Underwater Visual Multi-Target Tracking Algorithm Integrating Re-parameterization and Attention Mechanism
-
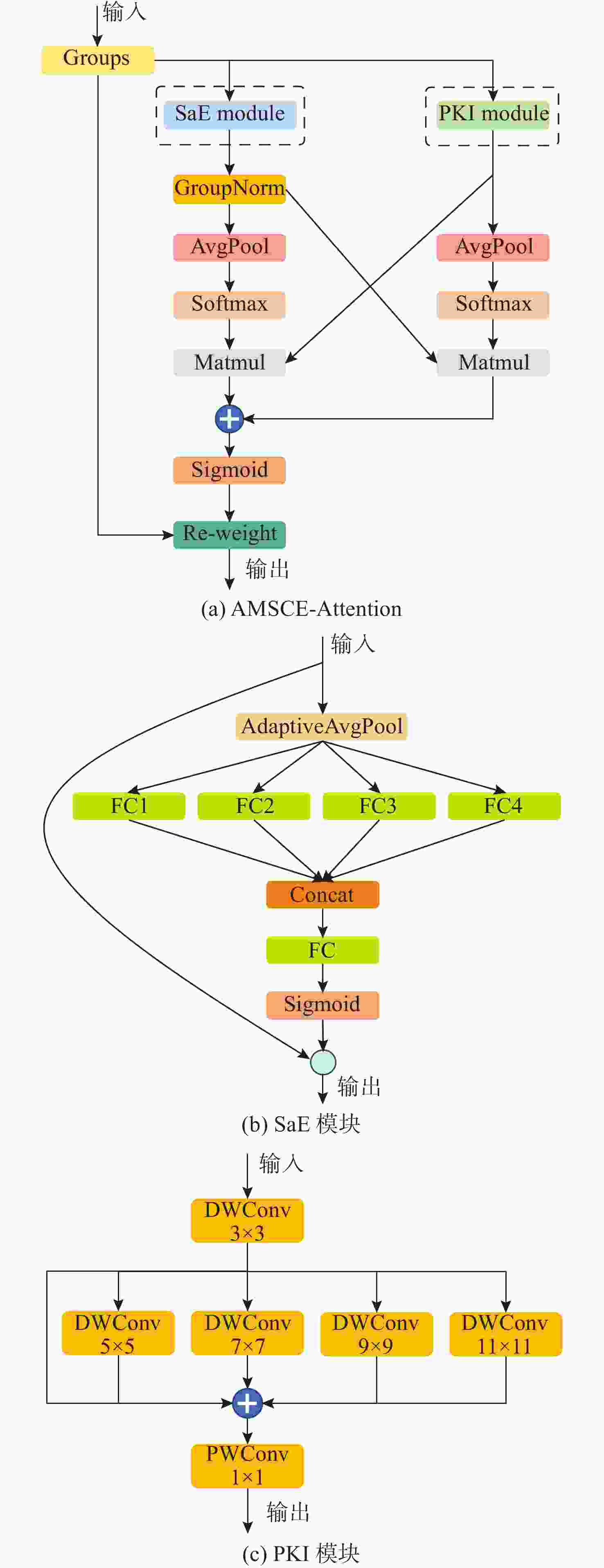
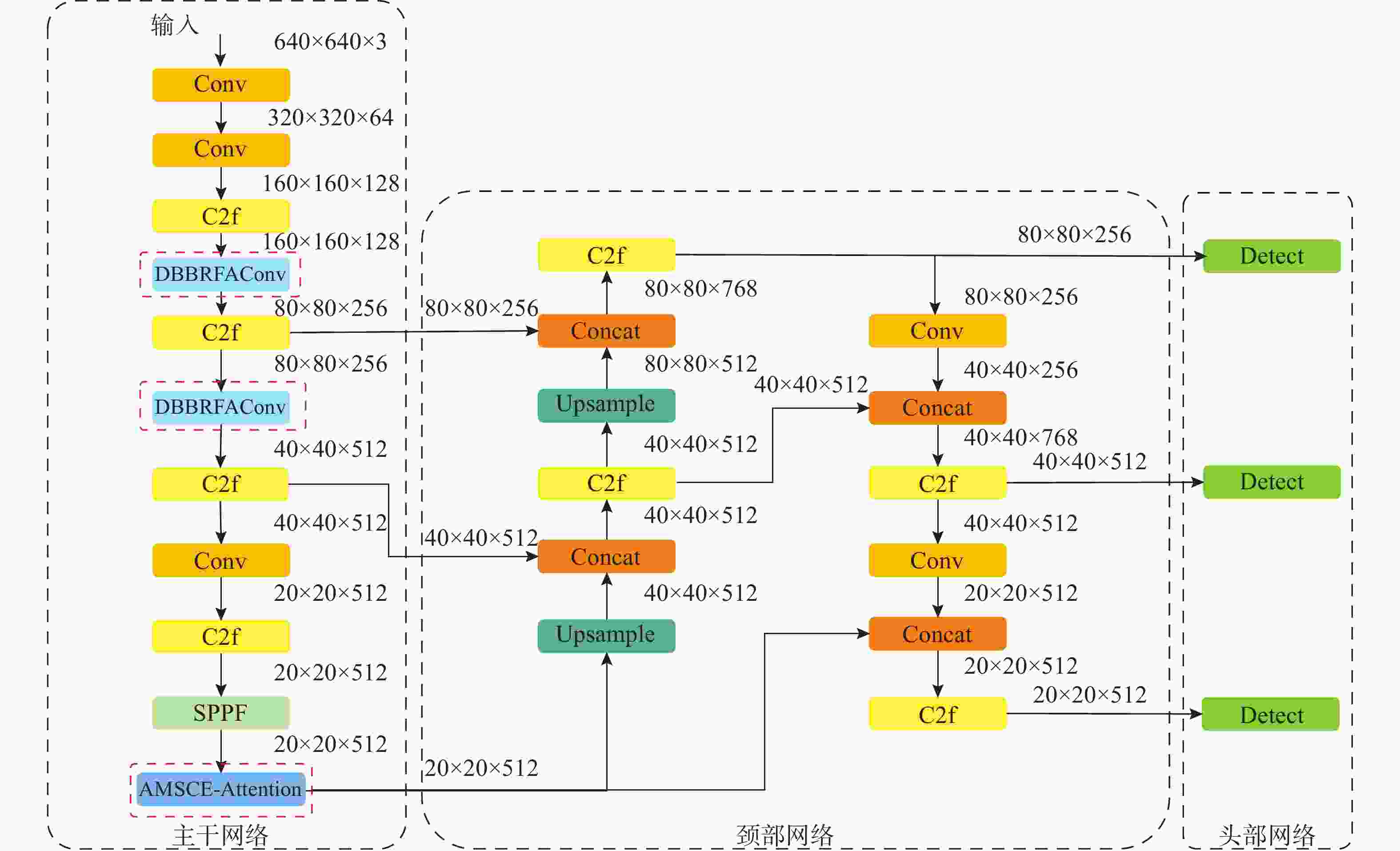
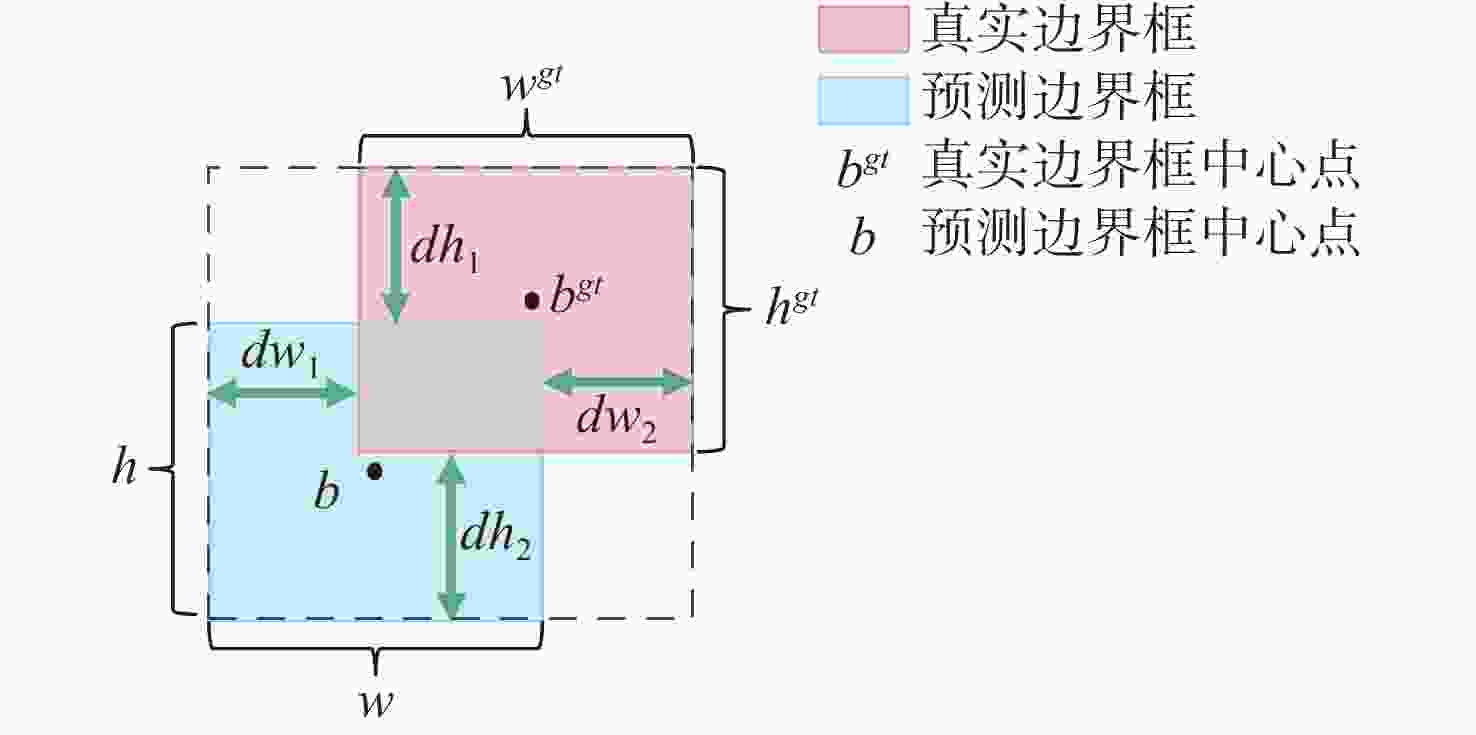
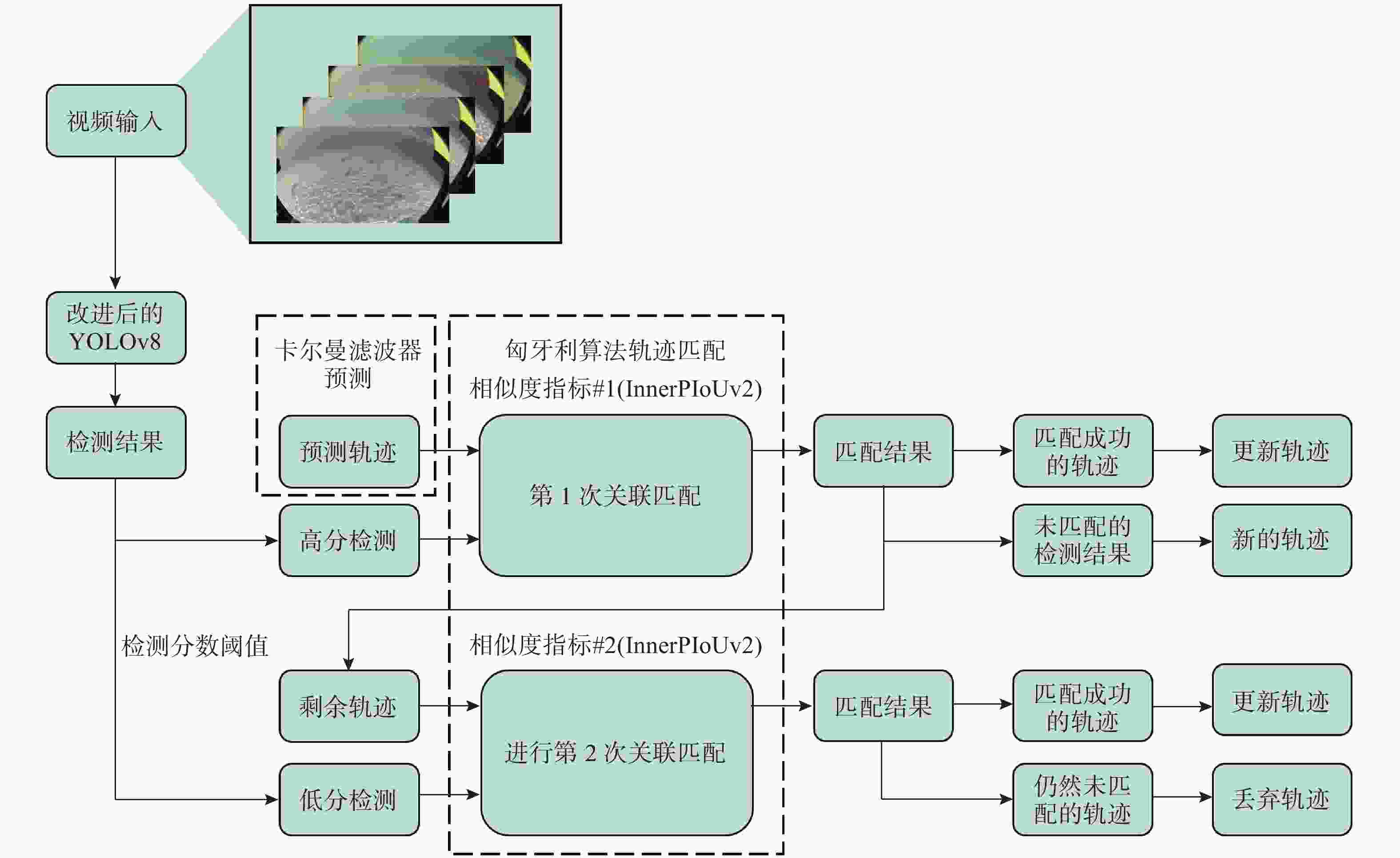
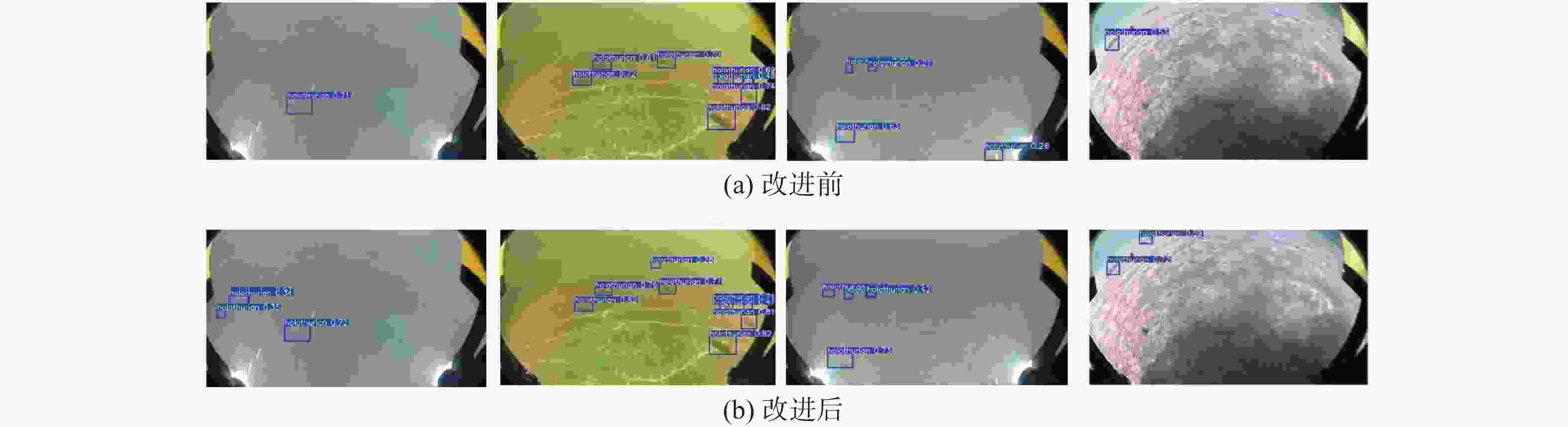
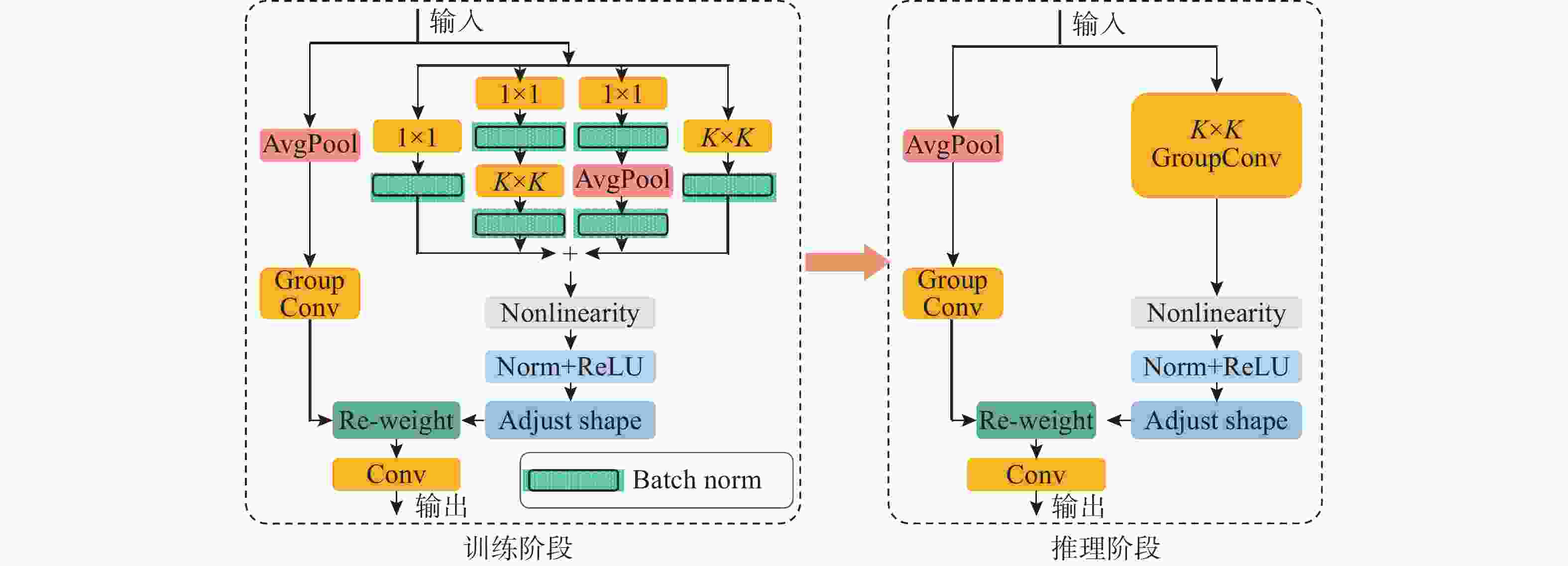
摘要: 复杂的水下环境会严重影响成像设备的稳定性和获取图像的质量, 从而给水下无人自主系统视觉多目标跟踪带来极大挑战。为了解决水下相机抖动和图像退化带来的问题, 文中提出一种适用于水下无人自主系统的融合重参数化与注意力机制的水下视觉多目标跟踪算法。首先, 针对水下目标多样及图像退化等问题, 提出基于重参数化和注意力机制改进的YOLOv8 算法(RA-YOLOv8), 通过融合结构重参数化的多尺度特征提取卷积结构(DBB-RFAConv)和注意力机制, 有效增强网络的多尺度特征提取能力和提高模型的检测精度; 然后, 针对水下相机抖动问题给目标实时跟踪带来的挑战, 提出基于Inner-PIoUv2 改进的ByteTrack算法(IP2-ByteTrack), 使用 Inner-PIoUv2 作为跟踪算法匹配过程中的相似度度量, 增强模型在水下检测和跟踪任务中的性能, 提高跟踪轨迹匹配准确性; 最后, 基于RA-YOLOv8 和IP2-ByteTrack 算法, 提出一种用于水下无人自主系统的融合重参数化与注意力机制的水下视觉多目标跟踪算法。实验结果表明, 所提算法在复杂水下环境中表现出优异的性能, 能够有效解决现有方法在水下多目标跟踪中的不足。
-
关键词:
- 水下视觉 /
- 多目标跟踪 /
- YOLO /
- ByteTrack /
- 重参数化; 注意力机制
Abstract: The complex underwater environment can severely impact the stability of imaging devices and the quality of captured images, posing significant challenges for visual multi-target tracking in underwater unmanned autonomous systems. To address the difficulties arising from underwater camera jitter and image degradation, this paper proposed an underwater visual multi-target tracking algorithm that integrated re-parameterization and attention mechanisms, specifically tailored for underwater unmanned autonomous systems. First, to tackle the diversity of underwater targets and image degradation, an improved YOLOv8 algorithm based on re-parameterization and attention mechanism(RA-YOLOv8) was proposed. This algorithm effectively enhanced the network’s multi-scale feature extraction capability and improved the detection accuracy of the model by integrating a structurally re-parameterized multi-scale feature extraction convolutional structure(DBB-RFAConv) and the AMSCE-attention mechanism. Then, to address the challenges of real-time target tracking caused by underwater camera jitter, an Inner-PIoUv2-enhanced ByteTrack algorithm(IP2-ByteTrack) was proposed. Inner-PIoUv2 was used as the similarity measure in the matching process of the tracking algorithm, which enhanced the model’s performance in underwater detection and tracking tasks, improving the accuracy of tracking trajectory matching. Finally, based on the RA-YOLOv8 and IP2-ByteTrack algorithms, an underwater visual multi-target tracking algorithm that integrated re-parameterization and attention mechanisms for underwater autonomous systems was proposed. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm exhibits excellent performance in complex underwater environments and can effectively address the shortcomings of existing methods in underwater multi-target tracking.-
Key words:
- underwater visual /
- multi-target tracking /
- YOLO /
- ByteTrack /
- re-parameterization; attention mechanism
-
表 1 实验环境配置
Table 1. The configuration of the experimental environment
名称 版本 CPU Intel 13th Gen i9-13900HX GPU NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4060 内存 64G 操作系统 Windows11 Python 3.11 表 2 不同YOLO系列模型性能对比实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results of performance comparison of different YOLO series models
模型 精确度
/%召回率
/%mAP50
/%mAP50-95
/%FPS
/(帧/s)YOLOv7 81.5 72.0 75.0 31.6 35.46 YOLOv8 83.2 73.5 82.1 36.6 35.58 YOLOv10 72.0 71.7 77.5 36.4 35.84 表 3 DBB-RFAConv消融试验实验结果
Table 3. The experimental results of ablation studies on DBB-RFAConv
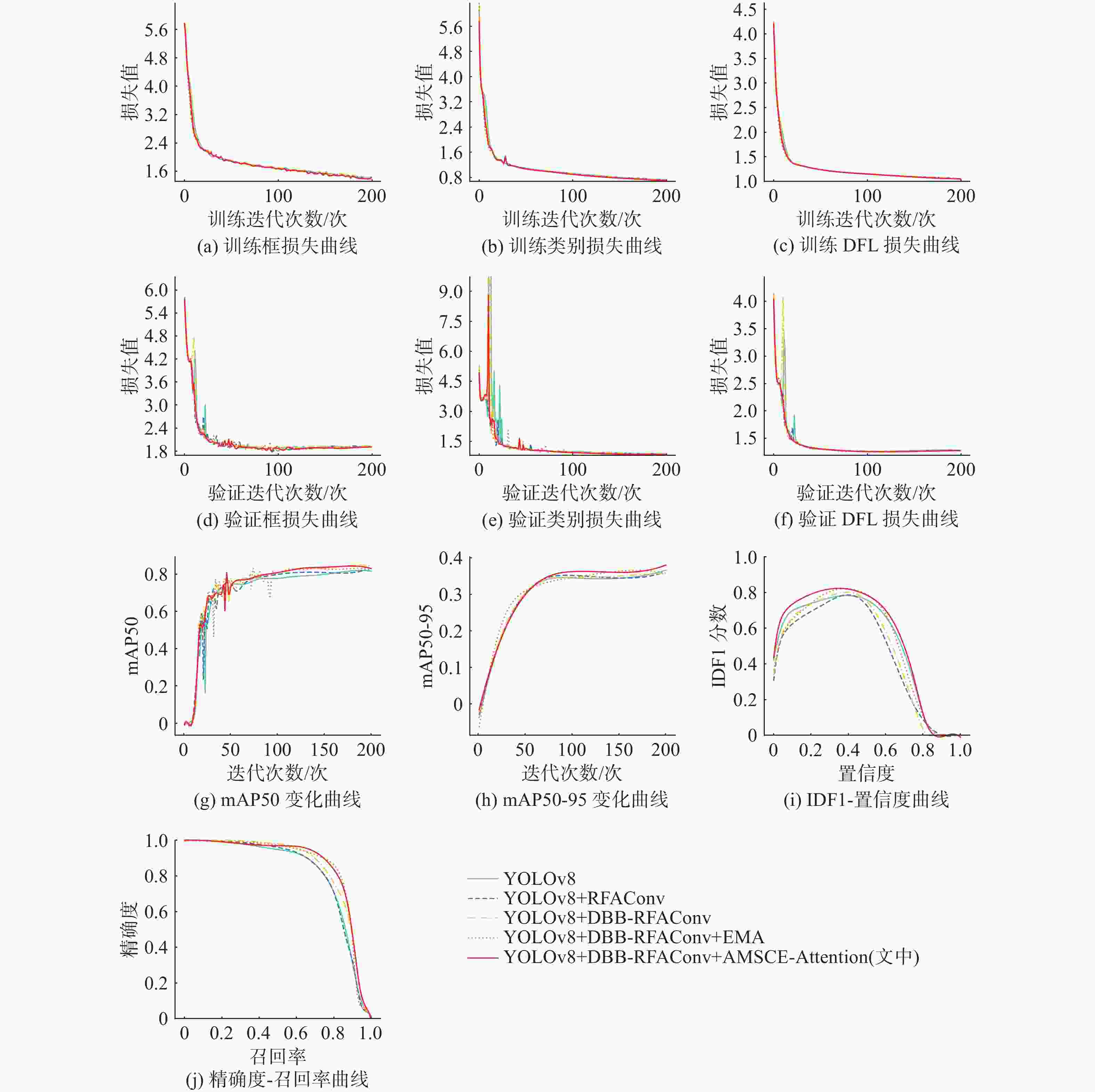
模型 精确度/% 召回率/% mAP50/% mAP50-95/% GFLOPs 参数量 YOLOv8基线 83.2 73.5 82.1 36.6 8.1 3 005 843 YOLOv8 + RFAConv 84.9 72.9 82.2 37.4 8.2 3 016 211 YOLOv8 +DBB-RFAConv 84.3 75.8 85.4 37.6 8.2 3 017 075 表 4 不同注意力消融实验结果
Table 4. The experimental results of ablation studies on different types of attention
模型 精确度
/%召回率
/%mAP50
/%mAP50-
95/%GFLOPs YOLOv8 + DBB-
RFAConv(基线)84.3 75.8 85.4 37.6 8.2 基线+SimAM 82.7 72.3 82.7 36.6 8.2 基线+CBAM 82.9 75.7 83.6 37.5 8.2 基线+DHSA 87.8 72.4 83.2 37.6 8.5 基线+EMA 87.9 79.1 85.9 37.8 8.2 基线+MAB 83.1 74.9 82.3 37.4 8.6 基线+MSCA 87.0 75.2 83.8 37.9 8.4 基线+CPCA 86.4 77.3 83.5 38.2 8.3 基线+文中 89.4 77.0 86.2 38.8 8.2 表 5 不同多目标跟踪算法实验结果
Table 5. Experimental results of different multi-object tracking algorithms
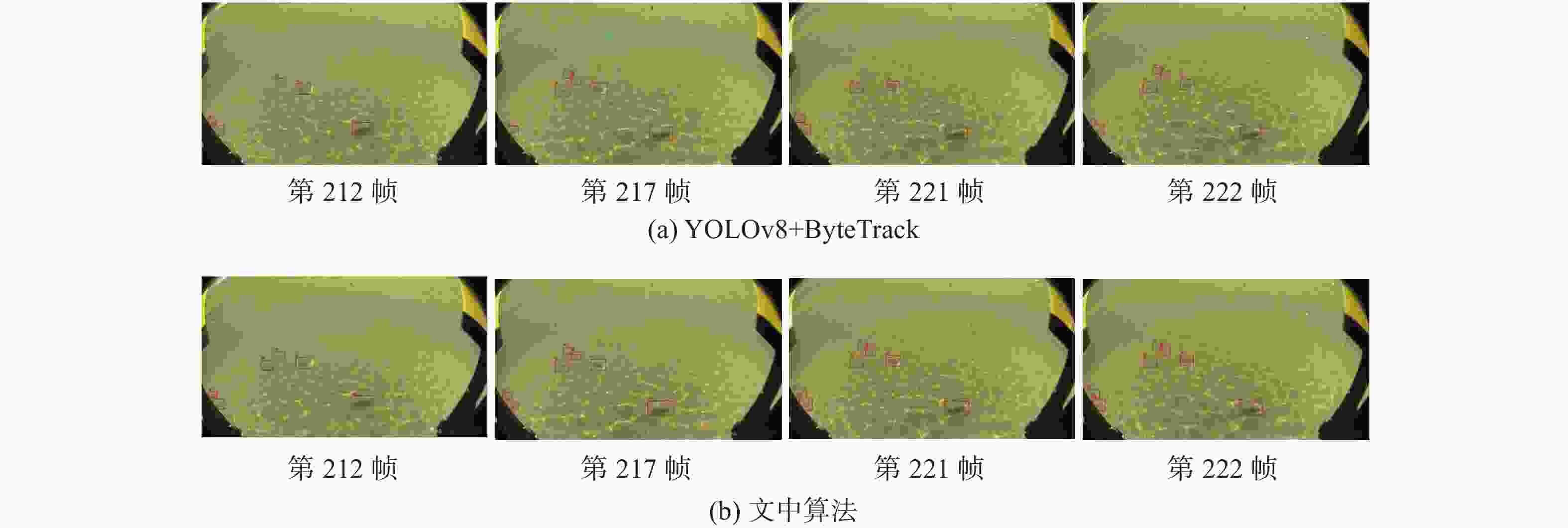
模型 IDF1/% IDP/% IDR/% IDs MOTA/% MOTP FPS/(帧/s) YOLOv8 + ByteTrack 65.50 86.20 52.80 21.4 54.0 0.387 24.92 YOLOv8 + BoT-SORT 69.68 90.64 56.59 14.5 60.6 0.431 10.02 YOLOv8 + OC-SORT 60.60 85.30 47.20 22.2 49.2 0.342 24.11 YOLOv8 + DeepOC-SORT 60.60 85.50 47.10 21.4 49.1 0.339 23.18 表 6 多目标跟踪算法消融实验结果
Table 6. Ablation experiment results of multi-object tracking algorithms
模型 IDF1/% IDP/% IDR/% IDs MOTA/% MOTP FPS/(帧/s) YOLOv8 + ByteTrack(基线) 65.5 86.2 52.8 21.4 54 0.387 24.92 YOLOv8 + DBB-RFAConv+AMSCEA 70.0 87.4 58.4 18.4 58.7 0.402 24.24 YOLOv8 + DBB-RFAConv + AMSCE-Attention + InnerPIoUv2(文中) 71.5 88.9 59.8 15.3 59.3 0.393 24.05 -
[1] 徐正兴, 诸云, 吴祎楠. 基于改进Sigma点的无迹卡尔曼滤波水下目标跟踪算法[J]. 无人系统技术, 2023, 6(4): 22-30. [2] 张博宇, 齐滨, 王晋晋, 等. 密集杂波背景下的水下多目标跟踪方法[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2023, 10(5): 31-39. [3] 王学敏, 于洪波, 张翔宇, 等. 基于Hough变换检测前跟踪的水下多目标被动检测方法[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(7): 2114-2121. [4] 郑繁亭, 邢关生. 基于改进DeepSort的行人多目标跟踪算法[J]. 现代电子技术, 2023, 46(5): 40-46. [5] 何水龙, 张靖佳, 张林俊, 等. 基于Transformer改进的YOLOv5+DeepSORT的车辆跟踪算法[J]. 汽车技术, 2024(7): 9-16. [6] 陈辉, 杜双燕, 连峰, 等. Track-MT3: 一种基于Transformer的新型多目标跟踪算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2024, 13 (6): 1202-1219. doi: 10.12000/JR24164 [7] 赵海翔, 崔鸿武, 黄桢铭, 等. 基于Bytetrack的多目标跟踪算法在斑马鱼毒性行为识别中的应用[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2024, 45(2): 136-149. [8] REDMON J. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]//Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. [9] JIAN M W, LIU X Y, LUO H J, et al. Underwater image processing and analysis: A review[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2021, 91(1): 116088. [10] CHEN S, CHEN S, SHAN W, et al. A self-supervised underwater image denoising method based on pseudo-siamese neural network[C]//2023 5th International Conference on Robotics and Computer Vision. Nanjing, China: ICRCV, 2023: 130-134. [11] ZHANG X, LIU C, YANG D, et al. RFAConv: Innovating spatial attention and standard convolutional operation[EB/OL]. (2023-04-06) [2025-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2304.03198. [12] DING X, ZHANG X, HAN J, et al. Diverse branch block: Building a convolution as an inception-like unit[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Nashville, Tennessee, USA: IEEE, 2021: 10886-10895. [13] OUYANG D, HE S, ZHANG G, et al. Efficient multi-scale attention module with cross-spatial learning[C]//ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP). Rhodes, Greece: IEEE, 2023: 1-5. [14] NARAYANAN M. SENetV2: Aggregated dense layer for channelwise and global representations[EB/OL]. (2023-11-17) [2025-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2311.10807. [15] CAI X, LAI Q, WANG Y, et al. Poly kernel inception network for remote sensing detection[EB/OL]. (2024-03-10)[2025-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2403.06258. [16] ZHANG Y, SUN P, JIANG Y, et al. Bytetrack: Multi-object tracking by associating every detection box[C]//European conference on computer vision. Tel Aviv, Israel: ECCV, 2022: 1-21. [17] LIU C, WANG K, LI Q, et al. Powerful-IoU: More straight forward and faster bounding box regression loss with a nonmonotonic focusing mechanism[J]. Neural Networks, 2024, 170(1): 276-284. [18] ZHANG H, XU C, ZHANG S. Inner-iou: More effective intersection over union loss with auxiliary bounding box[EB/OL]. (2023-11-06) [2025-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2311.02877. [19] ZHANG X, ZENG H, LIU X, et al. In situ holothurian noncontact counting system: A general framework for holothurian counting[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 210041-210053. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3038643 [20] YANG L, ZHANG R Y, LI L, et al. A simple, parameter-free attention module for convolutional neural networks[C]//International conference on machine learning.Vienna, Austria: PMLR, 2021: 11863-11874. [21] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision. Munich, Germany: ECCV, 2018: 3-19. [22] SUN S, REN W, GAO X, et al. Restoring images in adverse weather conditions via histogram transformer[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Shanghai, China: ECCV, 2025: 111-129. [23] WANG Y, LI Y, WANG G, et al. Multi-scale attention network for single image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. [24] GUO M H, LU C Z, HOU Q, et al. Segnext: Rethinking convolutional attention design for semantic segmentation[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2022, 35: 1140-1156. [25] HUANG H, CHEN Z, ZOU Y, et al. Channel prior convolutional attention for medical image segmentation[EB/OL]. (2023-11-06) [2025-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2306.05196 [26] MAGGIOLINO G, AHMAD A, CAO J, et al. Deep oc-sort: Multi-pedestrian tracking by adaptive re-identification[C]//2023 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing(ICIP). KL, Malaysia: IEEE, 2023: 3025-3029. -




 下载:
下载: