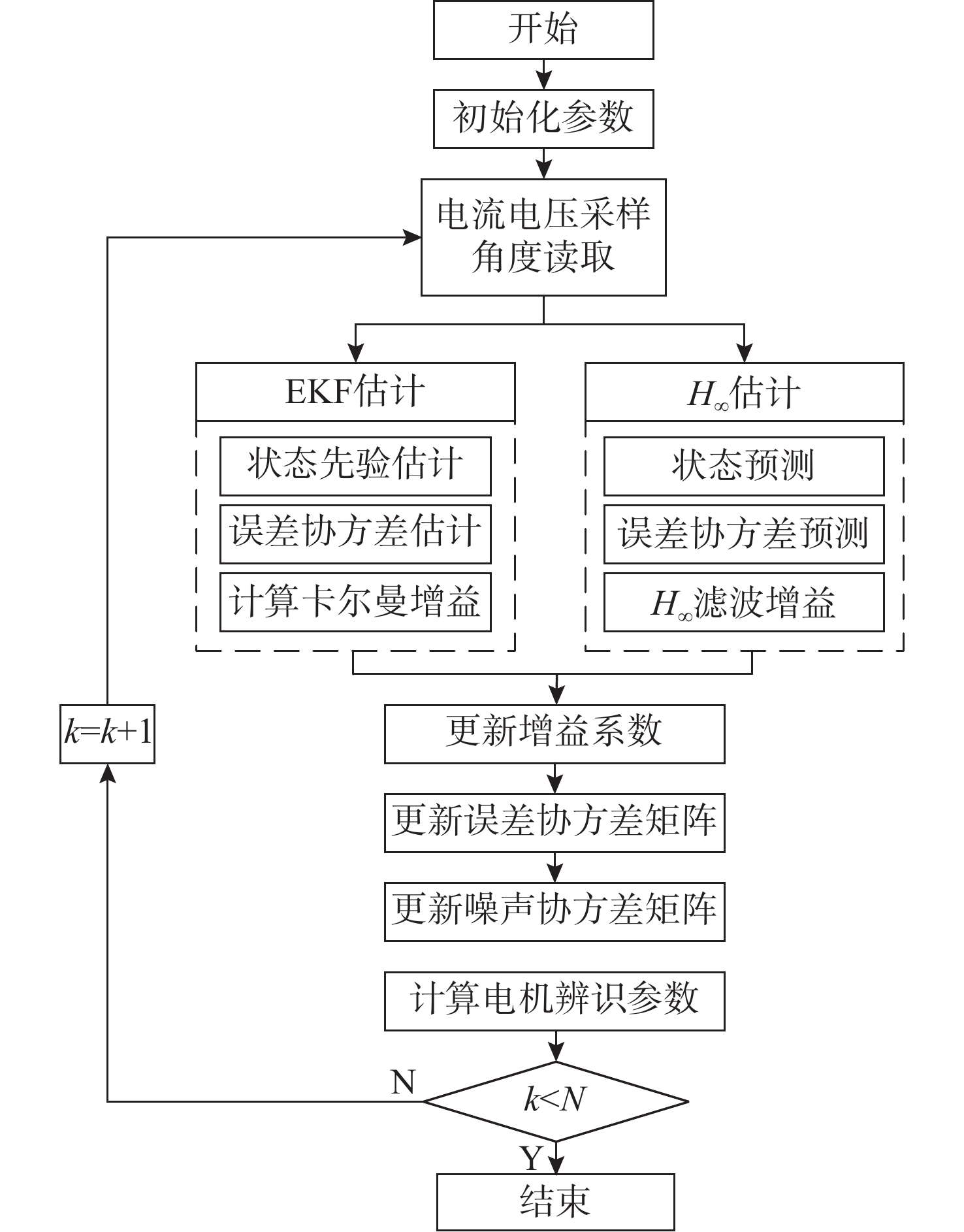
Multi-parameter Identification of Underwater Equipment Joint Motor
-
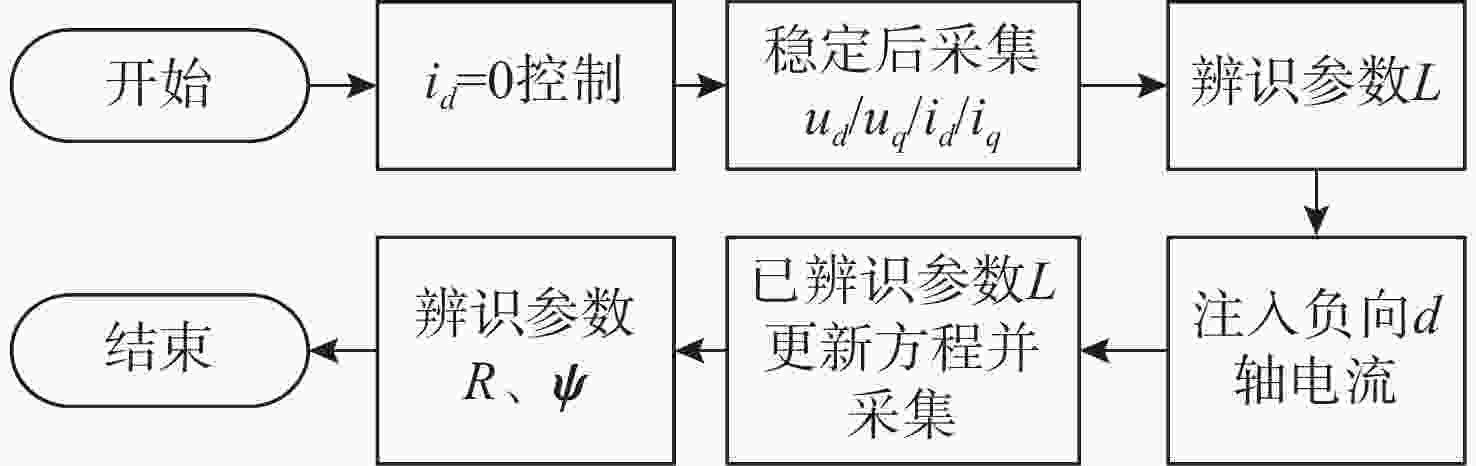
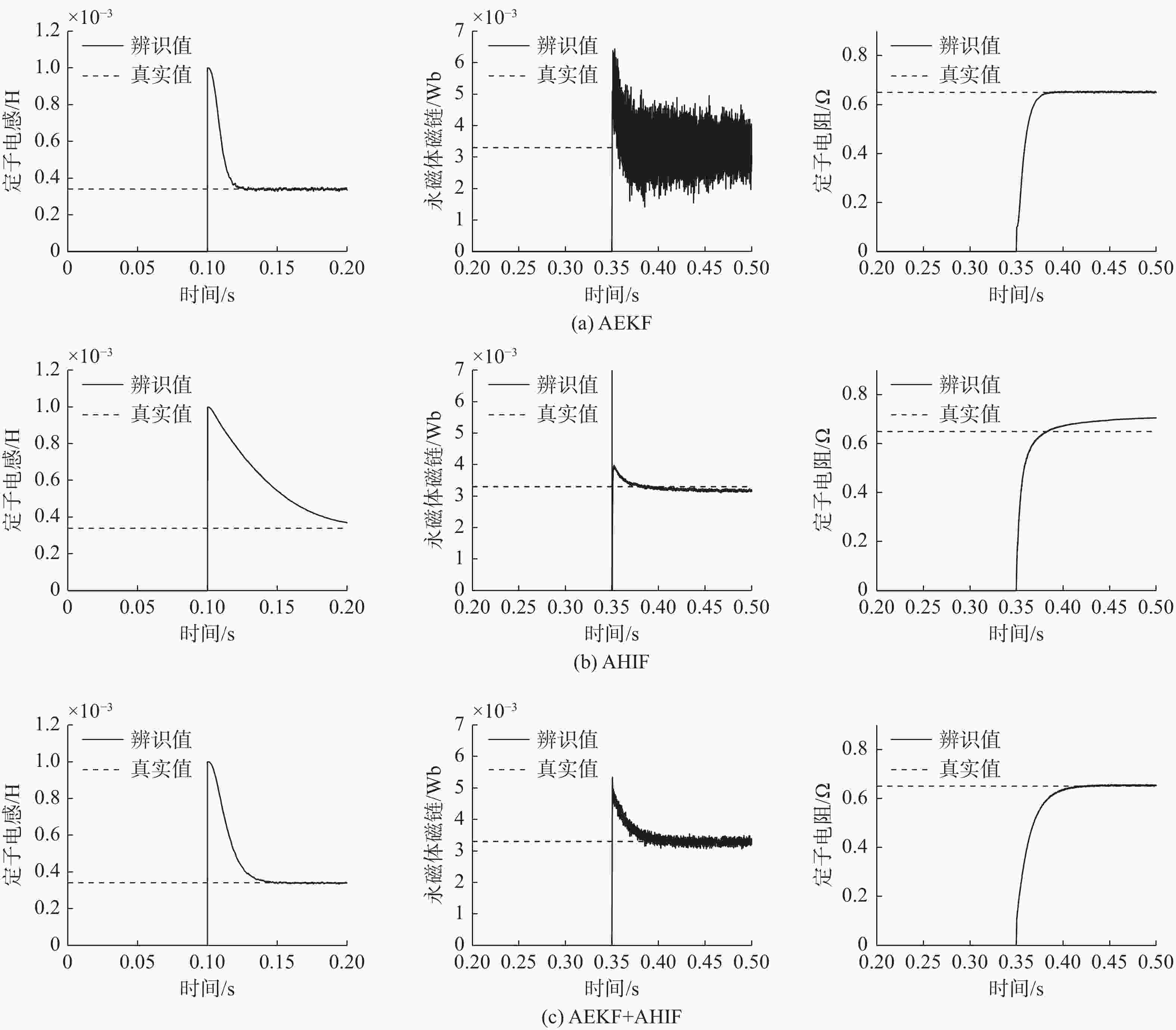
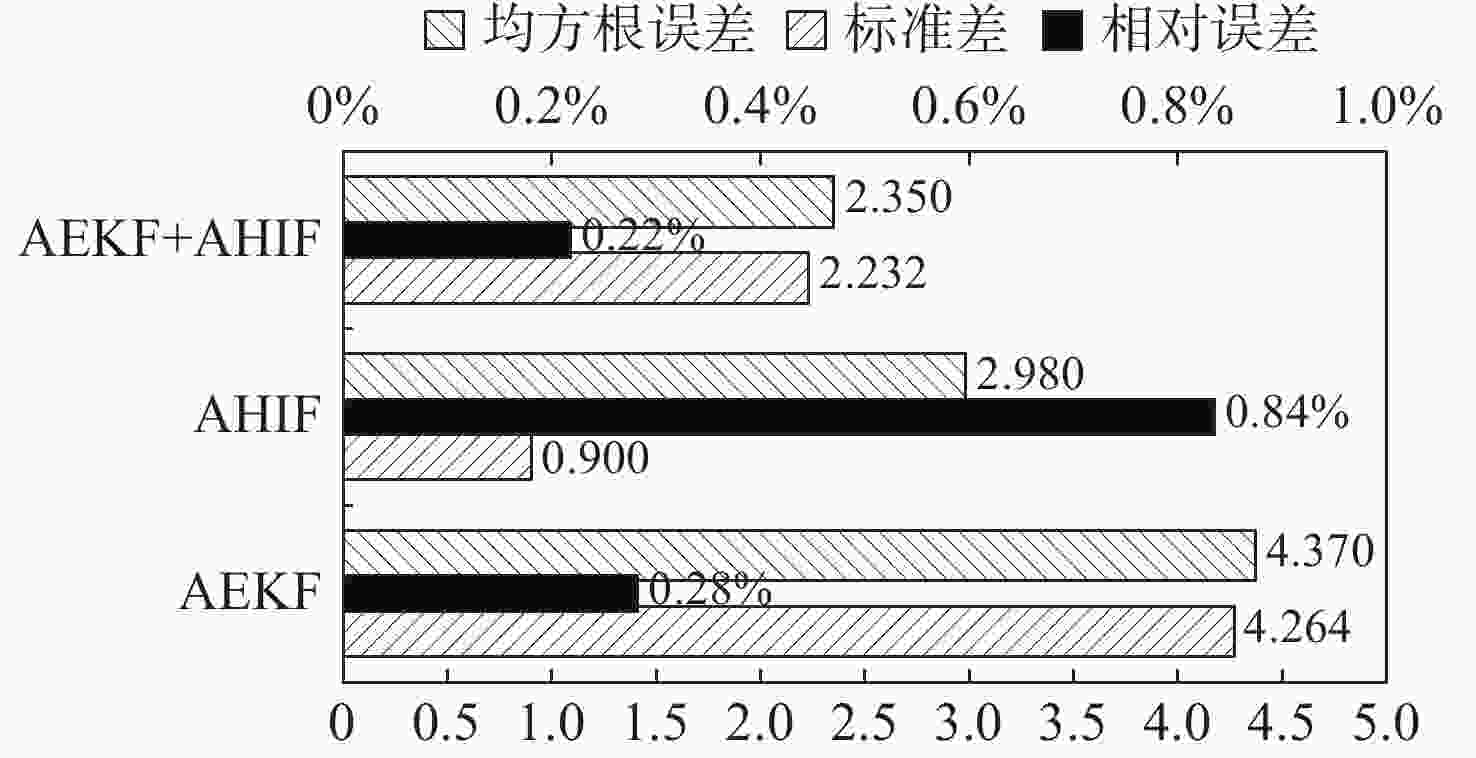
摘要: 随着水下无人系统的快速发展, 关节电机作为水下机器人、水下机械臂等水下装备的核心驱动装置发挥着重要的作用。文中针对不同工作环境影响下导致的关节电机参数改变, 从而引起的电机控制的精确性和稳定性变差的问题, 开展电机多参数在线辨识研究。采用增加稳态工作点方法实现多参数的满秩辨识。同时, 为提高辨识方法的精度和鲁棒性, 研究了扩展卡尔曼滤波(EKF)和H∞滤波(HIF)算法在电机参数辨识方面的可行性, 进而提出了一种基于自适应EKF(AEKF)和自适应HIF(AHIF)的联合估计方法。通过仿真对比发现, 在参数辨识时, 所提出的AEKF+AHIF联合估计方法相较于AEKF算法稳态标准差最大减少了84.7%, 相较于AHIF算法精确度最大提升了91.7%。该联合估计方法可为水下装备关节电机的稳定高效运行提供理论和技术支撑。Abstract: With the rapid development of unmanned undersea systems, joint motors play an important role as the core driving devices of underwater robots, underwater manipulators, and other underwater equipment. In this paper, the on-line multi-parameter identification of an underwater joint motor is studied to solve the problem that the precision and stability of motor control are deteriorated due to the change of motor parameters under the influence of different working environments. Specifically, the method of increasing steady-state operating points is used to realize multi-parameter full rank identification. At the same time, to improve the accuracy and robustness of the identification method, this study investigates the feasibility of extended Kalman filter(EKF) and H∞ filter(H-infinity filter, HIF) in the identification of motor parameters. Then a new joint estimation method based on adaptive EKF(AEKF) and adaptive HIF(AHIF) is proposed. Through simulation comparison, it is found that in parameter identification, the steady-state standard deviation of the proposed AEKF+AHIF joint estimation method is reduced by 84.7% compared with that of the AEKF method, and the accuracy is increased by 91.7% compared with that of the AHIF method. The joint estimation method can provide theoretical and technical support for the stable and efficient operation of underwater joint motors.
-
表 1 仿真系统PMSM参数
Table 1. Parameters of the PMSM in simulation system
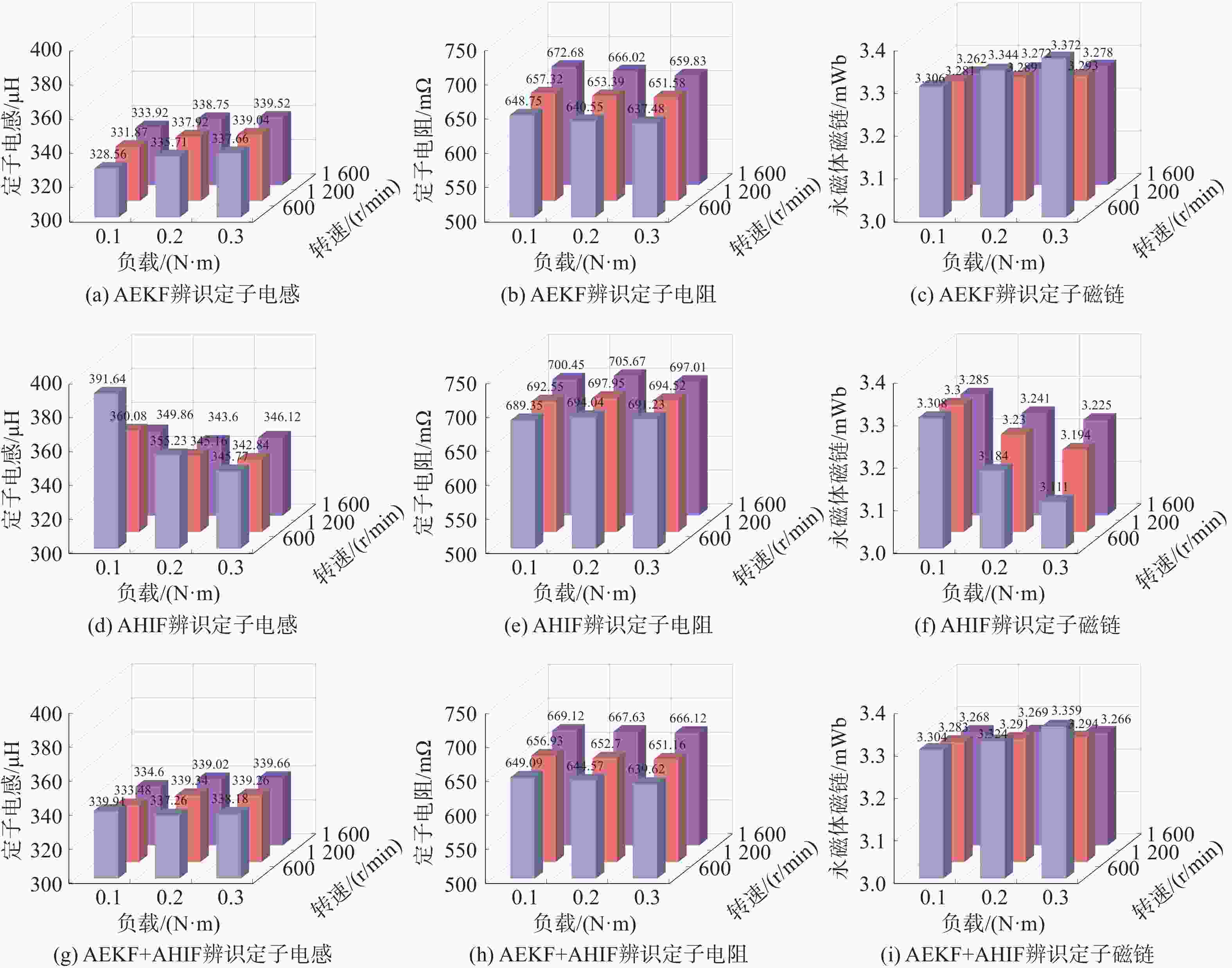
参数 数值 参数 数值 额定电压/V 24 d轴电感/µH 340 额定电流/A 2.5 q轴电感/µH 340 额定扭矩/(N·m) 0.3 定子电阻/mΩ 650 额定转速/(r/min) 1 200 转子磁链/Wb 0.003 3 转动惯量/(kg·m2) 1.8×10−5 极对数 14 表 2 额定工况下不同辨识方法性能对比
Table 2. Comparison of the performance of different identification methods under rated working conditions
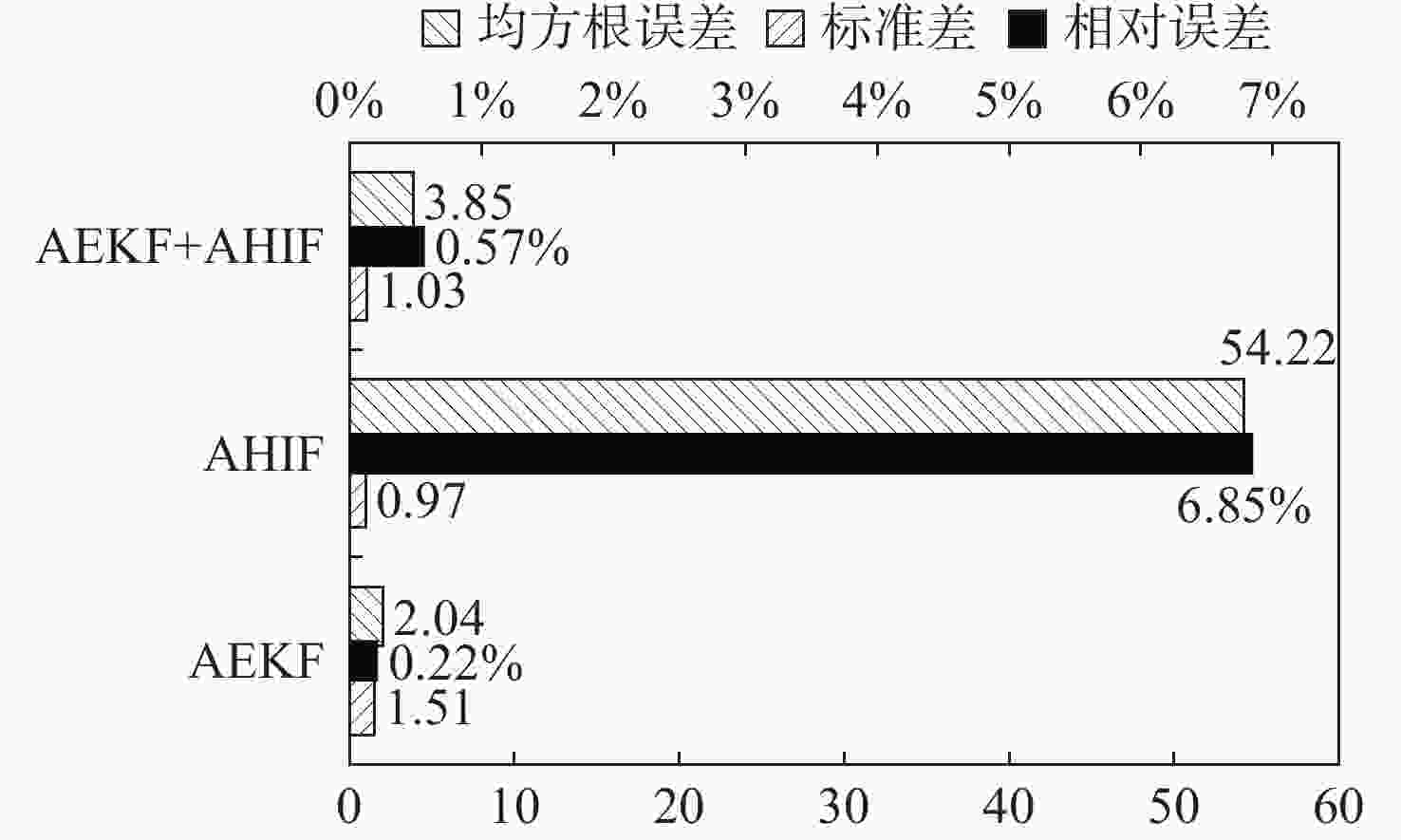
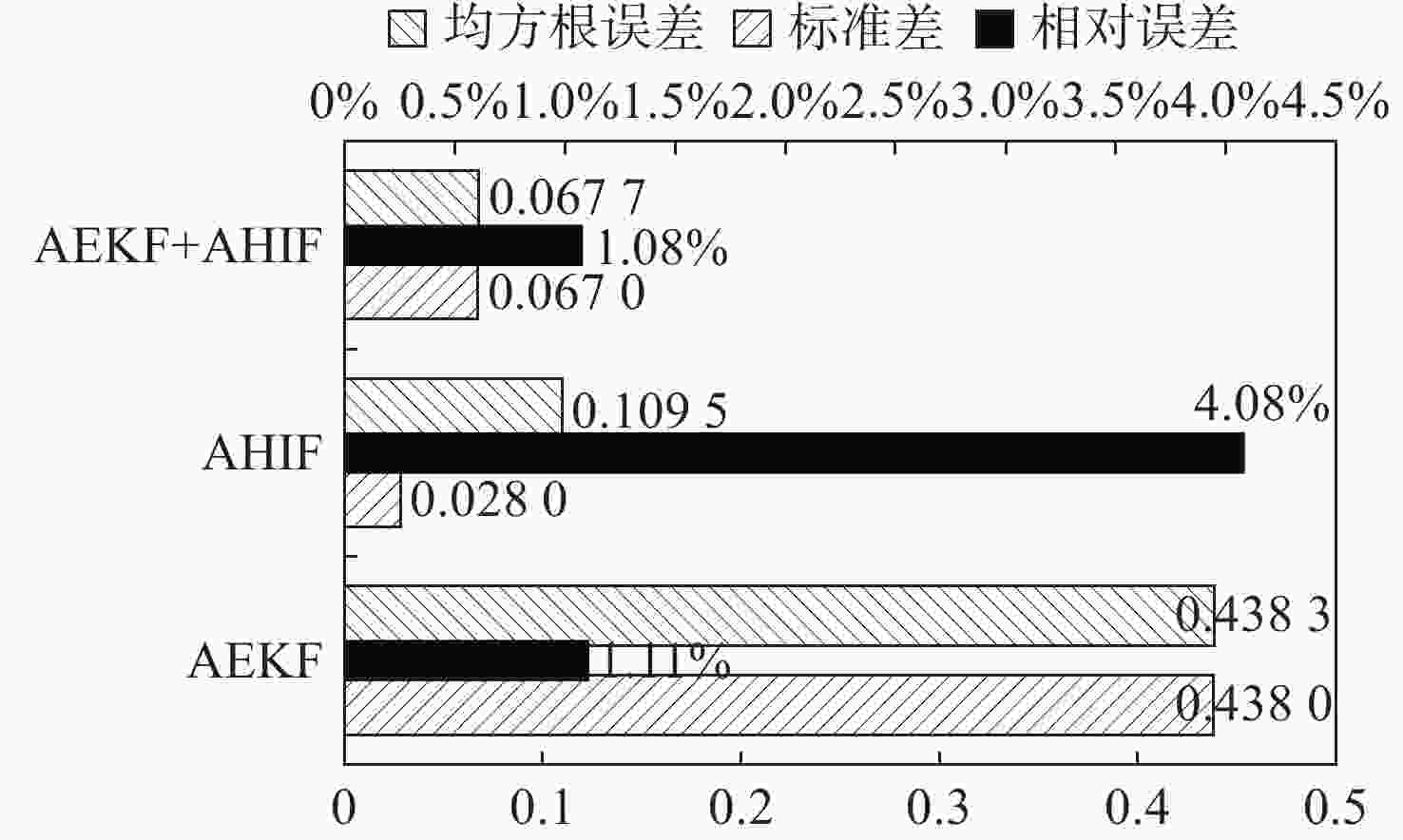
参数 方法 均值 相对误差/% 标准差 均方根误差 ${L_{s}}$/μH AEKF 339.040 0.28 4.264 4.370 0 AHIF 342.840 0.84 0.900 2.980 0 AEKF+AHIF 339.260 0.22 2.232 2.350 0 ${R_{s}}$/mΩ AEKF 651.400 0.22 1.510 2.040 0 AHIF 694.520 6.85 0.970 54.220 0 AEKF+AHIF 653.700 0.57 1.030 3.850 0 $ \boldsymbol{\psi}_{f} $/(mWb) AEKF 3.293 1.11 0.438 0.438 3 AHIF 3.194 4.08 0.028 0.109 5 AEKF+AHIF 3.294 1.08 0.067 0.067 7 -
[1] ITO K, LIANG Y, ZOU J. Least-squares method for inverse medium problems[EB/OL]. [2022-01-02]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.00280. [2] SHE J, XIE M, LI Y, et al. A VFF-RLS method of inertia identification for PMSM[C]//2019 IEEE Conference on Control Technology and Applications(CCTA). Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2019: 942-943. [3] 董召强, 徐秋霞, 高瑾. 基于最小二乘法和硬件在环平台的永磁同步电机参数辨识[J]. 电机与控制应用, 2017, 44(6): 57-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6540.2017.06.011DONG Z Q, XU Q X, GAO J. Parameters identification of pmsm based on recurrence least square and hardware in the loop platform[J]. Electric Machines & Control Application, 2017, 44(6): 57-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6540.2017.06.011 [4] 娄天浩, 杨家强, 高健, 等. 基于递推辅助变量最小二乘法的永磁电机参数在线辨识策略[J]. 电工技术, 2022(5): 96-100, 104.LOU T H, YANG J Q, GAO J, et al. Online identification strategy of permanent magnet motor parameters based on RIVLS[J]. Electric Engineering, 2022(5): 96-100, 104. [5] 吴洪涛, 何宗卿, 朱亮, 等. 基于最小二乘法的永磁同步电机参数辨识[J]. 电子技术, 2021, 50(2): 48-49.WU H T, HE Z Q, ZHU L, et al. Parameter identification of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on least squares[J]. Electronic Technology, 2021, 50(2): 48-49. [6] 刘旭, 王旭平, 王淑红, 等. 基于最小二乘法的永磁同步电机电感辨识研究[J]. 电机与控制应用, 2020, 47(6): 1-5, 32. doi: 10.12177/emca.2020.033LIU X, WANG X P, WANG S H, et al. Inductance identification of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on least square method[J]. Electric Machines & Control Application, 2020, 47(6): 1-5, 32. doi: 10.12177/emca.2020.033 [7] 方桂花, 王鹤川, 高旭. 基于动态遗忘因子递推最小二乘法的永磁同步电机参数辨识算法[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2021, 38(1): 280-283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2021.01.047FANG G H, WAGN H C, GAO X. Parameter identification algorithm of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on dynamic forgetting factor recursive least square method[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2021, 38(1): 280-283 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2021.01.047 [8] HOAGG J B, BERNSTEIN D S. Retrospective cost model reference adaptive control for nonminimum-phase discrete-time systems, part 2: stability analysis[C]//Proceedings of the 2011 American Control Conference. San Francisco, CA, USA: IEEE, 2011: 2927-2932. [9] ELBULUK M, LIU T, HUSAIN I. Neural network-based model reference adaptive systems for high performance motor drives and motion controls[C]//Conference Record of the 2000 IEEE Industry Applications Conference. Thirty-Fifth IAS Annual Meeting and World Conference on Industrial Applications of Electrical Energy(Cat. No. 00CH37129). Rome, Italy: IEEE, 2000: 959-965. [10] 高东旭, 周兰, 陈静, 等. 基于扰动补偿的无微分模型参考自适应控制系统设计[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2023, 40(4): 735-743. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.10906GAO D X, ZHOU L, CHEN J, et al. Design of derivative-free model-reference adaptive control for a class of uncertain systems based on disturbance compensation[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2023, 40(4): 735-743. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.10906 [11] 齐放, 邓智泉, 仇志坚, 等. 基于MRAS的永磁同步电机无速度传感器[J]. 电工技术学报, 2007, 22(4): 53-58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6753.2007.04.009QI F, DENG Z Q, CHOU Z J, et al. Sensorless technology of permanent magnet synchronous motors based on MRAS[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2007, 22(4): 53-58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6753.2007.04.009 [12] WANG Q, ZHANG X, ZHANG C. Double sliding-mode model reference adaptive system speed identification for vector control of permanent magnet synchronous motors[J]. Proceedings of the Csee, 2014, 34(6): 897-902. [13] 王飞宇, 田井呈, 卓克琼, 等. 基于改进模型参考自适应算法的永磁同步电机转动惯量辨识[J]. 电机与控制应用, 2016, 43(8): 63-67, 87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6540.2016.08.012WANG F Y, TIAN J C, ZHUO K Q, et al. Inertia identification of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on improved model reference adaptive system algorithm[J]. Electric Machines & Control Application, 2016, 43(8): 63-67, 87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6540.2016.08.012 [14] 李垣江, 董鑫, 魏海峰, 等. 基于改进模型参考自适应系统的永磁同步电机参数辨识[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(9): 1983-1988. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2020.90654LI Y J, DONG X, WEI H F, et al. Parameter identification method of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on improved model reference adaptive system[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(9): 1983-1988. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2020.90654 [15] BISHOP C H, ETHERTON B J, MAJUMDAR S J. Adaptive sampling with the ensemble transform Kalman filter. Part 2: Field Program Implementation[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2001, 129(3): 420-436. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(2001)129<0420:ASWTET>2.0.CO;2 [16] GAO X, YOU D, KATAYAMA S. Seam tracking monitoring based on adaptive Kalman filter embedded elman neural network during high-power fiber laser welding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(11): 4315-4325. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2012.2193854 [17] 徐会风, 苏少平, 杜庆诚, 等. 基于扩展卡尔曼滤波观测器的无刷直流电机无位置传感器控制系统研究[J]. 微电机, 2020, 53(5): 31-39, 50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6848.2020.05.007XU H F, SU S P, DU Q C, et al. Research on sensorless control system of brushless DC motor based on extended Kalman filter observer[J]. Micromotors, 2020, 53(5): 31-39, 50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6848.2020.05.007 [18] POTNURU D, CHANDRA K P B, ARASARATNAM I, et al. Derivative-free square-root cubature Kalman filter for non-linear brushless DC motors[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2016, 10(5): 419-429. doi: 10.1049/iet-epa.2015.0414 [19] 刘康安, 张伟伟, 肖永超, 等. 基于自适应无迹卡尔曼滤波的四旋翼无人机姿态解算[J]. 电光与控制, 2022, 29(7): 126-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2022.07.023LIU K A, ZHANG W W, XIAO Y C, et al. Attitude calculation of quadrotor UAV based on adaptive unscented Kalman filter[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2022, 29(7): 126-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2022.07.023 [20] YILDIZ R, BARUT M, ZERDALI E. A comprehensive comparison of extended and unscented Kalman filters for speed-sensorless control applications of induction motors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(10): 6423-6432. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.2964876 [21] YIN Z G, LI G Y, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Symmetric strong tracking extended Kalman filter based sensorless control of induction motor drives for modeling error reduction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(2): 650-662. doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2810850 [22] FRIDMAN E, SHAKED U. A descriptor system approach to H∞ control of linear time-delay systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2002, 47(2): 253-270. [23] 马静波, 杨洪耕. 自适应卡尔曼滤波在电力系统短期负荷预测中的应用[J]. 电网技术, 2005, 29(1): 75-79. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3673.2005.01.016MA J B, YANG H G. Application of adaptive Kalman filter in power system short-term load forecasting[J]. Power System Technology, 2005, 29(1): 75-79. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3673.2005.01.016 -




 下载:
下载: