Opportunistic Routing Protocol for Underwater Optical Sensor Networks Based on Fuzzy Logic
-
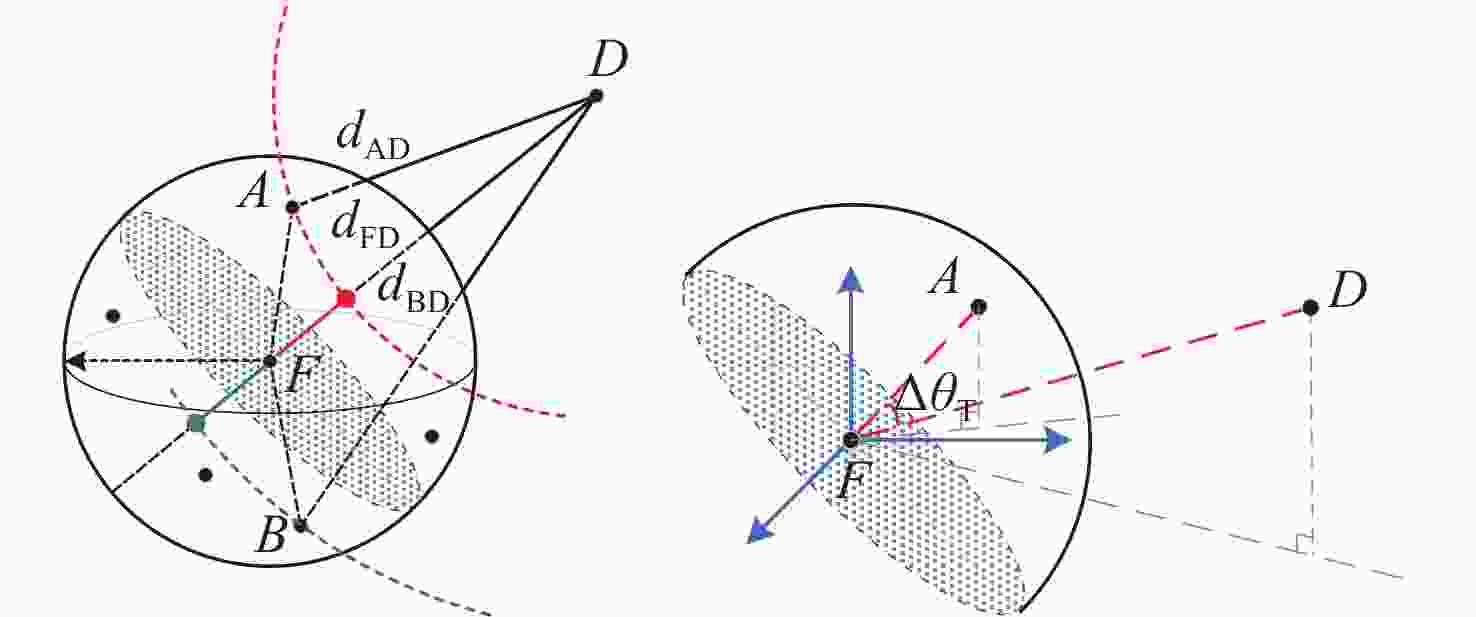
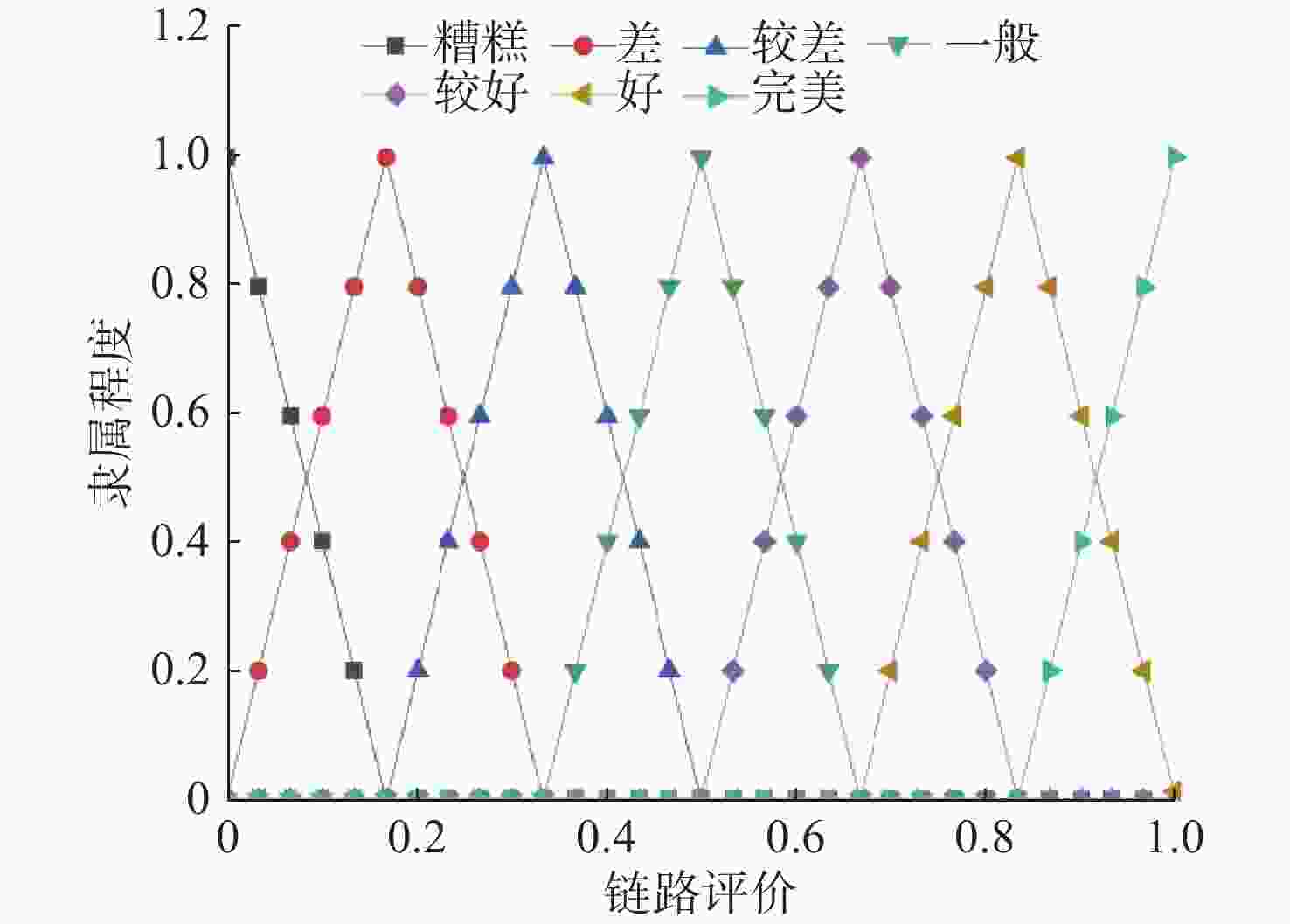
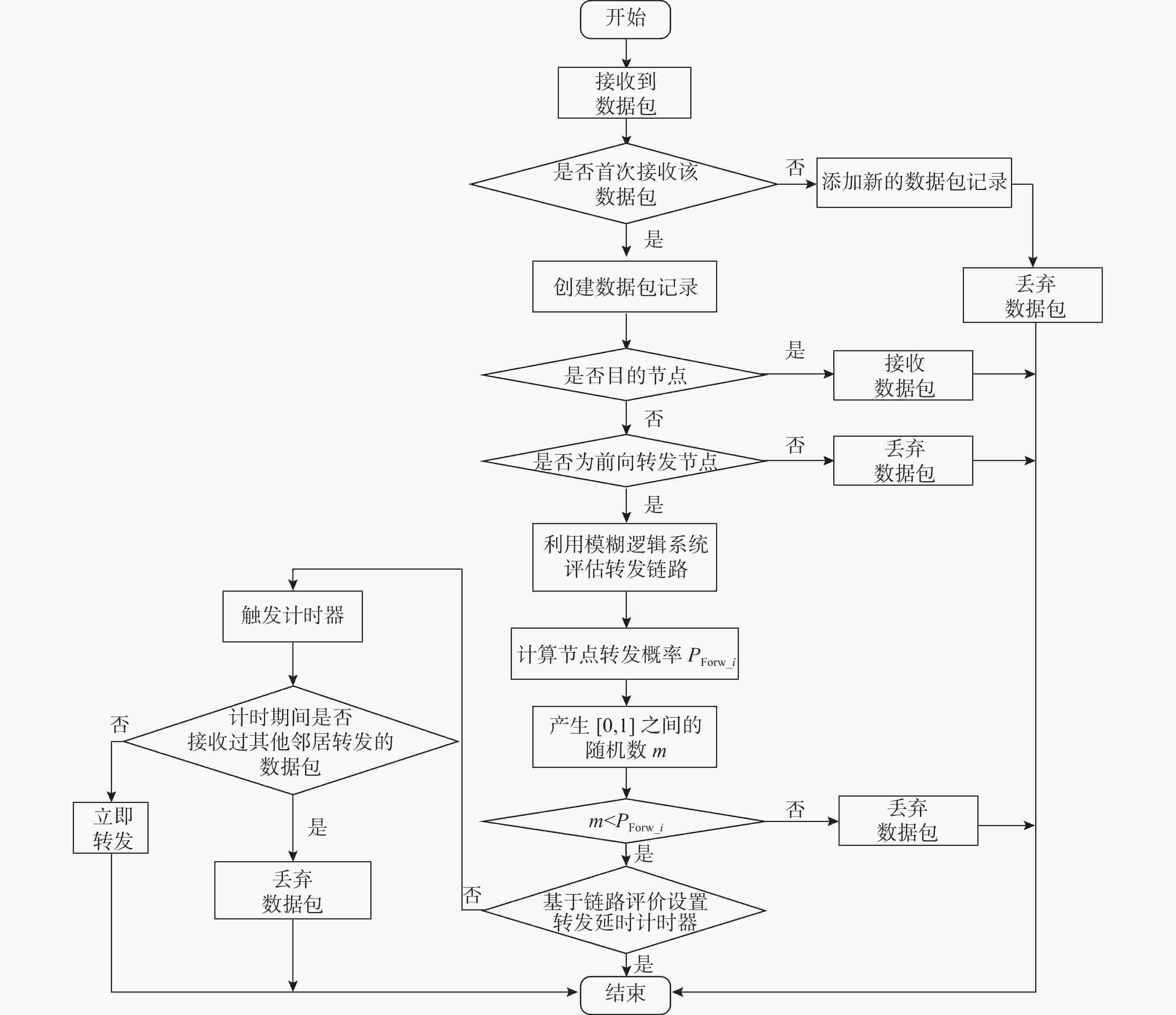
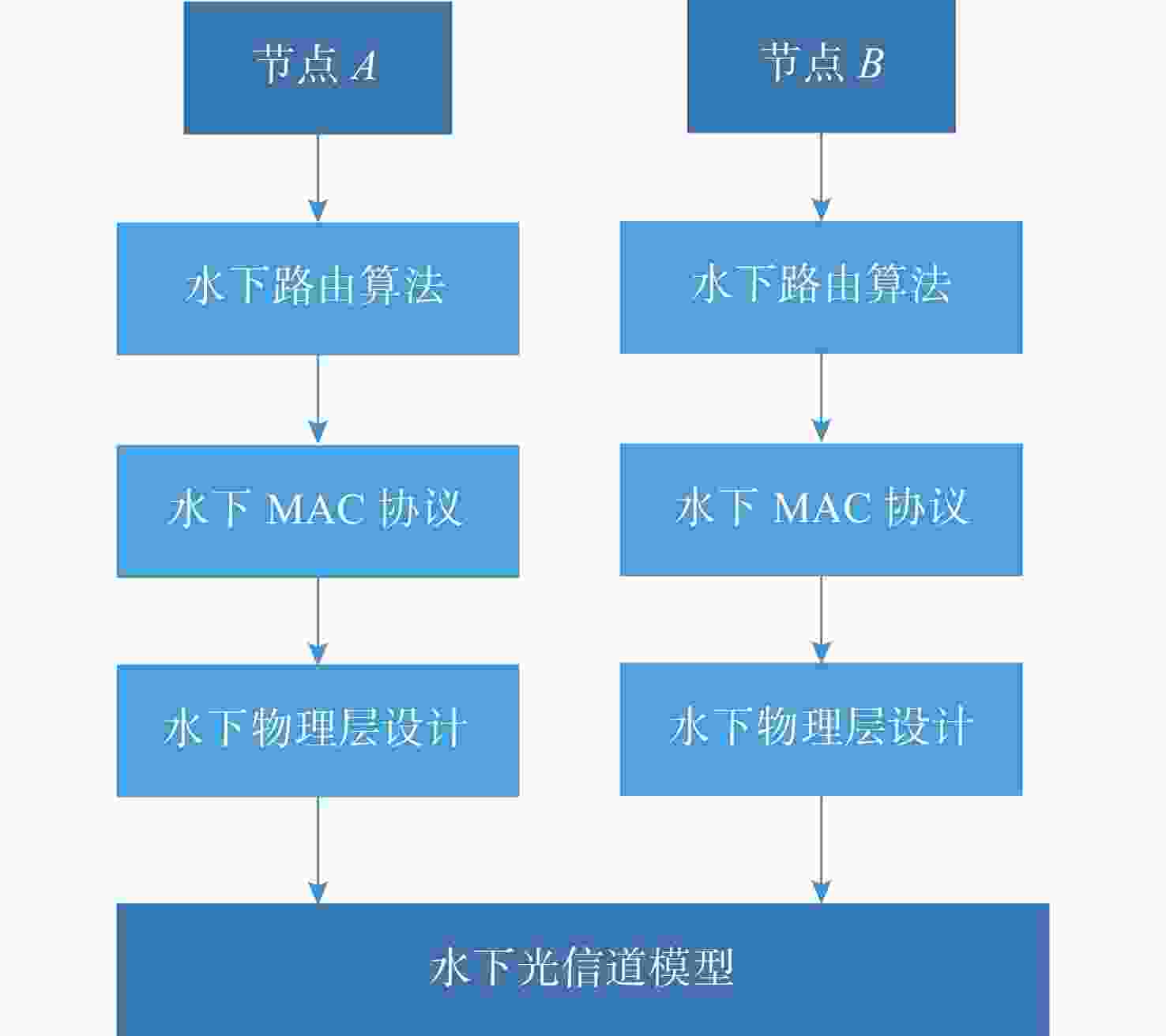
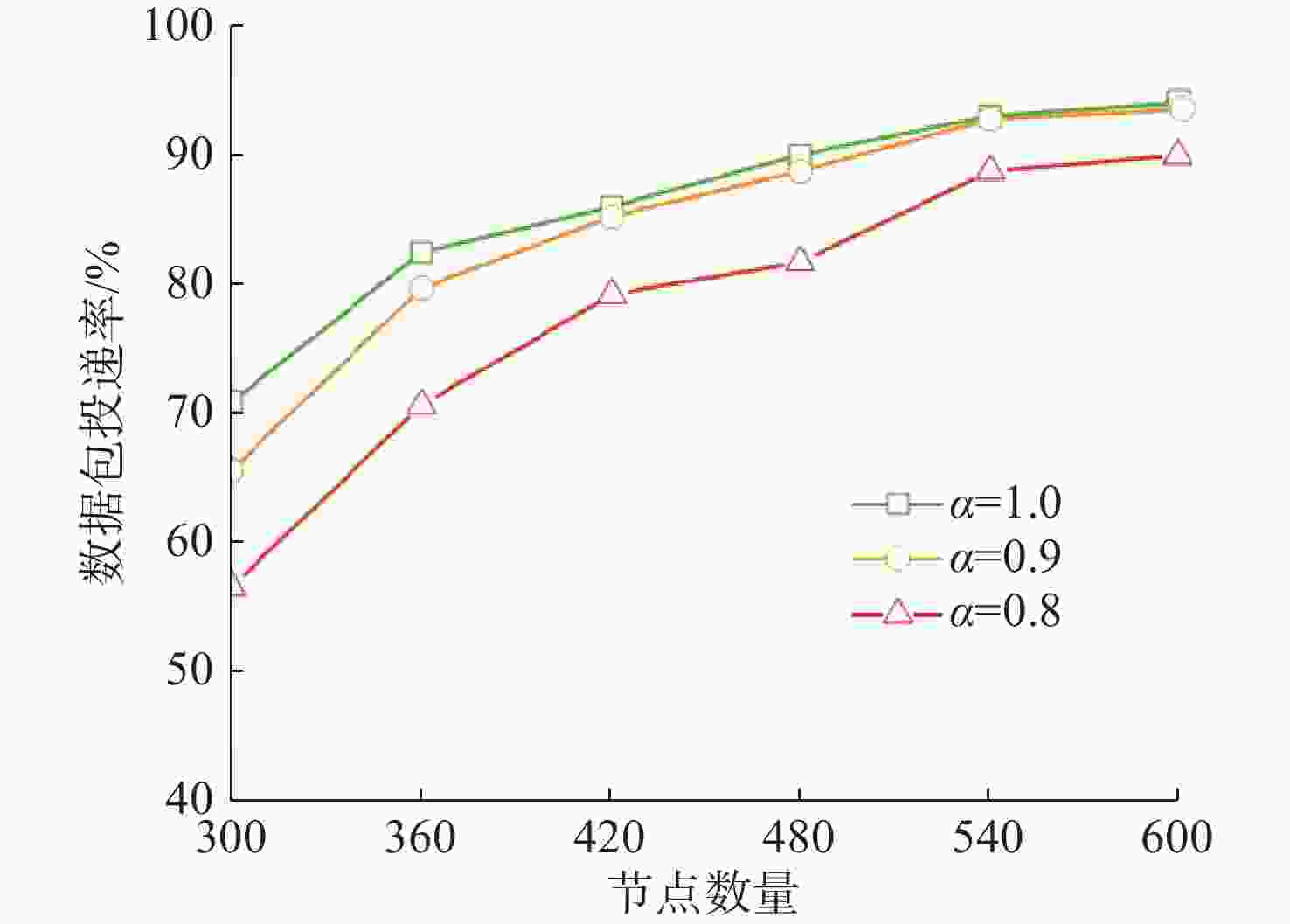
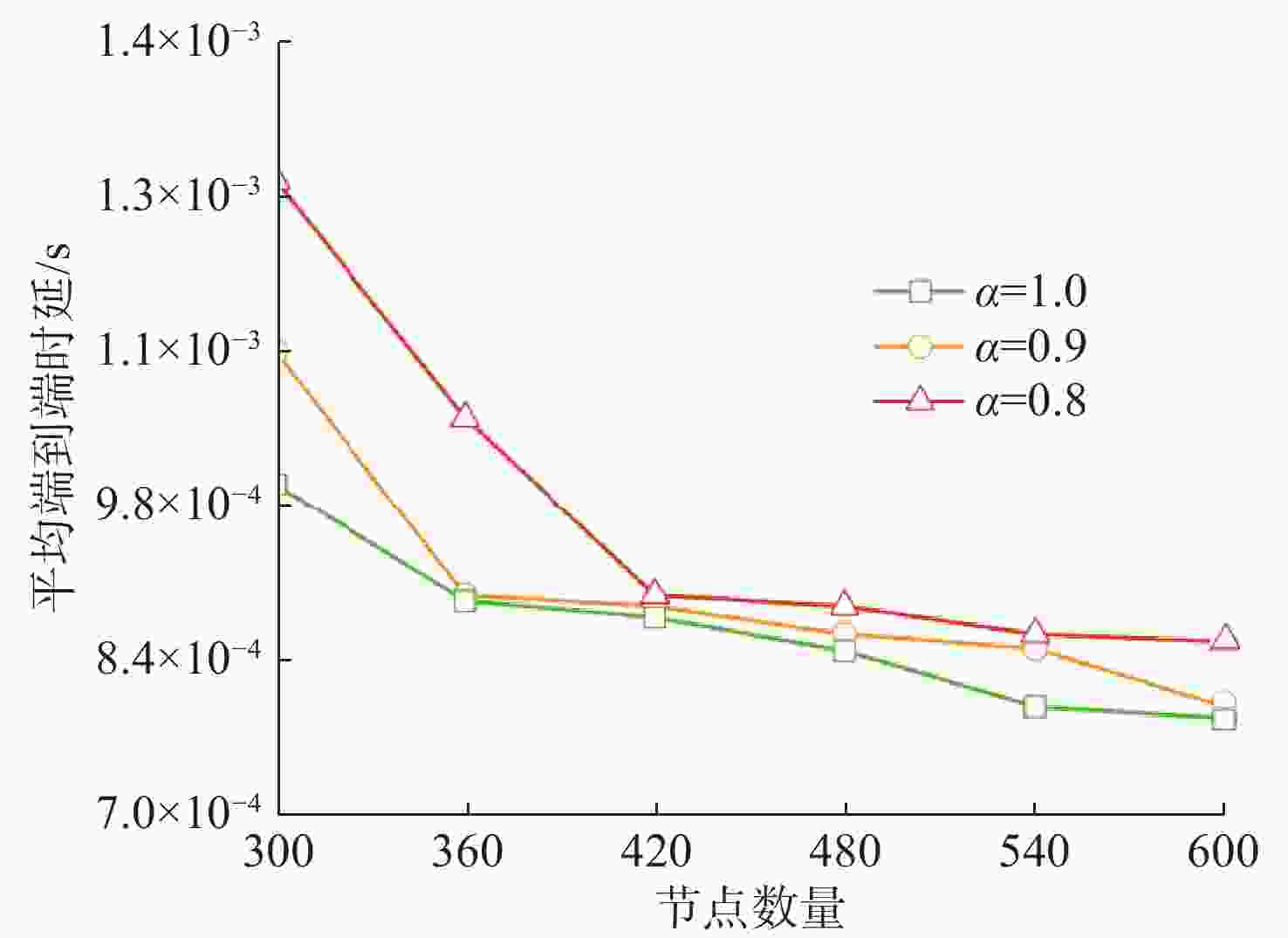
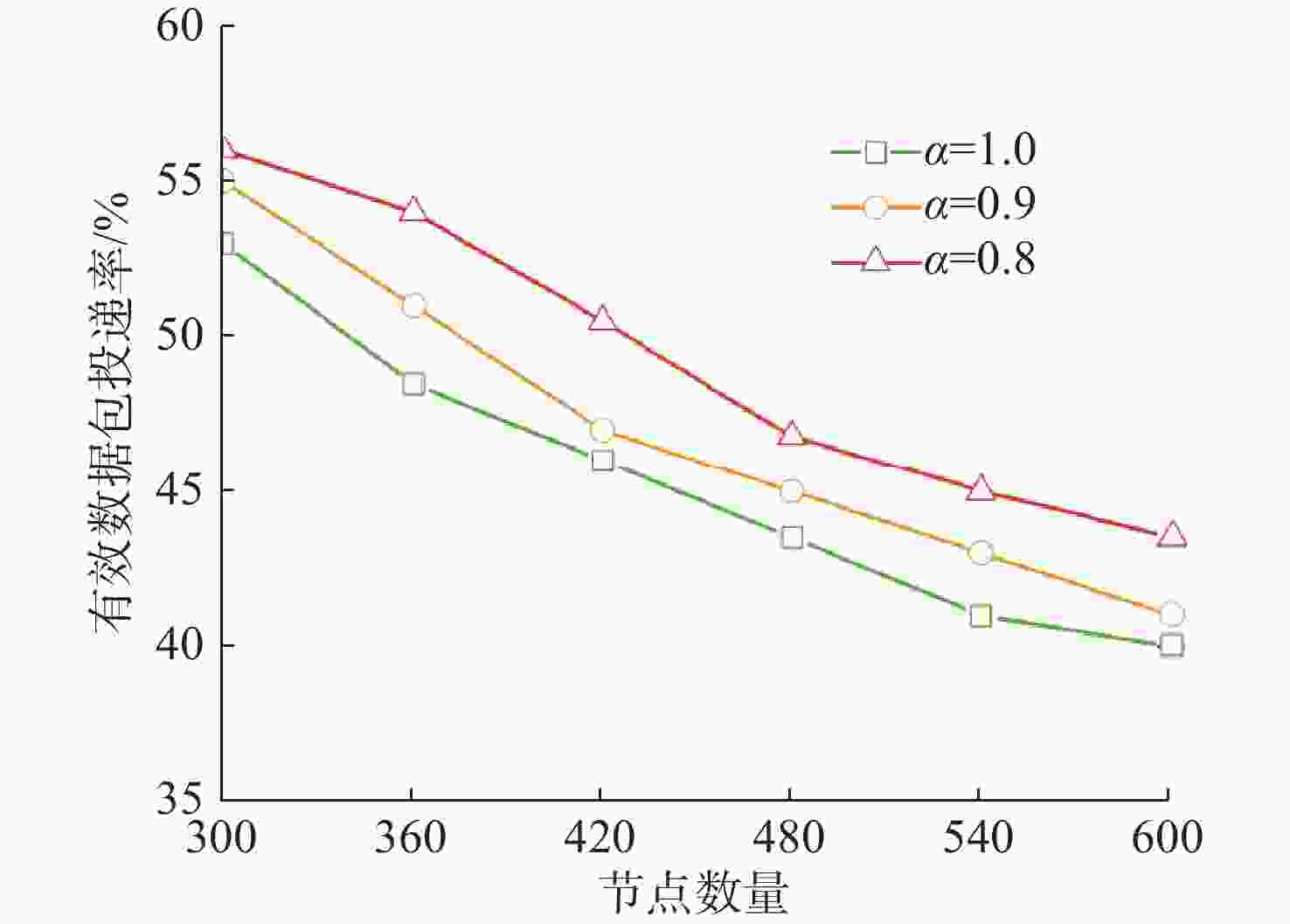
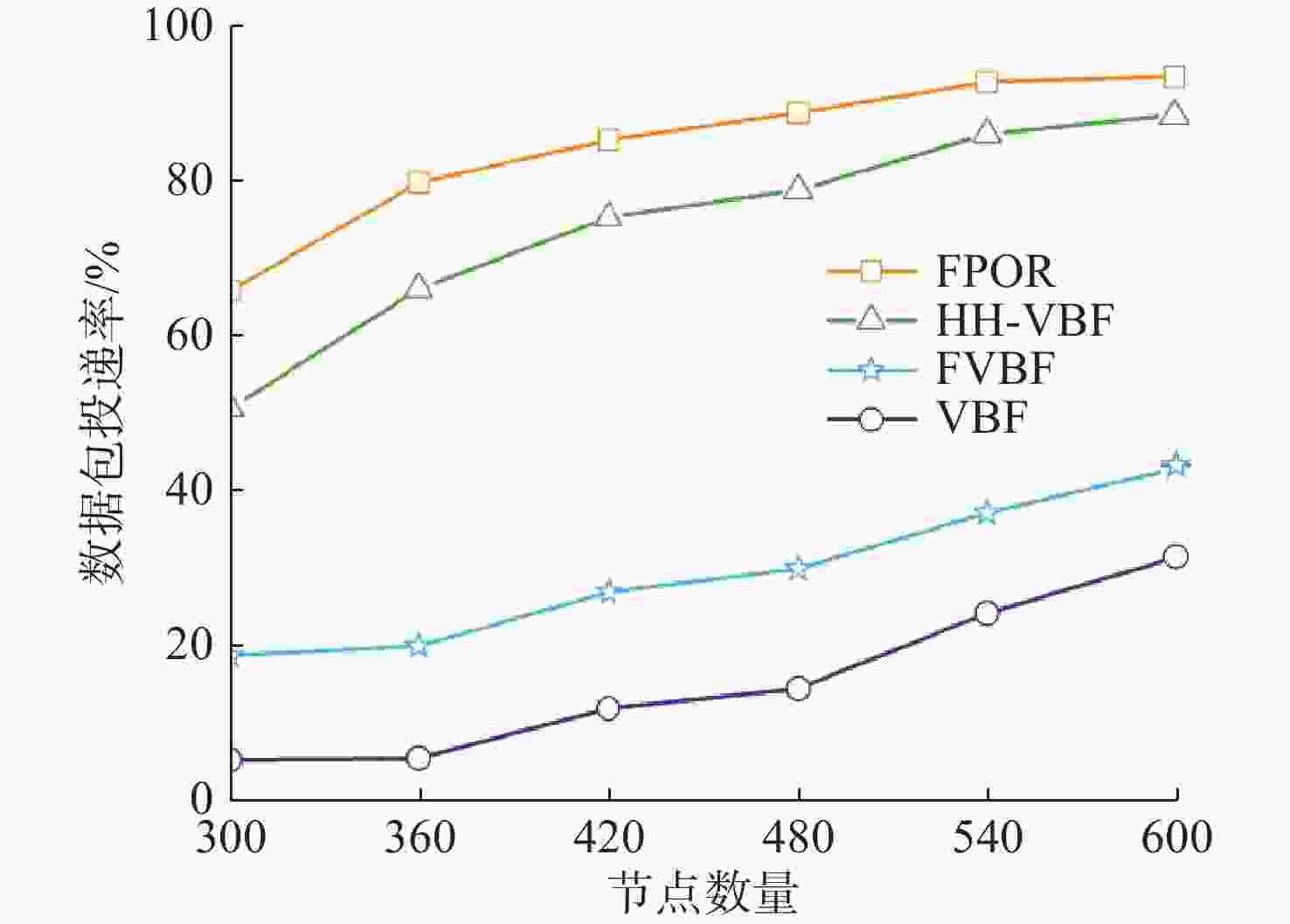
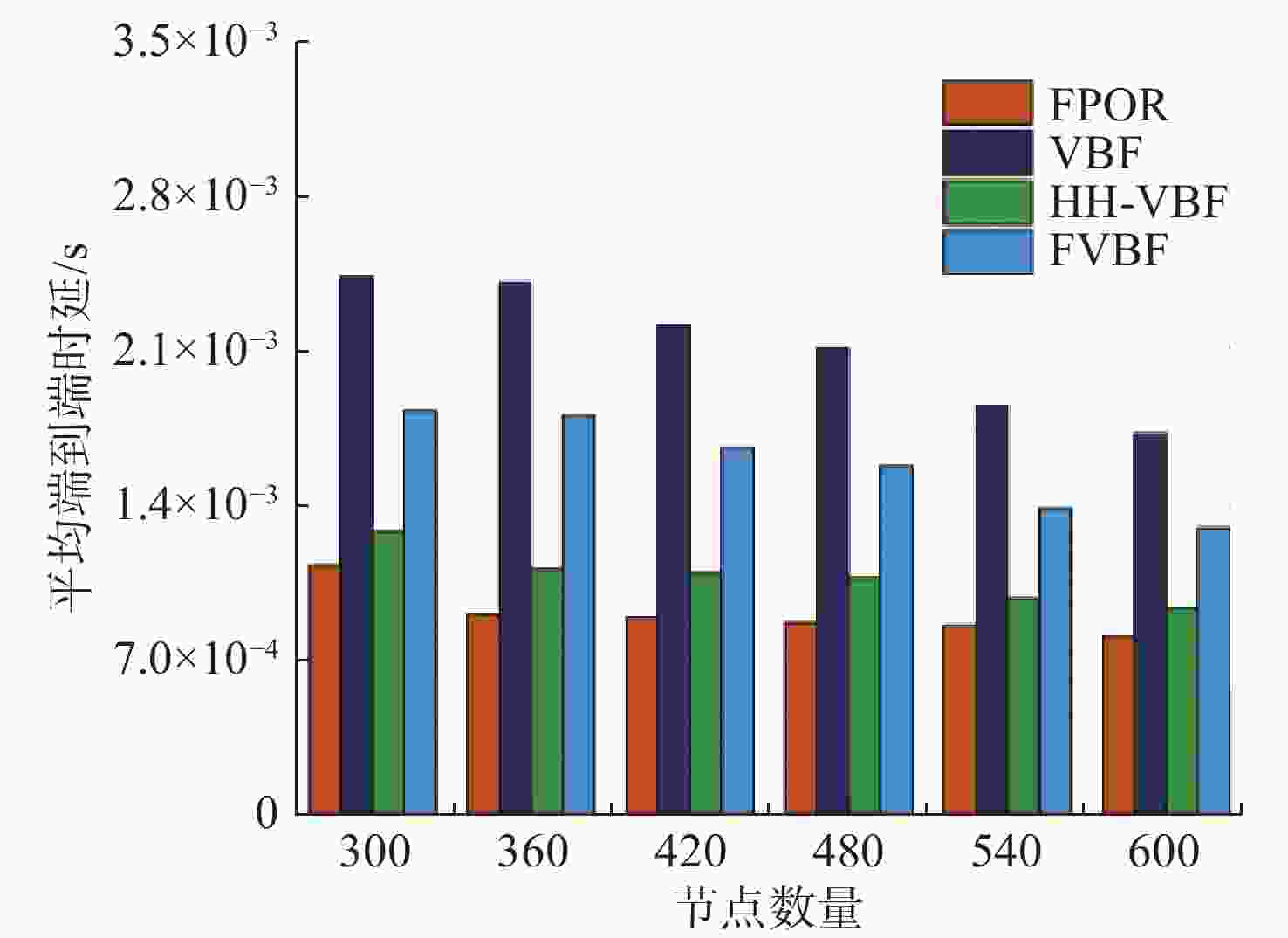
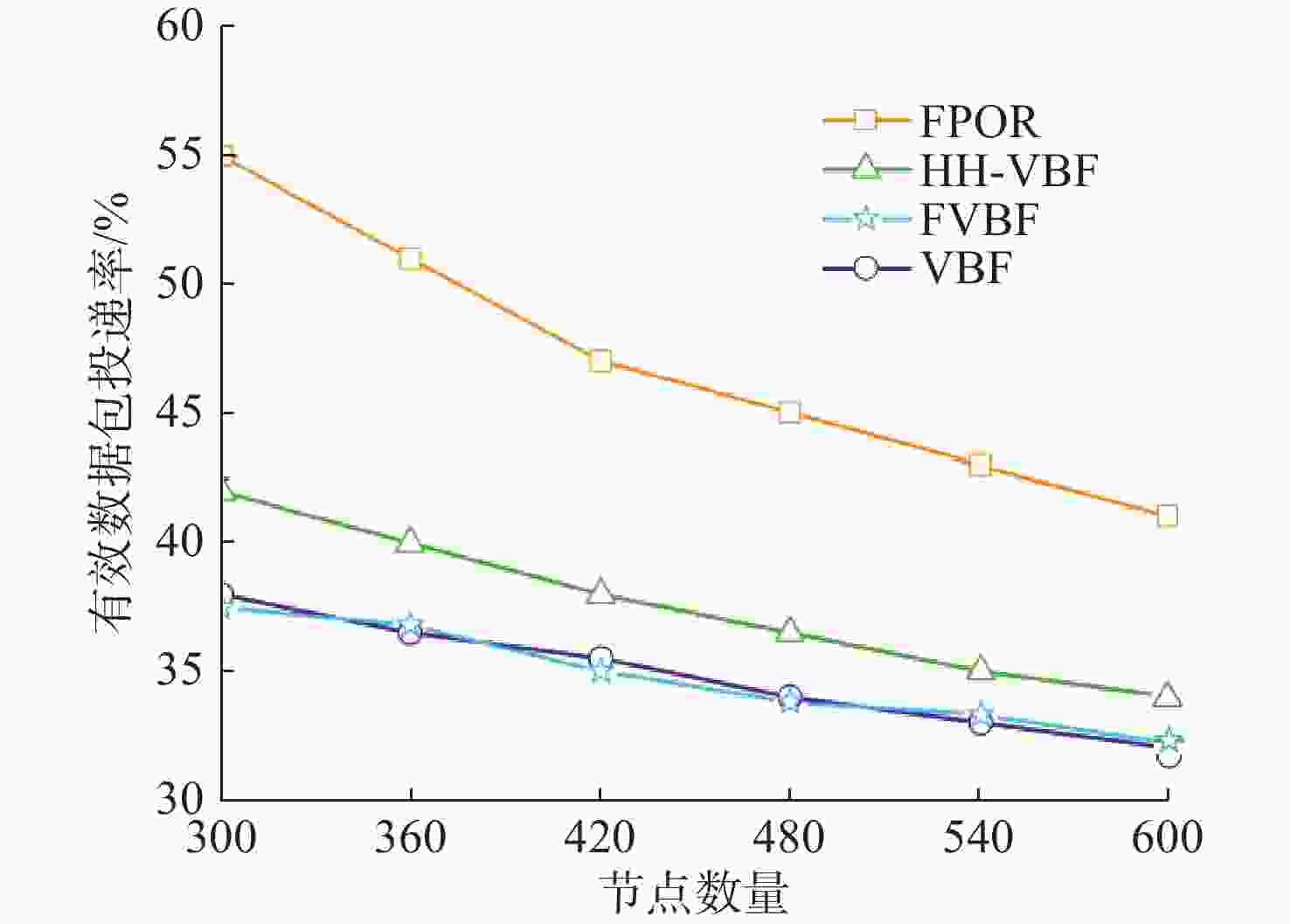
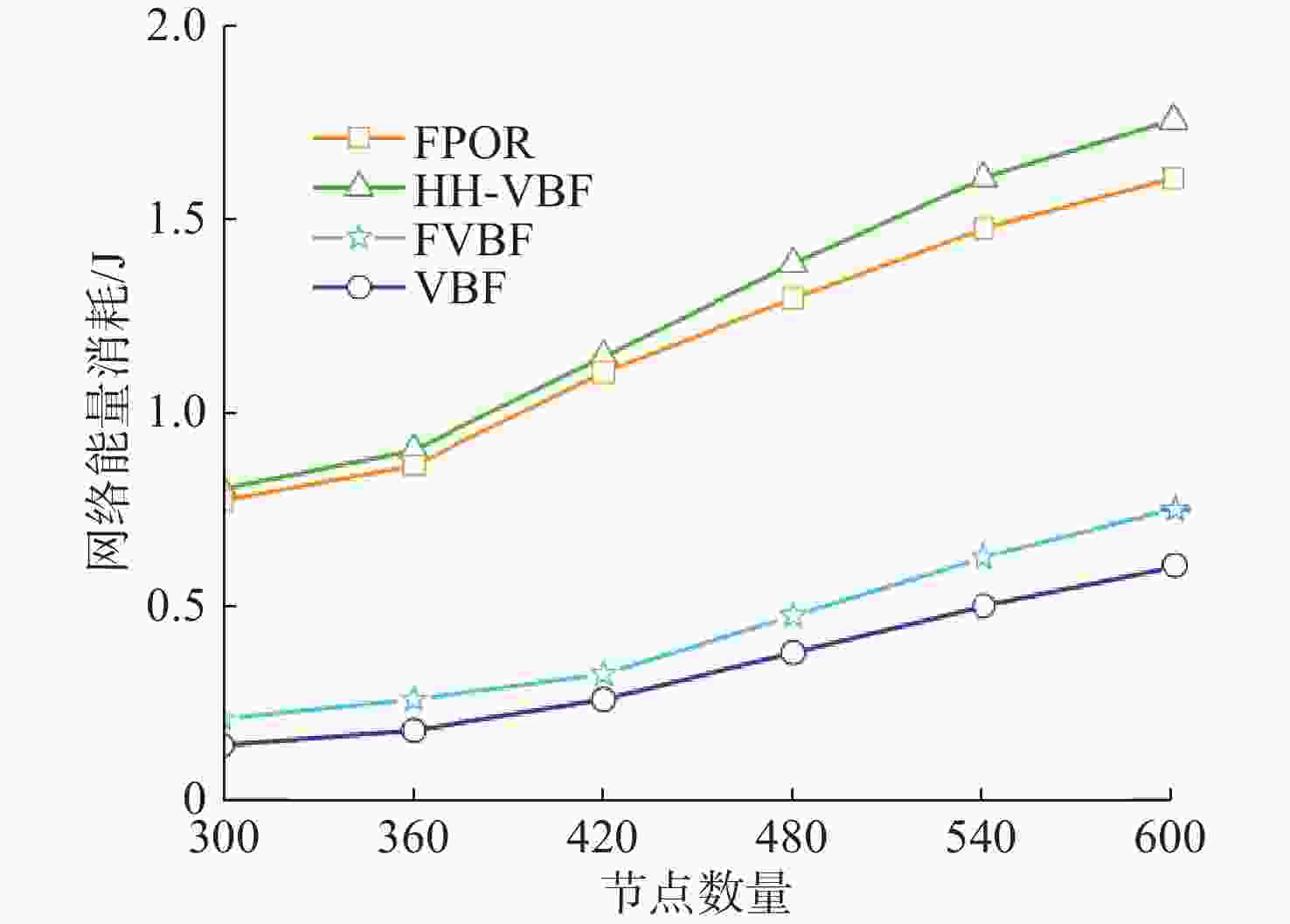
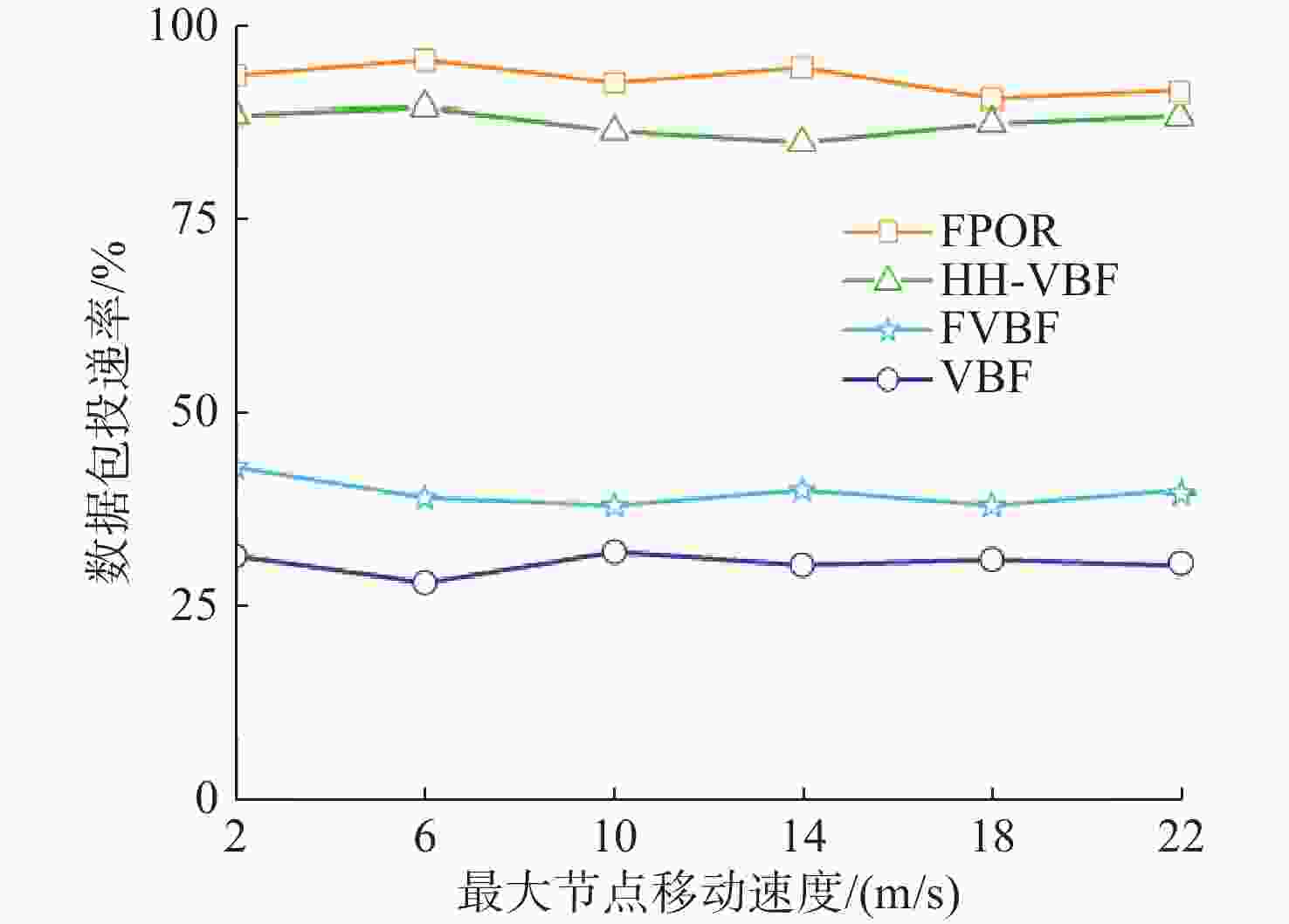
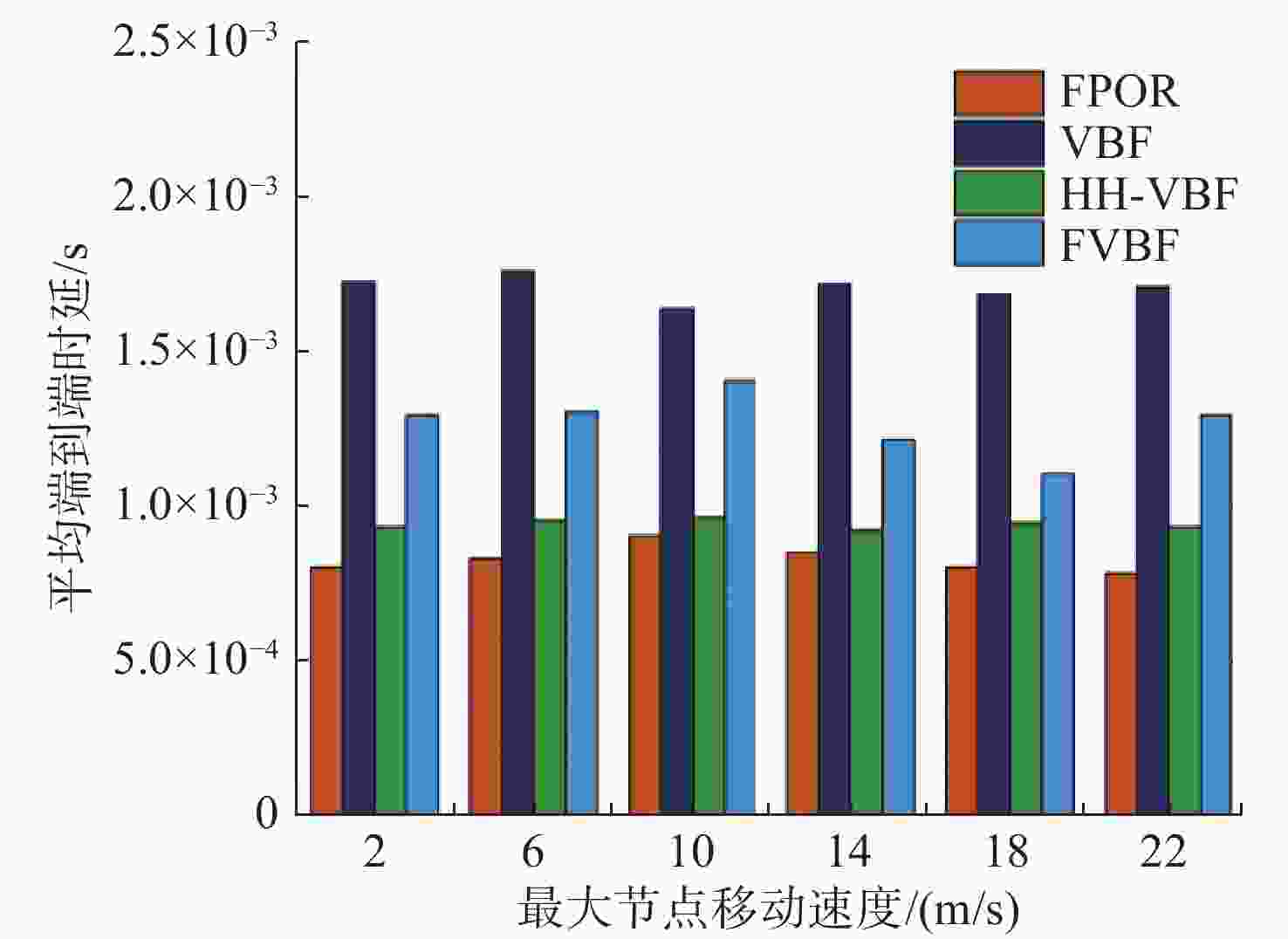
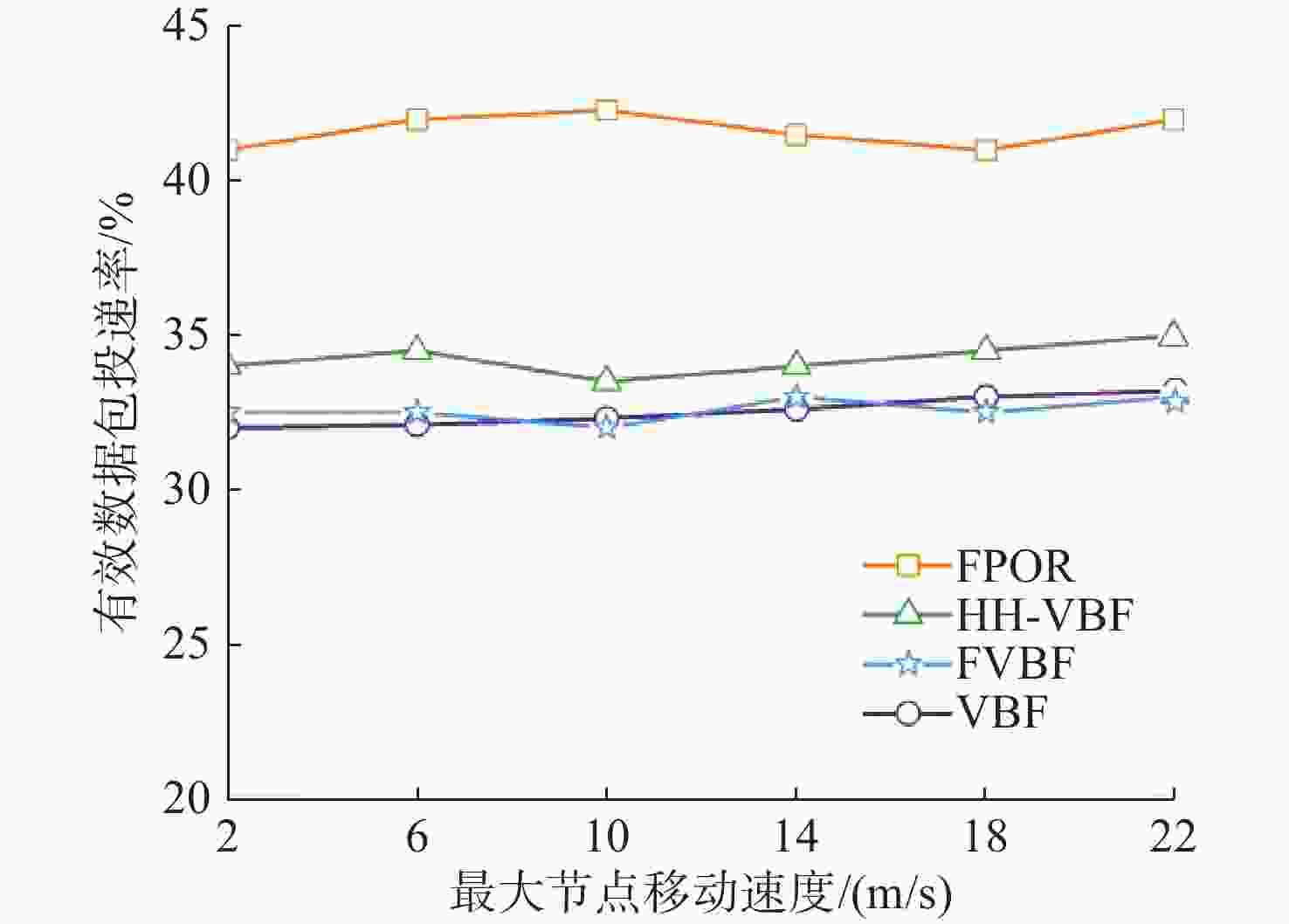
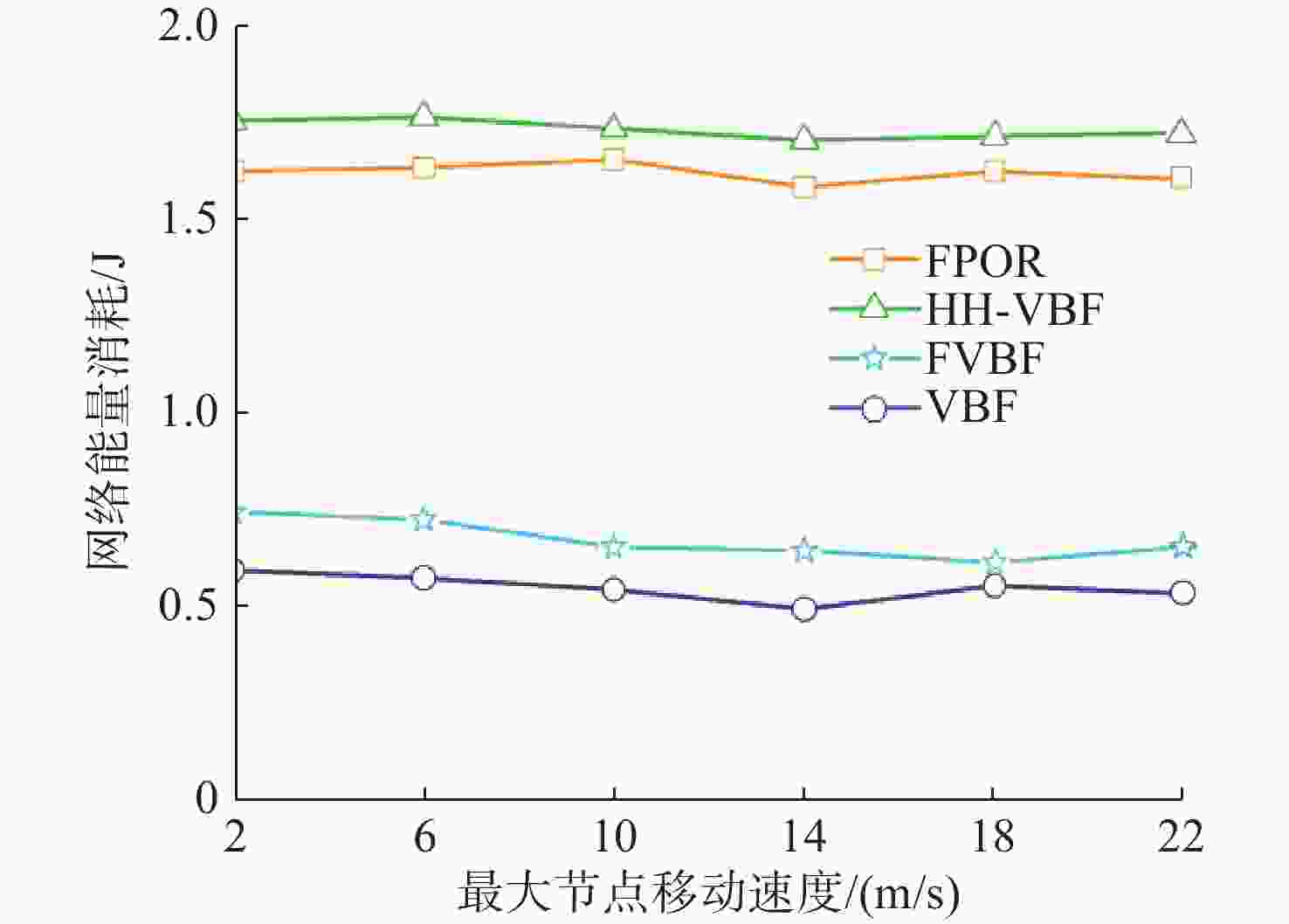
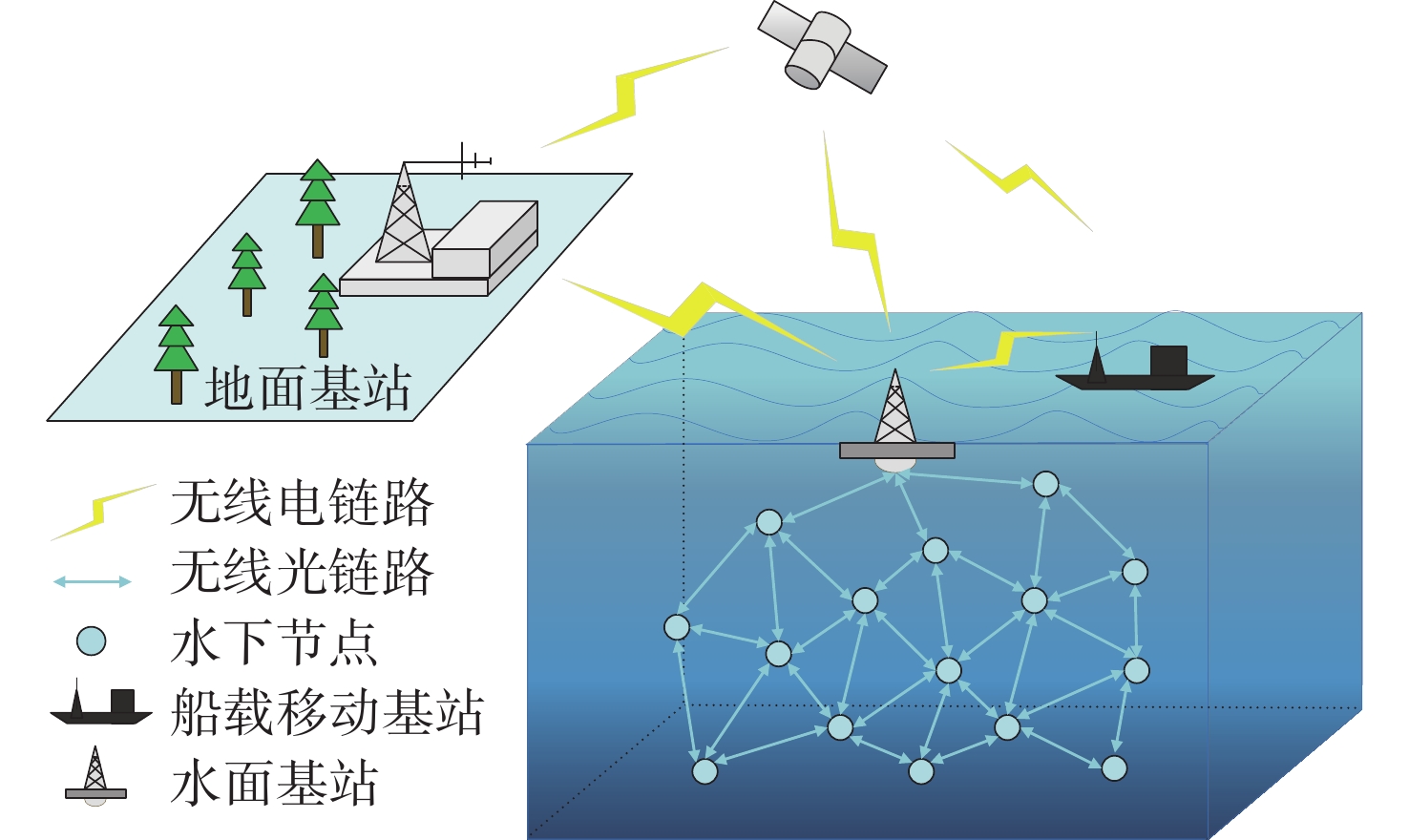
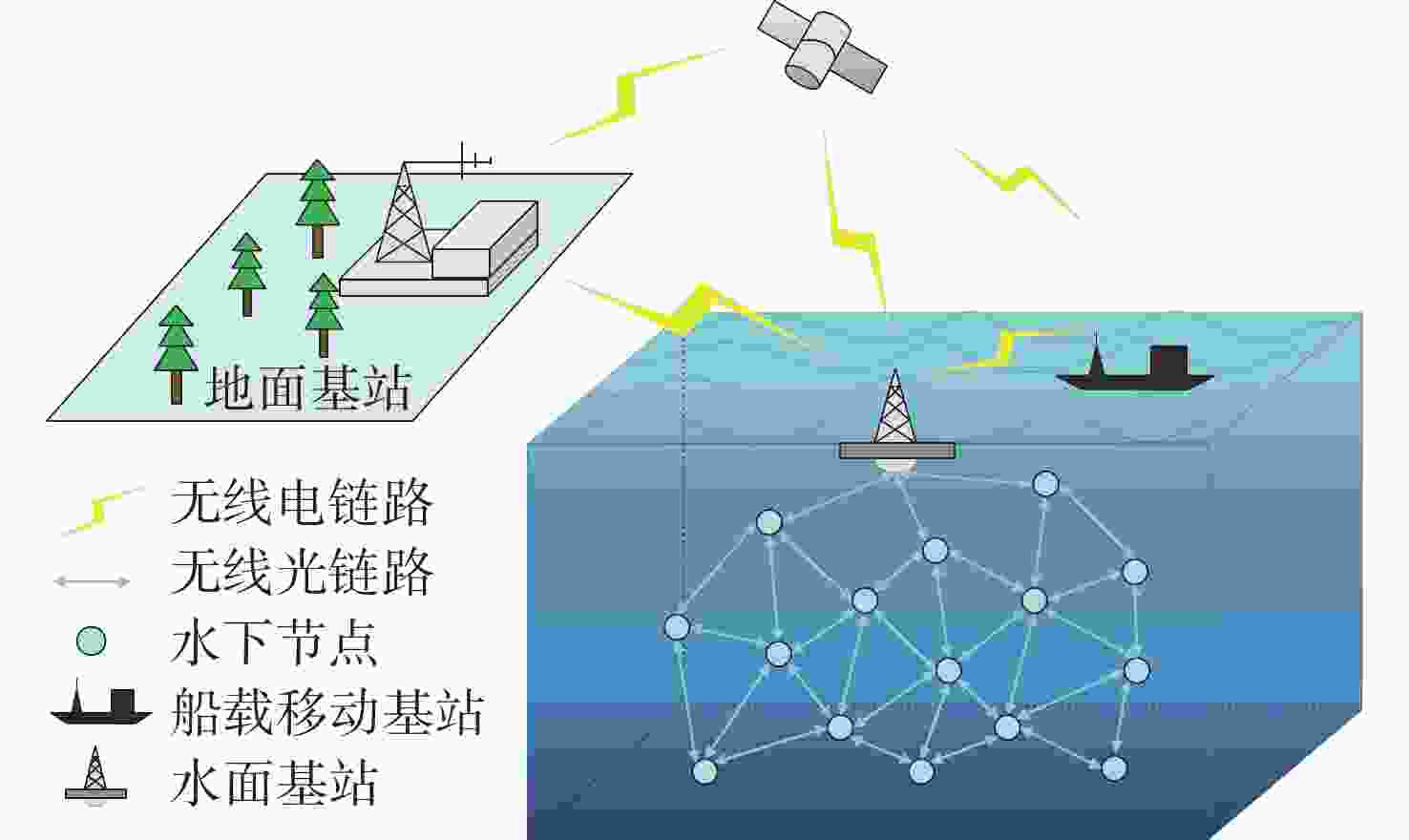
摘要: 水下无线光传感器网络相比传统声传感器网络具有高带宽、低时延等显著优势, 是实现水空跨域通信中水下数据高速实时传输的研究热点。但由于水下光节点的传输易受阻挡且节点需要指向对准等问题, 传统水下传感器网络路由协议不可避免地会出现路由空洞和冗余数据传输情况。针对上述问题, 文中提出了一种基于模糊逻辑的水下无线光传感器网络机会式路由协议。首先, 提出基于模糊逻辑系统的水下光信道链路评价算法, 结合水下复杂通信环境建模, 设计了路由度量指标的多因素融合评估; 然后, 基于实时链路评估数据设计节点, 数据转发概率和数据包保持时间的动态设定机制; 最后, 提出基于概率性的冗余抑制转发算法。仿真结果表明, 在典型海洋通信环境下, 所提路由协议可有效提高传输效率及减少端到端时延, 具有良好的网络动态适应性。
-
关键词:
- 跨域通信; 水下无线光传感器网络 /
- 机会式路由协议 /
- 模糊逻辑
Abstract: Underwater optical sensor networks offer significant advantages over traditional acoustic sensor networks, such as high bandwidth and low latency, making them a research hotspot to realize high-speed and real-time transmission of underwater data in sea-air cross-domain communication. However, traditional routing protocols for underwater sensor networks often encounter problems such as routing holes and redundant data transmission due to the transmission obstruction and directional alignment of underwater optical nodes. To address these issues, a fuzzy logic-based opportunistic routing protocol for underwater optical sensor networks was proposed. Firstly, a fuzzy logic-based algorithm was proposed to evaluate the underwater optical channel links. Combined with the modeling of an underwater complex communication environment, the multi-factor fusion evaluation of routing metrics was designed. Additionally, a dynamic mechanism was designed to set the node data forwarding probability and data packet retention time based on real-time link evaluation data. Finally, a probabilistic redundant suppression forwarding algorithm was proposed. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed routing protocol effectively improves transmission efficiency and reduces end-to-end latency in typical marine communication environments, exhibiting good network dynamic adaptability. -
表 1 水下无线通信技术对比
Table 1. Comparison of underwater wireless communication technologies
通信方式 优势 不足 水声通信 通信距离远 数据传输时延高、带宽受限、对海洋生物有害 水下射频通信 近距离速率适中 通信距离短、传输衰减大、带宽受限 UWOC 容量大、数据传输速率高、 时延低 通信距离较短 表 2 仿真参数设置
Table 2. Simulation parameters setting
参数 数值 网络拓扑空间尺度/m 300×300×300 节点初始能量/mJ 80 平均数据包大小/bit 200 节点的通信半径/m 70 数据速率/(Mbit/s) 10 节点处理1 bit数据耗能/nJ 50 发射功率/W 2 发射效率 0.81 接收效率 0.74 -
[1] FENG J, MA W J, LIU D, et al. Policy-driven autonomic network resource management for observation and detection data[C]//2009 International Conference on High Performance Computing, Networking and Communication Systems(HPCNCS-09). Orlando, FL, USA: ResearchGate, 2009: 132-138. [2] 陈健. 水下传感网络的能量优化组网技术研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2014. [3] 罗续业, 周智海, 曹东, 等. 海洋环境立体监测系统的设计方法[J]. 海洋通报, 2006, 25(4): 69-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2006.04.011LUO X Y, ZHOU Z H, CAO D, et al. Designing method for integrated ocean environmental monitoring system[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2006, 25(4): 69-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2006.04.011 [4] ZENG Z, FU S, ZHANG H, et al. A survey of underwater optical wireless communications[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 2017, 19(1): 204-238. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2016.2618841 [5] LUO J, CHEN Y, WU M, et al. A survey of routing protocols for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(1): 137-160. [6] WANG H, WANG S, ZHANG E, et al. An energy balanced and lifetime extended routing protocol for underwater sensor networks[J]. Sensors. 2018, 18(5): 1596. [7] INTANAGONWIWAT C, GOVINDAN R, ESTRIN D, et al. Directed diffusion for wireless sensor networking [J]. IEEE/ACM Trans, 2003, 11(1): 2-16. [8] WANG Z, HAN G, QIN H, et al. An energy-aware and void-avoidable routing protocol for underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 7792-7801. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2805804 [9] YAN H, SHI Z J, CUI J H. DBR: Depth-Based Routing for Underwater Sensor Networks[J]. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2008, 4982: 72-86. [10] ISMAIL M, ISLAM M, AHMAD I, et al. Reliable path selection and opportunistic routing protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks [J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 100346-100364. [11] DAI Y, JI J, QIU Y. A dual-hop topology-aware routing protocol for underwater optical wireless sensor networks[J]. Optical Switching and Networking, 2022, 45: 100682. doi: 10.1016/j.osn.2022.100682 [12] LI X, HU X, ZHANG R, et al. Routing protocol design for underwater optical wireless sensor networks: A multiagent reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(10): 9805-9818. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2989924 [13] AKYILDIZ I F , POMPILI D, MELODIA T. State of the art in protocol research for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. ACM, 2007, 11(4): 7-16. -




 下载:
下载: