Obstacle Avoidance Control of Autonomous Undersea Vehicle Based on DVFH+ in Ocean Current Environment
-
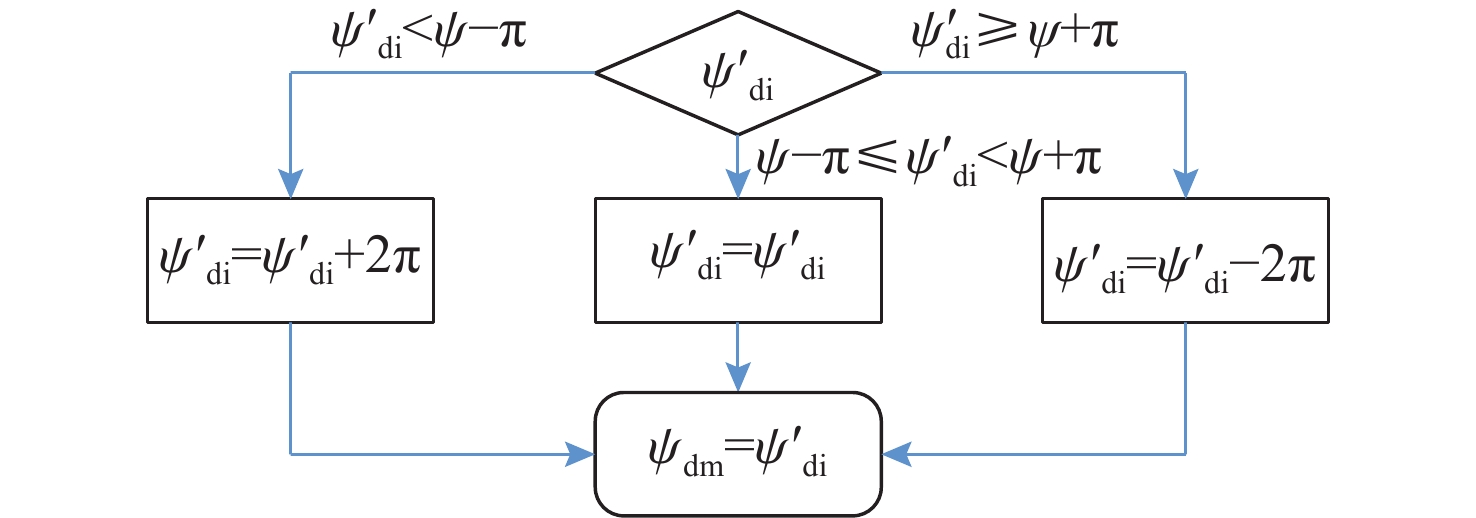
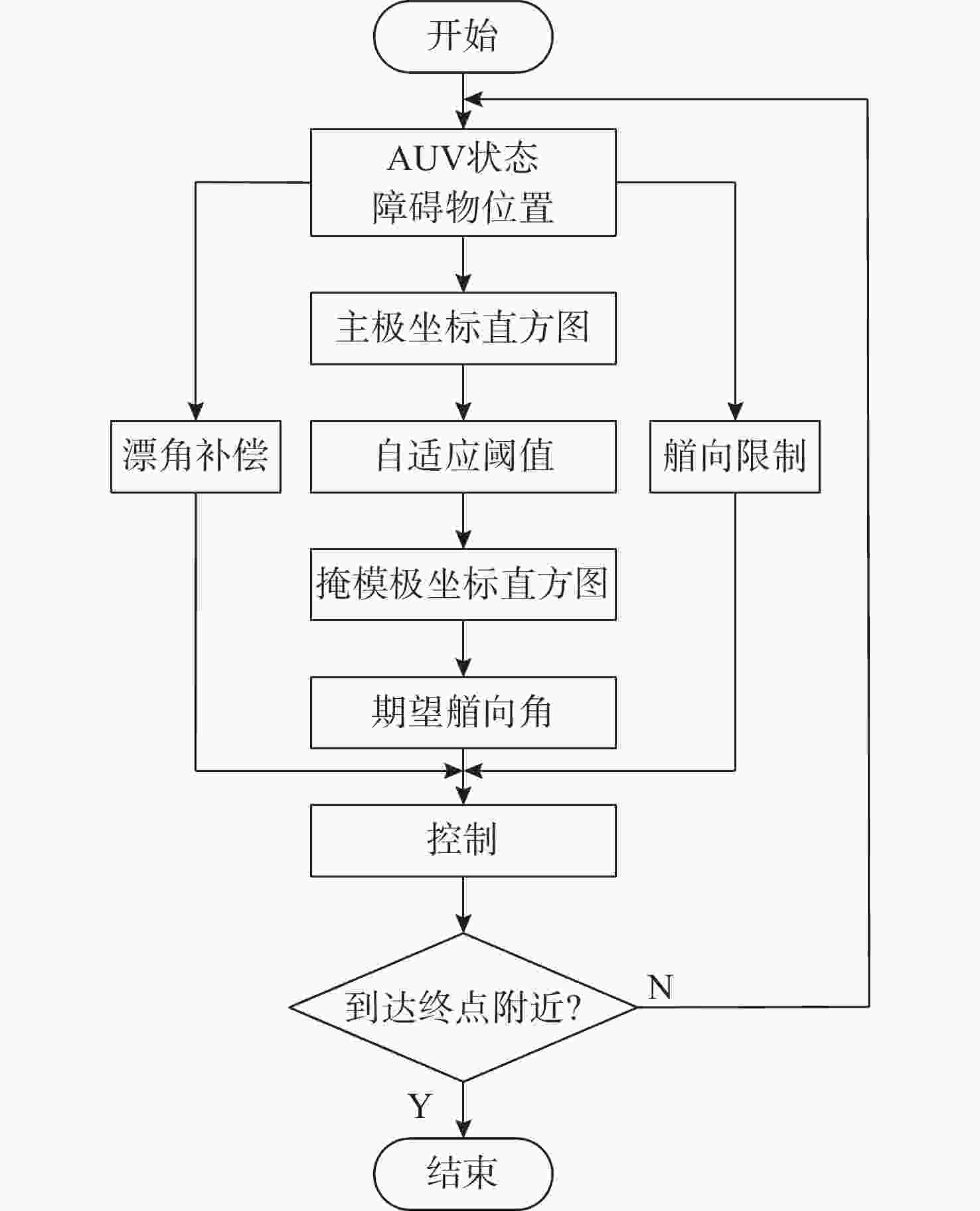
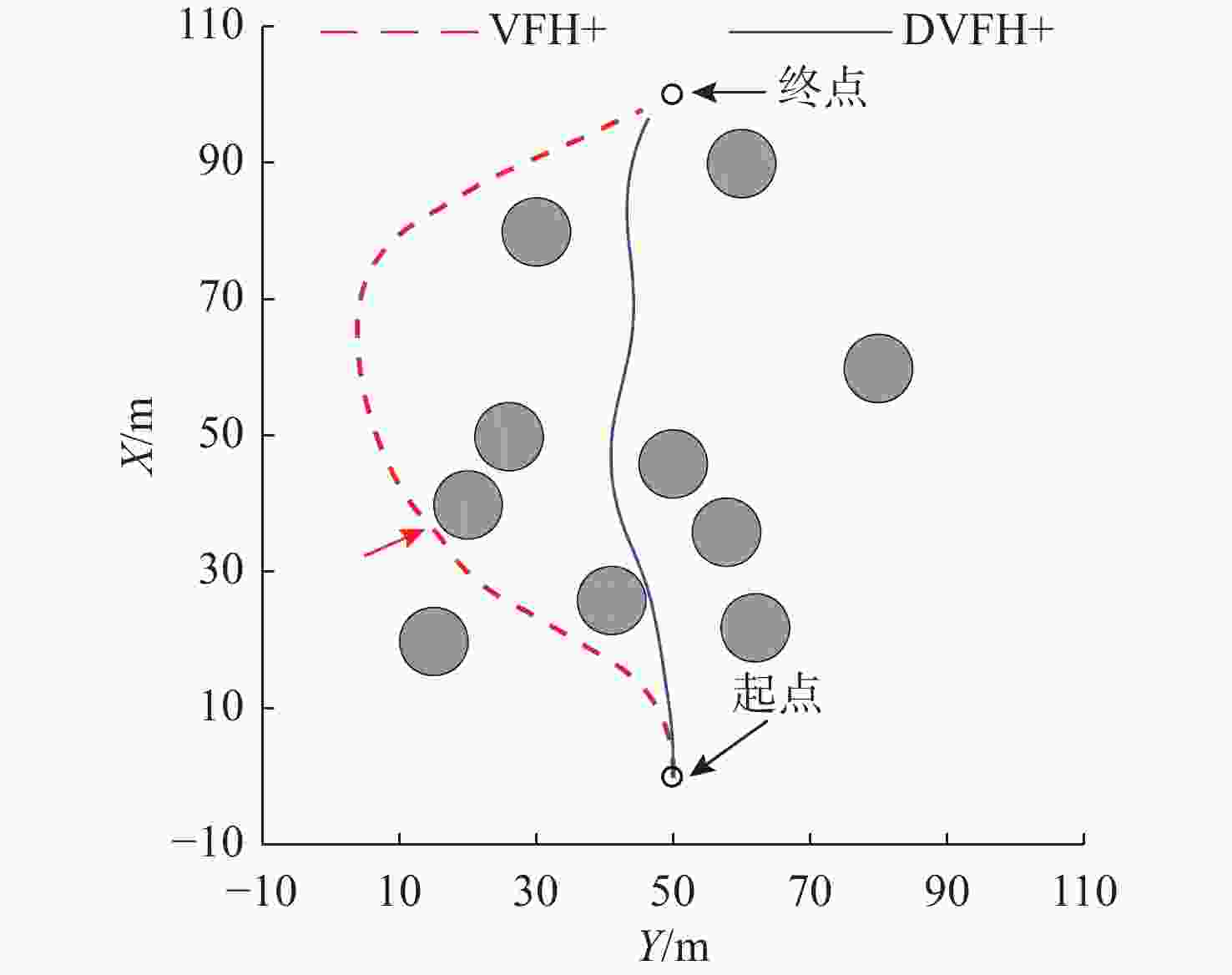
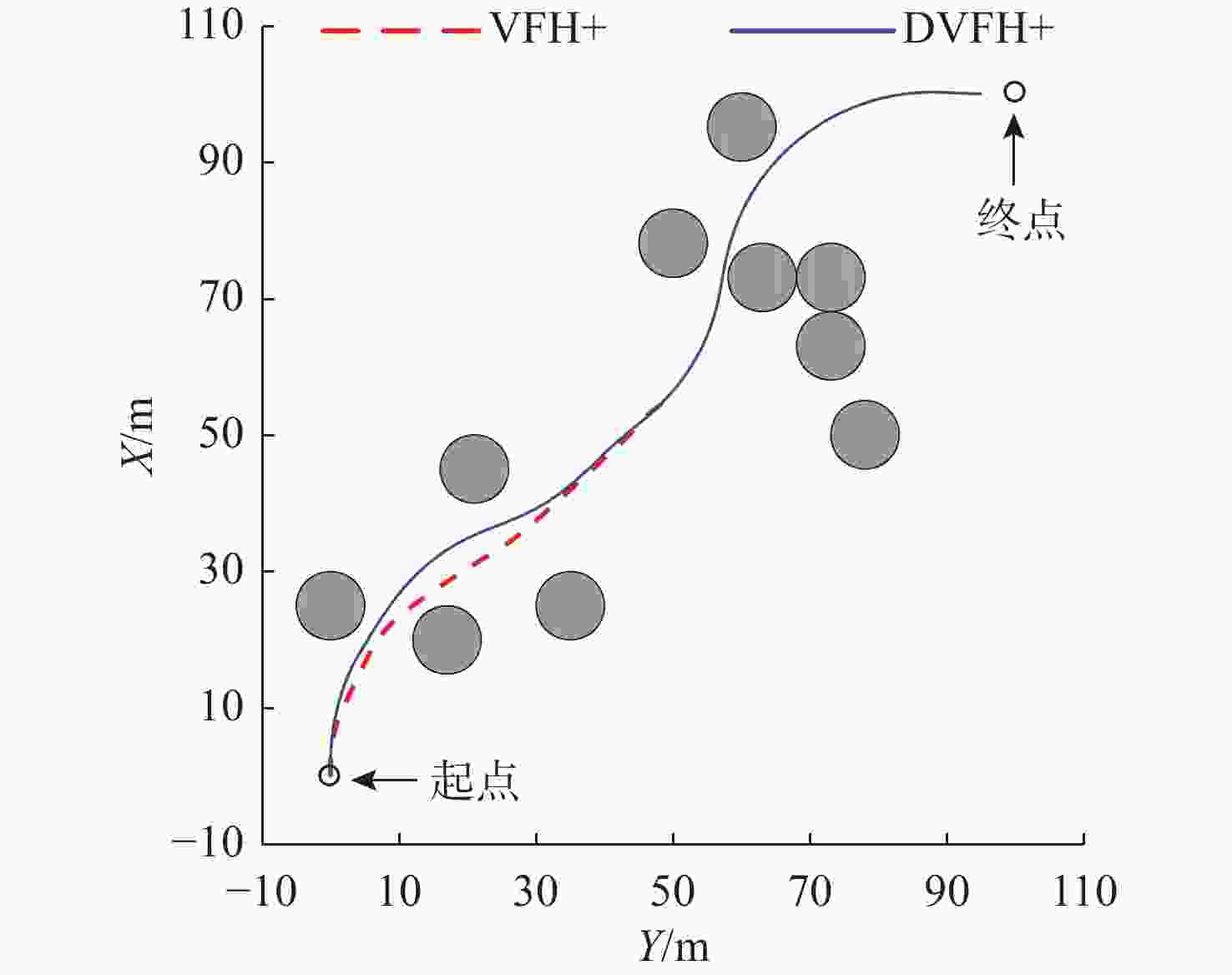
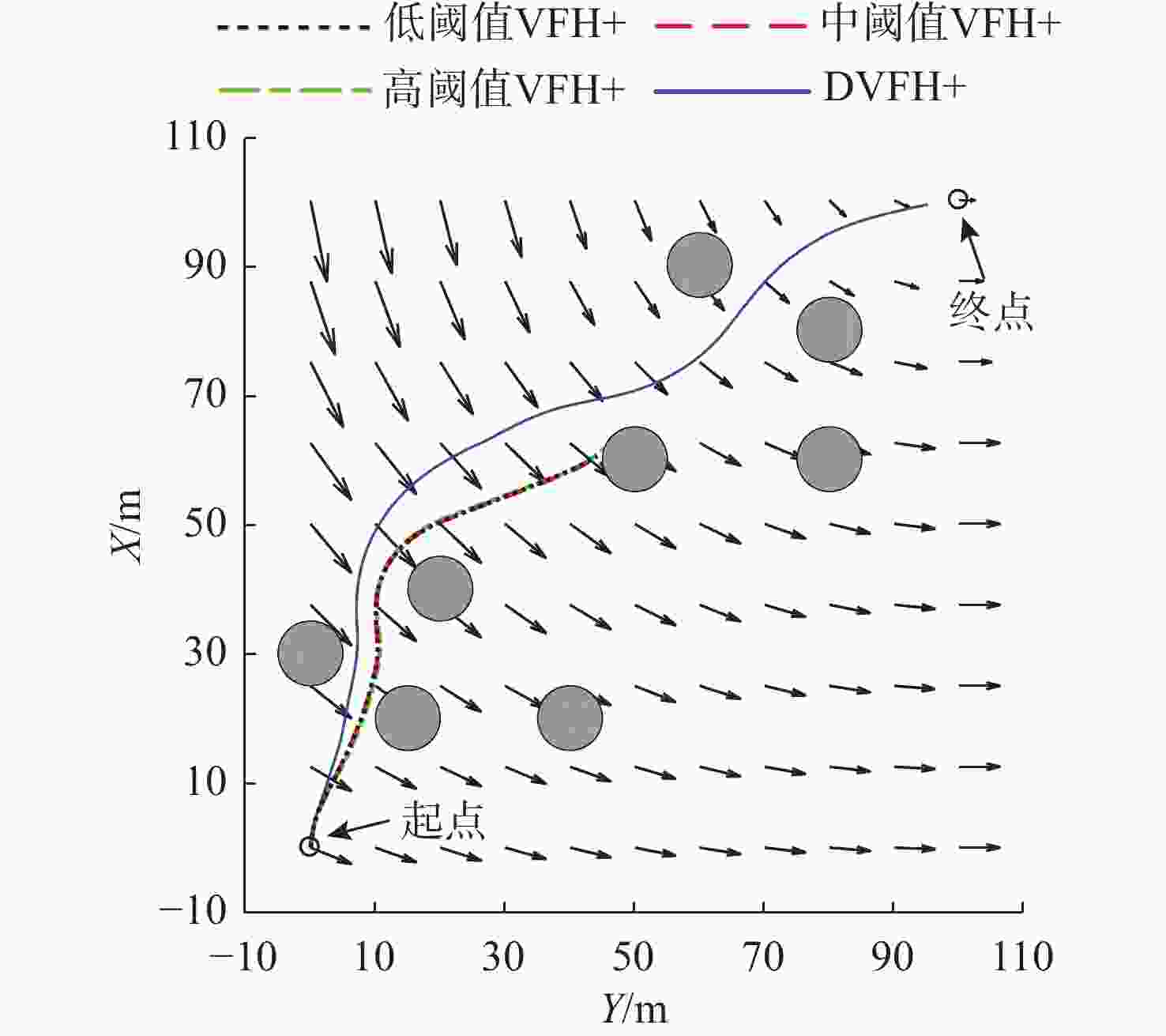
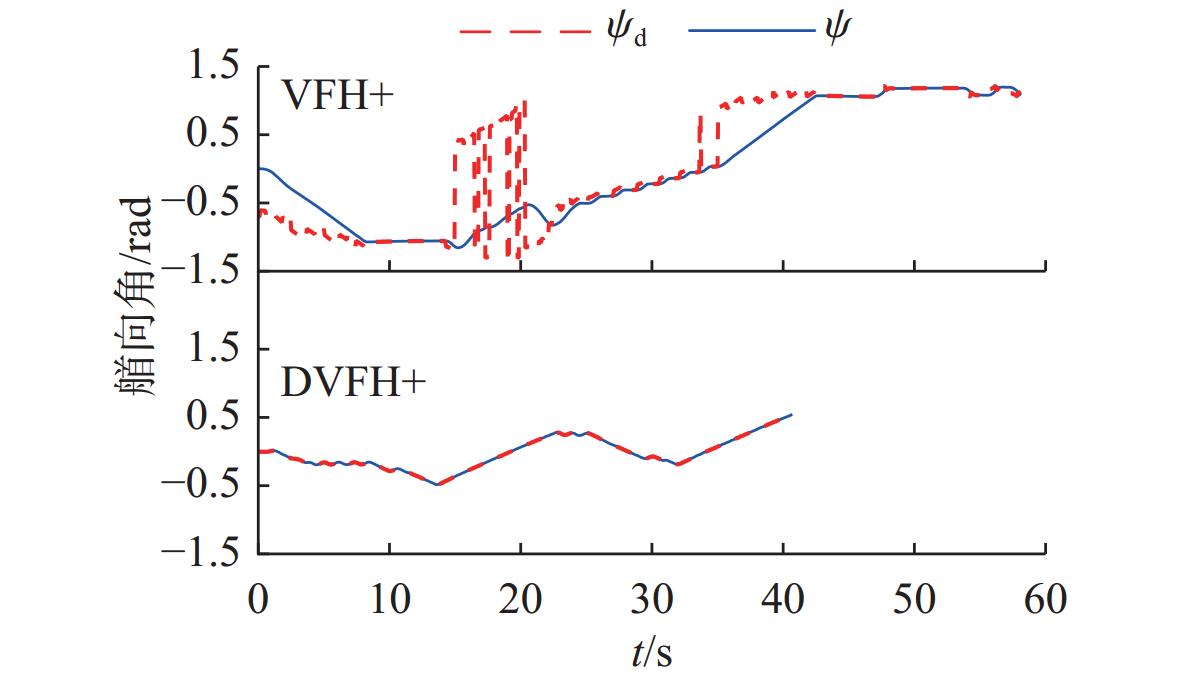
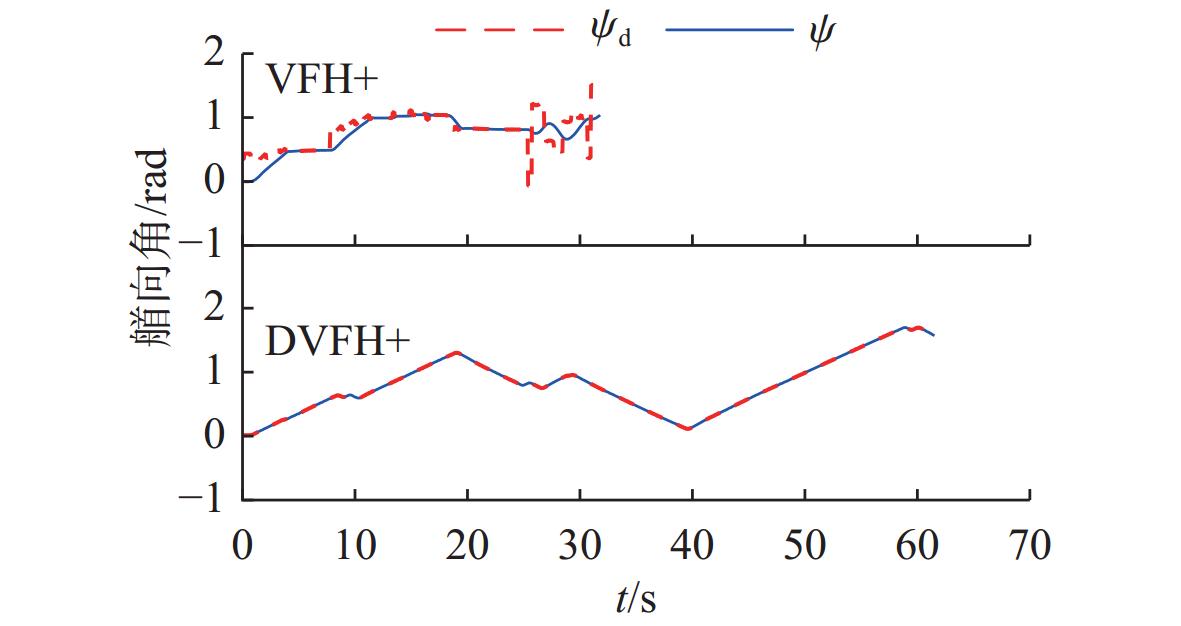
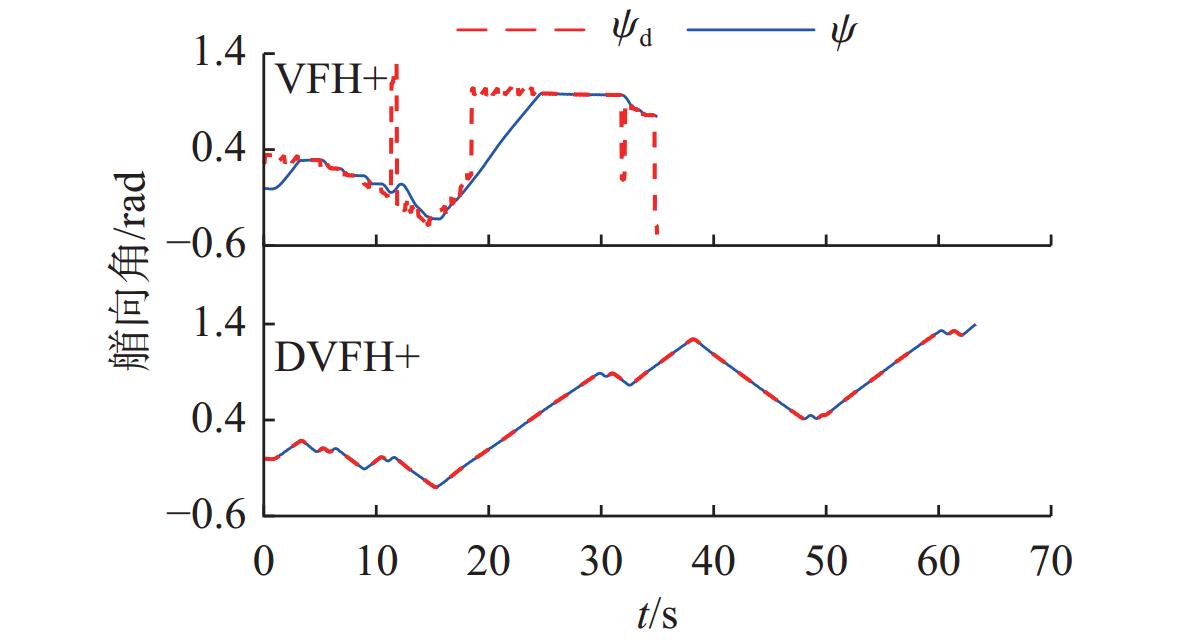
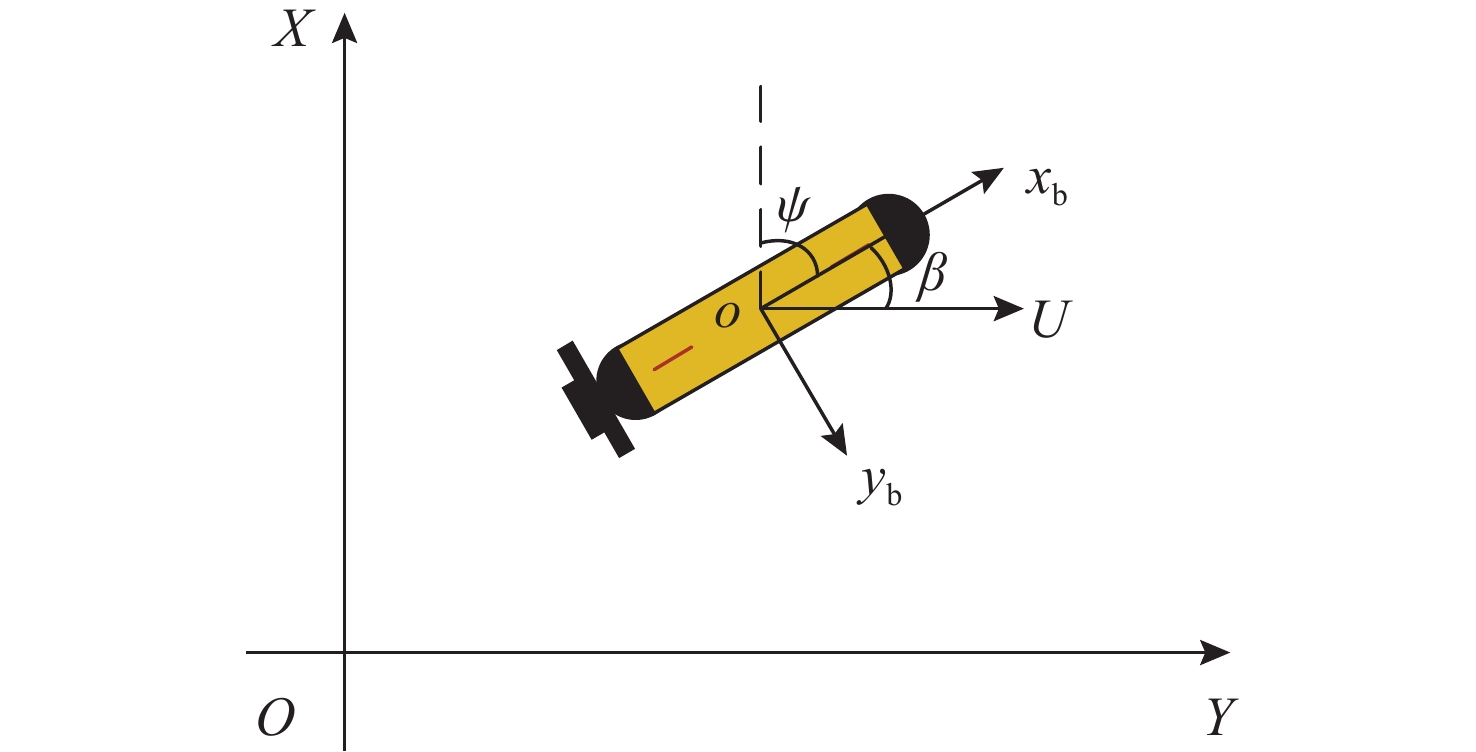
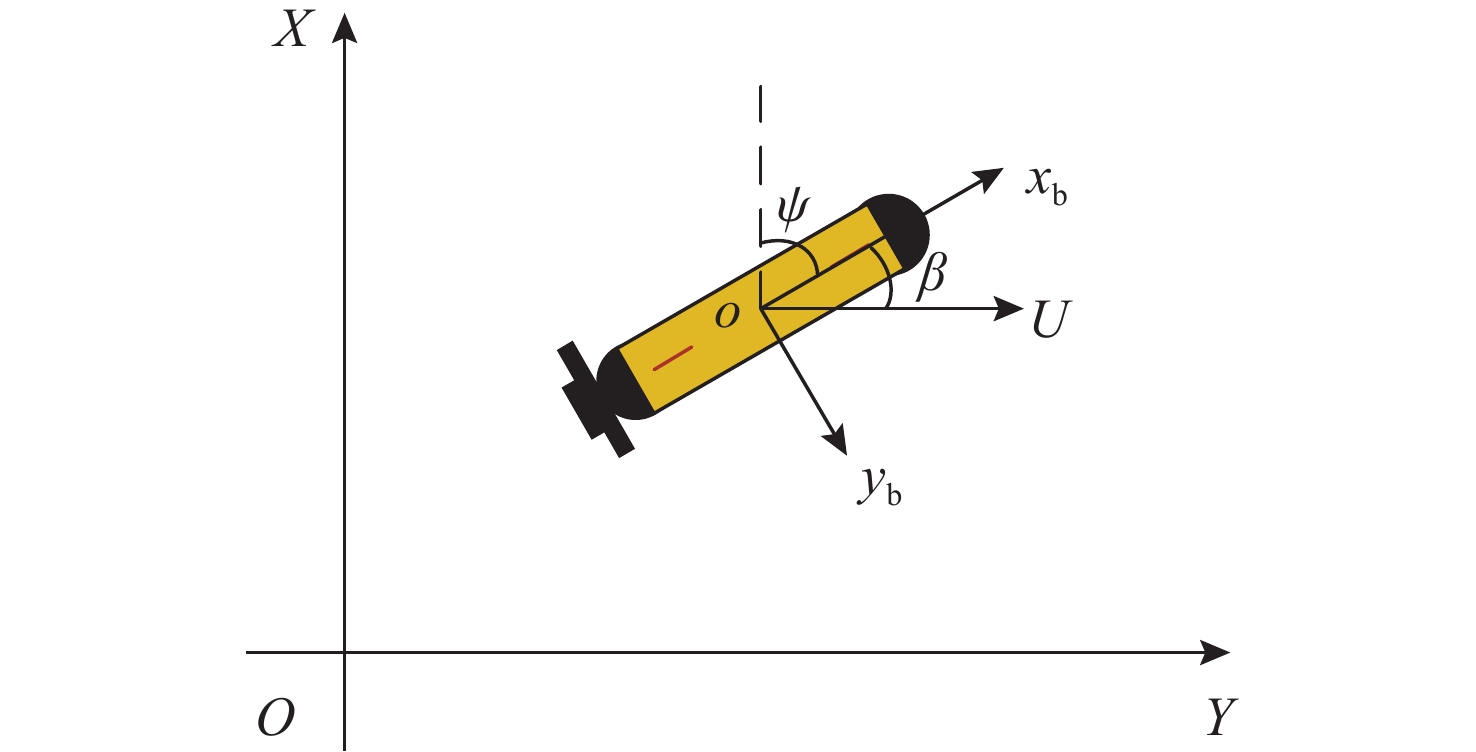
摘要: 针对向量场直方图法(VFH)的改进算法VFH+忽视自主水下航行器(AUV)动力学性能和洋流环境的影响, 且对阈值设置敏感的问题, 文中提出了一种基于动力学的VFH+(DVFH+)。通过AUV的动力学参数来限制期望艏向的输出, 解决了原算法期望输出跳变的问题, 从而改善了AUV的跟踪性能; 考虑真实洋流环境下的漂角补偿, 优化了避障算法, 提高了其鲁棒性和适应性; 根据障碍物信息自适应调节阈值大小, 从而计算得到符合AUV周围环境特征的规划指令, 保证航行的高效性和安全性。采用REMUS 100 AUV模型进行仿真实验, 结果表明, 文中所提出的DVFH+能给出更加光滑可行的避障路线, 适用于复杂环境下的AUV避障, 且有效避免了原算法因阈值设置不合理导致的路径绕远及规划失败等情况。Abstract: The improved vector field histogram algorithm(VFH+) tends to overlook the autonomous undersea vehicle(AUV) dynamics and ocean current effects, and it is sensitive to threshold selection. To address this issue, a dynamics-based VFH+(DVFH+) algorithm was proposed in this paper. By incorporating AUV dynamics parameters to limit the expected heading output, this method reduced abrupt changes in the expected algorithm output, thereby improving AUV’s tracking performance. Additionally, by considering the drift angle compensation in the real ocean current environment, the obstacle avoidance algorithm was optimized to improve its robustness and adaptability. By using information about obstacles, the threshold values were adjusted automatically. This enabled the calculation of the planning instructions based on environmental characteristics around AUVs, ensuring the efficiency and safety of navigation. Simulation experiments using the REMUS 100 AUV model show that DVFH+ can provide a smoother and more feasible obstacle avoidance route, making it suitable for AUV obstacle avoidance in complex environments while effectively preventing issues such as detouring and planning failure caused by improper threshold settings in the original algorithm.
-
表 1 REMUS 100 AUV模型参数
Table 1. Parameters of the REMUS 100 AUV model
参数 数值 质量/kg 31.9 长度/m 1.6 最大线速度/(m/s) 2.5 最大角速度/(rad/s) 0.1 最大角加速度/(rad/s2) 0.4 表 2 算法参数
Table 2. Algorithm parameters
参数 符号 数值 参数 符号 数值 活动窗口半径/m $ r_{\rm{\mathit{a}}} $ 50 控制律参数 ε 1 AUV安全半径/m $ r_{\mathrm{\mathit{s}}} $ 1.5 控制律参数 p 100 确定性值 ${c_{ij}}$ 15 控制律参数 κ 200 参数 a 6251 权重 ${\omega _1}$ 0.8 参数 b 2.5 权重 ${\omega _2}$ 0.2 环境分辨率/(°) α 5 阈值下界 ${T_{\min }}$ 300 宽窄谷区分度 s 18 阈值上界 ${T_{\max }}$ 1 000 000 代价函数系数 ${\mu _1}$ 0.6 低阈值 ${T_{\rm{l}}}$ 200 000 代价函数系数 ${\mu _2}$ 0.2 中阈值 ${T_{\rm{m}}}$ 500 000 代价函数系数 ${\mu _{_3}}$ 0.2 高阈值 $ T\mathrm{_h} $ 800 000 -
[1] 郭渊博, 李琦, 闵博旭, 等. 基于分布式模型预测控制的欠驱动AUV编队控制[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(3): 405-412. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.202204018GUO Y B, LI Q, MIN B X, et al. Formation control of an underactuated autonomous undersea vehicle based on distributed model predictive control[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2023, 31(3): 405-412. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.202204018 [2] 姚金艺, 曾庆军, 周启润, 等. 全驱动AUV系统路径跟踪设计与实现[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2019, 27(4): 452-458.YAO J Y, ZENG Q J, ZHOU Q R, et al. Design and implementation of a path tracking system for fully actuated AUV[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2019, 27(4): 452-458. [3] KRIEG M, MOHSENI K. Dynamic modeling and control of biologically inspired vortex ring thrusters for underwater robot locomotion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2010, 26(3): 542-554. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2010.2046069 [4] 张荣敏, 陈原, 高军. 无鳍舵矢量推进水下机器人纵向稳定性研究[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2017, 38(1): 133-139, 152.ZHANG R M, CHEN Y, GAO J. Longitudinal handling stability of vectored thrust underwater vehicle without fin and rudder[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2017, 38(1): 133-139, 152. [5] JOUNG T H, LEE J H, NHO I S, et al. A study on the design and manufacturing of a deep-sea unmanned underwater vehicle based on structural reliability analysis[J]. Ships and Offshore Structures, 2009, 4(1): 19-29. doi: 10.1080/17445300802315367 [6] 郭银景, 鲍建康, 刘琦, 等. AUV实时避障算法研究进展[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2020, 28(4): 351-358. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2020.04.001GUO Y J, BAO J K, LIU Q, et al. Research progress of real-time obstacle avoidance algorithms for unmanned undersea vehicle: A review[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2020, 28(4): 351-358. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2020.04.001 [7] ZENG Z, LIAN L, SAMMUT K, et al. A survey on path planning for persistent autonomy of autonomous underwater vehicles[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2015, 110: 303-313. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2015.10.007 [8] 章飞, 胡春磊. 基于滚动速度障碍法的AUV动态避障路径规划[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2021, 29(1): 30-38.ZHANG F, HU C L. Research on AUV dynamic obstacle avoidance path planning based on the rolling speed obstacle method[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2021, 29(1): 30-38. [9] MCMAHON J, PLAKU E. Mission and motion planning for autonomous underwater vehicles operating in spatially and temporally complex environments[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2016, 41(4): 1-20. [10] BORENSTEIN J, KOREN Y. The vector field histogram-fast obstacle avoidance for mobile robots[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1991, 7(3): 278-288. doi: 10.1109/70.88137 [11] ULRICH I, BORENSTEIN J. VFH+: Reliable obstacle avoidance for fast mobile robots[C]//Proceedings 1998 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat No98CH36146). Leuven, Belgium: IEEE, 1998: 1572-1577. [12] 徐茂竹, 李弘, 李亚光, 等. 单目视觉引导下的无人艇局部避障方法[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 35(4): 732-741.XU M Z, LI H, LI Y G, et al. Local obstacle avoidance for unmanned surface vehicle via monocular vision[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 35(4): 732-741. [13] PAPPAS P, CHIOU M, EPSIMOS G T, et al. VFH plus based shared control for remotely operated mobile robots[C]//IEEE International Symposium on Safety, Security, and Rescue Robotics(SSRR). Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates: IEEE, 2020: 366-373. [14] SARY I P, NUGRAHA Y P, MEGAYANTI M, et al. Design of obstacle avoidance system on hexacopter using vector field histogram-plus[C]//8th IEEE International Conference on System Engineering and Technology(ICSET). Bandung, Indonesia: IEEE, 2018: 18-23. [15] 娄虎, 赵泽钰, 阮文涛, 等. 基于自调节VFH+的水面无人艇雷达避障控制研究[J]. 机械制造与自动化, 2021, 50(3): 179-183.LOU H, ZHAO Z Y, RUAN W T, et al. Research on obstacle avoidance control of lidar for USV based on self-adjusting VFH+[J]. Machine Building & Automation, 2021, 50(3): 179-183. [16] 陈浩华, 赵红, 王宁, 等. 复杂扰动下水下机器人的轨迹精确跟踪控制[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2022, 17(2): 98-108.CHEN H H, ZHAO H, WANG N, et al. Accurate track control of unmanned underwater vehicle under complex disturbances[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2022, 17(2): 98-108. [17] 李亚鑫, 刘里宵, 王宇. 欠驱动水下机器人的最优等效补偿轨迹跟踪控制[J]. 控制与决策, 2024, 39(9): 2923-2931.LI Y X, LIU L X, WANG Y. Optimal equivalent compensation trajectory tracking control for underactuated underwater robots[J]. Control and Decision, 2024, 39(9): 2923-2931. [18] YUAN C, SHUAI C, FANG Y, et al. A novel real-time obstacle avoidance method in guidance layer for AUVs’ path following[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 73(2): 1845-1856. [19] FOSSEN T I. Handbook of marine craft hydrodynamics and motion control[M]. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 2011. [20] REIS M F, JAIN R P, AGUIAR A P, et al. Robust moving path following control for robotic vehicles: theory and experiments[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2019, 4(4): 3192-3199. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2019.2925733 [21] DIAZ D, MARIN L. VFH plus D: An improvement on the VFH plus algorithm for dynamic obstacle avoidance and local planning[C]//21st IFAC World Congress on Automatic Control-Meeting Societal Challenges. Berlin, Germany: Elsevier, 2020: 9590-9595. [22] 刘淑霞, 李立刚, 金久才, 等. 基于漂角估计的无人船局部动态避障方法[J]. 电光与控制, 2023, 30(1): 103-108, 119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2023.01.018LIU S X, LI L G, JIN J C, et al. Local dynamic avoidance method of USV with drift angle estimation[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2023, 30(1): 103-108, 119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2023.01.018 [23] 韩鹏, 刘志林, 周泽才, 等. 基于LOS法的自航模航迹跟踪控制算法实现[J]. 应用科技, 2018, 45(3): 66-70.HAN P, LIU Z L, ZHOU Z C, et al. Path tracking control algorithm based on LOS method for surface self-propulsion vessel[J]. Applied Science and Technology, 2018, 45(3): 66-70. [24] PEREZ T, FOSSEN T I. A matlab toolbox for parametric identification of radiation-force models of ships and offshore structures[J]. Modeling Identification and Control, 2009, 30(1): 1-15. doi: 10.4173/mic.2009.1.1 [25] WANG N, SU S F. Finite-time unknown observer-based interactive trajectory tracking control of asymmetric underactuated surface vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2021, 29(2): 794-803. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2019.2955657 [26] SHI L, ZHENG R, ZHANG S, et al. Cooperative estimation to reconstruct the parametric flow filed using multiple AUVs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 1-10. -




 下载:
下载: