Target Threat Assessment Method for UUVs Based on EBM
-
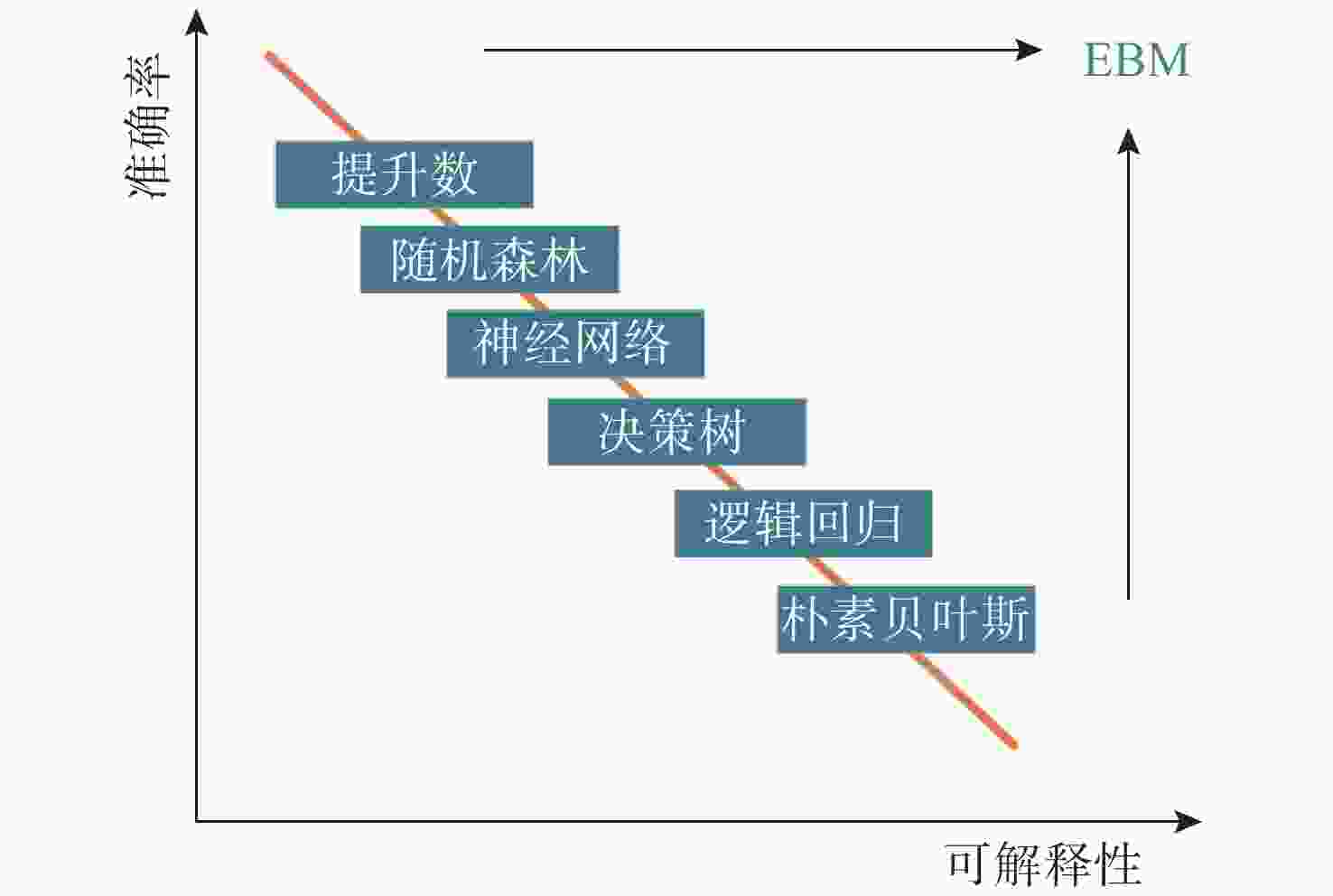
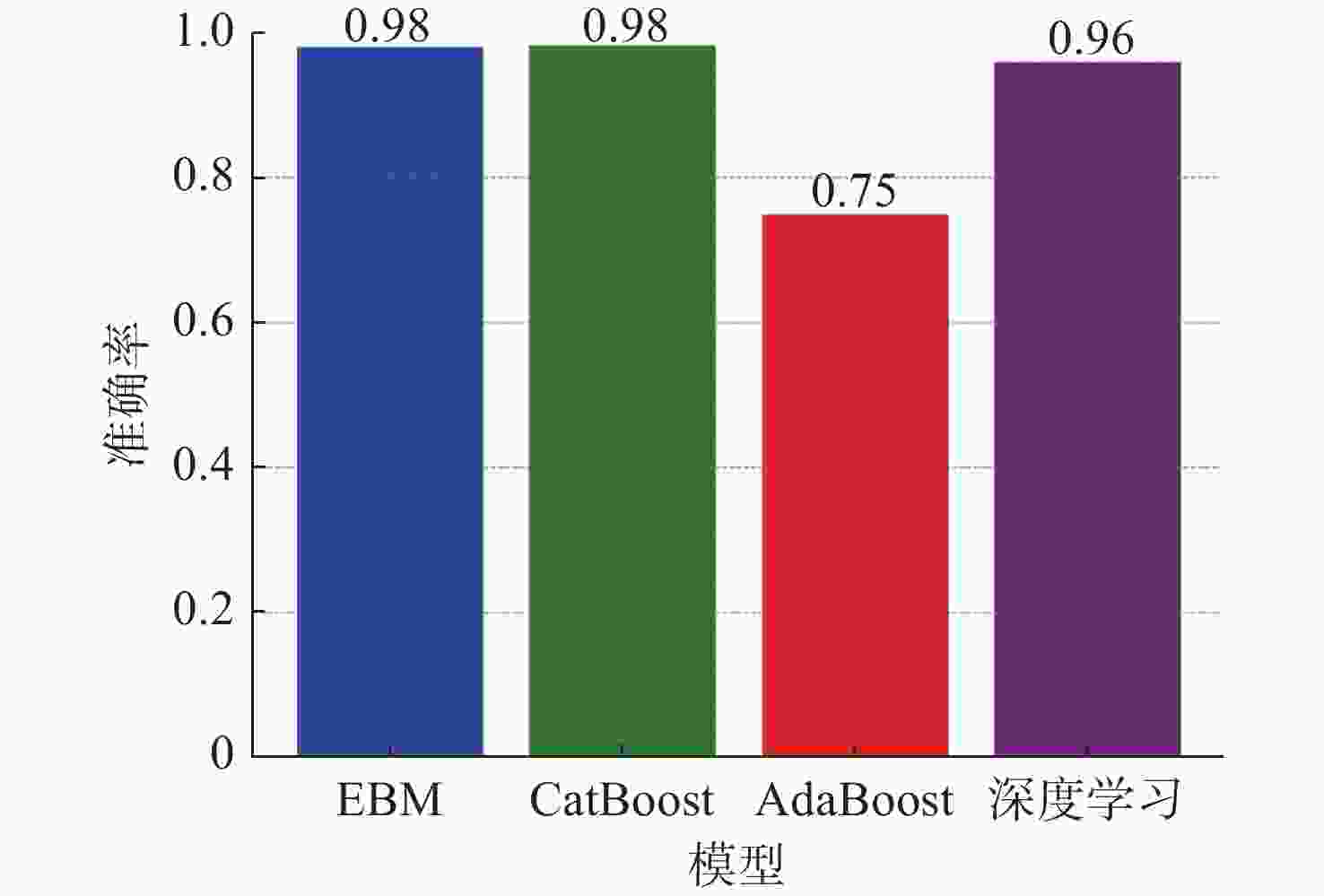
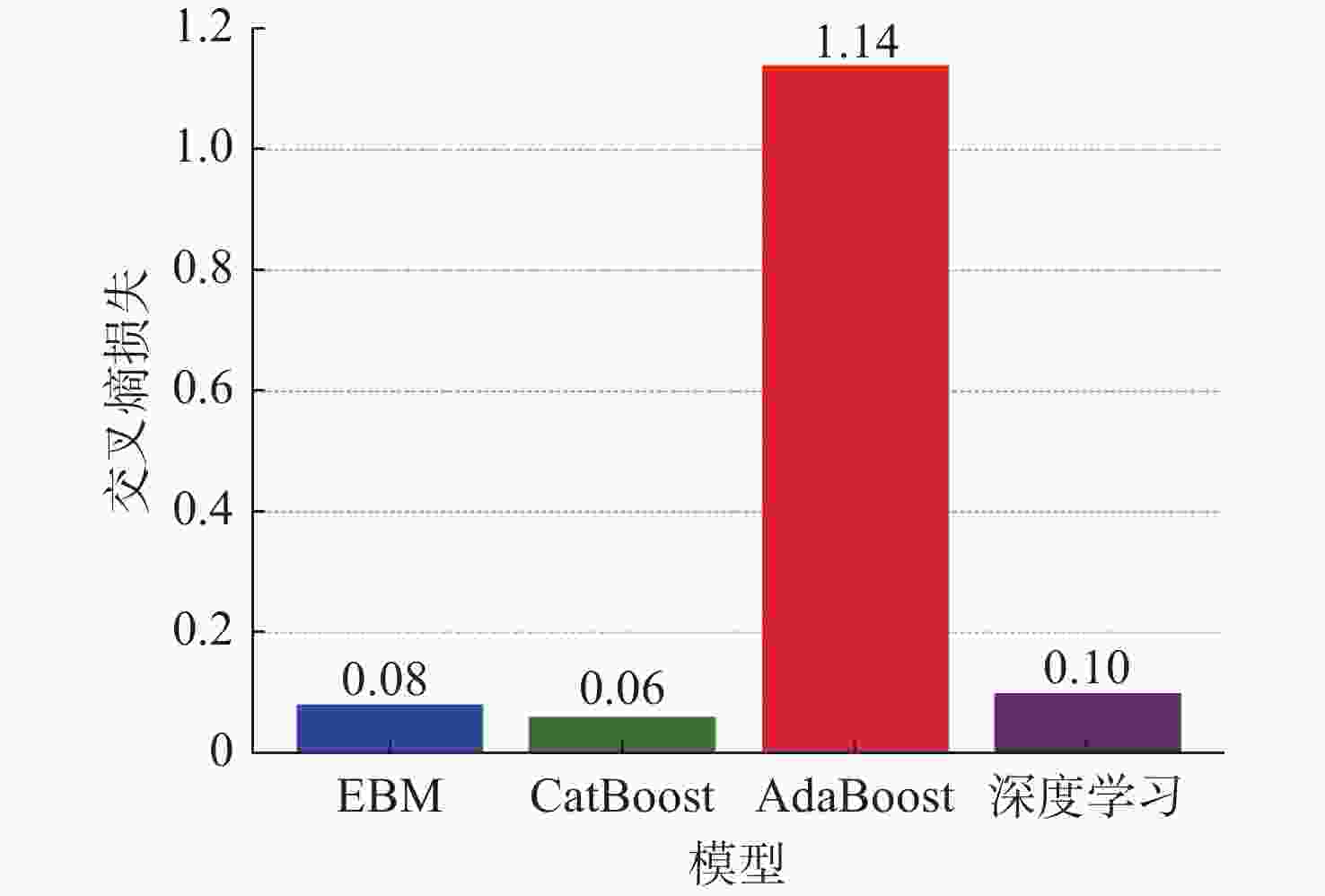
摘要: 针对传统的目标威胁评估方法处理复杂战场态势数据时, 缺乏数据挖掘能力和神经网络算法解释性不足等问题, 提出基于可解释增强机(EBM)的无人水下航行器(UUV)对目标威胁评估模型。EBM作为一种先进的机器学习技术, 巧妙融合了梯度提升与广义加性模型, 实现了线性模型的高可解释性与梯度提升算法准确性的完美结合。文中对EBM模型的性能进行了全面评估, 并与分类提升、自适应提升以及深度学习等几种主流机器学习方法进行了比较。通过仿真实验发现, EBM模型在保持高可解释性的同时, 对威胁等级识别的准确度也高达98.10%。这一结果不仅验证了EBM模型在复杂战场态势分析中的有效性, 也为UUV的自主决策提供了坚实的理论基础和技术支持。Abstract: In order to solve the problems of lack of data mining ability and insufficient explanatory nature of neural network algorithms when traditional target threat assessment methods process complex battlefield situation data, this paper proposed a threat assessment model for unmanned undersea vehicles(UUVs) based on explainable boosting machine(EBM). As an advanced machine learning technology, EBM cleverly integrates gradient boosting and generalized additive model to achieve the perfect combination of high interpretability of linear model and accuracy of gradient boosting algorithm. In this paper, the performance of the EBM model was comprehensively evaluated and compared with several other mainstream machine learning methods, including classification enhancement, adaptive enhancement, and deep learning. The simulation experiments find that the EBM model not only maintains high interpretability but also has an accuracy of 98.10% in the identification of threat levels. This result verifies the effectiveness of the EBM model in complex battlefield situation analysis and provides a solid theoretical foundation and technical support for UUV’s autonomous decision-making.
-
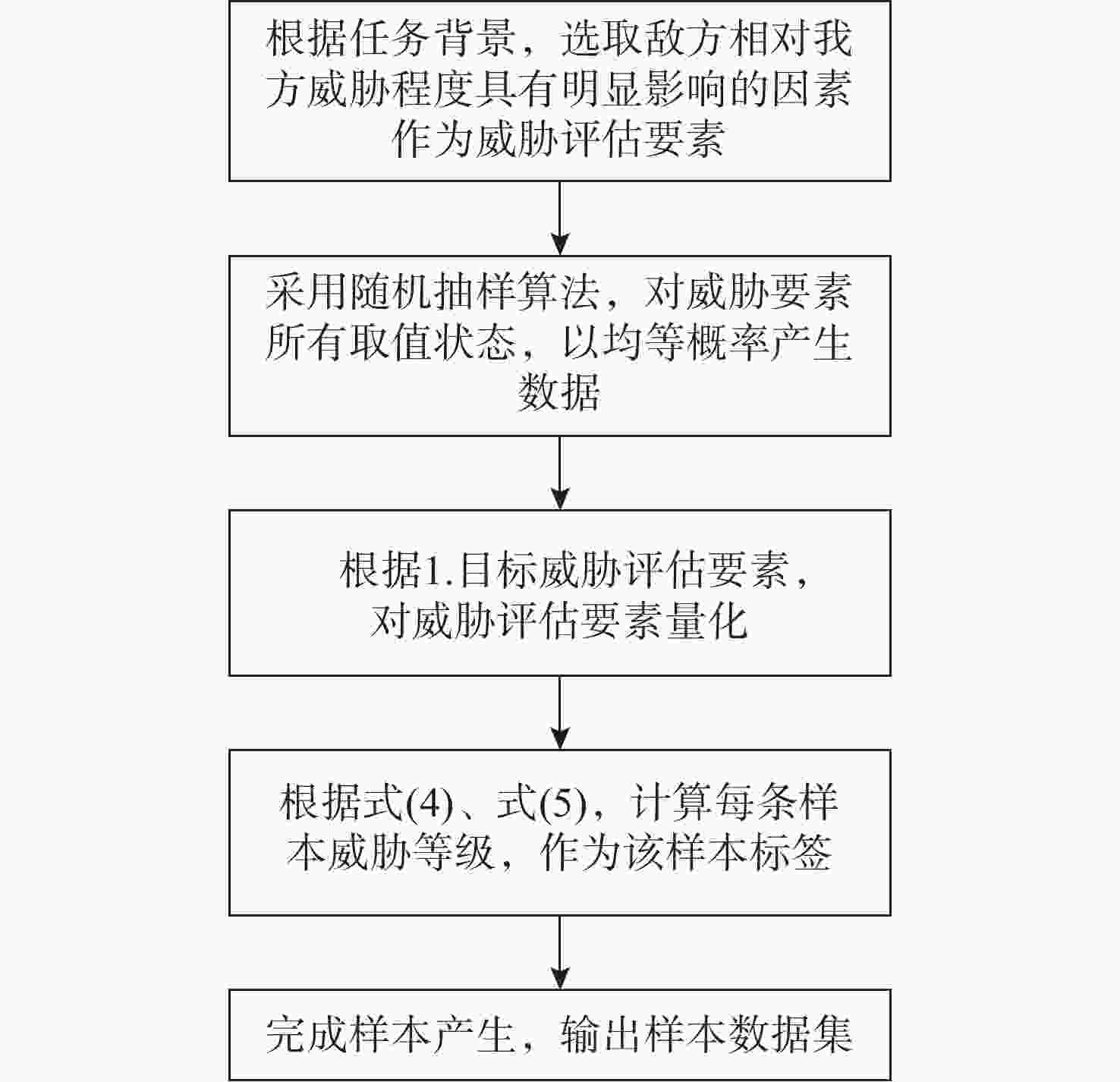
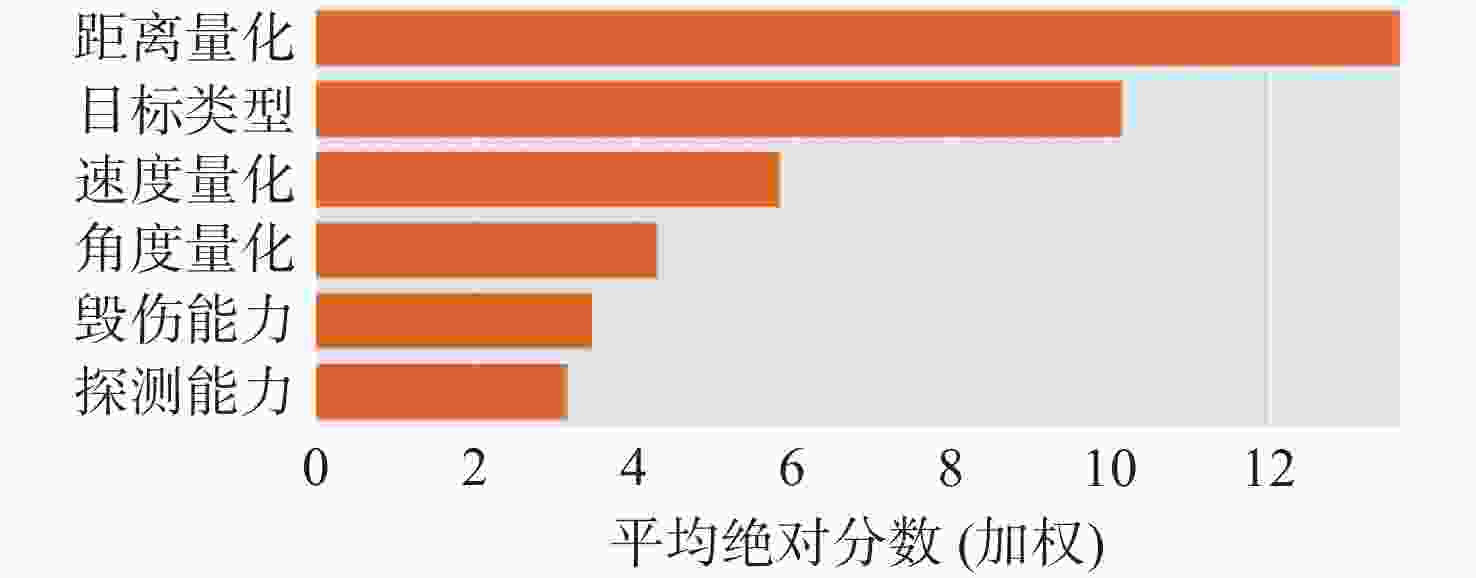
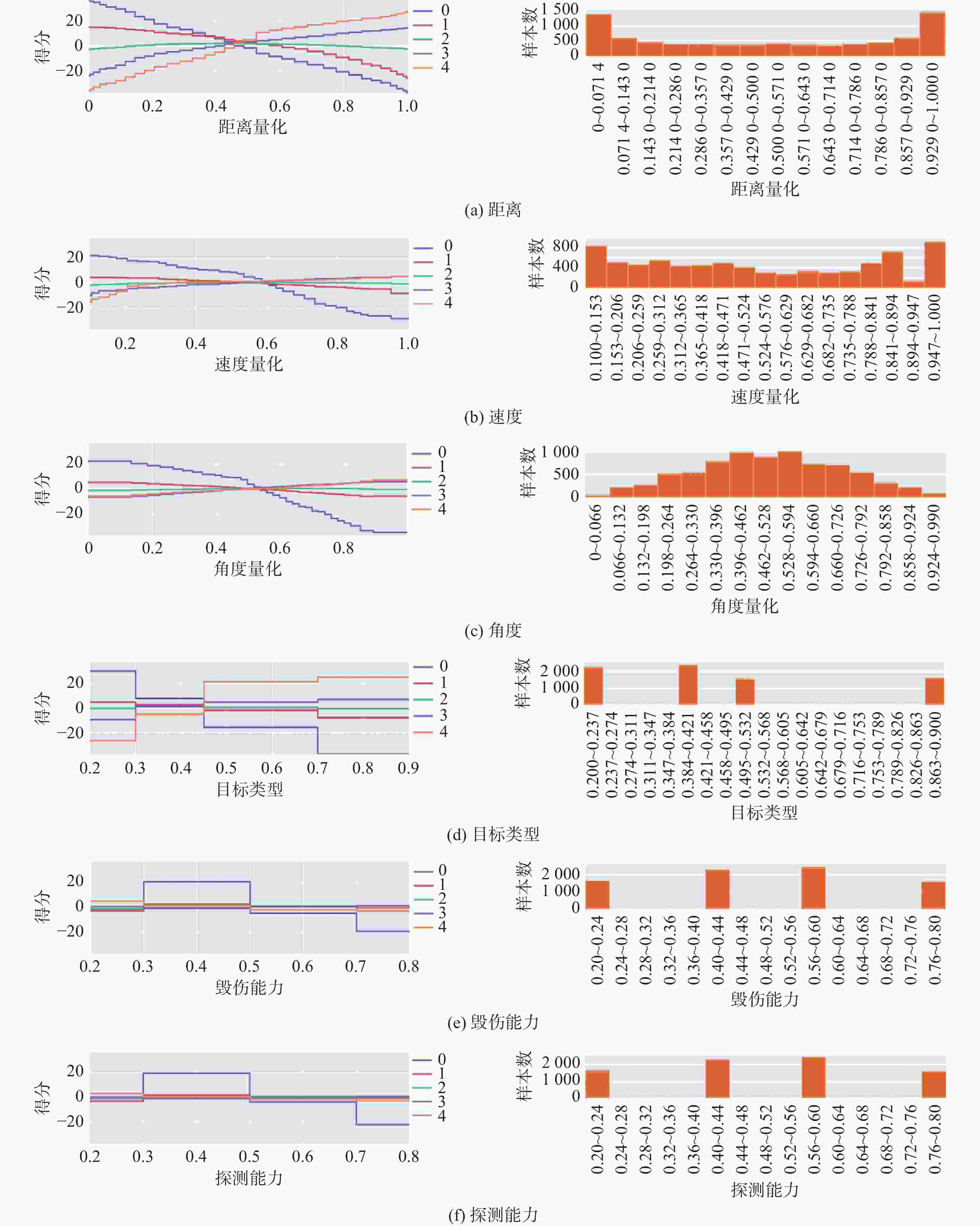
表 1 目标类型特点及威胁度量化表
Table 1. Characteristics of target types and threat quantification
目标类型 特点 威胁
隶属度巡逻艇 探测能力强、携带武器多、隐蔽性弱 0.5 鱼雷 航速大、体积小、杀伤力强、隐蔽性较强 0.9 USV 航速较大、隐蔽性较弱 0.4 中型UUV 航速小、隐蔽性强 0.2 表 2 目标毁伤能力威胁度量化表
Table 2. Quantification of the threat of target damage capability
目标类型 巡逻艇 USV UUV 鱼雷 毁伤能力 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 表 3 目标探测能力威胁度量化表
Table 3. Quantification of the threat of target detection capabilities
目标类型 巡逻艇 USV UUV 鱼雷 探测能力 0.8 0.4 0.6 0.2 表 4 部分样本数据
Table 4. Partial sample data
目标
类型毁伤
能力探测
能力距离
量化速度
量化角度
量化威胁
等级USV 0.6 0.6 0.1 0.41 0.42 1 巡逻艇 0.8 0.8 0.83 0.95 0.32 3 UUV 0.4 0.4 0.1 0.1 0.24 0 鱼雷 0.2 0.2 0.56 0.17 0.93 4 表 5 EBM模型参数设置
Table 5. Parameter settings of the EBM model
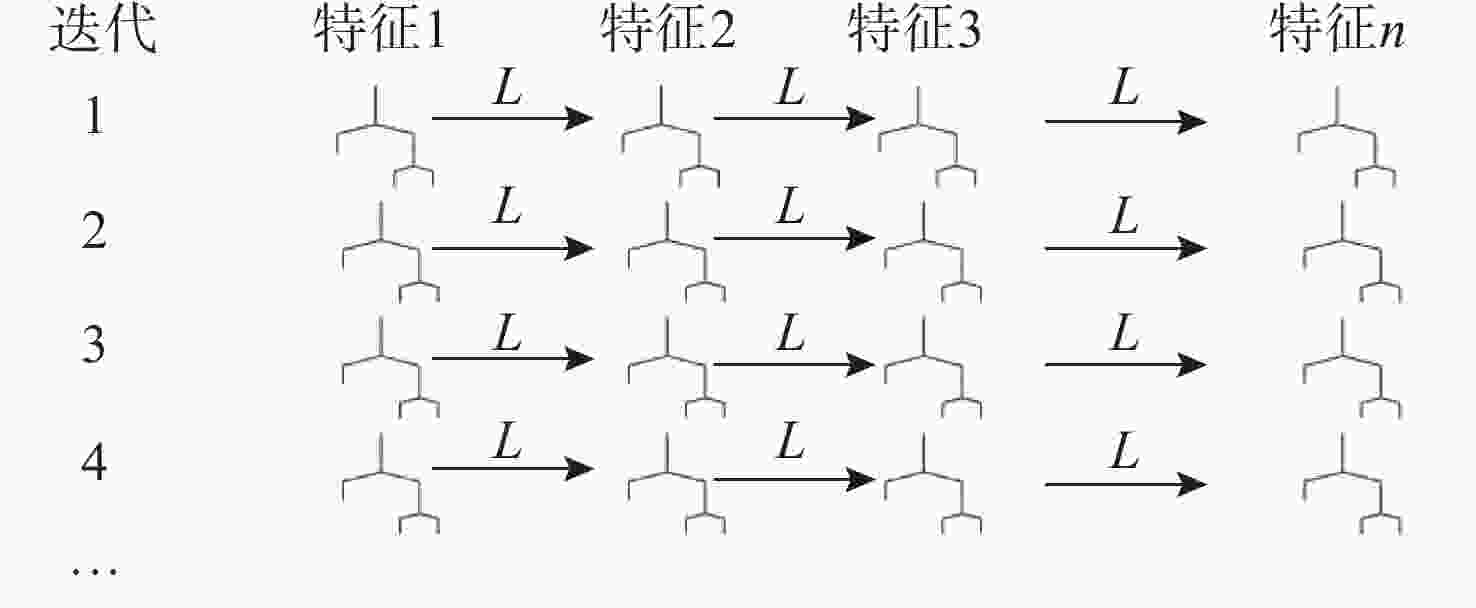
参数 值 参数 值 输入特征个数 6 学习率 0.35 输出节点个数 5 最大分箱数 35 最大叶子数 2 外袋数量 1 最小海森值 0.5 链接函数 $ \mathrm{Soft}\max $ -
[1] 汤志荔, 张安. 战场威胁估计理论与方法研究[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2011, 36(9): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2011.09.001TANG Z L, ZHANG A. Survey of methods and theory for battlefield threat assessment[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2011, 36(9): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2011.09.001 [2] 董泽委. 陆战场低空多域场景下的集群目标威胁动态评估[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 64(8): 1380-1390.DONG Z W. Dynamic assessment of swarm target threat in low-altitude multi-domain scenario of land battlefield[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 64(8): 1380-1390. [3] 郭佳. 基于多属性决策的空中目标威胁评估方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2017. [4] 冯卉, 宋宝军, 张春梅. 基于改进灰色关联法的空袭目标威胁评估方法[J]. 运筹与管理, 2023, 32(9): 1-6.FENG H, SONG B J, ZHANG C M. Threat assessment method of air raid target based on improved grey correlation method[J]. Operations Research and Management, 2023, 32(9): 1-6. [5] 王光源, 李浩民, 祝大程, 等. 基于熵权法-灰色关联法的海目标威胁度评估[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2023, 45(4): 57-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2023.04.009WANG G Y, LI H M, ZHU D C, et al. Threat assessment of sea surface targets based on entropy weight method-grey correlation method[J]. Command & Control & Simulation, 2023, 45(4): 57-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2023.04.009 [6] 李丹一. 基于贝叶斯网络的水下威胁评估方法研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2021. [7] 李叶. 基于贝叶斯网络的战场目标威胁评估方法研究[D]. 西安: 西安工业大学, 2022. [8] 方伟, 张婷婷, 余应福, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的单机空战威胁评估[J]. 电子设计工程, 2023, 31(23): 12-16, 21.FANG W, ZHANG T T, YU Y F, et al. Threat assessment of stand-alone air combat based on convolutional neural network[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2023, 31(23): 12-16, 21. [9] 杨童瑶, 杨风暴, 吉琳娜. 基于行为意图的海上目标动态威胁评估[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2021, 43(6): 84-91, 100.YANG T Y, YANG F B, JI L N. Dynamic threat assessment of maritime targets based on behavioral internet[J]. Journal of Detection and Control, 2021, 43(6): 84-91, 100. [10] 翟翔宇, 杨风暴, 吉琳娜, 等. 标准化全连接残差网络空战目标威胁评估[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2020, 45(6): 39-44.ZHAI X Y, YANG F B, JI L N, et al. Standardized fully connected residual network air combat target threat assessment[J]. Firepower and Command Control, 2020, 45(6): 39-44. [11] 柴慧敏, 张勇, 李欣粤, 等. 基于深度学习的空中目标威胁评估方法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2022, 34(7): 1459-1467.CHAI H M, ZHANG Y, LI X Y, et al. Threat assessment method for air targets based on deep learning[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2022, 34(7): 1459-1467. [12] 吕少楠. 基于深度学习的态势评估方法[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2020. [13] 江达伟, 董阳阳, 张立东, 等. 基于深度学习的空中目标威胁评估技术研究[EB/OL]. [2025-01-16]. https://doi.org/10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.23-1323.JIANG D W, DONG Y Y, ZHANG L D, et al. Research on threat assessment technology of air targets based on deep learning[EB/OL]. [2025-01-16]. https://doi.org/10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.23-1323. [14] 周鑫, 徐荣武, 程果, 等. 基于OTPA声源级估计的被动声呐探测距离评估方法[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2022, 17(4): 114-120, 133.ZHOU X, XU R W, CHENG G, et al. Passive sonar detection range evaluation method based on OTPA source level estimation[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2022, 17(4): 114-120, 133. [15] 徐齐胜, 许可乐, 窦勇, 等. 基于被动声呐音频信号的水中目标识别综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(4): 649-673.XU Q S, XU K L, DOU Y, et al. A review of underwater target recognition based on passive sonar audio signal[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(4): 649-673. [16] 张延风, 刘建书, 张士峰. 基于层次分析法和熵值法的目标多属性威胁评估[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2019, 39(2): 163-165.ZHANG Y F, LIU J S, ZHANG S F. Multi-attribute threat assessment of targets based on analytic hierarchy process and entropy method[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets and Guidance, 2019, 39(2): 163-165. [17] LOU Y, CARUANA R, GEHRKE J. Intelligible models for classification and regression[C]//Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, USA: ACM, 2012: 150-158. [18] REHMAN S, REHMAN E, IKRAM M, et al. Cardiovascular disease(CVD): assessment, prediction and policy implications[J]. BMC Public Health, 2021, 21: 1-14. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-10013-y -




 下载:
下载: