Underwater Object Detection Method with Enhanced Wavelet Transform Features
-
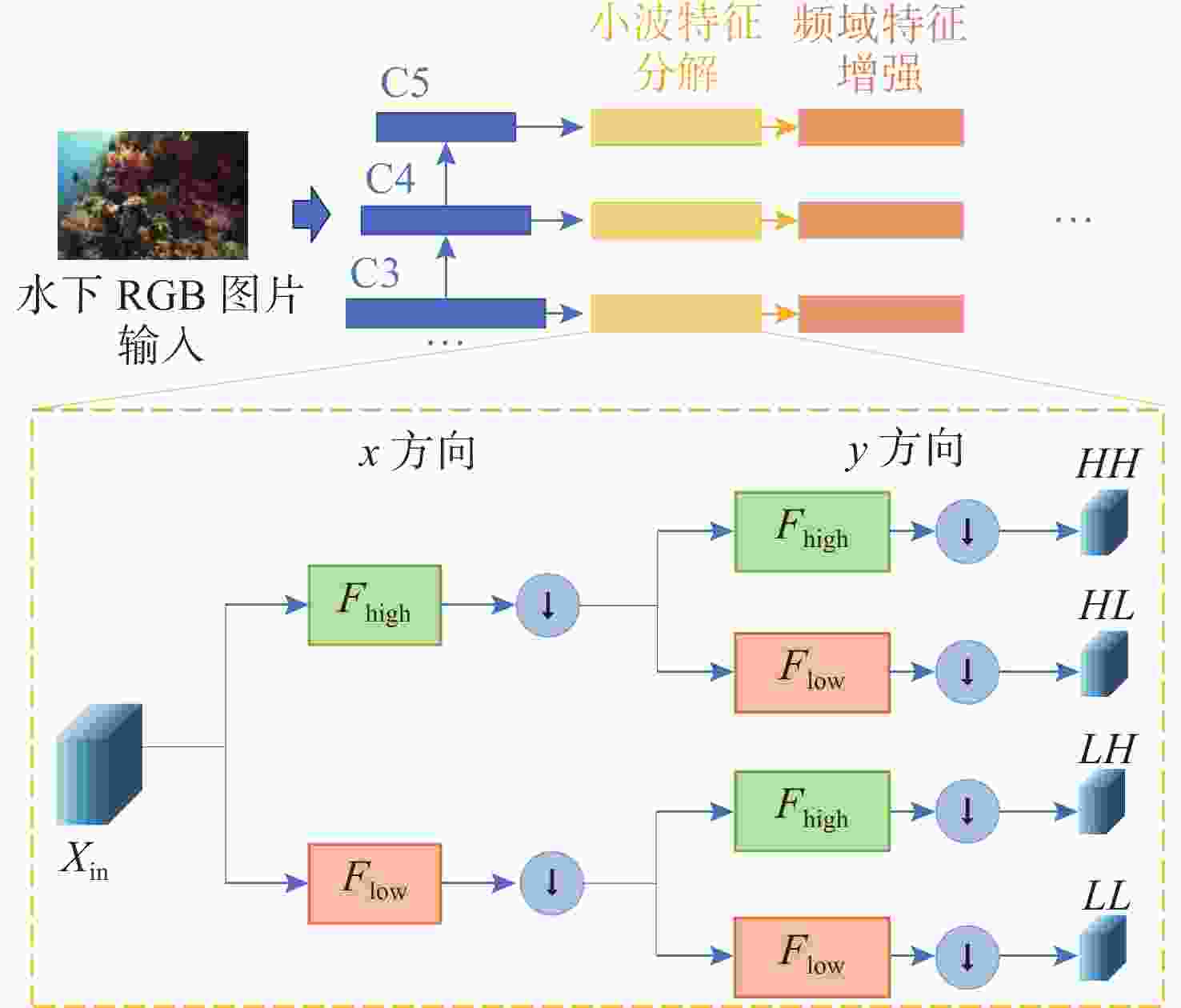
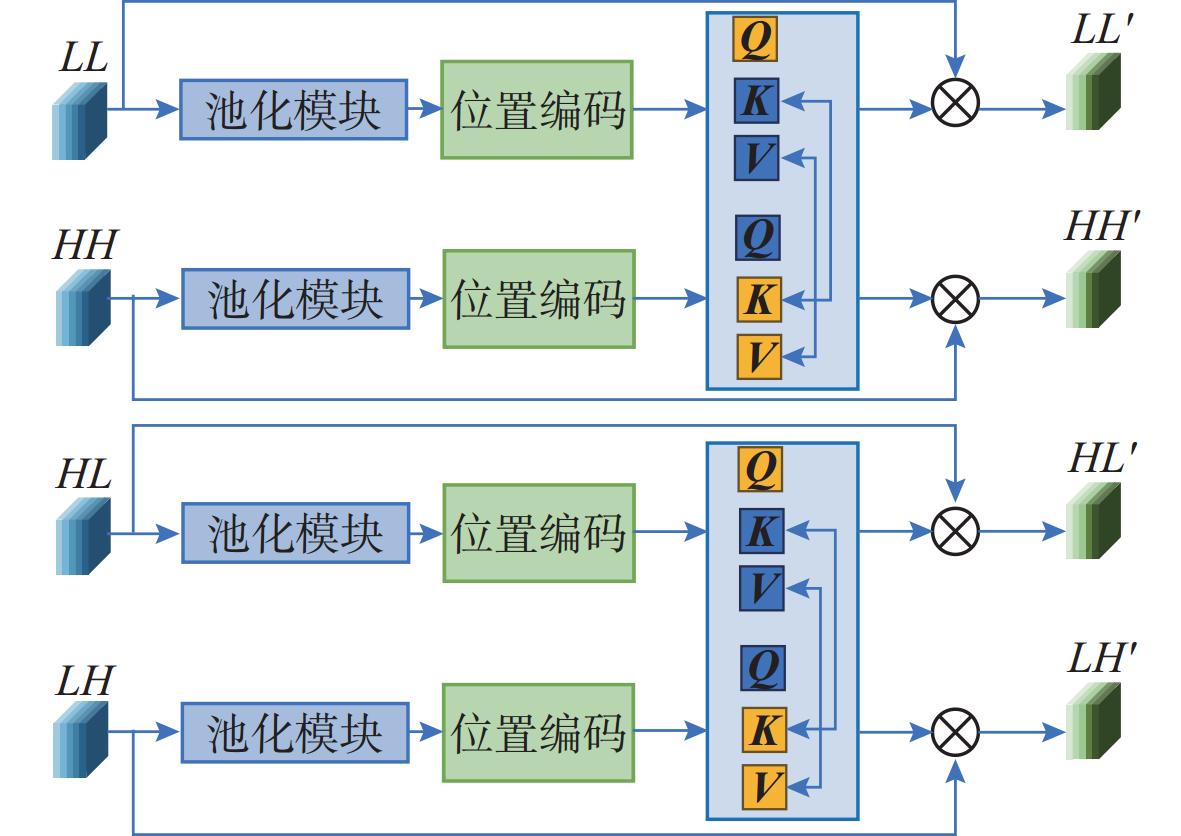
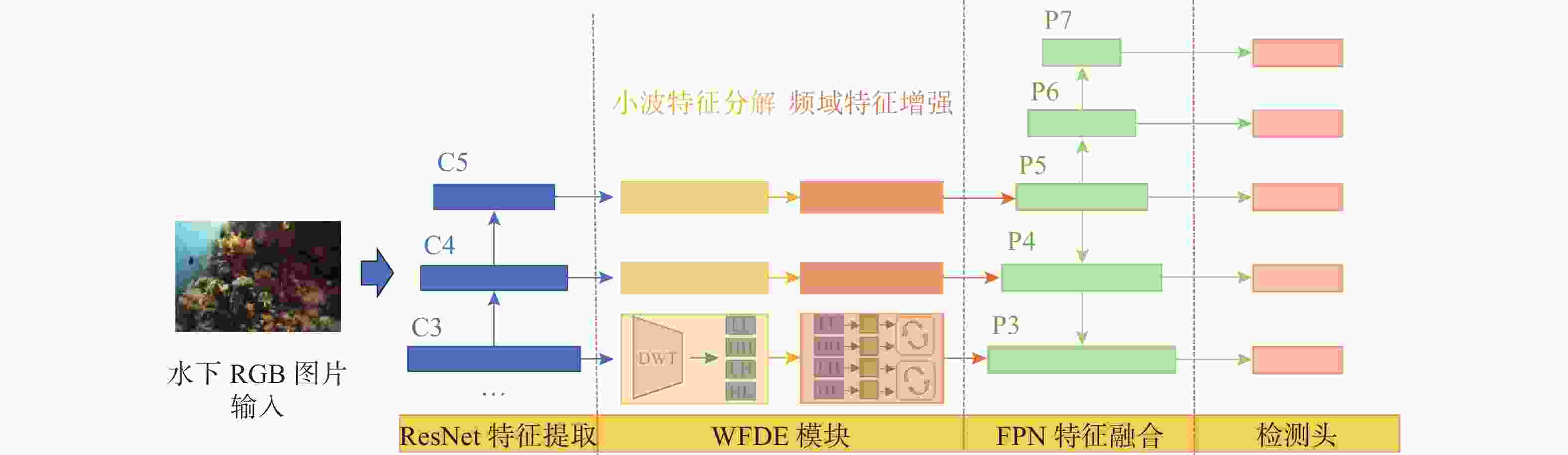
摘要: 复杂特殊的水下环境导致水下图像质量较低, 存在对比度低、模糊及水下退化等特性, 这极大地影响了水下目标检测性能。针对这一问题, 文中提出了一种基于小波变换特征增强的水下目标检测方法。引入了离散小波变换(DWT)将深度学习框架中提取到的多层次特征进行高低频分解, 进而将分解得到的频域特征分量通过文中设计的基于注意力机制的频域交互模块进行交互增强, 优化特征表达能力, 经过增强后的特征继续通入目标检测网络用于改善目标检测的性能。实验证明, 文中提出的水下目标检测方法与常见的目标检测方法相比, 在性能上具有一定优势, 能够有效提升水下目标检测能力。Abstract: The complex and unique underwater environment results in low-quality underwater images, characterized by low contrast, blurriness, and underwater degradation, which significantly affects the capabilities of underwater object detection. To address this issue, this paper proposed an underwater object detection method with enhanced wavelet transform features. The paper introduced discrete wavelet transform(DWT) to decompose the multi-level features extracted by the deep learning framework into high- and low-frequency components. These frequency domain feature components were then interactively enhanced using a frequency domain interaction module based on the attention mechanism designed in this work, optimizing the ability of feature expression. The enhanced features were subsequently fed into the object detection network to improve the object detection performance. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed underwater object detection method outperforms conventional object detection methods, significantly improving the ability to detect objects in underwater environments.
-
Key words:
- underwater object detection /
- deep learning /
- wavelet transform
-
表 1 各类目标检测方法性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of various target detection methods
方法 GFLOPS Params mAP/% AP50/% AP75/% APs/% APm/% APl/% FCOS[14] 51.730 32.155×106 39.2 62.4 43.6 25.5 36.4 37.8 Faster RCNN[15] 63.583 41.753×106 46.5 72.0 51.1 30.7 43.4 48.2 RepPoints[16] 48.581 36.845×106 33.6 54.8 35.8 21.1 31.0 35.6 GFL[17] 52.522 32.300×106 49.3 71.0 55.9 27.7 44.0 52.9 FSAF[18] 52.693 36.420×106 34.9 56.3 37.0 28.9 32.1 38.4 ATSS[19] 51.730 32.155×106 50.0 73.6 56.7 31.5 44.2 54.6 RetinaNet[20] 61.141 37.969×106 36.5 57.3 40.2 20.3 32.6 36.9 FCOS+WFDE 51.751 32.234×106 45.3(+6.1) 72.7 51.9 25.2 42.3 46.1 GFL+WFDE 52.543 32.379×106 51.0(+1.7) 74.1 58.4 29.3 44.3 55.3 表 2 其他水下数据集实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results of other underwater datasets
表 3 交互组合消融实验结果
Table 3. Interactive combination ablation experiment results
基线模型 HH/LL交互 LH/HL交互 mAP/% FCOS[14] × × 39.2 × √ 42.8(+3.6) √ × 41.5(+2.3) √ √ 45.3(+6.1) 表 4 注意力权重生成消融实验结果
Table 4. Experimental results of attentional weight generation ablation
基线模型 K是否交换 V是否交换 mAP/% FCOS[14] × × 39.2 × √ 41.9(+2.7) √ × 43.6(+4.4) √ √ 45.3(+6.1) -
[1] FU C P, LIU R S, FAN X, et al. Rethinking general underwater object detection: Datasets, challenges, and solutions[J]. Neurocomputing, 2023, 517: 243-256. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.10.039 [2] LIN W H, ZHONG J X, LIU S, et al. Roimix: Proposal-fusion among multiple images for underwater object detection[C]//ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2020: 2588-2592. [3] CHEN L, LIU Z, TONG L, et al. Underwater object detection using invert multi-class adaboost with deep learning[C]//2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks(IJCNN). Glasgow, United Kingdom: IEEE, 2020: 1-8. [4] LIANG X, SONG P. Excavating ROI attention for underwater object detection[C]//2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing(ICIP). Bordeaux, France: IEEE, 2022: 2651-2655. [5] SONG P, LI P, DAI L, et al. Boosting R-CNN: Reweighting R-CNN samples by RPN's error for underwater object detection[J]. Neurocomputing, 2023, 530: 150-164. [6] FU C, FAN X, XIAO J, et al. Learning heavily-degraded prior for underwater object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2023, 33(11): 6887-6896. [7] ZHOU J, HE Z, LAM K M, et al. AMSP-UOD: When vortex convolution and stochastic perturbation meet underwater object detection[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI, 2024, 38(7): 7659-7667. [8] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, Nevada, USA: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. [9] SUN S, REN W, WANG T, et al. Rethinking image restoration for object detection[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2022, 35: 4461-4474. [10] ALFRED H. Zur theorie der orthogonalen funktionensysteme[J]. Mathematische Annalen, 1910, 69: 331-371. [11] LIU C, LI H, WANG S, et al. A dataset and benchmark of underwater object detection for robot picking[C]//2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Wxpo workshops(ICMEW). Shenzhen, China: IEEE, 2021: 1-6. [12] PEDERSEN M , HAURUM J B , GADE R, et al. Detection of marine animals in a new underwater dataset with varying visibility[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Long Beach, California, USA: IEEE, 2019: 18-26. [13] DENG J, DONG W, SOCHER R, et al. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]//2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Florida, USA: IEEE, 2009: 248-255. [14] TIAN Z, SHEN C, CHEN H, et al. FCOS: A simple and strong anchor-free object detector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 44(4): 1922-1933. [15] REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 39(6): 1137-1149. [16] YANG Z, LIU S, HU H, et al. Reppoints: Point set representation for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2019: 9657-9666. [17] LI X, WANG W, WU L, et al. Generalized focal loss: Learning qualified and distributed bounding boxes for dense object detection[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 21002-21012. [18] ZHU C, HE Y, SAVVIDES M. Feature selective anchor-free module for single-shot object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, California, USA: IEEE, 2019: 840-849. [19] ZHANG S, CHI C, YAO Y, et al. Bridging the gap between anchor-based and anchor-free detection via adaptive training sample selection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, Washington, USA: IEEE, 2020: 9759-9768. [20] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017: 2980-2988. [21] SUN P, ZHANG R, JIANG Y, et al. Sparse R-CNN: End-to-end object detection with learnable proposals[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. Nashville, Tennessee, USA: IEEE, 2021: 14454-14463. [22] CAI Z, VASCONCELOS N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into high quality object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Utah, USA: IEEE, 2018: 6154-6162. [23] JIANG L, WANG Y, JIA Q, et al. Underwater species detection using channel sharpening attention[C]//Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Chengdu, China: ACM Multimedia, 2021: 4259-4267. -




 下载:
下载: