A Review of Terrain Elevation Matching Algorithms for Undersea Vehicles
-
摘要: 水下航行器惯性导航误差随时间推移会不断累积, 地形高程匹配技术以地形特征为定位依据, 能够根据实测地形为惯性导航系统提供所需的持续位置修正信息, 是国内外水下辅助导航领域的研究热点。文章以水下航行器地形匹配高程算法的发展为研究对象, 首先指出当前水下航行器导航定位所面临的问题, 在此基础上介绍了水下航行器地形匹配的基本原理及系统组成, 并以水下地形匹配算法的发展为脉络, 按序依次阐释了地形匹配算法发展中的主要阶段及典型算法的原理和优缺点; 然后, 分别介绍了国内外水下地形匹配算法的原理改进和试验应用情况; 最后, 简要总结国内外在水下地形匹配算法方面研究的侧重点, 并结合并行计算、多波束声呐和水下地形特征分析三方面技术的发展, 探讨了提高水下匹配算法性能的有效途径, 可为本领域研究人员提供借鉴参考。Abstract: The inertial navigation system (INS) errors of an undersea vehicle continuously accumulate over time. A terrain elevation matching technique offers a solution by using measured terrain features to provide continuous position corrections for INS, making it a key research area in underwater navigation aids worldwide. This paper took the development of terrain elevation matching algorithms for undersea vehicles as the research object. Firstly, challenges faced by undersea vehicle navigation and positioning were pointed out. The basic principle and system component of terrain matching for undersea vehicles were then introduced. Additionally, the development of underwater terrain matching algorithm was reviewed chronologically, highlighting the main developmental stages, principles of typical terrain matching algorithms, and their advantages and limitations. Then, advancements in algorithm principles and experimental applications both in China and abroad were examined. Finally, the primary research focus areas in underwater terrain matching algorithms worldwide were briefly summarized, and strategies for enhancing algorithm performance were explored by combining parallel computing, multibeam sonar, and underwater terrain feature analysis, providing references for researchers in this field.
-
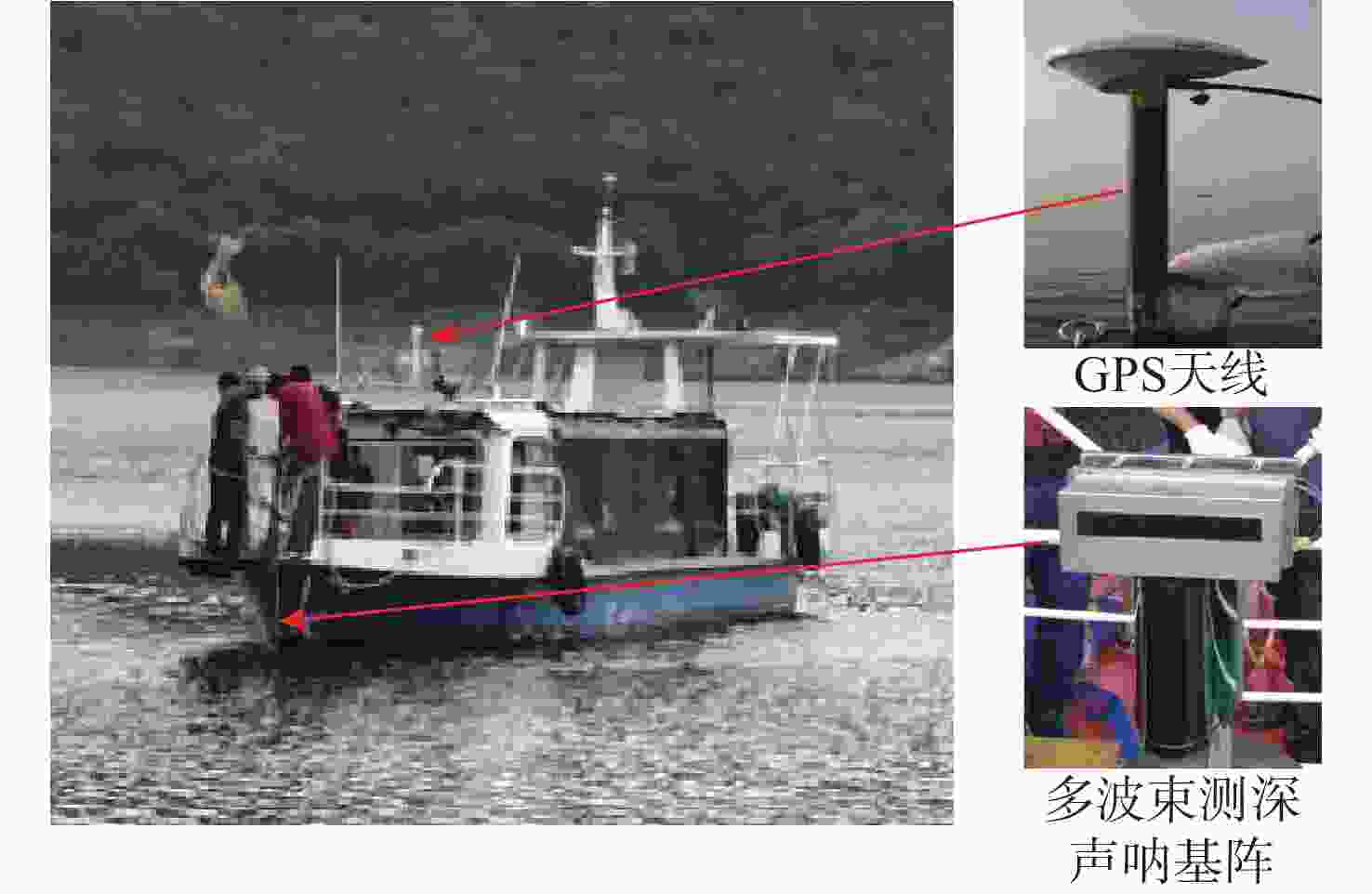
图 8 文献[92]试验船只及其测深和定位设备
Figure 8. Test vessel and on-board bathymetric and positioning equipment
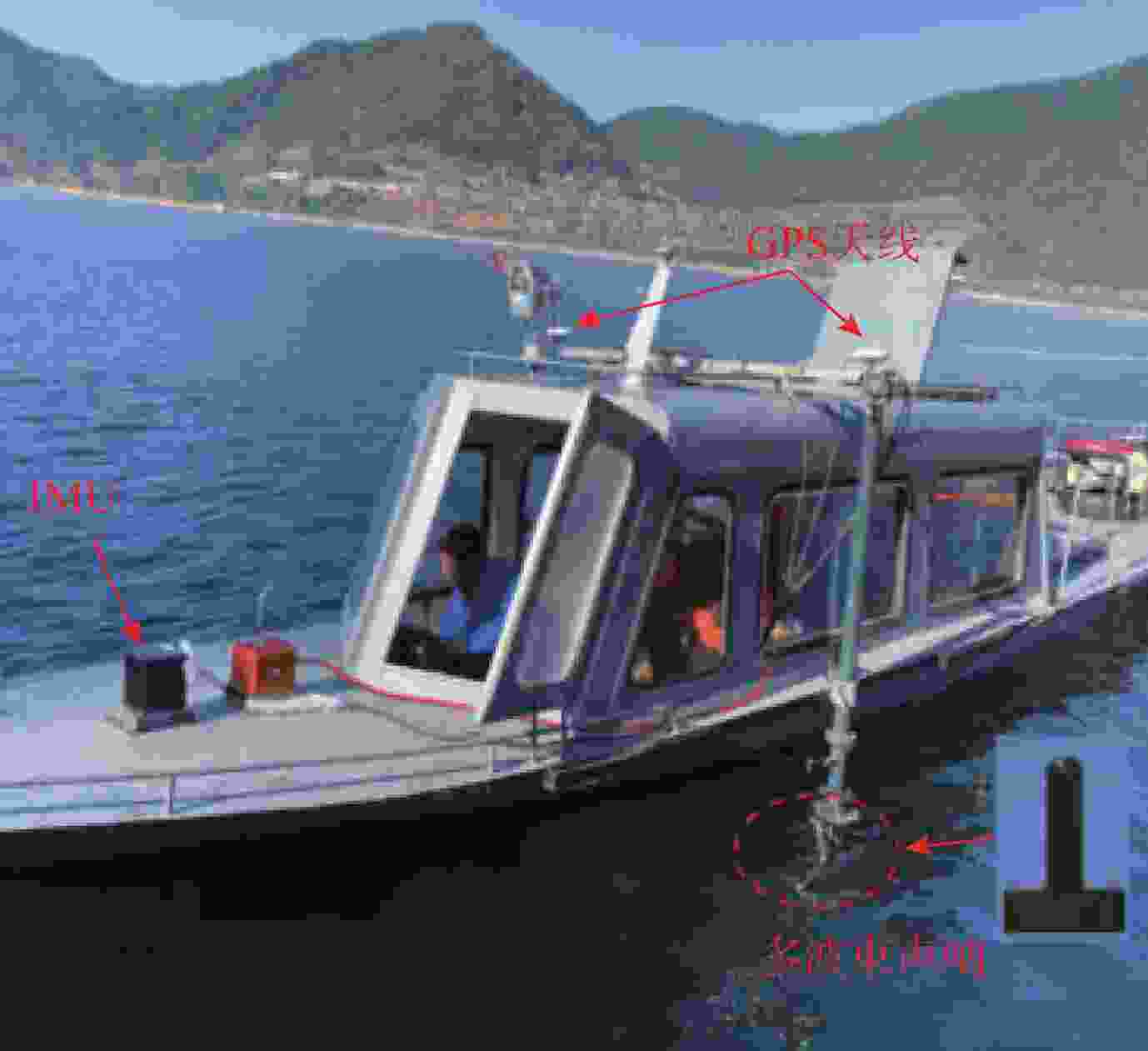
图 9 文献[94]试验船只及其试验设备
Figure 9. Test vessel and associated matching test equipment
表 1 典型水下地形匹配算法及其优缺点
Table 1. Typical underwater terrain matching algorithms and their advantages and disadvantages
类型 典型
算法优点 缺点 地形轮廓匹配 TERCOM
ICCP
MLE1) 流程简单, 算法相对成熟;
2) 较大初始误差条件下可正常工作;
3)易于硬件实现。1) 数据批处理方法实时性较差;
2) TERCOM对惯导指示航向、 ICCP对管道指示位置误 差敏感;
3) 对航行器机动有限制;
4) 在导航、测深存在野值时鲁棒性较差。线性卡尔曼滤波地形匹配 SITAN 1) 实时性好;
2) 对航行器机动限制少;
3) 以卡尔曼滤波为核心, 应用广泛。1) 大初始位置误差易导致匹配精度降低或滤波发散;
2) 地形线性化过程会引入截断误差, 不适合地形剧烈变 化区域。非线性卡尔曼滤波地形匹配 UKF 1) 无需计算Jacobi矩阵, 实时性好;
2) 对航行器机动限制少, 无需进行地形线性化处理。1) 系统误差随机变量需满足高斯分布;
2) 低信噪比条件匹配算法鲁棒性不足;
3) 影响算法性能的采样点参数不易量化。基于概论准则
匹配PF
PMF1) 状态、误差变量不受非线性、非高斯条件约束;
2) 理论上能够逼近任意概论分布;
3) 算法匹配精度较高, 具有一定鲁棒性。1) 计算量会随所估计状态维数大幅增加, 降低算法实 时性;
2) 粒子并行计算实现相对困难;
3) 存在粒子信息贫瘠和粒子退化问题;
4) 硬件实现成本高。 -
[1] 宋保维, 潘光, 张立川, 等. 自主水下航行器发展趋势及关键技术[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2022, 17(5): 27-44.SONG B W, PAN G, ZHANG L C, et al. Development trend and key technologies of autonomous underwater vehicles[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2022, 17(5): 27-44. [2] 张涛, 夏茂栋, 张佳宇, 等. 水下导航定位技术综述[J]. 全球定位系统, 2022, 47(4): 1-16.ZHANG T, XIA M D, ZHANG J Y, et al. Overview of underwater navigation and positioning techniques[J]. GNSS World of China, 2022, 47(4): 1-16. [3] 邱志明, 马焱, 孟祥尧, 等. 水下无人装备前沿发展趋势与关键技术分析[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(1): 1-9.QIU Z M, MA Y, MENG X Y, et al. Analysis on the development trend and key technologies of unmanned underwater equipment[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2023, 31(1): 1-9. [4] 邱志明, 孟祥尧, 马焱, 等. 海上无人系统发展及关键技术研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2023, 25(3): 74-83. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2023.03.005QIU Z M, MENG X Y, MA Y, et al. Development and key technologies of maritime unmanned systems[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2023, 25(3): 74-83. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2023.03.005 [5] WEI J, YU F, ZHANG Y, et al. A system-level calibration and integrated navigation technology of HRG-based SINSDVL system for underwater vehicles[C]//2023 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation(ICMA). Harbin, China: IEEE, 2023: 1096-1101. [6] CHANG J, YUAN M, CHEN P, et al. Underwater terrain-aided navigation method based on improved Gaussian sum particle filtering[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2019, 1(1): 1-7. [7] KAYES H, SHAMEEM A, ABRAR F L, et al. Oceanic challenges to technological solutions: A review of autonomous underwater vehicle path technologies in biomimicry, control, navigation, and sensing[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12(12): 46202-46231. [8] 孙宇. 水下地形匹配辅助导航方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2022. [9] 朱丹. 美军自主水下航行器发展研究[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2020, 42(1): 134-140.ZHU D. Development research on U. S. Navy autonomous underwater vehicle[J]. Command Control & Simulation, 2020, 42(1): 134-140. [10] MELO J, MATOS A. Survey on advances on terrain based navigation for autonomous underwater vehicles[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2017, 139(7): 250-264. [11] 张强, 张雯. 水下机器人导航技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2023. [12] 张红梅, 赵建虎, 杨鲲, 等. 水下导航定位技术[M]. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社, 2010. [13] 丁鹏, 杨申申, 王磊, 等. 水下地形匹配导航研究综述[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2024, 24(14): 5690-5706.DING P, YANG S S, WANG L, et al. Review of underwater terrain matching navigation research[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2024, 24(14): 5690-5706. [14] 王依能. 基于地形辅助的水下潜器导航技术研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2022. [15] 李临. 海底地形匹配辅助导航技术现状及发展[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2008, 28(2): 17-19.LI L. Current status and development of underwater terrain matching navigation technology[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2008, 28(2): 17-19. [16] DRAYTON D B, FELLERHOFF R. Terrain-aided navigation test results in the aircraft AFTI/F-16[J]. Journal of the Institute of Navigation, 1988, 35(2): 161-175. doi: 10.1002/j.2161-4296.1988.tb00949.x [17] 冯庆堂. 地形匹配新方法及其环境适应性研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2004. [18] TENG M, DING D D, LI Y, et al. A review of terrain aided navigation for underwater vehicles[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 281(8): 2-16. [19] ZHANG B, JI D, LIU S, et al. Autonomous underwater vehicle navigation: A review[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 273(4): 1-29. [20] 李雄伟, 刘建业, 康国华. TERCOM地形高程辅助导航系统发展及应用研究[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2006, 14(1): 34-40.LI X W, LIU J Y, KANG G H. Development and application of TERCOM elevation-aided navigation system[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2006, 14(1): 34-40. [21] INGEMAR N. Terrain navigation for underwater vehicles[D]. Stockholm, Sweden: Royal Institute of Technology, 2005. [22] CHEN P, LI Y, SU Y, et al. Review of AUV underwater terrain matching navigation[J]. Journal of Navigation, 2015, 68(6): 1155-1172. doi: 10.1017/S0373463315000429 [23] 高靖萱, 张亚, 孙风胜. AUV海底地形匹配导航方法综述[J]. 船舶工程, 2023, 45(2): 167-176.GAO J X, ZHANG Y, SUN F S. Review for AUV seabed terrain aided navigation methods[J]. Ship Engineering, 2023, 45(2): 167-176. [24] QIN H, WANG X, WANG G, et al. A novel INS/USBL/DVL integrated navigation scheme against complex underwater environment[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 286(8): 1-9. [25] KATHLEEN M D. Terrain relative navigation for sensor-limited systems with application to underwater vehicles[D]. Stanford, CA, USA: Stanford University, 2011. [26] PENG D, CHENG X H. A new contour-based combined matching algorithm for underwater terrain-aided strapdown inertial navigation system[J]. Measurement, 2022, 202(8): 1-10. [27] ZHANG J, ZHANG T, LIU S, et al. A robust particle filter for ambiguous updates of underwater terrain-aided navigation[J]. Mechatronics, 2024, 98(12): 1-11. [28] WANG Z S, ZHANG Q. Research on fault detection technology of autonomous underwater vehicle navigation system[C]//2022 IEEE International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Big Data and Algorithms (EEBDA). Changchun, China: IEEE, 2022: 35-38. [29] MA T, DING S, LI Y, et al. A review of terrain aided navigation for underwater vehicles[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 281(5): 1-16. [30] SHI W, XU J, HE H, et al. Fault-tolerant SINS/HSB/DVL underwater integrated navigation system based on variational Bayesian robust adaptive Kalman filter and adaptive information sharing factor[J]. Measurement, 2022, 196(4): 1-10. [31] 田峰敏. 水下地形导航模型求解与导航区初选策略研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2009. [32] 辛廷慧. 水下地形辅助导航方法研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2004. [33] 张静远, 徐振烊, 王新鹏. 基于TERCOM算法的水下地形辅助导航误差研究[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2020, 32(5): 44-49.ZHANG J Y, XU Z Y, WANG X P. Research on error of underwater terrain aided navigation based on TERCOM algorithm[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2020, 32(5): 44-49. [34] 杨绘弘. 基于ICCP的水下潜器地形辅助导航方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2009. [35] 张立, 杨惠珍. 基于ICCP和TERCOM的水下地形匹配组合算法研究[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2008, 28(3): 230-232.ZHANG L, YANG H Z. Research on assembled underwater terrain matching algorithm based on ICCP and TERCOM[J]. Journal of Projectiles Rockets Missiles and Guidance, 2008, 28(3): 230-232. [36] 程建华, 丁惠倩, 常乐, 等. 基于TERCOM-ICP联合算法的水下地形匹配方法研究[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2023, 10(2): 39-46.CHENG J H, DING H Q, CHANG L, et al. Research on underwater terrain matching method based on TERCOM-ICP joint algorithm[J]. Navigation positioning and timing, 2023, 10(2): 39-46. [37] ZHANG J, ZHANG T, ZHANG C, et al. An improved ICCP-based underwater terrain matching algorithm for large initial position error[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(16): 16381-16391. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3190304 [38] INGEMAR N. Terrain navigation for underwater vehicles using the correlator method[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2004, 29(3): 906-915. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2004.833222 [39] 刘勇. 海底地形匹配导航技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔冰工程大学, 2009. [40] 王涛. 桑迪亚惯性地形辅助导航算法及应用研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2006. [41] HOSTETLER L, ANDREAS R. Nonlinear Kalman filtering techniques for terrain-aided navigation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1983, 28(3): 315-323. doi: 10.1109/TAC.1983.1103232 [42] JUERGEN M, KATRIN W, JAN W, et al. Sigma-point filter for terrain referenced navigation[C]//2005 AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit. San Francisco, CA, USA: AIAA, 2005: 1-7. [43] KARLSSON T. Terrain aided underwater navigation using-Bayesian statistics[D]. Linköping: Linköpings Universitet, 2005. [44] JULIER S J, UHLMANN J K, DURRANT-WHYTE H. A new approach for the nonlinear transformation of means and covariances in linear filters[J]. IEEE Access, 2000, 45(3): 448-477. [45] JULIER S J, UHLMANN J K. Unscented filtering and nonlinear estimation[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2004, 92(3): 401-422. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2003.823141 [46] 谢建春, 张艳宁, 赵荣椿. 基于Sigma粒子Kalman滤波的地形辅助导航方法[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2007, 25(5): 703-706. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2007.05.019XIE J C, ZHANG Y N, ZHAO R C. Terrain-aided navigation method based on Sigma particle Kalman filtering[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2007, 25(5): 703-706. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2007.05.019 [47] LANG A. Estimation methods for terrain navigation[D]. Stockholm: School of Electrical Engineering, 2006. [48] GORDON N, SALMOND D. Novel approach to non-linearand non-Gaussian Bayesian state estimation[J]. Proceedings of Institute Electric Engineering, 1993, 4(5): 744-745. [49] 朱志宇. 粒子滤波算法及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 120-129. [50] 胡士强, 敬忠良. 粒子滤波原理及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 5-25. [51] BERGMAN N. Recursive Bayesian estimation navigation and tracking applications[D]. Sweden: Linkoping University, 1999. [52] KARLSSON T. Terrain aided underwater navigation using-Bayesian statistics[D]. Linköping: Linköping University, 2002. [53] ANONSEN K B, HALLINGSTAD O. Terrain aided underwater navigation using point mass and particle filters[C]//2006 IEEE/ION Position, Location, and Navigation Symposium. Coronado, CA, USA: IEEE, 2006: 1027-1035. [54] JALVING B, BOVIO E, GADE K. Integrated inertial navigation systems for AUVs for REA applications[C]// MREP 2003, La Spezia, Italy: NATO Underwater Research Center, 2003: 1-23. [55] MCPHAIL S. Autosub6000: A deep diving long range AUV[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2009, 16(6): 55-62. [56] MEDUNA D K, ROCK S M, Mcewen R. Low-cost terrain relative navigation for long-range AUVs[C]//OCEANS 2008, Quebec City, QC, Canada: IEEE, 2008: 1-7. [57] ORGUNER U, SKOGLAR P, TORNQVIST D, et al. Combined point-mass and particle filter for target tracking[C]//Proceeding of the 2010 IEEE Aerospace Conference. Big Sky, MT, USA: IEEE, 2010: 1-10. [58] BUCY R S, SENNE K D. Digital synthesis of non-linear filters[J]. Automatica, 1971, 7(3): 315-322. doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(71)90123-3 [59] BERGMAN N. Bayesian inference in terrain navigation[M]. Linköping: Studies in Science and Technology, 1997. [60] XIE Y H. Terrain aided navigation[D]. Stockholm: Royal Institute of Technology, 2005. [61] WANG X, CUI N, GUO J. Huber-based unscented filtering and its application to vision-based relative navigation[J]. IET Radar, Sonar, Navigation, 2010, 4(1): 134-141. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2009.0170 [62] KARLSSON R, GUSTAFSSON F. Particle filter for underwater terrain navigation[C]//2003 IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal Processing. St. Louis, MO, USA: IEEE, 2003: 526-529. [63] 刘洪, 高永琪, 谌剑. 基于PMF和TERCOM组合算法的水下地形匹配技术[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2012, 20(6): 437-442.LIU H, GAO Y Q, SHEN J. Underwater terrain matching techniques based on combination of PMF and TERCOM algorithms[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2012, 20(6): 437-442. [64] 史天放. 基于改进尺度不变方法的地形匹配算法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018. [65] SALAVASIDIS G, MUNAFÒ A, FENUCCI D, et al. Terrain aided navigation for long range AUVs in dynamicunder mapped environments[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2021, 38(3): 402-428. doi: 10.1002/rob.21994 [66] SALAVASIDIS G, HARRIS C A, ROGERS E. Cooperative use of marine autonomous systems to enhance navigational accuracy of autonomous underwater vehicles [C]//17th Annual Comference, TAROS 2016. Sheffield, UK: Springer, 2016: 275-281. [67] KIM T, KIM J, BYUN S-W. A comparison of nonlinear filter algorithms for terrain-referenced underwater navigation[J]. International Journal of Control Automation and Systems, 2018, 16(6): 2977-2989. [68] ÅNONSEN K B, HAGEN O K. An analysis of real-time terrain aided navigation results from a HUGIN AUV[C]// OCEANS 2010. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2010: 1-7. [69] BISHOP G C. Gravitational field maps and navigational error[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2002, 26(3): 726-737. [70] MELO J, MATOS A. A data-driven particle filter for terrain based navigation of sensor-limited autonomous underwater vehicles[J]. Asian Journal of Control, 2019, 21(4): 1659-1670. doi: 10.1002/asjc.2107 [71] PALMIER C, DAHIA K, MERLINGE N, et al. Adaptive approximate bayesian computational particle filters for underwater terrain aided navigation[C]//2019 22th International Conference on In-formation Fusion. Ottawa, ON, Canada: IEEE, 2019. [72] ANDERSON J, HOLLINGER G A. Communication planning for cooperative terrain-based underwater localization[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(5): 1675. doi: 10.3390/s21051675 [73] SALAVASIDIS G, HARRIS C, MCPHAIL S, et al. Terrain aided navigation for long range AUV operations at arctic latitudes[C]//2016 IEEE/OES Autonomous Underwater Vehicles(AUV). Tokyo, Japan: IEEE, 2016: 115-123. [74] CASAGRANDE D, KRASNOSKY K, ROMA C. Localization of a drifting underwater vehicle using a terrain-based particle filter[C]//OCEANS 2019. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2019: 1-8. [75] JURIGA J T. Terrain aided navigation for REMUS autonomous underwater vehicle[D]. California: Naval postgraduate school, 2014. [76] CHOWDHARY A. Terrain aided navigation for autonomous underwater vehicles with local Gaussian processes[D]. Virginia: Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, 2017. [77] FRANCISCO C. T, JOÃO Q, ANTÓNIO P. AUV terrain-aided navigation using a Doppler velocity logger[J]. IFAC-Papers On Line, 2015, 48(3): 137-142. [78] CHOI J, PARK J, JUNG J, et al. Validation of acoustic and geophysics based underwater localization with an autonomous surface vehicle[J]. IFAC-Papers On Line, 2019, 52(21): 367-371. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2019.12.334 [79] ÅNONSEN K B, HAGEN O K, HEGRENÆS Ø, et al. The HUGIN AUV terrain navigation module[C]//2013 OCEANS. San Diego, CA, USA: IEEE, 2013: 1-8. [80] FRANCISCO C T, JOÃO Q, ANTÓNIO P. Experimental validation of magnetic navigation of marine robotic vehicles[J]. IFAC-Papers On Line, 2016, 49(23): 273-278. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2016.10.354 [81] HAGEN O K, ANONSEN K, MANDT M. The HUGIN real-time terrain navigation system[C]//OCEANS 2010. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2010: 1-7. [82] HAGEN P E, STORKERSEN N, VESTGARD K, et al. The HUGIN 1000 autonomous underwater vehicle for military applications[C]//Oceans 2003. San Diego, CA, USA: IEEE, 2003: 1-7. [83] 翟国君, 黄谟涛. 我国海洋测绘发展历程[J]. 海洋测绘, 2009, 29(4): 74-81.ZHAI G J, HUANG M T. Development history of China’s marine surveying and mapping[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2009, 29(4): 74-81. [84] 陆秀平, 黄谟涛, 翟国君, 等. 多波束测深数据处理关键技术研究进展与展望[J]. 海洋测绘, 2016, 36(4): 1-6.LU X P, HUANG M T, ZHAI G J, et al. Progress and prospects of key technology research on multi-beam bathymetric data processing[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2016, 36(4): 1-6. [85] 黄谟涛, 翟国君, 欧阳永忠, 等. 海洋测量技术的研究进展与展望[J]. 海洋测绘, 2008, 28(5): 77-82.HUANG M T, ZHAI G J, OUYANG Y Z, et al. Research progress and prospects of marine measurement technology[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2008, 28(5): 77-82. [86] 范时秒. 基于地形辅助的ARV组合导航技术研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2019. [87] 李璇, 解禹. 水下定位导航系统展望[J]. 无人系统技术, 2022, 5(3): 79-86.LI X, XIE Y. Envision to the development of underwater position and navigation systems[J]. Unmanned Systems Technology, 2022, 5(3): 79-86. [88] 王汝鹏, 李晔, 马腾, 等. 水下地形匹配定位置信区间估计[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019, 44(6): 830-836.WANG R P, LI Y, MA T, et al. Confidence interval estimation of underwater terrain aided position[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(6): 830-836. [89] WANG R P, LI Y, MA T. A new model and method of terrain-aided positioning confidence interval estimation[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 2021, 27(4): 1-13. [90] WANG D, LIU L, BEN Y, et al. Seabed terrain-aided navigation algorithm based on combining artificial bee colony and particle swarm optimization[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(2): 1166. doi: 10.3390/app13021166 [91] 彭东东. 基于多波束测深声呐的海底地形辅助定位导航方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2022. [92] 程向红, 王依能, 丁鹏. 基于仿射因子补偿的改进地形匹配ICCP算法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2022, 30(3): 352-358.CHENG X H, WANG Y N, DING P. Improved terrain matching ICCP algorithm based on affine actor compensation[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2022, 30(3): 352-358. [93] 张涛, 张驰, 张佳宇. 基于改进遗传算法的多波束水下地形匹配方法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2022, 30(4): 485-491.ZHANG T, ZHANG C, ZHANG J Y. Multi-beam underwater terrain matching method based on improved genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2022, 30(4): 485-491. [94] 廖世康, 冷悦. 一种基于改进粒子滤波的水下地形匹配导航方法[J]. 光学与光电技术, 2020, 18(2): 98-102.LIAO S K, LENG Y. An underwater terrain matching navigation method based on improved particle filter[J]. Optics & Optoelectronic Technology, 2020, 18(2): 98-102. [95] LIU Y, ZHANG G, HUANG Z. Study on the arctic underwater terrain-aided navigation based on fuzzy-particle filter[J]. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 2021, 23(4): 1017-1026. doi: 10.1007/s40815-020-01047-w [96] 张鹏. 基于改进樽海鞘群算法的水下地形辅助导航研究[D]. 连云港: 江苏海洋大学, 2022. [97] 韩月, 陈鹏云, 沈鹏. 基于高斯和粒子滤波的AUV水下地形辅助导航方法[J]. 无人系统技术, 2020, 3(1): 48-54.HAN Y, CHEN P Y, SHEN P. Underwater terrain-aided navigation method based on Gaussian sumparticle filtering for AUVs[J]. Unmanned Systems Technology, 2020, 3(1): 48-54. [98] LI Y, MA T, CHEN P Y, et al. Autonomous underwater vehicle optimal path planning method for seabed terrain matching navigation[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2017, 133(3): 107-115. [99] 刘东东. 基于粒子滤波的海底地形辅助导航技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2021. [100] 王立辉, 乔楠, 余乐. 水下地形导航匹配区选取的模糊推理方法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2017, 44(1): 140-145.WANG L H, QIAO N, YU L. Fuzzy deduction methods of selecting the underwater terrain navigation matching area[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2017, 44(1): 140-145. [101] 刘现鹏, 张立华, 贾帅东, 等. 基于TIN模型的水下地形匹配定位算法[J]. 海洋测绘, 2018, 38(2): 66-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2018.02.016LIU X P, ZHANG L H, JIA S D, et al. Underwater terrain matching algorithm based on triangulated irregular network[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2018, 38(2): 66-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2018.02.016 [102] 张凯, 赵建虎, 张红梅. 一种基于M估计的水下地形抗差匹配算法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2015, 40(4): 558-562.ZHANG K, ZHAO J H, ZHANG H M. Robust underwater terrain matching navigation based on M estimation[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2015, 40(4): 558-562. [103] 饶喆, 张静远, 冯炜. 一种地形匹配导航区域的可导航性评价方法[J]. 河南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 46(1): 89-95.RAO Z, ZHANG J Y, FENG W. Navigability evaluation method of terrain matching navigation area[J]. Journal of Henan University(Natural Science), 2016, 46(1): 89-95. [104] 徐振烊, 张静远, 王鹏, 等. 基于PMF算法的水下地形辅助导航性能研究[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2019, 27(6): 614-623. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2019.06.003XU Z Y, ZHANG J Y, WANG P, et al. Analysis on performance of underwater terrain aided navigation using PMF algorithm[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2019, 27(6): 614-623. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2019.06.003 [105] 高嘉淇. 基于梯度拟合的水下地形匹配导航算法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2020. [106] 宋子奇. 基于声呐图像处理的水下地形地貌匹配定位方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2017. [107] 周玲. 自主水下潜器海底地形辅助导航技术研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2018. [108] 龙涛. 基于组合算法的水下地形匹配技术[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院精密测量科学与技术创新研究院), 2022. -




 下载:
下载: