Cooperative Control and Intelligent Optimization for Air-Sea Heterogeneous Unmanned Systems
-
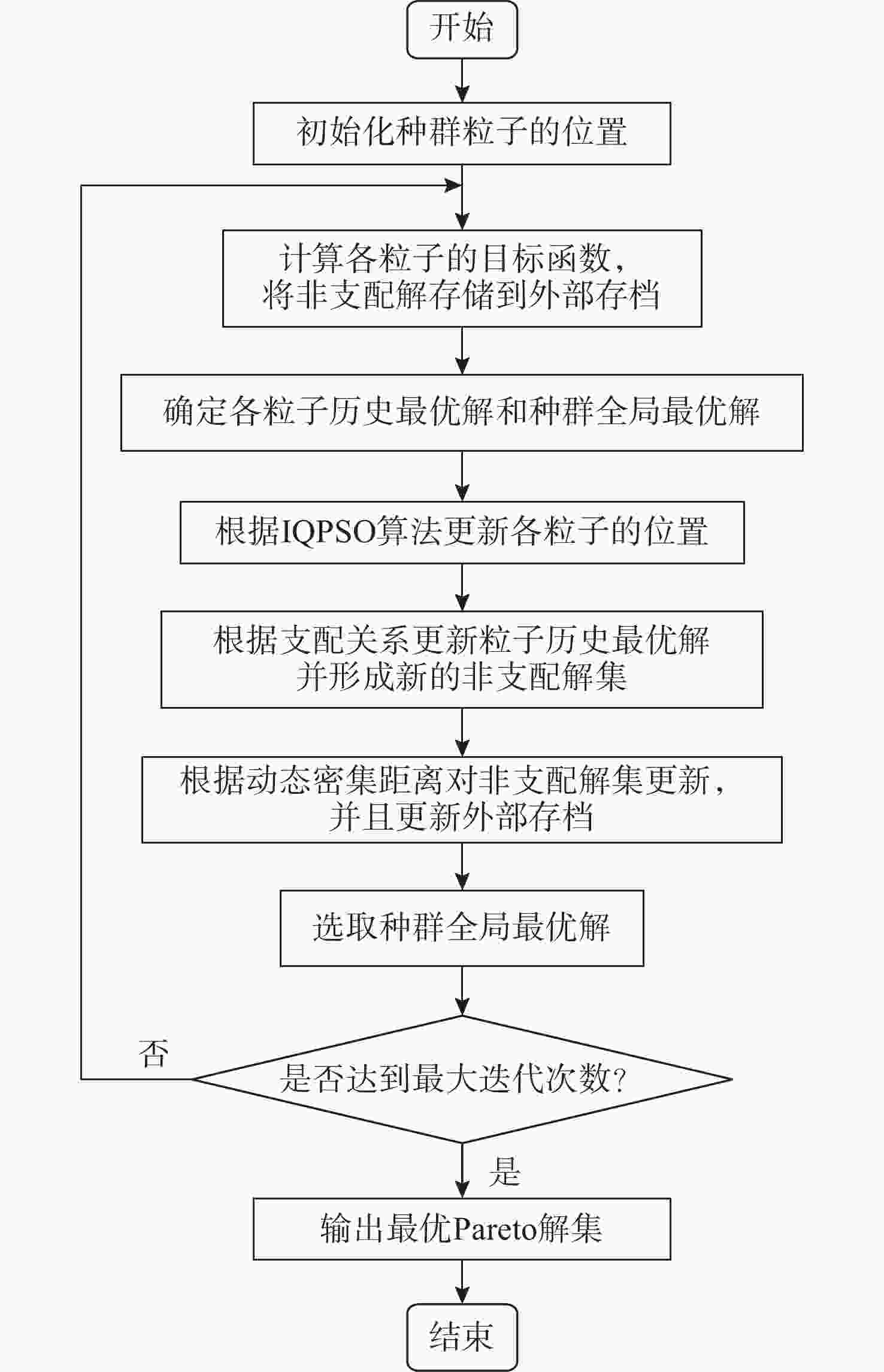
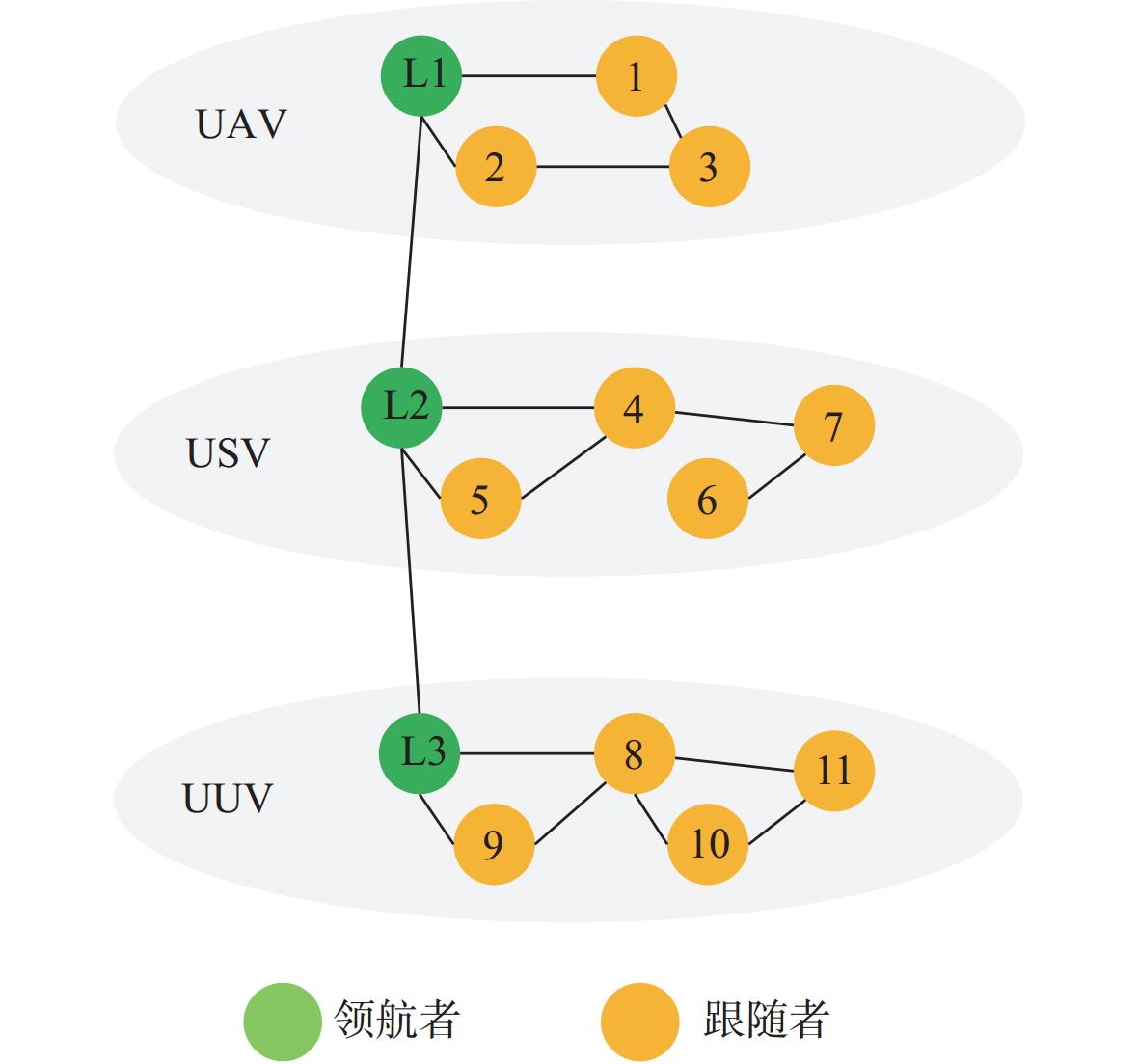
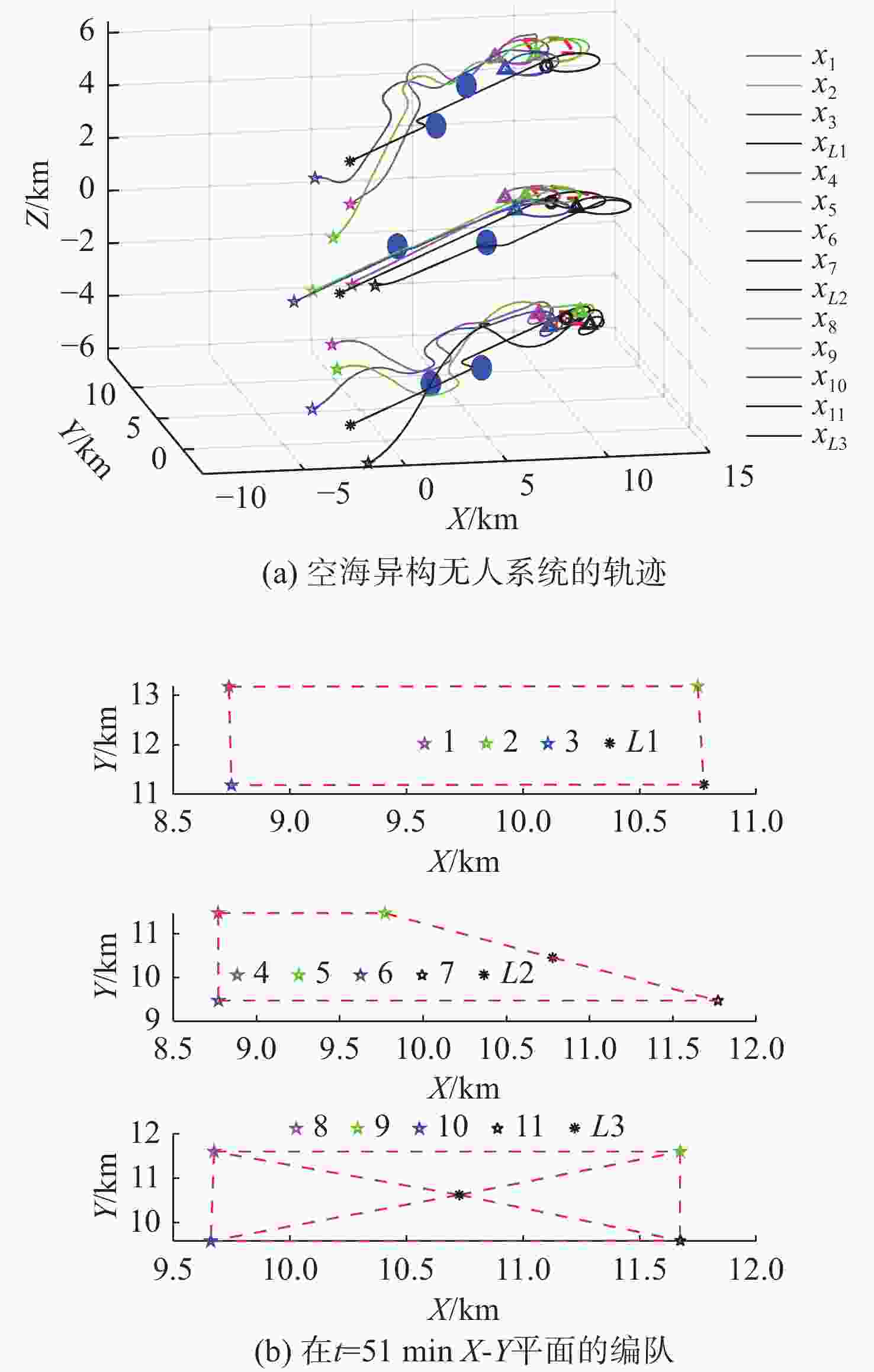
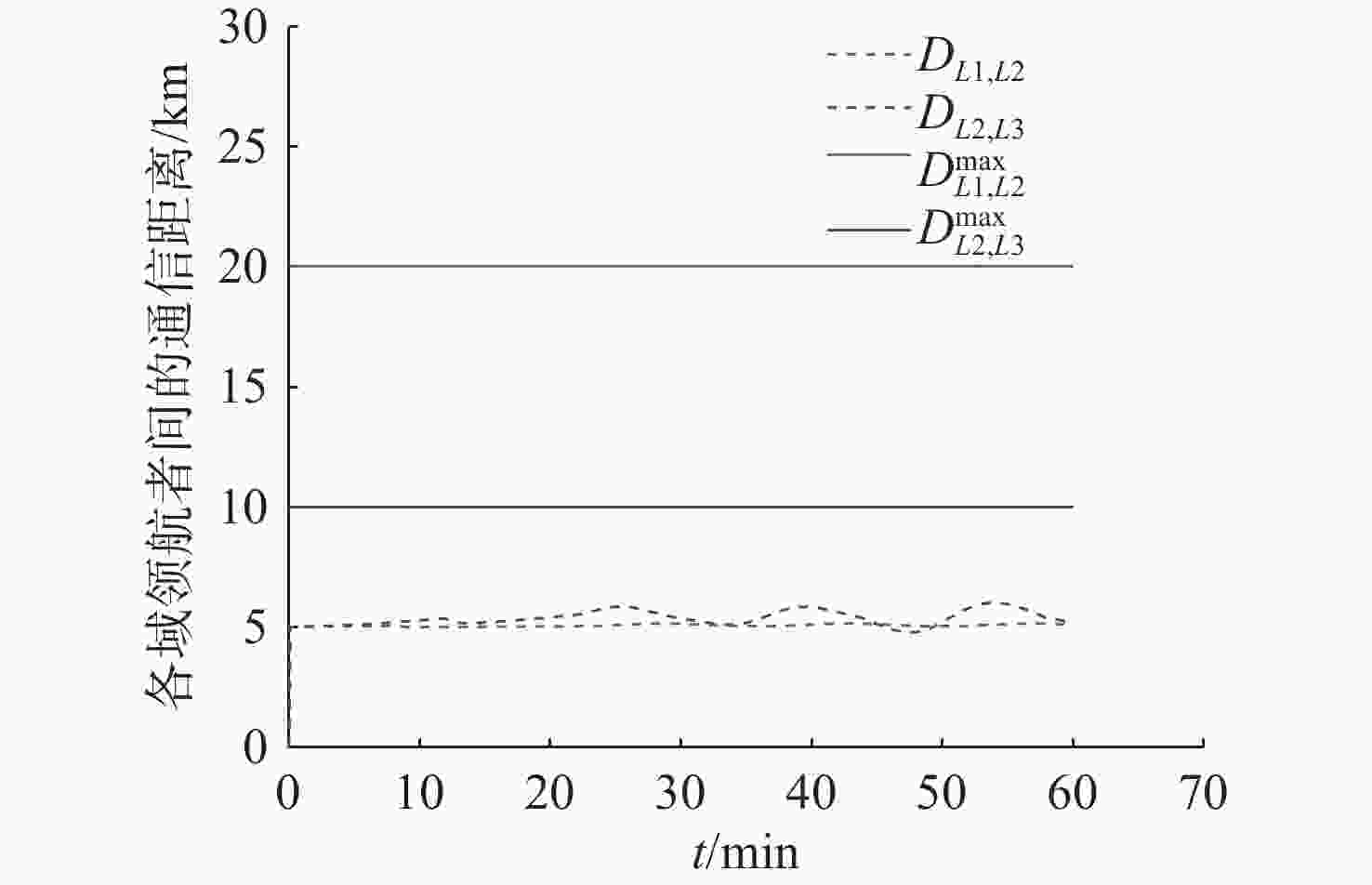
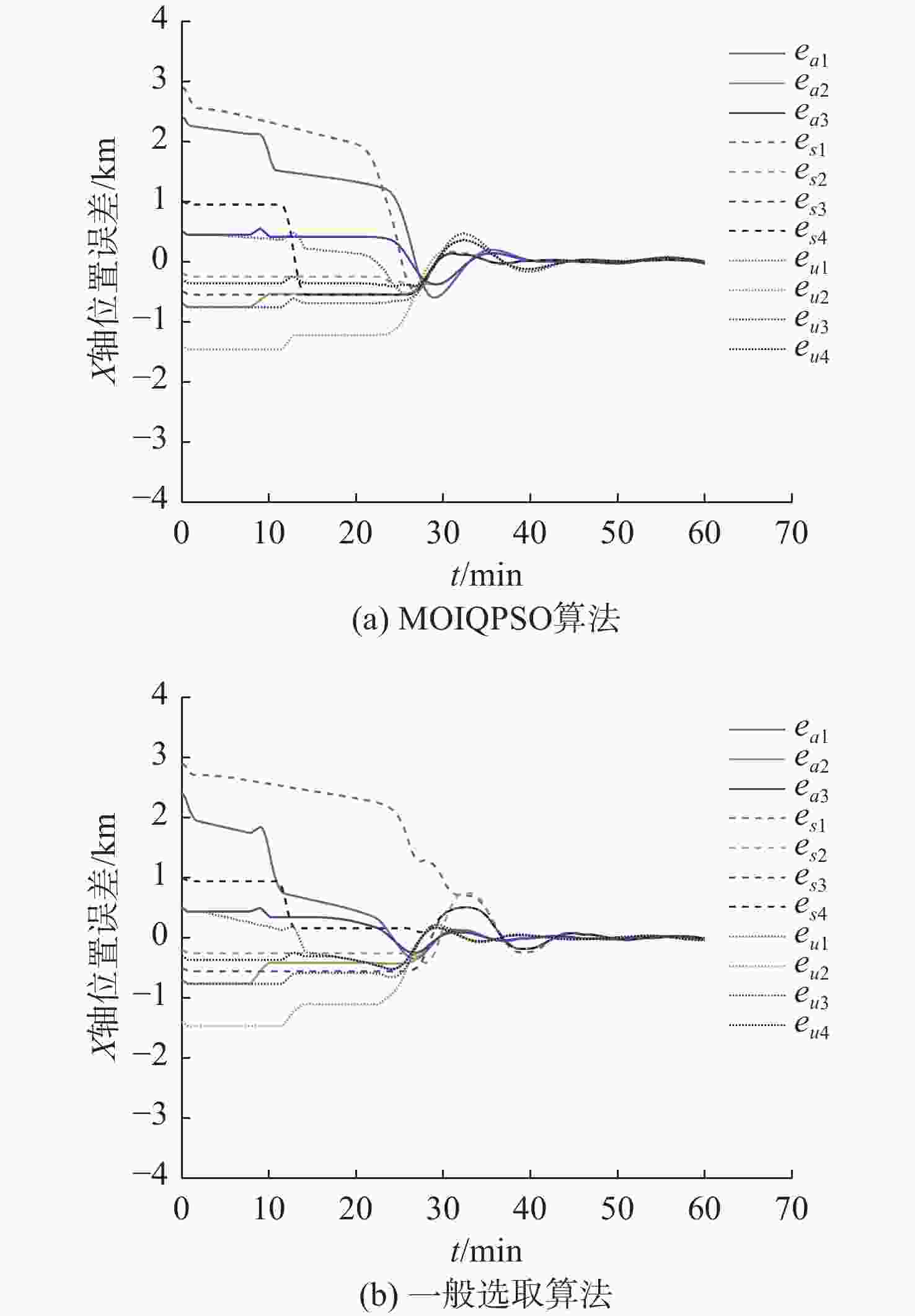
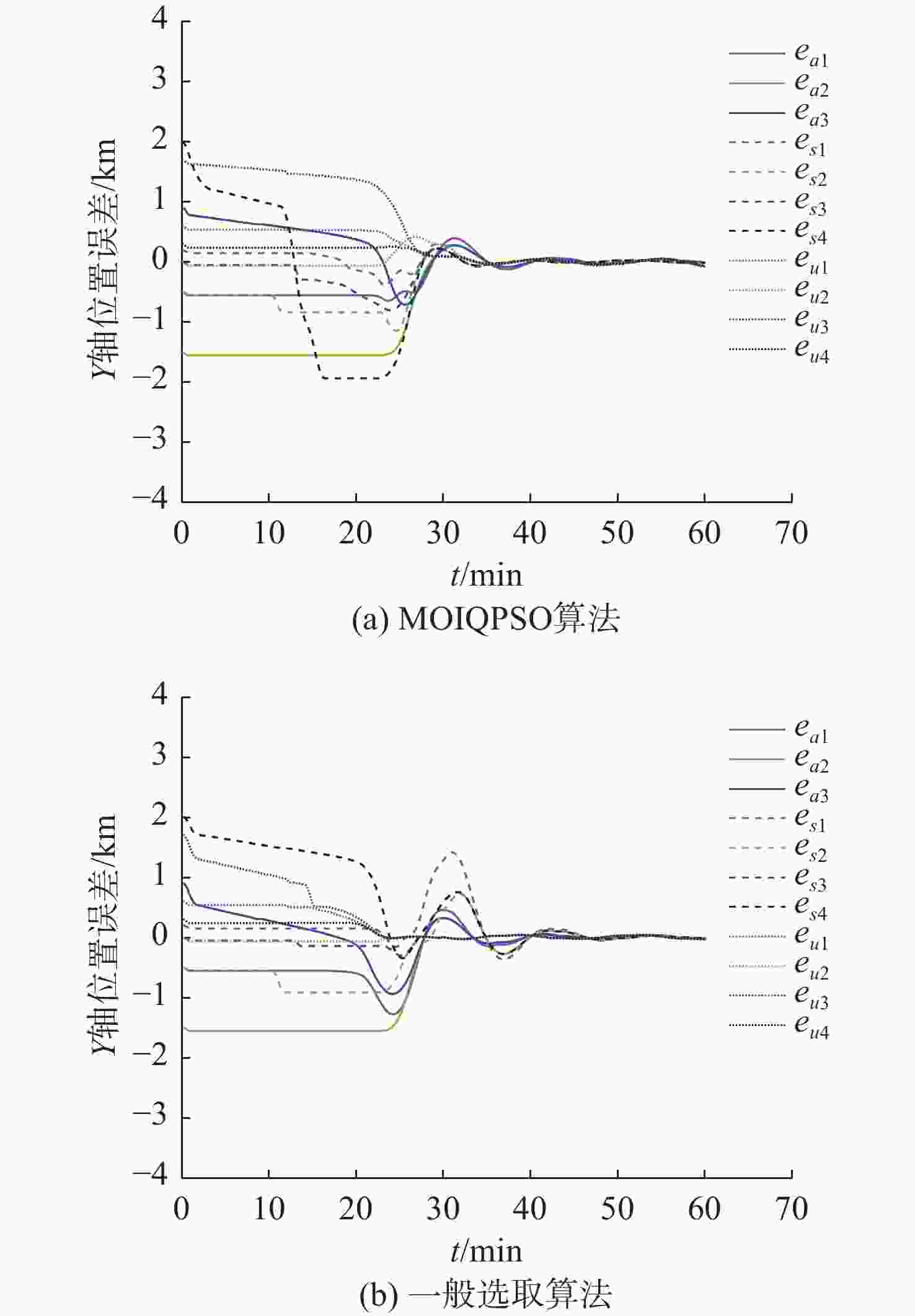
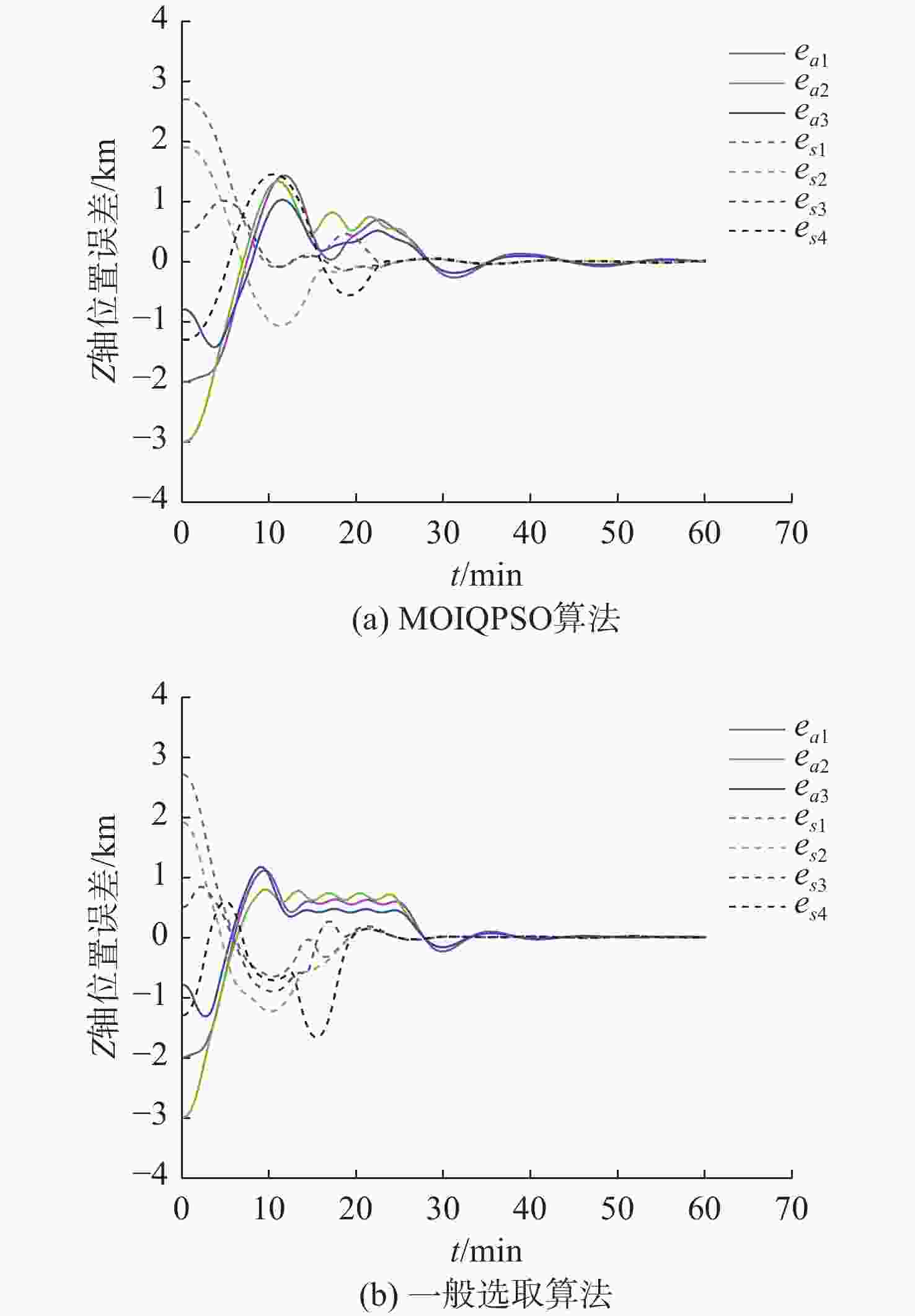
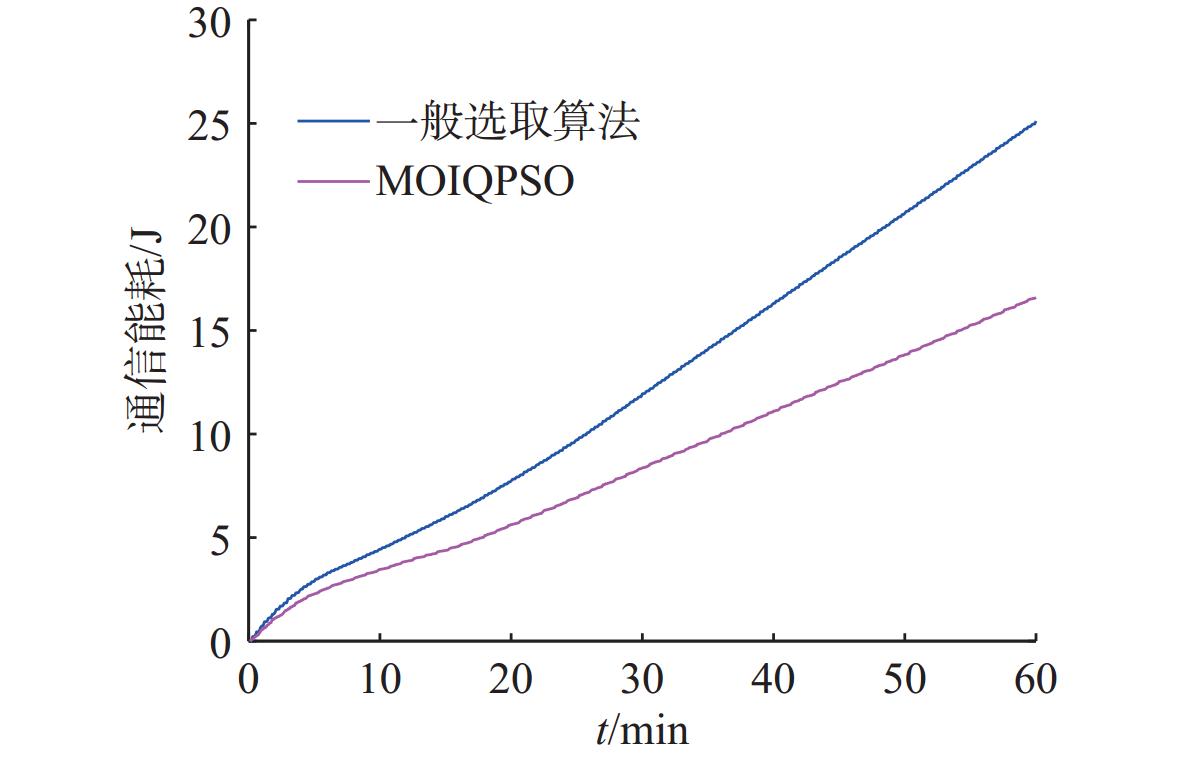
摘要: 为应对日益复杂的海洋任务, 文中构建了一个由空中无人机-无人水面艇-无人水下航行器组成的空海异构无人系统, 研究其协同控制问题。对于异构无人系统的信息交互问题, 各域均由1个领航者与多个跟随者组成, 跨域通信由各域领航者完成。同时, 针对各域领航者轨迹问题, 提出了一种基于人工势场法的协同轨迹规划算法, 使各域领航者能够在避障情况下到达目标位置。对于受限的通信资源问题, 为各域跟随者设计了一种基于间歇通信的脉冲层级编队控制协议, 实现了避障下的编队控制, 且减少了通信开销。另外, 针对协同控制算法的收敛时间和通信能耗的多目标优化问题, 通过设计收缩-扩张系数和动态密集距离策略, 提出了一种改进的多目标量子行为粒子群优化算法, 用于智能选择各域脉冲间隔, 从而使协同控制算法的收敛时间与通信能耗间达到良好折衷。仿真结果表明, 该空海异构无人系统能够在避障下实现编队控制, 同时减少通信开销, 与传统的多目标量子行为粒子群优化算法相比, 所提算法具有更好的收敛性与全局搜索能力。Abstract: In order to cope with increasingly complex ocean missions, an air-sea heterogeneous unmanned system composed of unmanned aerial vehicles(UAVs), unmanned surface vessels(USVs), and unmanned undersea vehicles(UUVs) was constructed to study the cooperative control problem. For the information exchange problem of a heterogeneous unmanned system, each domain consisted of a leader and multiple followers, where cross-domain communication was required between the leaders of each domain. Meanwhile, for the trajectory planning issue of the leader in each domain, a cooperative trajectory planning algorithm based on the artificial potential field method was proposed for the leader in each domain to reach the target location while avoiding obstacles. For the limited communication resources, an impulsive hierarchical formation control protocol with intermittent communication was designed for followers in each domain, which reduces communication overhead while achieving formation control under obstacle avoidance. Besides, for the multi-objective optimization problem of convergence time and communication energy consumption in cooperative control algorithm, an improved multi-objective quantum-behavior particle swarm optimization algorithm was proposed by designing contraction-expansion coefficient and dynamic dense distance strategy, which was used to intelligently select the impulsive interval for each domain, achieving a good compromise between the convergence time and communication energy consumption of cooperative control algorithm. Simulation results demonstrate that the air-sea heterogeneous unmanned system can achieve formation control while avoiding obstacles and reducing communication overhead, and the proposed algorithm has better convergence and global search ability than the traditional multi-objective quantum-behavior particle swarm optimization algorithm.
-
表 1 2种算法性能比较
Table 1. Comparison of performance between two algorithms
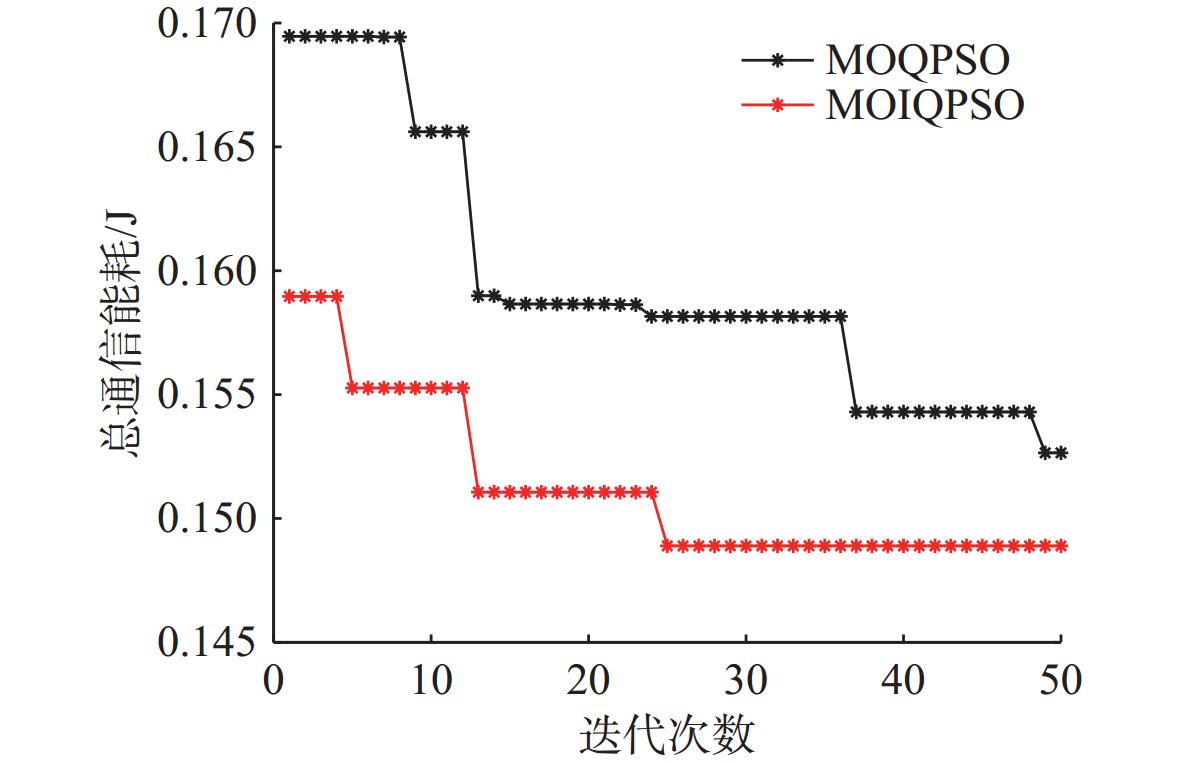
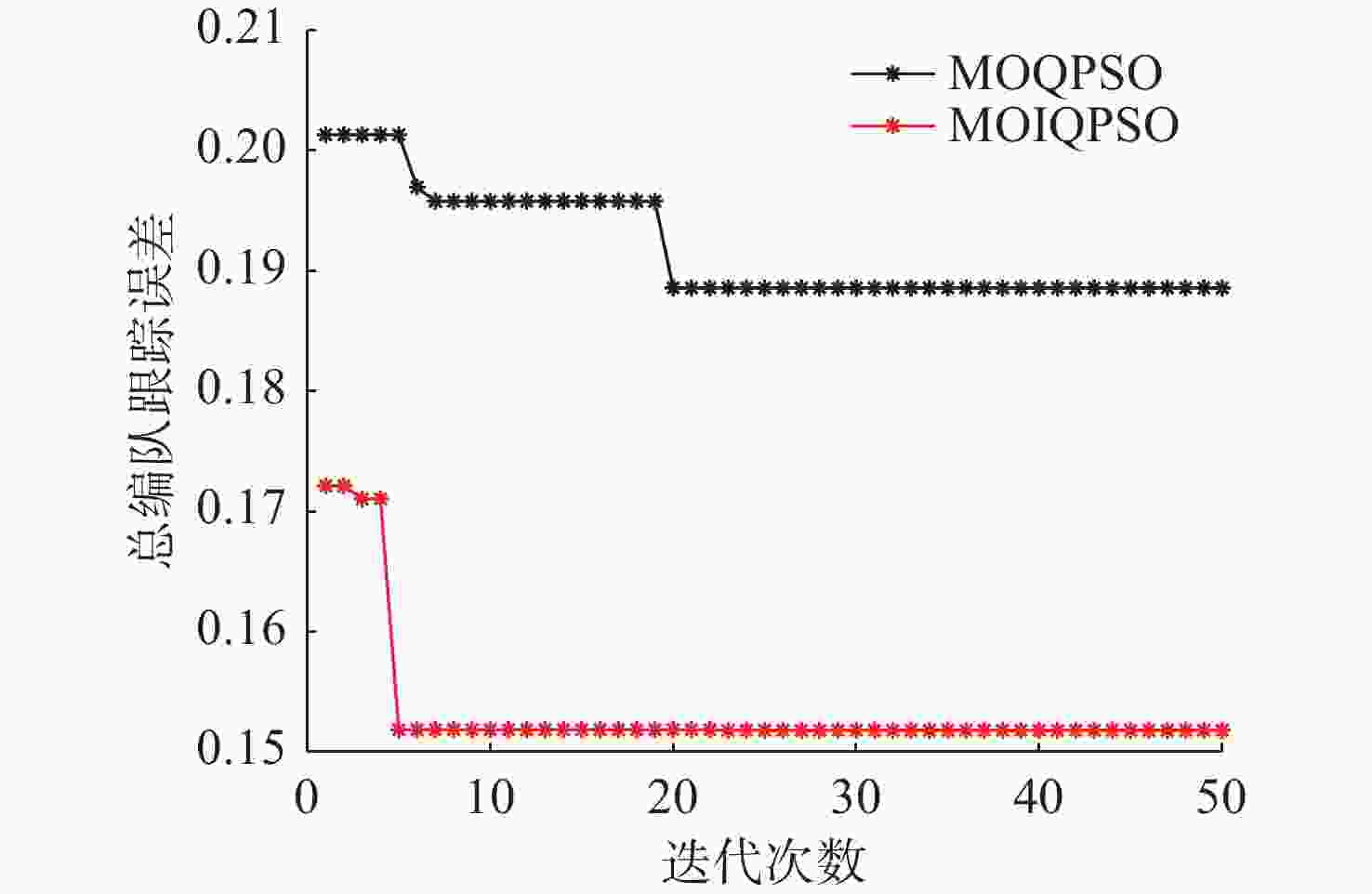
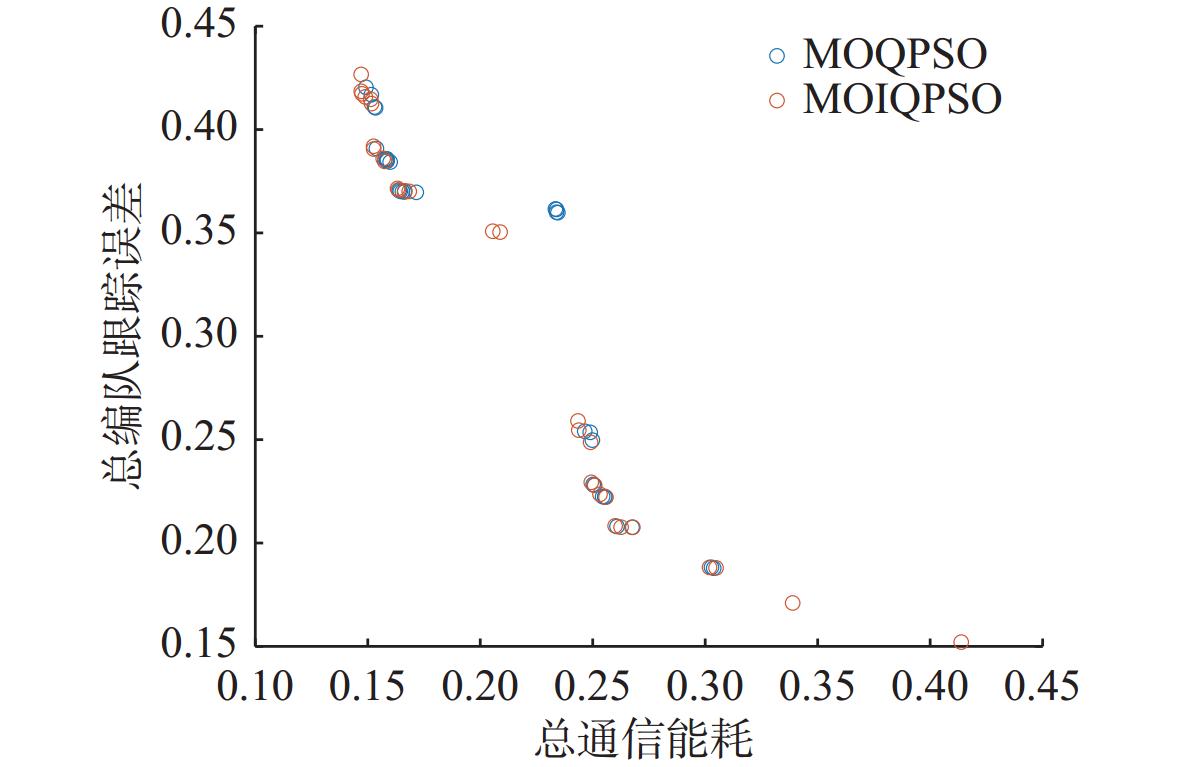
算法 外部解 IS $ I_{\mathrm{HV}} $ $ {e_{{\mathrm{nf}}}} $ $ {\tilde W_{{\mathrm{total}}}} $ MOQPSO 0.1843 0.1481 0.033 16.05 MOIQPSO 0.1574 0.1351 0.023 18.81 -
[1] 杨惠珍, 李建国, 吴天宇, 等. 基于逃逸角的多ASV微分博弈协同围捕方法[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(4): 730-738.YANG H Z, LI J G, WU T Y, et al. Cooperative hunting method for multiple ASVs using differential games based on escape angle[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(4): 730-738. [2] 宋保维, 潘光, 张立川, 等. 自主水下航行器发展趋势及关键技术[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2022, 17(5): 27-44.SONG B W, PAN G, ZHANG L C, et al. Development trend and key technologies of autonomous underwater vehicles[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2022, 17(5): 27-44. [3] 邱志明, 孟祥尧, 马焱, 等. 海上无人系统跨域协同运用与技术发展[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(2): 184-193.QIU Z M, MENG X Y, MA Y, et al. Cross-domain collaborative application and technology development of maritime unmanned systems[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(2): 184-193. [4] 孙海文, 王溪野, 王兆辰, 等. 海上异构无人集群协同运用发展概况及启示[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(2): 275-281.SUN H W, WANG X Y, WANG Z C, et al. Development overview and inspiration of collaborative application of heterogeneous unmanned clusters at sea[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(2): 275-281. [5] JIA Z H, LU H B, LI S Q, et al. Distributed dynamic rendezvous control of the AUV-USV joint system with practical disturbance compensations using model predictive control[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 258: 111268. [6] 于建宇, 林景胜, 闫敬, 等. 一种UAV-USV-UUV跨域协同时钟同步算法[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(4): 678-687.YU J Y, LIN J S, YAN J, et al. Clock synchronization algorithm of UAV-USV-UUV cross-domain cooperation[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(4): 678-687. [7] MA L, YE H M, GU B, et al. Formation tracking for the heterogeneous multi-agents under deception attacks: An impulsive control approach[C]//2023 2nd Conference on Fully Actuated System Theory and Applications (CFASTA). Qingdao, China, 2023: 355-360. [8] WAN Q, CHEN W H, LU X M. Secure consensus tracking of multi-agent systems with network-induced delays under deception attacks via guaranteed performance impulsive control[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2023, 111(13): 12213-12232. [9] DAI H Y, GUO X, JI L H, et al. Bipartite synchronization of multi-agent systems under deception attacks via pinning delayed-impulsive control[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2023, 33(13): 7718-7734. [10] LIN W L, PENG S G, FU Z W, et al. Consensus of fractional-order multi-agent systems via event-triggered pinning impulsive control[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 494: 409-417. [11] ZHANG W, HUANG Q, WANG X, et al. Bipartite consensus for quantization communication multi-agent systems with event-triggered random delayed impulse control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2024, 1-16. [12] 王万良. 人工智能导论[M]. 5版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2022. [13] 冯茜, 李擎, 全威, 等. 多目标粒子群优化算法研究综述[J]. 工程科学学报, 2021, 43(6): 745-753.FENG Q, LI Q, QUAN W, et al. Overview of multiobjective particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2021, 43(6): 745-753. [14] HU L, YANG Y, TANG Z H, et al. FCAN-MOPSO: An improved fuzzy-based graph clustering algorithm for complex networks with multi-objective particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2023, 31(10): 3470-3484. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2023.3259726 [15] CHENG W L, ZHANG K, JIANG B, et al. Fixed-time fault-tolerant formation control for heterogeneous multi-agent systems with parameter uncertainties and disturbances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2021, 68(5): 2121-2133. [16] YAN Z P, PAN X L, YANG Z W, et al. Formation control of leader-following multi-UUVs with uncertain factors and time-varying delays[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 118792-118805. [17] 苏博. 自主水下机器人轨迹跟踪及编队一致性固定时间控制研究[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2021. [18] LI H Y, LI X. Distributed consensus of heterogeneous linear time-varying systems on UAVs-USVs coordination[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2019, 67(7): 1264-1268. [19] SEMSAR E, KHORASANI K. Team consensus for a network of unmanned vehicles in presence of actuator faults[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2009, 18(5): 1155-1161. [20] HARDY G, LITTLEWOOD J. An inequality[J]. Mathematische Zeitschrift, 1936, 40(1): 1-40. [21] COELLO C, PULIDO G, LECHUGA M. Handling multiple objectives with particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on evolutionary computation, 2004, 8(3): 256-279. [22] RAQUEL C, NAVAL J. An effective use of crowding distance in multiobjective particle swarm optimization [C]//Proceedings of the 7th Annual conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation. NY, USA: GEC, 2005: 257-264. -





 下载:
下载: