Prediction of Lightweight AIS-Based Ship Trajectories with Spline Interpolation
-
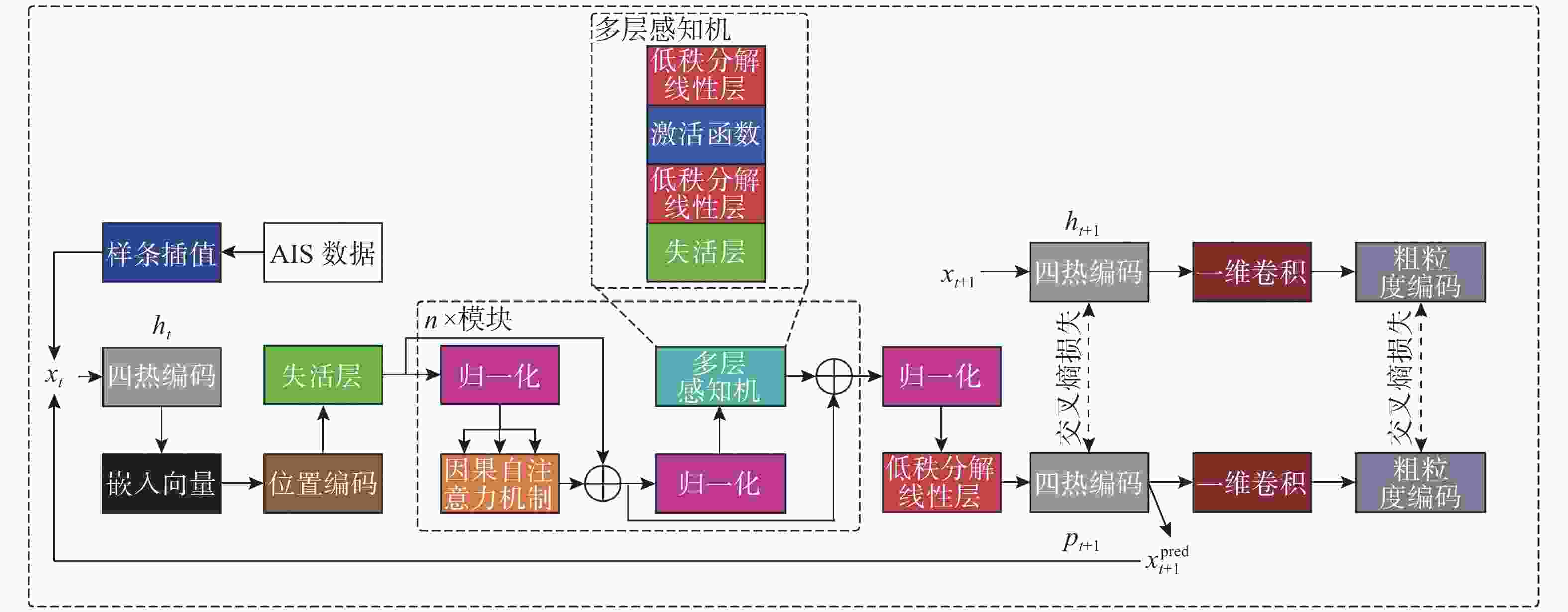
摘要: 船舶自动识别系统(AIS)能够提供大量实时船舶航行数据, 已成为海上交通管理、搜救行动和风险评估等诸多领域不可或缺的关键数据来源。其中船舶轨迹预测问题受到广泛关注。然而, 实现精准的长时间轨迹预测面临两大问题: 一是AIS数据本身的完整性问题; 二是预测模型的效率问题。因此, 如何有效地处理AIS数据缺失以及如何构建轻量且高效的预测模型,成为了亟待解决的重要问题。文中提出了一种基于样条插值的轻量化AIS船舶轨迹预测方法, 采用样条插值来填补缺失的AIS数据, 并引入了一种轻量化的线性层结构以降低深度学习模型的复杂度。实验结果表明, 该方法能够有效插值缺失的AIS数据, 显著减少深度学习模型的参数量和计算量, 进而提升对船舶轨迹的预测精度。Abstract: Automatic identification system(AIS) of ships provides a large amount of real-time ship navigation data, which has become an indispensable key data source in many fields such as maritime traffic management, search and rescue operations, and risk assessment. Among them, ship trajectory prediction has received wide attention. However, realizing accurate long-time trajectory prediction faces two major problems: One is the integrity of AIS data itself, and the other is the efficiency of prediction models. Therefore, how to effectively deal with the missing AIS data and how to construct a lightweight and efficient prediction model have become the key problems to be solved. In this paper, a lightweight AIS-based ship trajectory prediction method with spline interpolation was proposed. Spline interpolation was used to fill in the missing AIS data, and a lightweight linear layer structure was introduced to reduce the complexity of the deep learning model. The experimental results show that the method can effectively interpolate the missing AIS data, significantly reduce the number of parameters and computation of the deep learning model, and then improve the prediction accuracy of ship trajectories.
-
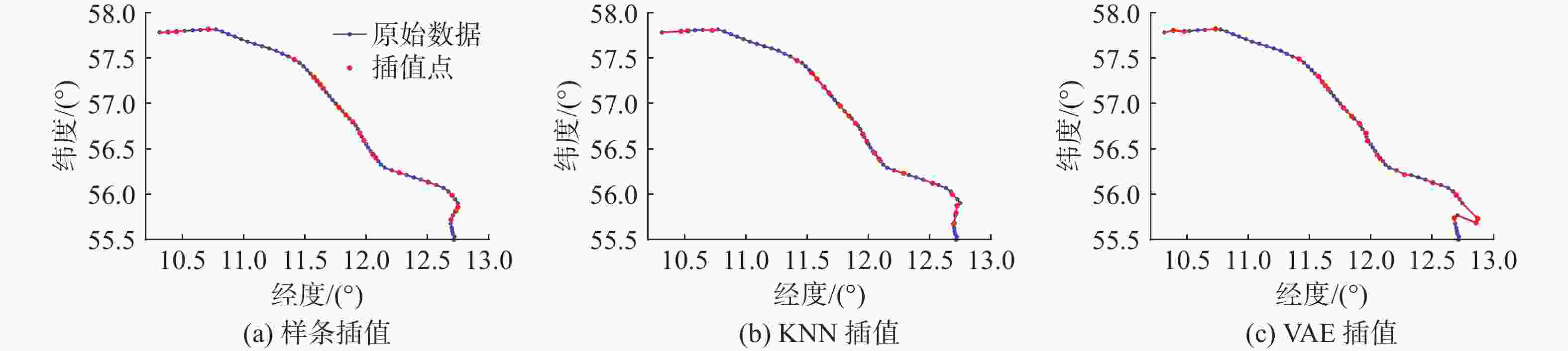
表 1 不同AIS缺失率下各类插值方法平均绝对误差和均方根误差结果
Table 1. Mean absolute error and root mean square error results of various interpolation methods under different AIS deletion rates
插值
方法平均绝对误差/m 均方根误差/m 10% 20% 30% 10% 20% 30% 样条
插值124.31 144.89 181.10 220.30 256.83 337.21 KNN 1 217.81 1 443.74 1 728.32 1 435.59 1 443.74 2 198.57 VAE 5 929.95 3 574.67 2 266.12 104 563.78 135 865.43 4 140.36 表 2 模型轻量化前后性能对比
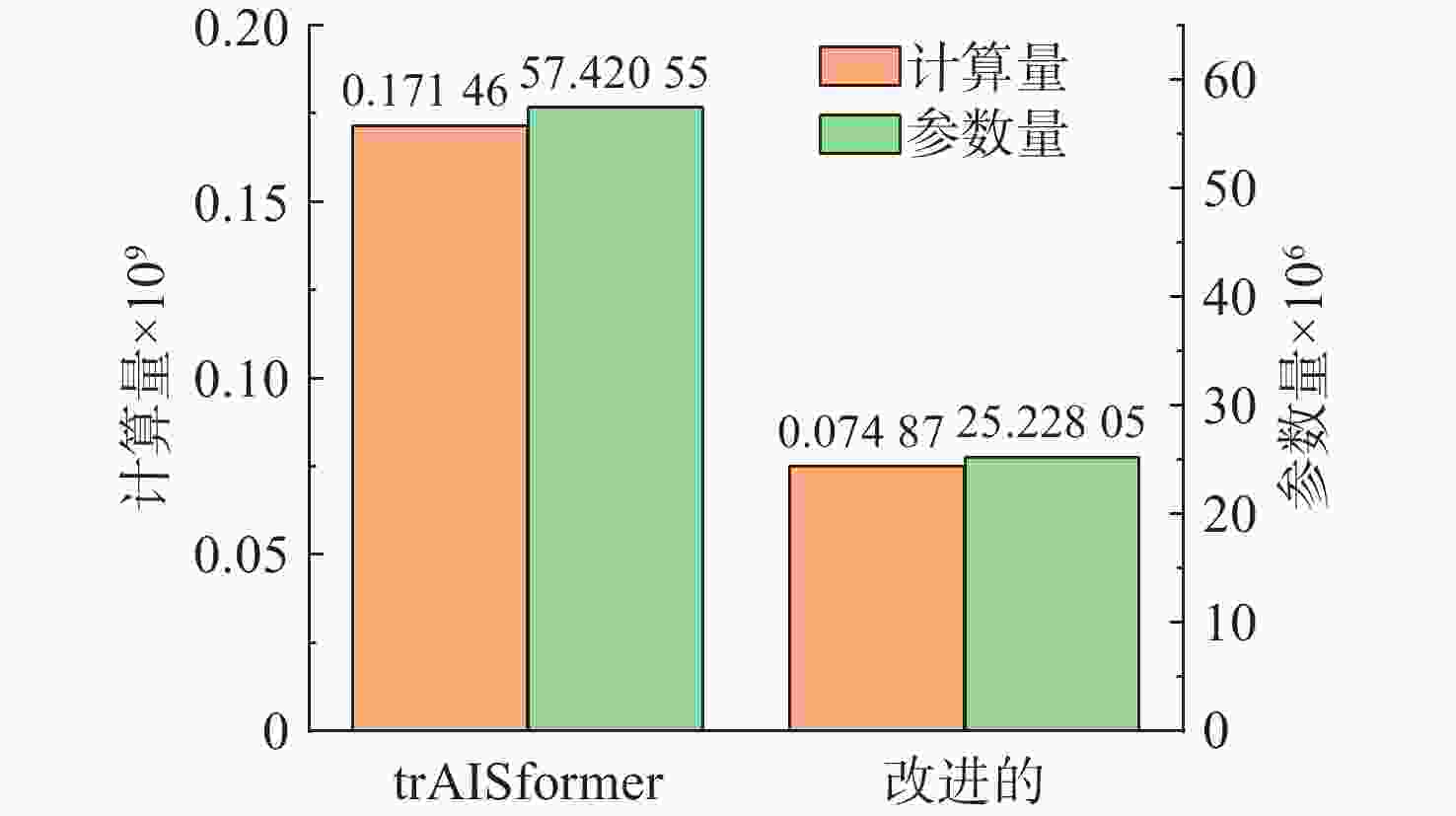
Table 2. Comparison of model performance before and after lightweighting
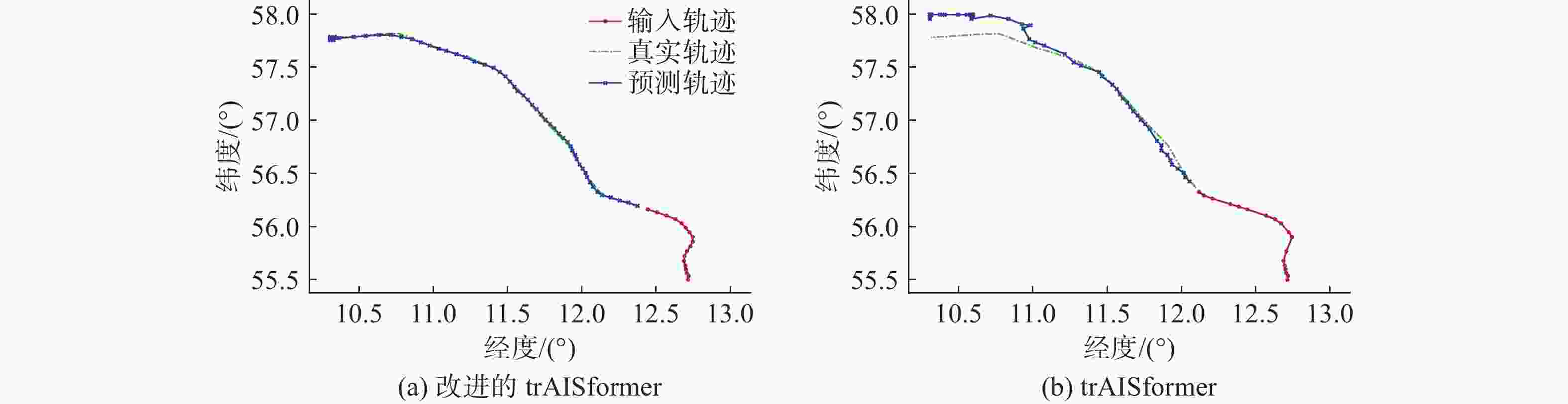
预测模型 平均预测误差/km 训练时间/s 评估时间/s 1 h 2 h 3 h trAISformer 0.9147 1.7800 2.9592 882.4580 102.7633 改进的
trAISformer0.7875 1.5427 2.6187 648.2574 91.6179 表 3 不同AIS缺失率下各插值方法的轨迹预测误差对比
Table 3. Comparison of trajectory prediction errors of each interpolation method under different AIS deletion rates
数据缺失率/% 预测模型 平均预测误差/km 1 h 2 h 3 h 10 trAISformer 1.498 2 2.622 2 3.869 2 改进的trAISformer 0.787 5 1.542 7 2.618 7 20 trAISformer 1.905 3 3.264 4 5.115 9 改进的trAISformer 0.829 2 1.586 8 2.702 7 30 trAISformer 2.606 1 4.506 1 6.847 1 改进的trAISformer 0.828 0 1.634 8 2.666 7 表 4 基于消融方法评估10%缺失率下船舶轨迹预测模型的预测误差
Table 4. An ablation-based approach to evaluate the prediction error of ship trajectory prediction model at 10% missing rate
预测模型 平均预测误差/km 1 h 2 h 3 h 缺乏样条插值以及
轻量化方法1.498 2 2.622 2 3.869 2 缺乏样条插值 1.359 4 2.361 0 3.595 0 缺乏轻量化方法 0.855 0 1.681 4 2.716 3 改进的trAISformer 0.787 5 1.542 7 2.618 7 -
[1] 田延飞, 乔慧, 滑林, 等. 海上船舶碰撞贝叶斯网络模型及其应用[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2023, 35(6): 28-33. doi: 10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2023.06.006TIAN Y F, QIAO H, HUA L, et al. Bayesian network model for ship collisions at sea and its applications[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2023, 35(6): 28-33. doi: 10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2023.06.006 [2] LIANG M H, SU J L, LIU R W, et al. AISClean: AIS data-driven vessel trajectory reconstruction under uncertain conditions[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 306: 117987. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.117987 [3] 张莉莉. 舰船交通管理系统信息融合系统中的云计算应用[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2018, 40(4): 43-45. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2018.04.009ZHANG L L. The application of cloud computing system information fusion ship traffic management system[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2018, 40(4): 43-45. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2018.04.009 [4] ZHANG X Y, WANG C B, JIANG L L, et al. Collision-avoidance navigation systems for maritime autonomous surface ships: A state of the art survey[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 235(1): 109380. [5] VARLAMIS I, TSERPES K, SARDIANOS C. Detecting search and rescue missions from AIS data[C]//2018 IEEE 34th International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops(ICDEW). San Francisco, California, USA: IEEE, 2018: 60-65. [6] DANG X K, TRUONG H N, DO V D. A path planning control for a vessel dynamic positioning system based on robust adaptive fuzzy strategy[J]. Automatika, 2022, 63(3): 580-592. doi: 10.1080/00051144.2022.2056289 [7] FORTI N, MILLEFIORI L M, BRACA P, et al. Prediction of vessel trajectories from AIS data via sequence-to-sequence recurrent neural networks[C]//ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP). Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2020: 8936-8940. [8] GEHRING J, AULI M, GRANGIER D, et al. Convolutional sequence to sequence learning[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia: PMLR, 2017: 1243-1252. [9] CAPOBIANCO S, MILLEFIORI L M, FORTI N, et al. Deep learning methods for vessel trajectory prediction based on recurrent neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(6): 4329-4346. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3096873 [10] NGUYEN D, FABLET R. A transformer network with sparse augmented data representation and cross entropy loss for AIS-based vessel trajectory prediction[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 21596-21609. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3349957 [11] 刘博翀, 蔡怀宇, 杨诗远, 等. 一种用于自动驾驶场景的轻量级语义分割网络[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2023, 50(1): 118-128.LIU B C, CAI H Y, YANG S Y, et al. Lightweight semantic segmentation network for autonomous driving scenarios[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2023, 50(1): 118-128. [12] 何戚天, 李为相, 程明, 等. 面向航拍图像的轻量化目标检测算法[J]. 电光与控制, 2025, 32(3): 56-61, 81.HE Q T, LI W X, CHENG M, et al. Lightweight target detection algorithm for aerial images[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2025, 32(3): 56-61, 81. [13] WANG W, CHEN Y, LIN M. MFLD: Lightweight object detection with multi-receptive field and long-range dependency in remote sensing images[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Computing and Cybernetics, 2024, 17(4): 805-823. doi: 10.1108/IJICC-01-2024-0020 [14] 汪玉秀, 苏战波. 基于轻量化神经网络的多语音识别方法研究[J]. 自动化与仪器仪表, 2023(10): 167-169, 174.WANG Y X, SU Z B. Research on multi-speech recognition method based on lightweight network[J]. Automation and Instrumentation, 2023(10): 167-169, 174. [15] 周子垚, 刘庆玲, 陶剑英, 等. 智能6G: 网络的边缘部署和轻量化[J]. 移动通信, 2023, 47(2): 2-7.ZHOU Z Y, LIU Q L, TAO J Y, et al. Smart 6G: Edge deployment and lightweight networks[J]. Mobile Communications, 2023, 47(2): 2-7. [16] YAN R, MO H, YANG D, et al. Development of denoising and compression algorithms for AIS-based vessel trajectories[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 252: 111207. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.111207 [17] 贺健平, 林永君, 孙孟超, 等. 考虑数据缺失的短期光伏功率预测模型[J]. 电力科学与工程, 2024, 40(11): 35-44. doi: 10.3969/j.ISSN.1672-0792.2024.11.004HE J P, LIN Y J, SUN M C, et al. Short-term photovoltaic power prediction model considering data missing[J]. Electric Power Science and Engineering, 2024, 40(11): 35-44. doi: 10.3969/j.ISSN.1672-0792.2024.11.004 [18] LIU C, CHEN X. Vessel track recovery with incomplete AIS data using tensor CANDECOM/PARAFAC decomposition[J]. The Journal of Navigation, 2014, 67(1): 83-99. doi: 10.1017/S0373463313000398 [19] GUO S, MOU J, CHEN L, et al. Improved kinematic interpolation for AIS trajectory reconstruction[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 234: 109256. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.109256 [20] KONTOPOULOS I, VARLAMIS I, TSERPES K. A distributed framework for extracting maritime traffic patterns[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2021, 35(4): 767-792. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2020.1792914 [21] ZHANG D, LI J, WU Q, et al. Enhance the AIS data availability by screening and interpolation[C]//2017 4th International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety(ICTIS). Wuhan, China: IEEE, 2017: 981-986. [22] LIU Y, FU R, PENG X, et al. AIS trajectory classification via improved IMM approach[C]//2024 43rd Chinese Control Conference(CCC). Kunming, China: IEEE, 2024: 3441-3445. [23] ANDREW G, MENGLONG Z. Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[J]. MobileNets, 2017, 10: 151. [24] LI C, SHI C J. Constrained optimization based low-rank approximation of deep neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018: 732-747. [25] SWAMINATHAN S, GARG D, KANNAN R, et al. Sparse low rank factorization for deep neural network compression[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 398(7): 185-196. [26] MCKINLEY S, LEVINE M. Cubic spline interpolation[J]. College of the Redwoods, 1998, 45(1): 1049-1060. [27] 张颖, 杨廷尧. 基于样条插值的水沙通量时间序列预测算法[J]. 现代信息科技, 2024, 8(20): 145-148.ZHANG Y, YANG T Y. Time series prediction algorithm of water and sediment flux based on spline interpolation[J]. Modern Information Technology, 2024, 8(20): 145-148. [28] LIU H, JIA C, SHI F, et al. Staircase cascaded fusion of lightweight local pattern recognition and long-range dependencies for structural crack segmentation[J]. Automation in Construction. 2024, 154: 104459. [29] CHOPDE N R, NICHAT M. Landmark based shortest path detection by using A* and haversine formula[J]. International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering, 2013, 1(2): 298-302. -




 下载:
下载: