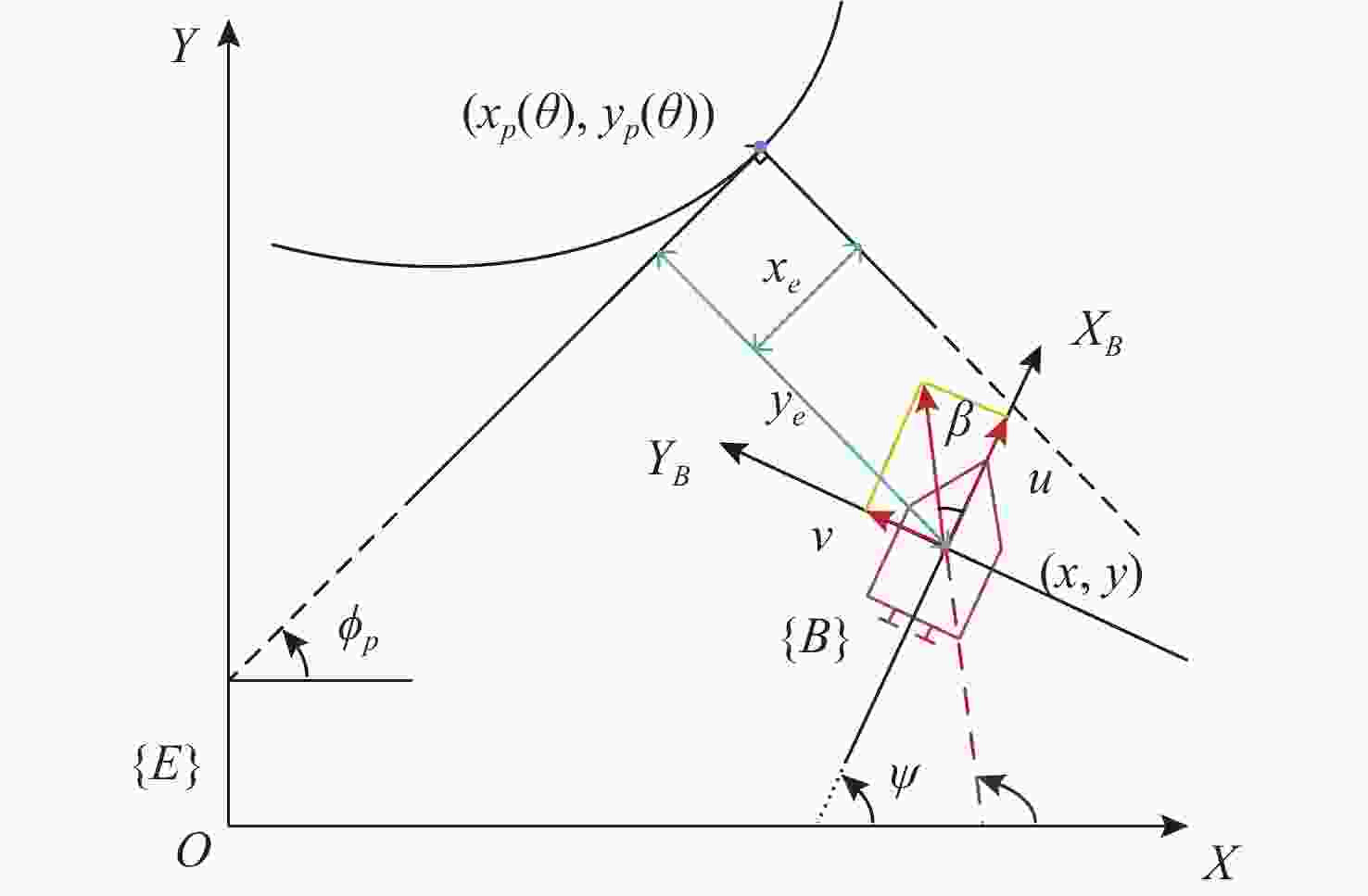
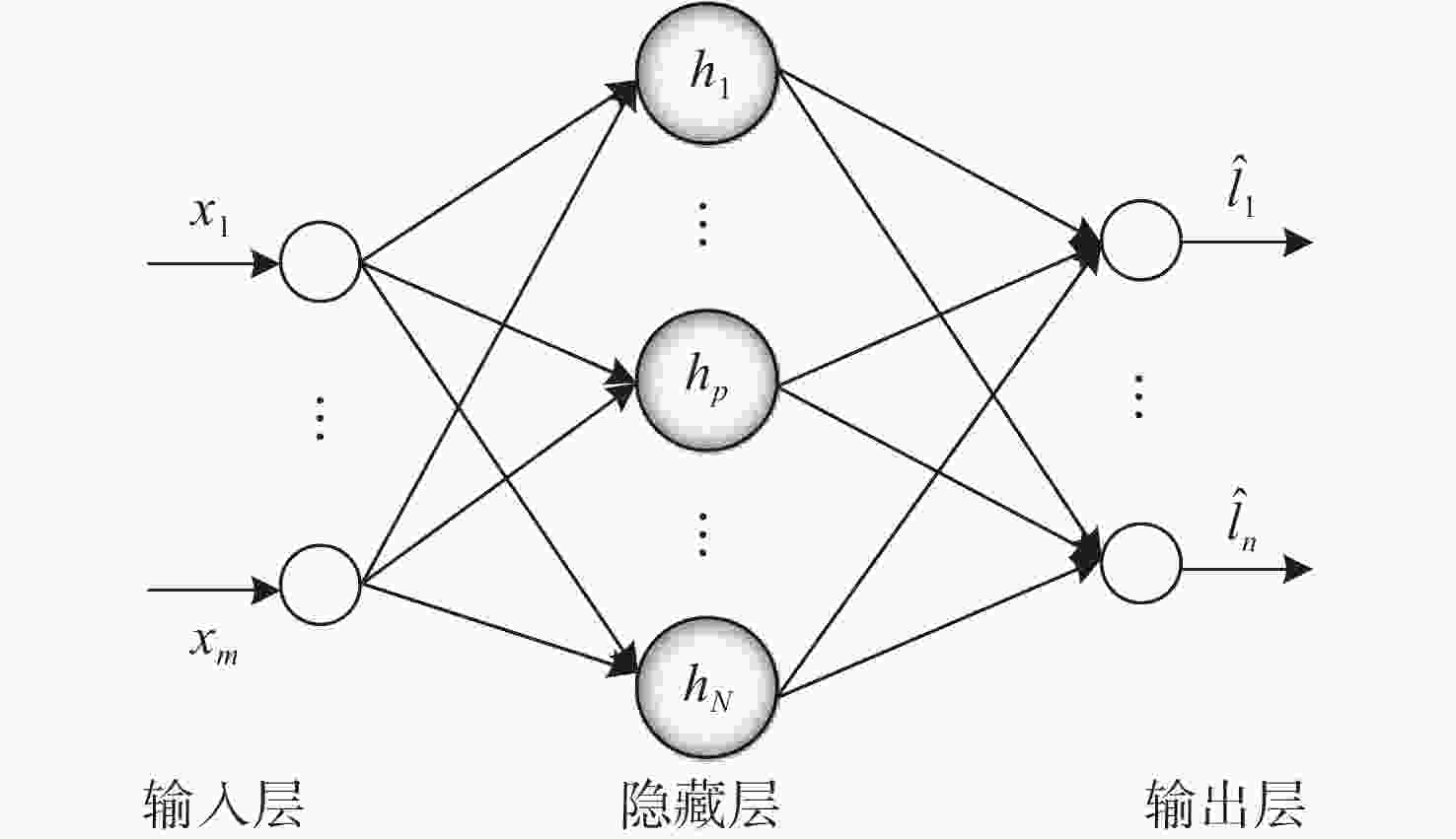
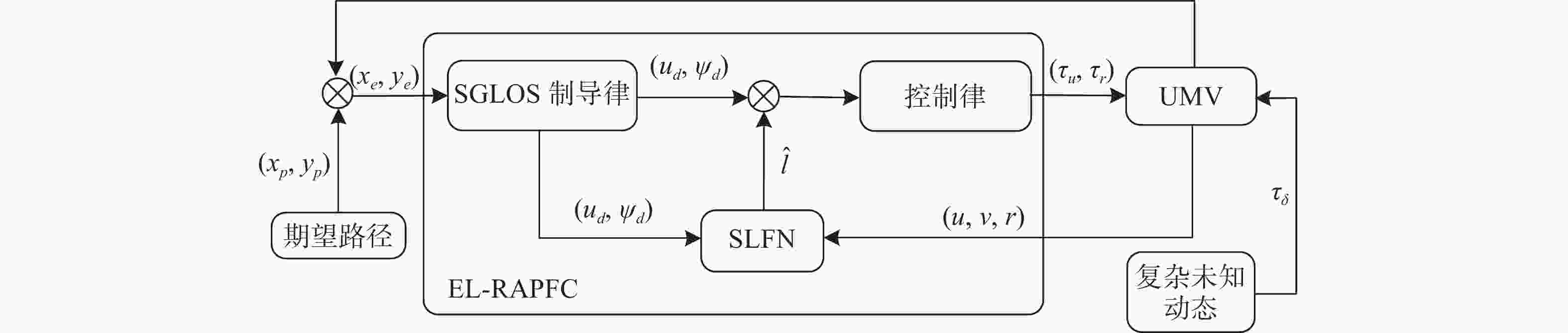
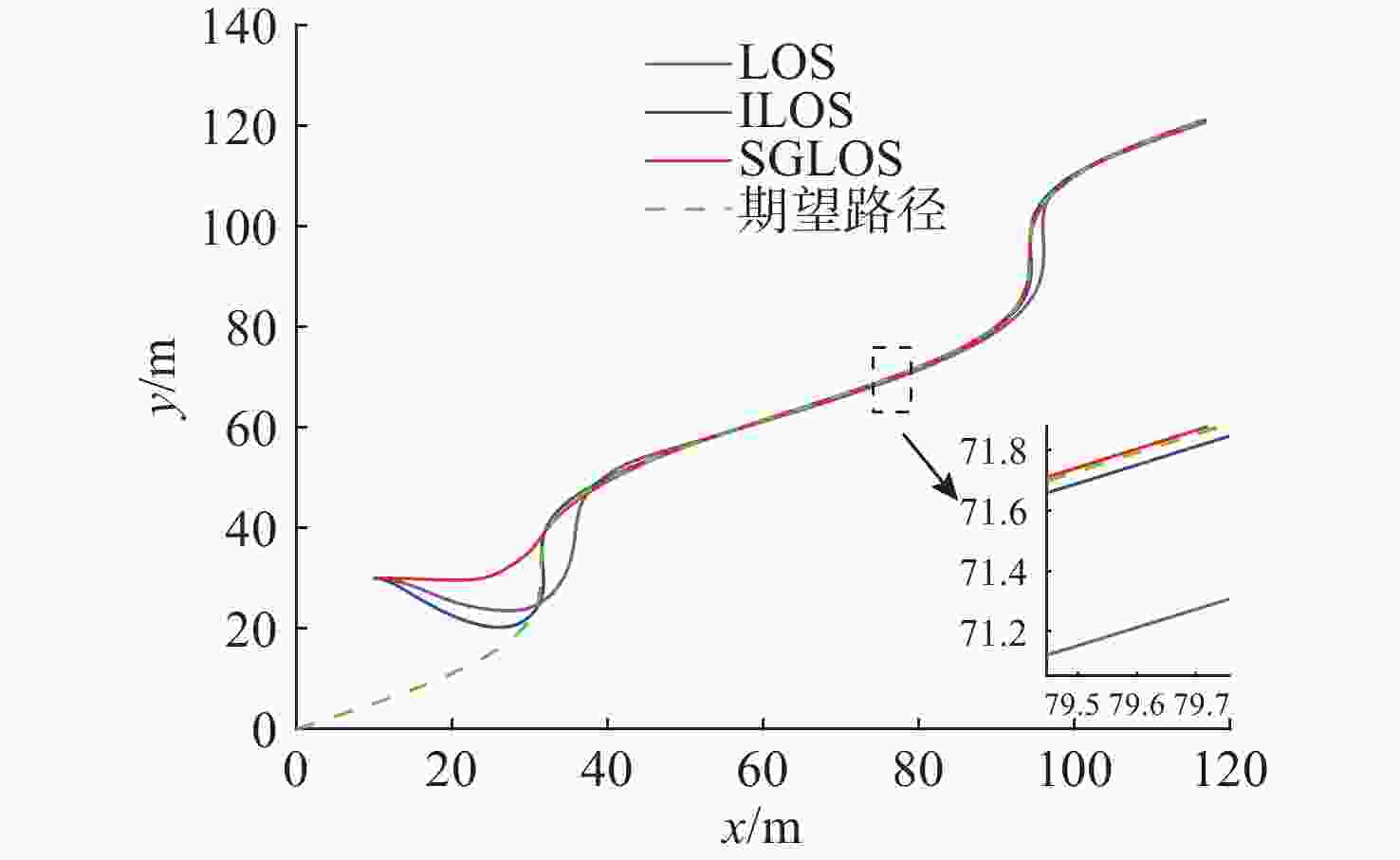
| [1] |
XU Z S, HE S M, ZHOU W J, et al. Path following control with sideslip reduction for underactuated unmanned surface vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(9): 11039-11047. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3340191
|
| [2] |
于长东, 刘新阳, 陈聪, 等. 基于多智能体深度强化学习的无人艇集群博弈对抗研究[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(1): 79-86. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2023-0159YU C D, LIU X Y, CHEN C, et al. Research on game confrontation of unmanned surface vehicles swarmbased on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(1): 79-86. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2023-0159
|
| [3] |
谢少荣, 刘坚坚, 张丹. 复杂海况无人艇集群控制技术研究现状与发展[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2020, 28(6): 584-596. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2020.06.001XIE S R, LIU J J, ZHANG D. Current development of control technology for unmanned surface vessel clusters under complex sea conditions[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2020, 28(6): 584-596. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2020.06.001
|
| [4] |
何红坤, 王宁. 欠驱动无人船单目视觉伺服镇定控制[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2022, 17(5): 166-174,183.HE H K, WANG N. Monocular visual servo-based stabilization control of underactuated unmanned surface vehicle[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2022, 17(5): 166-174,183.
|
| [5] |
WANG N, GAO Y, YANG C, et al. Reinforcement-learning-based finite-time tracking control of an unknown unmanned surface vehicle with input constraints[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 484: 26-37. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.04.133
|
| [6] |
WANG N, AHN C K. Hyperbolic-tangent LOS guidance-based finite-time path following of underactuated marine vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 67(10): 8566-8575.
|
| [7] |
FOSSEN T I, PETTERSEN K Y. On uniform semiglobal exponential stability(USGES) of proportional line-of-sight guidance laws[J]. Automatica, 2014, 50(11): 2912-2917. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.10.018
|
| [8] |
FOSSEN T I, BREIVIK M, SKJETNE R. Line-of-sight path following of underactuated marine craft[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2003, 36(21): 211-216.
|
| [9] |
CAHARIJA W, PETTERSEN K Y, BIBULI M, et al. Integral line-of-sight guidance and control of underactuated marine vehicles: Theory, simulations, and experiments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2016, 24: 1623-1642. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2015.2504838
|
| [10] |
FOSSEN T I, PETTERSEN K Y, GALEAZZI R. Line-of-Sight path following for dubins paths with adaptive sideslip compensation of drift forces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2014, 23(2): 820-827.
|
| [11] |
MOE S, PETTERSEN K Y, FOSSEN T I, et al. Line-of-sight curved path following for underactuated usvs and auvs in the horizontal plane under the influence of ocean currents[C]//2016 24th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation(MED). Athens, Greece: IEEE, 2016: 38-45.
|
| [12] |
WANG N, SUN Z, YIN J C, et al. Fuzzy unknown observer-based robust adaptive path following control of underactuated surface vehicles subject to multiple unknowns[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 176: 57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.02.017
|
| [13] |
WANG N, SUN Z, JIAO Y H, et al. Surge-heading guidance-based finite-time path following of underactuated marine vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(9): 8523-8532. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2927893
|
| [14] |
刘炳文, 于金鹏, 刘加朋, 等. 考虑输入饱和的无人艇神经网络命令滤波反步控制[J]. 船舶工程, 2024, 46(4): 123-129.LIU B W, YU J P, LIU J P, et al. Neural network-based command filtered backstepping control for USV with input saturation[J]. Ship Engineering, 2024, 46(4): 123-129.
|
| [15] |
XIAO Y F, FENG Y, LIU T, et al. Integral sliding mode based finite-time tracking control for underactuated surface vessels with external disturbances[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9(11): 1204. doi: 10.3390/jmse9111204
|
| [16] |
CHEN H, CHEN Y, WANG M Q. Trajectory tracking for underactuated surface vessels with time delays and unknown control directions[J]. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2022, 16(6): 587-599. doi: 10.1049/cth2.12250
|
| [17] |
RUBIO J D J. Robust feedback linearization for nonlinear processes control[J]. ISA Transactions, 2018, 74: 155-164. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2018.01.017
|
| [18] |
ROUT R, CUI R X, YAN W S. Sideslip-compensated guidance-based adaptive neural control of marine surface vessels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 52(5): 2860-2871.
|
| [19] |
HUANG G B, ZHU Q Y, SIEW C K. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications[J]. Neurocomputing, 2006, 70(1): 489-501.
|
| [20] |
HUANG G B, CHEN L, SIEW C K. Universal approximation using incremental constructive feedforward networks with random hidden nodes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2006, 17(4): 879-892. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2006.875977
|
| [21] |
WANG N, SUN J C, ER M J, et al. A novel extreme learning control framework of unmanned surface vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(5): 1106-1117. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2423635
|
| [22] |
SUN J C, WANG N, ER M J, et al. Extreme learning control of surface vehicles with unknown dynamics and disturbances[J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 167: 535-542. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.04.039
|
| [23] |
FOSSEN T I. Handbook of marine craft hydrodynamics and motion control[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2011.
|
| [24] |
KHALIL H K. Nonlinear systems[M]. 2nd, Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA: Prentice-Hall, 1996.
|
| [25] |
GHOMMAM J, MNIF F, BENAL A, et al. Observer design for Euler-Lagrange systems: Application to path following control of an underactuated surface vessel[C]// IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. San Diego, CA, USA: IEEE, 2007: 2883-2888.
|




 下载:
下载: