Analysis of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Equipment Shock Response Based on Deep Learning
-
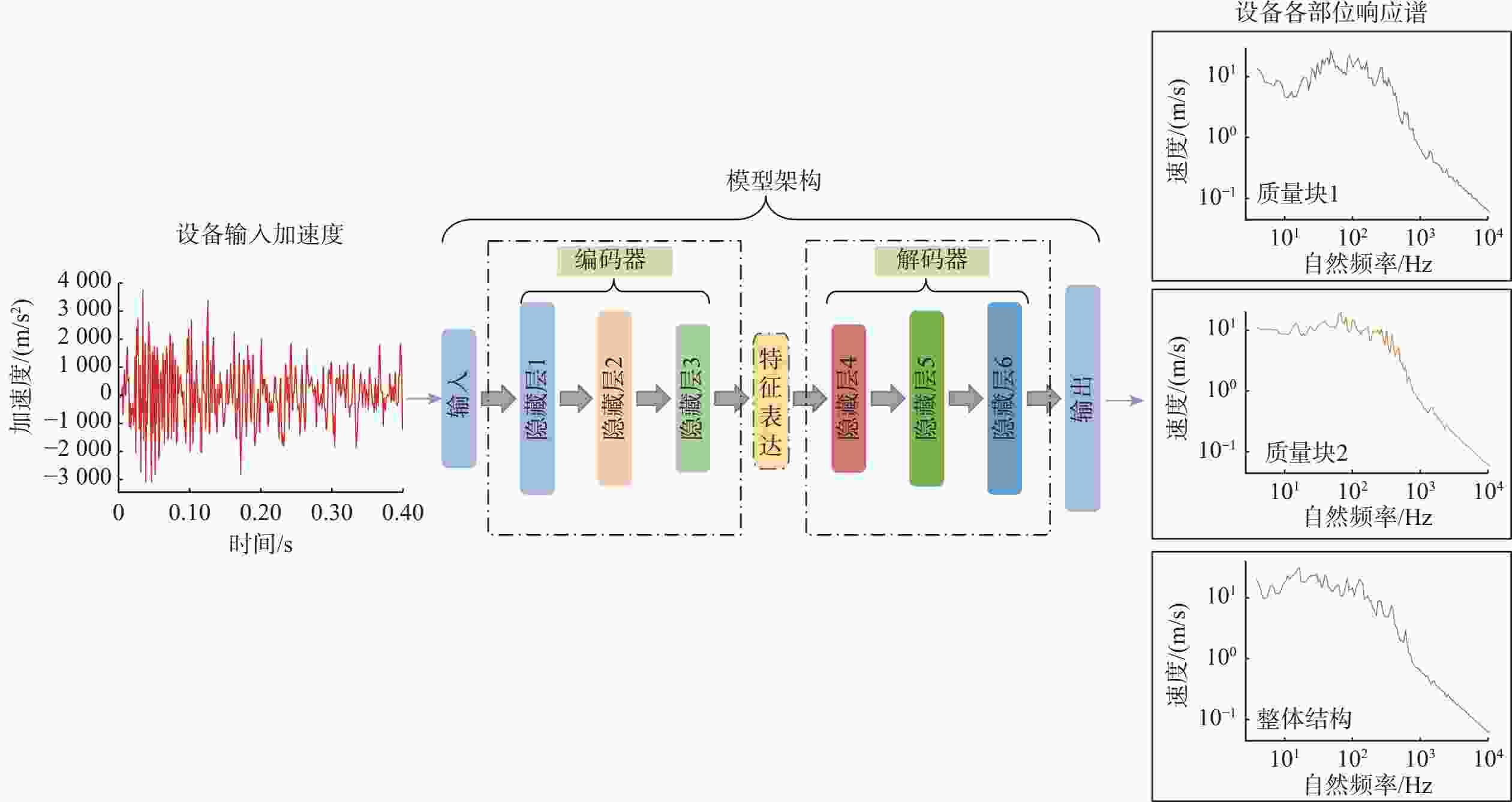
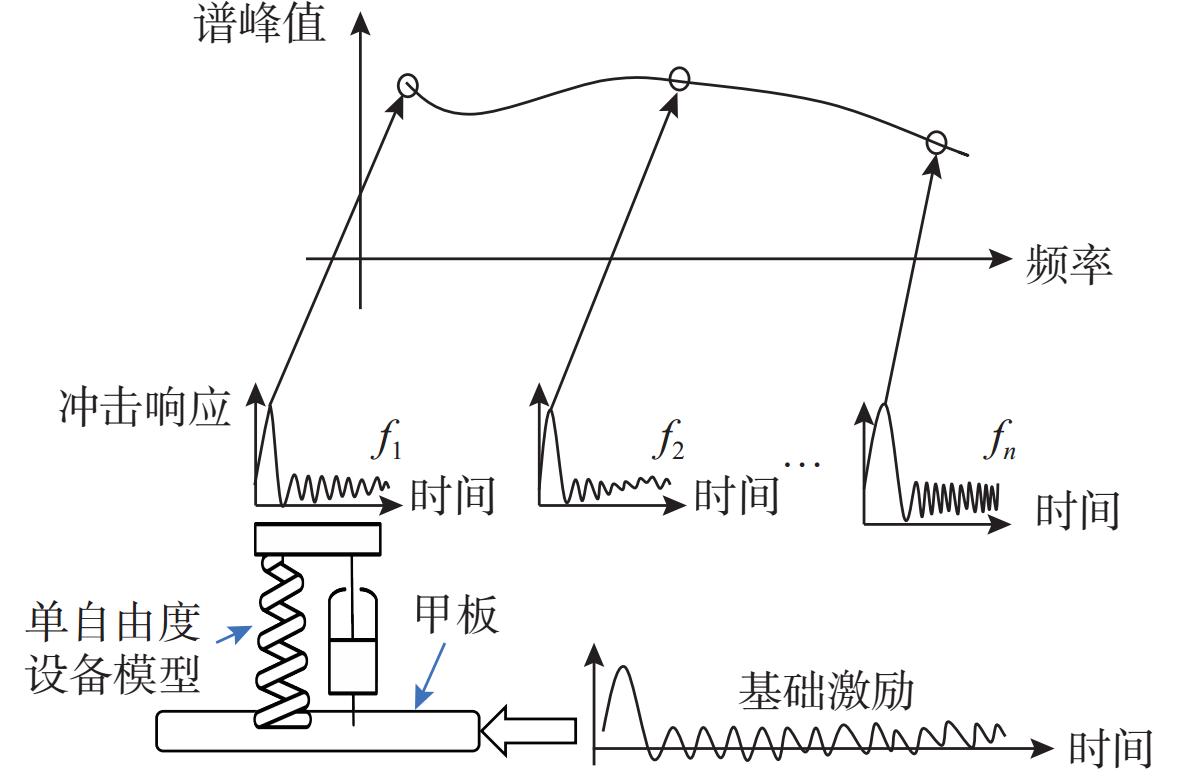
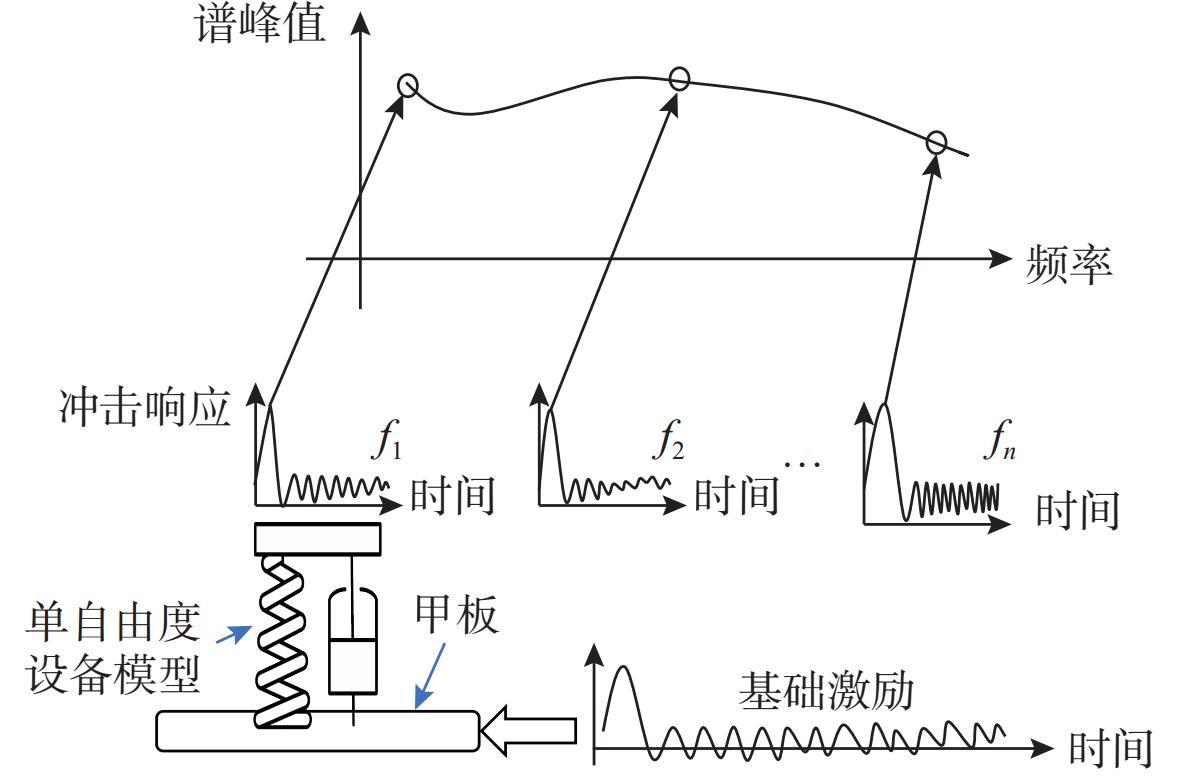
摘要: 针对船舶多自由度设备在爆炸冲击载荷下的响应分析难题, 文中提出了一种基于深度学习的冲击响应预测模型。传统单自由度模型无法高效分析多自由度系统的复杂冲击响应, 而该模型通过深度学习技术, 特别是利用神经网络的数据特征提取和非线性建模能力, 从数值仿真数据中学习冲击谱与输入冲击载荷的关联, 实现了对船舶结构中关键点冲击响应谱的高效准确计算。该方法弥补了现有模型在处理多自由度设备时的不足, 满足了对复杂系统冲击响应快速准确分析的需求。实验结果表明, 该模型能准确预测多自由度设备的冲击响应谱, 与仿真数据的相对误差控制在8%以内, 有效解决了传统模型在多自由度系统分析中的局限性。Abstract: To analyze the response of multi-degree-of-freedom ship equipment under explosive shock loads, this study proposed a deep learning-based shock response prediction model. Traditional single-degree-of-freedom models struggle to efficiently analyze the complex shock responses of multi-degree-of-freedom systems. By leveraging deep learning technology, especially the data feature extraction and nonlinear modeling capabilities of neural networks, this model learned the correlation between shock spectra and input shock loads from numerical simulation data, enabling efficient and accurate calculation of shock response spectra at critical points in ship structures. This approach overcame the limitations of existing models in handling multi-degree-of-freedom equipment and met the demand for rapid and precise analysis of complex system shock responses. Experimental results show that the model can accurately predict the shock response spectra of multi-degree-of-freedom equipment, with a relative error of less than 8% compared to simulation data, effectively resolving the bottlenecks of traditional models in multi-degree-of-freedom system analysis.
-
Key words:
- explosive shock /
- shock response /
- deep learning /
- multi-degree-of-freedom equipment
-
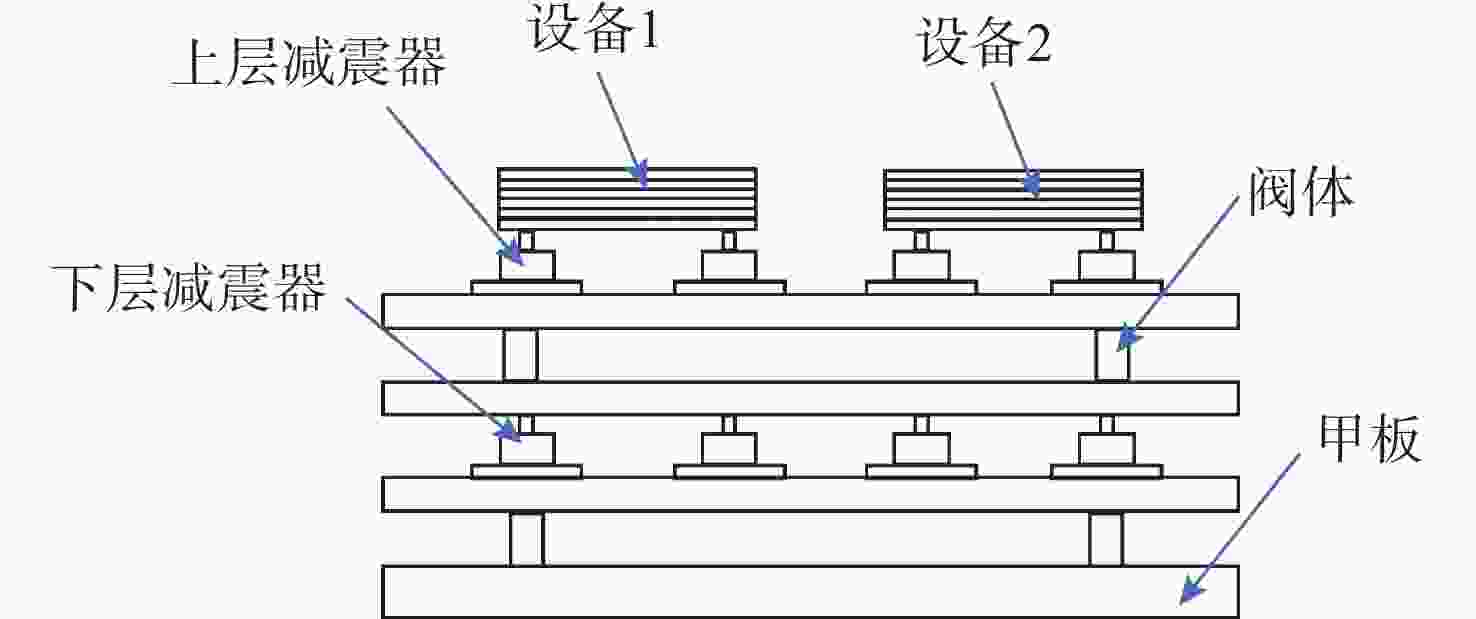
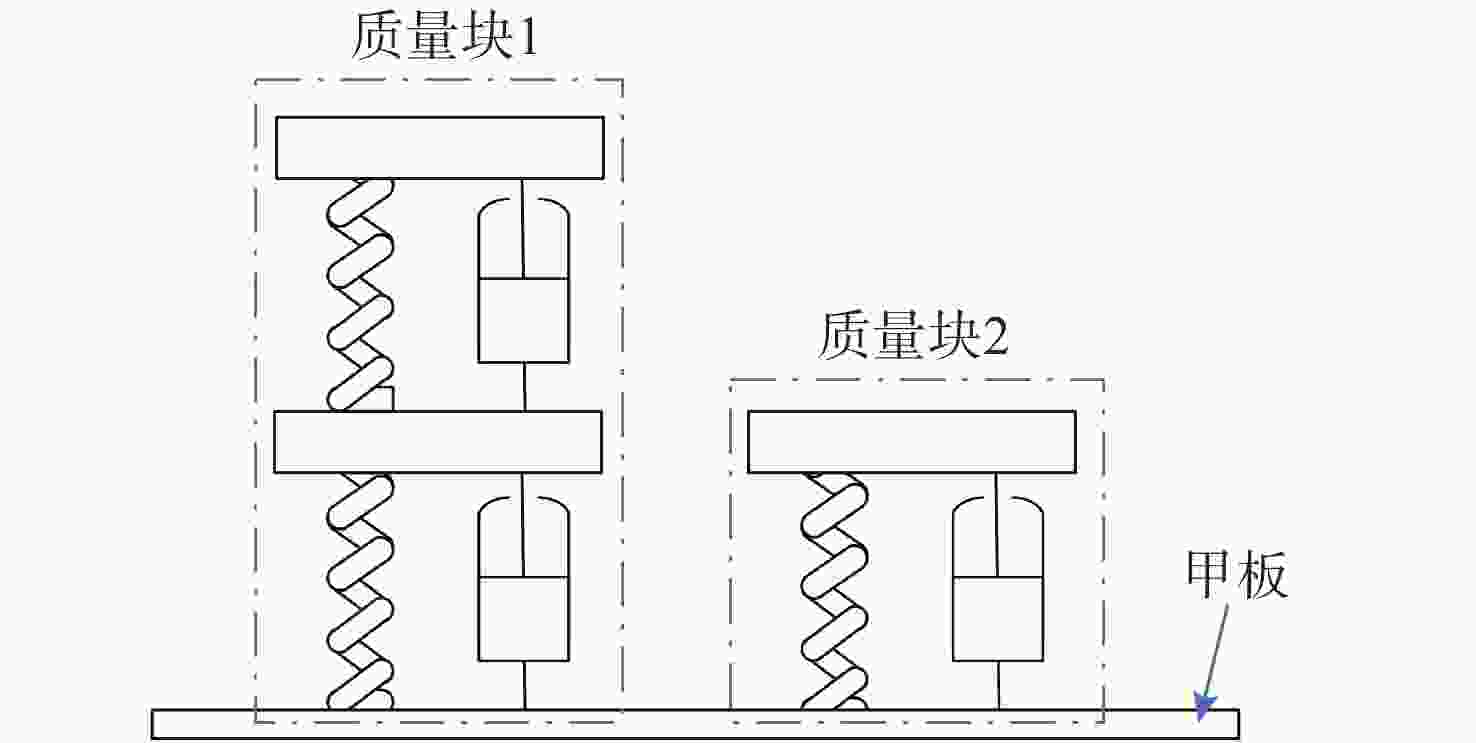
表 1 数值仿真工况
Table 1. Working conditions of numerical simulation
序号 水深/m 爆距/m 装药量/kg 方位 1 100 7 295 侧前方 2 100 7 295 正下方 3 100 7 295 侧后方 4 100 7 45 正下方 表 2 多工况下RMSE均值和RE均值
Table 2. Average RMSE and average RE under multiple operating conditions
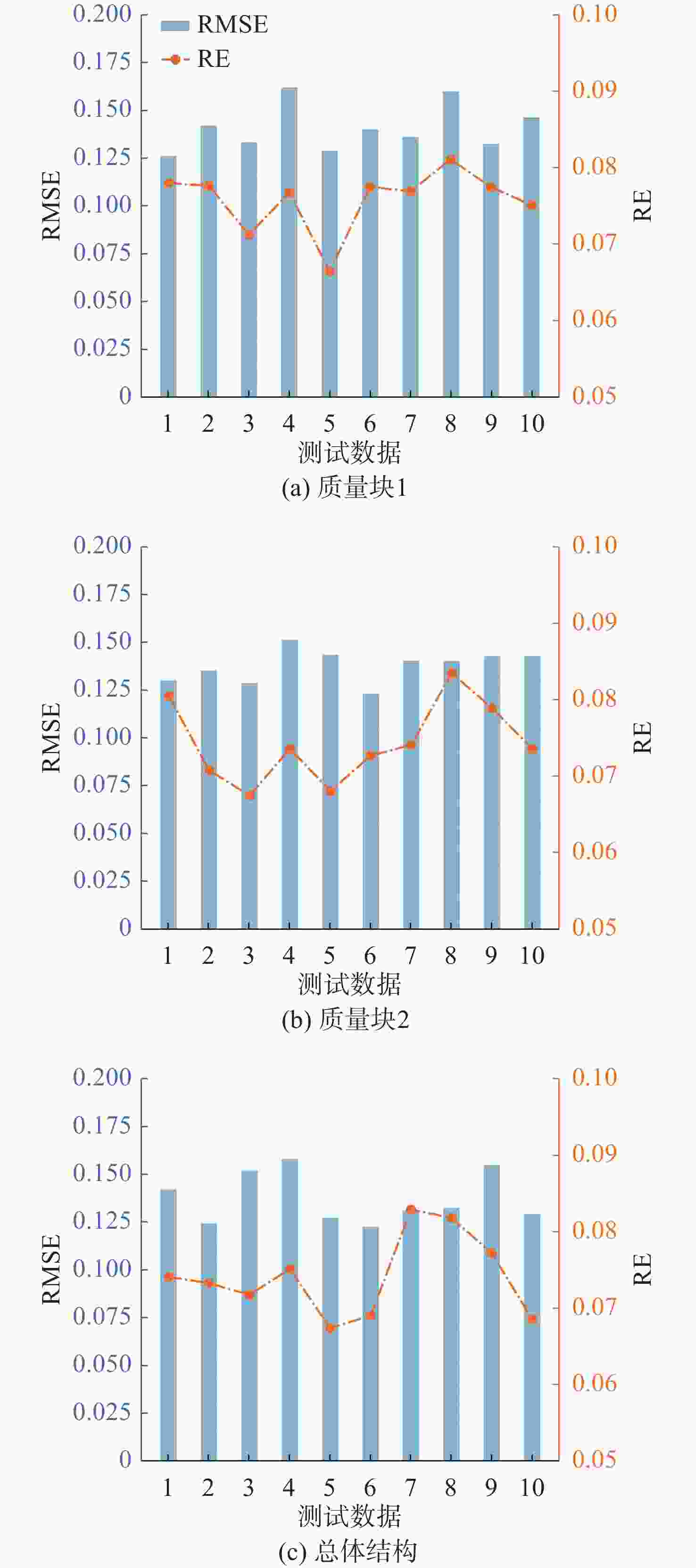
工况 感兴趣点 RMSE均值 RE均值/% 1 质量块1 0.126 6.1 质量块2 0.115 6.9 总体结构 0.093 6.3 2 质量块1 0.134 6.6 质量块2 0.151 6.8 总体结构 0.096 7.2 3 质量块1 0.122 7.6 质量块2 0.148 6.4 总体结构 0.121 7.5 4 质量块1 0.139 7.2 质量块2 0.094 7.8 总体结构 0.112 6.7 表 3 4种标准化方法计算公式
Table 3. Formulas for four standardization methods
标准化方法 计算公式 L1范数标准化 $ {y_i} = \dfrac{{{x_i}}}{{{{\left\| {{x_i}} \right\|}_p}}} $ 偏差标准化 $ {y_i} = \dfrac{{{x_i} - {x_{\min }}}}{{{x_{\max }} - {x_{\min }}}} $ 标准差标准化 $ {y_i} = \dfrac{{{x_i} - \mu }}{\sigma } $ 非线性标准化 $ {y_i} = \dfrac{1}{{1 + {{\mathrm{e}}^{ - {x_i}}}}} $ 表 4 4种标准化方法模型的RE均值和最大值
Table 4. Comparison of average RE and maximum RE among four standardization method models
标准化方法 RE均值/% RE最大值/% L1范数标准化 7.8 8.7 偏差标准化 7.1 8.8 标准差标准化 10.5 13.7 非线性标准化 13.1 14.5 表 5 感兴趣点冲击响应谱计算效率对比
Table 5. Comparison of calculation efficiency for shock response spectra at key points
方法 感兴趣点数 运行时间/s 多自由度模型 3 5 5 8 传统方法 3 360 5 600 -
[1] 刘永明, 孙焕新, 杨裕根. 多自由度系统冲击谱研究[J]. 上海铁道大学学报(自然科学版), 1998, 23(6): 52-57.LIU Y M, SUN H X, YANG Y G. A study on shock spectrum of multiple degrees of freedom system[J]. Journal of Shanghai Tiedao University(Natural Science Edition), 1998, 23(6): 52-57. [2] 姜涛, 周方毅, 张可玉, 等. 水面舰艇甲板设备抗冲击设计谱分析[J]. 工程爆破, 2009, 15(4): 8-12.JIANG T, ZHOU F Y, ZHANG K Y, et al. Analysis on design shock-resistant spectrum of equipment fixed on deck[J]. Engineering Blasting, 2009, 15(4): 8-12. [3] OH J S, LEE TH, CHOI S B. Design and analysis of a new magnetorheological damper for generation of tunable shock-wave profiles[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2018: 8963491. [4] TRUONG D D, JANG B S, JU H B. Development of simplified method for prediction of structural response of stiffened plates under explosion loads[J]. Marine Structures, 2021, 79: 103039. doi: 10.1016/j.marstruc.2021.103039 [5] LIU Y, REN S F, ZHAO P F. Application of the deep neural network to predict dynamic responses of stiffened plates subjected to near-field underwater explosion[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 247: 110537. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.110537 [6] BRUNTON S L, KUTZ J N. Data-driven science and engineering: Machine learning, dynamical systems, and control[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022. [7] 钱丽娜. 基于神经网络的水下加筋圆柱壳冲击环境预报[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2021. [8] 冯麟涵, 杨俊杰, 焦立启. 基于RBF神经网络的船舶冲击谱速度数据挖掘与预报[J]. 振动与冲击, 2022, 41(13): 189-194, 210.FENG L H, YANG J J, JIAO L Q. Data mining and prediction of ship shock spectral velocity based on RBF neural network[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2022, 41(13): 189-194, 210. [9] ZHANG M, DRIKAKIS D, LI L, et al. Machine-learning prediction of underwater shock loading on structures[J]. Computation, 2019, 7(4): 58. doi: 10.3390/computation7040058 [10] HEMATI M S, SAPSIS T P. Physics-informed machine learning for predicting extreme events in complex systems[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2017, 118: 084501. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.084501 [11] YU Y, YAO H, LIU Y. Structural dynamics simulation using a novel physics-guided machine learning method[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 96: 103947. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2020.103947 [12] MCKAY M D, BECKMAN R J, CONOVER W J. A comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code[J]. Technimetrics, 1979, 21(2): 239-245. [13] GUO J, GU C, YANG J, et al. Data mining and application of ship impact spectrum acceleration based on PNN neural network[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 203: 107193. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107193 -




 下载:
下载: