Effect of Hub-to-tip Ratio on Performance of High Speed Pump-jet Propulsor for Undersea Vehicle
-
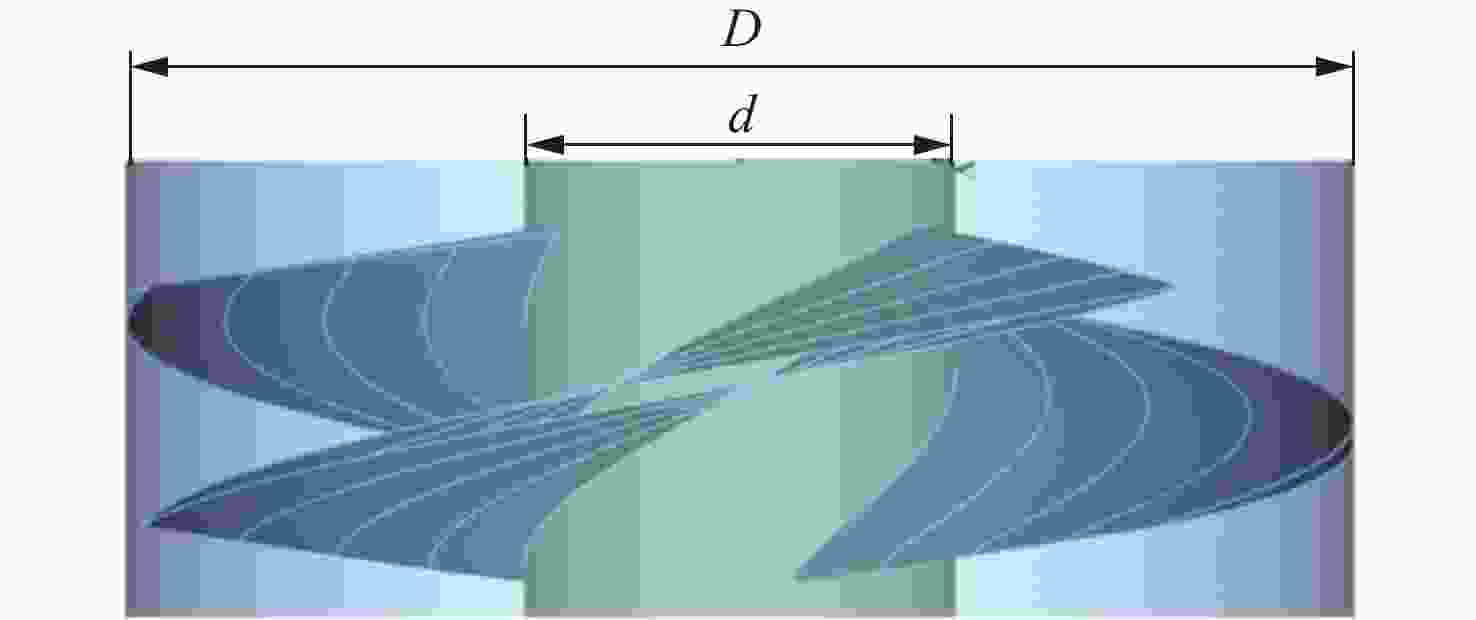
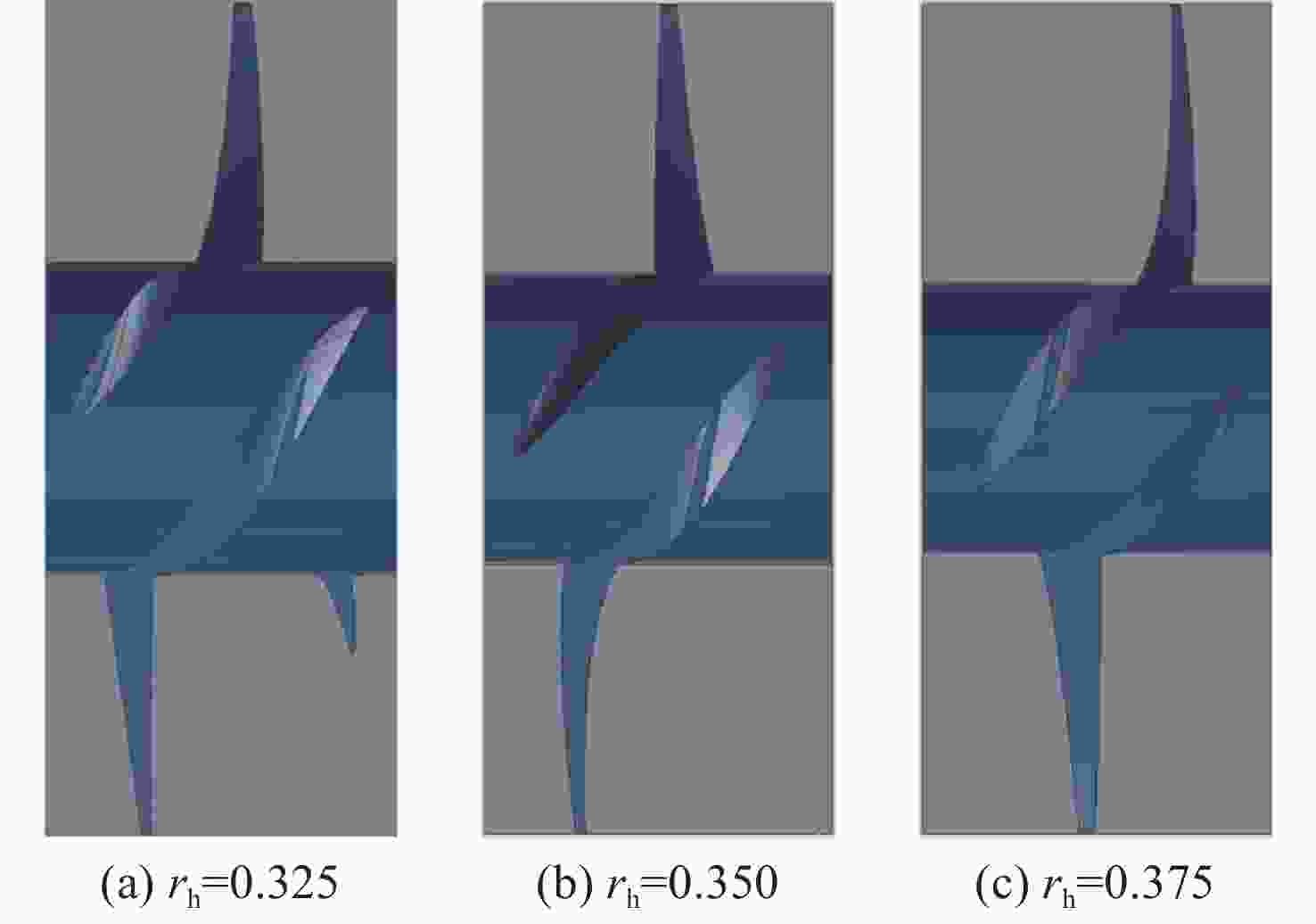
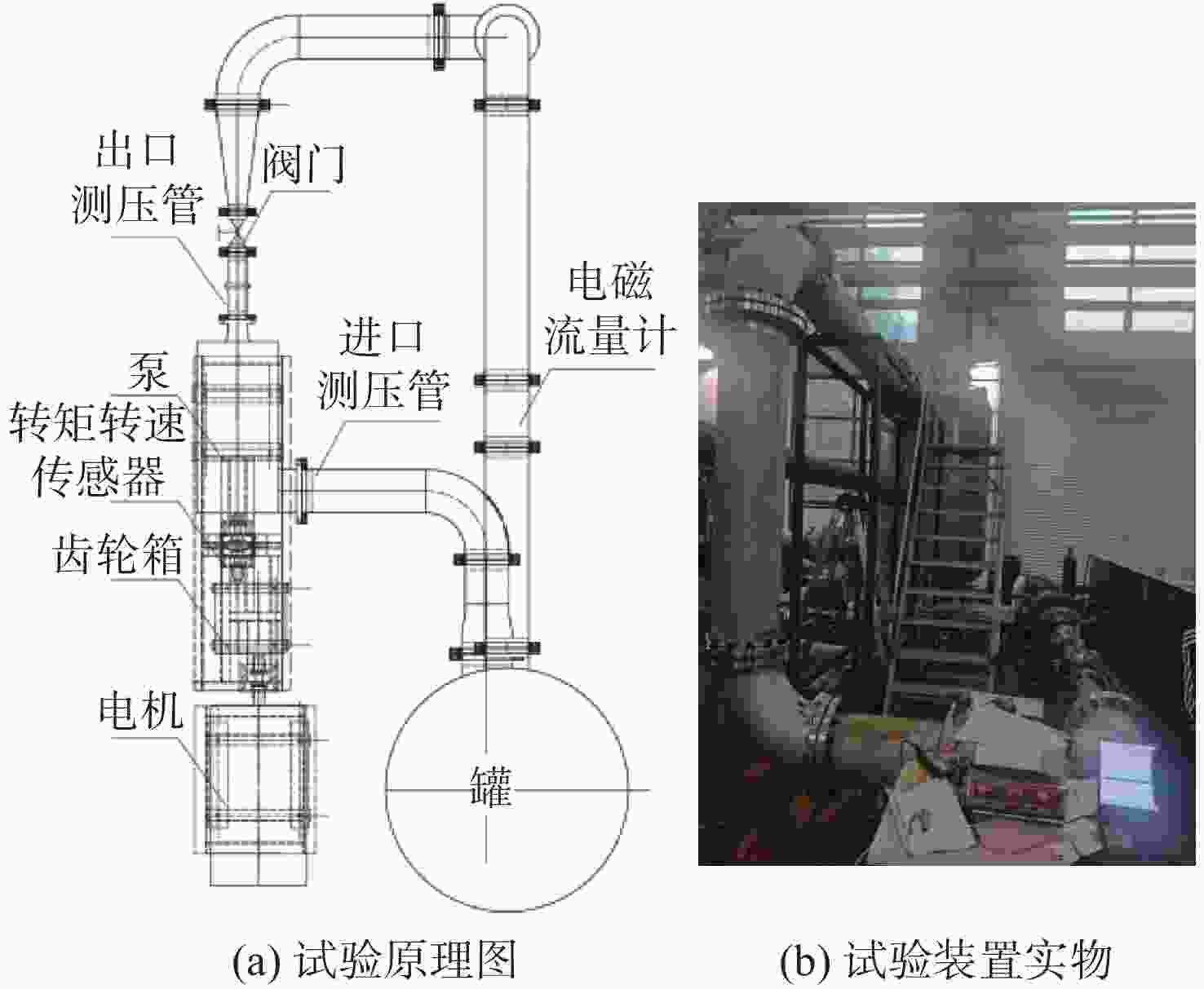
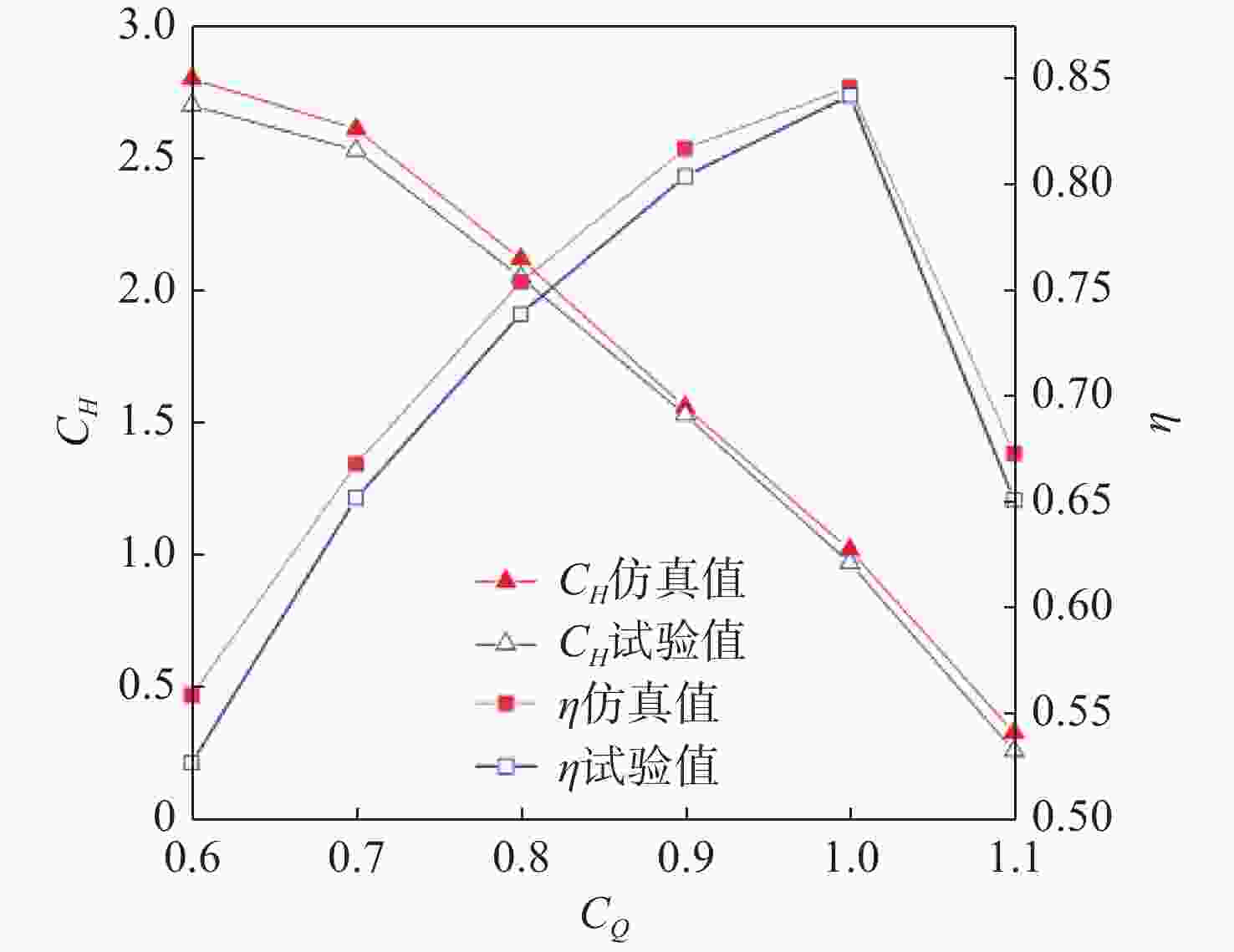
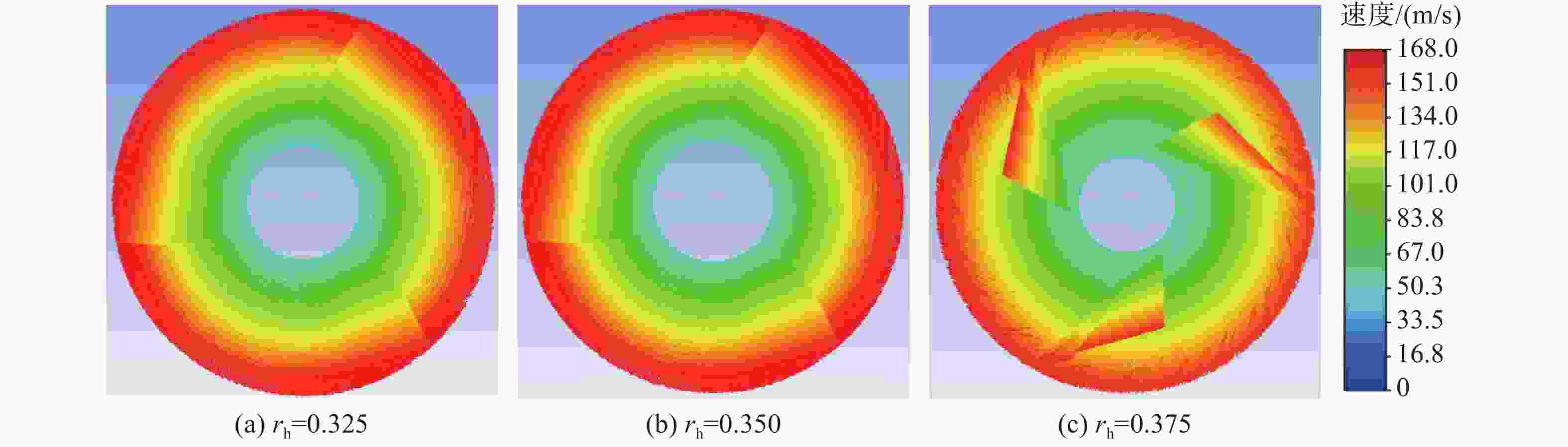
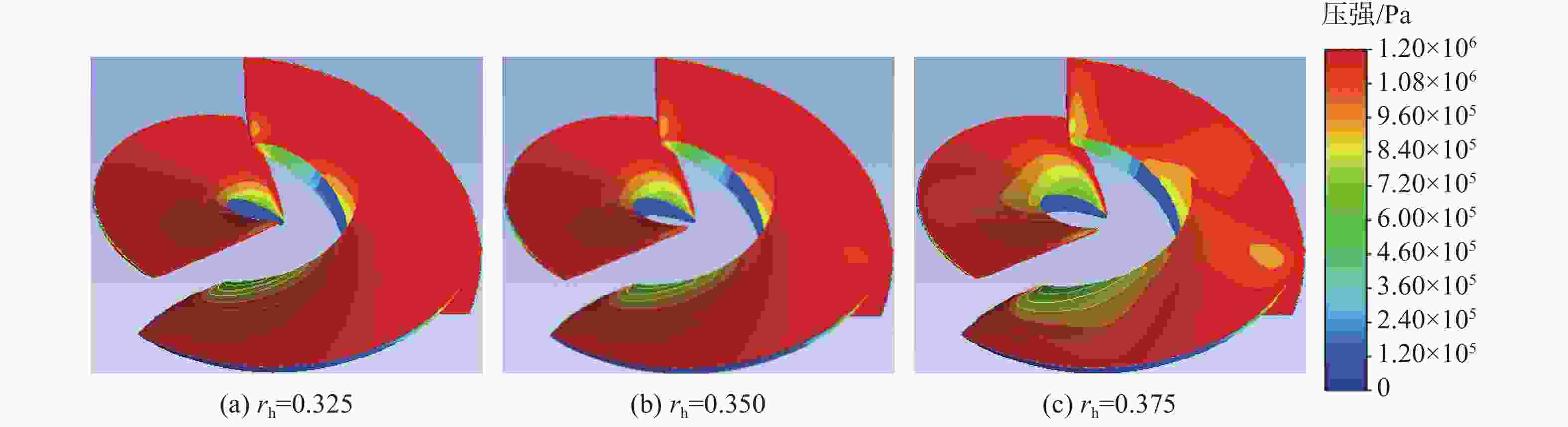
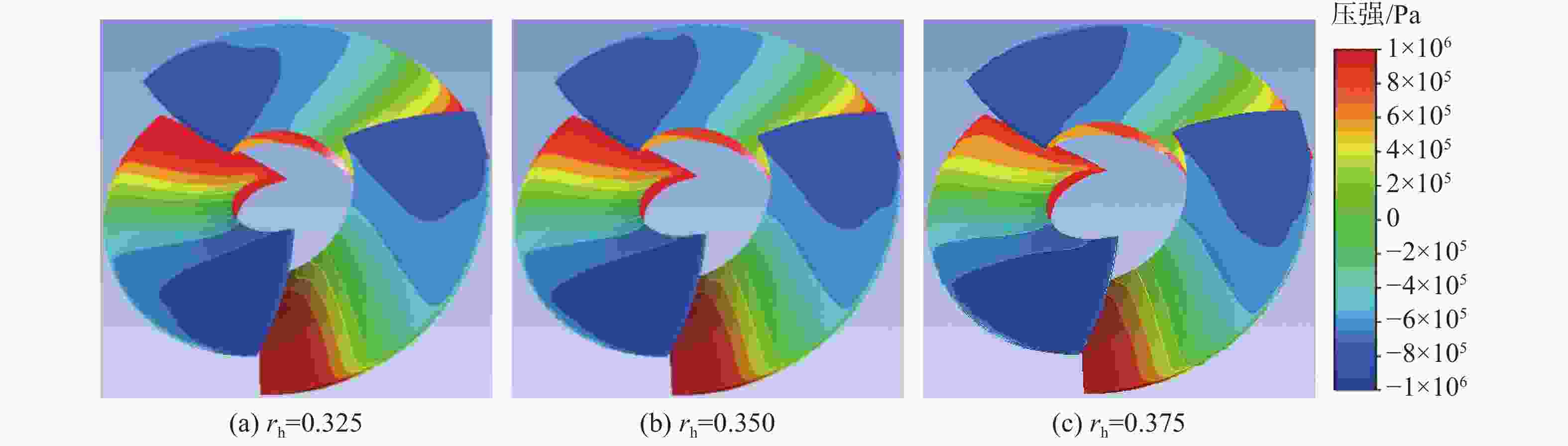
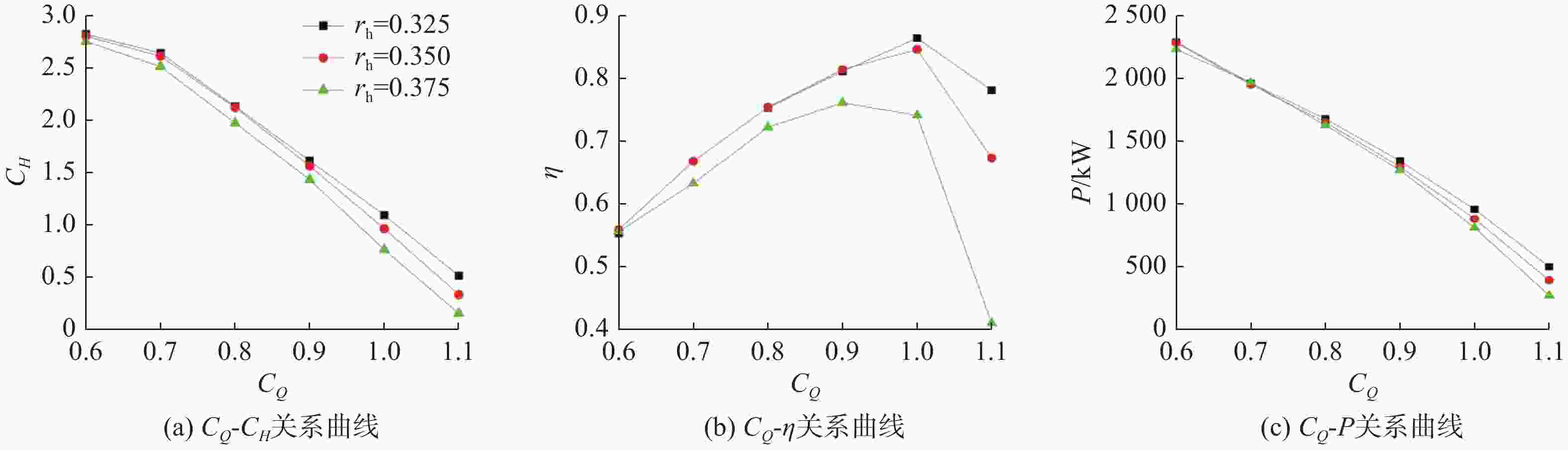
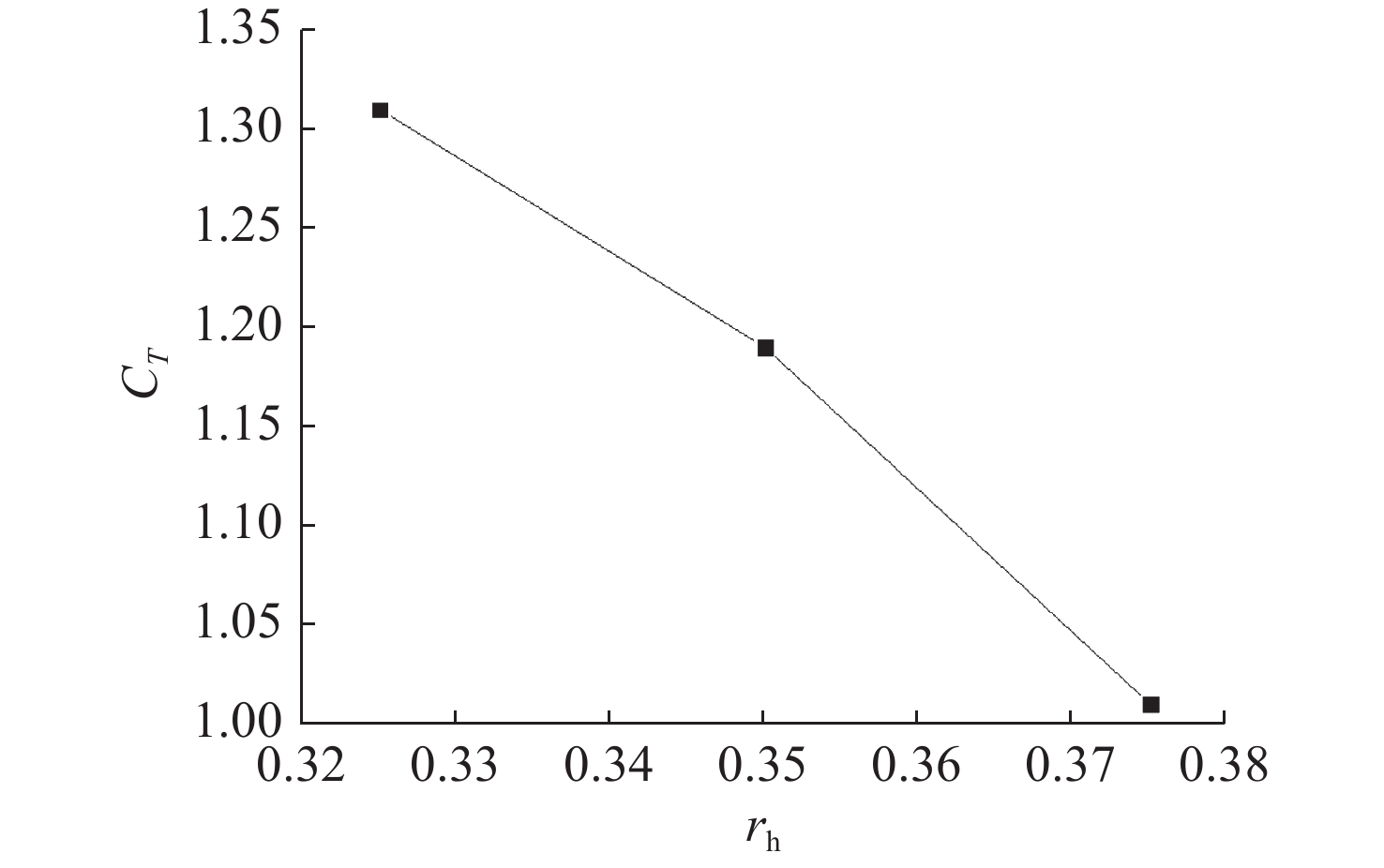
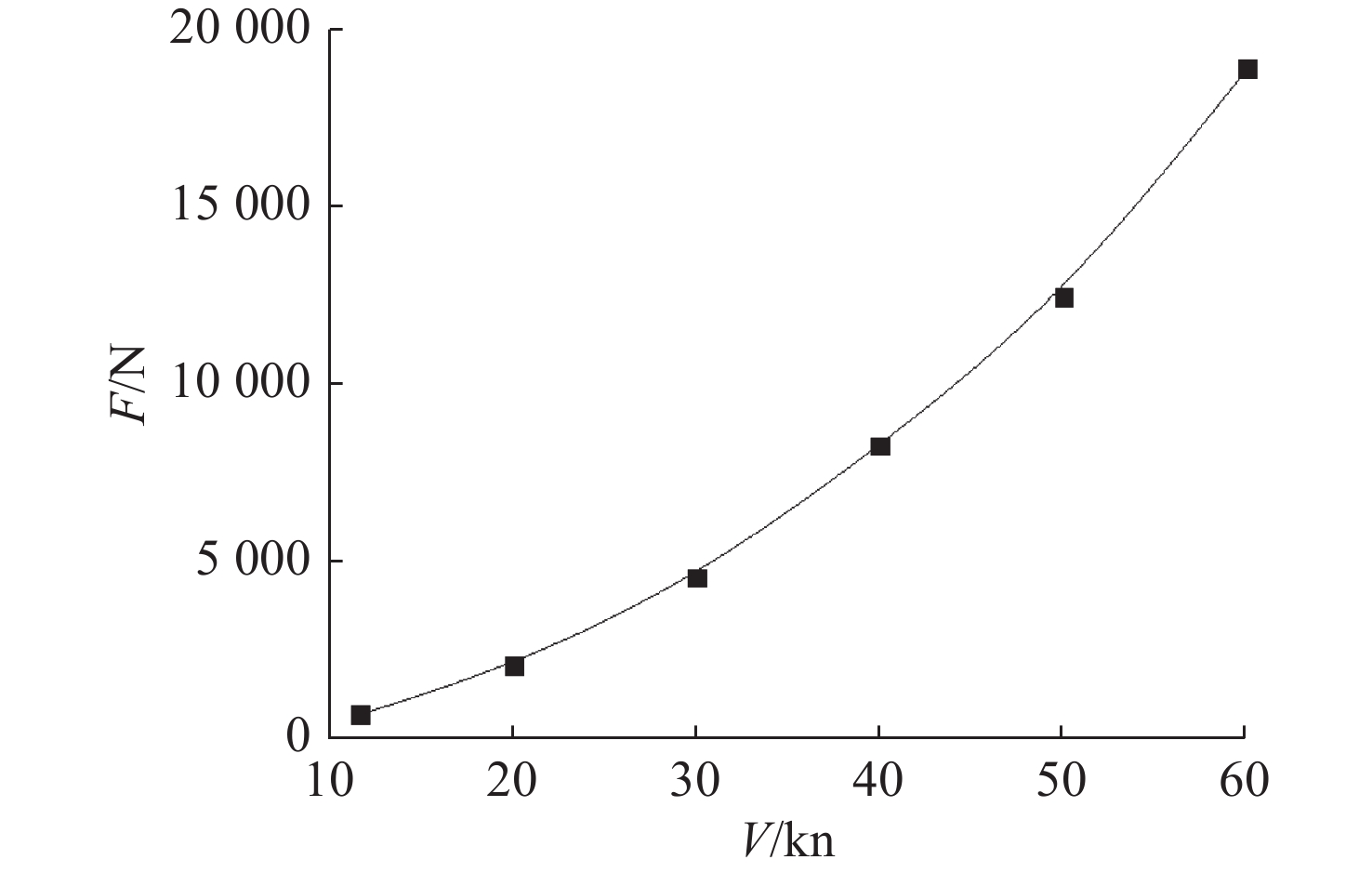
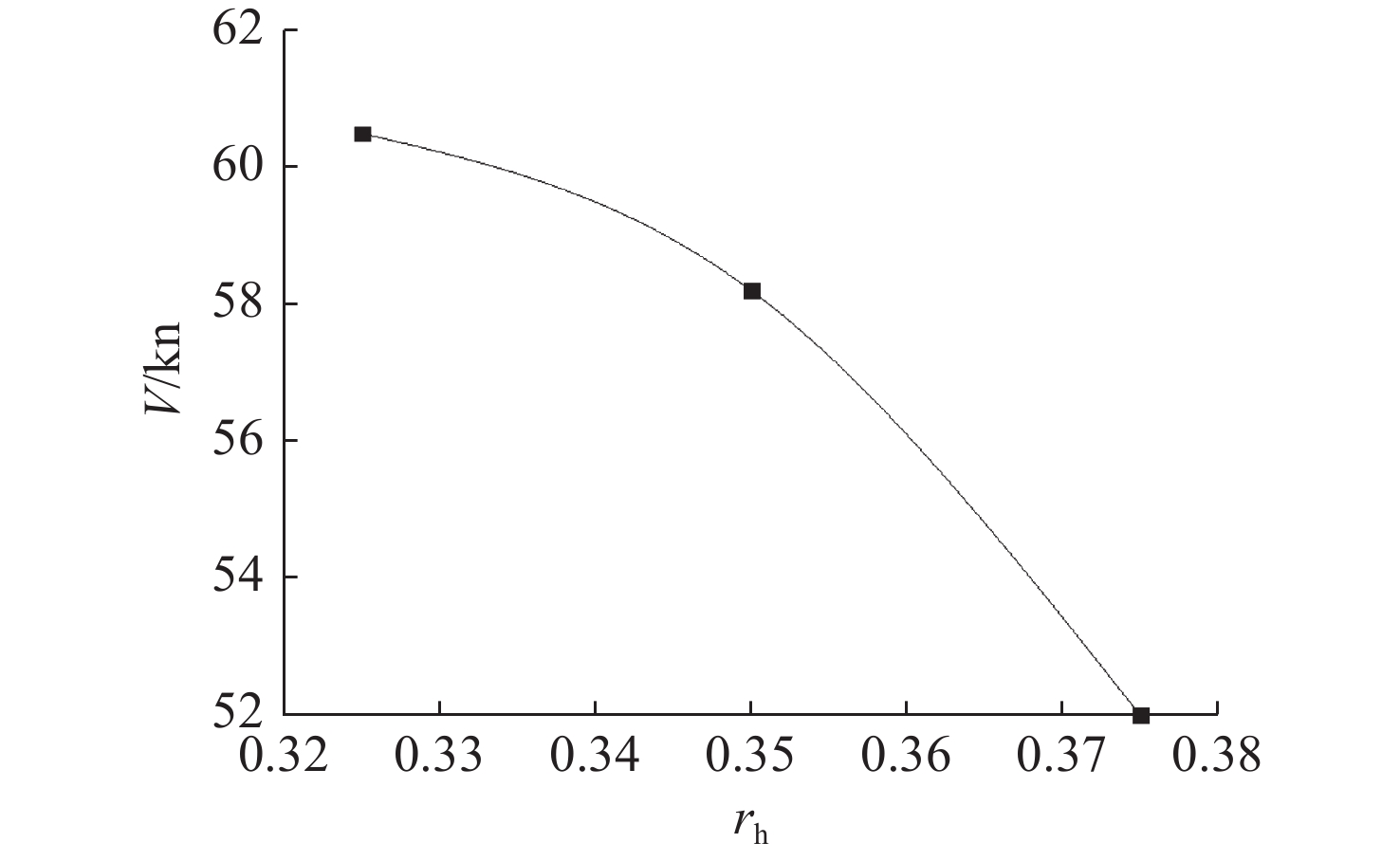
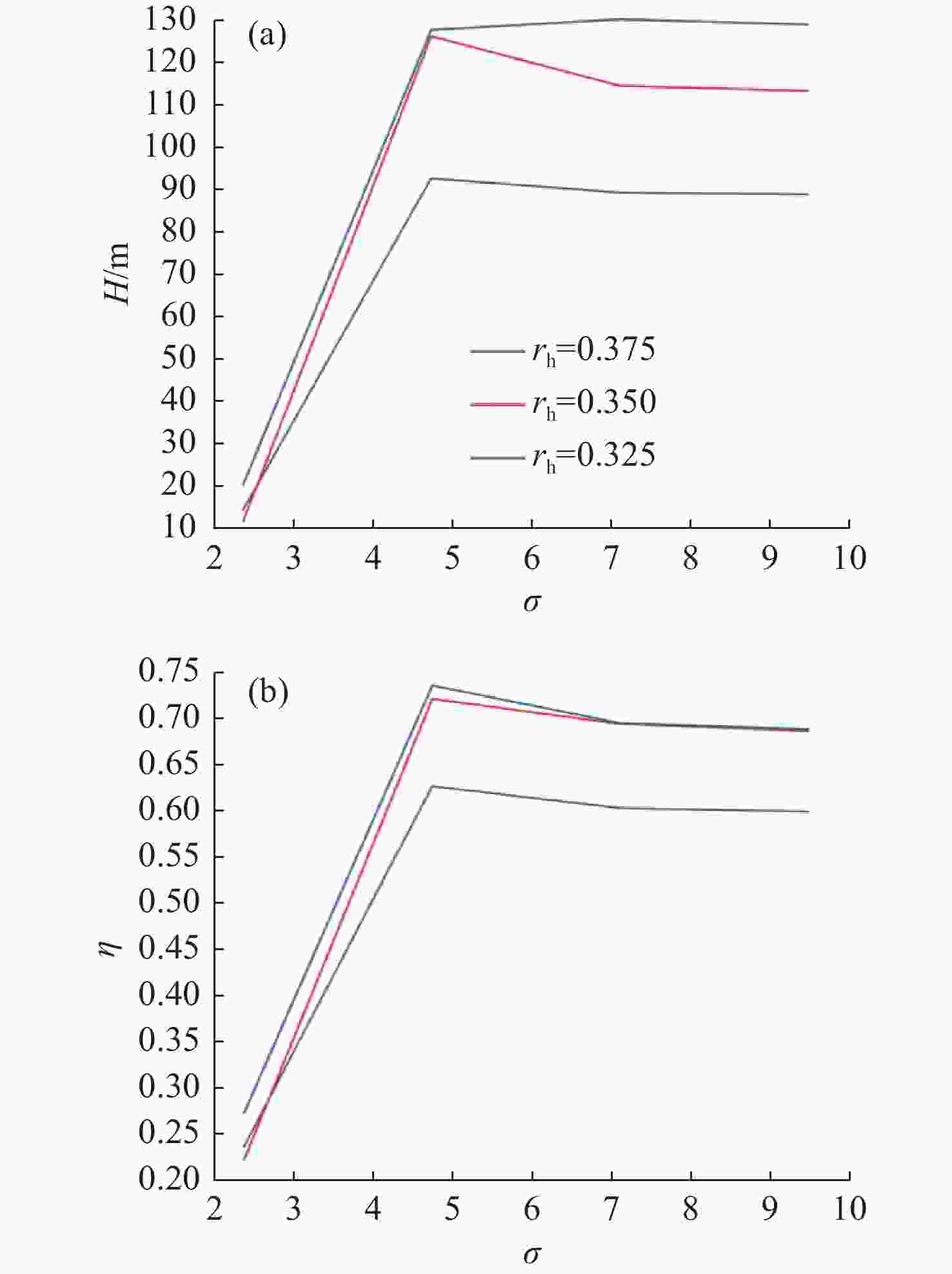
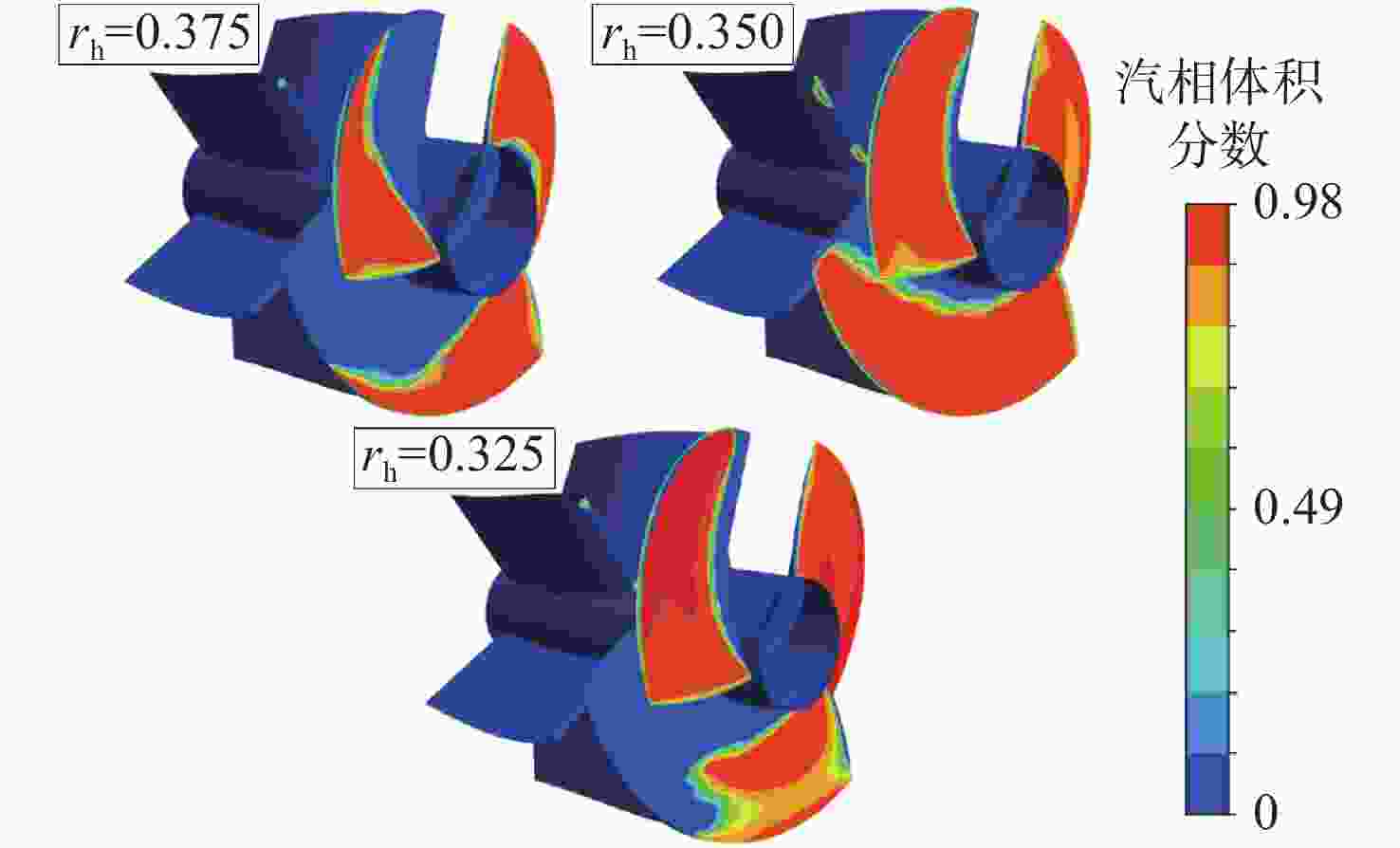
摘要: 为了探究轮毂比对水下航行器高速泵喷推进器的影响, 以比转速1 920的叶轮为研究对象, 对水下航行器高速泵喷推进器3种不同的轮毂比开展数值计算、性能结果分析比对和试验验证。应用Fluent软件, 采用基于雷诺平均N-S方程和SST k-ω模型, 预测叶轮的扬程、效率及推力。通过数值仿真计算, 得到不同轮毂比叶轮的性能曲线、空化性能数据及内流场状态。结果表明: 叶片表面从叶梢到轮缘的压力梯度逐渐变小, 随着轮毂比的增大, 叶片上最大静压下降, 泵喷推进器的扬程和效率均有所降低, 且空化性能下降明显, 但在空化状态上优于小轮毂比。研究结果可为水下航行器高速泵喷推进器结构优化设计提供参考。Abstract: To investigate the influence of the hub-to-tip ratio on the high-speed pump-jet propulsors of undersea vehicles, this study took an impeller with specific speed of 1 920 as the research object and conducted numerical calculation, performance result analysis and comparison, and experimental verification of three different hub-to-tip ratios of a high-speed pump-jet propulsor for undersea vehicles. Using Fluent software, it adopted a Reynolds-averaged N-S equation and an shear stress transport k-ω model to predict the head, efficiency, and thrust of the impeller. The performance curves, cavitation performance data, and internal flow field conditions of the impeller under different hub-to-tip ratios were obtained through numerical simulation calculations. The results show that the pressure gradient on the blade surface from the blade tip to the rim decreases. With the increase in the hub-to-tip ratio, the maximum static pressure on the blade and the head and efficiency of the pump-jet propulsor all decrease, and the cavitation performance significantly declines. However, the cavitation state is superior to that at the small hub-to-tip ratio. The research findings can provide certain reference for the structure optimization design of high-speed pump-jet propulsors for undersea vehicles.
-
Key words:
- undersea vehicle /
- hub-to-tip ratio /
- pump jet propulsor /
- cavitation
-
表 1 网格无关性检验方案
Table 1. Schemes of grid independence test
方案 网格数量 效率/% 轴功率
(无量纲)扬程
(无量纲)1 3 054 015 71.2 0.967 0.95 2 3 831 030 72.5 0.987 0.97 3 4 875 584 73.8 0.995 0.98 4 6 500 471 75.0 1.000 1.00 5 7 849 631 75.1 1.011 1.01 -
[1] 张明宇, 王永生, 林瑞霖, 等. 泵喷推进器低噪声优化设计[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(3): 7-12.ZHANG M Y, WANG Y S, LIN R L, et al. Low-noise optimization design of pump jet thruster[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(3): 7-12. [2] 张帅, 肖晶晶. 水下矢量推进器研究综述[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2019, 41(7): 5-9.ZHANG S, XIAO J J. Review of underwater vector propulsion system research[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2019, 41(7): 5-9. [3] 刘业宝. 水下航行器泵喷推进器设计方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2013. [4] 成科, 陈启明, 崔宝玲, 等. 多级离心泵扬程预测及内部流场数值模拟[J]. 流体机械, 2021, 49(3): 60-67.CHENG K, CHEN Q M, CUI B L, et al. Prediction of head and numerical simulation of internal flow field for multi-stage centrifugal pump[J]. Fluid Machinery, 2021, 49(3): 60-67. [5] 常书平, 王永生, 丁江明, 等. 基于 CFD 的船舶喷水推进器优化设计[J]. 船舶力学, 2013, 17(4): 369-374.CHANG S P, WANG Y S, DING J M, et al. Optimization design of ship waterjet propulsion based on CFD[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2013, 17(4): 369-374. [6] Ivanell S. Hydrodynamic simulation of a torpedo with pumpjet propulsion system[D]. Stockholm, Sweden: Royal Institute of Technology, 2001. [7] Altosole M, Benvenuto G, Figari M, et al. Dimensionless numerical approaches for the performance prediction of marine waterjet propulsion units[J]. International Journal of Rotating Machinery, 2012, 2012: 321306. [8] 郝宗睿, 李超, 任万龙, 等. 基于改进粒子群算法的喷水推进泵叶片优化设计[J]. 排灌机械工程学报, 2020, 38(6): 566-570.HAO Z R, LI C, REN W L, et al. Blade optimization design of waterjet pump based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2020, 38(6): 566-570. [9] ZANGENEH M, GOTO A. Turbodesign-1: next generation design software for pumps[J]. World Pumps, 2003(437): 32-36. [10] ZANGENEH M. Advanced design software for pumps[J]. World Pumps, 2007(489): 28-31. [11] ZANGENEH M, DANESHKHAH K, DACOSTA B. A multi-objective automatic optimization strategy for design of waterjet pumps[C]//Royal Institution of Naval Architects International Conference-Waterjet Propulsion 5-Papers. [S.l.]: [s.n.], 2008: 27-32. [12] BULTEN N W H, VERBEEK R. Design of optimal inlet duct geometry based on vessel operational profile[C]//International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation. Ischia, Italy: FAST, 2003. [13] RAZAGHIAN A H, EBRAHIMI A, ZAHEDI F, et al. Investigating the effect of geometric parameters on hydrodynamic and hydro-acoustic performances of submerged propellers[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2021, 114: 102773. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2021.102773 [14] JI X Q, DONG X Q, YANG C J. Attenuation of the tip-clearance flow in a pump-jet propulsor by thickening and raking the tips of rotor blades: A numerical study[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2021, 113: 102723. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2021.102723 [15] 李臣. 喷水推进轴流泵水力设计及性能仿真[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2015. [16] HUANG Q, LI H, PAN G, et al. Effects of duct parameter on pump-jet propulsor unsteady hydrodynamic performance[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 221: 108509. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.108509 [17] 邓辉, 张志宏, 王克彬, 等. 跨临界航速船舶水压场数值模拟研究[J]. 船舶力学, 2020, 24(11): 1383-1392.DENG H, ZHANG Z H, WANG K B, et al. Numerical simulation study on water pressure field of ships at transcritical speed[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2020, 24(11): 1383-1392. [18] 覃小瑞, 王名扬, 徐增丙, 等. 混流式喷水推进泵叶轮结构稳定性研究[J]. 机床与液压, 2022, 50(19): 179-184.QIN X R, WANG M Y, XU Z B, et al. Research on structural stability of mixed-flow waterjet pump impeller[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2022, 50(19): 179-184. [19] ZHANG X, TANG F, LIU C, et al. Numerical simulation of transient characteristics of start-up transition process of large vertical siphon axial flow pump station[J]. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2021, 9: 706975. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2021.706975 [20] 刘厚林, 华旭辉, 吴贤芳, 等. 轮毂比对无轴泵喷推进器性能的影响[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2022, 12: 1-8.LIU H L, HUA X H, WU X F, et al. The impact of hub-to-tip ratio on the performance of axial-free pump jet propulsor[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2022, 12: 1-8. -




 下载:
下载: