Control System for Underwater Hexapod Robot Based on Inverse Kinematics and Foot Trajectory Optimization
-
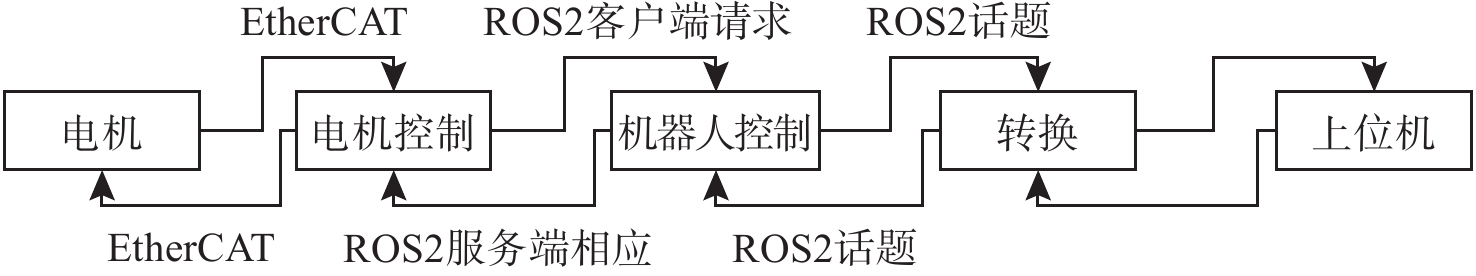
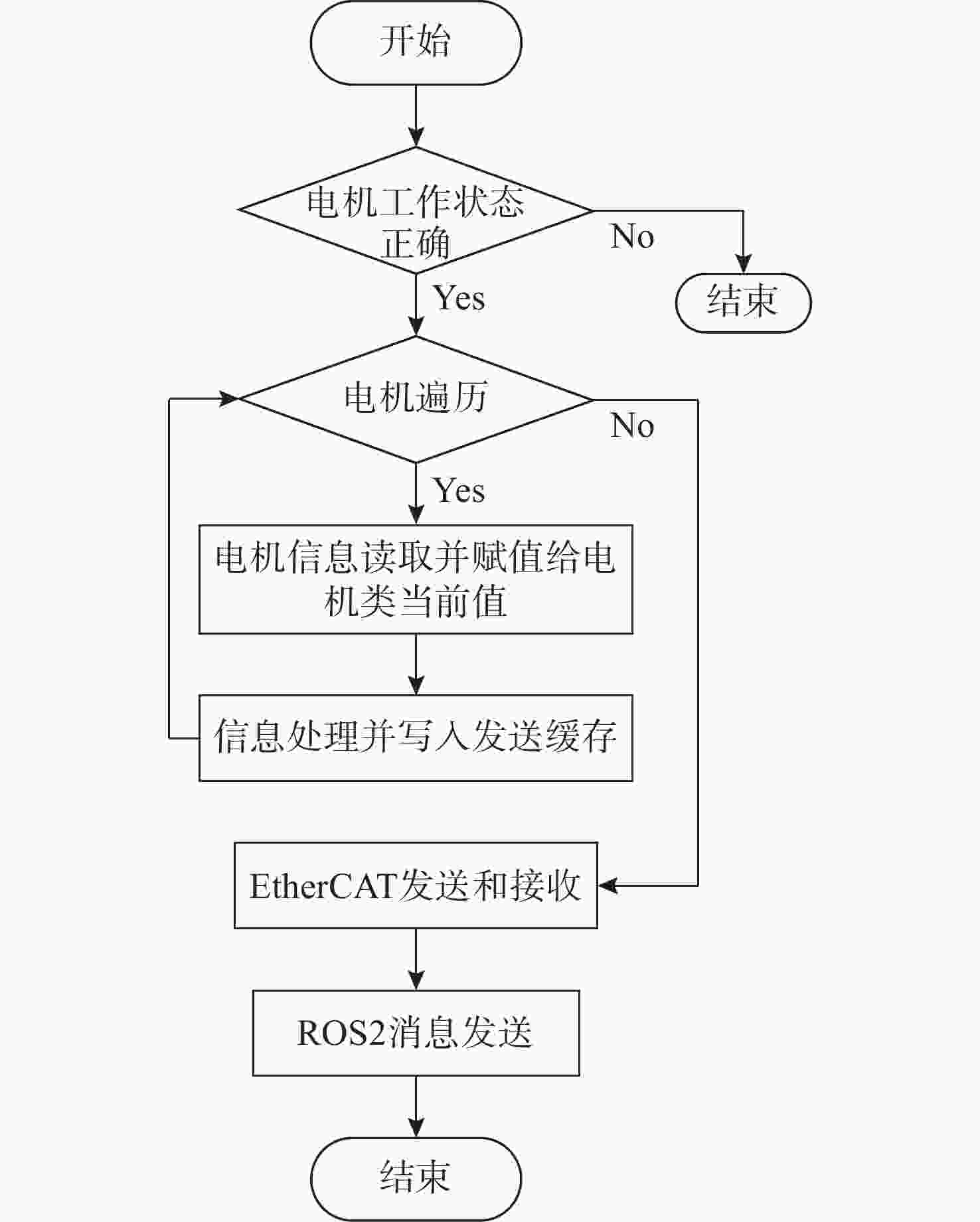
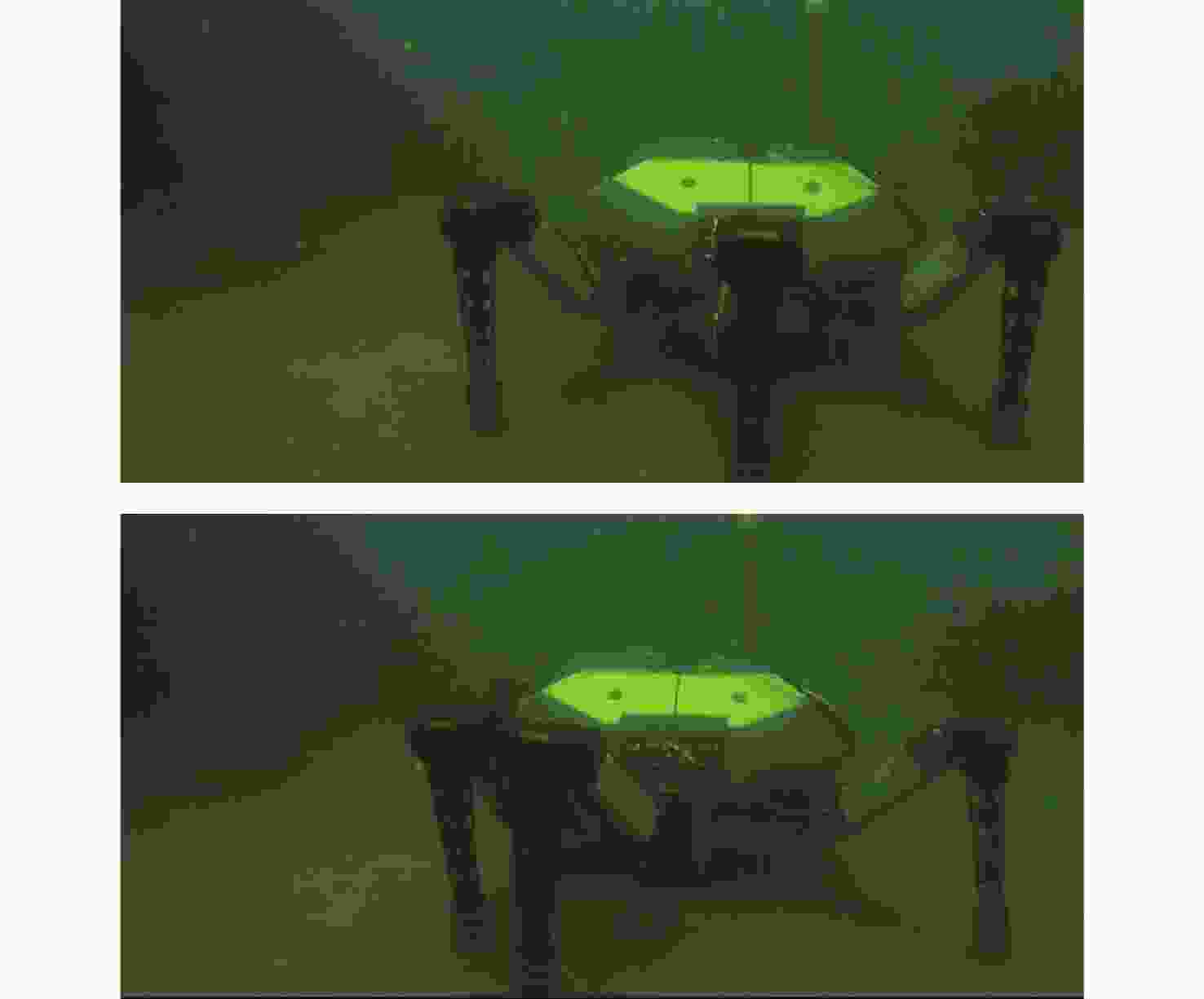
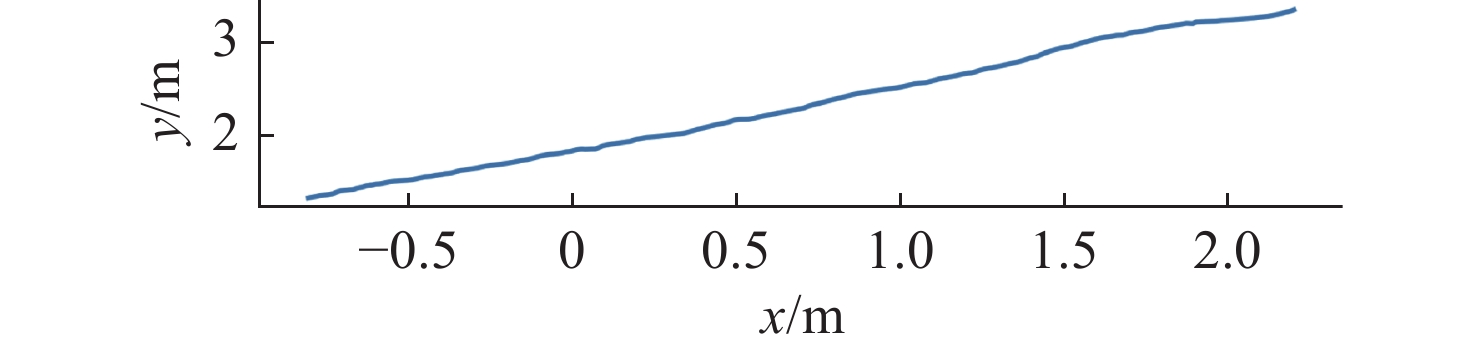
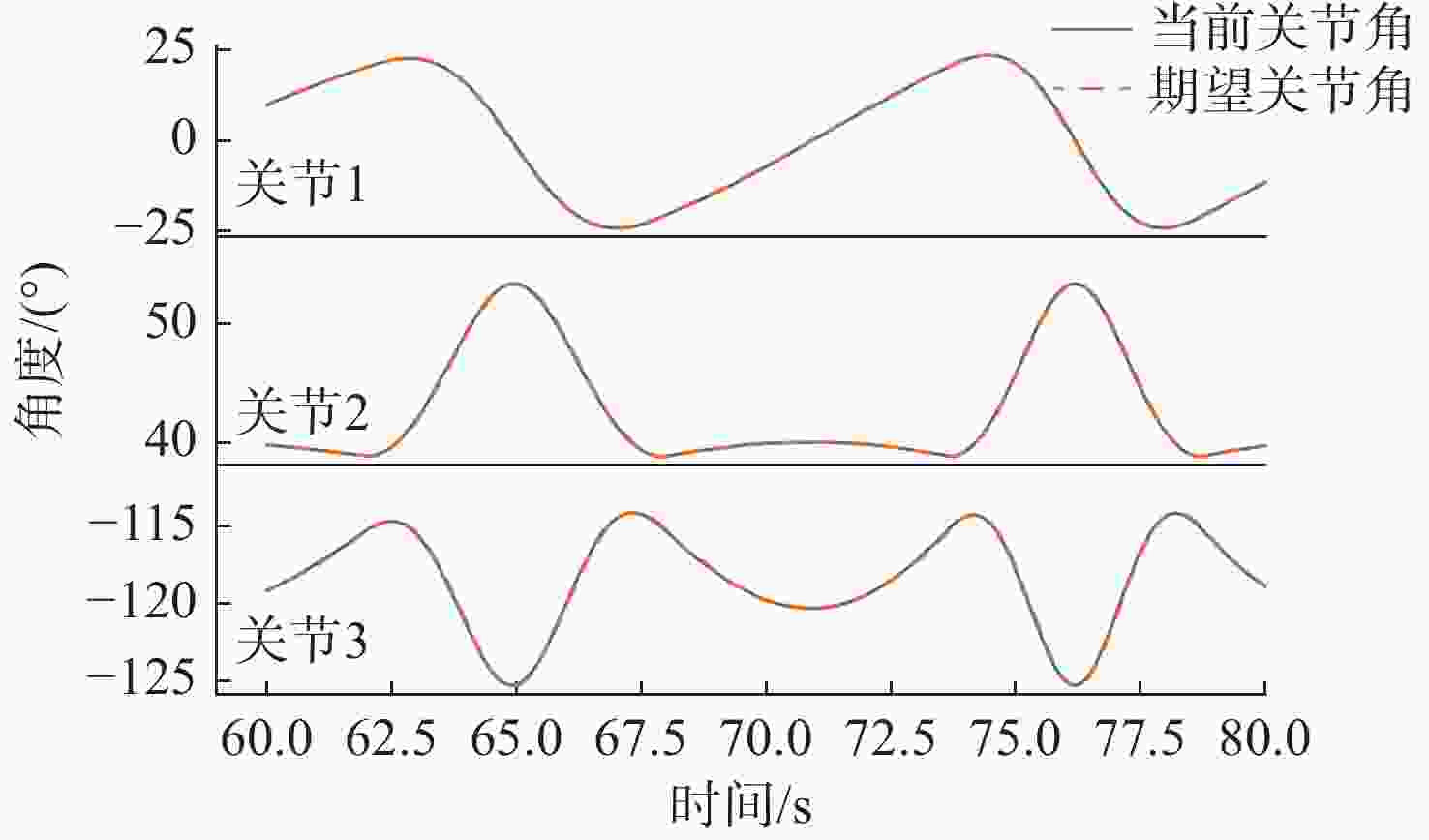
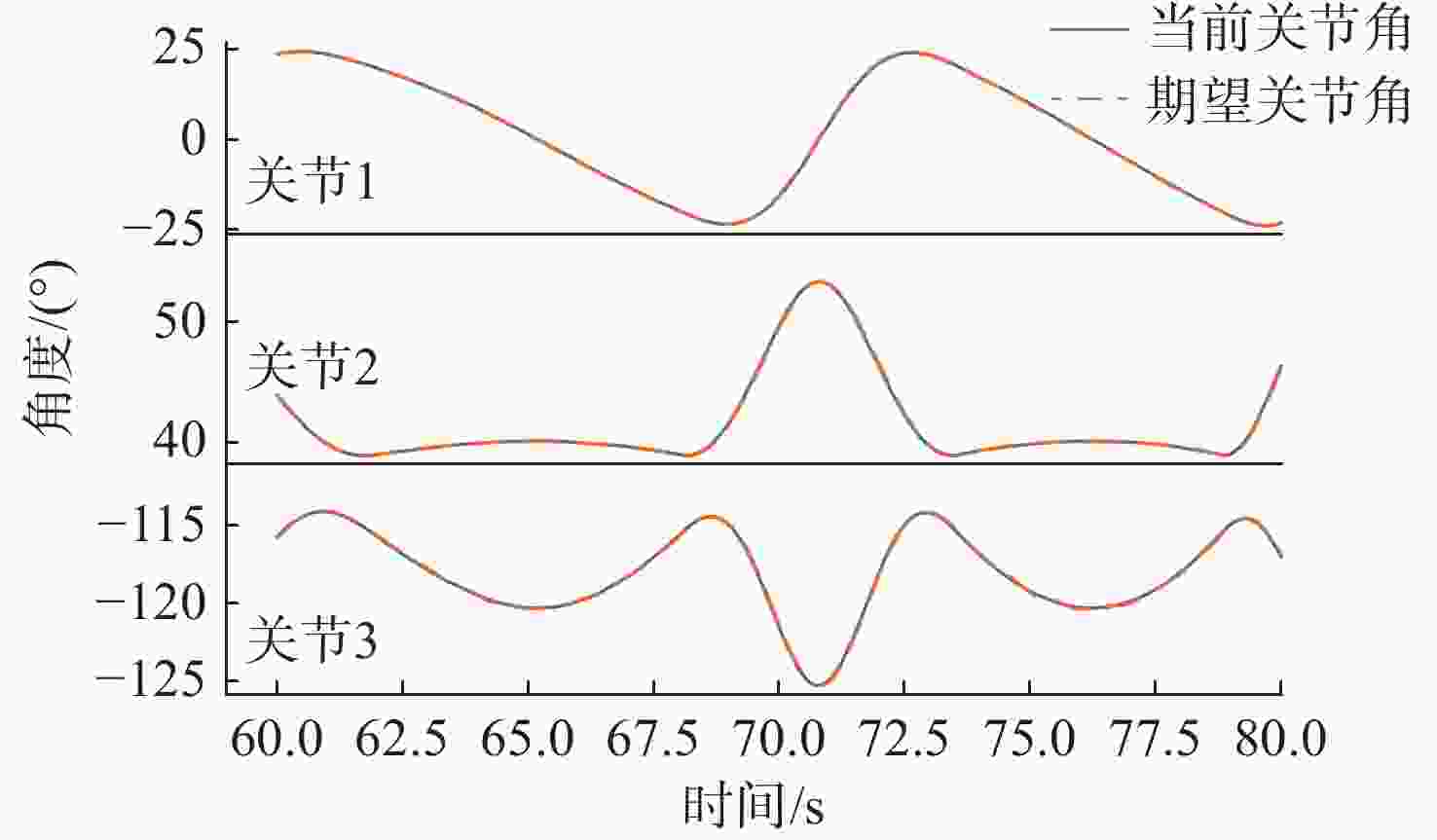
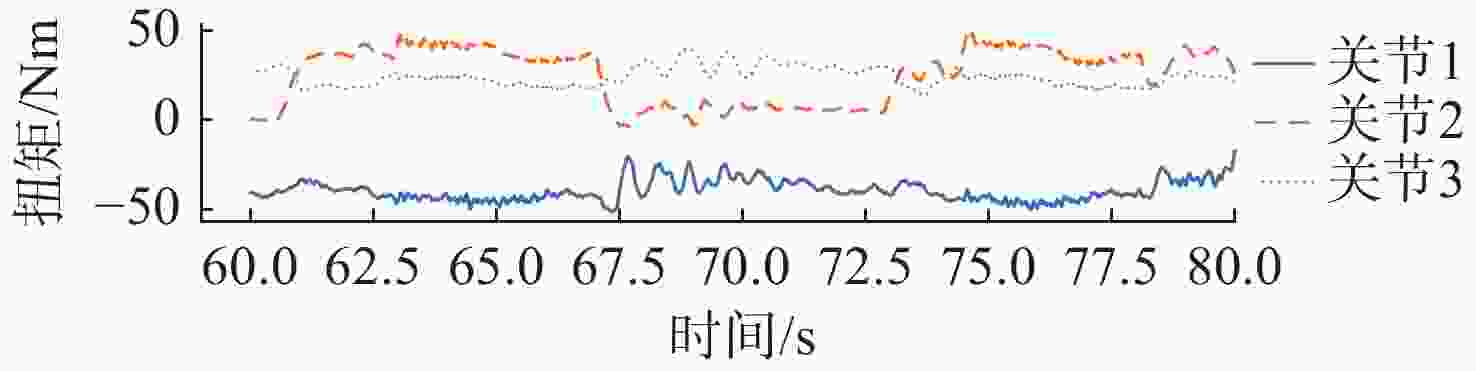
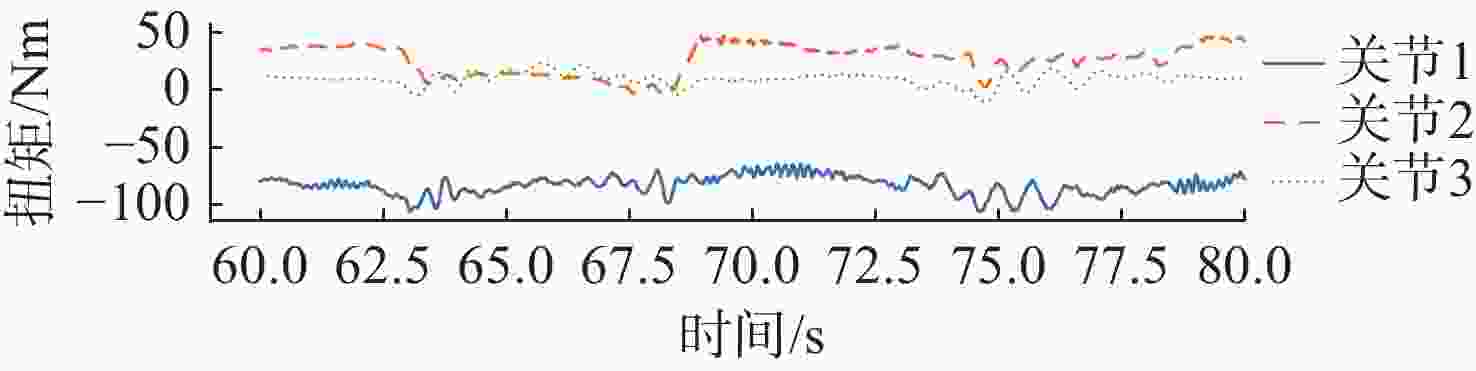
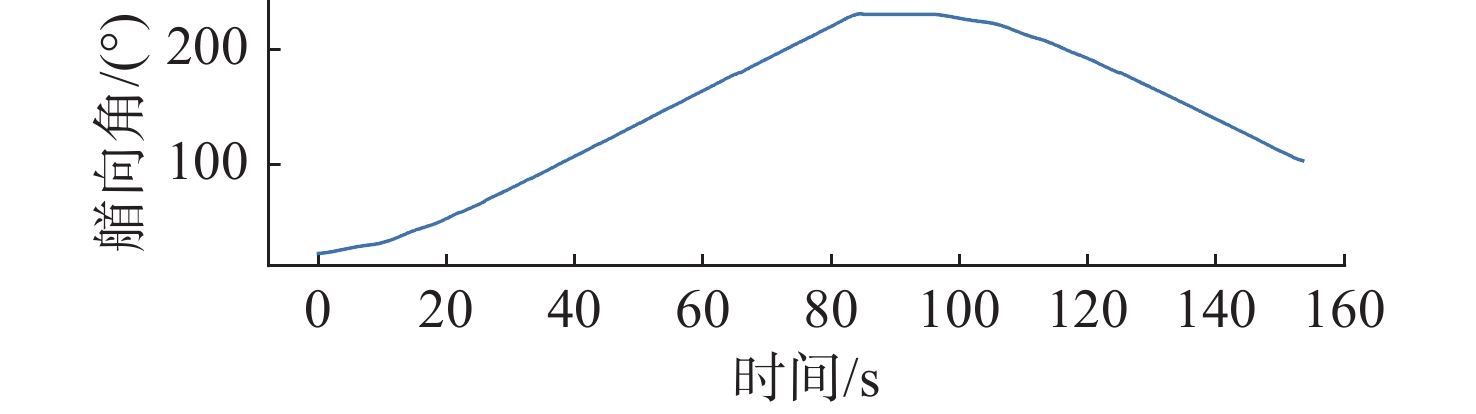
摘要: 水下六足机器人具有强带负载能力和地形适应能力, 非常适合在复杂多变的海底环境进行近地观测和采样。控制系统是实现水下六足机器人稳定行走的关键技术。文中提出了基于逆运动学和足端轨迹优化的水下六足机器人控制系统设计方法。建立D-H坐标系, 推导出足端轨迹与关节角之间的解析关系(正运动学); 通过多项式优化的方式规划出平滑的足端轨迹, 进而求解出对应的关节角(逆运动学); 以PC104为主控单元, 在ROS2环境中进行足端轨迹优化和逆运动学求解, 通过EtherCAT技术实现关节电机的同步跟踪, 设计出适用于水下六足机器人的控制系统。在水池中对水下六足机器人的典型运动方式(直行和转动)进行了验证,实验结果表明, 文中设计的控制系统可以实现水下六足机器人的稳定行走。Abstract: The underwater hexapod robot has a strong load carrying ability and terrain adaptability, which is very suitable for near-earth observation and sampling in complex and changeable seabed environments. The control system is the key technology to realize the stable walking of underwater hexapod robots. In this paper, a control system design method for underwater hexapod robots based on inverse kinematics and foot trajectory optimization was proposed. The D-H coordinate system was established to derive the analytical relationship between the foot trajectory and the joint angle(positive kinematics). Through polynomial optimization, a smooth foot trajectory was planned, and then the corresponding joint angle(inverse kinematics) was solved. With PC104 as the main control unit, the foot trajectory optimization and inverse kinematics solving were conducted in the ROS2 environment, and the synchronous tracking of the joint motor was realized through EtherCAT technology. The control system suitable for underwater hexapod robots was designed. The typical movement patterns(straight and turning) of the underwater hexapod robot were verified in the pool. Experimental results show that the control system designed in this paper can realize the stable walking of the underwater hexapod robot.
-
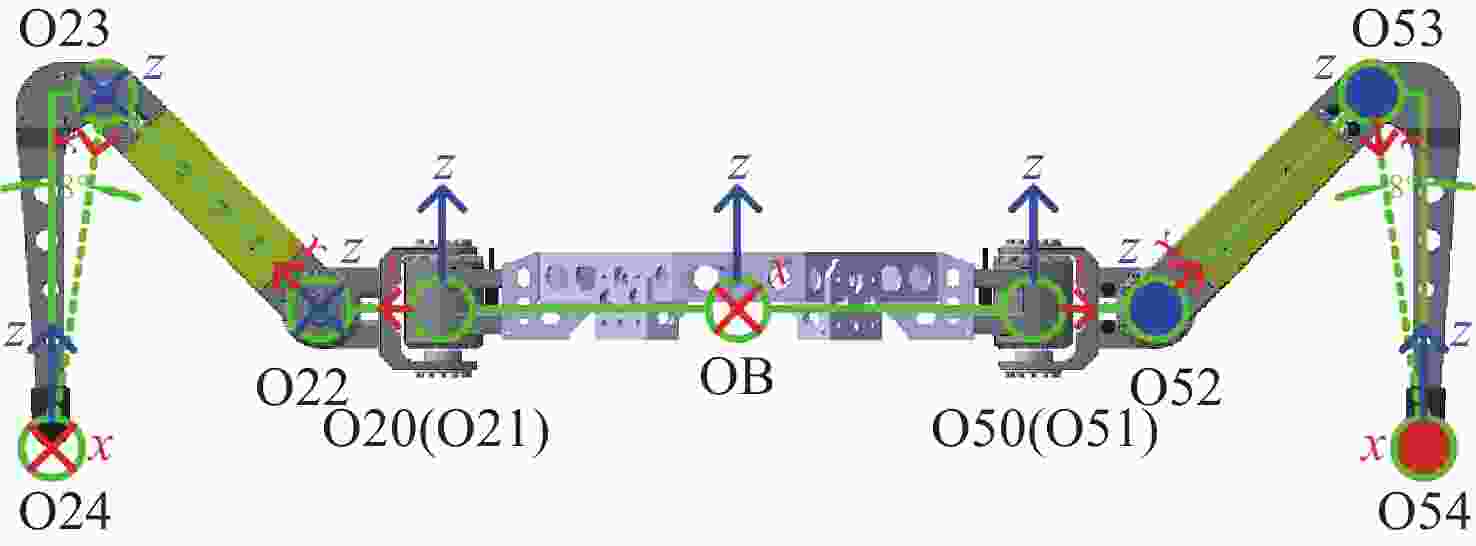
表 1 机械腿D-H参数表
Table 1. D-H parameters of mechanical leg
i ${a_{j\left( {i - 1} \right)}}/{\text{m}}$ ${\alpha _{j\left( {i - 1} \right)}}/({\text{°}})$ ${d_{ji}}/{\text{m}}$ ${\theta _{ji}}/({\text{°}} )$ 0 ${l_{j{\text{0}}}}$ 0 0 ${\theta _{j{\text{0}}}}$ 1 0 0 0 ${\theta _{j1}}$ 2 ${l_{j1}}$ $90$ 0 ${\theta _{j2}}$ 3 ${l_{j2}}$ 0 0 ${\theta _{j3}}$ 4 ${l_{j3}}$ 0 0 0 表 2 机器人控制节点相关变量
Table 2. Related variables contained in robot control node
变量名 含义 origin_thigh_trans[6,4] 0号关节在基座下的位置 joint_length[3] $ {l}_{j1}、{l}_{j2}、{l}_{j3} $ theta_stand[6,3] 初始关节角度 theta_now[6,3] 实际关节角度 theta_target[6,3] 期望关节角度 ground_base_coord[3] 机体路径 foot_coordinate_base[6,3] 当前足端位置 foot_coordinate_base_target[6,3] 期望足端位置 speed_target[3] 期望机器人移动速度 step_size[3] 机器最大横纵步幅和
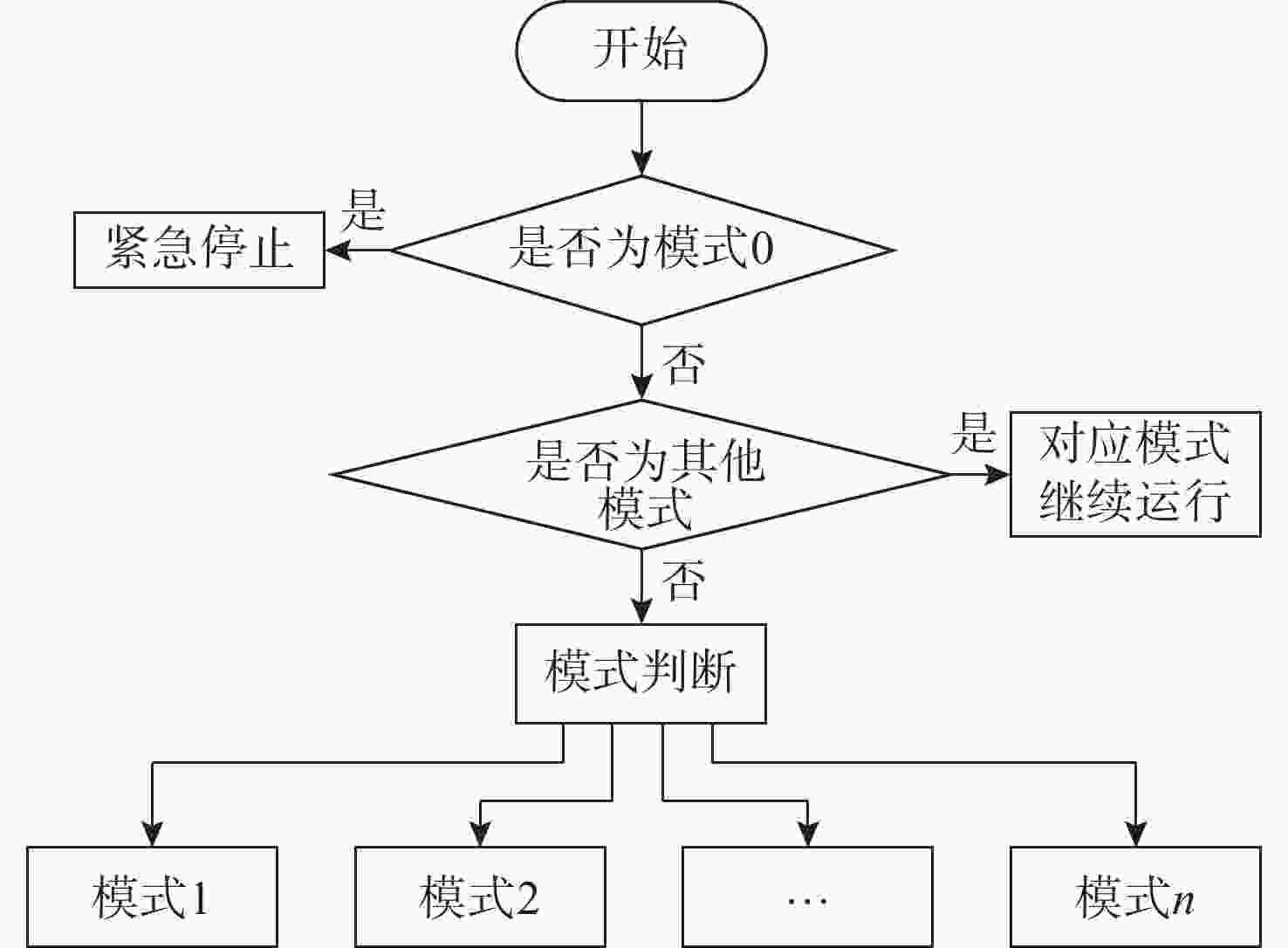
零半径旋转幅度centroid_h 机器人足端离底最大高度 gait_mode 步态模式 robot_mode 工作模式 表 3 机器人控制节点相关函数
Table 3. Related functions contained in robot control node
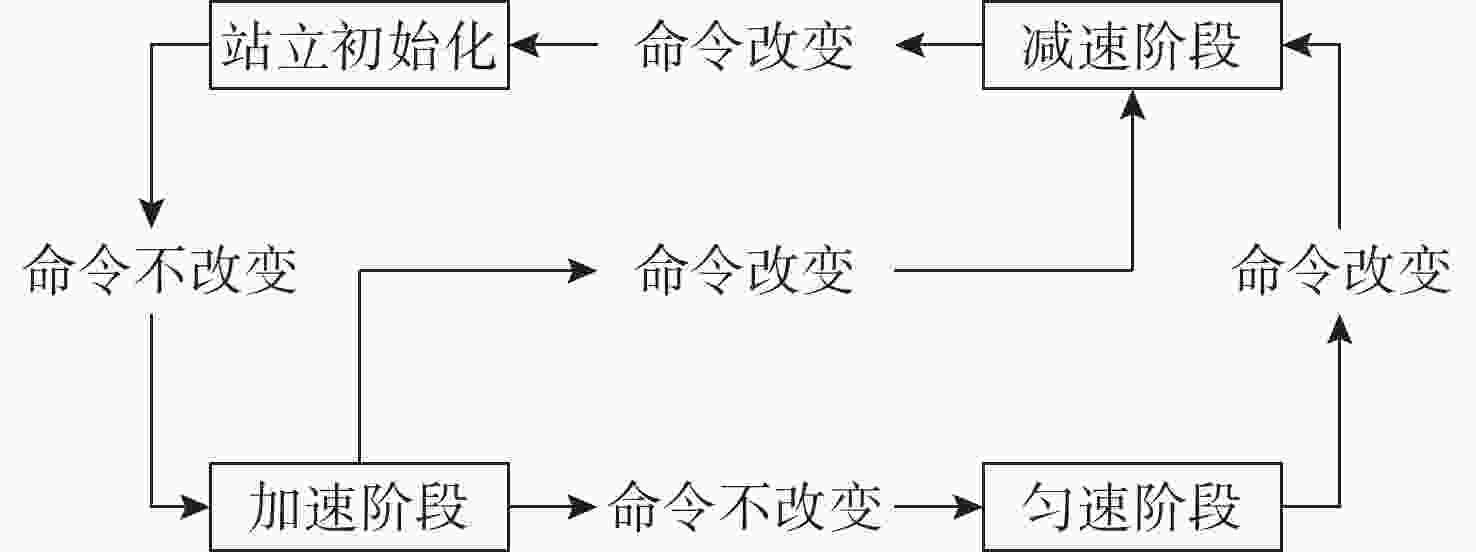
函数名 含义 Init() 变量初始化 T_joint_state_init() 正运动学计算 Inverse_Kinematics() 逆运动学计算 Point_to_point_arc() 空间点到点轨迹生成 Foot_track_ground() 摆动腿足端轨迹生成 Stand_init() 站立初始化 Walk_init() 移动速度加速行走 Walk() 移动速度匀速行走 Walk_end() 移动速度减速行走 Period_cal() 状态转换周期计算 Walking_pattern_3() 三角步态工作模式 Walking_pattern_5() 五足步态工作模式 Robot_walk_mode_swap() 移动控制指令是否改变 Robot_interface() 类接口函数 -
[1] ZHU X, SONG B, ZHANG D, et al. Analysis of landing strategies and influencing factors of an autonomous underwater vehicle[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 237: 1-10. [2] KATZSCHMANN R K, DELPRETO J, MACCURDY R, et al. Exploration of underwater life with an acoustically controlled soft robotic fish[J]. Science Robotics, 2018, 3(16): 1-27. [3] PICARDI G, CHELLAPURATH M, IACOPONI S, et al. Bioinspired underwater legged robot for seabed exploration with low environmental disturbance[J]. Science Robotics, 2020, 5(42): 1-14. [4] SHIM H, YOO S Y, KANG H, et al. Development of arm and leg for seabed walking robot CRABSTER200[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2016, 116: 55-67. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2016.02.028 [5] WANG L, LU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Design and soft-landing control of underwater legged robot for active buffer landing on seabed[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 266(24): 1-16. [6] 陈铭, 冷静. 深海大型爬行机器人研究现状[J]. 海洋工程, 2020, 38: 156-168.CHEN M, LENG J. The development of deep-sea large-scale crawling robots[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 38: 156-168. [7] 陈虹, 王心亮, 魏伟, 等. 深海爬游机器人概念及关键技术分析[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2018, 13(6): 19-26.CHEN H, WANG X L, WEI W, et al. Concept and key technology analysis of deep-sea walking-swimming robot[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2018, 13(6): 19-26. [8] CHEN T, LI Y, RONG X, et al. Design and control of a novel leg-arm multiplexing mobile operational hexapod robot[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(1): 382-389. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3127639 [9] BAL C. Neural coupled central pattern generator based smooth gait transition of a biomimetic hexapod robot[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 420: 210-226. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.07.114 [10] YU H, GAO H, DENG Z. Enhancing adaptability with local reactive behaviors for hexapod walking robot via sensory feedback integrated central pattern generator[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2020, 124: 1-17. [11] CHEN C, ZHA F, GUO W, et al. Trajectory adaptation of biomimetic equilibrium point for stable locomotion of a large-size hexapod robot[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2020, 45(1): 155-174. [12] 王心亮, 肖前进, 马哲松, 等. 水下爬游机器人足端运动空间分析[J]. 中国造船, 2019, 60(增刊1): 444-451. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2019.z1.062 [13] DAVLIAKOS I, RODITIS I, LIKA K, et al. Design, development, and control of a tough electrohydraulic hexapod robot for subsea operations[J]. Advanced Robotics, 2018, 32(9): 477-499. doi: 10.1080/01691864.2018.1461684 -




 下载:
下载: