Real-Time Transformer Detection of Underwater Objects Based on Lightweight Gated Convolutional Network
-
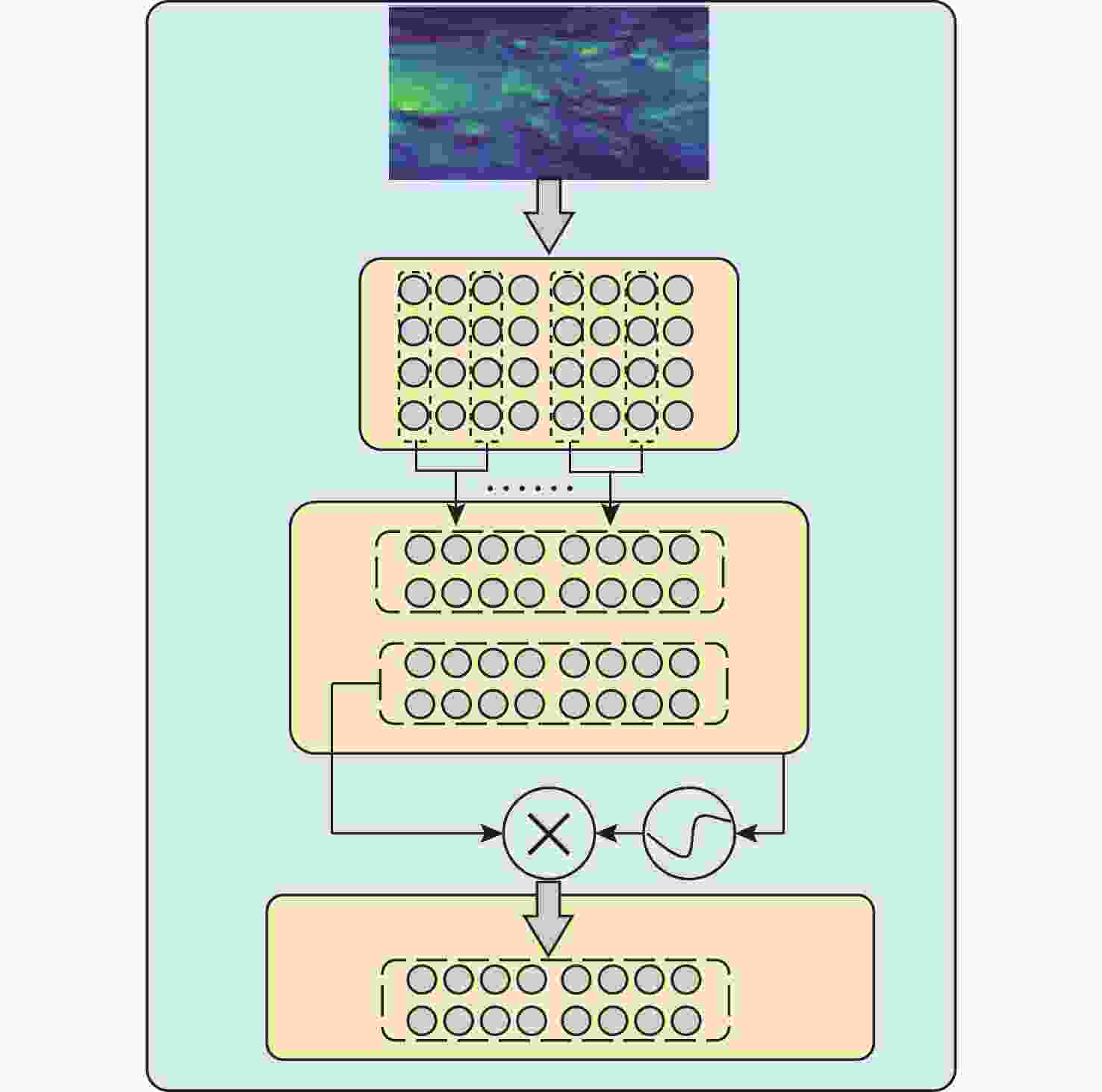
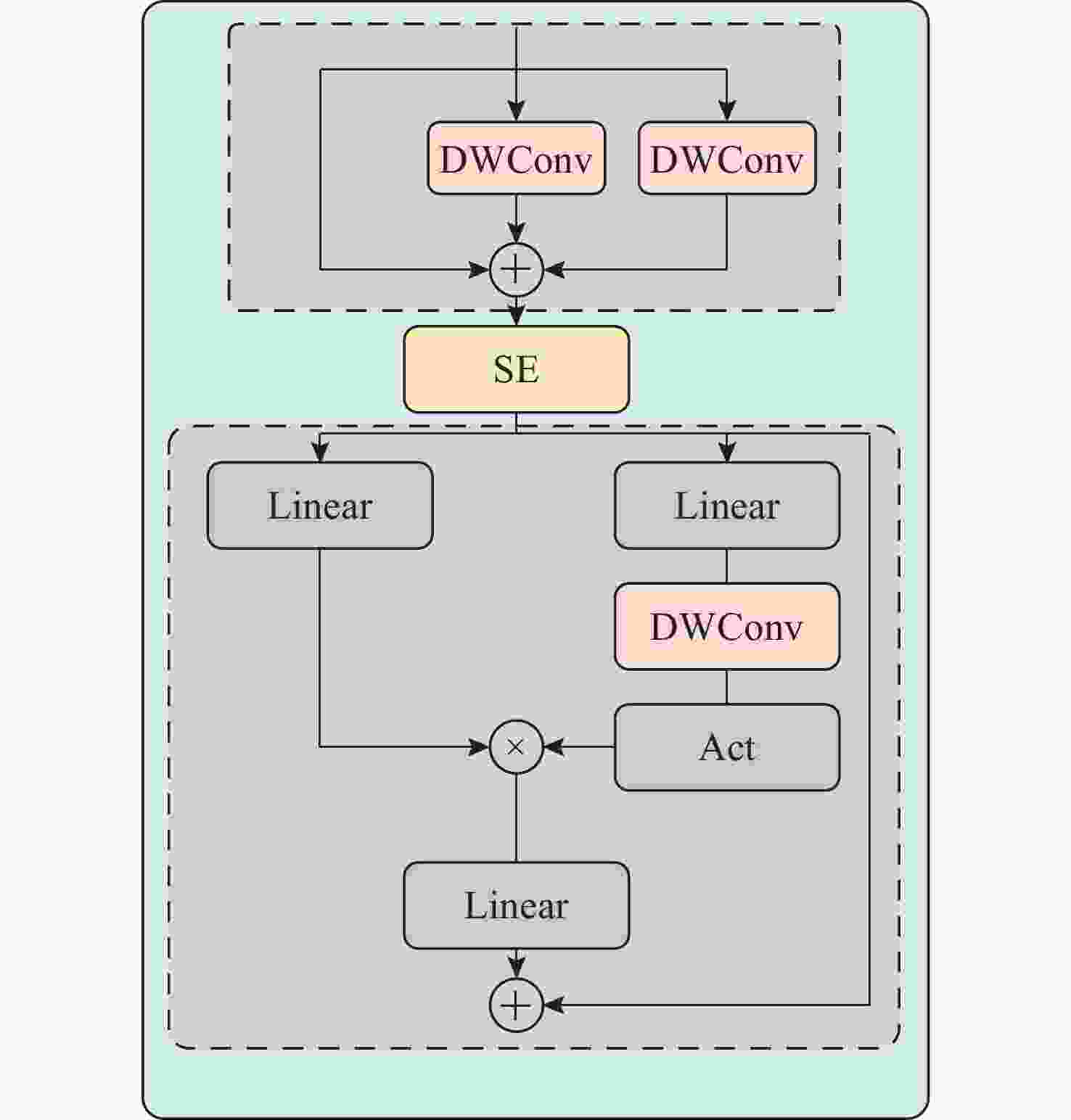
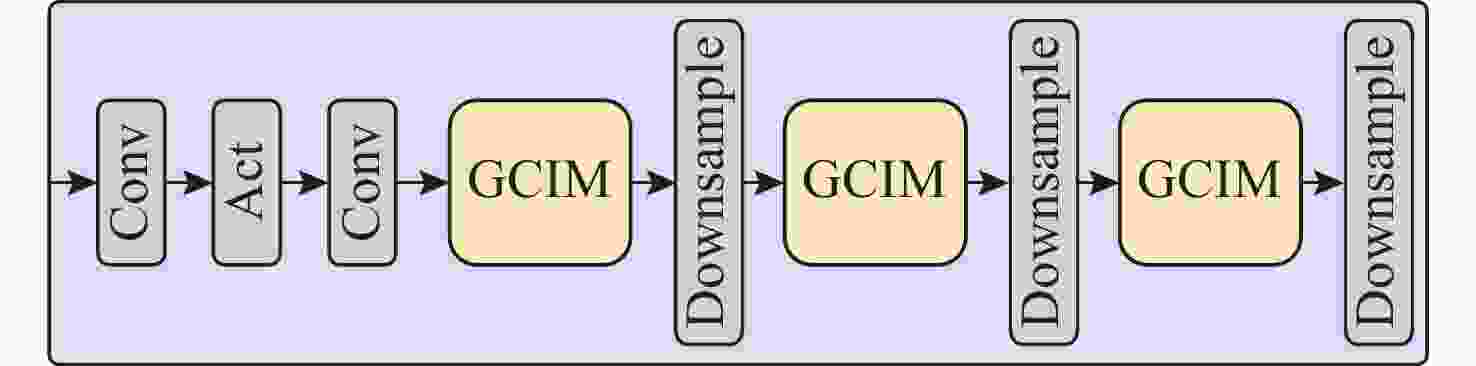
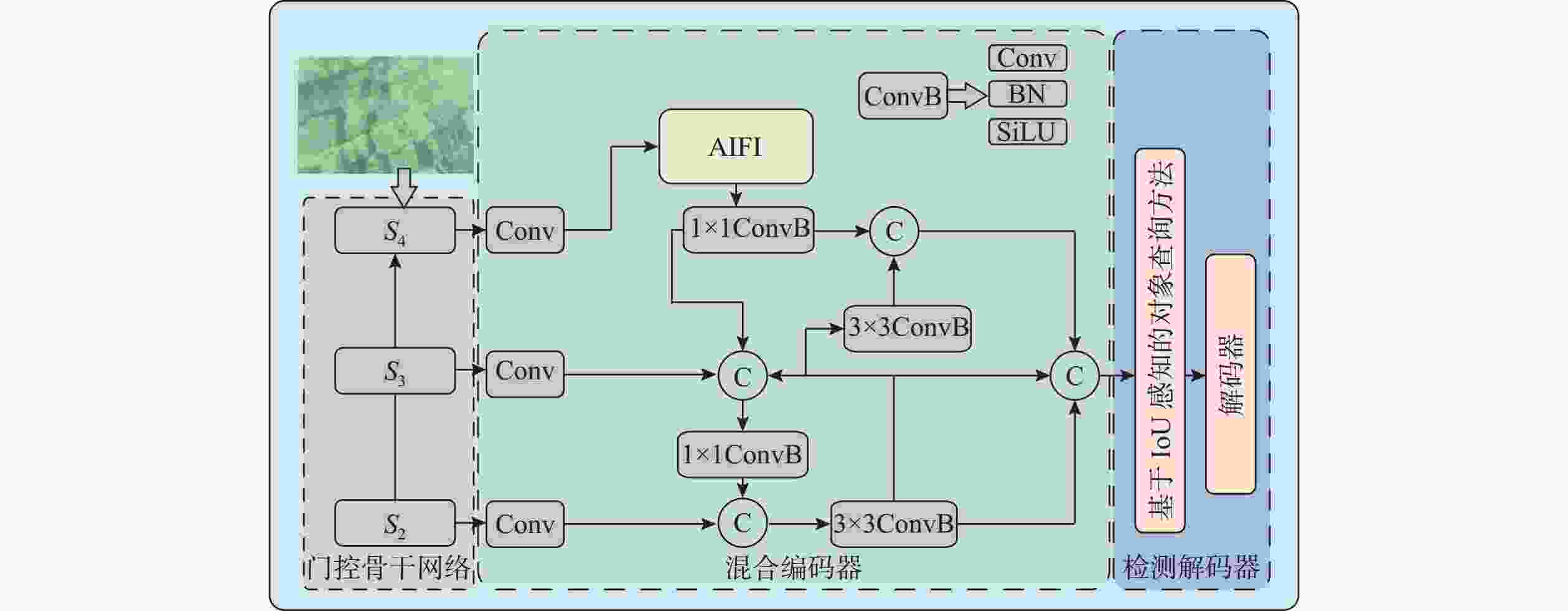
摘要: 针对水下目标检测算法图像特征处理困难、模型结构冗余以及参数量庞大等问题, 提出一种基于轻量化门控卷积网络的实时Transformer水下目标检测方法。该方法首先基于门控思想构建卷积门控线性单元, 动态调节特征的传递, 并以此为基础提出门控通道交互模块, 该模块通过完全解耦token mixer(词元混合器)和channel mixer(通道混合器), 并针对token mixer部分引入结构重新参数化技术, 极大降低了模型在推理过程中的计算成本。混合编码器针对门控骨干网络提取的3个特征分别进行尺度内信息交互和多尺度特征融合, 实现浅层高频率信息和深层语义空间信息之间的高度融合。文中模型在多个不同模态数据集上进行了大量实验, 实验结果显示, 模型的mAP@0.5达到了0.849, 整体参数量为23.3×106, 检测帧率为136.8。该模型在保持优秀检测精度的同时, 实现了较小的模型参数量和较高的检测速度, 整体性能优于其他模型。结果表明, 与一系列优秀的目标检测模型相比, 文中模型具备较高的检测性能和高效的实时检测能力。
-
关键词:
- 水下目标检测 /
- 轻量化网络 /
- 门控卷积 /
- Transformer
Abstract: To address the challenges in underwater object detection algorithms, including difficult image feature processing, redundant model architectures, and excessive parameter numbers, this paper proposed a real-time Transformer detection method for underwater objects based on a lightweight gated convolutional network. This method first constructed a convolutional gated linear unit based on the gating mechanism to dynamically modulate feature transmission. Furthermore, on this basis, a gated channel interaction module was proposed to fully decouple the token mixer from the channel mixer. Additionally, for the token mixer, the structural reparameterization technique was introduced to significantly reduce the computational cost of the model during inference. The hybrid encoder conducted the intra-scale information exchange and multi-scale feature fusion of the three features extracted by the gated backbone network, thus realizing the high fusion of shallow high-frequency information and deep semantic spatial information. The proposed model carried out a large number of experiments on different modal datasets. The results show that the model’s mAP@0.5 reaches 0.849, the overall number of parameters is 23.3×106, and the FPS detection frame rate is 136.8. While maintaining excellent detection accuracy, this model achieves a smaller number of model parameters and higher detection speed, with better overall performance than other models. The results reveal that compared to a series of excellent object detection models, the proposed model features sound detection performance and efficient real-time detection.-
Key words:
- underwater object detection /
- lightweight network /
- gated convolution /
- Transformer
-
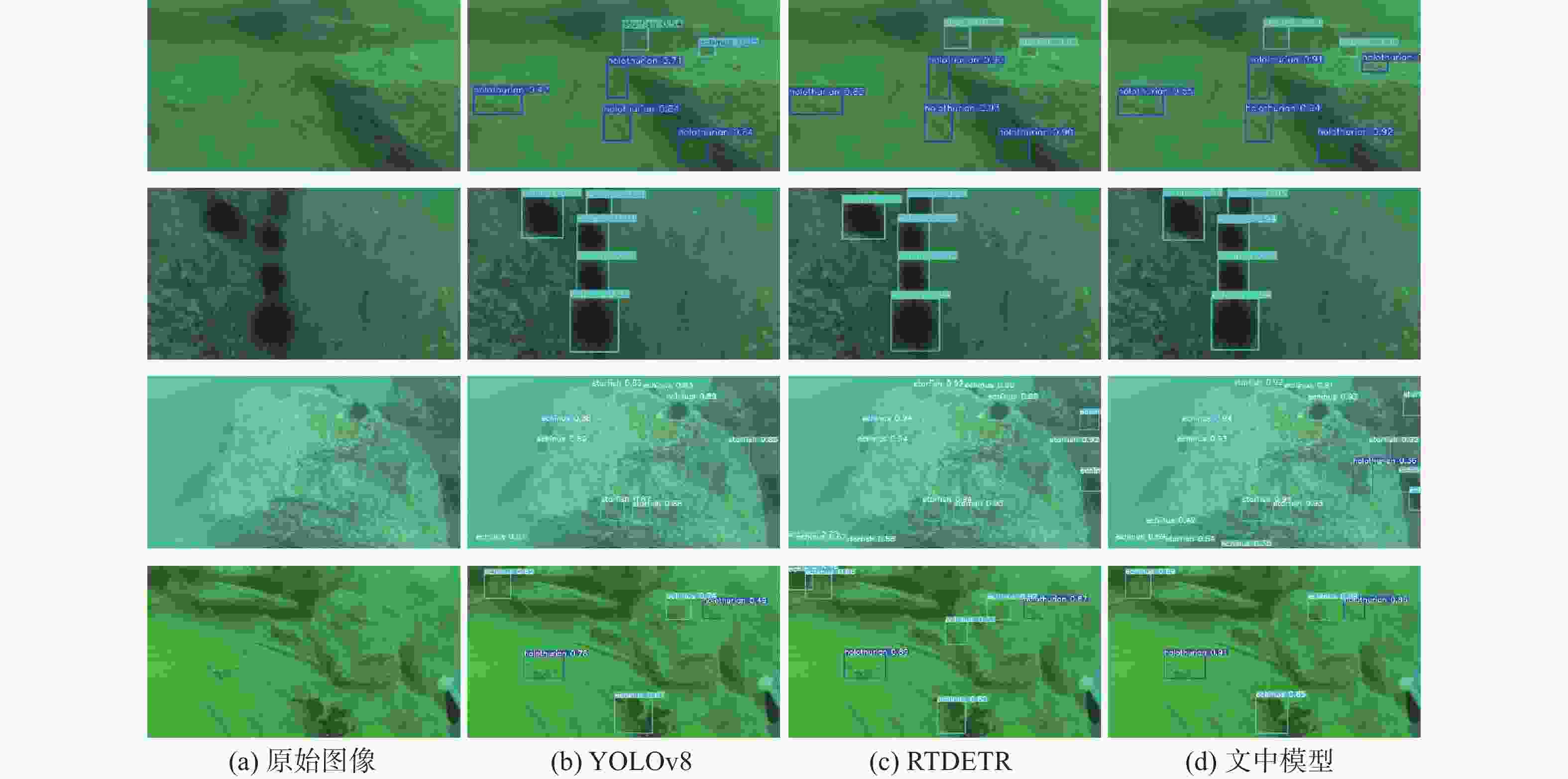
表 1 在DUO数据集上对比实验结果
Table 1. Comparative experimental results on the DUO dataset
模型 mAP@0.5 mAP@
0.5∶0.95Params FLOPs FPS
/(帧/s)Faster
R-CNN0.819 0.613 41.14×106 63.26×109 19.2 Cascade
R-CNN0.839 0.500 69.00×106 72.00×109 27.3 RetinaNet 0.704 0.461 36.17×106 52.62×109 39.2 GFL 0.837 0.655 74.20×106 47.50×109 19.8 YOLOv5s 0.813 0.492 7.03×106 16.00×109 164.2 YOLOv7 0.801 0.559 6.00×106 13.30×109 191.0 YOLOv8 0.812 0.573 3.20×106 8.70×109 205.6 Deformable
DETR0.844 0.637 41.30×106 193.00×109 16.0 RTDETR 0.844 0.635 38.60×106 57.00×109 131.1 RTDETR+
GLbone0.849 0.639 23.30×106 30.60×109 136.8 表 2 水下目标检测算法在DUO数据集上对比实验
Table 2. The underwater target detection algorithms are compared on DUO dataset
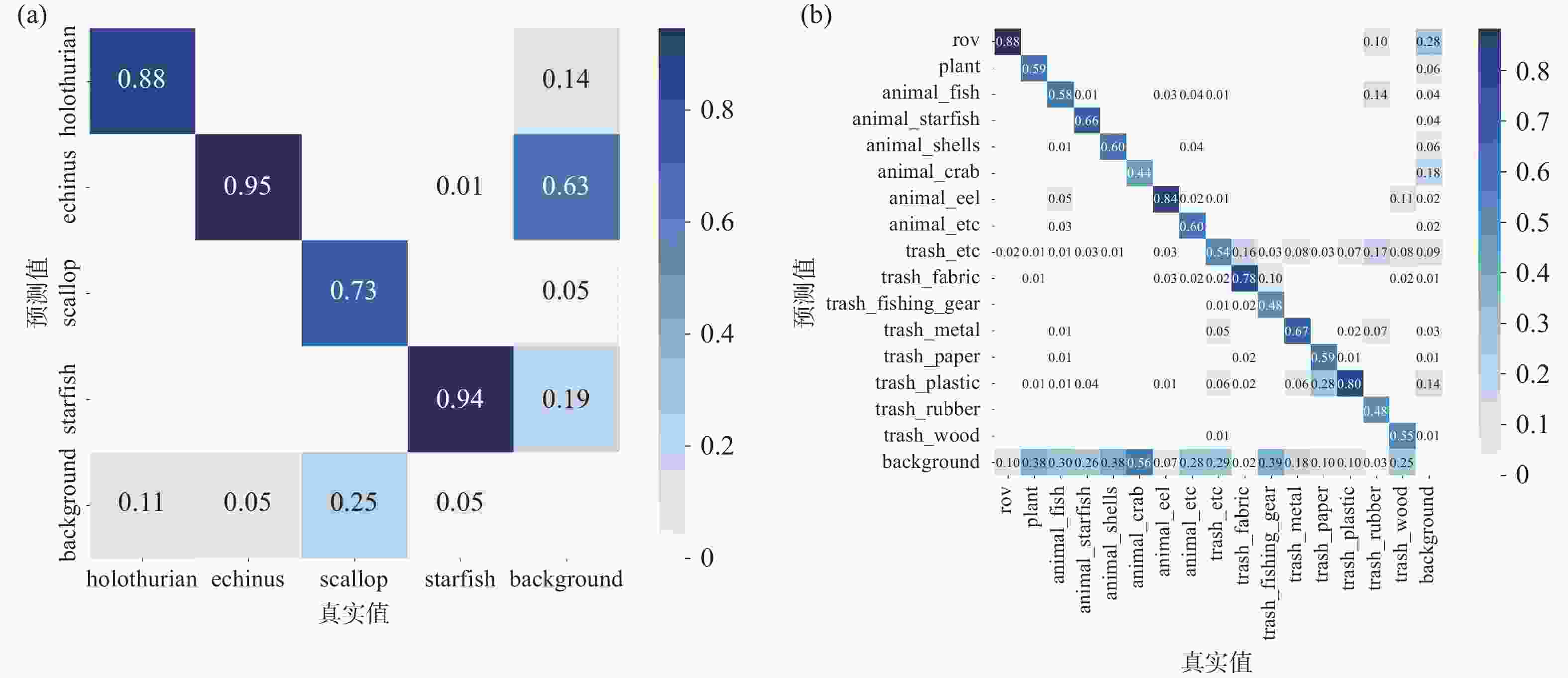
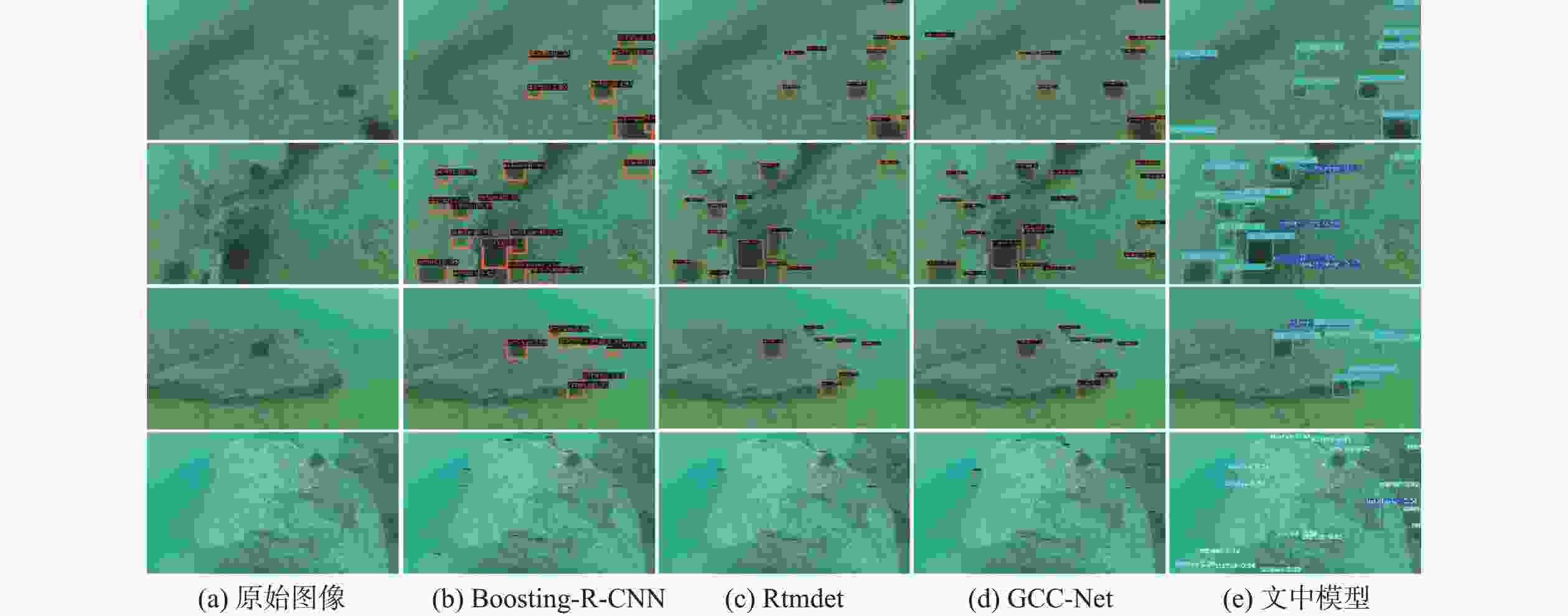
模型 mAP@0.5 精确率 召回率 F1-score Holothurian Echinus Scallop Starfish Holothurian Echinus Scallop Starfish Boosting-R-CNN 0.832 0.710 0.745 0.416 0.793 0.903 0.919 0.746 0.910 0.754 RoIA 0.828 0.839 0.731 0.451 0.849 0.750 0.896 0.422 0.843 0.723 Rtmdet 0.846 0.755 0.825 0.589 0.794 0.870 0.893 0.644 0.894 0.781 GCC-Net 0.839 0.839 0.731 0.452 0.849 0.750 0.896 0.422 0.843 0.723 文中方法 0.849 0.842 0.864 0.783 0.857 0.800 0.859 0.783 0.857 0.811 表 3 Trashcan数据集对比实验结果
Table 3. Comparative experimental results on the Trashcan dataset
模型 mAP@0.5 mAP@
0.5∶0.95Params FLOPs FPS/
(帧/s)Faster
R-CNN0.553 0.312 41.14×106 63.26×109 19.2 Cascade
R-CNN0.543 0.341 42.00×106 270.30×109 9.6 Dino 0.286 0.183 47.56×106 226.30×109 61.2 YOLOv7 0.434 0.241 6.00×106 13.30×109 191.0 Deformable
DETR0.569 0.361 41.30×106 193.00×109 16.0 RTDETR 0.578 0.387 38.60×106 57.00×109 131.1 RTDETR+
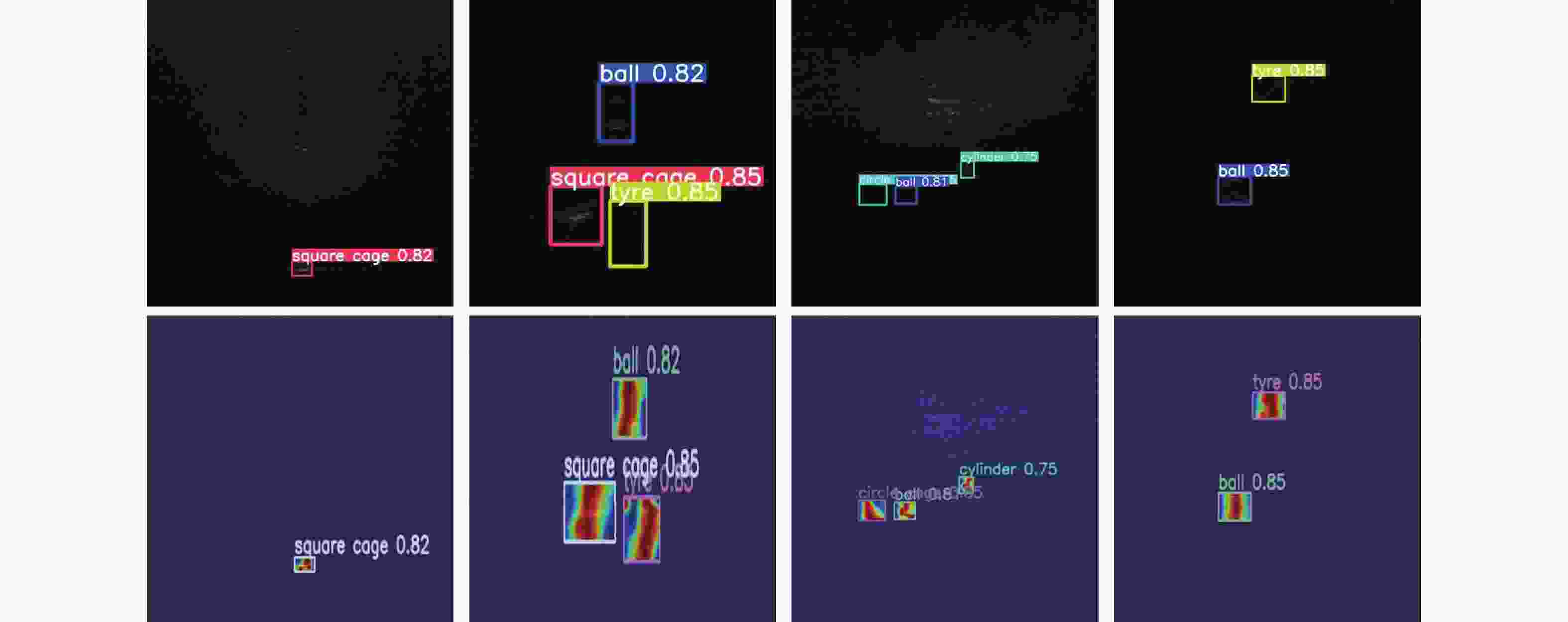
GLbone0.577 0.384 23.30×106 30.60×109 136.8 表 4 URPC数据集各类别实验结果
Table 4. Experimental results on URPC dataset
目标 精确率 召回率 mAP@0.5 球 0.929 0.938 0.945 圆形笼子 0.943 0.947 0.936 立方体 0.963 0.999 0.995 圆柱体 0.946 0.846 0.902 人体 0.901 0.898 0.907 金属桶 0.771 0.931 0.928 方形笼子 0.894 0.881 0.837 轮胎 0.960 0.728 0.783 -
[1] XU S, ZHANG M, SONG W, et al. A systematic review and analysis of deep learning-based underwater object detection[J]. Neurocomputing, 2023, 527: 204-232. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.01.056 [2] YEH C H, LIN C H, KANG L W, et al. Lightweight deep neural network for joint learning of underwater object detection and color conversion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 33(11): 6129-43. [3] KAUR R, SINGH S. A comprehensive review of object detection with deep learning[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2023, 132: 103812. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2022.103812 [4] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014: 580-587. [5] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904-16. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [6] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015: 1440-48. [7] HE K, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2020. [8] REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-49. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [9] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 21-37. [10] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016: 779-788. [11] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, HI, USA : IEEE, 2017: 7263-7271. [12] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[EB/OL]. [2025-02-13]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934. [13] DOSOVITSKIY A. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[EB/OL]. [2025-02-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929. [14] 刘麒东, 沈鑫, 刘海路, 等. 基于GPA+CBAM的域自适应水下目标检测方法[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(5): 846-854. [15] 徐凤强. 水下机器人视域中小目标检测方法研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2021. [16] KHAN A, FOUDA M M, DO D T, et al. Underwater target detection using deep learning: methodologies, challenges, applications and future evolution[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 12618-35. [17] DAI L, LIU H, SONG P, et al. A gated cross-domain collaborative network for underwater object detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2024, 149: 110222. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.110222 [18] FANG P, ZHENG M, FEI L, et al. S-FPN: A shortcut feature pyramid network for sea cucumber detection in underwater images[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 182: 115306. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115306 [19] GAO J, ZHANG Y, GENG X, et al. PE-Transformer: Path enhanced transformer for improving underwater object detection[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 246: 123253. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.123253 [20] KNAUSGÅRD K M, WIKLUND A, SØRDALEN T K, et al. Temperate fish detection and classification: A deep learning based approach[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2022, 52(6): 6988-7001. doi: 10.1007/s10489-020-02154-9 [21] CARION N, MASSA F, SYNNAEVE G, et al. End-to-end object detection with transformers[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020: 213-229. [22] ZHANG L, YANG K, HAN Y, et al. TSD-DETR: A lightweight real-time detection transformer of traffic sign detection for long-range perception of autonomous driving[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2025, 139: 109536. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2024.109536 [23] ZHAO Y, LV W, XU S, et al. Detrs beat YOLOs on real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024: 16965-74. [24] WANG A, CHEN H, LIN Z, et al. Repvit: Revisiting mobile cnn from vit perspective[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024: 15909-20. [25] DAUPHIN Y N, FAN A, AULI M, et al. Language modeling with gated convolutional networks[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2017, 70: 933-941. [26] YU W, LUO M, ZHOU P, et al. Metaformer is actually what you need for vision[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022: 10819-29. [27] SHI D. TransNeXt: Robust foveal visual perception for vision transformers[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2024: 17773-83. -




 下载:
下载: