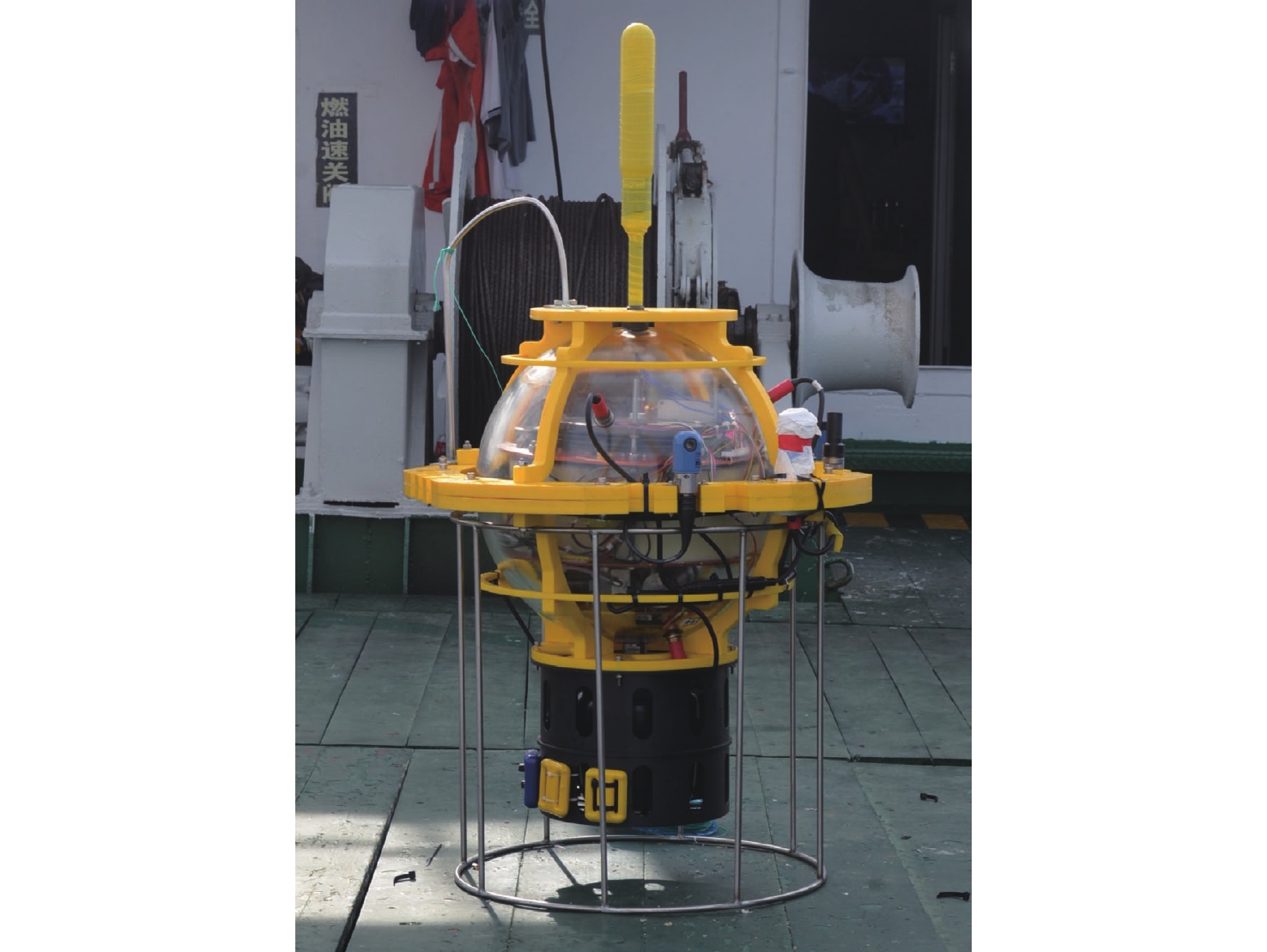
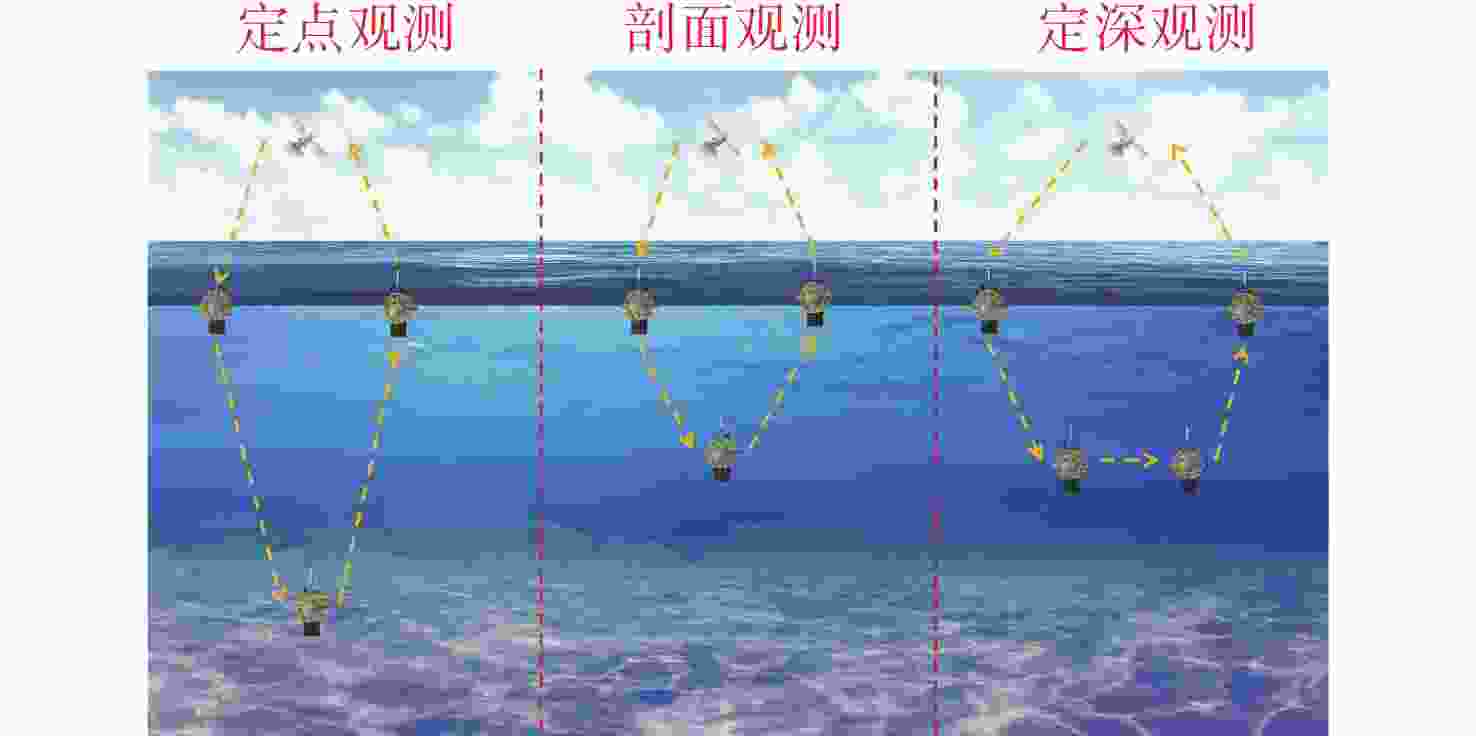
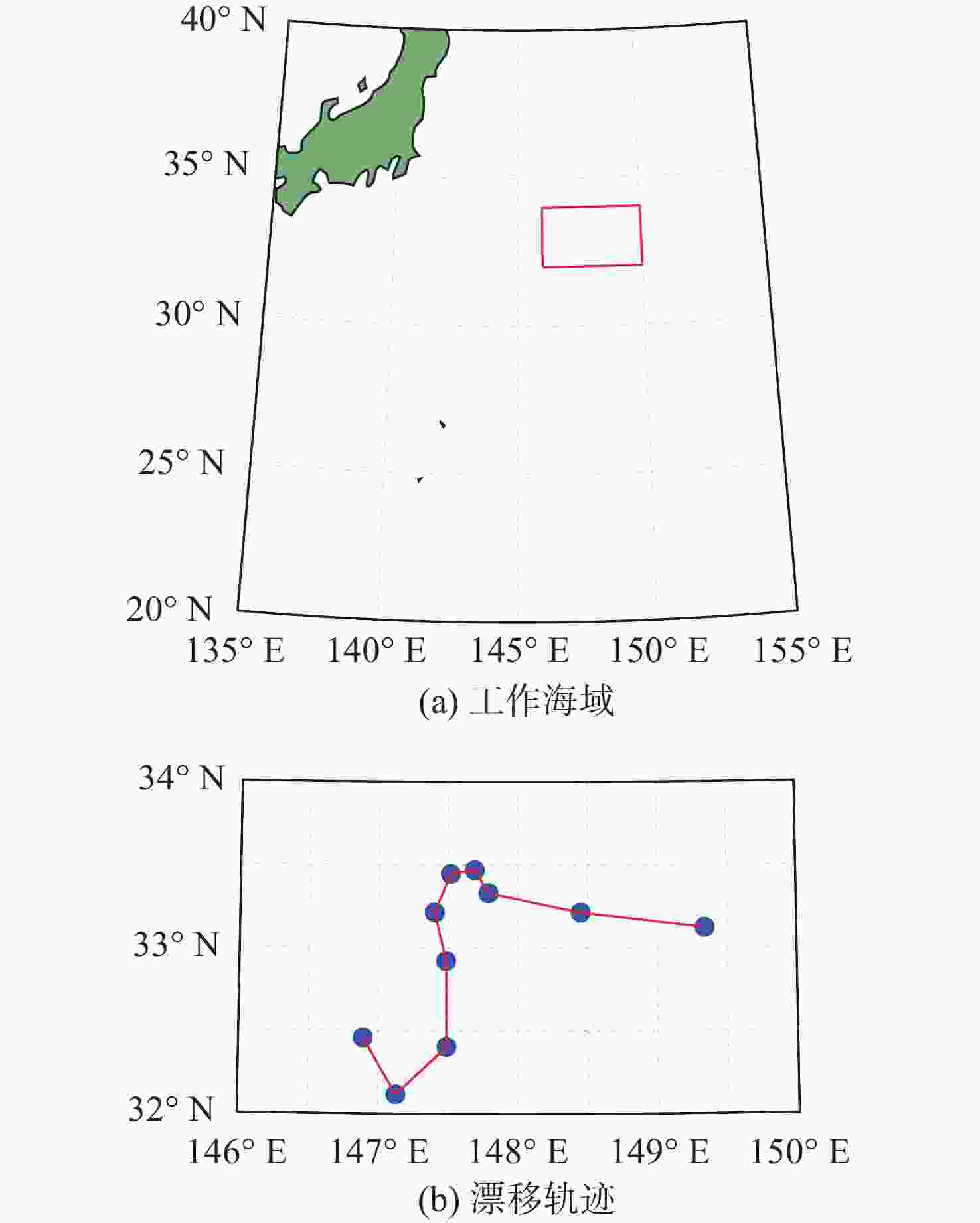
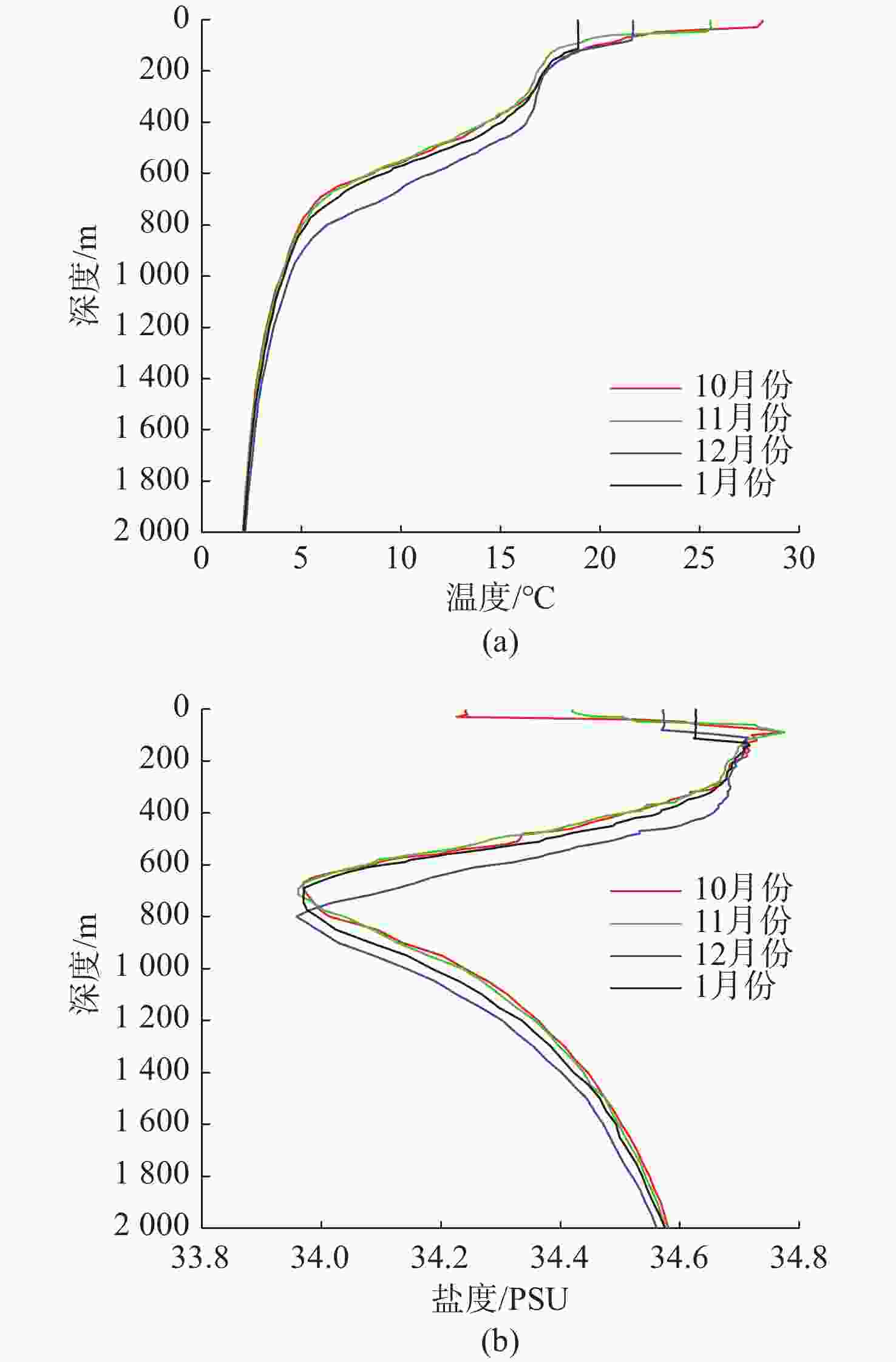
Adaptive Observation Method for CTD Data Based on Dolphin Deep-Sea Profiling Buoy
-
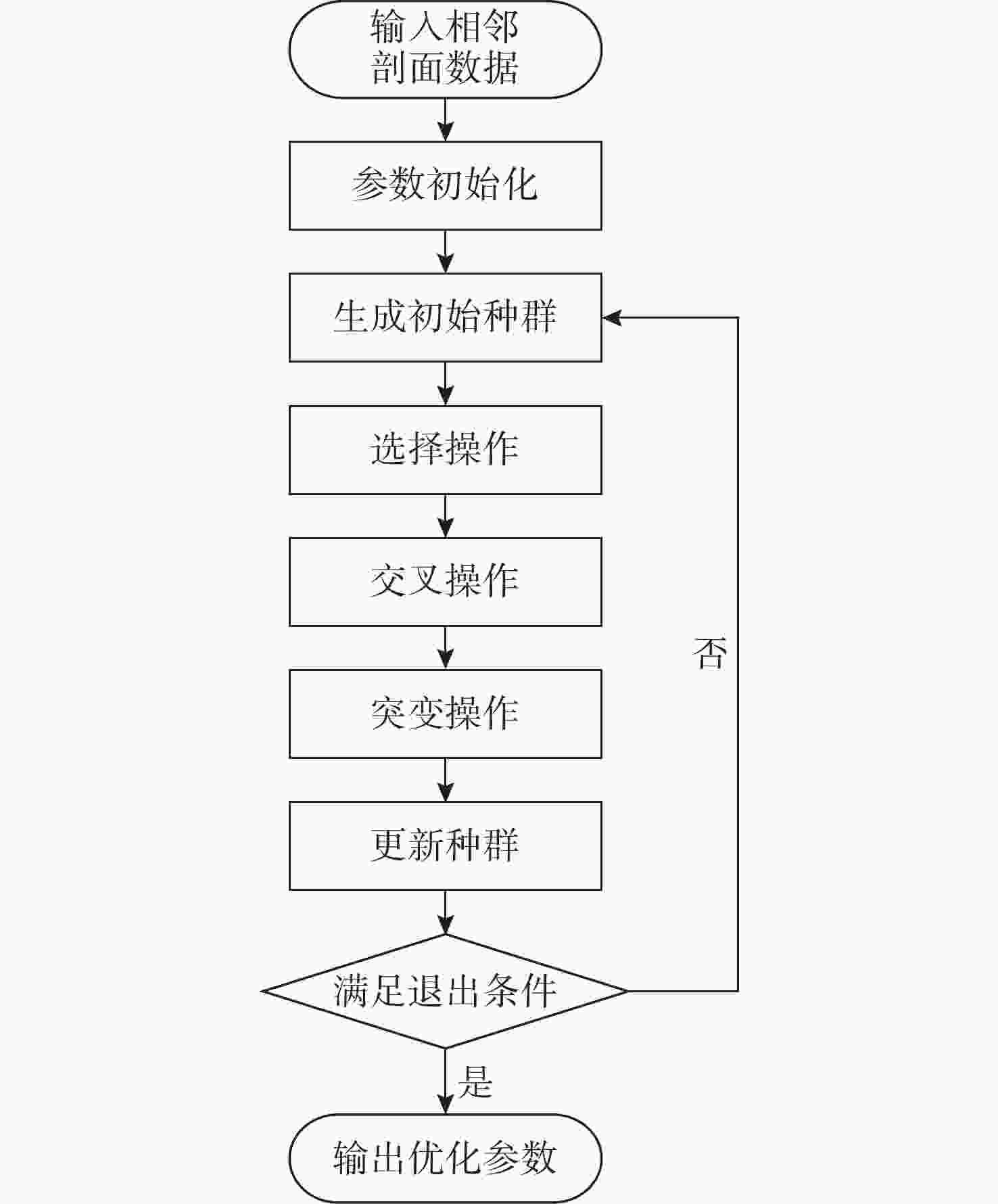
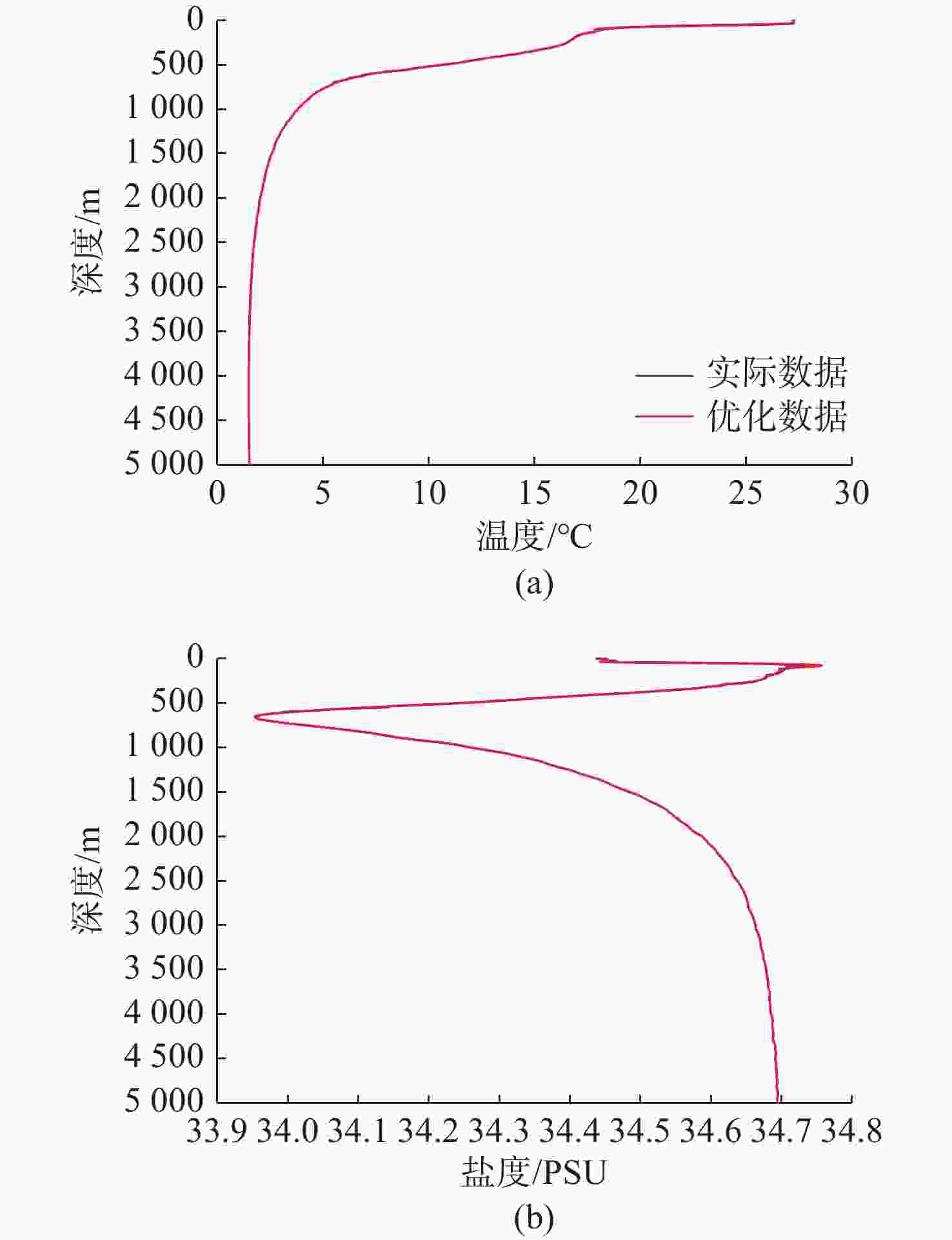
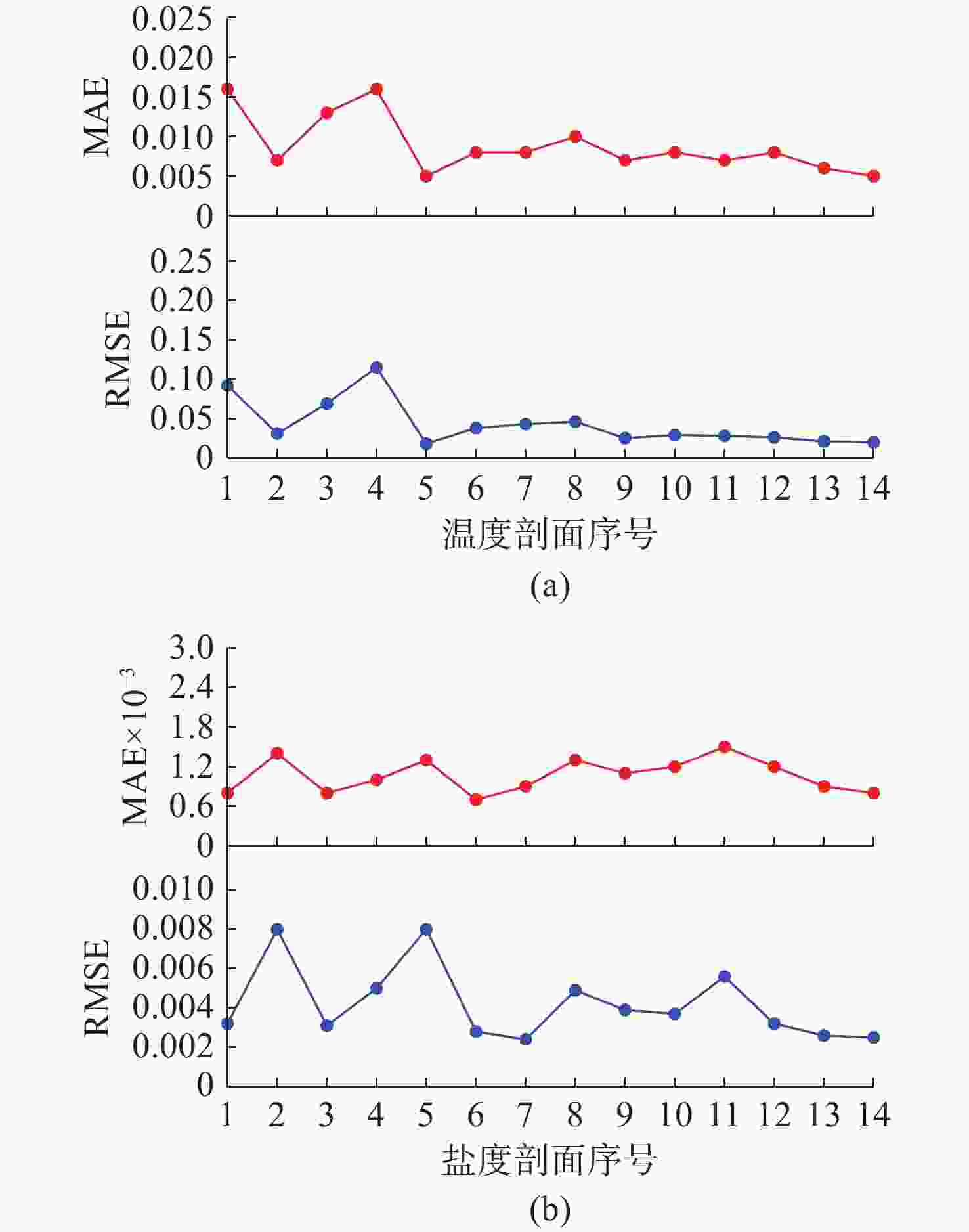
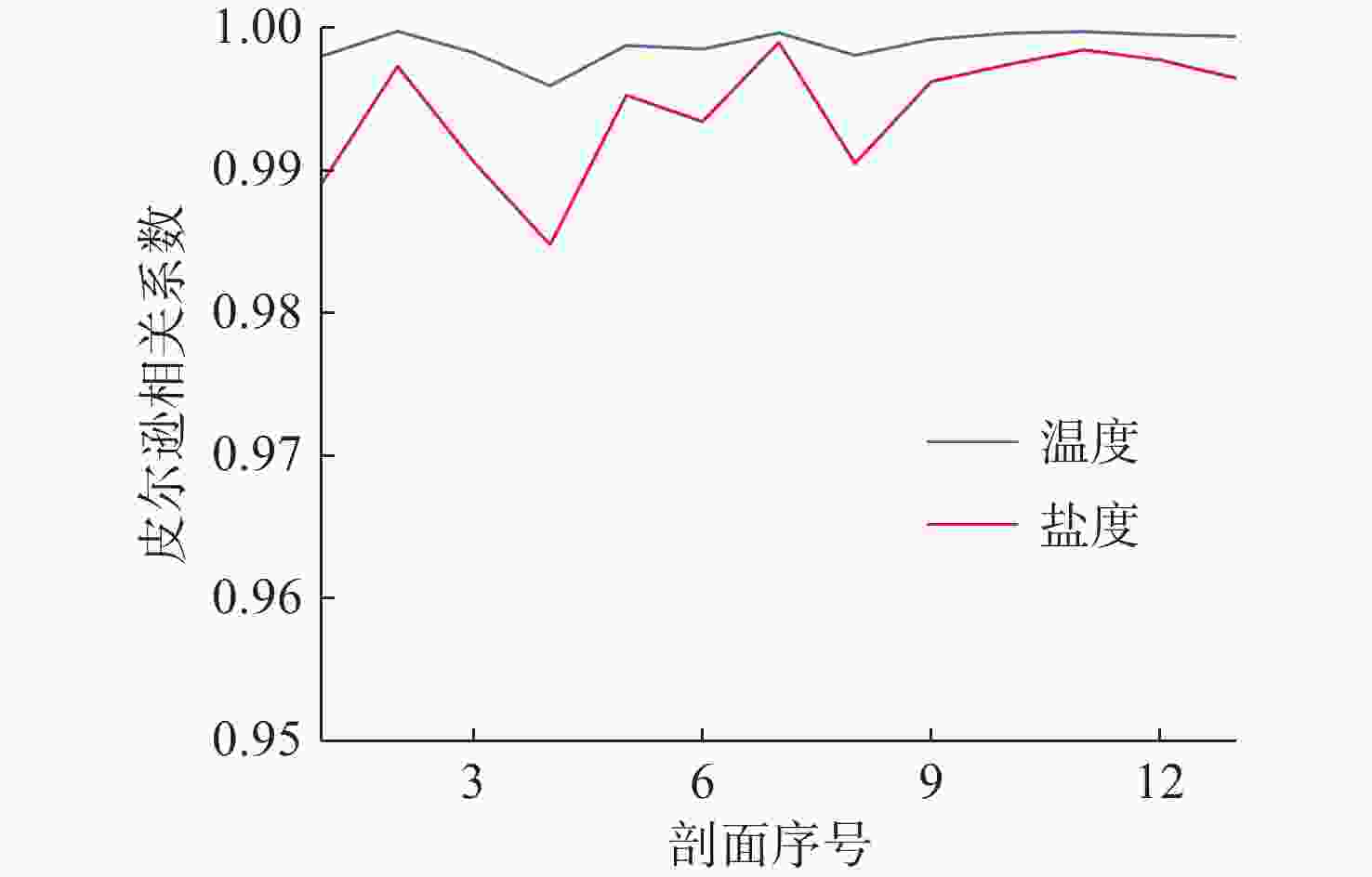
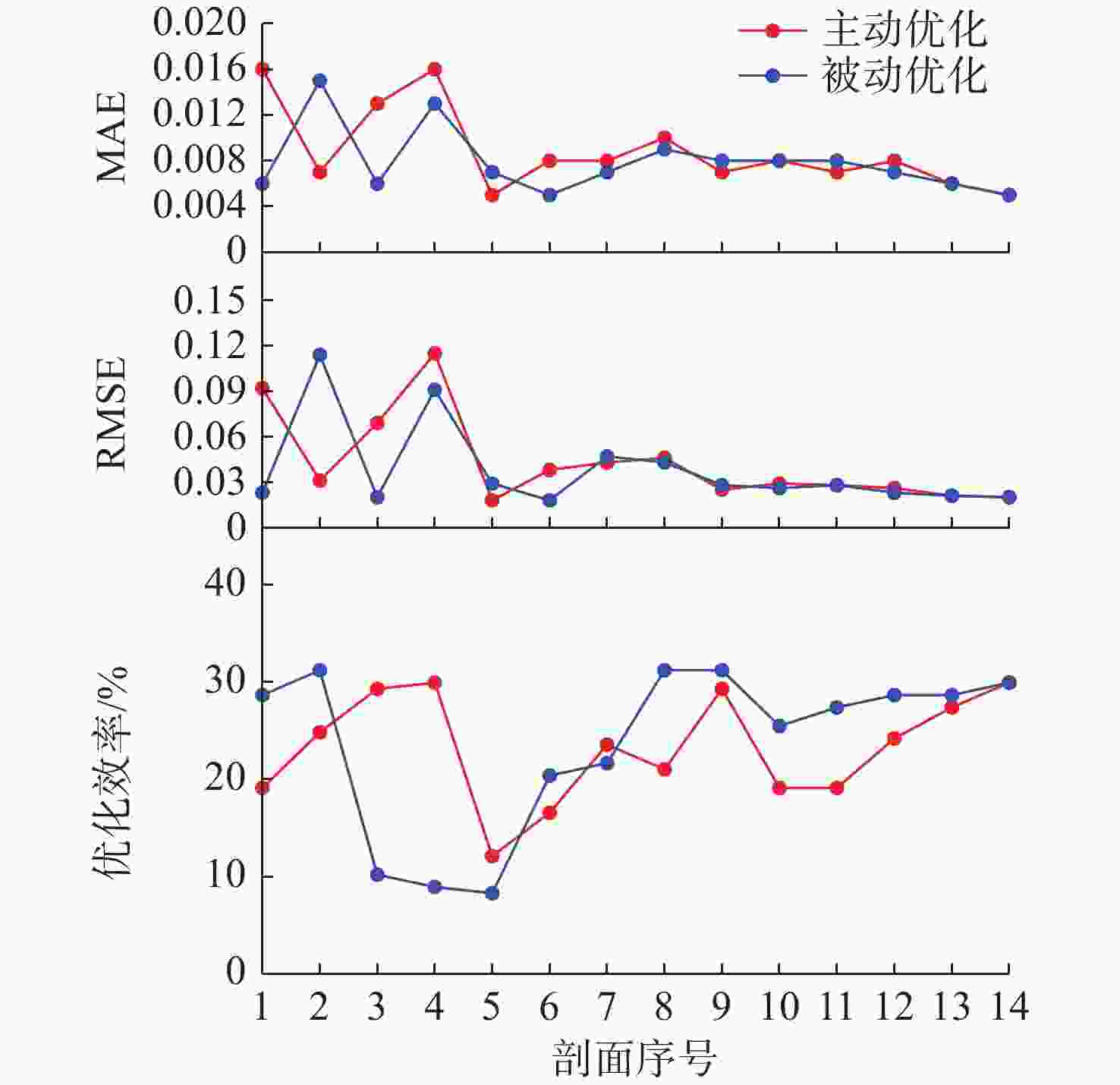
摘要: 在深海剖面浮标的剖面观测过程中, 出于浮标的低功耗设计需求, 需要采取合适的传感器采集频率以降低数据采集和传输过程中的功耗。基于自主研发的“海豚”深海剖面浮标, 结合搭载外设的具体功耗以及Argo计划中获取的温盐深(CTD)剖面数据进行仿真分析, 提出了一种基于自适应遗传算法的温盐数据采集策略优化模型, 根据相邻剖面数据具有强相关性的特点, 通过分析历史剖面数据特征规划新一轮剖面的采样方案, 在采样过程中根据数据的变化趋势适应性调整采样频率。基于实际数据的仿真分析结果表明, 通过该观测方法获取的剖面数据与实际数据相差较小, 同时相较于预编程的深度分层观测方案进一步降低了剖面浮标的整体功耗。Abstract: During the profiling observation process of deep-sea profiling buoys, an appropriate sensor sampling frequency must be implemented to reduce power consumption in data acquisition and transmission due to low-power design requirements. Based on the independently developed Dolphin deep-sea profiling buoy, this study established an optimized model for temperature and salinity data collection strategy using an adaptive genetic algorithm through simulation analysis combining peripheral device power consumption specifications and conductivity, temperature, and depth(CTD) profile data from the Argo program. Leveraging the strong correlation characteristics between adjacent profile data, the proposed method planned new-round sampling schemes by analyzing historical profile data features, while adaptively adjusting sampling frequency according to data variation trends during acquisition. The simulation analysis based on real-world data demonstrates that the profile data acquired through this observation method exhibits minimal deviation from actual measurements, while significantly reducing the overall power consumption of the profiling buoy compared to the pre-programmed deep-layer observation scheme.
-
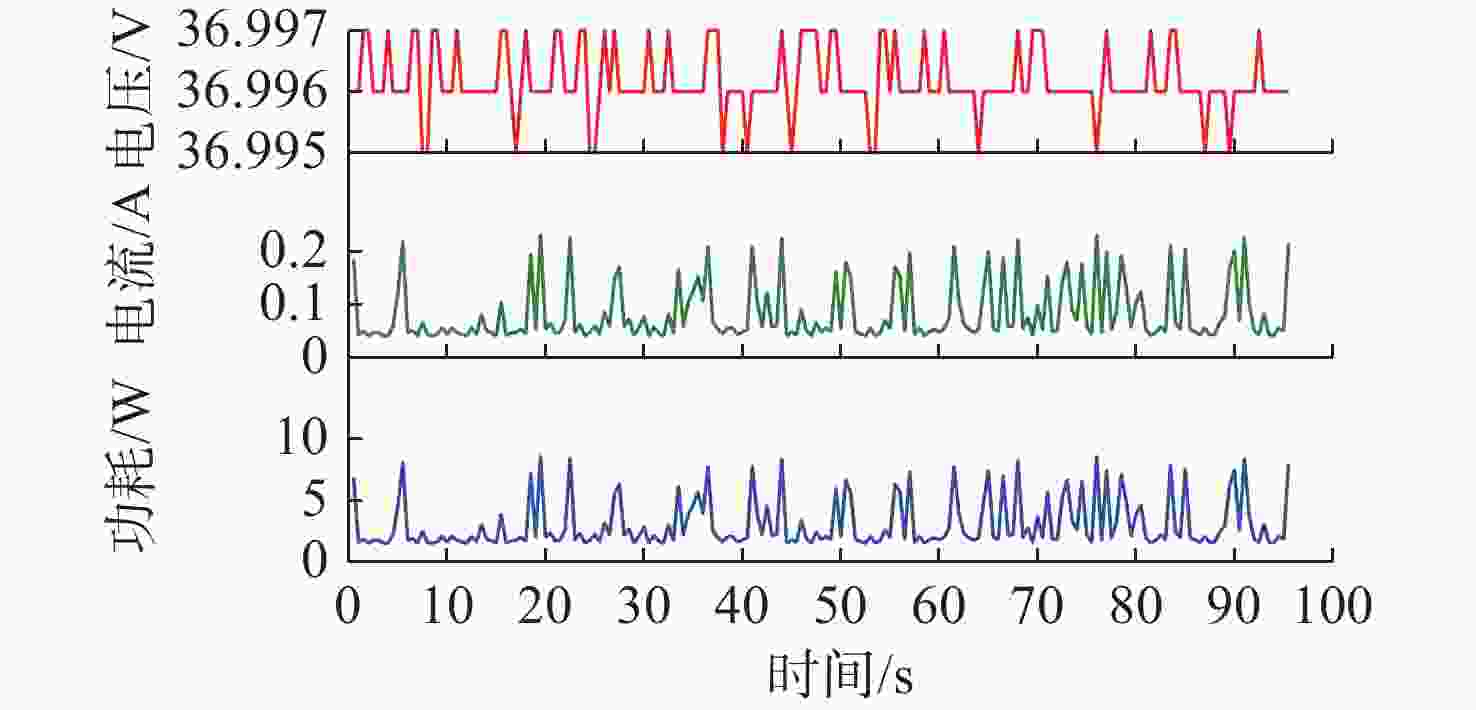
表 1 电导率传感器功耗情况
Table 1. Power consumption of conductivity sensor
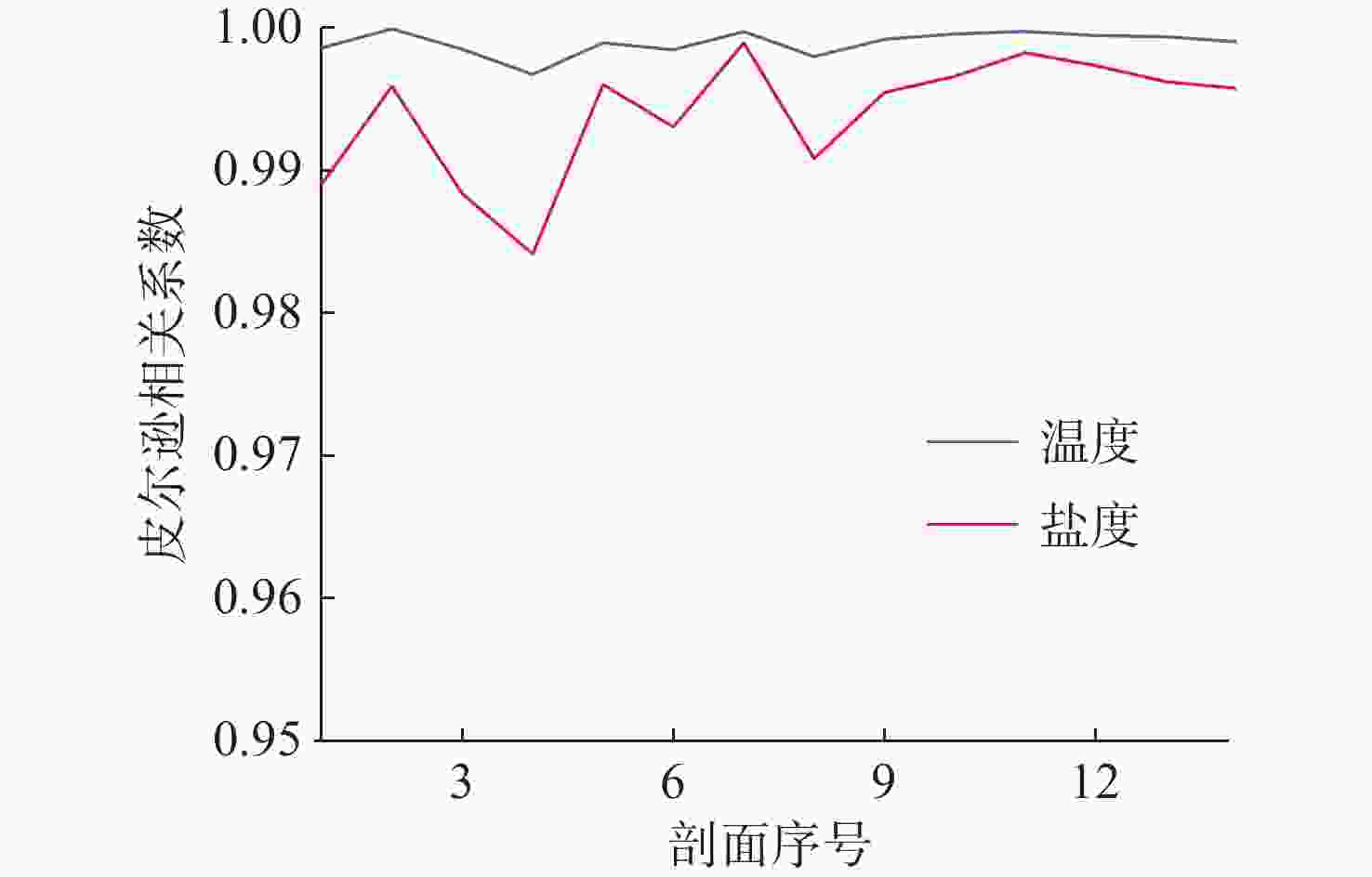
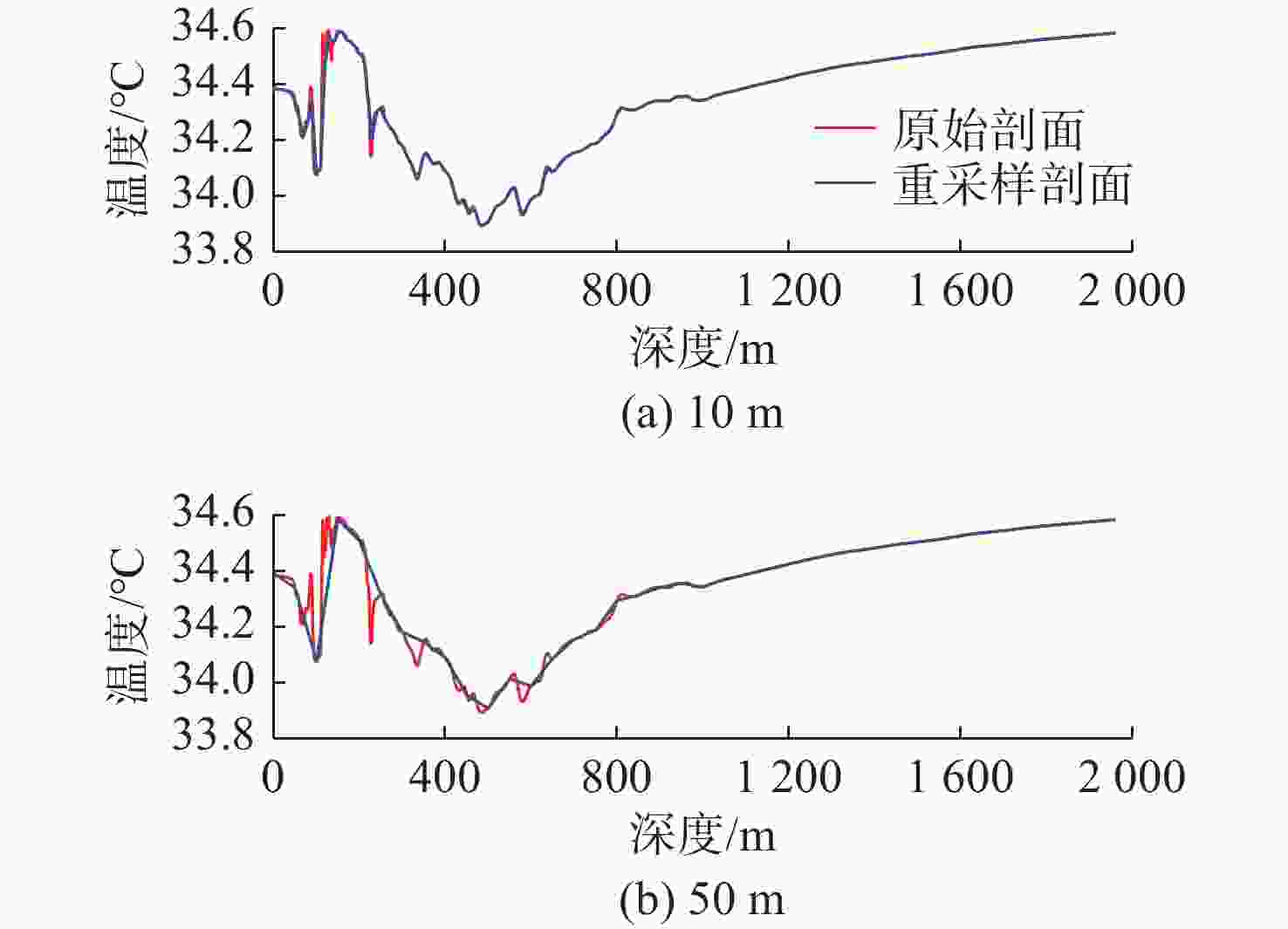
工作阶段 工作电流/mA 能耗/mWs 采样 34.22 410.64 休眠唤醒 3.90 46.80 待机 7.75 93.00 休眠 0.07 0.84 表 2 2902901号剖面浮标采样策略
Table 2. Profiling buoy sampling strategy of the No. 2902901
深度区间/m 采样间隔/m 0~10 2 10~600 10 600~800 20-25-30 800~6 000 50 表 3 连续优化剖面数据量变化情况
Table 3. Changes in data volume of continuously optimized profiles
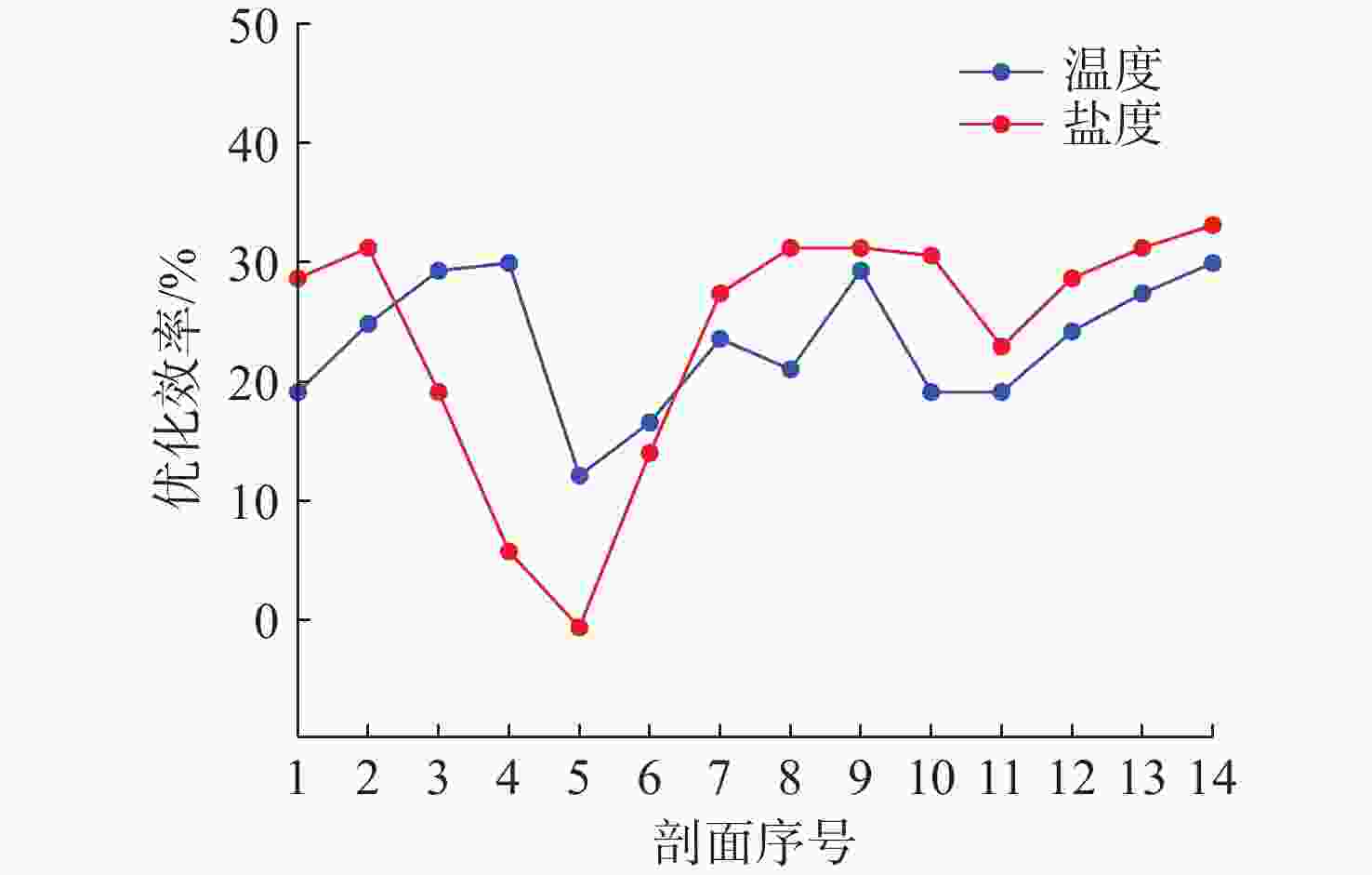
剖面
序号温度总
数据量温度优化
效率/%盐度总
数据量盐度优化
效率/%1 127 19.1 112 28.7 2 118 24.8 108 31.2 3 111 29.3 127 19.1 4 110 29.9 148 5.7 5 138 12.1 158 −0.64 6 131 16.6 135 14.0 7 120 23.6 114 27.4 8 124 21.0 108 31.2 9 115 26.8 108 31.2 10 113 28.0 117 25.5 11 108 31.2 108 31.2 12 109 30.6 126 19.7 13 111 29.2 121 22.9 14 115 26.8 113 28.0 -
[1] 王波, 李民, 刘世萱, 等. 海洋资料浮标观测技术应用现状及发展趋势[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2014, 35(11): 2401-14.WANG B, LI M, LIU S X, et al. Current status and trend of ocean data buoy observation technology applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2014, 35(11): 2401-14. [2] 陈鹿, 潘彬彬, 曹正良, 等. 自动剖面浮标研究现状及展望[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2017, 36(2): 1-9.CHEN L, PAN B B, CAO Z L, et al. Research Status and prospects of automatic profiling floats[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2017, 36(2): 1-9. [3] PU Y, SAMSON G, SHI C, et al. Blackghost: An ultra-low-power all-in-one 28 nm CMOS SoC for Internet-of-Things[C]//2017 IEEE Symposium in Low-Power and High-Speed Chips(COOL CHIPS). Yokohama, Japan: IEEE, 2017: 1-3. [4] SHAFIEE N, TEWARI S, CALHOUN B, et al. Infrastructure circuits for lifetime improvement of ultra-low power IoT devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2017, 64(9): 2598-2610. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2017.2693181 [5] ZHU W B, ZHANG Y F, YAZDI N. An ultra-low power switch array of temperature and humidity sensors with direct digital output[C]//2013 Transducers & Eurosensors XXVII: The 17th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2013: 108-111. [6] LEE C, KIM S. The sampling period estimation based adaptive sampling algorithm for a self-sustainable disaster monitoring system[C]//2020 European Conference on Networks and Communications. Dubrovnik, Croatia: IEEE, 2020: 165-169. [7] CAI W, ZHANG M. Spatiotemporal correlation-based adaptive sampling algorithm for clustered wireless sensor networks[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2018, 14(8): 69815662. [8] FATTOUM M, JELLALI Z, ATALLAH L N. Adaptive sampling approach exploiting spatio-temporal correlation and residual energy in periodic wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 7670-81. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3237024 [9] SUN Y, YUAN Y, LI X, et al. An adaptive sampling algorithm for target tracking in underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 68324-36. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2879536 [10] ALGABROUN H, HÅKANSSON L. Parametric machine learning-based adaptive sampling algorithm for efficient IoT data collection in environmental monitoring[J]. Journal of Network and Systems Management, 2024, 33: 5. [11] HEO S, MAYER P, MAGNO M. Predictive energy-aware adaptive sampling with deep reinforcement learning[C]//2022 29th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems(ICECS). Glasgow, UK: IEEE, 2022: 1-4. [12] GIORDANO M, CORTESI S, MEKIKIS P, et al. Energy-aware adaptive sampling for self-sustainability in resource-constrained IoT devices[C]//Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Energy Harvesting & Energy-Neutral Sensing Systems. New York, USA: ACM, 2023: 65-71. [13] CHEN F, XU S Z, ZHAO Y, et al. An adaptive genetic algorithm of adjusting sensor acquisition frequency[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20: 990. doi: 10.3390/s20040990 [14] SHU T X, XIA M, CHEN J H, et al. An energy efficient adaptive sampling algorithm in a sensor network for automated water quality monitoring[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17: 2551. doi: 10.3390/s17112551 [15] ZHOU H, ZENG Z, LIAN L. Adaptive re-planning of AUVs for environmental sampling missions: A fuzzy decision support system based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization[J]. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 2017, 20: 650-671. [16] 杭州全球海洋Argo系统野外科学观测研究站. China Argo profiling float[DB]. (2024-10-04)[2025-03-17]. https://pic.argo.org.cn. [17] KATOCH S, CHAUHAN S S, KUMAR V. A review on genetic algorithm: past, present, and future[J]. Multimed Tools Appl, 2021, 80: 8091-8126. doi: 10.1007/s11042-020-10139-6 [18] ALHIJAWI B, AWAJAN A. Genetic algorithms: Theory, genetic operators, solutions, and applications[J]. Evol. Intel, 2024, 17: 1245-56. doi: 10.1007/s12065-023-00822-6 [19] 李昆鹏, 刘腾博, 李文莉. 改进自适应遗传算法求解“货到人”拣选系统订单分批问题[J]. 机械工程学报, 2023, 59(4): 308-317. doi: 10.3901/JME.2023.04.308LI K P, LIU T B, LI W L. Improved adaptive genetic algorithm for order batching of “part-to-picker” picking system[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 59(4): 308-317. doi: 10.3901/JME.2023.04.308 -





 下载:
下载: