Vector Propulsion AUV Path Planning Method Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning
-
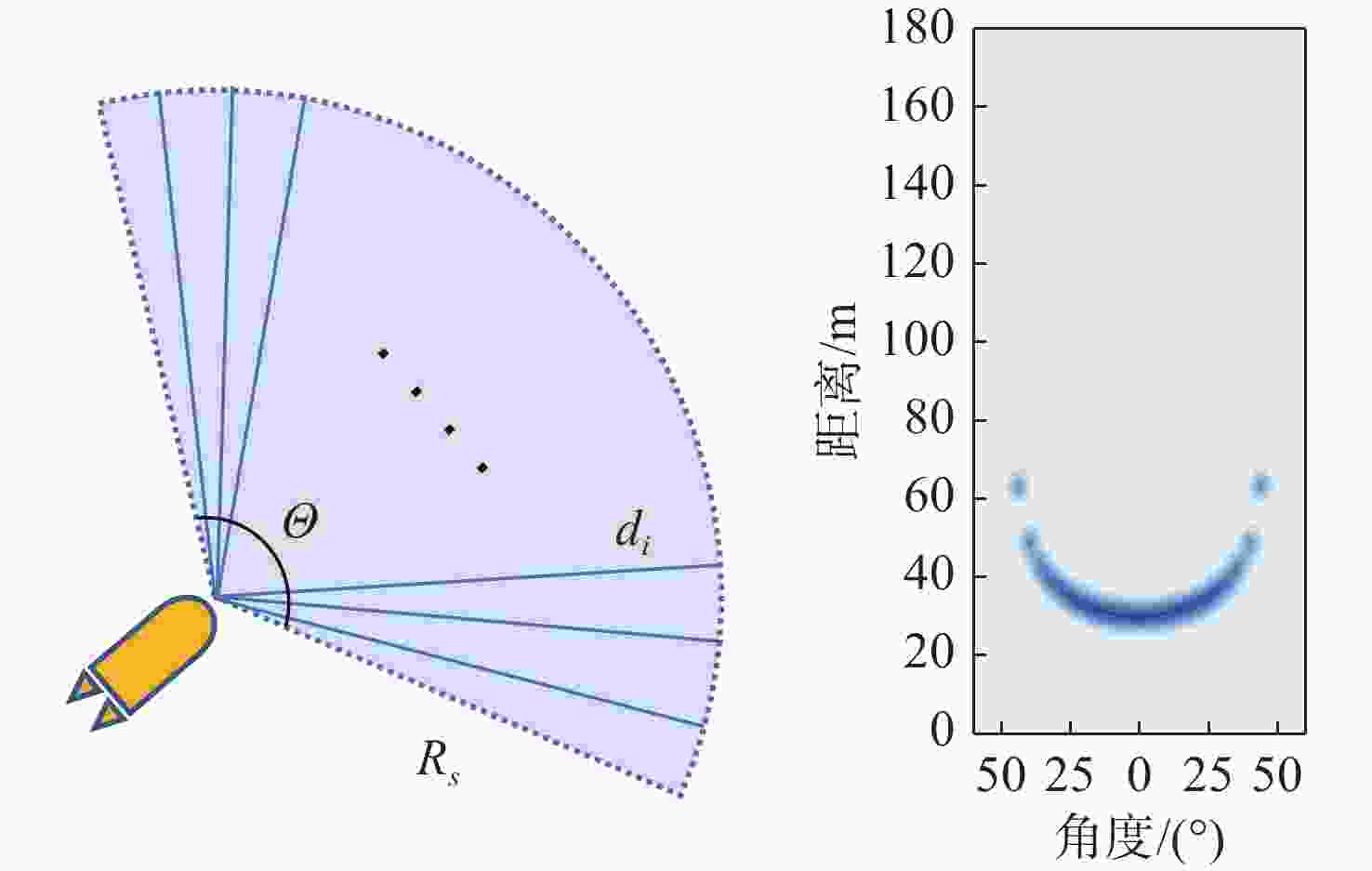
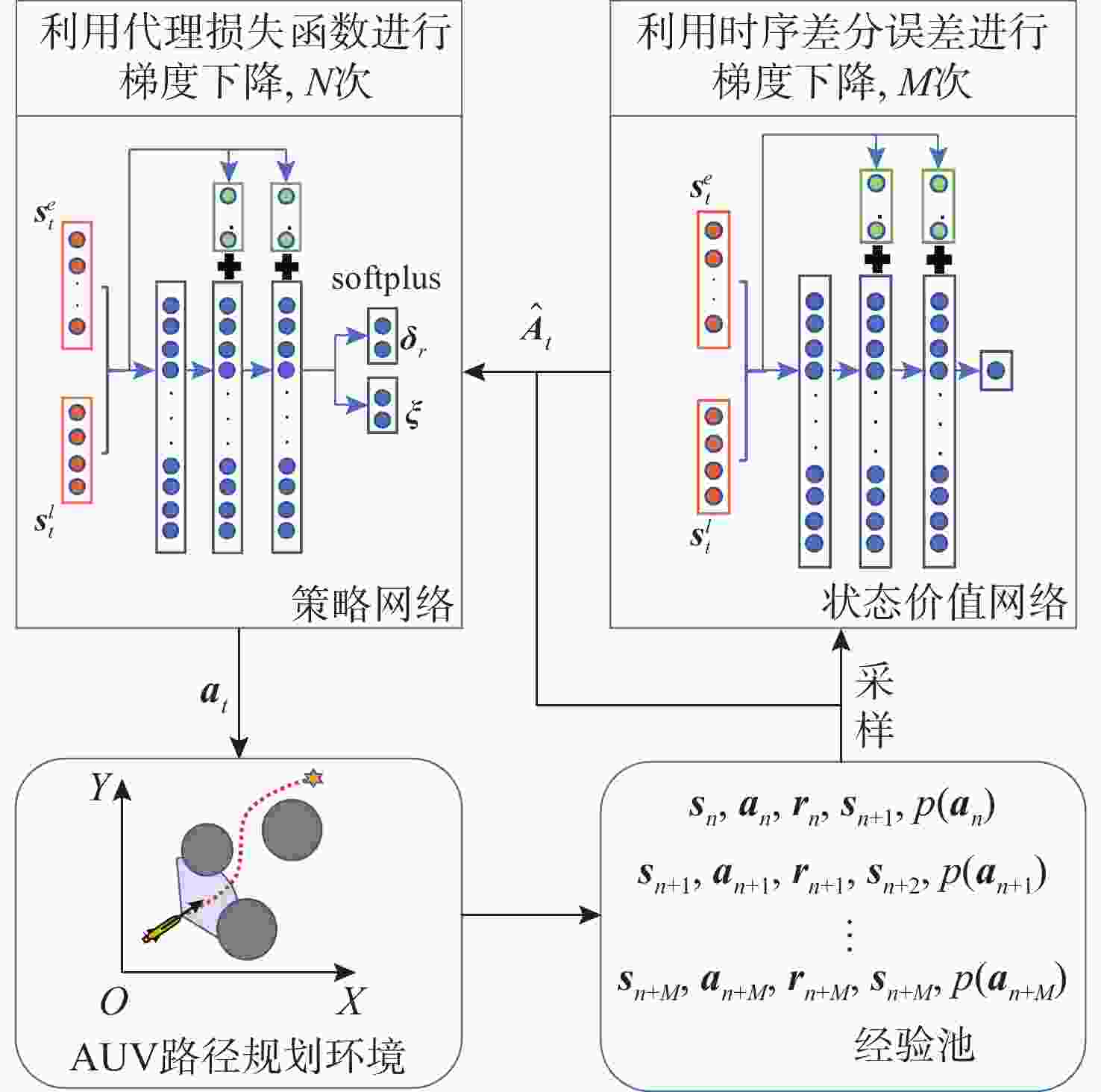
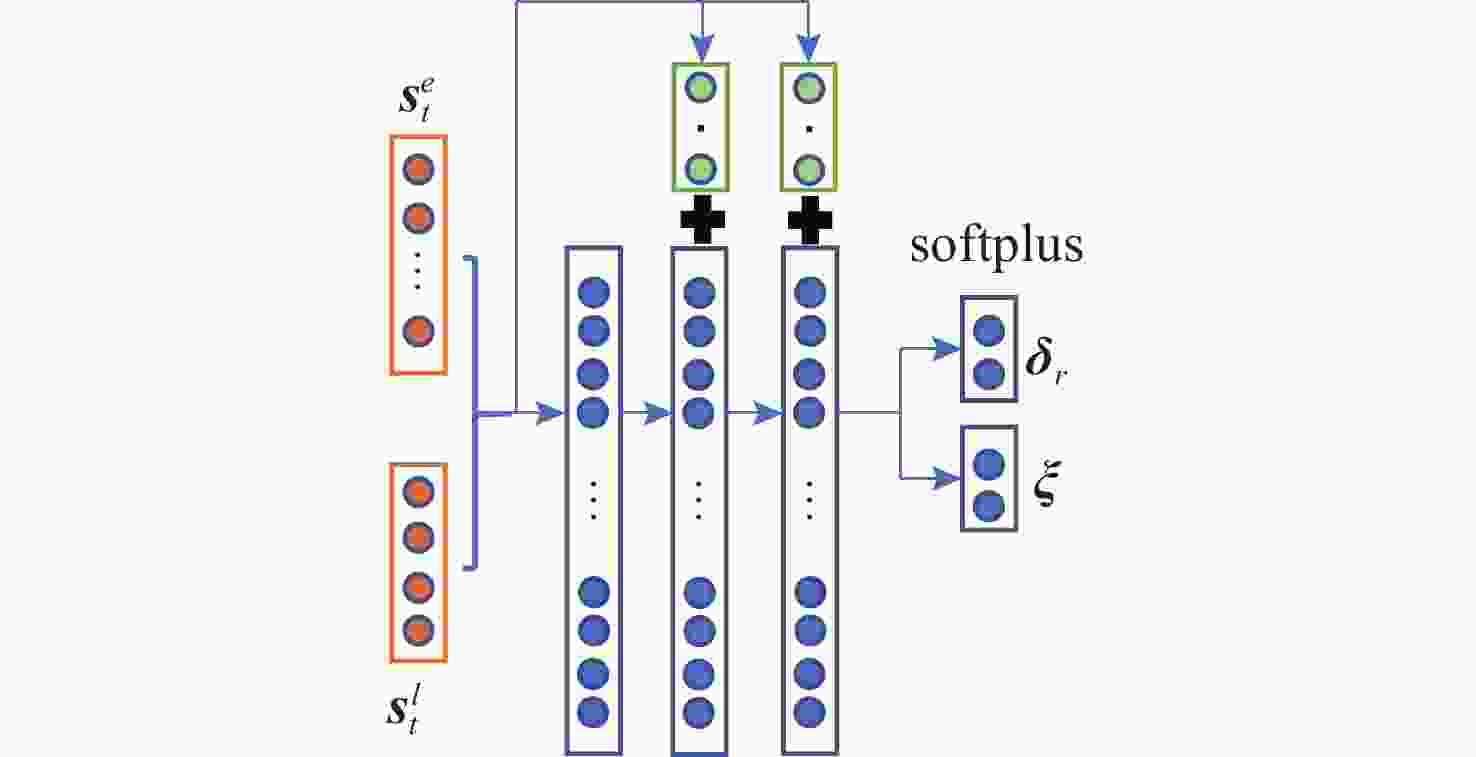
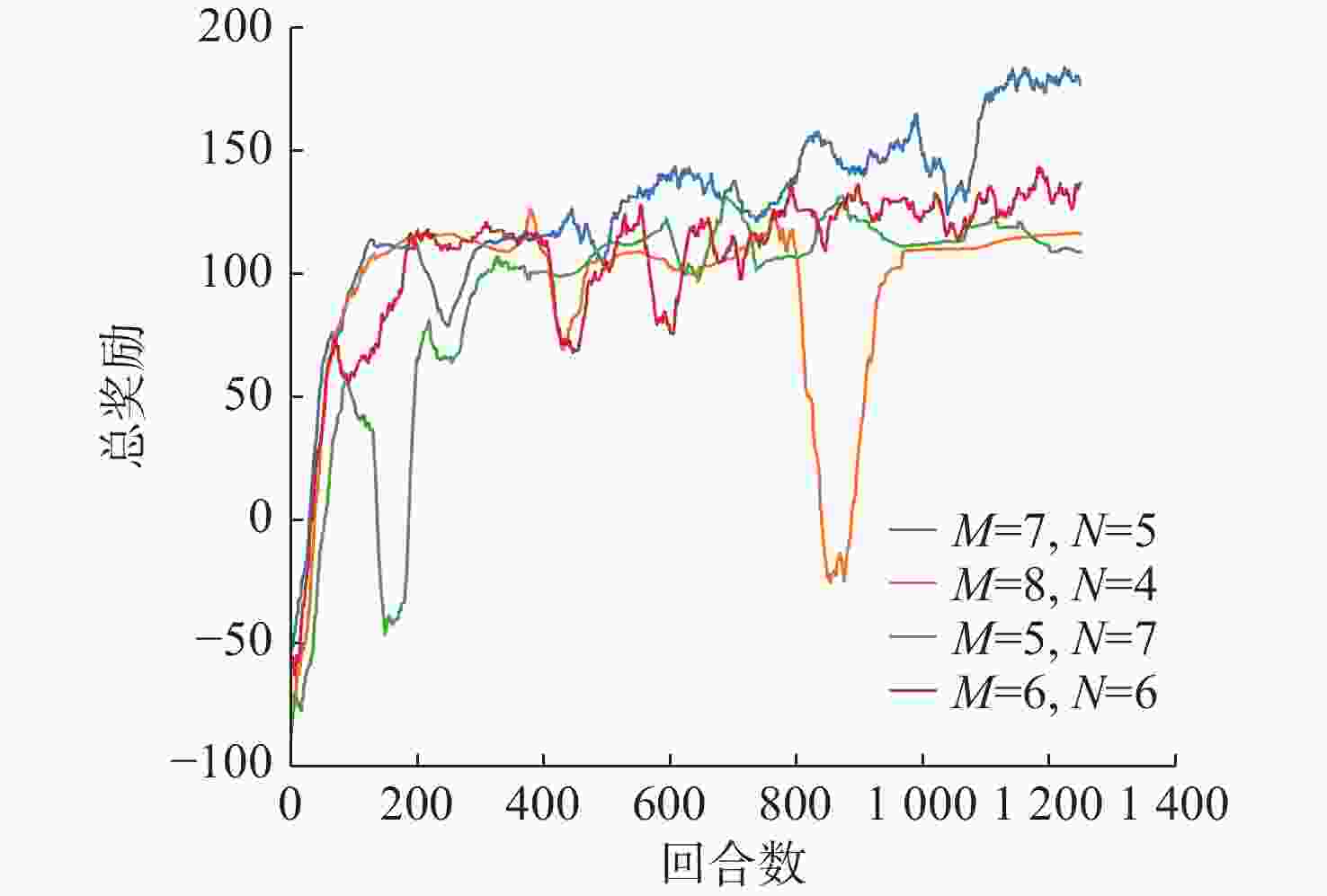
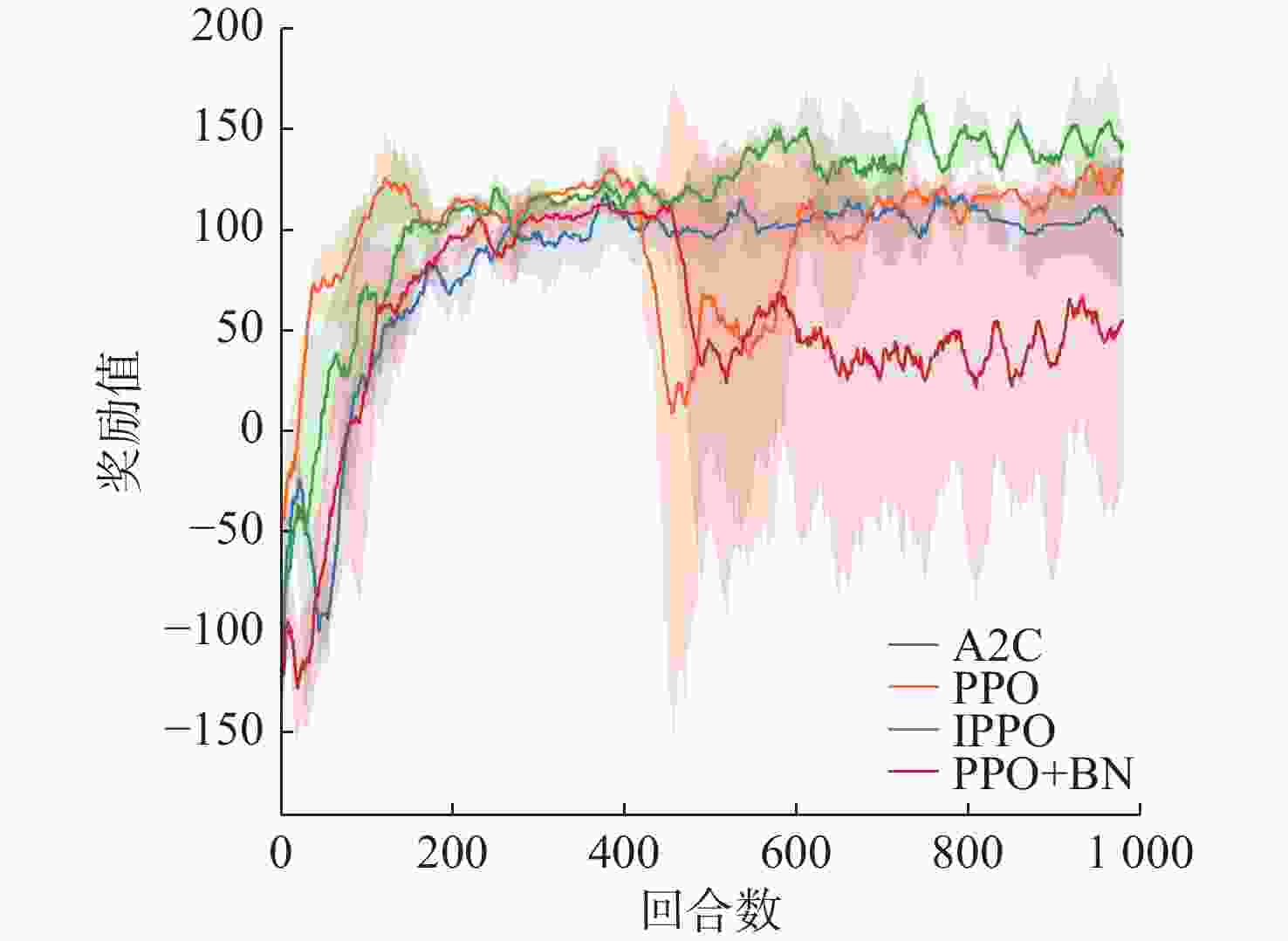
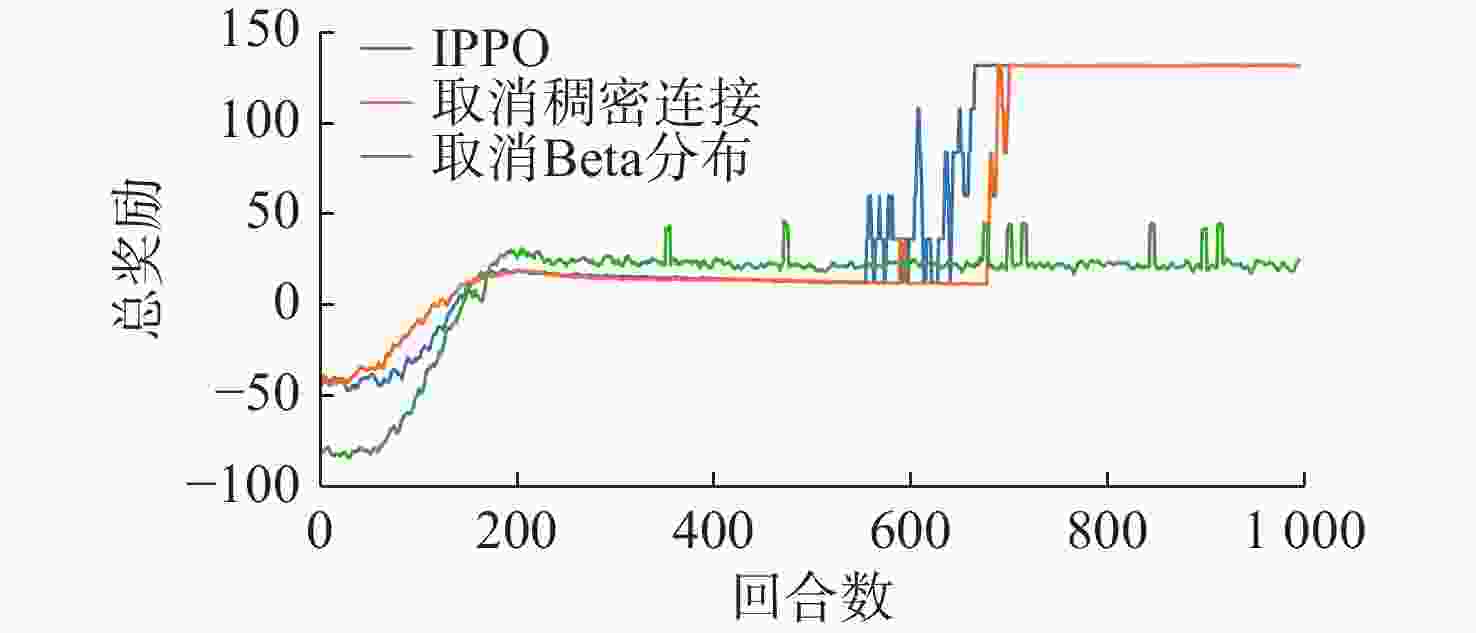
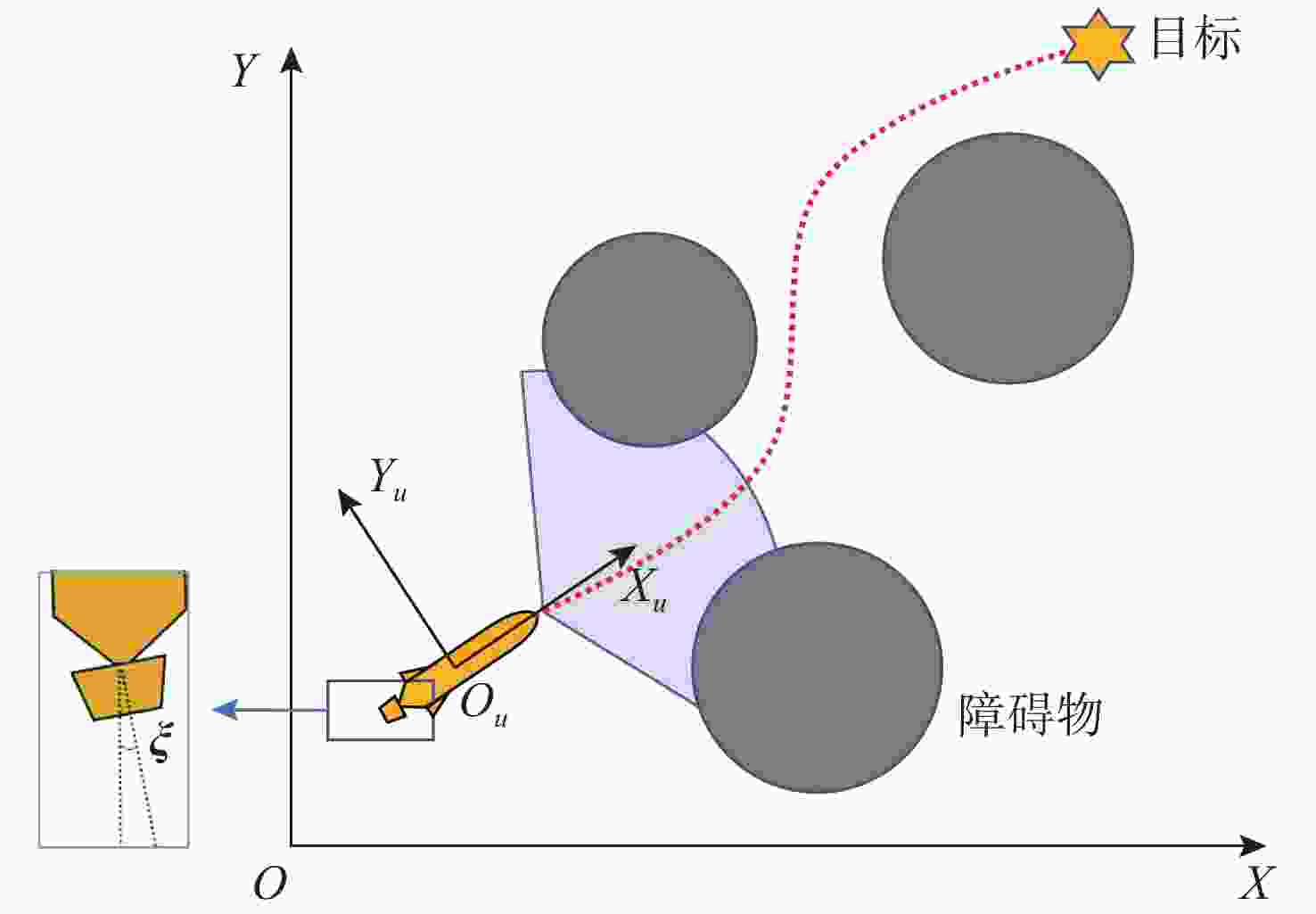
摘要: 为了赋予自主水下航行器(AUV)更强的路径规划能力, 文中提出了舵板+矢量推进器的联合控制方法, 并利用深度强化学习技术分配舵板和矢量喷管的使用比例, 用以在舵板控制的高能效性和矢量喷管控制的高机动性之间进行权衡, 使得AUV以较低能耗到达目标点。一方面, 构建起矢量推进AUV的动力学模型, 验证了矢量推进器能提高AUV的机动性, 但同时存在降低AUV能效的问题; 另一方面, 文中利用改进的近端策略优化算法(IPPO)解决联合控制背景下的路径规划问题, 该方法首先针对问题的动作空间有界的特点利用Beta分布建模策略分布, 并根据矢量推进器的特性在奖励函数中加大对矢量喷管控制的惩罚; 其次改进了近端策略优化算法(PPO)的参数更新策略并引入了“回滚机制”提高了算法的收敛效率。仿真结果验证了文中所提算法能够在联合控制的背景和复杂的环境中完成路径规划任务, 且在收敛速度及路径的最优性上优于未改进的算法。Abstract: This study proposed a joint control method of “rudder + vector thruster” and utilized deep reinforcement learning technology to allocate the usage ratio of rudder and vector nozzle, enabling autonomous undersea vehicles(AUVs) to achieve enhanced path planning capabilities. This method balanced the high energy efficiency of rudder control and the high maneuverability of vector nozzle control, allowing the AUV to reach the target point with lower energy consumption. On the one hand, the study established a dynamic model of vector propulsion AUVs and verified that vector thrusters improved the maneuverability of AUVs but simultaneously reduced the AUV’s energy efficiency. On the other hand, the study employed an improved proximal policy optimization(IPPO) algorithm to solve the path planning problem under joint control mode. Firstly, considering the bounded nature of the action space for the problem, this method modeled the policy distribution using a Beta distribution and increased the penalty for vector nozzle control in the reward function based on the characteristics of the vector thruster. Secondly, the study improved the parameter update strategy of (proximal policy optimization)PPO and introduced a “rollback mechanism” to enhance the convergence efficiency of the algorithm. The simulation results verified that the proposed algorithm completed path planning tasks in complex environments under joint control, and it outperformed the unimproved algorithm in terms of convergence speed and path optimality.
-
表 1 算法主要超参数表
Table 1. Main hyper-parameters of the algorithm
超参数 数值 超参数 数值 奖励$ {r}_{{\textit{z}}} $超参M 100 隐藏层神经元数 100 奖励$ {r}_{s} $超参b 1 循环次数K 1 奖励$ {r}_{d} $超参d 0.5 折扣因子$ \gamma $ 0.95 奖励$ {r}_{s} $超参a 1 $ {L}^{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{e}}\left(\theta \right) $超参$ \delta $ 0.05 奖励$ {r}_{d} $超参c 0.2 经验池容量$ {M}_{b} $ 2 048 $ \hat{{A}_{t}} $超参$ \lambda $ 0.9 探索程度$ {{c}}_{0} $ 0.01 $ {L}^{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{e}}\left(\theta \right) $超参$ \alpha $ 5 拼接神经元数 16 批处理量$ {b}_{s} $ 64 表 2 2种环境下3种算法路径特征
Table 2. Path feature for three algorithms in two environments
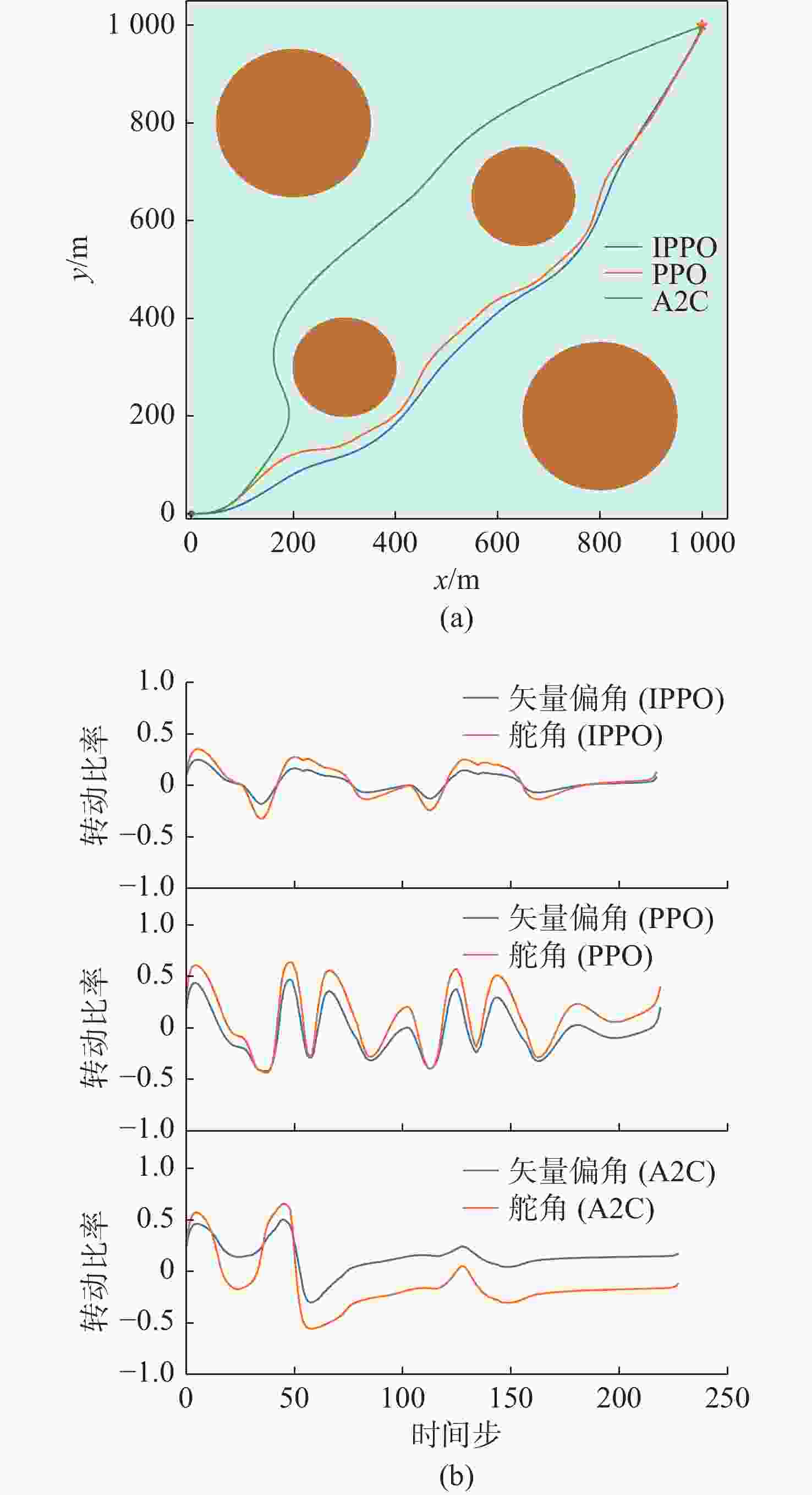
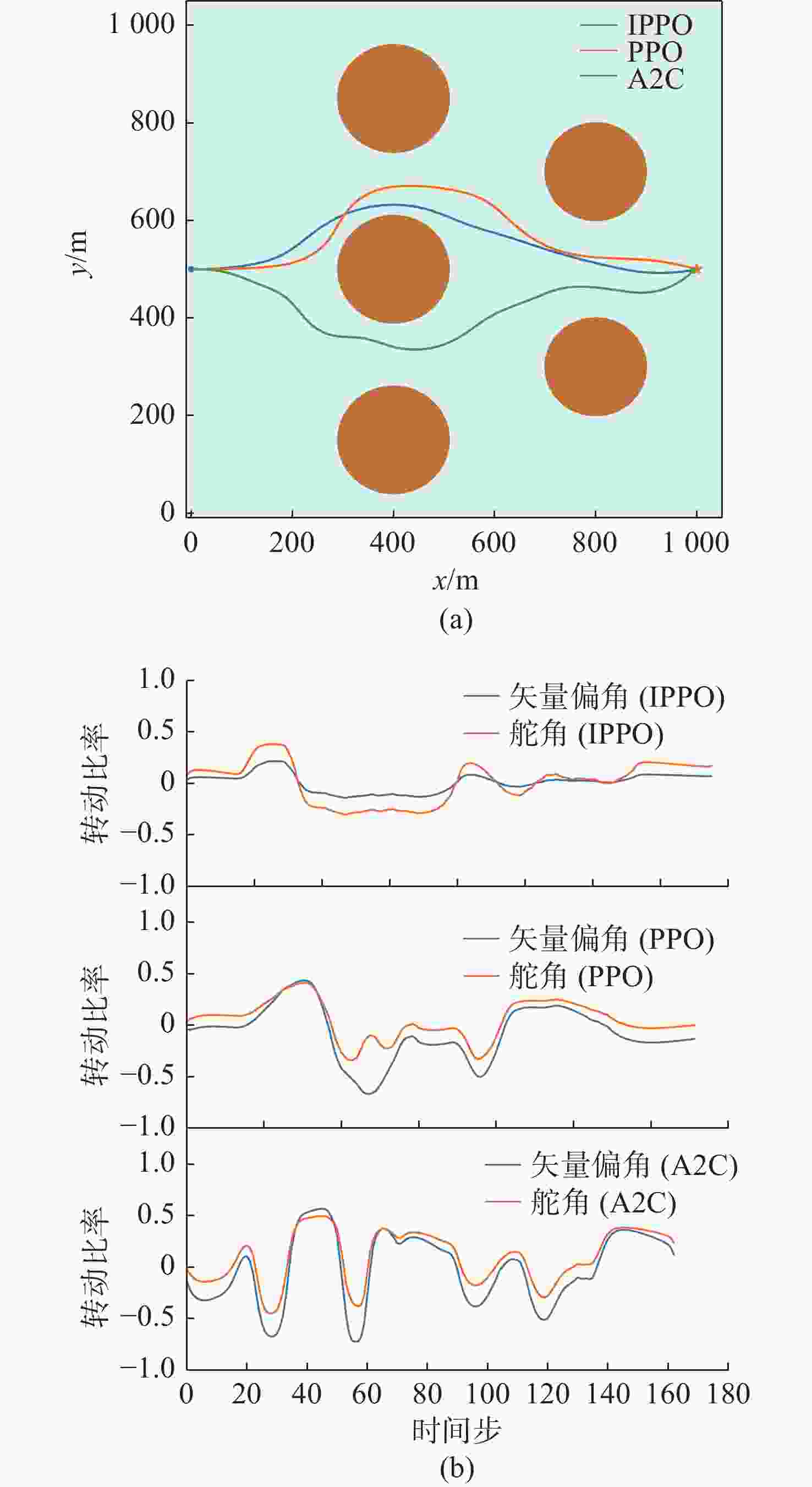
环境 算法 规划时长/s 规划长度/m 环境1 PPO 220 1 477.6 IPPO 218 1 471.4 A2C 227 1 533.5 环境2 PPO 165 1 107.5 IPPO 155 1 046.7 A2C 164 1 083.7 表 3 2种环境下2种控制方式路径特征
Table 3. Path feature of two control modes in two environments
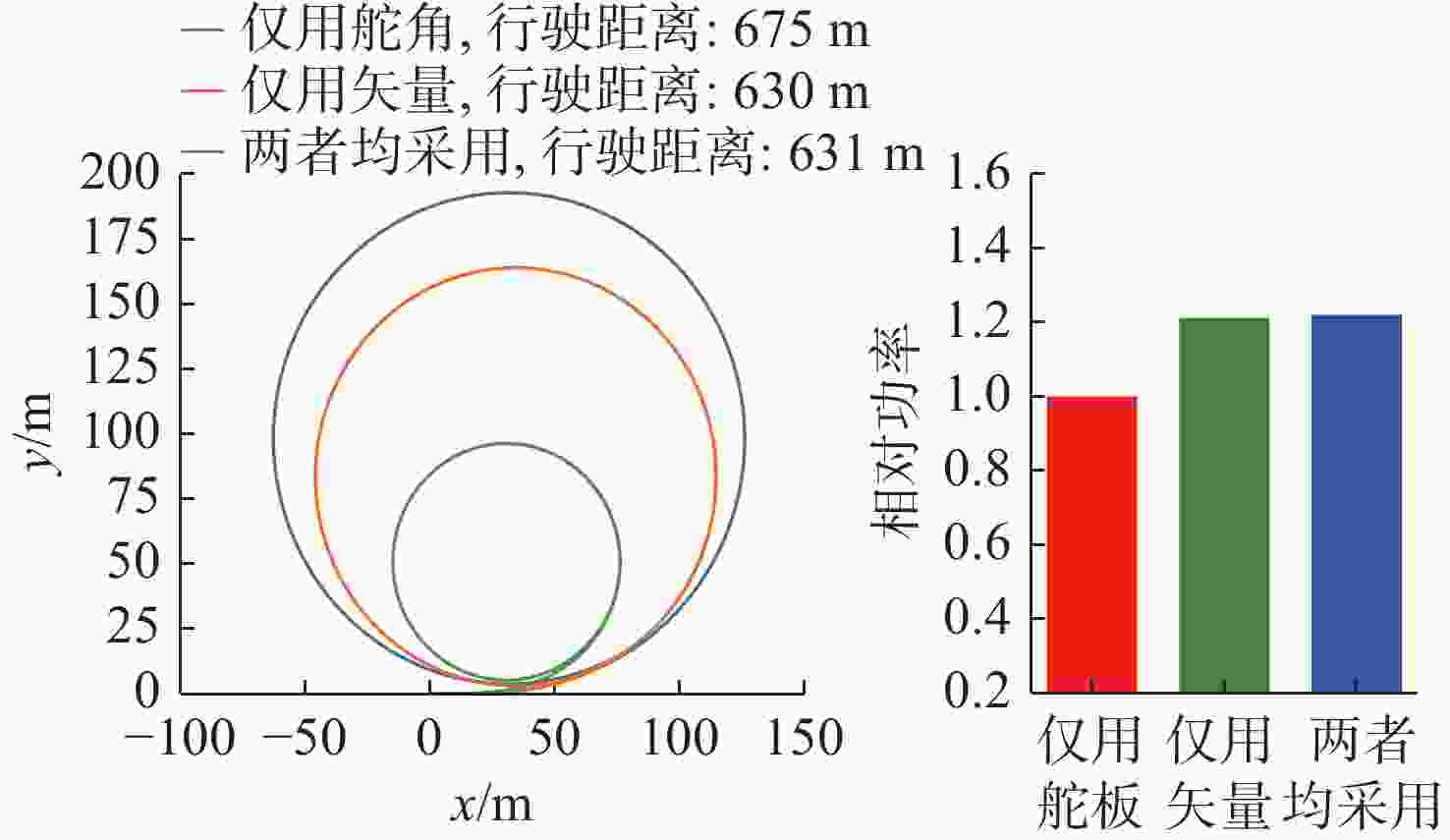
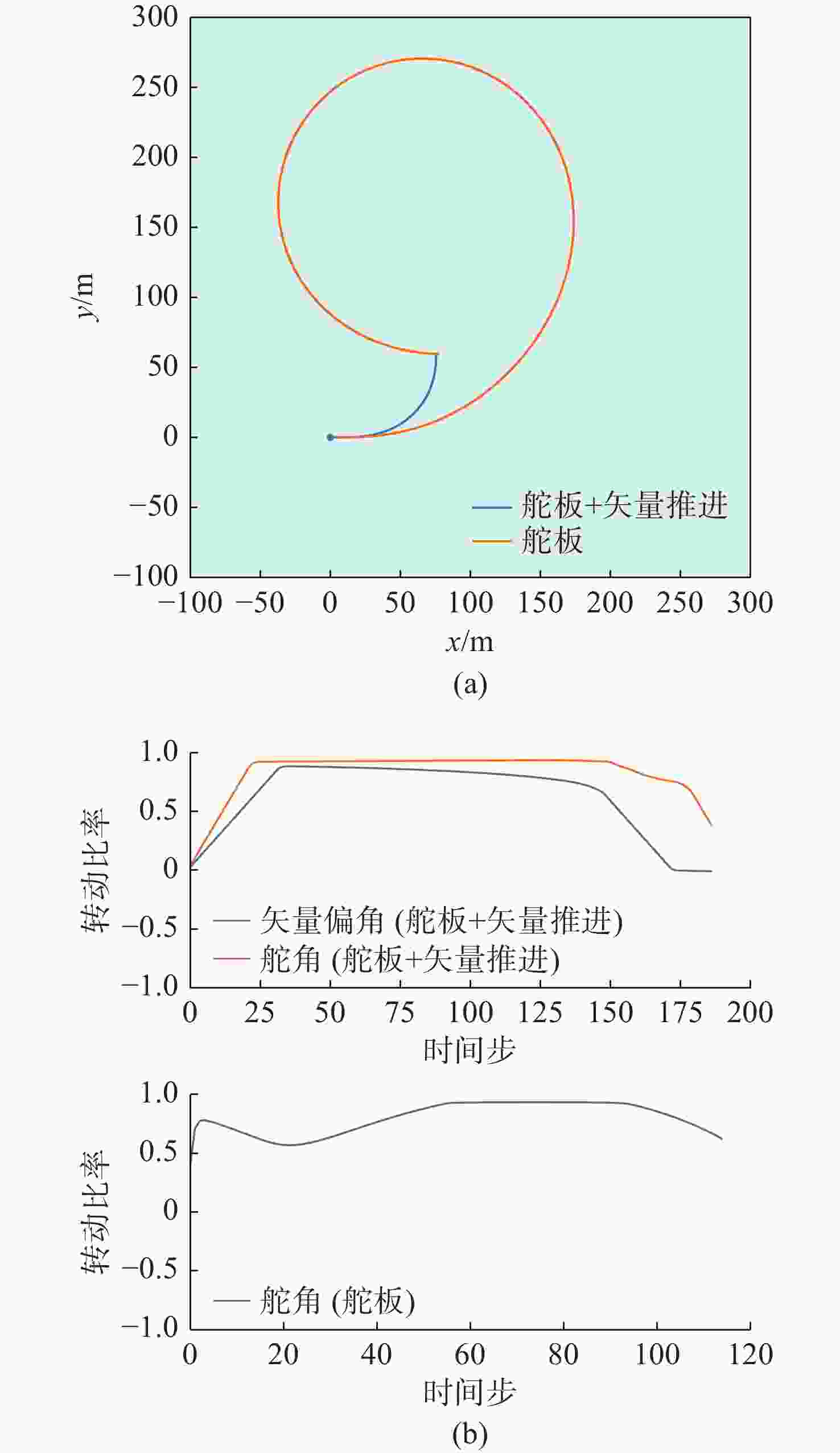
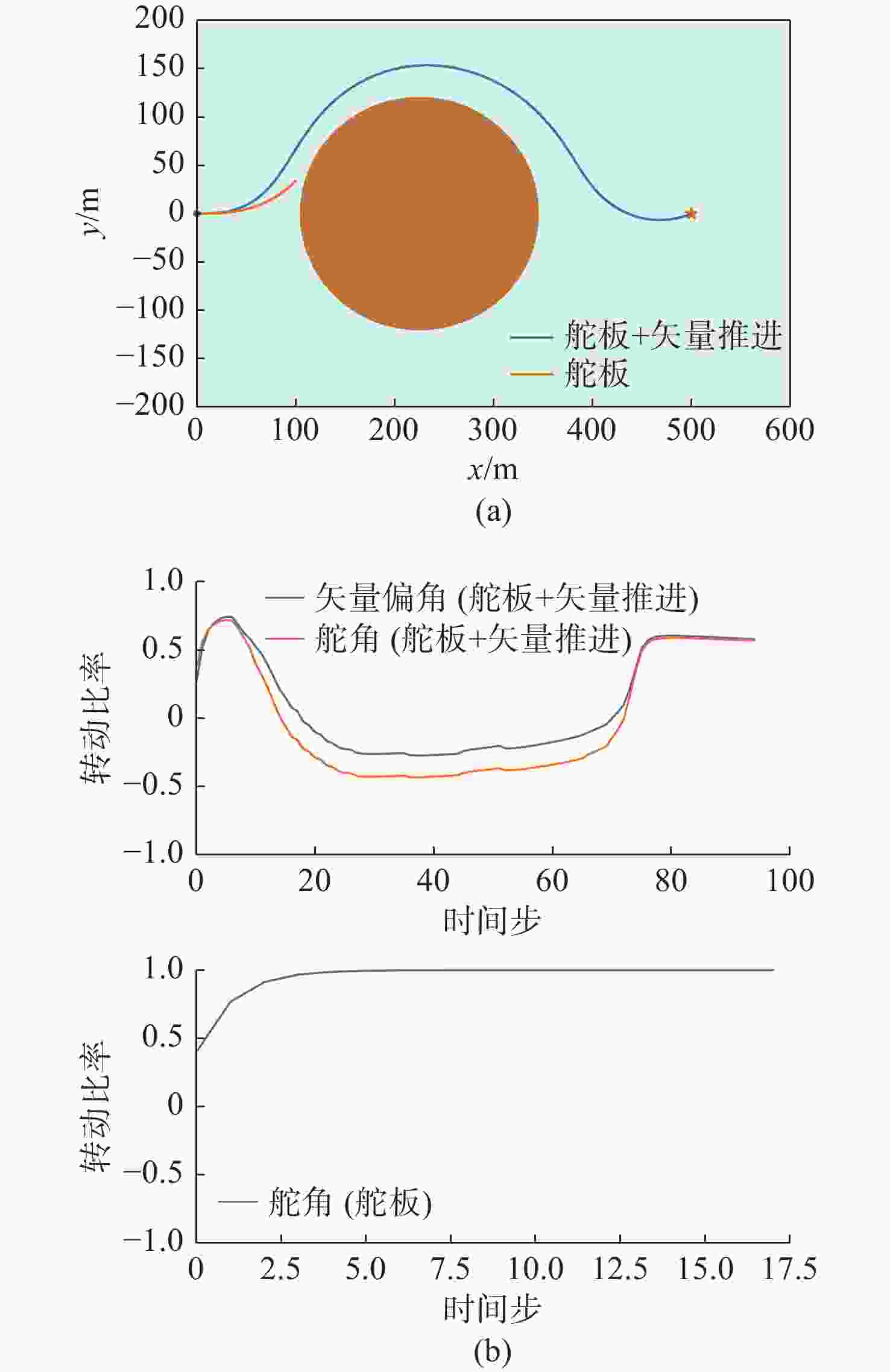
环境 控制方式 规划时长/s 规划长度/m 环境3 舵角 115.0 706.7 舵板+矢量推进 18.7 106.9 环境4 舵角 — — 舵板+矢量推进 95 621.9 -
[1] 崔荣鑫, 徐德民, 严卫生. 一种自主水下航行器路径规划算法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2006, 18(12): 3373-3376. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2006.12.012CUI R X, XU D M, YAN W S. A path planning algorithm for autonomous underwater vehicles[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2006, 18(12): 3373-3376. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2006.12.012 [2] FAN X J, GUO Y J, LIU H, et al. Improved artificial potential field method applied for AUV path planning[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020, 4(1): 1-21. [3] ZHANG W, WANG N, WU W. A hybrid path planning algorithm considering AUV dynamic constraints based on improved A* algorithm and APF algorithm[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 285(10): 115333. [4] LI J, YANG C. AUV path planning based on improved RRT and Bezier curve optimization[C]//2020 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA). China, Beijing: IEEE, 2020: 1359-1364. [5] HAO K, ZHAO J, LI Z, et al. Dynamic path planning of a three-dimensional underwater AUV based on an adaptive genetic algorithm[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 263(4): 112421. [6] MINH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529-533. doi: 10.1038/nature14236 [7] HUANG H Q, JIN C. A novel particle swarm optimization algorithm based on reinforcement learning mechanism for AUV path planning[J]. Complexity, 2021, 12(1): 1-13. [8] ZHANG H B, SHI X P. An improved quantum behaved particle swarm optimization algorithm combined with reinforcement learning for AUV path planning[J]. Journal of Robotics, 2023, 5(1): 8821906. [9] 李佩娟, 颜庭武, 杨书涛, 等. 基于强化学习的无人水面艇能耗最优路径规划算法[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(2): 237-243.LI P J, YAN T W, YANG S T, et al. Optimization path planning algorithm for energy consumption of unmanned surface vessels based on reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2023, 31(2): 237-243. [10] XI M, YANG J C, WEN J B, et al. Comprehensive ocean information-enabled AUV path planning via reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(18): 17440-17451. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3155697 [11] YANG J, NI J, XI M, et al, Intelligent path planning of underwater robot based on reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2022, 20(3): 1983-1996. [12] CHU Z Z, WANG F L, LEI T J, et al. Path planning based on deep reinforcement learning for autonomous underwater vehicles under ocean current disturbance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2022, 8(1), 108-120. [13] YUAN J, WANG H, ZHANG H, et al. AUV obstacle avoidance planning based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. J. Mar. Sci. Eng, 2021, 9(11): 1166. [14] HE Z, DONG L, SUN C. Asynchronous multithreading reinforcement-learning-based path planning and tracking for unmanned underwater vehicle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(5): 2757-2769. [15] WANG Z, ZHANG S, FENG X, et al. Autonomous underwater vehicle path planning based on actor-multi-critic reinforcement learning[C]//Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part I: Journal of Systems and Control Engineering, 2021, 235(10): 1787-1796. [16] TANG Z C, CAO X, ZHOU Z H, et al, Path planning of autonomous underwater vehicle in unknown environment based on improved deep reinforcement learning[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 301(11): 117547. [17] LYU X, SUN Y, WANG L, et al. End-to-end AUV local motion planning method based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2023, 11(9): 1796. [18] BEHNAZ H, ALIREZA K, POURIA S, Deep reinforcement learning for adaptive path planning and control of an autonomous underwater vehicle[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2022, 129(10), 103326. [19] WANG H, GAO W, WANG Z, et al. Research on obstacle avoidance planning for UUV based on A3C algorithm[J]. J. Mar. Sci. Eng, 2024, 12(1): 63. [20] SUN Y, CHENG J, ZHANG G, et al. Mapless motion planning system for an autonomous underwater vehicle using policy gradient-based deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2019, 96(5): 591-601. [21] JIANG D, FANG Z, CHENG C, et al. Action guidance-based deep interactive reinforcement learning for AUV path planning[C]//2022 International Conference on Machine Learning, Control, and Robotics(MLCR). Suzhou, China: IEEE, 2022: 158-165. [22] SCHULMAN J, WOLSKI F, DHARIWAL P, et al. Proximal policy optimization algorithms[EB/OL]. (2017-08-28)[2025-08-01]. http://arXiv.1707.06347. [23] SAMARTH S, HOMANGA B, D2RL: Deep dense architectures in reinforcement learning[C]//NeurIPS. Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2020. [24] 屈裕安, 谢寿生, 宋志平. 矢量喷管控制对发动机性能的影响[J]. 航空动力学报, 2004, 19(3): 300-304. [25] WANG Y H, HE H, TAN X Y, Truly proximal policy optimization[C]//Proceedings of the 35th Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence Conference. Tel Aviv, Israel: PMLR, 2020(115): 113-122. [26] 郭可建, 林晓波, 郝程鹏, 等. 基于神经网络状态估计器的高速AUV强化学习控制[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2022, 30(2): 147-156. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2022.02.002GUO K J, LIN X B, HAO C P, et al. High speed AUV reinforcement learning control based on neural network state estimator[J]. Journal of Unmanned Underaea Systems, 2022, 30(2): 147-156. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2022.02.002 -




 下载:
下载: