Passive Localization of Underwater Broadband High-Frequency Targets Based on Frequency Difference Matching Field
-
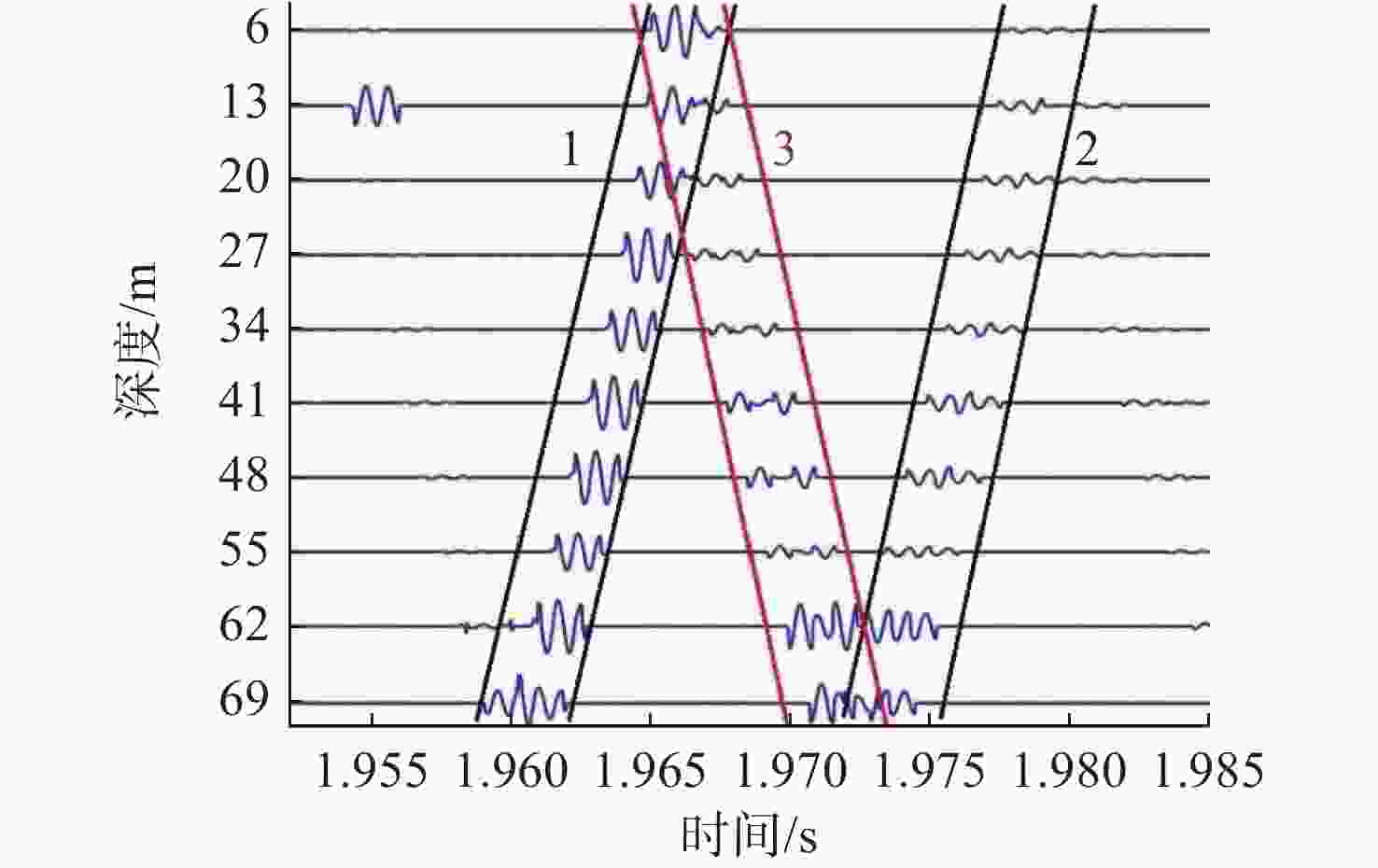
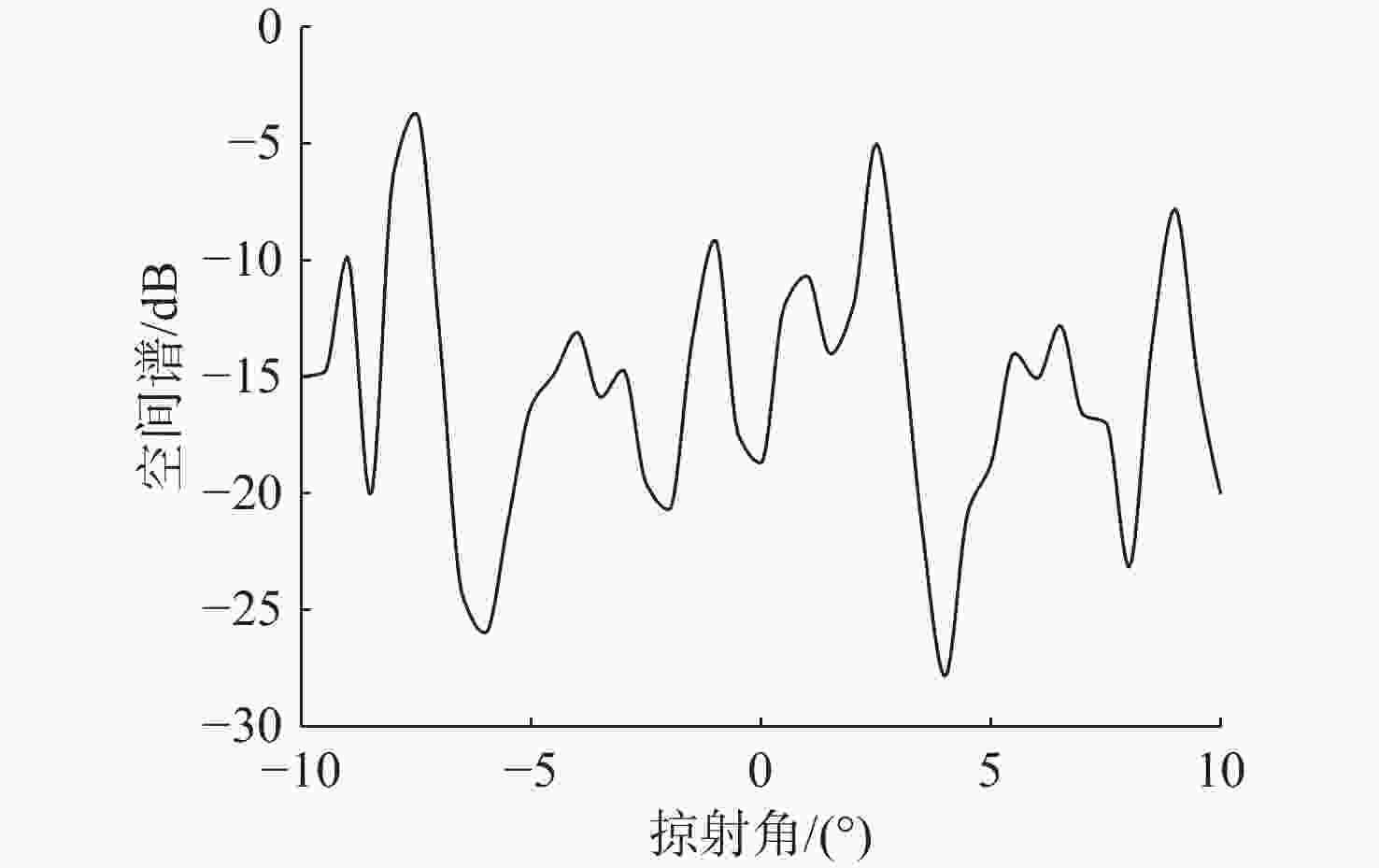
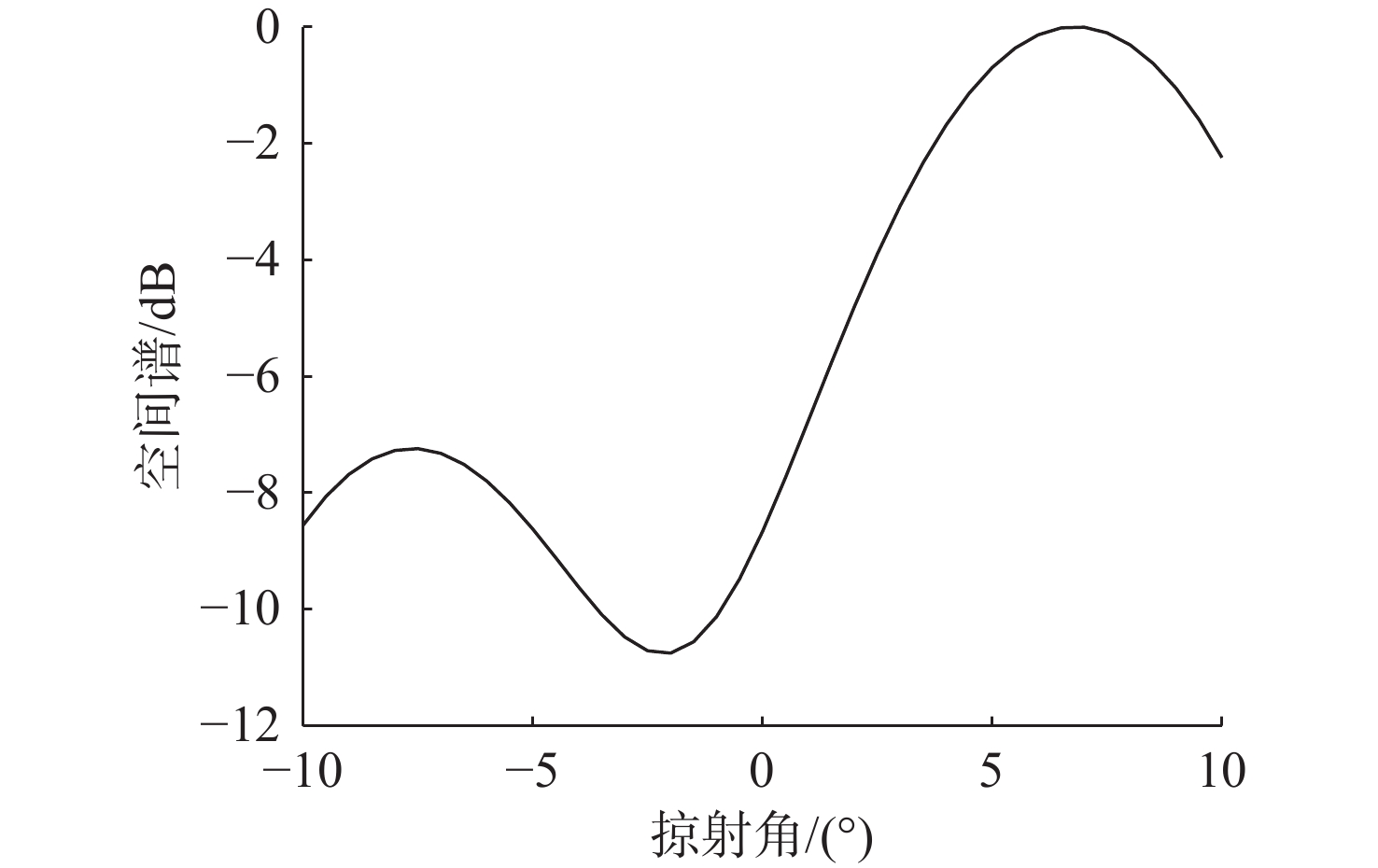
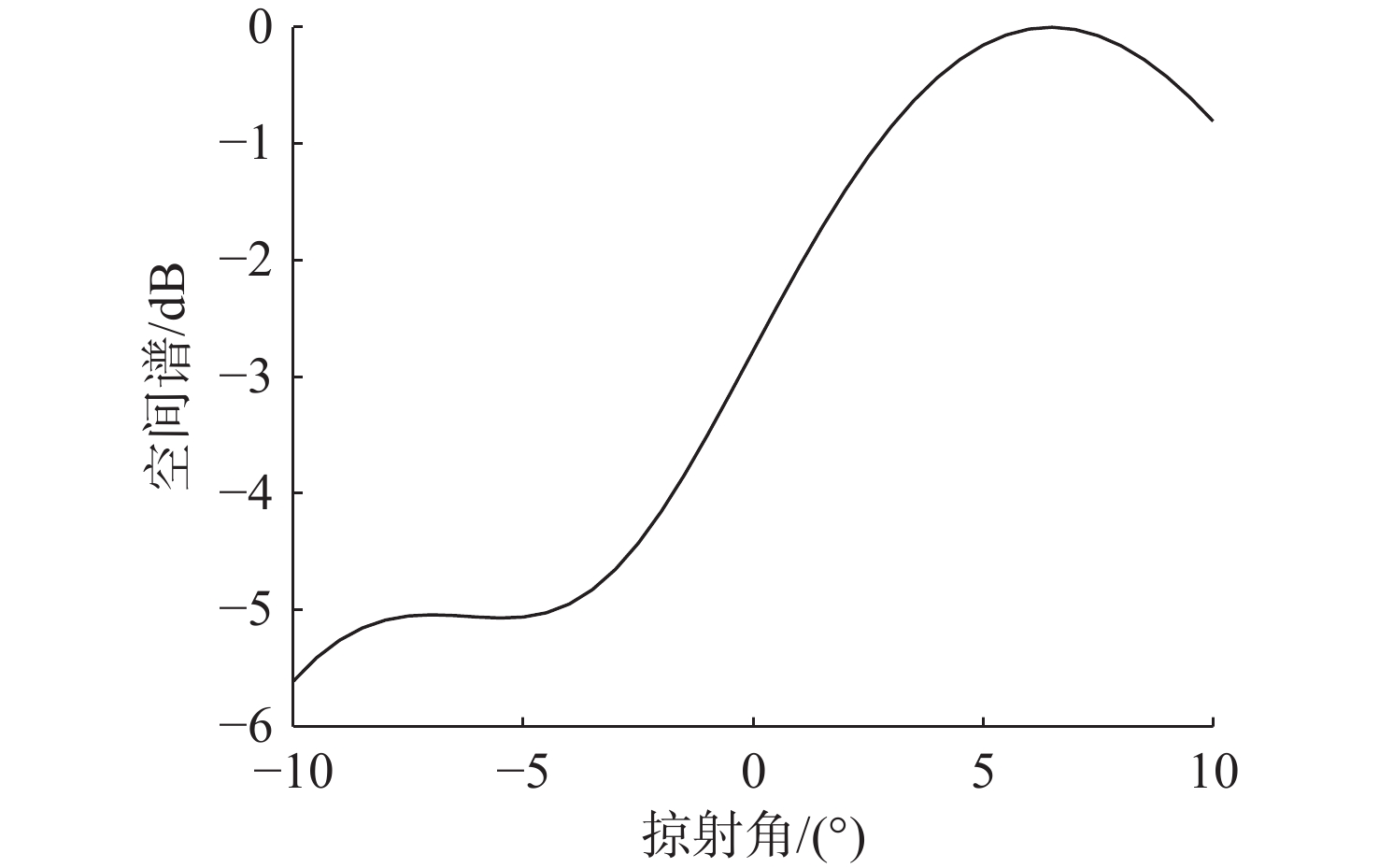
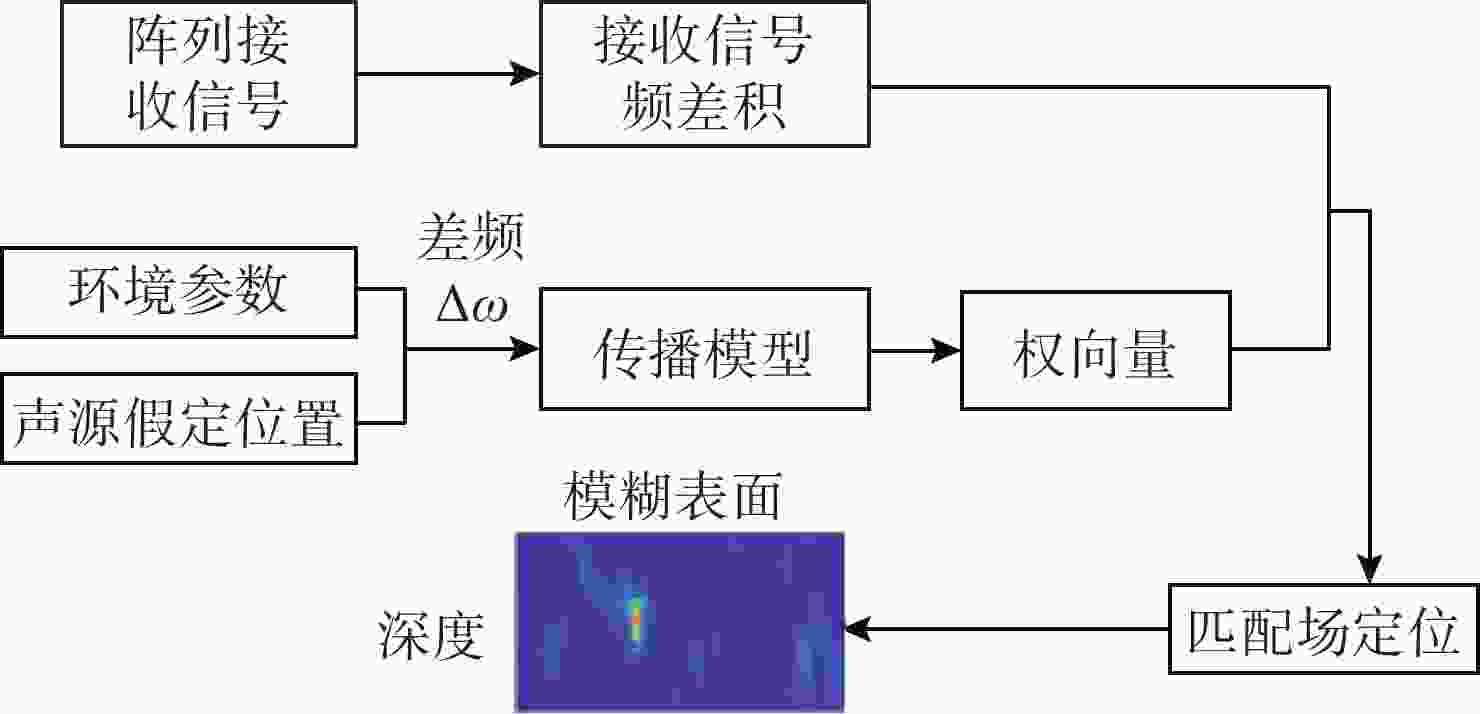
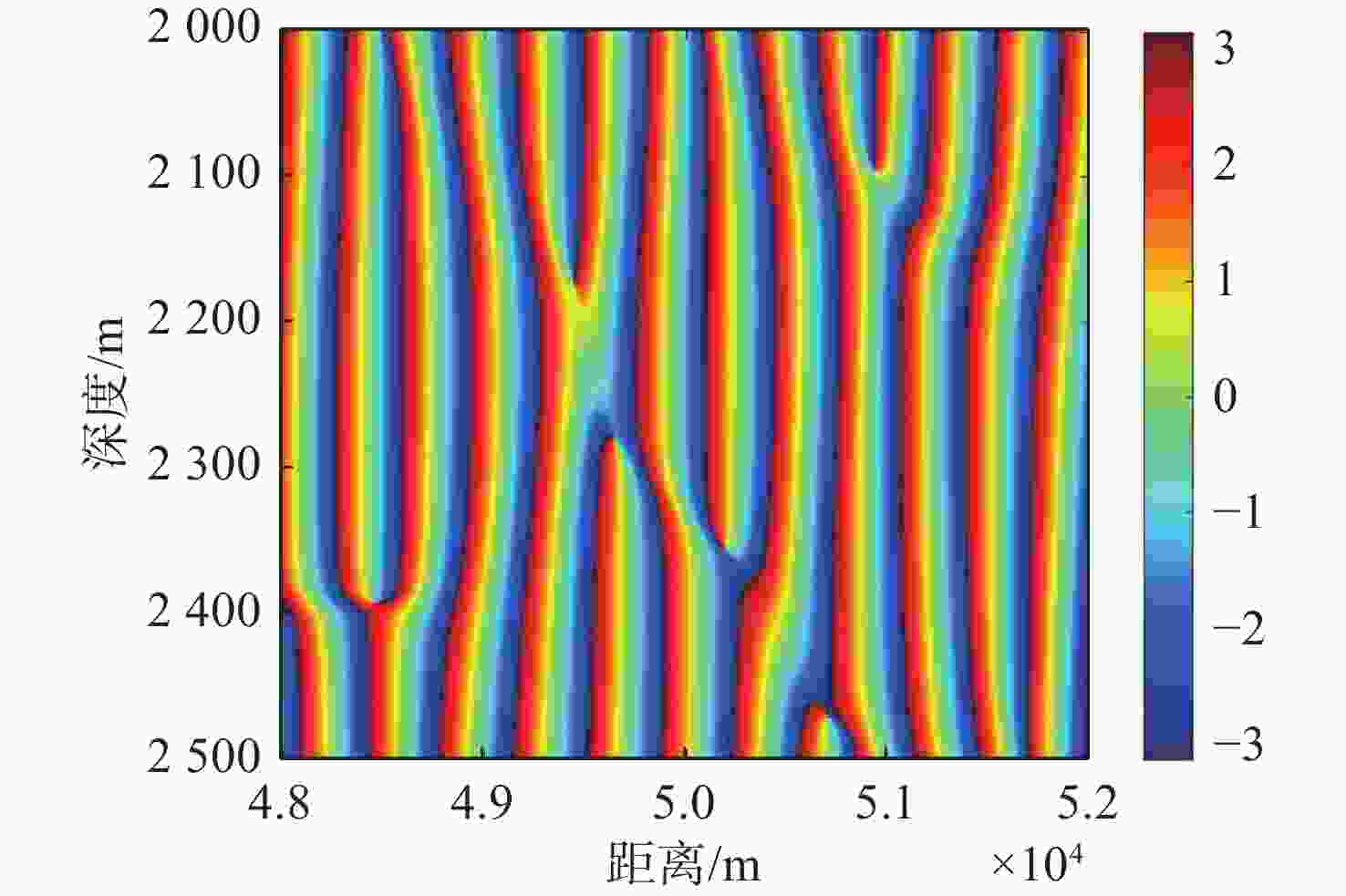
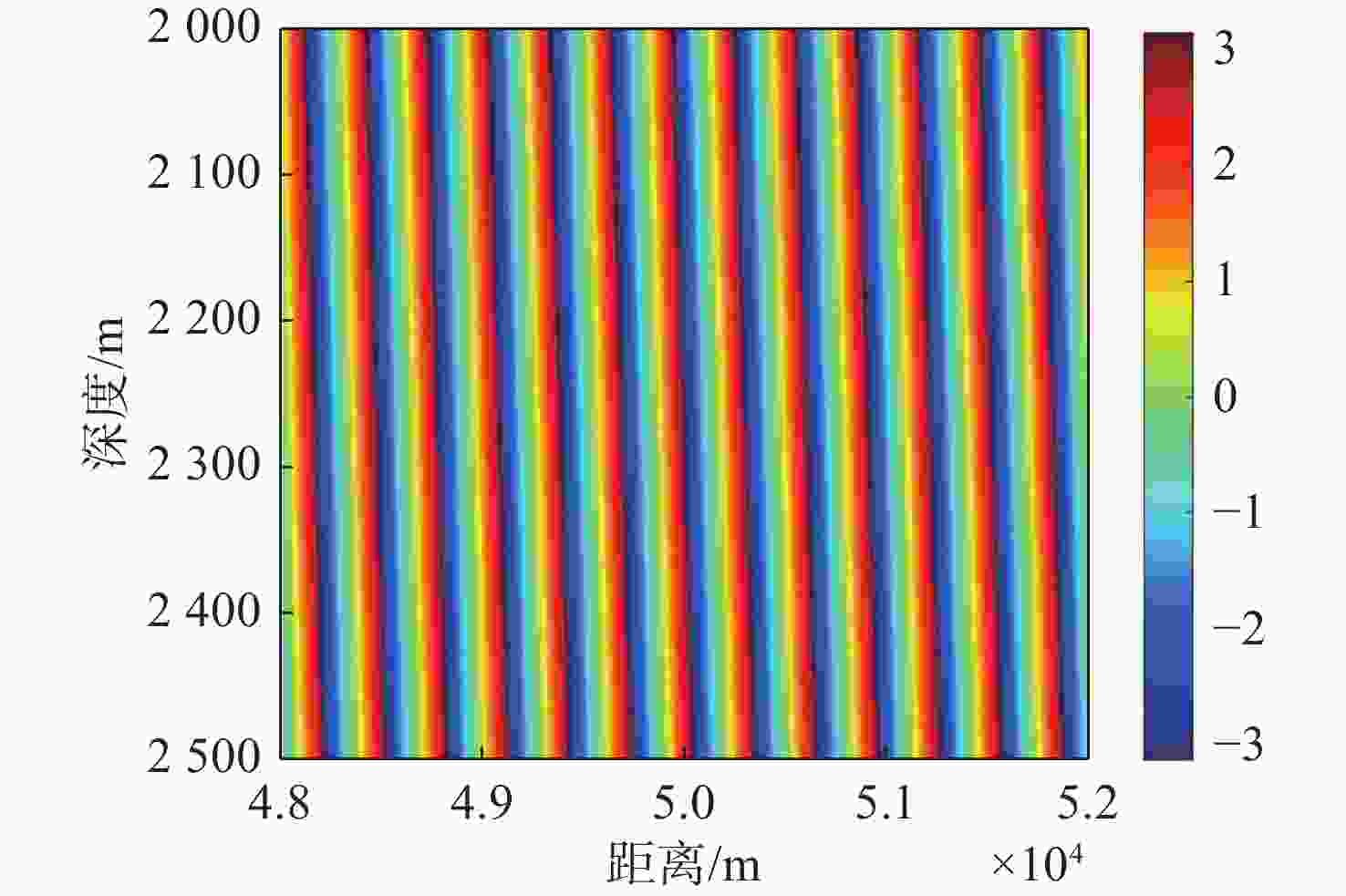
摘要: 高频信号在传播过程中易受环境不确定性的影响, 导致传统匹配场方法在高频段定位性能退化。为改善这一问题, 文中给出了基于频差匹配场的高频信号被动定位方法, 对高频带宽内不同频率的阵列接收数据进行二次积处理, 以构造远小于原频率差频处的声场结构。在差频处应用已建立的匹配场定位算法, 将宽带高频信号降低到低频段处理。首先, 给出了频差法的原理并对浅海多径传播到达掠射角进行准确估计, 在此基础上, 分别给出了适用于浅海和深海的频差匹配场物理模型。最后, 通过仿真证明了文中所提方法在不确定环境中对高频信号定位性能明显优于传统方法。Abstract: High-frequency signals are susceptible to environmental uncertainties during propagation, leading to degraded localization performance when using traditional matching field methods. To address this issue, this paper proposed a passive localization method for high-frequency signals based on the frequency difference matching field. This method performed quadratic product processing on the received data of arrays at different frequencies within the high-frequency bandwidth, constructing a sound field structure at a difference frequency much lower than the original frequency. By applying the established localization algorithm based on the matching field at difference frequency, the high-frequency broadband signal was reduced to the low-frequency range for processing. Firstly, the principle of the frequency difference method was presented, and the grazing angle of multipath propagation in shallow water was estimated. On this basis, physical models for frequency difference matching fields suitable for shallow and deep-sea environments were proposed. Finally, simulation results show that the proposed method substantially outperforms traditional methods in terms of high-frequency signal localization in uncertain environments.
-
表 1 浅海仿真环境参数
Table 1. Environment parameters of shallow water simulation
海深/m 海底声速/(m/s) 海底密度/(g/cm3) 海底衰减/(dB/λ) 75 1 668 1.806 0.692 表 2 深海仿真环境参数
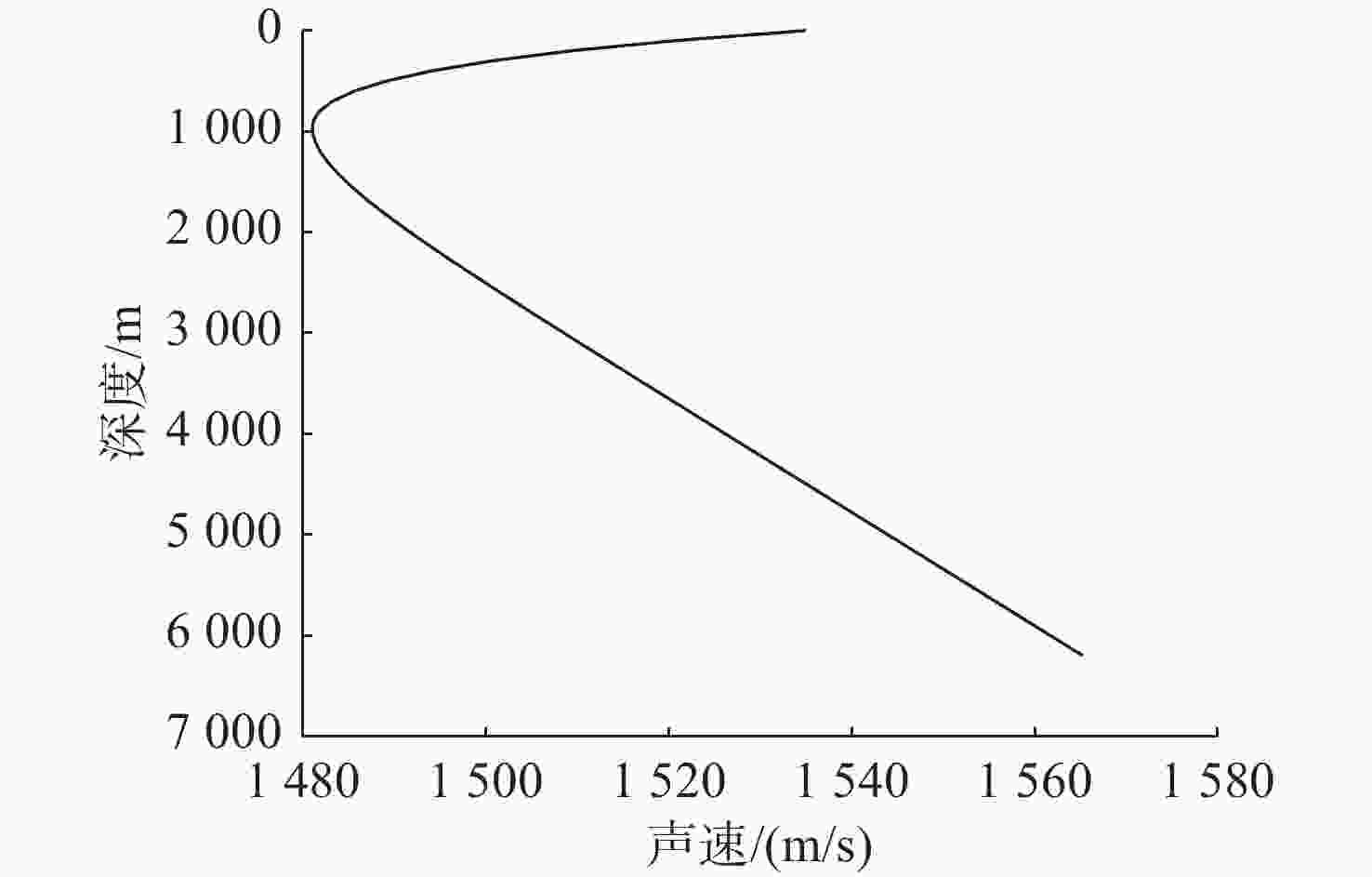
Table 2. Deep sea simulation environment parameters
海深/m 海底声速/(m/s) 海底密度/(g/cm3) 海底衰减/(dB/λ) 6 370 2 000 1.8 0.1 表 3 4种定位算法对比
Table 3. Comparison of four positioning algorithms
算法 频率 权向量 范围 实测数
据处理幅度权重 相位权重 宽带匹配场定位 带内频率 $p(\omega )$ $ \left| {p(\omega )} \right| $ $ \arg \left| {p(\omega )} \right| $ 浅海频差匹配场定位 带内频
率之下$A{_\Delta}(\omega ,\Delta \omega )$ $ \left| {p(\omega )} \right| $ $ \arg \left| {p(\omega )} \right| $ 深海频差匹配场定位 带内频
率之下$A{_\Delta}(\omega ,\Delta \omega )$ $ \left| {p(\omega )} \right| $ $ \arg \left| {A(\Delta \omega )} \right| $ 基于相位匹配的深
海频差匹配场定位带内频
率之下$A{_\Delta}(\omega ,\Delta \omega )$ 1 $ \arg \left| {A(\Delta \omega )} \right| $ 表 4 浅海定位算法偏移对比
Table 4. Deviation comparison of shallow water positioning algorithms
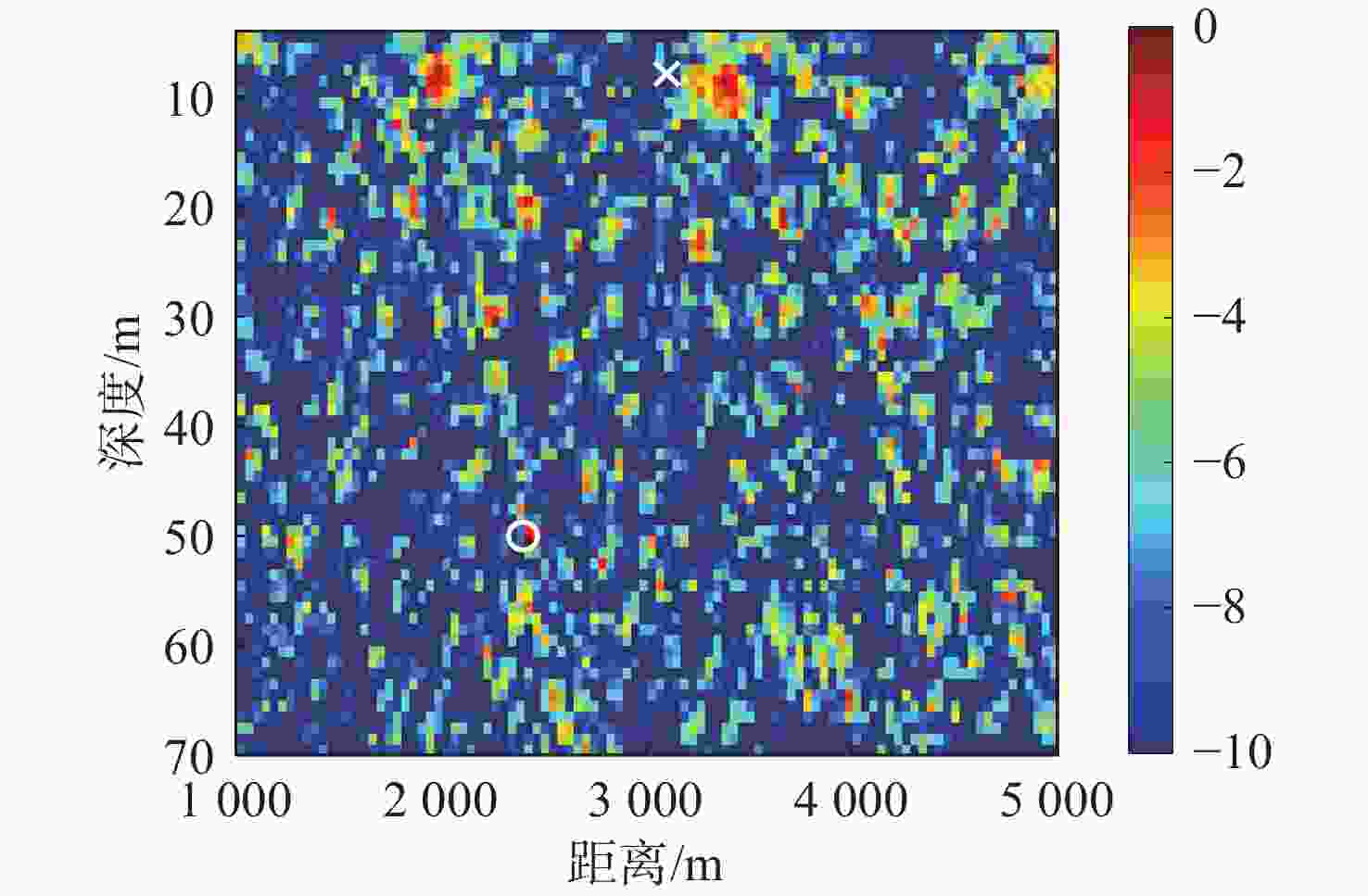
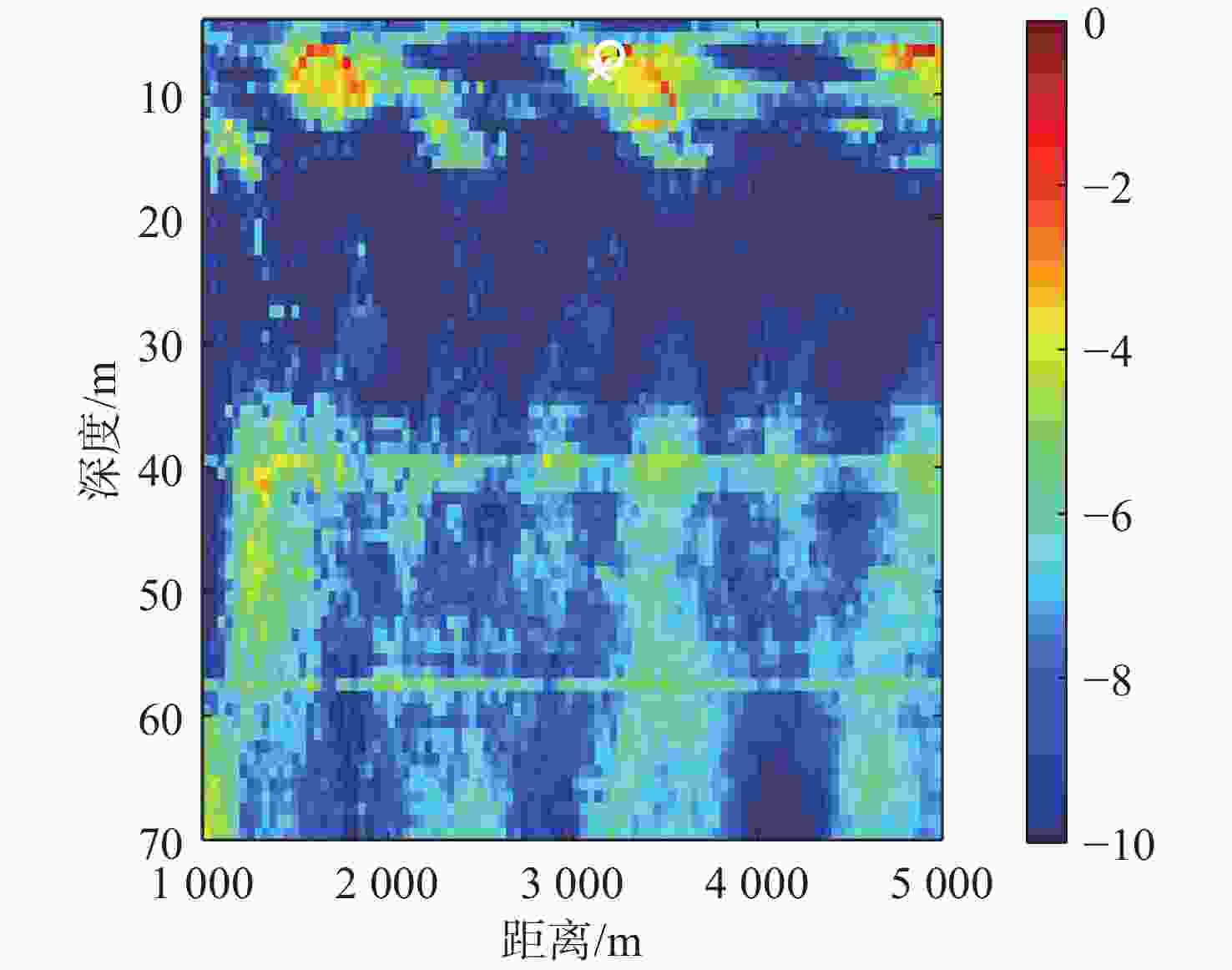
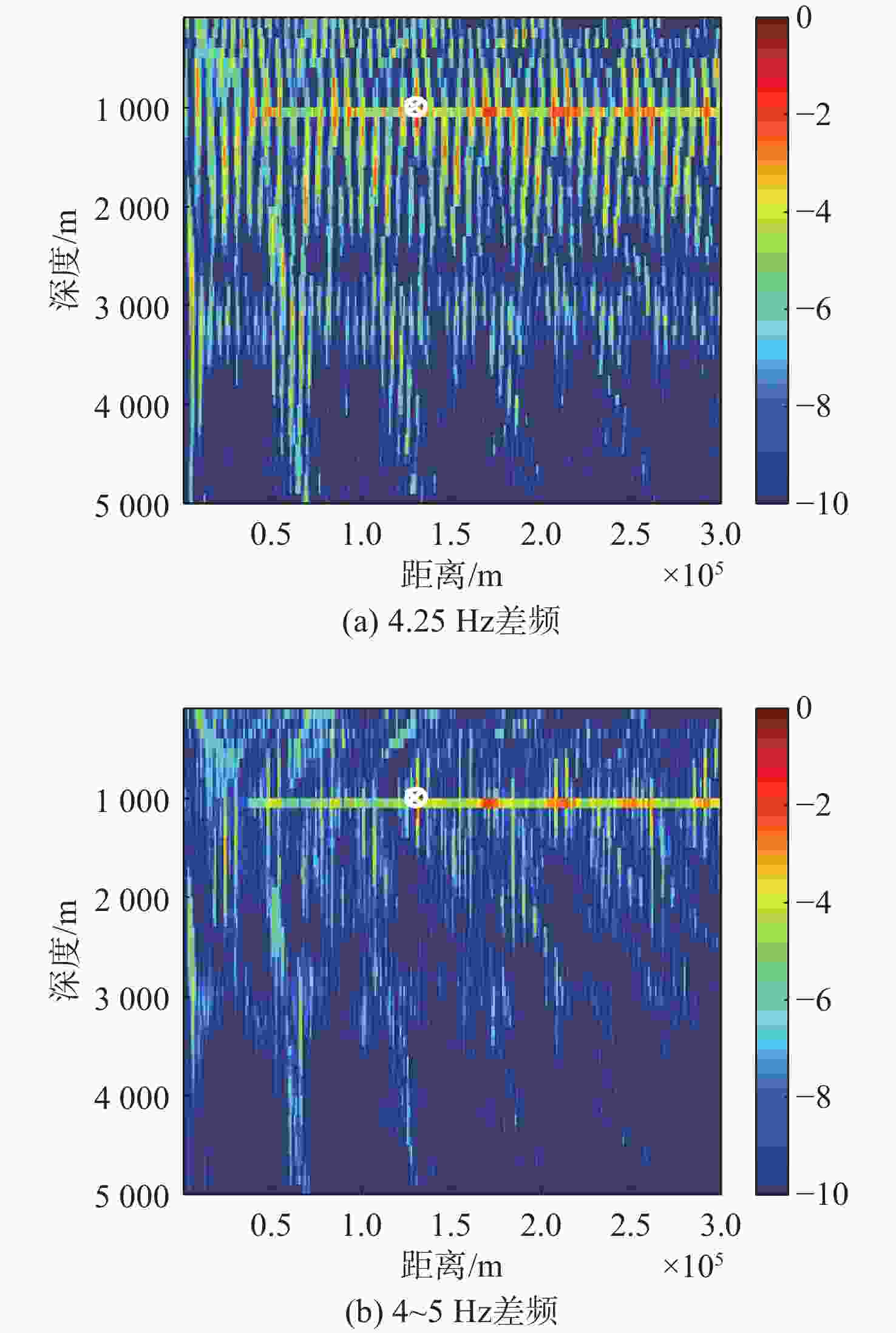
算法 深度偏移/m 距离偏移/km 常规匹配场定位 42 0.6 浅海频差匹配场定位 1.0 0.2 表 5 深海定位算法偏移对比
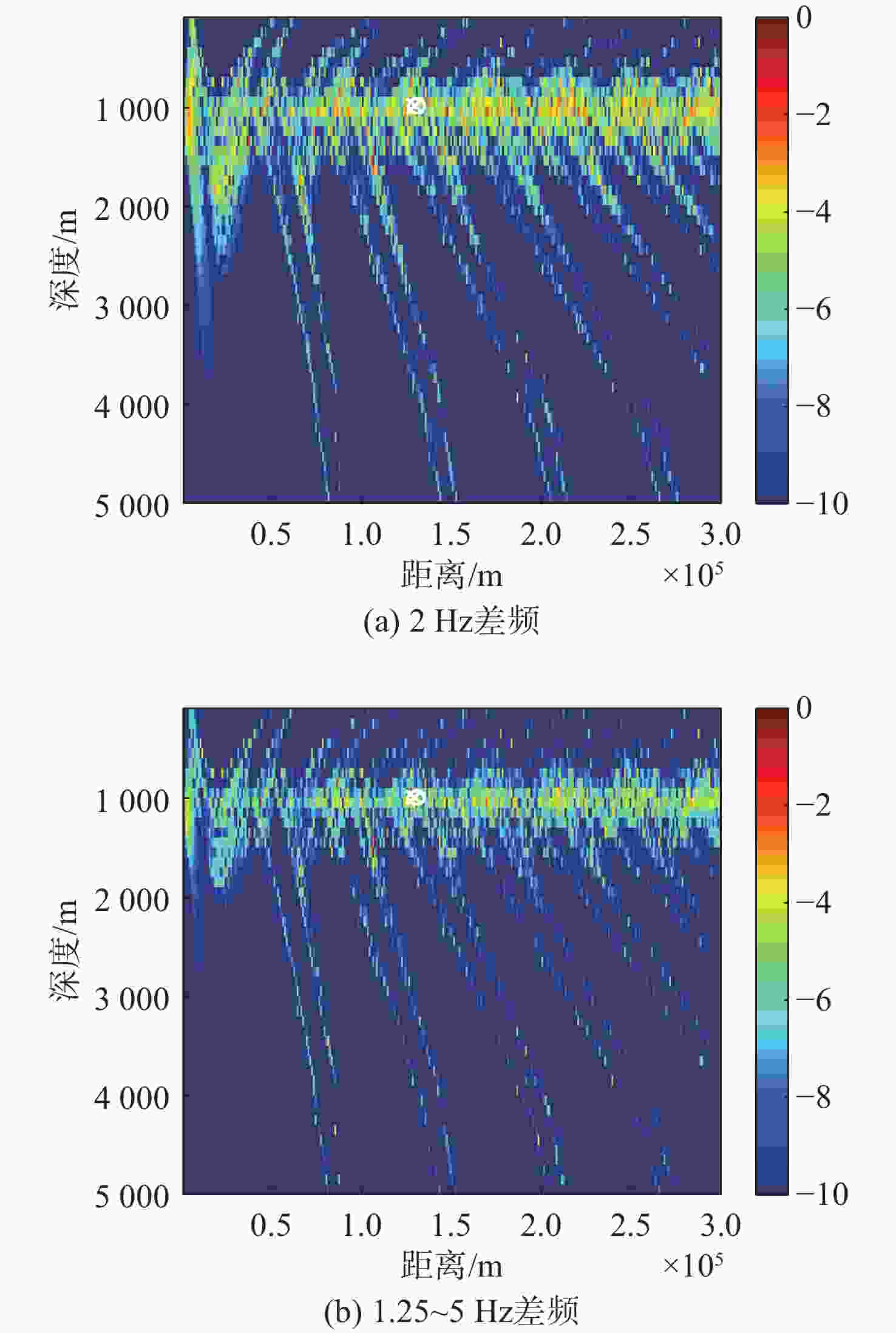
Table 5. Deviation comparison of deep-sea positioning algorithms
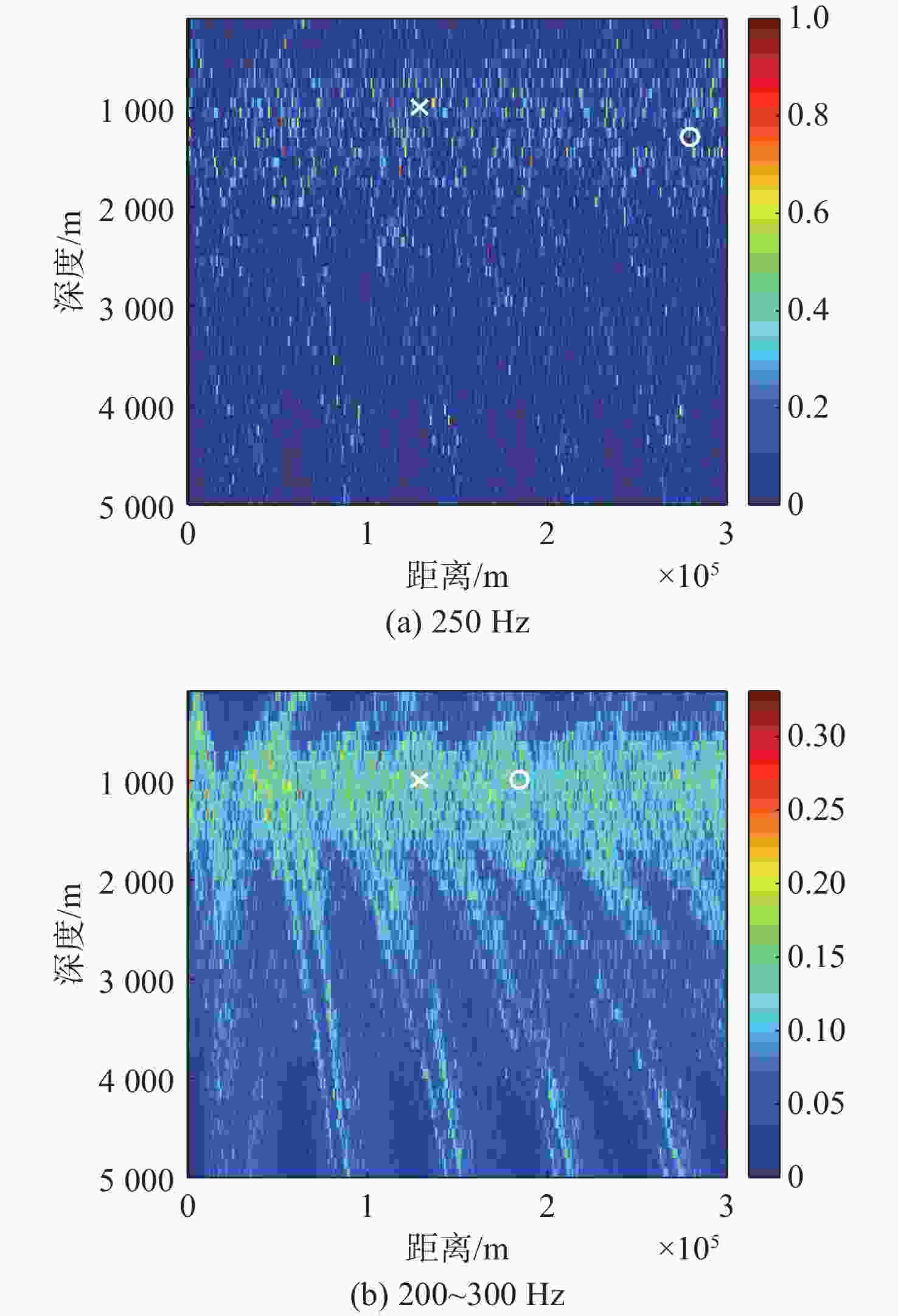
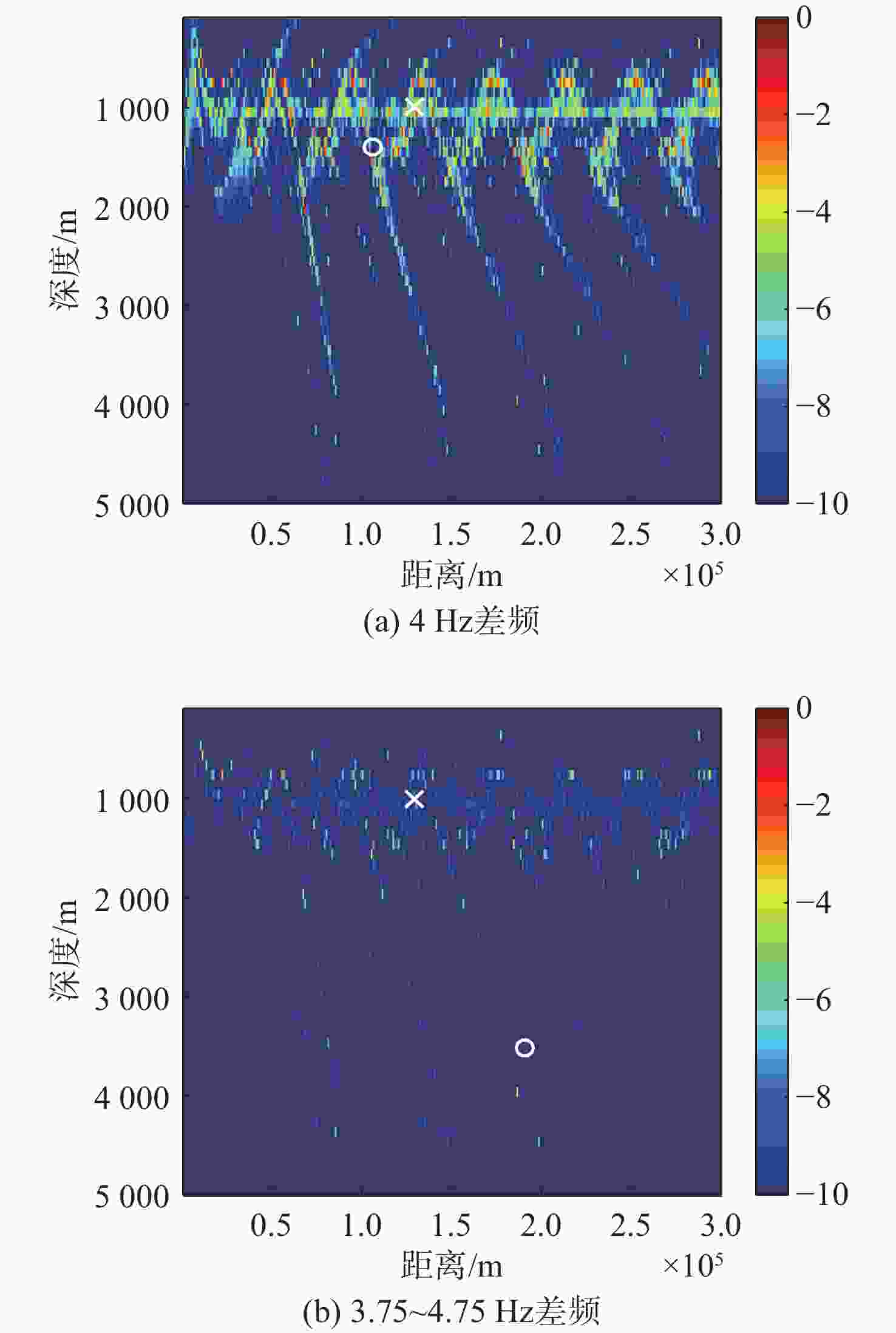
算法 深度偏移/m 距离偏移/km 单个频
率/差频多个频率
/差频非相
干平均单个
差频多个频率
/差频非相
干平均常规匹配场定位 300 0 150 55 浅海频差匹配场定位 1 400 3 500 106 191 深海频差匹配场定位 0 0 0 0 基于相位匹配的深海
频差匹配场定位0 0 0 0 -
[1] 杨坤德, 马远良, 邹士新, 等. 基于环境扰动的线性匹配场处理方法[J]. 声学学报, 2006, 31(6): 496-505 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-0025.2006.06.004YANG K D, MA Y L, ZOU S X, et al. Linear matched field processing based on environmental perturbation[J]. Acta Acustica, 2006, 31(6): 496-505. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-0025.2006.06.004 [2] 王学志, 涂英, 吴克桐, 等. 应用匹配场实现单矢量水听器的三维定位[J]. 声学技术, 2012, 31(1): 72-76 doi: 10.3969/j.issn1000-3630.2012.01.012 [3] 李倩倩, 李整林, 张仁和. 不确知海洋环境下的贝叶斯声源定位法[J]. 声学学报, 2014, 39(5): 535-543.LI Q Q, LI Z L, ZHANG R H. Bayesian localization in an uncertain ocean environment[J]. Acta Acustica, 2014, 39(5): 535-543. [4] 段睿. 深海环境水声传播及声源定位方法研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2016. [5] ARASE E M, ARASE T. Ambient sea noise in the deep and shallow ocean[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1967, 42(1): 73-77. doi: 10.1121/1.1910577 [6] 王奇, 王英民, 苟艳妮. 浅海环境参数失配对匹配场处理的影响分析[J]. 计算机仿真, 2013, 30(6): 252-256, 413. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2013.06.059 [7] WORTHMANN B M, SONG H C, DOWLING D R. High frequency source localization in a shallow ocean sound channel using frequency difference matched field processing.[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2015, 138(6): 3549-3562. doi: 10.1121/1.4936856 [8] BAGGEROER A B, KUPERMAN W A. An overview of matched field methods in ocean acoustics[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1993, 18(4): 401-424. doi: 10.1109/48.262292 [9] HURSKY P, PORTER M B, SIDERIUS M, et al. High-frequency (8–16 kHz) model-based source localization[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2004, 115(6): 3021-3032. doi: 10.1121/1.1690078 [10] COLLINS M D, KUPERMAN W A. Focalization: Environmental focusing and source localization[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1991, 90(3): 1410-1422. doi: 10.1121/1.401933 [11] ABADI S H, SONG H C, DOWLING D R. Broadband sparse-array blind deconvolution using frequency-difference beamforming[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2012, 132(5): 3018-3029. doi: 10.1121/1.4756920 [12] DOUGLASS A S, SONG H C, DOWLING D R. Performance comparisons of frequency-difference and conventional beamforming[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2017, 142(3): 1663-1673. doi: 10.1121/1.5003787 [13] LIPA J E, WORTHMANN B M, DOWLING D R. Measurement of autoproduct fields in a Lloyd’s mirror environment[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2018, 143(4): 2419-2427. [14] WORTHMANN B M, DOWLING D R. Autoproducts in and near acoustic shadow zones created by barriers[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2020, 147(3): 1863-1873. doi: 10.1121/10.0000953 [15] WORTHMANN B M, DOWLING D R. The effects of refraction and caustics on autoproducts[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2020, 147(6): 3959-3968. doi: 10.1121/10.0001399 -




 下载:
下载: