A Secure Communication Method for Unmanned Undersea Systems Oriented to Federated Learning
-
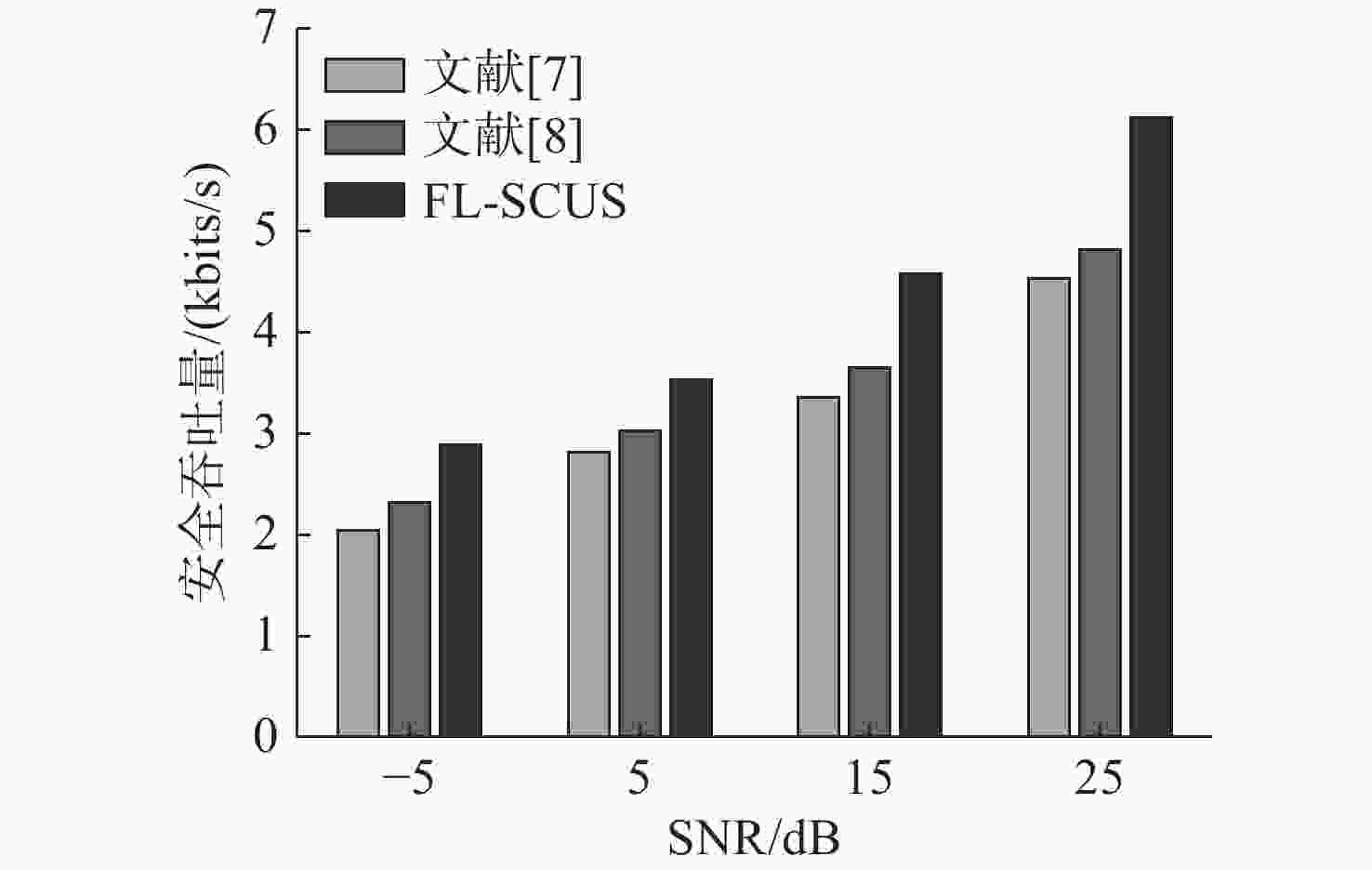
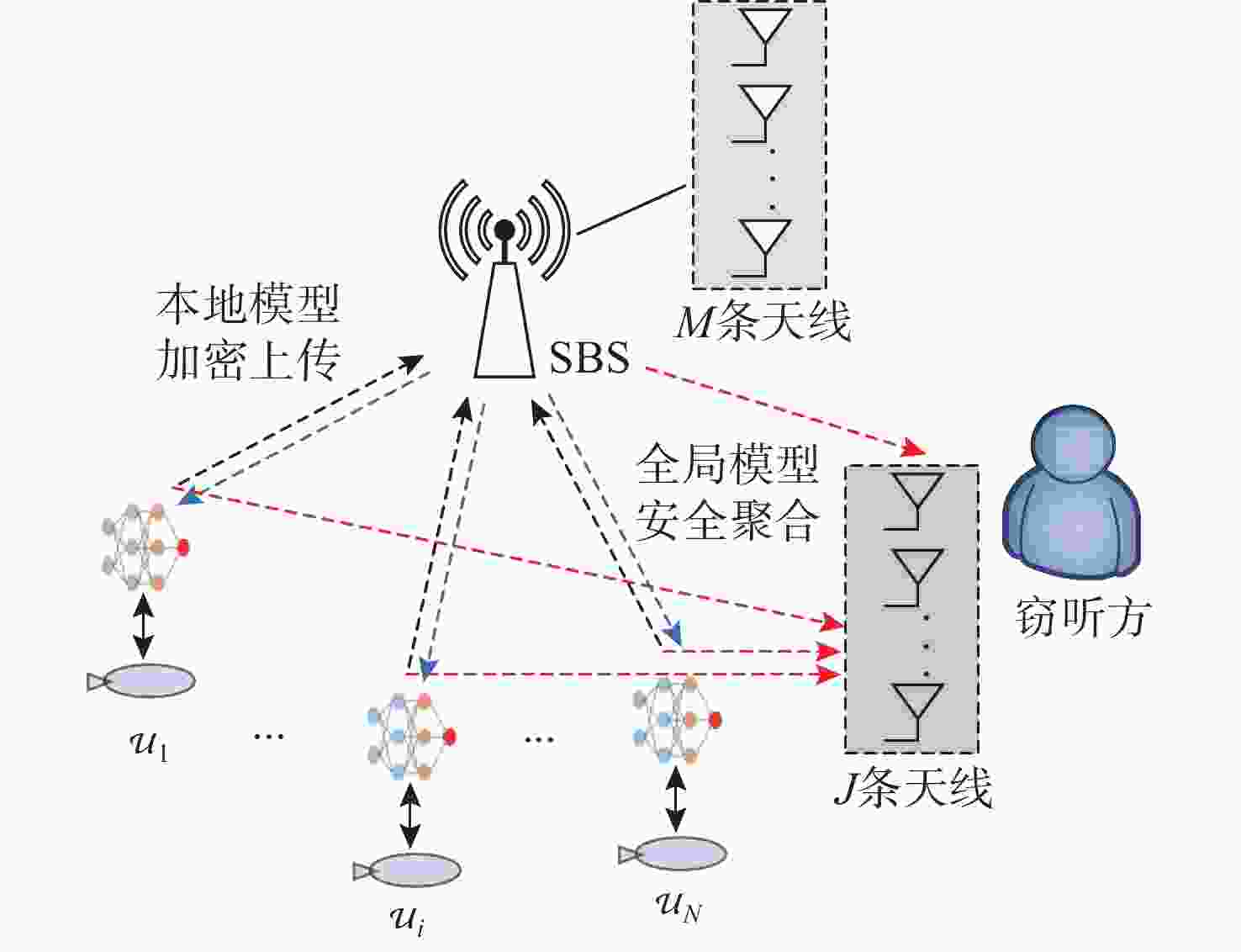
摘要: 针对水下无人系统中的信息泄露问题, 提出了一种面向联邦学习的安全通信方案。考虑水声信道复杂性和带宽限制, 引入了基于Kashin压缩的无偏梯度压缩方法, 通过正交投影和量化操作降低传输梯度维度, 减少通信成本并保持信息完整性。为应对信息泄露, 设计了基于反馈信道的保密方案, 利用归一化水声信道传递矩阵和随机序列生成密钥, 确保窃听方无法解密模型参数。通过结合多目标优化技术, 找到Pareto最优解实现模型精度和安全吞吐量的平衡。仿真结果显示, 与现有方案相比, 所提方案能够有效提升训练精度和安全吞吐量, 同时保持较低通信延迟。Abstract: To address the information leakage issue in unmanned undersea systems, a secure communication method oriented to federated learning was proposed in this paper. By considering the complexities and bandwidth limitations of acoustic channels, an unbiased gradient compression method using Kashin compression was introduced. This method reduced the dimensionality of transmission gradients through orthogonal projection and quantization, thereby decreasing communication costs while preserving information integrity. To mitigate information leakage, a privacy-preserving method utilizing a feedback channel was designed, and the normalized acoustic channel transmission matrix and random sequences were employed to generate secret keys, so as to ensure that eavesdroppers cannot decrypt the model parameters. By adopting multi-objective optimization techniques, the Pareto optimal solution was found to strike a balance between model accuracy and secure throughput. Simulation results show that compared with the existing methods, the proposed method in this paper can effectively improve training accuracy and secure throughput while maintaining low latency.
-
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Parameters of simulation
参数名称 参数值 中心频率/kHz 15.5 带宽/kHz 3.75 合法天线数 10 窃听天线数 8 模型大小/(kbit/s) 400 表 2 训练精度
Table 2. Training accuracy
-
[1] ZUO M, TU X, YANG S, et al. Channel distribution and noise characteristics of distributed acoustic sensing underwater communications[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(21): 24185-94. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3115581 [2] MEECHAM A, ACKER T. Underwater threat detection and tracking using multiple sensors and advanced processing[C]//IEEE International Carnahan Conference on Security Technology. Orlando, USA: IEEE, 2016: 1-7. [3] HE Y, HAN G, LI A, et al. A federated deep reinforcement learning-based trust model in underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2024, 23(5): 5150-61. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2023.3301825 [4] AFZAL M U, ABDELLATIF A A. Energy-efficient secure federated learning for UAV swarms[C]//International Conference on Energy Conservation and Efficiency. Lahore, Pakistan: IEEE, 2024: 1-5. [5] PARK J, YU N Y, LIM H. Privacy-preserving federated learning using homomorphic encryption with different encryption keys[C]//International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence. Jeju Island, Korea: IEEE, 2022: 1869-71. [6] XU G, LI H, LIU S, et al. VerifyNet: secure and verifiable federated learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 911-926. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2019.2929409 [7] WANG T, LI Y, WU Y, et al. Secrecy driven federated learning via cooperative jamming: An approach of latency minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2022, 10(4): 1687-1703. doi: 10.1109/TETC.2022.3159282 [8] YANG X, LIU Z, TANG X, et al. An efficient and multi-private key secure aggregation scheme for federated learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2024, 17(5): 1998-2011. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2024.3451165 [9] ISIAM K Y, AHMAD I, RONG Y, et al. Joint energy and security optimization in underwater wireless communication networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(8): 14282-95. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3340269 [10] QARABAQI P, STOJANOVIC M. Statistical characterization and computationally efficient modeling of a class of underwater acoustic communication channels[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2013, 38(4): 701-717. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2013.2278787 [11] LI H, ZHANG Q. Multiobjective optimization problems with complicated Pareto sets, MOEA/D and NSGA-II[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2009, 13(2): 284-302. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2008.925798 [12] LIU Y, ZHAO T, SHOU G, et al. Joint optimization of latency and energy consumption via deep reinforcement learning for proximity detection in road networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(12): 19457-68. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2024.3448627 [13] LinkQuest Inc. Linkquest underwater acoustic modems UWM4000 specifications[EB/OL]. (2006-04-02) [2025-02-24]. https://www.link-quest.com/html/uwm4000.htm. [14] 冼敏元, 赵春燕, 何轲, 等. 基于被动时反-随机共振的水下弱信号参数优化检测方法[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2020, 28(5): 480-496. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2020.05.002XIAN M Y, ZHAO C Y, HE K, et al. Optimal approach of weak underwater acoustic signal detection based on passive time-reversal stochastic resonance[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2020, 28(5): 480-496. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2020.05.002 -




 下载:
下载: