Intelligent Trust Evaluation Method for Underwater Sensor Networks Based on Fuzzy Clustering and Dynamic Weight Allocation
-
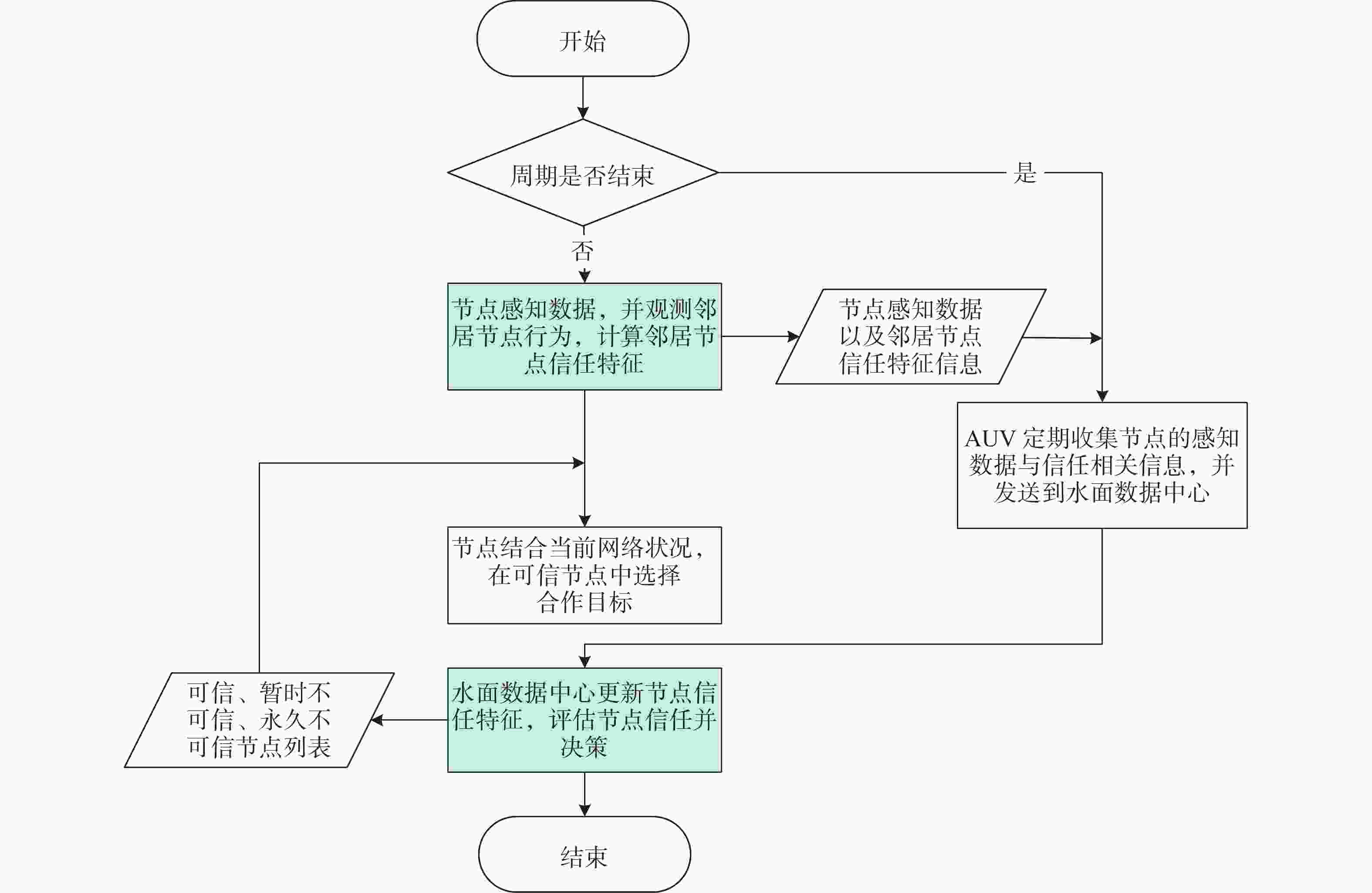
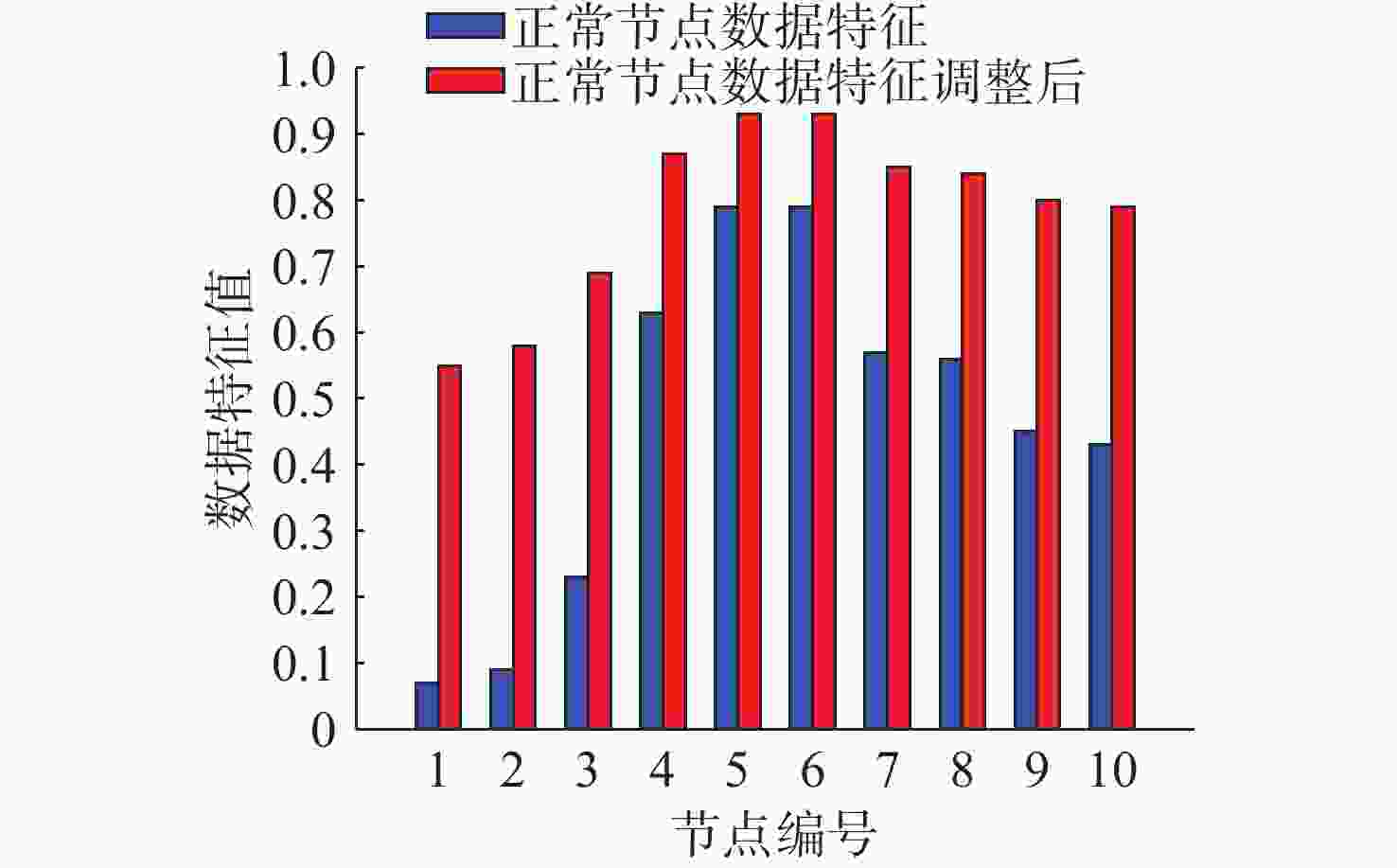
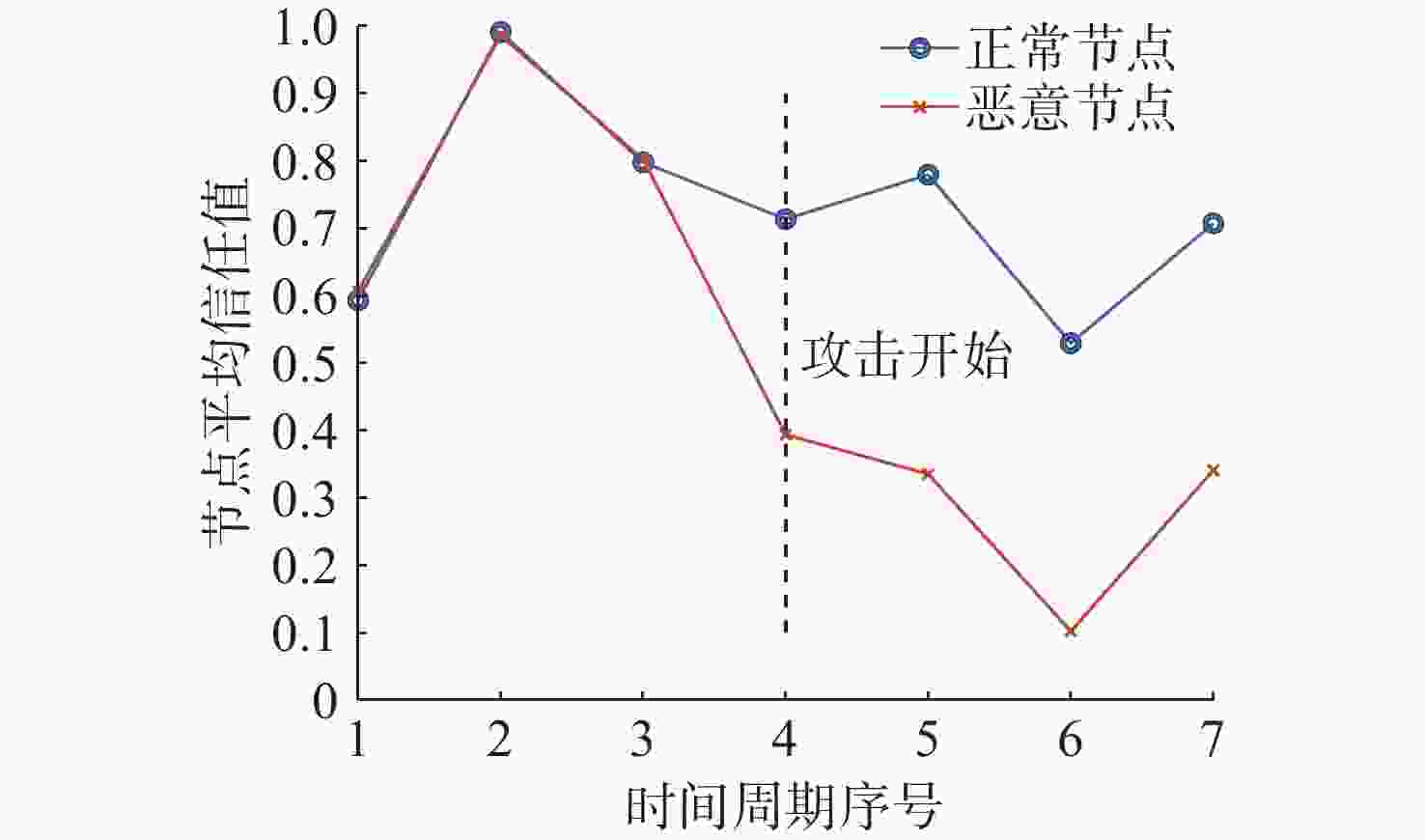
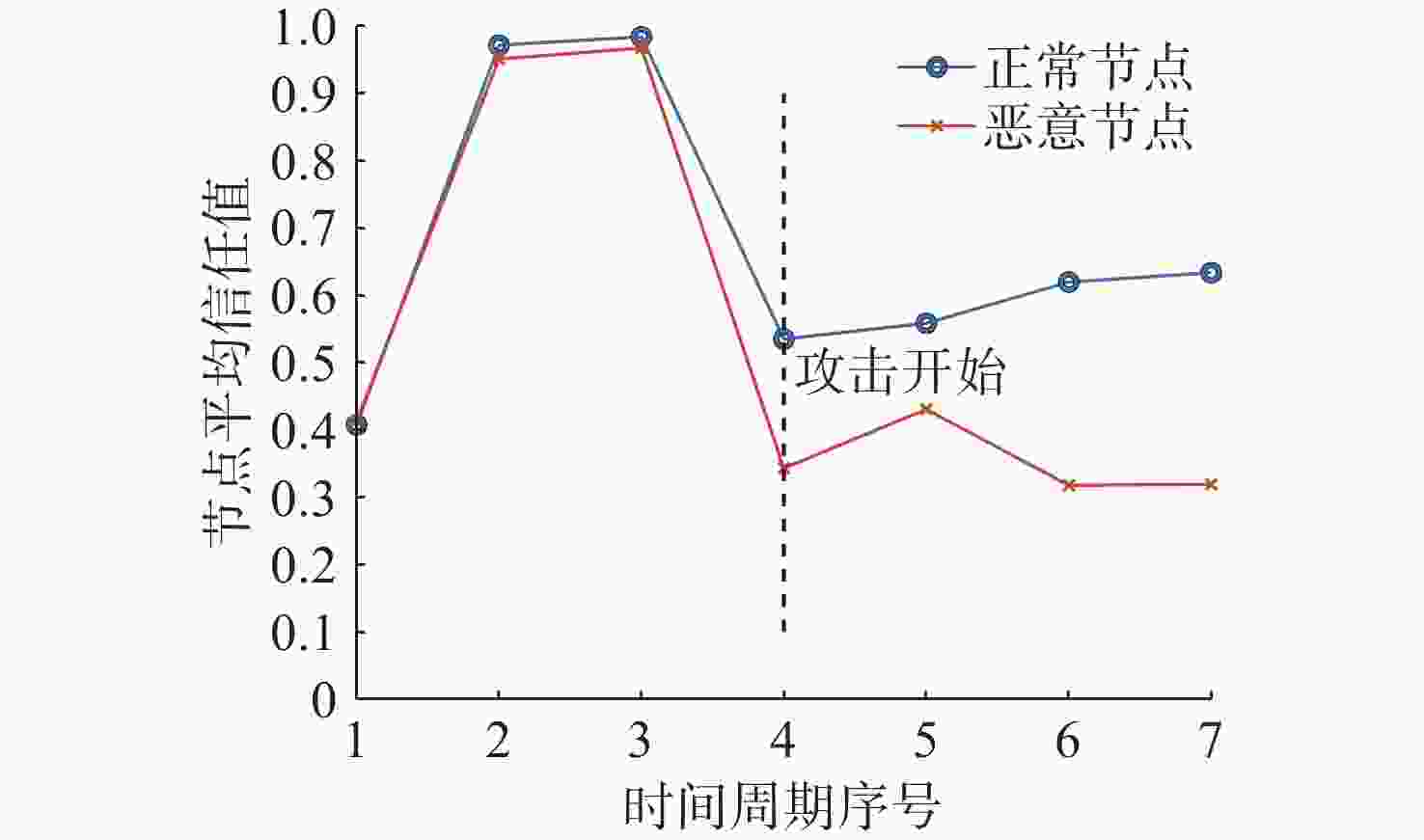
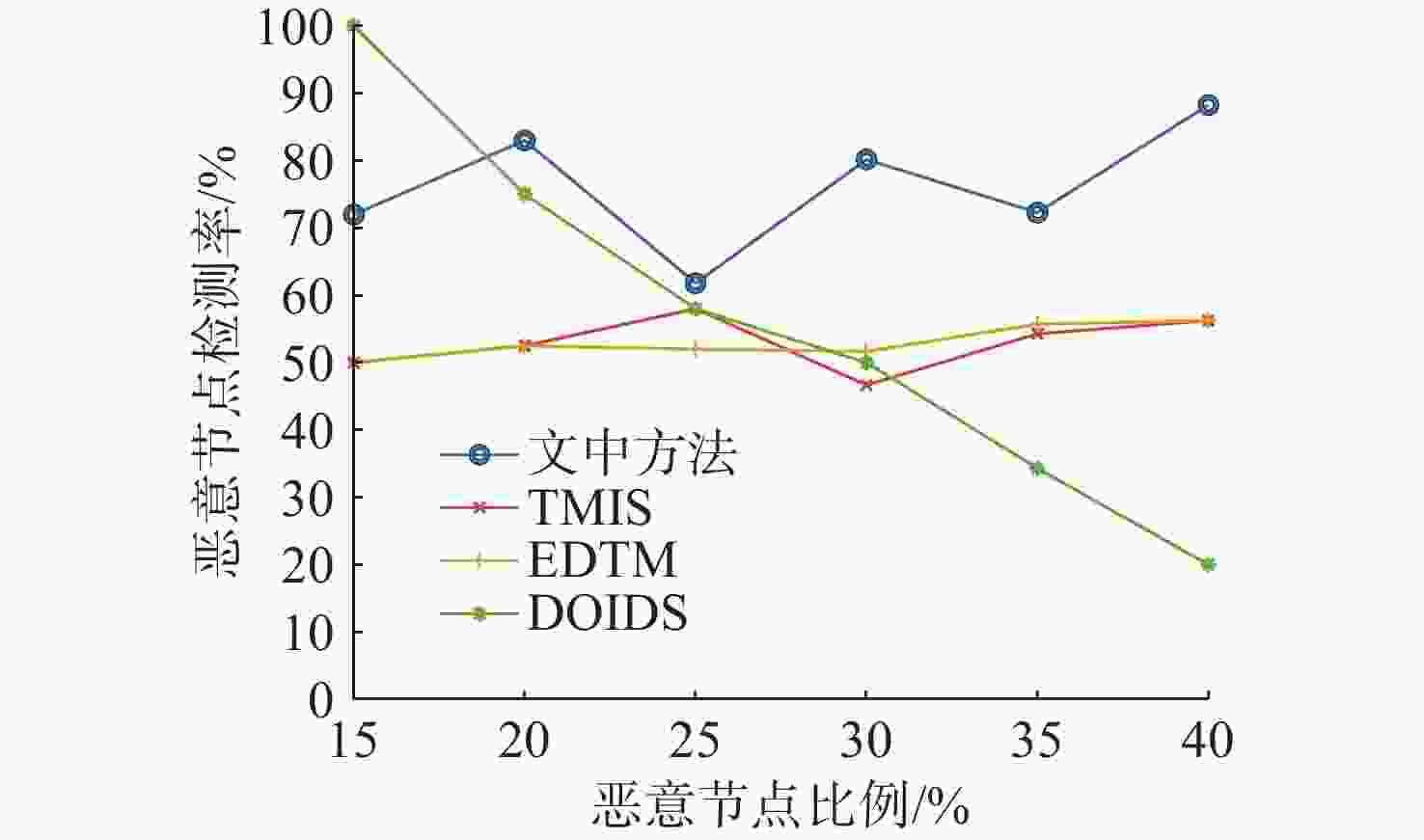
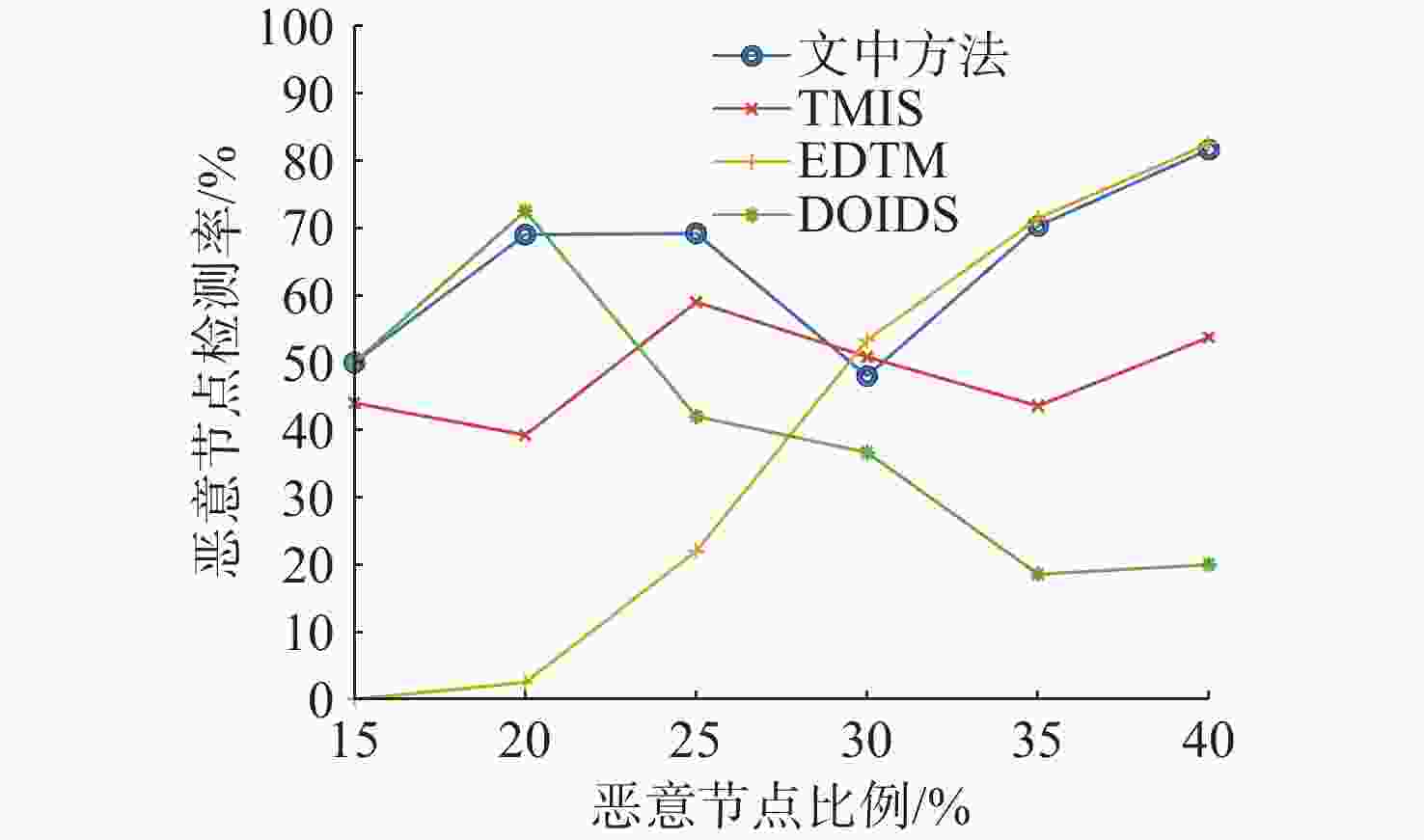
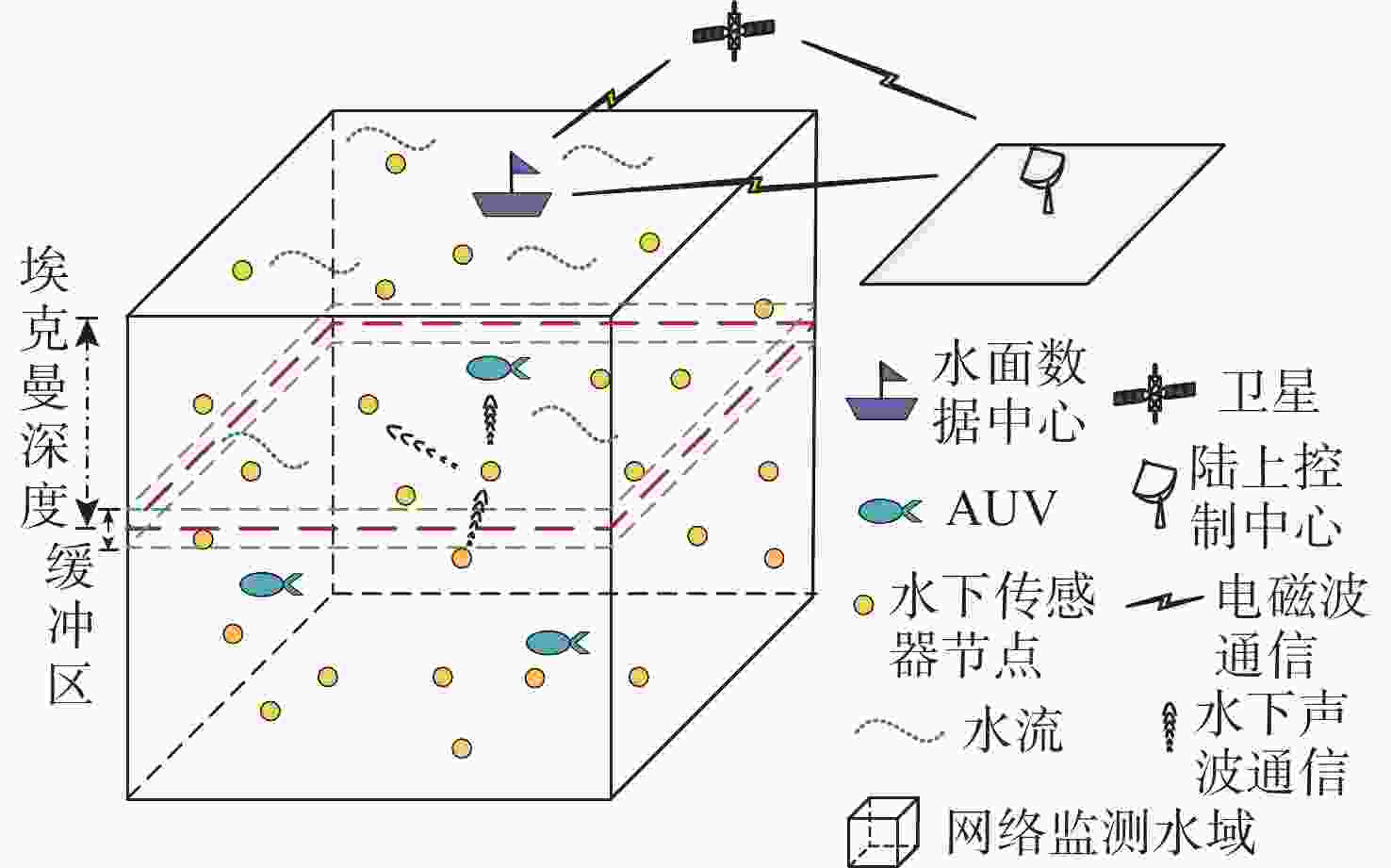
摘要: 水下传感器网络(USN)在海洋环境监测等领域具有重要作用, 同时面临诸多的安全挑战。信任模型虽能有效抵御内部攻击, 保障网络可靠性,但现有信任评估方法大多依赖于信任特征的线性加权和阈值比较的决策方式。在水下动态环境中, 水流和温度等因素在时空上的不断变化, 会导致节点信任特征的变化差异和信任值的整体波动, 使得最优权重和合理阈值难以有效确定, 影响评估的准确性与决策的可靠性。为解决这一问题, 文中提出了一种基于模糊聚类和动态权重分配的智能信任评估方法。该方法首先对USN进行分层动态拓扑建模, 以增强普适性; 在此基础上综合计算节点的通信、能量和数据特征, 以全面反映节点的状态; 然后使用无监督机器学习算法模糊C均值聚类, 实现自适应的节点信任决策, 同时采用主客观结合策略, 根据网络和环境条件为特征动态分配权重, 从而实现对节点信任度的智能评估。仿真实验结果表明, 该方法能够有效评估水下环境中节点的信任度, 提高信任决策的可靠性, 增强网络安全性。Abstract: Underwater sensor networks (USN) play a crucial role in marine environmental monitoring and other fields while facing significant security challenges. Trust models can effectively defend against insider attacks and ensure network reliability. However, most existing trust evaluation methods rely on the linear weighting of trust features and the decision-making method based on threshold comparison. In dynamic underwater environments, factors such as water flow and temperature are constantly changing in time and space, leading to differences in the variations of node trust features and overall fluctuations of trust values. This makes it challenging to effectively determine the optimal weights and the reasonable threshold, thereby affecting the accuracy of evaluation and the reliability of decision-making. To solve this issue, this paper proposed an intelligent trust evaluation method based on fuzzy clustering and dynamic weight allocation. First, a hierarchical dynamic topology model of the USN was developed to enhance universality. On this basis, communication, energy, and data features were comprehensively calculated to fully reflect node states. Then, the unsupervised machine learning algorithm, namely fuzzy C-means clustering, was employed to enable adaptive node trust decision-making. Meanwhile, a subjective and objective combination strategy was adopted to dynamically allocate weights to features according to network and environmental conditions. Consequently, the intelligent evaluation of node trust was achieved. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method can effectively evaluate the trust of nodes in underwater environments, improve the reliability of trust decision-making, and enhance the security of the network.
-
Key words:
- underwater sensor network /
- trust evaluation /
- fuzzy clustering /
- dynamic weight
-
表 1 仿真参数列表
Table 1. Parameters of simulation
参数 取值 纬度/(°) 45 海面10米处风速/(m/s) 10 网络范围/m3 2 000×2 000× 1000 节点数量/个 200 节点通信范围/m 500 节点初始能量/J 1000 节点通信频率/kHz 26 节点数据速率/(kbit/s) 10 数据包大小/Byte 100 评估周期/s 60 表 2 不同方法下特征线性加权值
Table 2. Linear weighting of features under different methods
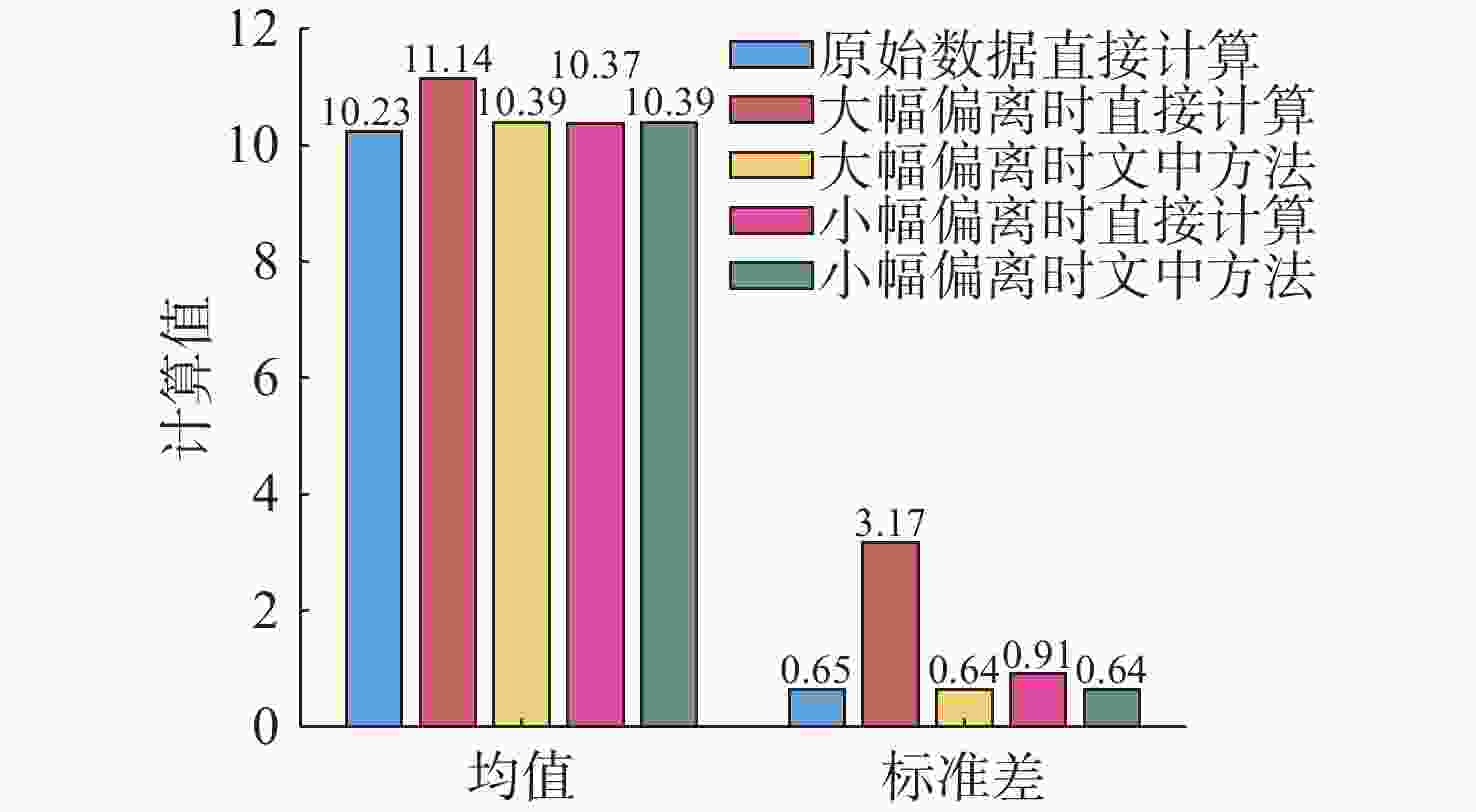
节点特征值 相等权重 综合权重 (0.90, 0.78, 0.10) 0.59 0.34 (0.68, 0.56, 0.17) 0.47 0.31 (0.77, 0.86, 0.62) 0.75 0.70 (0.73, 0.78, 0.18) 0.56 0.38 (0.77, 1.00, 0.04) 0.60 0.36 (0.82, 0.86, 0.24) 0.64 0.45 (0.81, 0.88, 0.34) 0.67 0.52 (0.76, 0.66, 0.56) 0.66 0.60 (0.84, 0.39, 0.02) 0.42 0.16 (0.83, 0.58, 0.53) 0.65 0.55 -
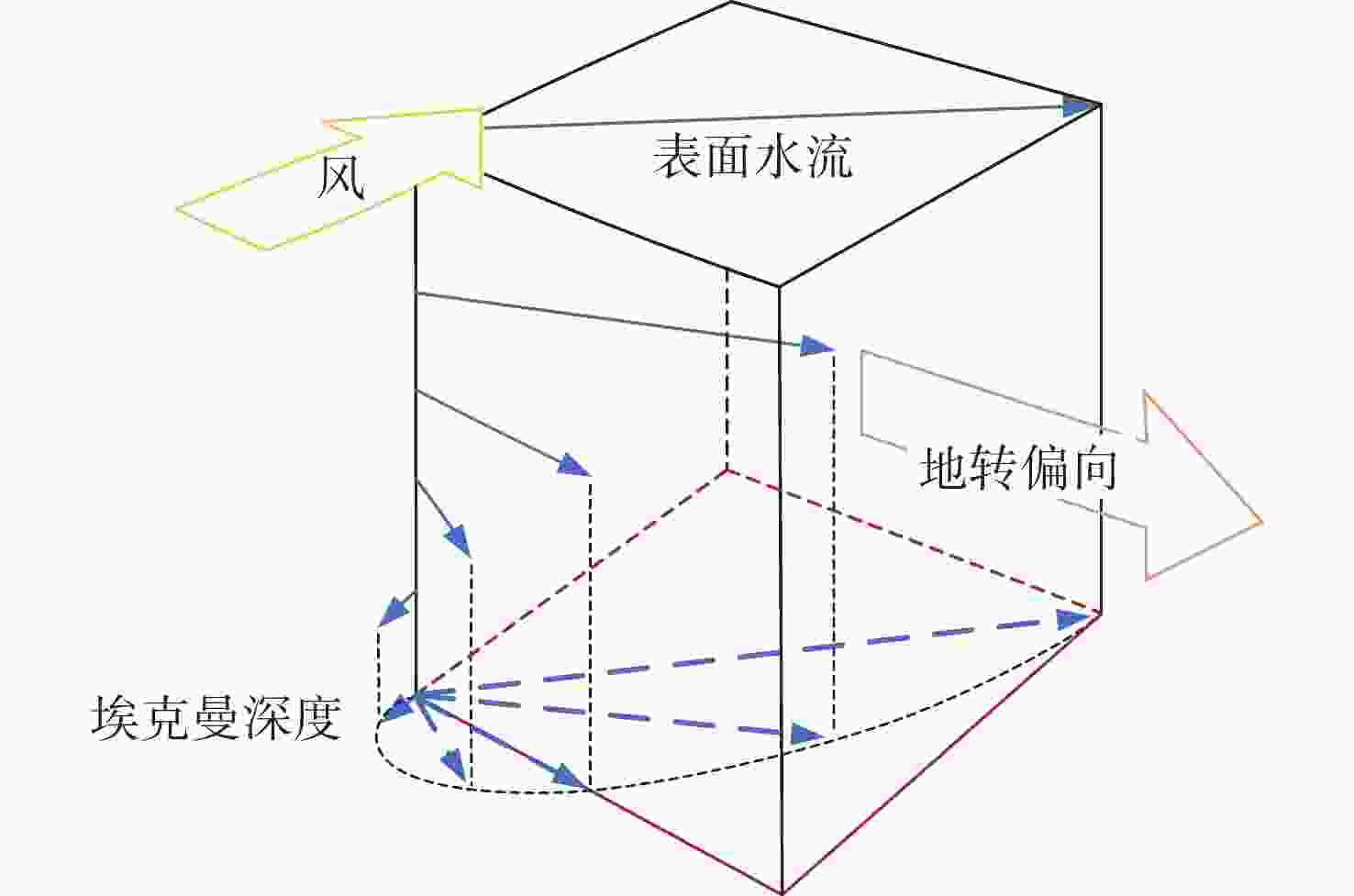
[1] 苏毅珊, 张贺贺, 张瑞, 等. 水下无线传感器网络安全研究综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(3): 1121-1133. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211576SU Y S, ZHANG H H, ZHANG R, et al. Review of security for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(3): 1121-1133. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211576 [2] ZHU R, BOUKERCHE A, LONG L, et al. Design guidelines on trust management for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2024, 26(4): 2547-2576. [3] JIANG J, HAN G, WANG F, et al. An efficient distributed trust model for wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2014, 26(5): 1228-1237. [4] JIANG J, ZHU X, HAN G, et al. A dynamic trust evaluation and update mechanism based on C4.5 decision tree in underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(8): 9031-9040. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2999566 [5] JIANG B, ZHOU R, LUO F, et al. Hybrid trust model for identifying malicious attacks in underwater acoustic sensor network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(16): 26743-26754. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3424252 [6] LIANG K, SUN S, HUANG X, et al. A trust-based malicious detection scheme for underwater acoustic sensor networks[C]//International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Security. Qinghai, China: CCIS, 2022: 427-440. [7] ZHU R, BOUKERCHE A, LI P, et al. A traffic-aware trust model based on edge computing for underwater wireless sensor networks[C]//ICC 2024-IEEE International Conference on Communications. Denver, CO, USA: IEEE, 2024: 2390-2395. [8] DU J, HAN G, LIN C, et al. ITrust: An anomaly-resilient trust model based on isolation forest for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2020, 21(5): 1684-1696. [9] ZHANG R, ZHANG J, WANG Q, et al. DOIDS: An intrusion detection scheme based on DBSCAN for opportunistic routing in underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(4): 2096. doi: 10.3390/s23042096 [10] ZHU R, BOUKERCHE A, HUANG X, et al. DESLR: Energy-efficient and secure layered routing based on channel-aware trust model for UASNs[J]. Computer Networks, 2023, 234(10): 1-11. [11] 于洋, 孙思卿, 张立川, 等. 自主水下航行器集群组网技术发展与展望[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(2): 194-207. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2024-0055YU Y, SUN S Q, ZHANG L C, et al. Development and prospects of networking technologies for autonomous undersea vehicles[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(2): 194-207. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2024-0055 [12] PRICE J F, WELLER R A, SCHUDLICH R R. Wind-driven ocean currents and Ekman transport[J]. Science, 1987, 238(4833): 1534-1538. doi: 10.1126/science.238.4833.1534 [13] HAN G, SHEN S, SONG H, et al. A stratification-based data collection scheme in underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(11): 10671-10682. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2867021 [14] CARUSO A, PAPARELLA F, VIEIRA L F M, et al. The meandering current mobility model and its impact on underwater mobile sensor networks[C]//IEEE INFOCOM 2008-The 27th Conference on Computer Communications. Phoenix, AZ, USA: IEEE, 2008: 221-225. [15] LUO J, YANG Y, WANG Z, et al. Localization algorithm for underwater sensor network: A review[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(17): 13126-13144. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3081918 [16] CUSHMAN-ROISIN B, BECKERS J M. Introduction to geophysical fluid dynamics: Physical and numerical aspects[M]. Waltham, MA, USA: Academic press, 2011. [17] COUTINHO R W L, BOUKERCHE A. OMUS: Efficient opportunistic routing in multi-modal underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(9): 5642-5655. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3069117 [18] JIANG J, HAN G, SHU L, et al. A trust model based on cloud theory in underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2015, 13(1): 342-350. [19] HAN G, JIANG J, SHU L, et al. An attack-resistant trust model based on multidimensional trust metrics in underwater acoustic sensor network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2015, 14(12): 2447-2459. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2015.2402120 [20] ROUSSEEUW P J , HUBERT M. Anomaly detection by robust statistics[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews Data Mining & Knowledge Discovery, 2017, 8(2): 1236. [21] BEZDEK J C. Pattern recognition with fuzzy objective function algorithms[M]. Berlin, Germany: Springer Science & Business Media, 2013. [22] HUNG W L, YANG M S, CHEN D H. Bootstrapping approach to feature-weight selection in fuzzy C-means algorithms with an application in color image segmentation[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2008, 29(9): 1317-1325. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2008.02.003 [23] ZHANG B, LI C C, DONG Y, et al. A comparative study between analytic hierarchy process and its fuzzy variants: A perspective based on two linguistic models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 29(11): 3270-3279. [24] HE X, CAI D, NIYOGI P, et al. Laplacian score for feature selection[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: MIT Press, 2005: 507-514. -




 下载:
下载: