.002 91 66.46 113.022 47 21.015 11 62.93 113.020 84 21.009 51 69.00 113.012 11 21.015 57 445.65 113.001 03 21.013 16 57.63 -
[1] 熊勇, 余嘉俊, 张加, 等. 无人艇研究进展及发展方向[J]. 船舶工程, 2020, 42(2): 12-19. [2] 王秀玲, 尹勇, 赵延杰, 等. 无人艇海上搜救路径规划技术综述[J]. 船舶工程, 2023, 45(4): 50-57.WANG X L, YIN Y, ZHAO Y J, et al. Overview of USV maritime search and rescue path planning technology[J]. Ship Engineering, 2023, 45(4): 50-57. [3] BAI X, LI B, XU X, et al. A review of current research and advances in unmanned surface vehicles[J]. J. Marine. Sci. Appl, 2022, 21: 47-58. doi: 10.1007/s11804-022-00276-9 [4] 马勇, 王雯琦, 严新平. 水域无人系统平台自主航行及协同控制研究进展[J]. 无人系统技术, 2022, 5(1): 1-16.MA Y, WANG W Q, YAN X P, et al. Research progress on autonomous navigation and cooperative control of water area unmanned system platform[J]. Unmanned Systems Technology, 2022, 5(1): 1-16. [5] 徐筱波, 叶锴, 王登峰. 无人水面艇关键技术及军事应用[J]. 广东造船, 2023, 42(4): 35-38.XU X B, YE K, WANG D F, et al. Key technologies and military applications of USV[J]. Guangdong Shipbuilding, 2023, 42(4): 35-38. [6] XING B, YU M, LIU Z, et al. A review of path planning for unmanned surface vehicles[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2023, 11(8): 1556. doi: 10.3390/jmse11081556 [7] MAO S, YANG P, GAO D, et al. A motion planning method for unmanned surface vehicle based on improved RRT algorithm[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2023, 11(4): 687. doi: 10.3390/jmse11040687 [8] 周瑞红, 李彩虹, 张耀玉, 等. 基于改进RRT算法的移动机器人路径规划[J]. 山东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 38(5): 54-60.ZHOU R H, LI C H, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Path planning of mobile robot based on the improved RRT algorithm[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 38(5): 54-60. [9] 张喜超, 尹勇. 基于改进RRT*算法的无人船路径规划[J]. 中国航海, 2023, 46(1): 143-147, 154.ZHANG X C, YIN Y. Path planning for unmanned surface vehicle based on improved RRT* algorithm[J]. Navigation of China, 2023, 46(1): 143-147, 154. [10] DOBREVSKI M, SKOČAJ D. Dynamic adaptive dynamic window approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2024, 40: 3068-3081. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2024.3400932 [11] 李忠坤, 姜媛媛, 刘子厚. 基于蚁群算法融合改进动态窗口法的动态路径规划方法[J]. 佳木斯大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 42(2): 19-23.LI Z K, JIANG Y Y, LIU Z H, et al. Dynamic path planning method based on ant colony algorithm fusion improved dynamic window method[J]. Journal of Jiamusi University(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 42(2): 19-23. [12] 王征, 杨洋, 周帅, 等. 基于A*-动态窗口法的无人船动态路径规划算法[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2024, 36(2): 13-18.WANG Z, YANG Y, ZHOU S, et al. Dynamic path planning algorithm of unmanned ship based on A*-dynamic window approach[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2024, 36(2): 13-18. [13] XIE S R, WU P, PENG Y, et al. The obstacle avoidance planning of USV based on improved artificial potential field[C]//2014 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation. Hailar, China: IEEE, 2014. [14] 李家林, 张建强, 李春来. 基于优化人工势场法的无人艇局部路径规划[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2022, 44(16): 69-73.LI J L, ZHANG J Q, LI C L, et al. Local path planning of unmanned boat based on optimized artificial potential field method[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2022, 44(16): 69-73. [15] 邱朋, 汪光, 赵理, 等. 采用改进人工势场法的动态无人车路径规划[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2023(3): 291-296.QIU P, WANG G, ZHAO L, et al. Unmanned vehicle path planning based on structured road improved artificial potential field method[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2023(3): 291-296. [16] 刘涛. 基于模糊改进人工势场法的无人船路径规划研究[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2022, 44(3): 63-66.LIU T. Research on path planning of unmanned ship based on fuzzy improved artificial potential field method[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2022, 44(3): 63-66. [17] 刘琨, 张永辉, 任佳. 基于改进人工势场法的无人船路径规划算法[J]. 海南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016(2): 99-104.LIU K, ZHANG Y H, REN J. Path planning algorithm for unmanned surface vehicle based on an improved artificial potential field method[J]. Natural Science Journal of Hainan University, 2016(2): 99-104. [18] 姜文, 崔化超, 戚志刚, 等. 基于多目标粒子群-人工势场法的无人艇局部航路规划[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2023, 18(9): 814-820.JIANG W, CUI H C, QI Z G, et al. Path planning of USV based on MOPSO and APF method[J]. Journal of China Academy of Electronics and Information Technology, 2023, 18(9): 814-820. [19] 陈凯翔, 周姝婧, 许强, 等. 基于改进人工势场法的无人船动态路径规划算法研究[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2023, 46(5): 43-48, 97.CHEN K X, ZHOU S J, XU Q, et al. Research into dynamic path planning algorithm of unmanned ship based on improved artificial potential field method[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2023, 46(5): 43-48, 97. -





 下载:
下载: