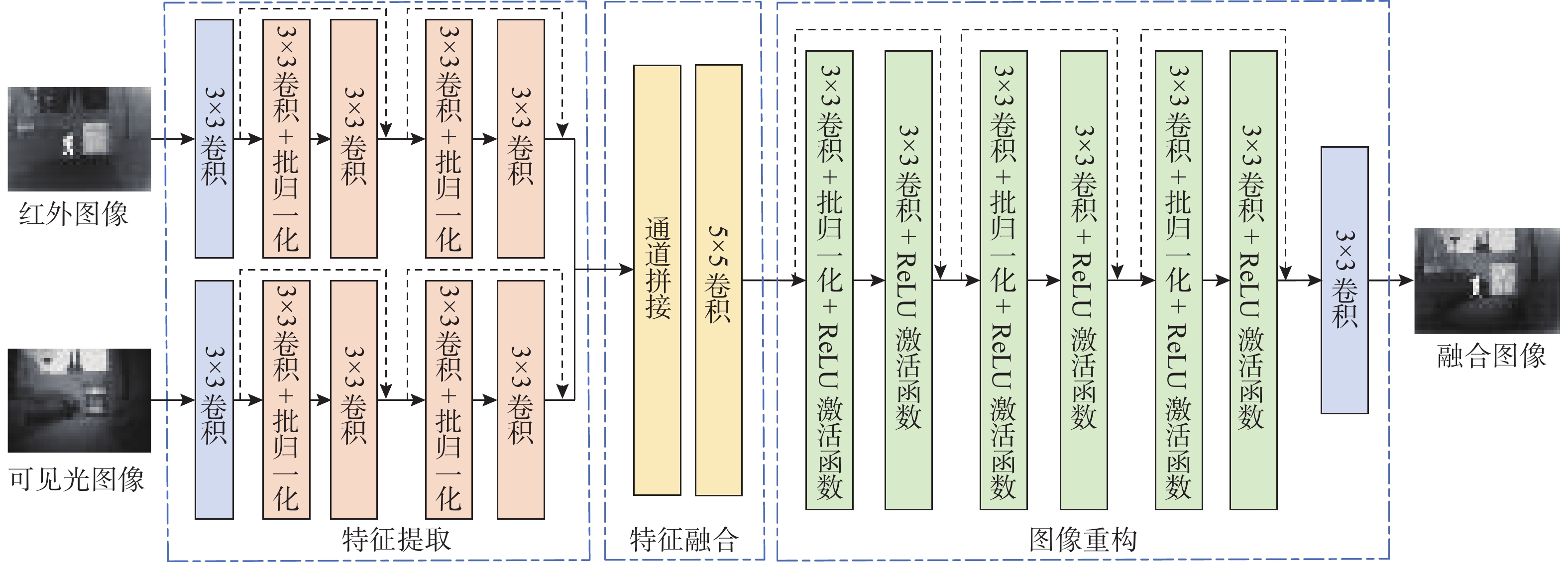
Application of Structure Tensor-Based Image Fusion Method in Marine Exploration
-
摘要: 单一传感器无法在海上探测中取得良好的效果。红外与可见光具有很强的互补性, 将二者融合可以得到高质量的融合图像, 能够更准确、全面地感知海上目标。然而现有的融合方法并未应用于海上探测领域, 融合方法均缺少针对性, 融合效果差, 并且缺少应用于海上融合的深度学习数据集。文中对基于结构张量的深度学习图像融合方法进行研究, 针对海上目标的特点进行改进与优化, 加入多尺度卷积并按照通道对图像进行融合, 旨在获取目标显著且信息全面的高质量彩色融合图像。使用采集的数据进行实验, 综合选取多种评价指标开展对比仿真实验研究。研究结果表明, 改进的图像融合方法在6个指标上的融合效果优于原始算法, 综合性能优于其他常用的10种图像融合算法, 改进方法的泛化性在其他公开数据集上得到了验证。改进后的基于结构张量的图像融合方法在海上感知中有优异的表现, 融合结果突出目标特征, 融合性能优于其他方法。Abstract: A single sensor is insufficient for effective marine detection. Infrared light and visible light have strong complementarity, and fusing them can generate high-quality images that enable more accurate and comprehensive detection of marine targets. However, existing fusion methods have not been applied in marine detection and are not specifically developed for it, leading to poor fusion results. Additionally, there is a lack of deep learning datasets tailored for marine image fusion. To obtain high-quality color fusion images with a prominent performance in detecting targets and obtaining comprehensive information, the deep learning-based image fusion method using structure tensors was optimized based on the characteristics of marine targets. Multi-scale convolution was incorporated, and image fusion was performed according to channels. The collected data were used for comparative simulation experiments, with a variety of evaluation metrics applied. The results indicate that the improved image fusion method outperforms the original algorithm in six metrics, and its overall performance is better than the other ten commonly used image fusion algorithms. Furthermore, its generalization has been validated on other public datasets. The improved structure tensor-based image fusion method has an excellent performance in maritime situational awareness, with fusion results highlighting target features and surpassing the performance of other methods.
-
Key words:
- marine exploration /
- image fusion /
- deep learning /
- structure tensor
-
表 1 6种融合指标评价结果
Table 1. Evaluation results of original DIF-Net and improved method on six fusion indexes
评价指标 DIF-Net 改进DIF-Net MI 4.401 4.526 PSNR 65.091 65.996 CC 0.671 0.733 $ {N}^{AB/F} $ 0.003 0.006 SSIM 0.901 0.951 FMI_pixel 0.950 0.952 表 2 11种方法在海上数据集上的评价结果
Table 2. Evaluation results of 11 methods on offshore data sets
融合算法 MI PSNR CC $ {N}^{AB/F} $ SSIM FMI_pixel ADF 3.789 65.791 0.712 0.145 0.927 0.931 CBF 3.331 63.592 0.665 0.461 0.759 0.941 GTF 4.758 62.847 0.603 0.164 0.876 0.940 LatLRR 3.612 60.407 0.681 0.497 0.876 0.927 MGFF 3.496 65.492 0.694 0.227 0.950 0.933 TIF 3.470 65.531 0.690 0.200 0.940 0.937 DenseFuse 4.516 65.789 0.721 0.009 0.943 0.950 MFEIF 4.829 65.031 0.684 0.029 0.955 0.948 RFN-Nest 3.998 59.817 0.681 0.186 0.902 0.943 FusionGAN 3.671 61.322 0.621 0.248 0.858 0.936 文中方法 4.526 65.996 0.733 0.006 0.951 0.952 表 3 11种方法在TNO数据集上的评价结果
Table 3. Evaluation results of 11 methods on TNO dataset
融合算法 MI PSNR CC $ {N}^{AB/F} $ SSIM FMI_pixel ADF 2.074 64.351 0.527 0.086 0.831 0.866 CBF 2.174 62.465 0.365 0.271 0.716 0.857 GTF 2.444 61.551 0.351 0.198 0.785 0.876 LatLRR 2.200 58.944 0.491 0.386 0.826 0.873 MGFF 2.207 57.746 0.501 0.197 0.903 0.877 TIF 1.966 64.121 0.516 0.181 0.894 0.882 DenseFuse 2.391 64.405 0.533 0.089 0.871 0.885 MFEIF 2.612 63.471 0.517 0.041 0.873 0.879 RFN-Nest 2.286 62.111 0.523 0.114 0.825 0.871 FusionGAN 2.171 61.322 0.449 0.091 0.754 0.868 文中方法 2.452 64.636 0.501 0.033 0.865 0.884 -
[1] 邱志明, 孟祥尧, 马焱, 等. 海上无人系统发展及关键技术研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2023, 25(3): 74-83.QIU Z M, MENG X Y, MA Y, et al. Development and key technologies of maritime unmanned systems[J]. Strategic Study of Chinese Academy of Engineering, 2023, 25(3): 74-83. [2] 贲可荣, 王斌. 海洋装备智能化与智能化装备思考[J]. 江苏科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 35(2): 1-11.BEN K R, WANG B. Thinking on the intellectualization of marine equipment and marine intelligent equipment[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 35(2): 1-11. [3] 张蕾. 红外与可见光图像融合技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院研究生院(长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2015. [4] TOET A. Image fusion by a ratio of low-pass pyramid[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 1989, 9(4): 245-253. [5] PAJARES G, JESÚS M D L C. A wavelet-based image fusion tutorial[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2004, 37(9): 1855-1872. [6] 杨晓慧, 金海燕, 焦李成. 基于DT-CWT的红外与可见光图像自适应融合[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2007, 26(6): 419-424. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9014.2007.06.005YANG X H, JIN H Y, JIAO L C. Adaptive image fusion algorithm for infrared and visible light images based on DT-CWT[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2007, 26(6): 419-424. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9014.2007.06.005 [7] LI S, KANG X, HU J. Image fusion with guided filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(7): 2864-2875. [8] BAVIRISETTI D P, DHULI R. Fusion of infrared and visible sensor images based on anisotropic diffusion and Karhunen-Loeve transform[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2015, 16(1): 203-209. [9] KUMAR B K S. Image fusion based on pixel significance using cross bilateral filter[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2015, 5: 1193-1204. [10] MA J, CHEN C, LI C, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization[J]. Information Fusion, 2016, 31: 100-109. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2016.02.001 [11] LI H, WU X. Infrared and visible image fusion using latent low-rank representation[EB/OL]. [2018-01-29]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.08992. [12] BAVIRISETTI D P, XIAO G, ZHAO J, et al. Multi-scale guided image and video fusion: A fast and efficient approach[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2019, 38(1): 5576-5605. [13] BAVIRISETTI D P, DHULI R. Two-scale image fusion of visible and infrared images using saliency detection[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2016, 76: 52-64. [14] 罗迪. 无人机平台下的可见光与热红外图像融合和目标检测研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2021. [15] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 30: 5998-6008. [16] MA J, YU W, LIANG P, et al. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 48: 11-26. [17] XU H, LIANG P, YU W, et al. Learning a generative model for fusing infrared and visible images via conditional generative adversarial network with dual discriminators[C]//Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Macao, China: IJCAI, 2019. [18] PRABHAKAR K R, SRIKAR V S, BABU R V. DeepFuse: A deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: ICCV, 2017. [19] LI H, WU X J. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 28(5): 2614-2623. [20] LI H, WU X J, KITTLER J. RFN-Nest: An end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images[J]. Information Fusion, 2021, 2: 72-86. [21] TANG W, HE F, LIU Y. TCCFusion: An infrared and visible image fusion method based on transformer and cross correla-tion[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 137: 109295. [22] LI H, WU X J, KITTLER J. Infrared and visible image fusion using a deep learning framework[C]//2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Beijing, China: ICPR, 2018. [23] LONG Y, JIA H, ZHONG Y, et al. RXDNFuse: A aggregated residual dense network for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2021, 69(1): 128-141. [24] MA J, TANG L, XU M, et al. STDFusionNet: An infrared and visible image fusion network based on salient target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70(1): 1-13. [25] LIU J, FAN X, JIANG J, et al. Learning a deep multi-scale feature ensemble and an edge-attention guidance for image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 99(1): 105-119. [26] TANG L, ZHANG H, XU H, et al. Rethinking the necessity of image fusion in high-level vision tasks: A practical infrared and visible image fusion network based on progressive semantic injection and scene fidelity[J]. Information Fusion, 2023, 99:101870. [27] JUNG H, KIM Y, JANG H, et al. Unsupervised deep image fusion with structure tensor representations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29(99): 3845-3858. [28] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, USA: CVPR, 2016. [29] IOFFE S, SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[EB/OL]. [2015-02-11]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167. [30] MISRA D. Mish: A self regularized non-monotonic activation function[EB/OL]. [2019-08-23]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.08681. [31] LIN M, CHEN Q, YAN S. Network In Network[EB/OL]. [2013-11-16]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.4400. [32] WANG Z, BOVIK A C. A universal image quality index[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2002, 9(3): 81-84. doi: 10.1109/97.995823 [33] 唐霖峰, 张浩, 徐涵, 等. 基于深度学习的图像融合方法综述[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2023, 28(1): 3-36. doi: 10.11834/jig.220422TANG L F, ZHANG H, XU H, et al. Deep learning-based image fusion: A survey[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2023, 28(1): 3-36. doi: 10.11834/jig.220422 [34] TOET A. The TNO multiband image data collection[J]. Data in Brief, 2017, 15: 249-251. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.09.038 -





 下载:
下载: