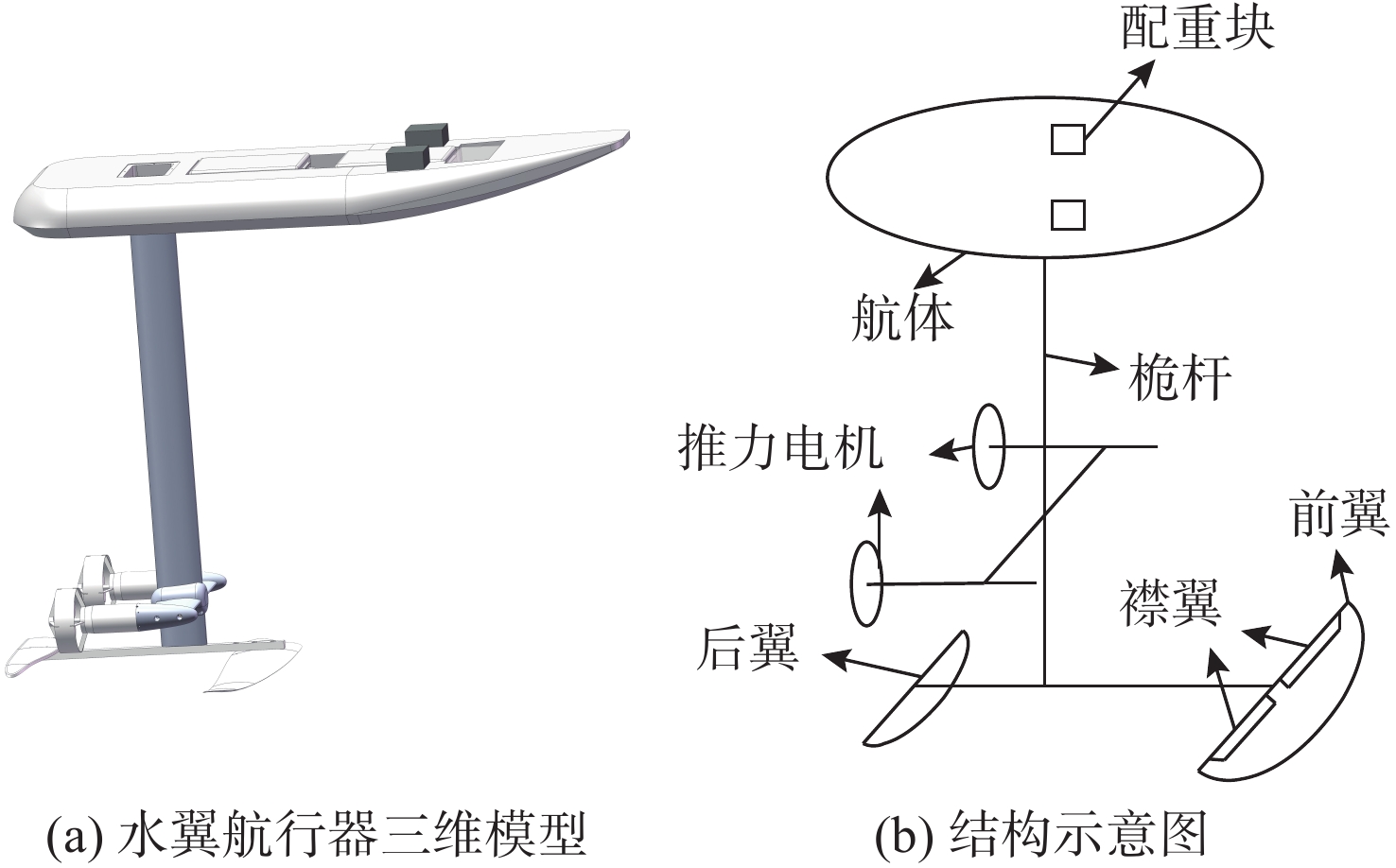
Seakeeping of Hydrofoil-Equipped Unmanned Surface VehicleBased on LQR and ZOA
-
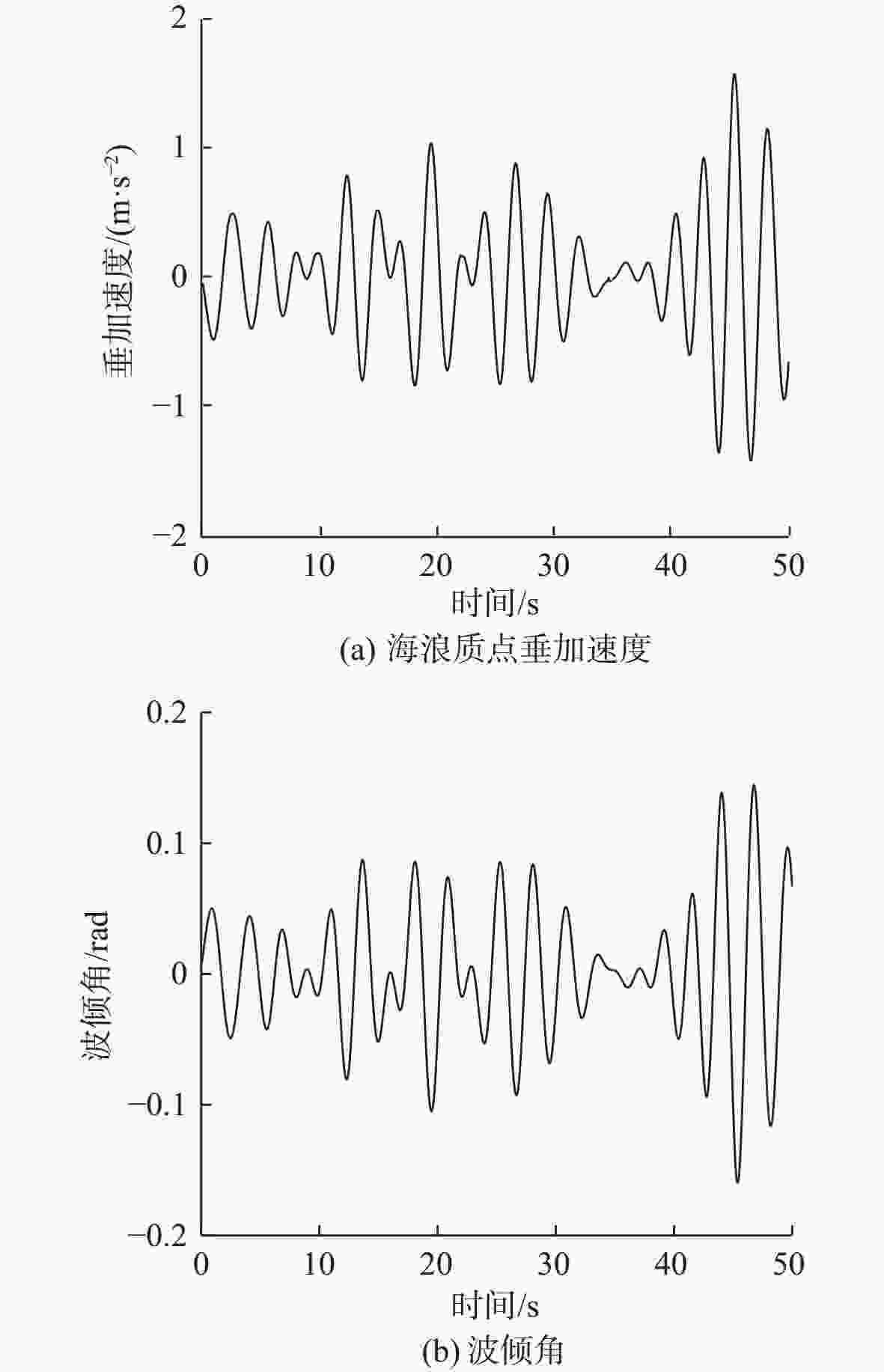
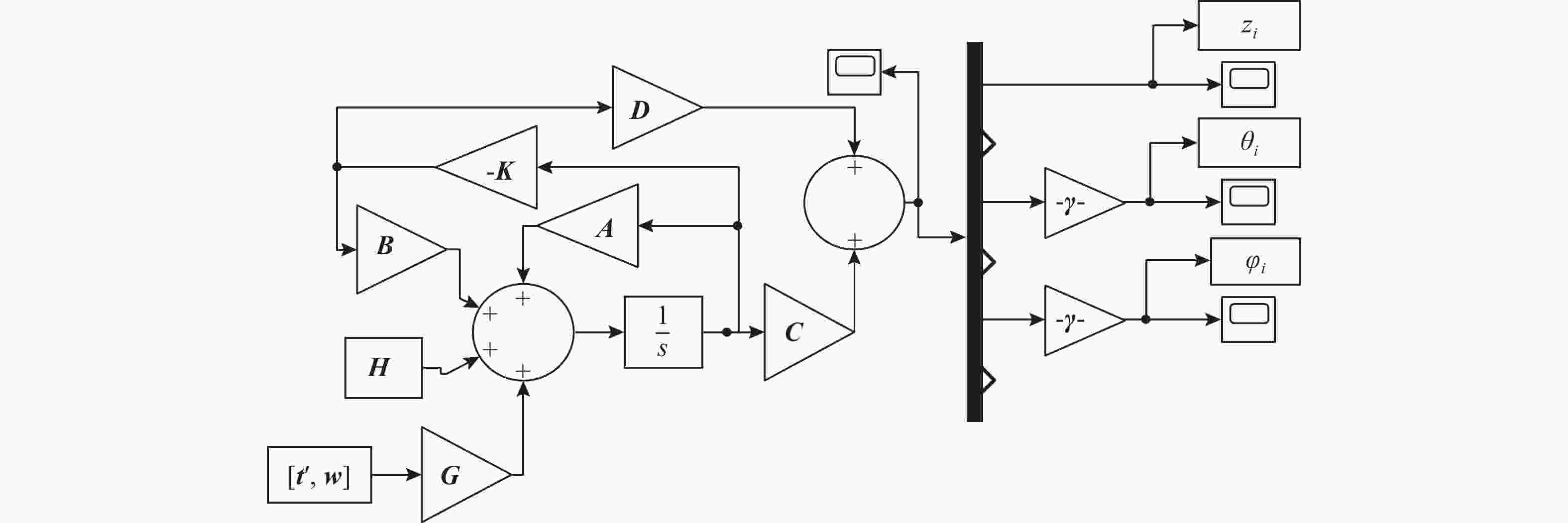
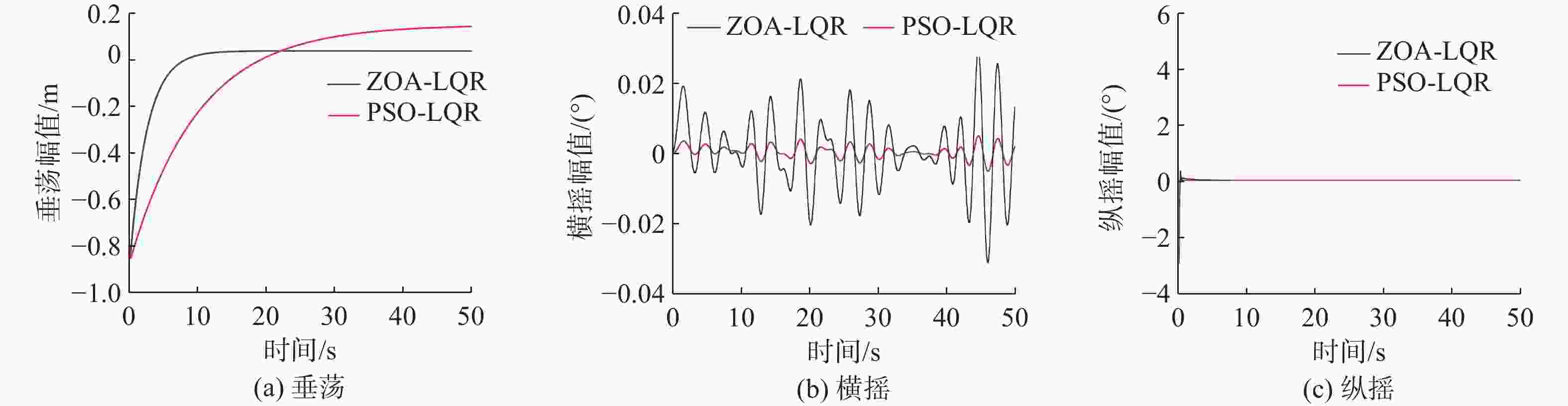
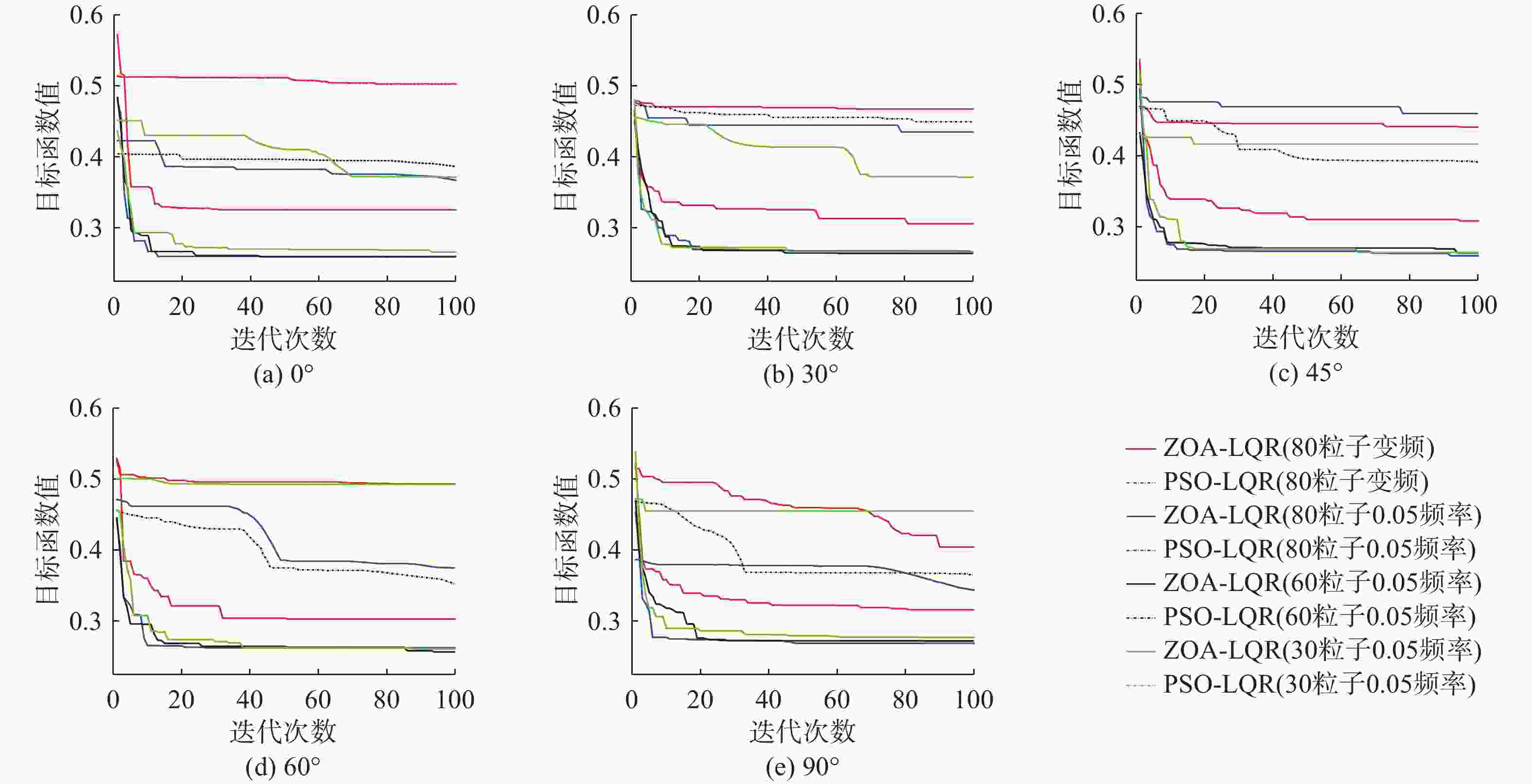
摘要: 文中选取横摇、纵摇和垂荡运动幅值为衡量耐波性的指标, 采用线性二次型调节器(LQR), 并用斑马优化算法(ZOA)优化LQR参数, 完成了无人水面水翼航行器耐波性研究。首先, 以无人水面水翼航行器为研究对象, 以差动襟翼转动角度和电机推力作为控制变量, 建立其运动学与动力学模型, 并将数学模型进行线性化处理; 然后, 将不规则海浪的质点垂加速度与波倾角作为干扰, 采用Simulink进行LQR仿真; 以降低无人水面水翼航行器航行过程中的运动幅值为目标, 在不同采样频率及种群数量下, 分别使用ZOA和粒子群算法对LQR的参数进行寻优并作对比; 最后在不同遭遇角的随机海浪干扰下对耐波性指标进行仿真分析, 验证LQR和ZOA算法的有效性与可行性, 并给出无人水面水翼航行器的合理航向角, 为其姿态控制及耐波性研究提供理论参考。Abstract: To evaluate the seakeeping of a hydrofoil-equipped unmanned surface vessel(USV), a linear quadratic regulator(LQR) was adopted, and its parameters were optimized using the zebra optimization algorithm(ZOA), with the amplitudes of roll, pitch, and heave motions as key metrics. First, the kinematics and dynamics models of the hydrofoil-equipped USV were established with differential flap rotation angles and motor thrust as the control variables, and the mathematical model was linearized. Next, the vertical particle acceleration and slope of irregular waves were introduced as disturbance, and the LQR was simulated using Simulink. To minimize the motion amplitude of hydrofoil-equipped USV during navigation, the LQR parameters were optimized using ZOA and particle swarm optimization(PSO) algorithms, respectively under different sampling frequencies and population sizes for comparison. Finally, simulation under random wave disturbances at different encounter angles was performed to validate the effectiveness and feasibility of LQR and ZOA methods, providing the optimal course angle and references for the attitude control and seakeeping research of hydrofoil-equipped USVs.
-
表 1 航行器结构参数
Table 1. Structure parameters of the vehicle
参数 数值 m/kg 5.39×10 g/(m·s−2) 9.80 Iyy/(kg·m2) 10.41 l1/m 7.54×10−1 b1/m 1.47×10−1 l2/m 4.75×10−1 b2/m 9.00×10−2 lx1/m 2.57×10−1 lx2/m 8.57×10−1 Nφ 5.48×10−2 ρ/(kg·m−3) 1.02×103 h/m 1.11 表 2 目标函数最优值
Table 2. Optimal value of objective function
遭遇角/(°) 0 30 45 60 90 最优值 0.266 0.264 0.263 0.257 0.271 -
[1] 万接喜. 外军无人水面艇发展现状与趋势[J]. 国防科技, 2014, 35(5): 91-96.WAN J X. Development status and trend of foreign unmanned surface craft[J]. National Defense Science and Technology, 2014, 35(5): 91-96. [2] LÜ C, LU D, XIONG C, et al. Toward a gliding hybrid aerial underwater vehicle: design, fabrication, and experiments[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2022, 39(5): 543-556. doi: 10.1002/rob.22063 [3] 张刚, 孙晓晶. 襟翼形式对扑翼获能特性影响的对比分析[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2023, 41(5): 35-47. doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2021.0412ZHANG G, SUN X J. Comparative analysis of the effects of flap forms on energy acquisition characteristics of flapping wings[J]. Chinese Journal of Aerodynamics, 2023, 41(5): 35-47. doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2021.0412 [4] TELLO M, SILVA S, SOARES C G. Seakeeping performance of fishing vessels in irregular waves[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2011, 38(5-6): 763-773. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2010.12.020 [5] KUDINOV Y I, PASHCHENKO F F, KELINA A Y, et al. Analysis of control system models with conventional LQR and fuzzy LQR controller[C]//13th International Symposium on Intelligent Systems(INTELS). St Petersburg Electrotechn Univ LETI. St Petersburg, Russia: INTELS, 2019, 150: 737-742. [6] PRIYATMADI, SANDIWAN A P, WIJAYA H, et al. Application of SPSA LQR tuning on quadrotor[C]//6th International Annual Engineering Seminar(InAES). Yogyakarta, Indonesia: IEEE, 2016, (54): 32-36. [7] TROJOVSKÁ E, DEHGHANI M, TROJOVSKY P. Zebra optimization algorithm: A new bio-inspired optimization algorithm for solving optimization algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2022(10): 49445-49473. [8] 王鹏飞, 杜忠华, 牛坤, 等. 基于改进粒子群算法的倒立摆LQR优化控制[J]. 计算机仿真, 2021, 38(2): 220-224, 272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2021.02.048WANG P F, DU Z H, NIU K, et al. LQR optimization control of inverted pendulum based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Computer Simulation, 2021, 38(2): 220-224, 272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2021.02.048 [9] 郭惜久, 程翔. 随机海浪模型仿真[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2010, 31(8): 134-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0707.2010.08.044GUO X J, CHENG X. Random ocean wave model simulation[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2010, 31(8): 134-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0707.2010.08.044 [10] 任俊生. 高速水翼船运动控制[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015. [11] 胡寿松. 自动控制原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019. [12] 李进富. 大风浪中船舶“Z”字航法探讨[C]//中国航海学会2006年学术年会. 中国, 广州: 广州远洋运输公司, 2006: 158-164. -




 下载:
下载: