Combined Homing Guidance Law of Torpedo Based on Fuzzy Control
-
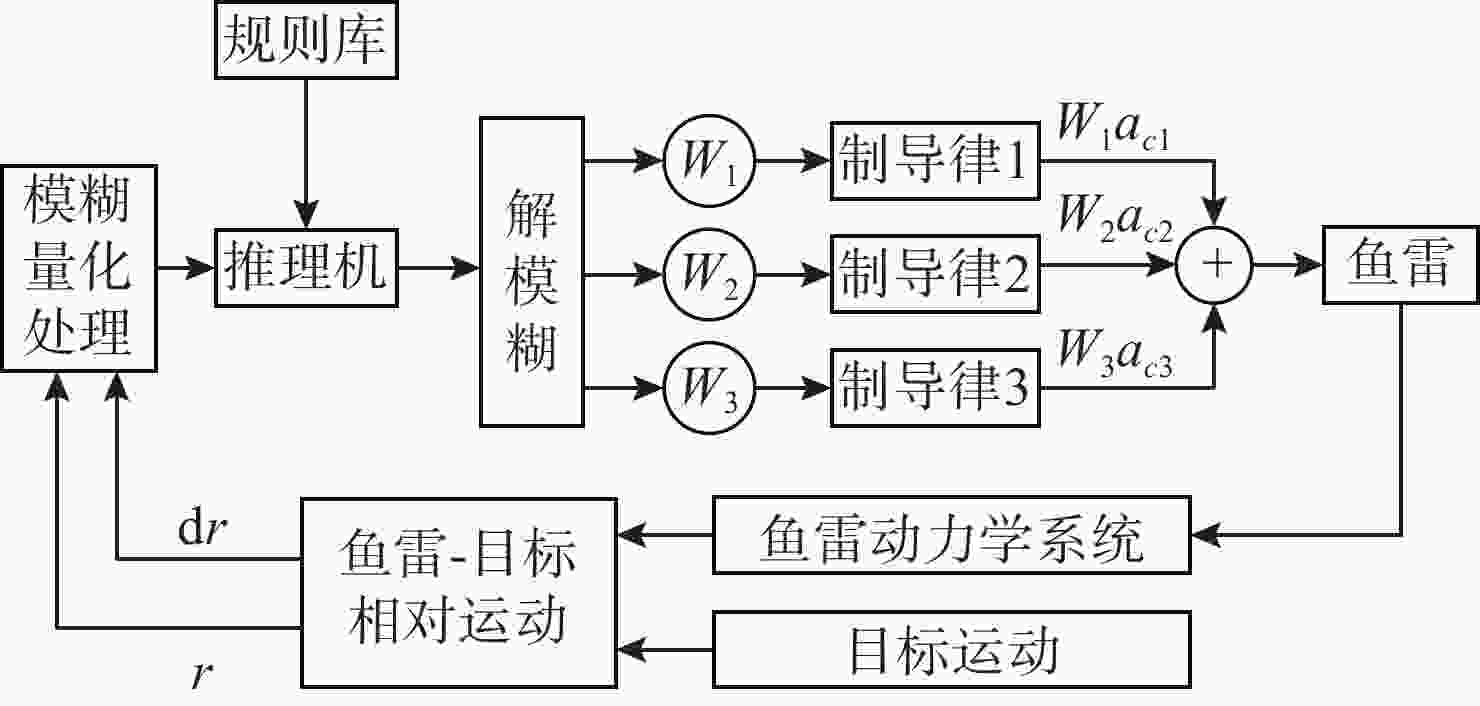
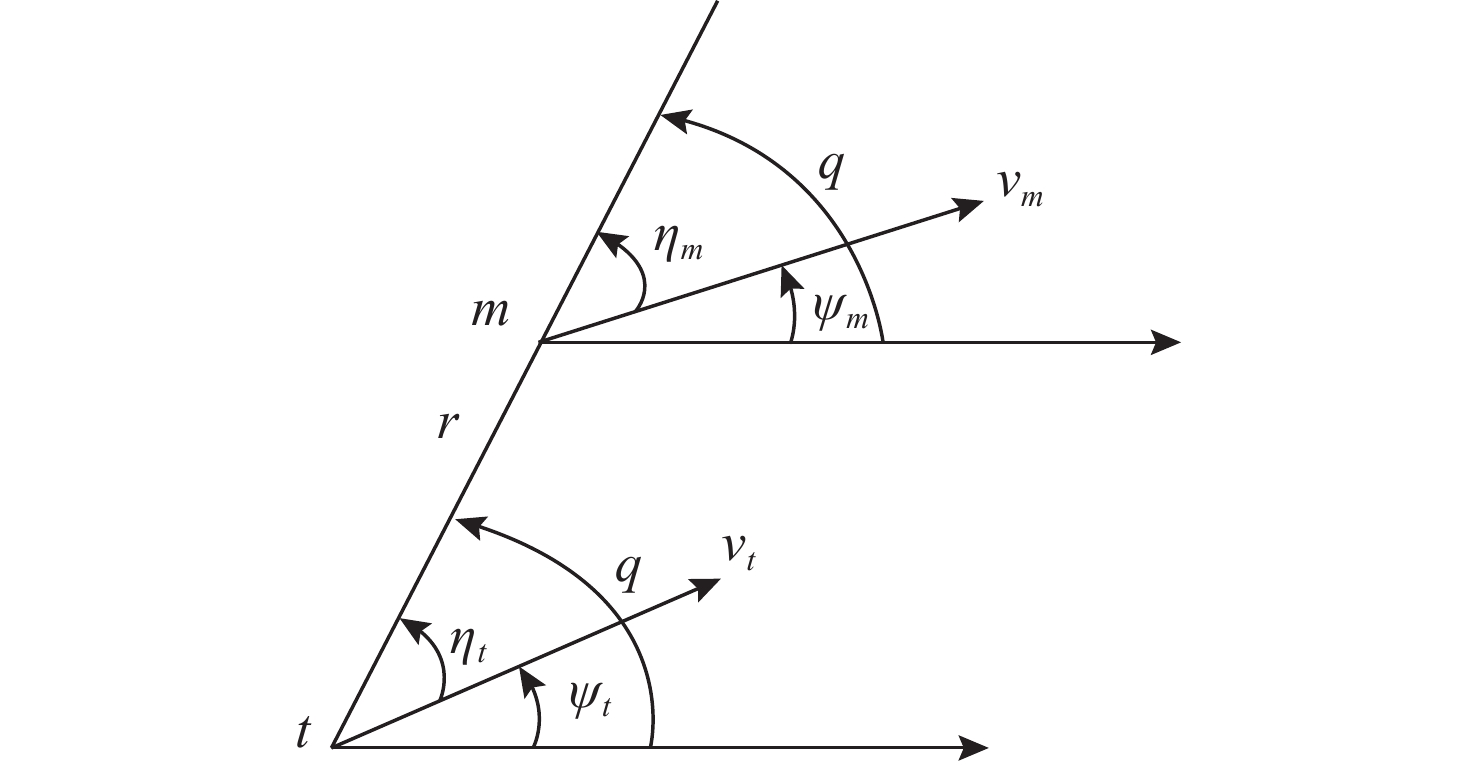
摘要: 在鱼雷自导导引过程中, 单一导引方法不能适应不同导引阶段, 难以有效保证鱼雷导引效果。为此, 文中结合固定提前角导引法、比例导引法以及变结构导引法等3种不同典型导引方法, 基于模糊控制原理, 设计出一种模糊组合导引律。通过在不同环境下的仿真对比, 结果表明, 模糊组合导引律的综合性能优于其他典型导引律, 可为鱼雷自导导引的实际应用提供借鉴。Abstract: In the process of torpedo homing guidance, it is difficult for a single guidance method to adapt to different guidance phases and ensure the torpedo guidance effect effectively. For this reason, this paper designs a fuzzy combined guidance law based on the principle of fuzzy control by combining three different typical guidance methods, namely, fixed lead angle guidance method, proportional guidance method, and variable structure guidance method. The results of simulation and comparison in different environments show that the comprehensive performance of the fuzzy combined guidance law is better than that of other typical guidance laws, which can provide reference for the practical application of torpedo homing guidance.
-
Key words:
- torpedo /
- fuzzy control /
- guidance law
-
表 1 常用自导导引方法优缺点
Table 1. Comparison table of advantages and disadvantages of commonly used guiding methods
导引方法 优点 缺点 追踪法 工程上极易实现 弹道弯曲, 浪费航程; 不能实现全向攻击, 只能命中目标尾部 固定提前角导引法 易于工程实现, 对制导信息精度要求较低 对机动目标跟踪效果较差 比例导引法 对机动目标跟踪效果较好; 拦截时间短 不能满足终端角约束 自动调整提前角导引法 对机动目标跟踪效果较好 只适用装备多波束自导装置鱼雷; 雷目较近时弹道弯曲程度大 最优导引法 对机动目标跟踪效果好; 满足终端角约束 鲁棒性差; 需要估计剩余导引时间 变结构导引法 对机动目标跟踪效果好; 鲁棒性好; 能满足终端角约束 所需制导信息种类较多; 对制导信息精度要求高; 拦截时间长 表 2 导引系数规则库
Table 2. Rule base for guidance coefficient
${W_A}$ ${W_B}$ ${W_C}$ r $\dot r$ r $\dot r$ r $\dot r$ P Z N P Z N P Z N PB PB PB PM PB Z Z PS PB Z Z Z PM PM PS PS PM PS PM PM PM Z Z PS PS PM PS Z PS PM PB PB PS PS PS PM Z Z Z Z Z PM PS Z Z PB PB PB 表 3 不同语言变量隶属度函数的中心点和宽度
Table 3. Centroids and widths of the affiliation functions of different language variables
i $\mu \left( r \right)$ $\mu \left( {\dot r} \right)$ $\mu \left( {{W_A}} \right)$ $\mu \left( {{W_B}} \right)$ $\mu \left( {{W_C}} \right)$ $C_r^i\big/{\mathrm{m}}$ $\delta _r^i\big/{\mathrm{m}}$ $C_{\dot r}^i\big/{\mathrm{m}}$ $\delta _{\dot r}^i\big/{\mathrm{m}}$ $C_{{W_A}}^i$ $\delta _{{W_A}}^i$ $C_{{W_B}}^i$ $\delta _{{W_B}}^i$ $C_{{W_C}}^i$ $\delta _{{W_C}}^i$ 1 — [400, 500] — [0, 500] — [0.8, 1.0] — [0.8, 1.0] — [0.8, 1.0] 2 400 [300, 500] — [–1, 1] 0.7 [0.5, 0.9] 0.7 [0.5, 0.9] 0.7 [0.5, 0.9] 3 300 [200, 400] 0 [–500, 0] 0.4 [0.2, 0.6] 0.4 [0.2, 0.6] 0.4 [0.2, 0.6] 4 — [0, 300] — — — [0, 0.3] — [0, 0.3] — [0, 0.3] 表 4 目标非机动时鱼雷法向指令加速度平均值和方差对比
Table 4. Comparison of mean and variance of normal command acceleration of the torpedo when the target is non-motorized
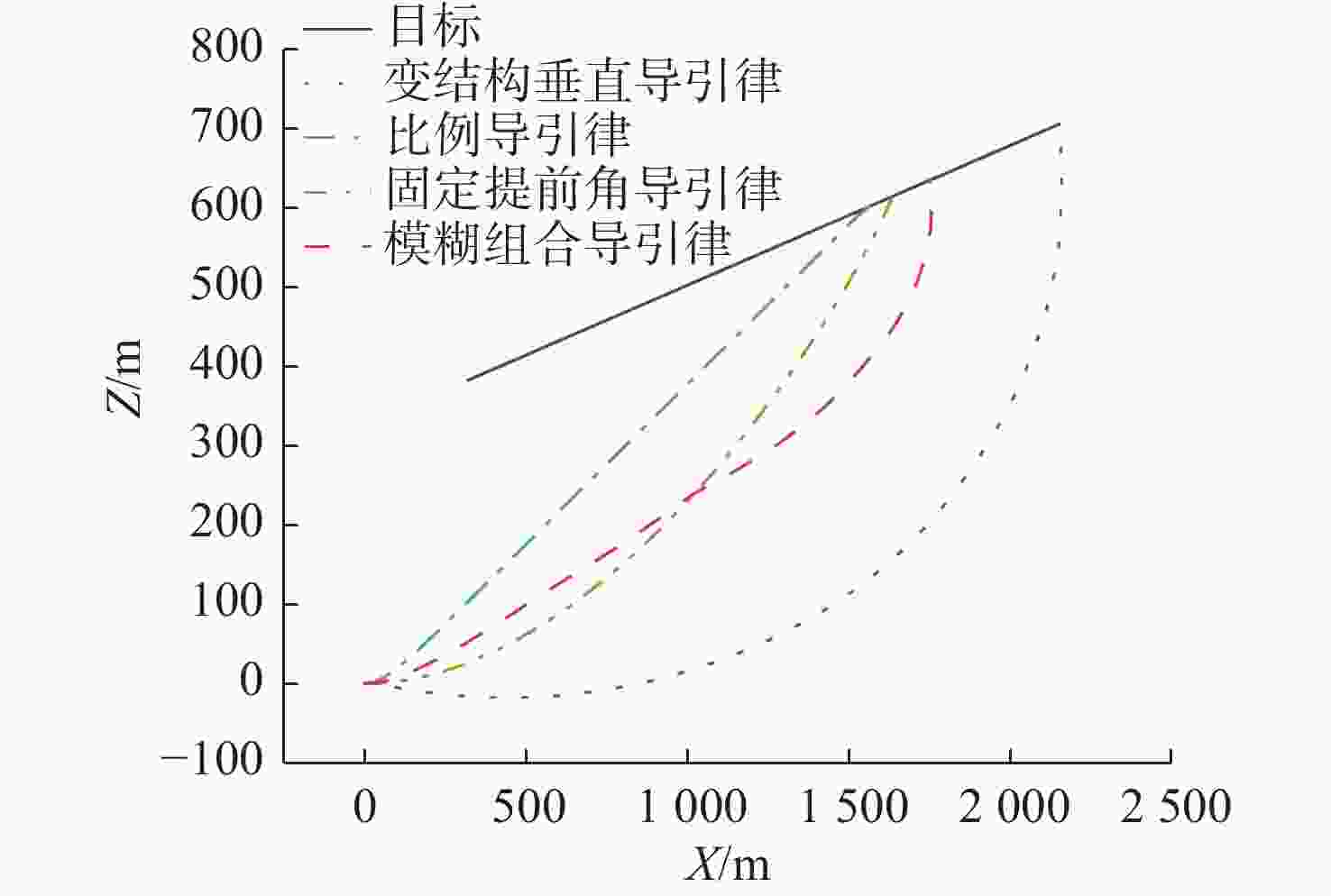
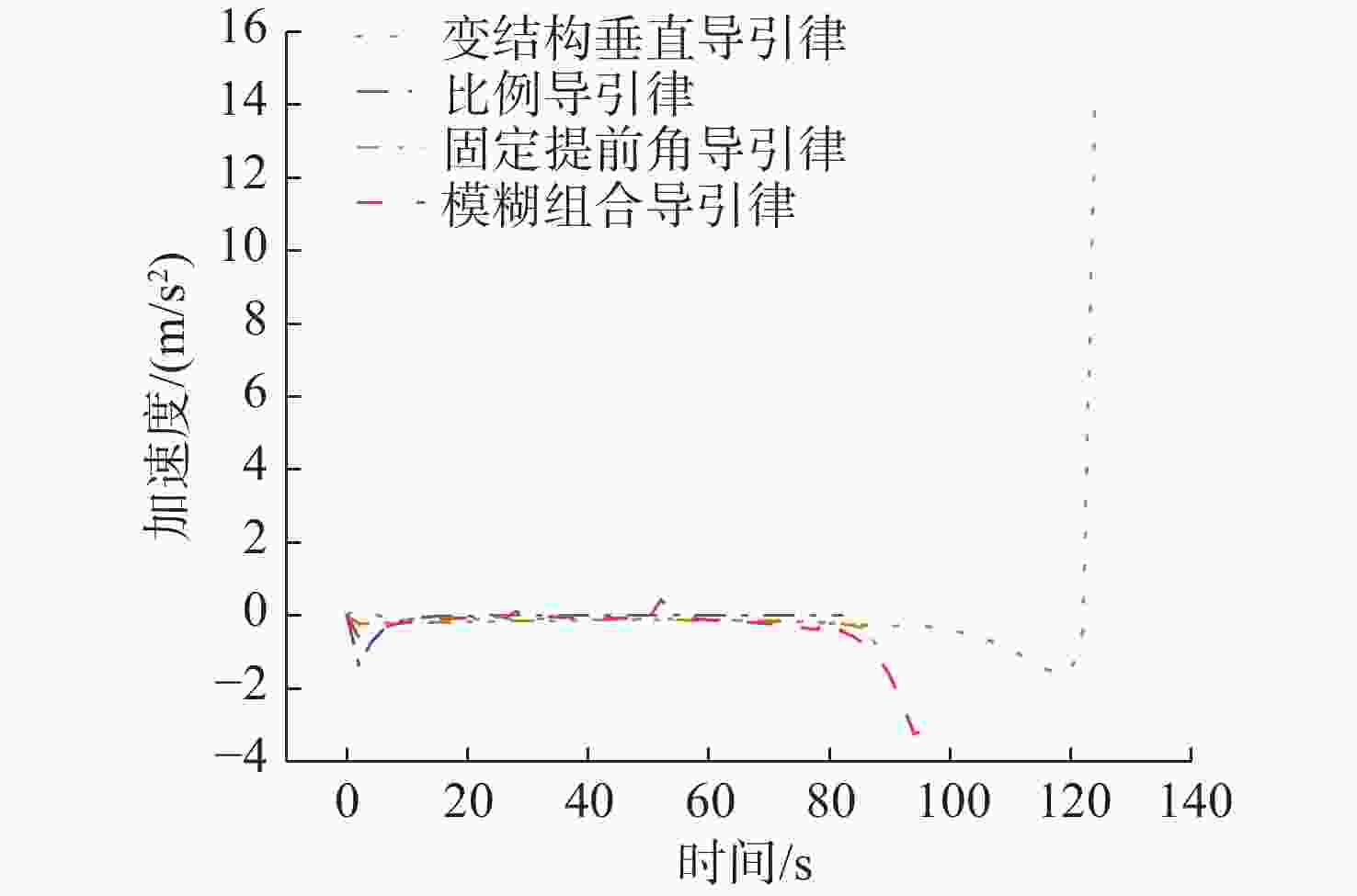
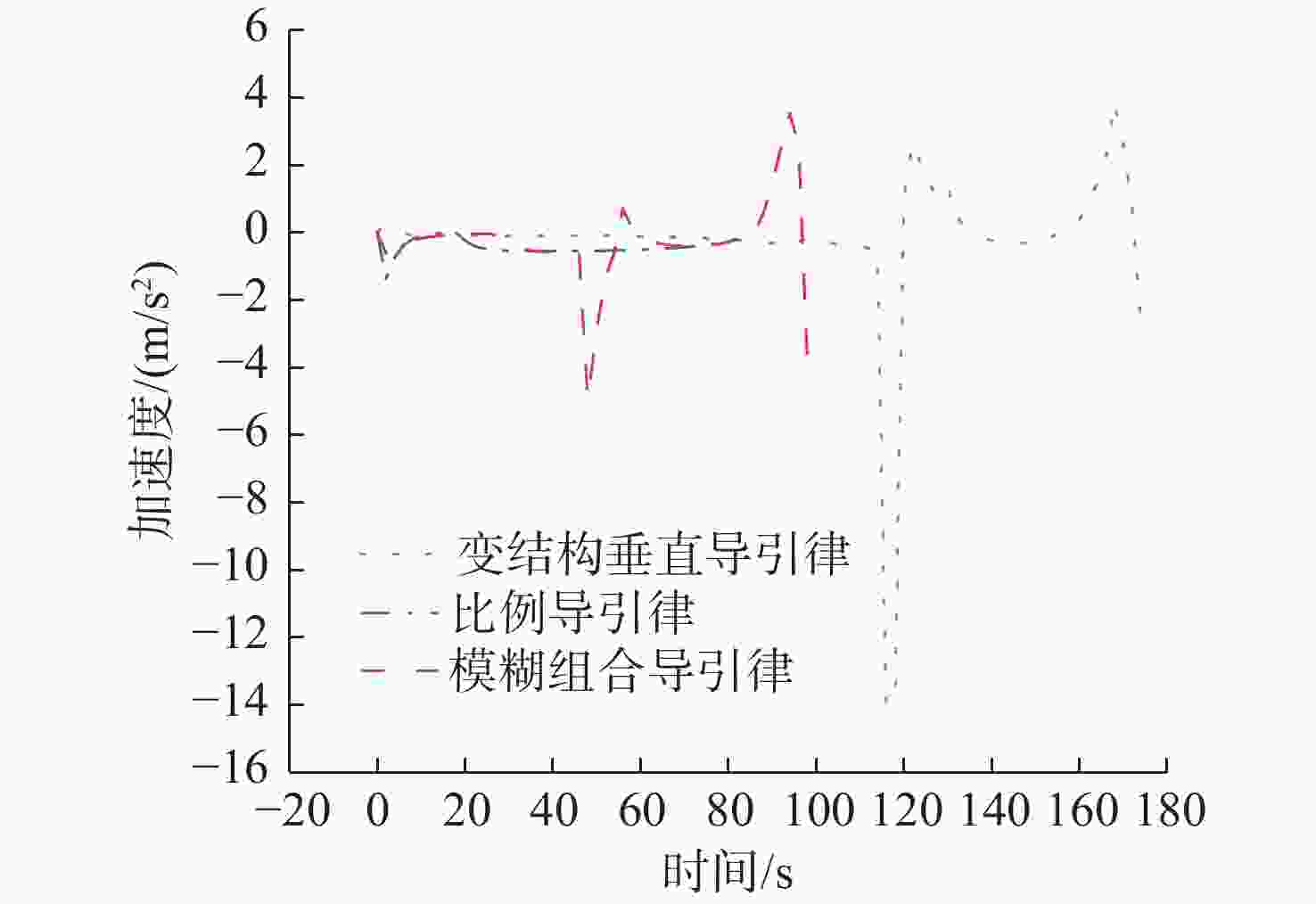
导引律 加速度平均值/(m/s2) 加速度方差/(m/s2)2 固定提前角导引律 −0.173 95 0.014 189 比例导引律 −0.068 08 0.058 802 变结构导引律 −0.051 23 3.364 590 模糊组合导引律 −0.364 49 0.543 573 表 5 目标非机动时鱼雷脱靶量、速度交会角和拦截时间对比
Table 5. Comparison of off-target volume, velocity intersection angle and intercept time of the torpedo when the target is non-motorized
导引律 脱靶量/m 速度交会角/(°) 拦截时间/s 固定提前角导引律 0.097 2 37.496 0 89.04 比例导引律 0.011 5 11.950 3 83.42 变结构导引律 0.566 4 97.776 8 124.02 模糊组合导引律 0.061 4 89.866 8 97.16 表 6 目标机动时鱼雷法向指令加速度平均值和方差对比
Table 6. Comparison of mean and variance of normal command acceleration of the torpedo when the target is motorized
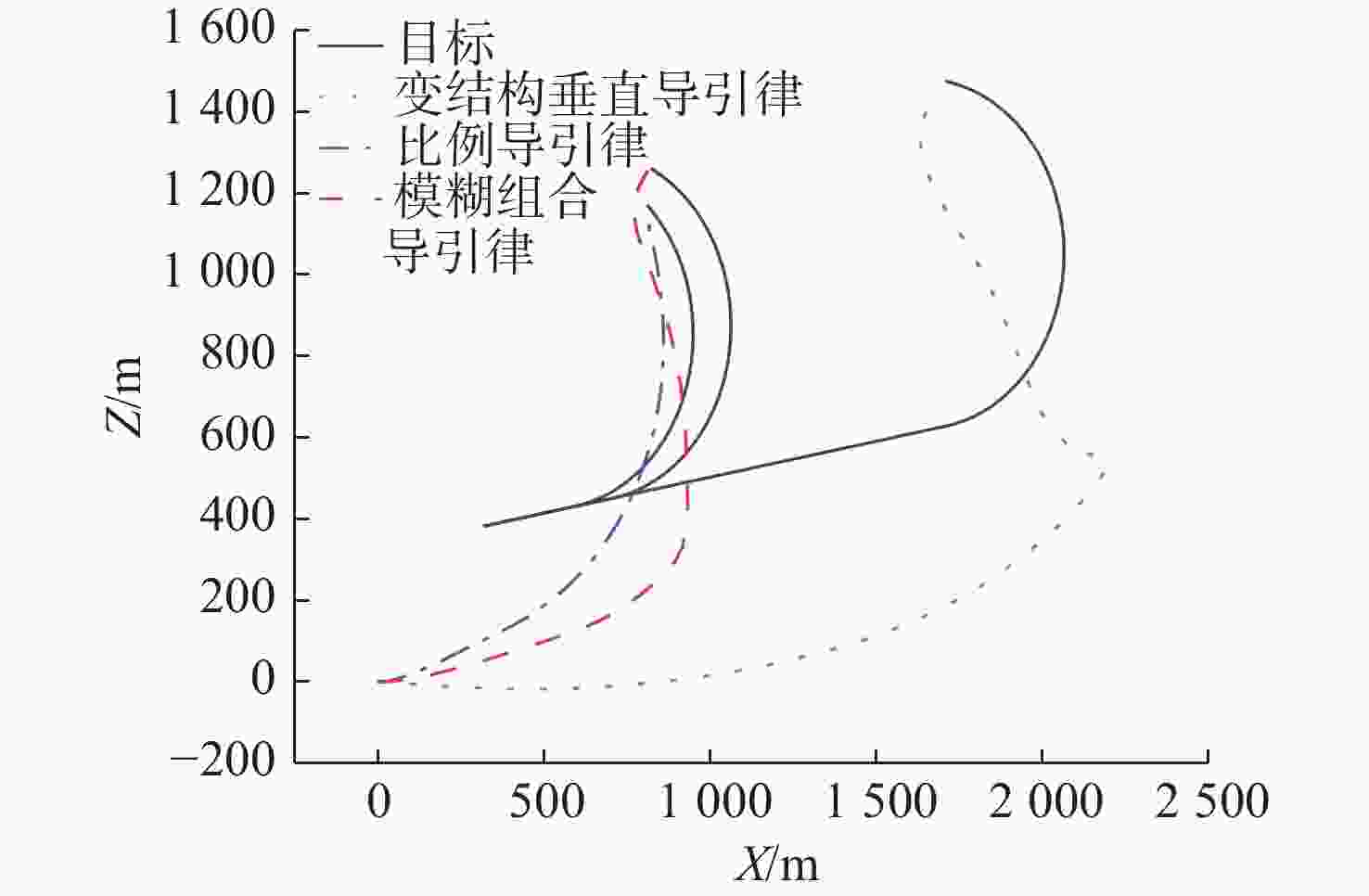
导引律 加速度平均值/(m/s2) 加速度方差/(m/s2)2 比例导引律 −0.425 81 0.054 463 变结构导引律 −0.222 76 5.273 470 模糊组合导引律 −0.255 21 1.723 062 表 7 目标机动时鱼雷脱靶量、速度交会角和拦截时间对比
Table 7. Comparison of off-target volume, velocity intersection angle and intercept time of the torpedo when the target is motorized
导引律 脱靶量/m 速度交会角/(°) 拦截时间/s 比例导引律 0.099 1 31.658 5 83.52 变结构导引律 0.139 5 90.265 8 175.68 模糊组合导引律 0.235 2 89.836 1 98.64 -
[1] 梁增顺, 冯西安, 薛昱. 水下智能航行体跟踪目标的自适应加权导引律设计[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2021, 39(2): 302-308. doi: 10.1051/jnwpu/20213920302LIANG Z S, FENG X A, XUE Y. Design on adaptive weighted guidance law for underwater intelligent vehicle tracking target[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2021, 39(2): 302-308. doi: 10.1051/jnwpu/20213920302 [2] 谢超, 樊华, 周景军, 等. 超空泡航行体自导作用距离需求分析[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2022, 44(8): 79-83. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2022.08.016XIE C, FAN H, ZHOU J J, et al. Analysis of necessary homing distance of supercavitating vehicle[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2022, 44(8): 79-83. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2022.08.016 [3] 高永琪, 张毅, 刘洪. 声自导鱼雷导引方法的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2014, 39(4): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2014.04.001GAO Y Q, ZHANG Y, LIU H. Study on status and development trend about guidance methods of acoustic homing torpedo[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2014, 39(4): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2014.04.001 [4] 李斌, 张靖康, 李刚. 基于模糊控制的线导鱼雷方位导引法[J]. 兵工自动化, 2014, 33(5): 11-14. doi: 10.7690/bgzdh.2014.05.004 [5] 杨益兴. 自适应模糊滑模变结构制导律研究[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2015, 37(3): 122-125. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2015.03.026YANG Y X. Study of fuzzy adaptive sliding-mode control guidance law[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2015, 37(3): 122-125. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2015.03.026 [6] 杨柱, 许哲, 王雪梅, 等. 基于扩张状态观测器的自抗扰滑模导引律[J]. 中国测试, 2018, 44(6): 140-145. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2018.06.026 [7] 赵健宏. 自主无人潜航器(AUV)运动控制系统设计与实现[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2017. [8] 王雪梅, 邵国豪俊, 许哲, 等. 一种落角约束的自适应模糊滑模导引律[J]. 电光与控制, 2017, 24(9): 36-41, 63.WANG X M, SHAO G H J, XU Z, et al. Adaptive fuzzy-sliding mode control guidance law with impact angle constraints[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2017, 24(9): 36-41, 63. [9] 敦晓彪, 张新博, 尹童, 等. 一种有视线角约束的模糊变系数变结构制导律[J]. 现代防御技术, 2023, 51(5): 67-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2023.05.009DUN X B, ZHANG X B, YIN T, et al. A fuzzy variable coefficient variable structure guidance law with terminal line-of-sight angle constraint[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2023, 51(5): 67-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2023.05.009 [10] 宋明玉. 基于模糊控制的线导鱼雷组合导引方法[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2008, 16(3): 52-56.SONG M Y. An integrated guidance law based on fuzzy control for wire guidance torpedo[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2008, 16(3): 52-56. [11] 陈克喆, 程咏梅, 禹亮, 等. 水声对抗环境下自导鱼雷自适应导引方法[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2014, 22(4): 262-266.CHEN K Z, CHENG Y M, YU L, et al. Adaptive guidance method of homing torpedo under underwater acoustic countermeasure condition[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2014, 22(4): 262-266. [12] 陈路伟. 萤火虫算法在鱼雷垂直命中导引方法中的仿真研究[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2020, 40(6): 89-91. [13] 禹亮. 复杂水声环境下反对抗一体化方法研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2018. [14] 陈乐鹏. 无人船协同导引与控制研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2018. -




 下载:
下载: