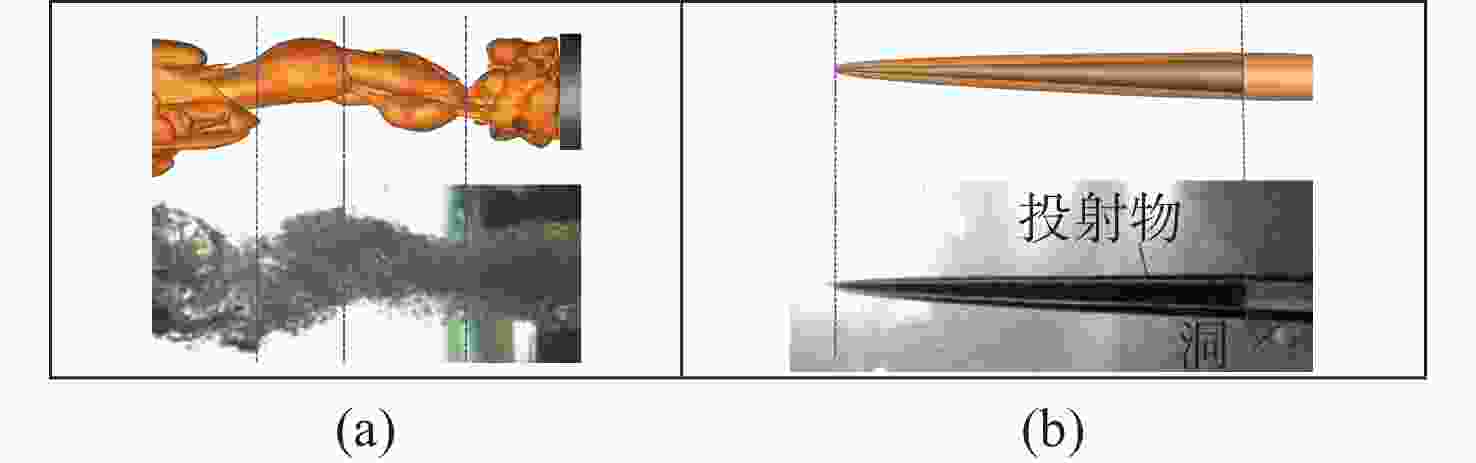
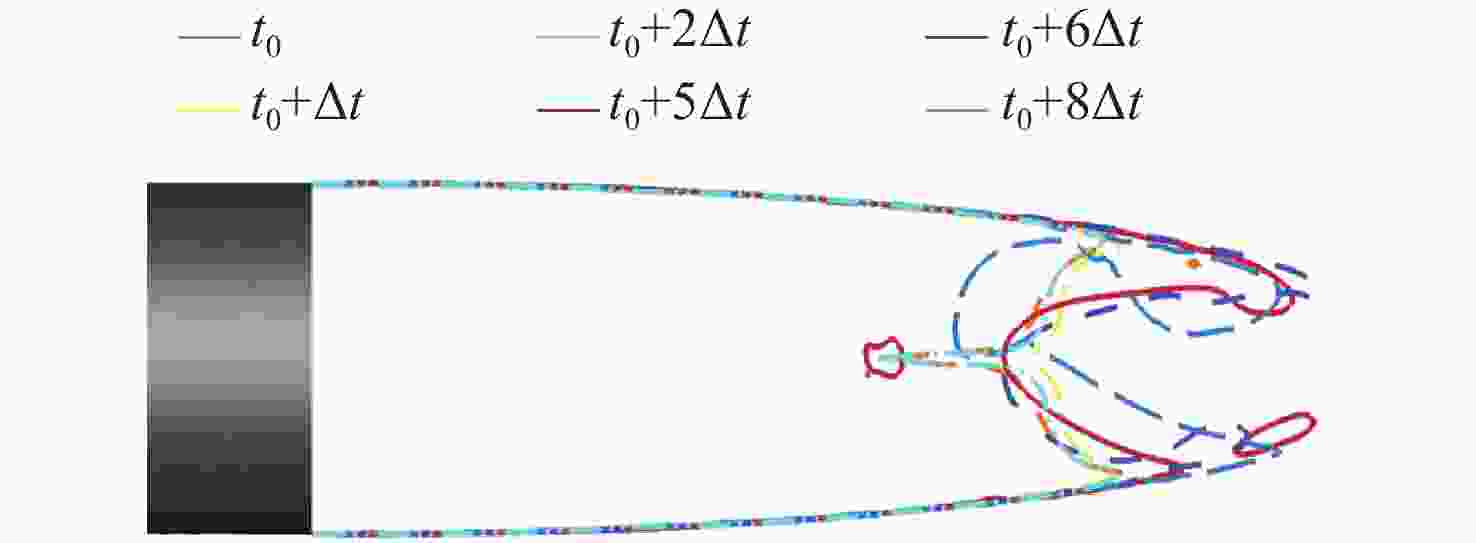
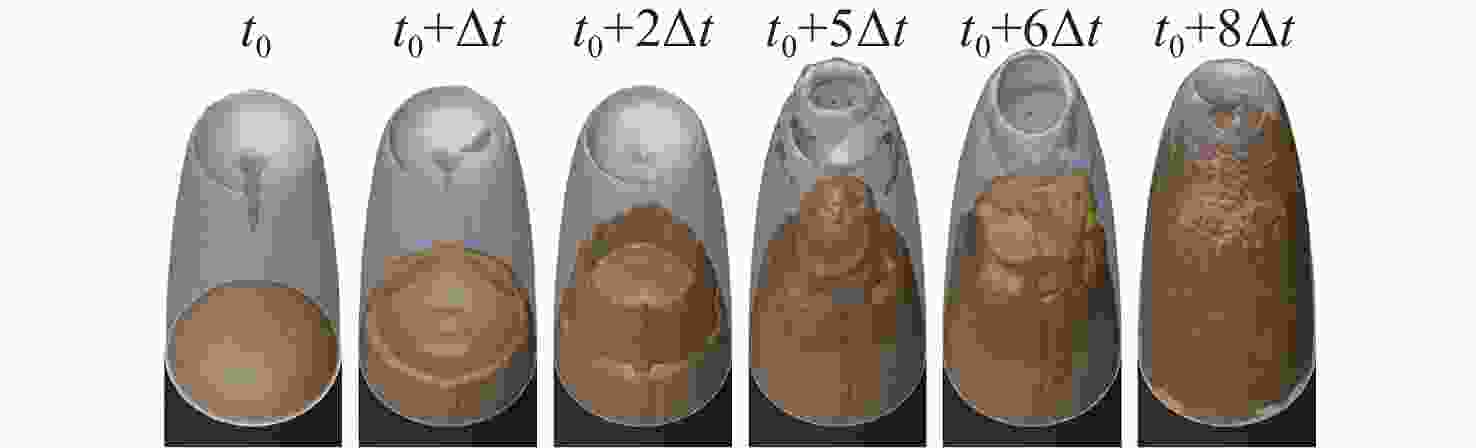
Numerical Simulation of Flow Field Characteristics of Supersonic Jet in Natural Cavitating Tail Cavity
-
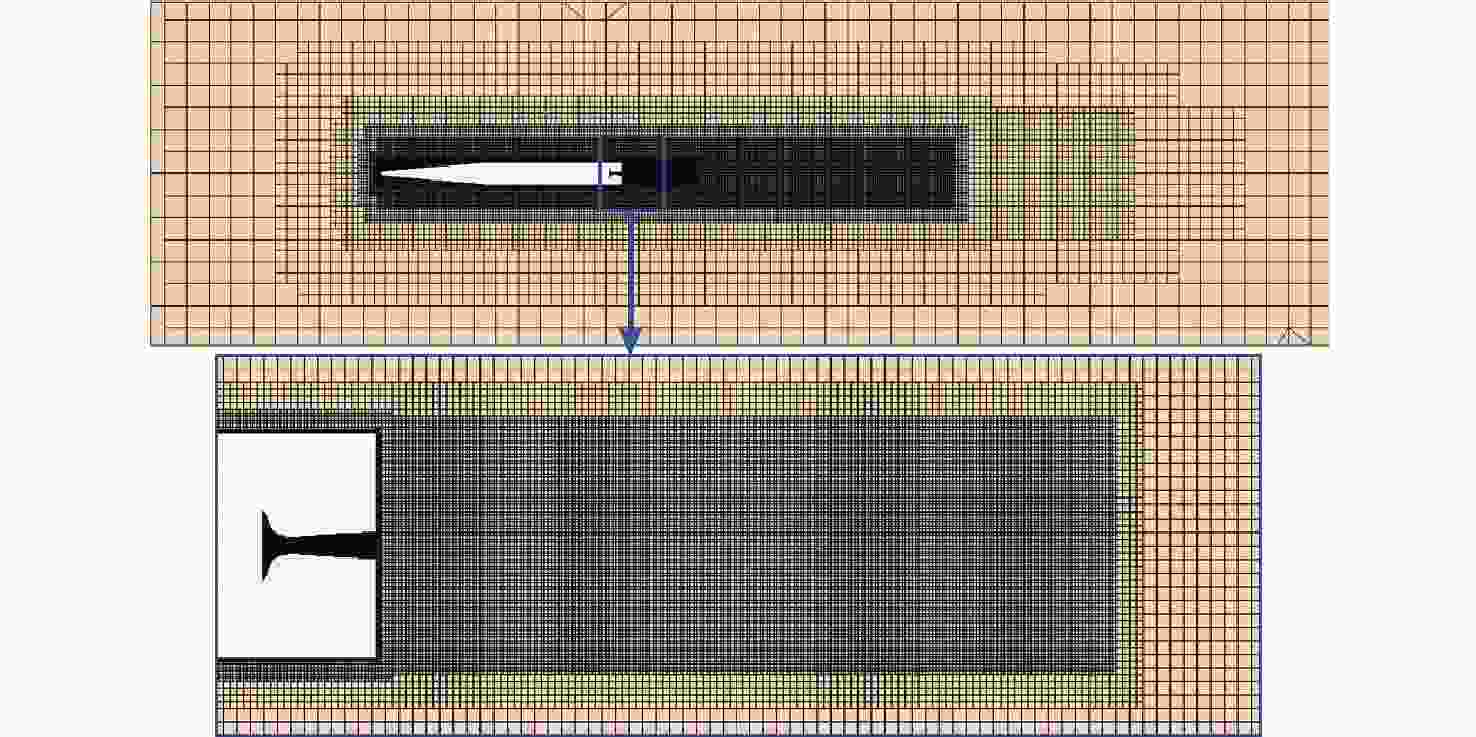
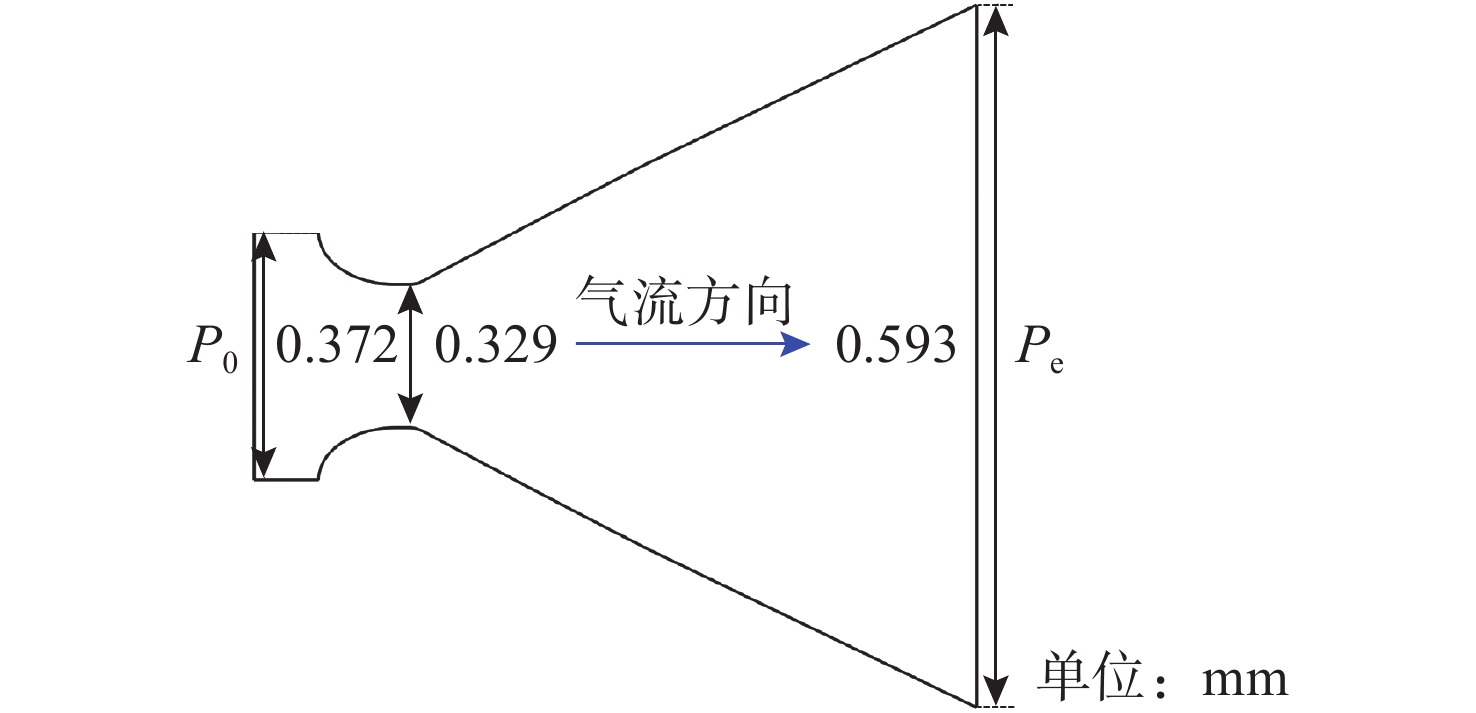
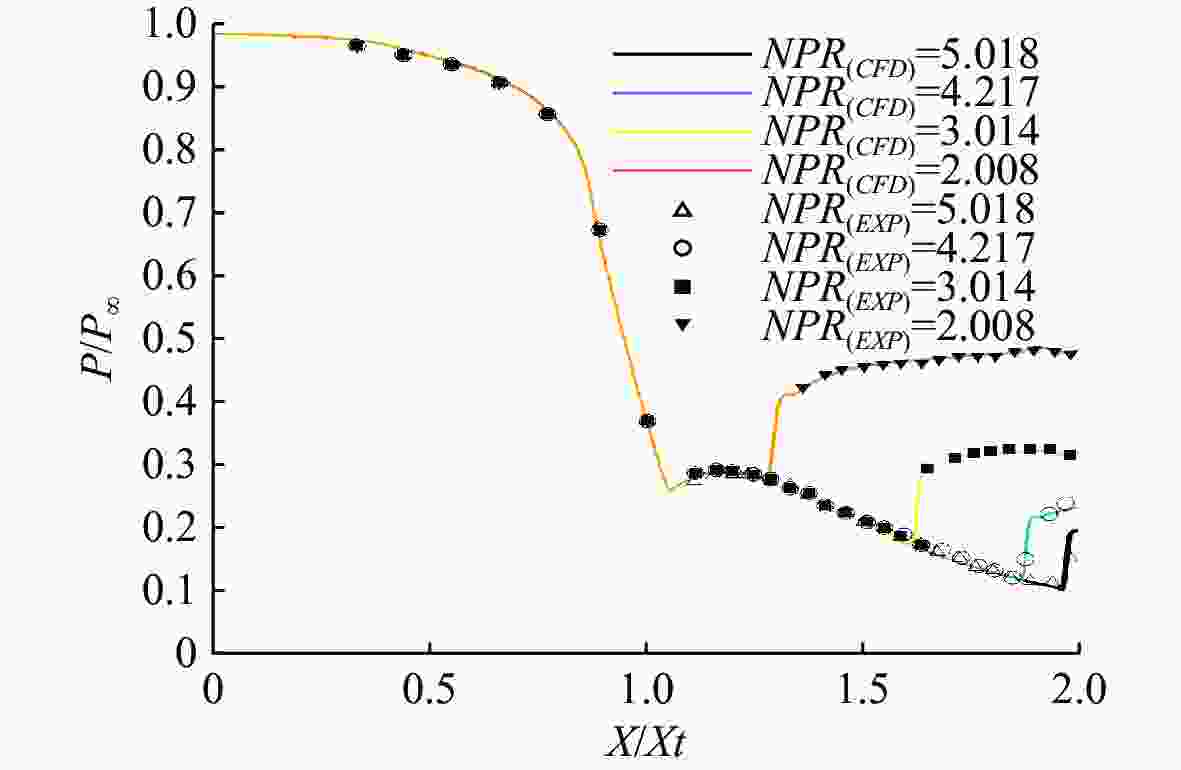
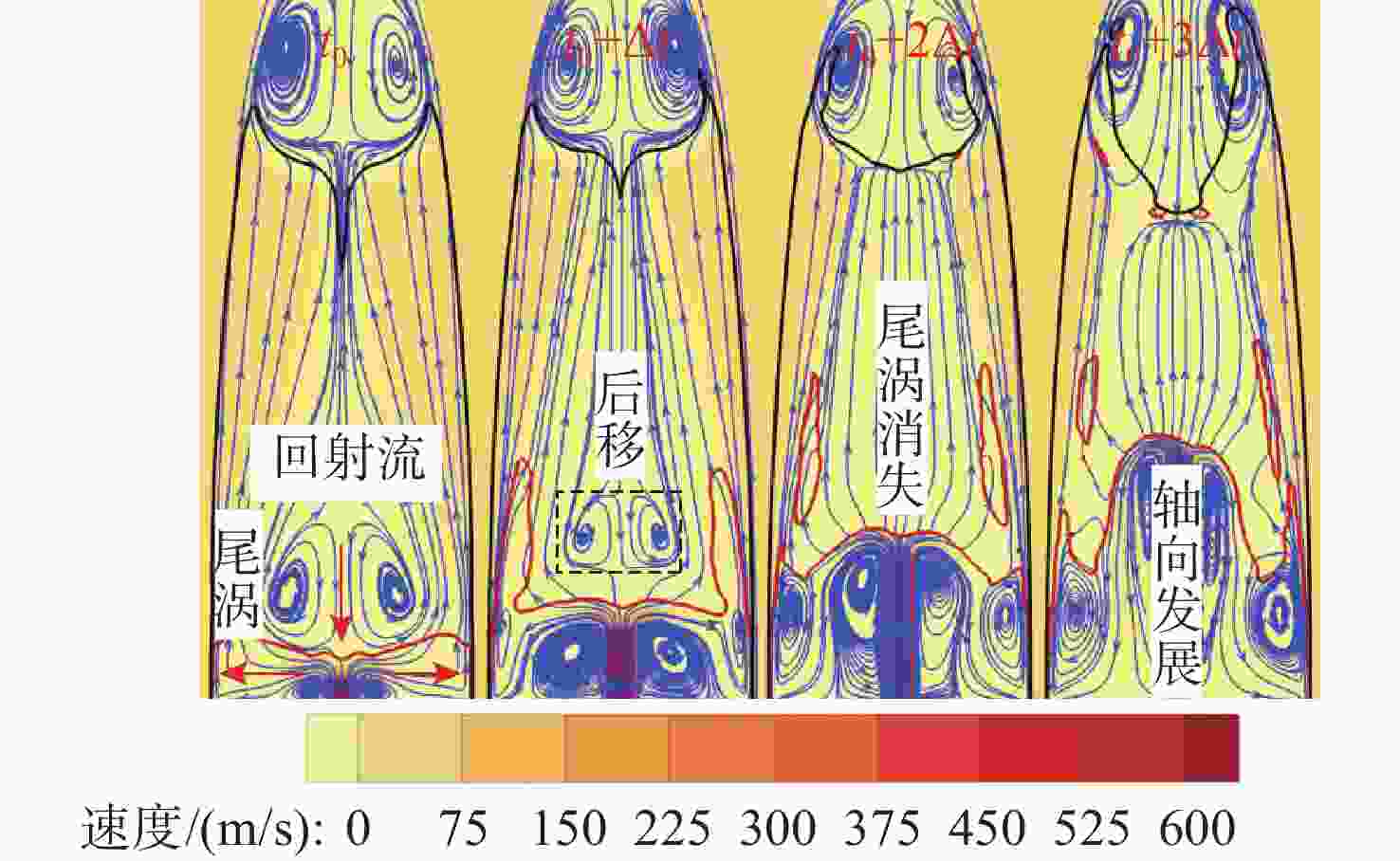
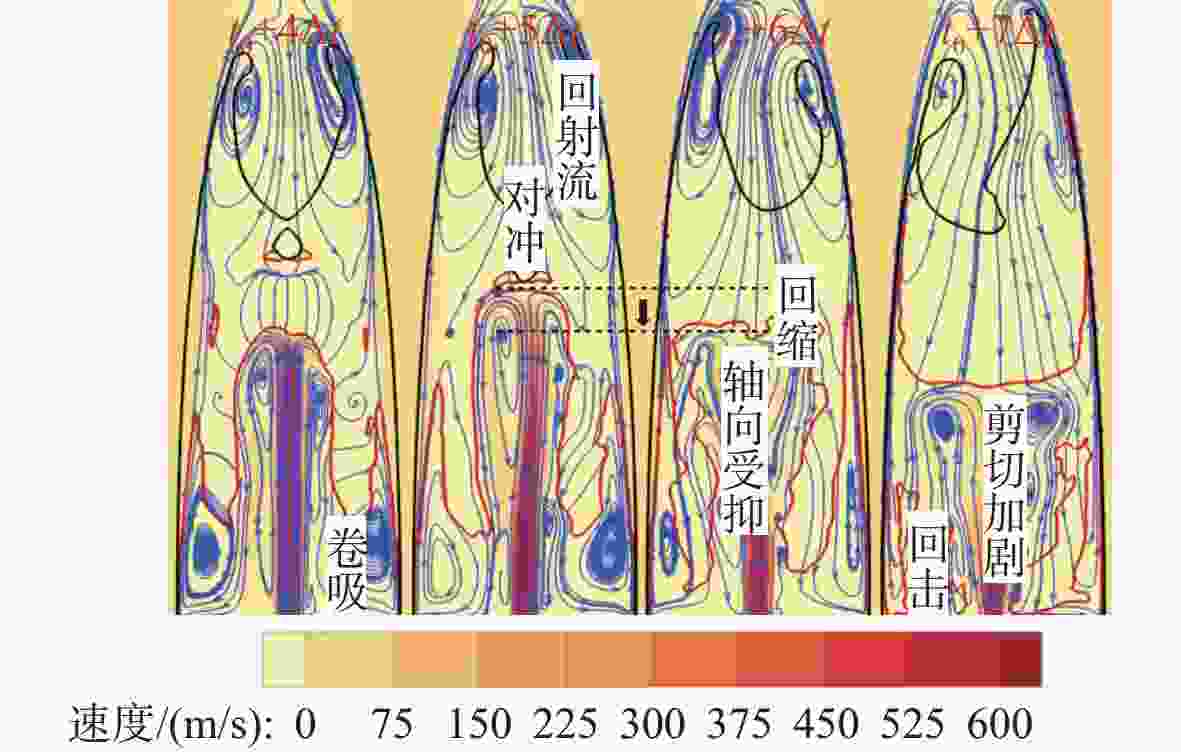
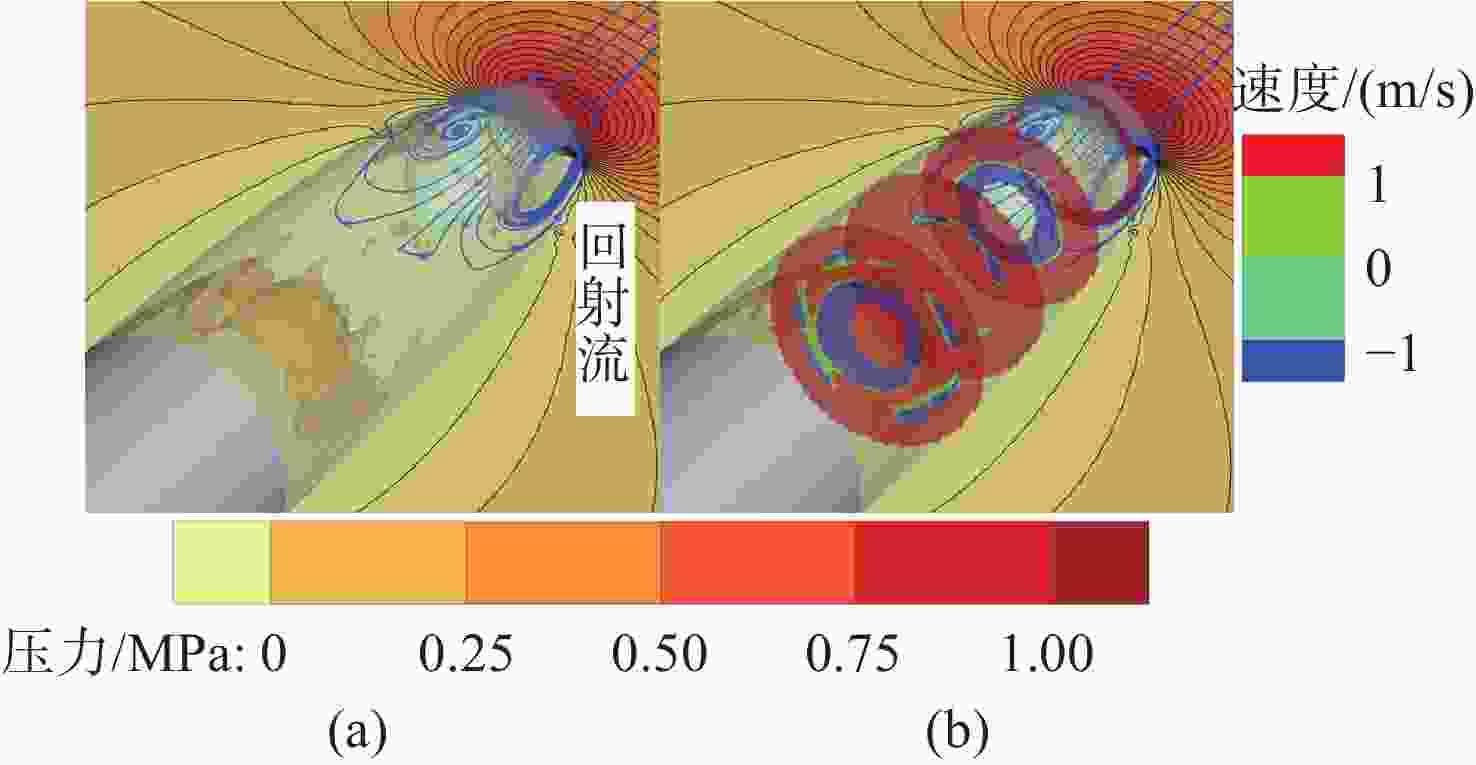
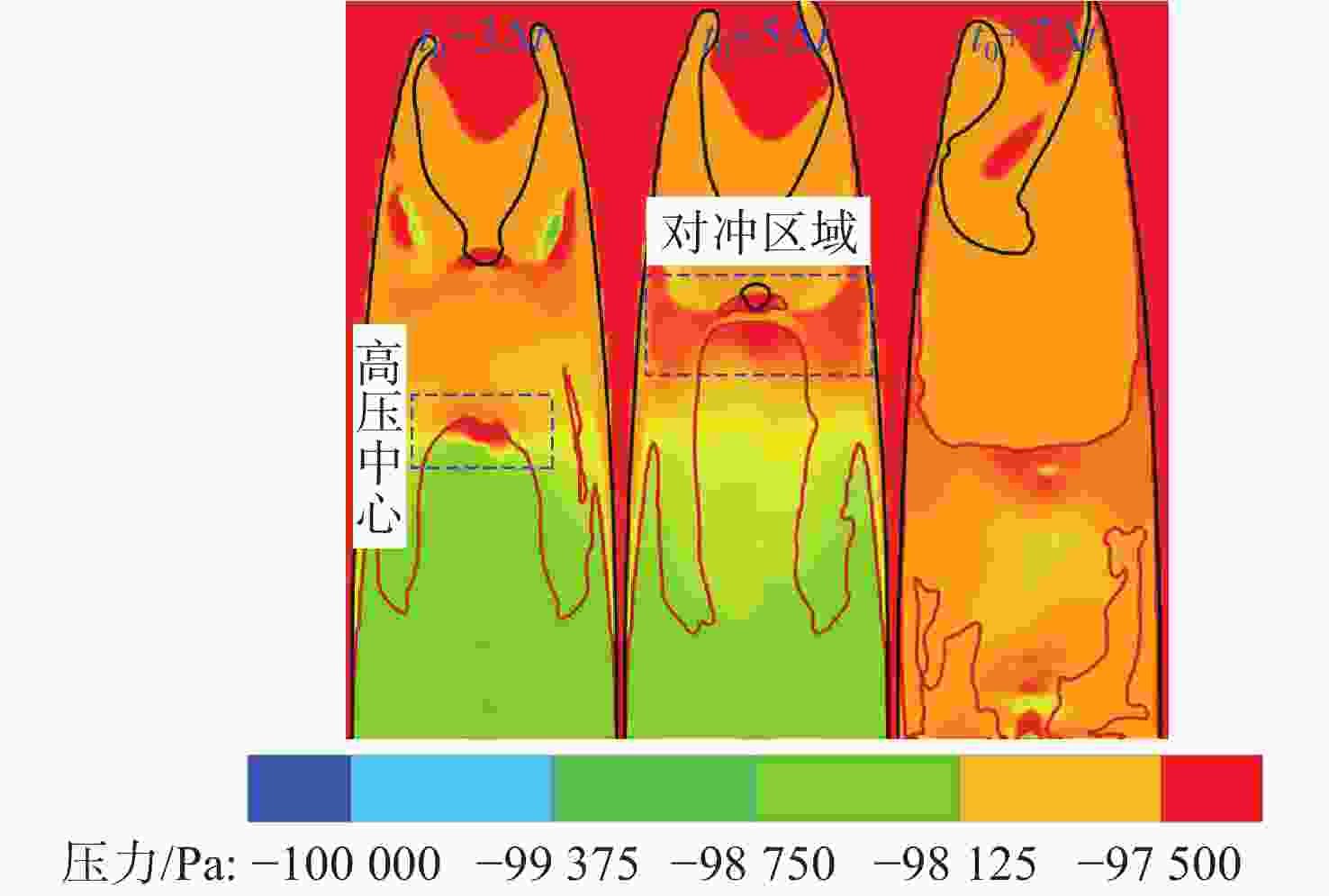
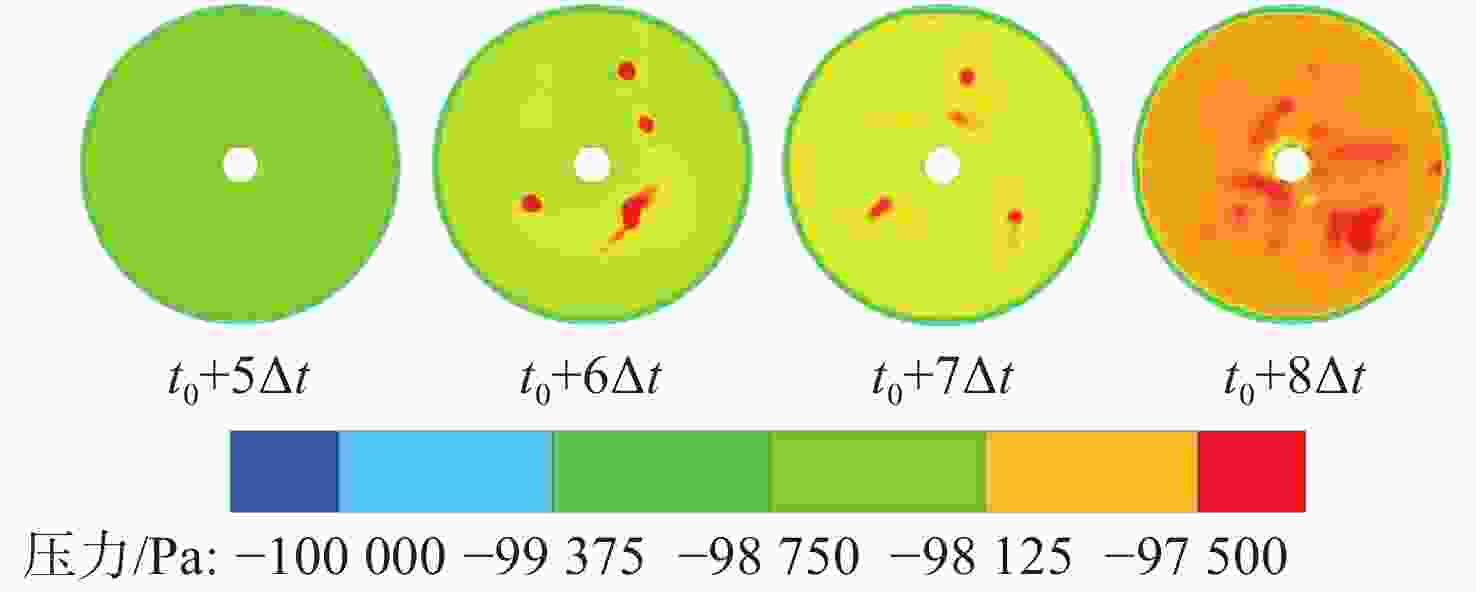
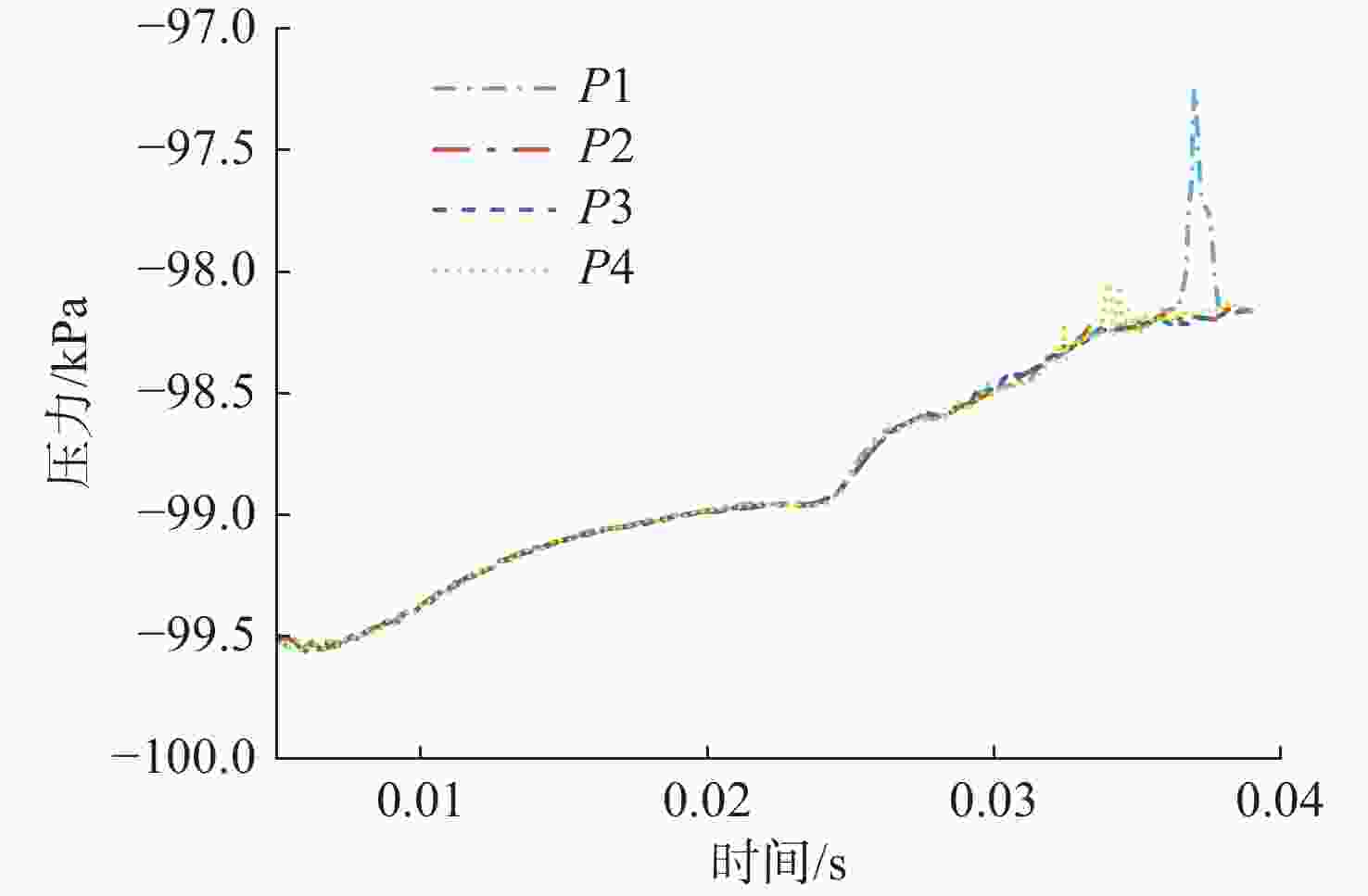
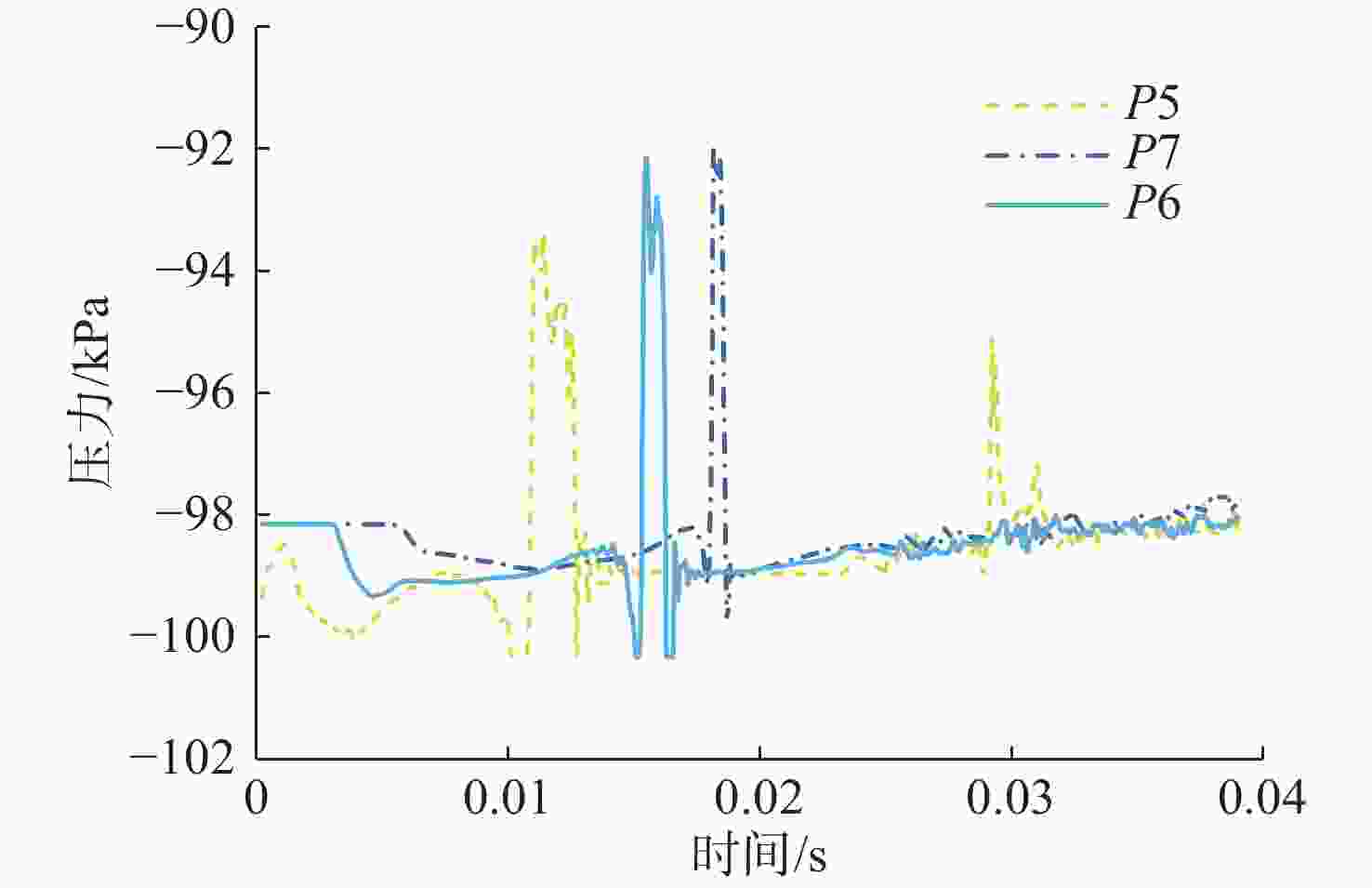
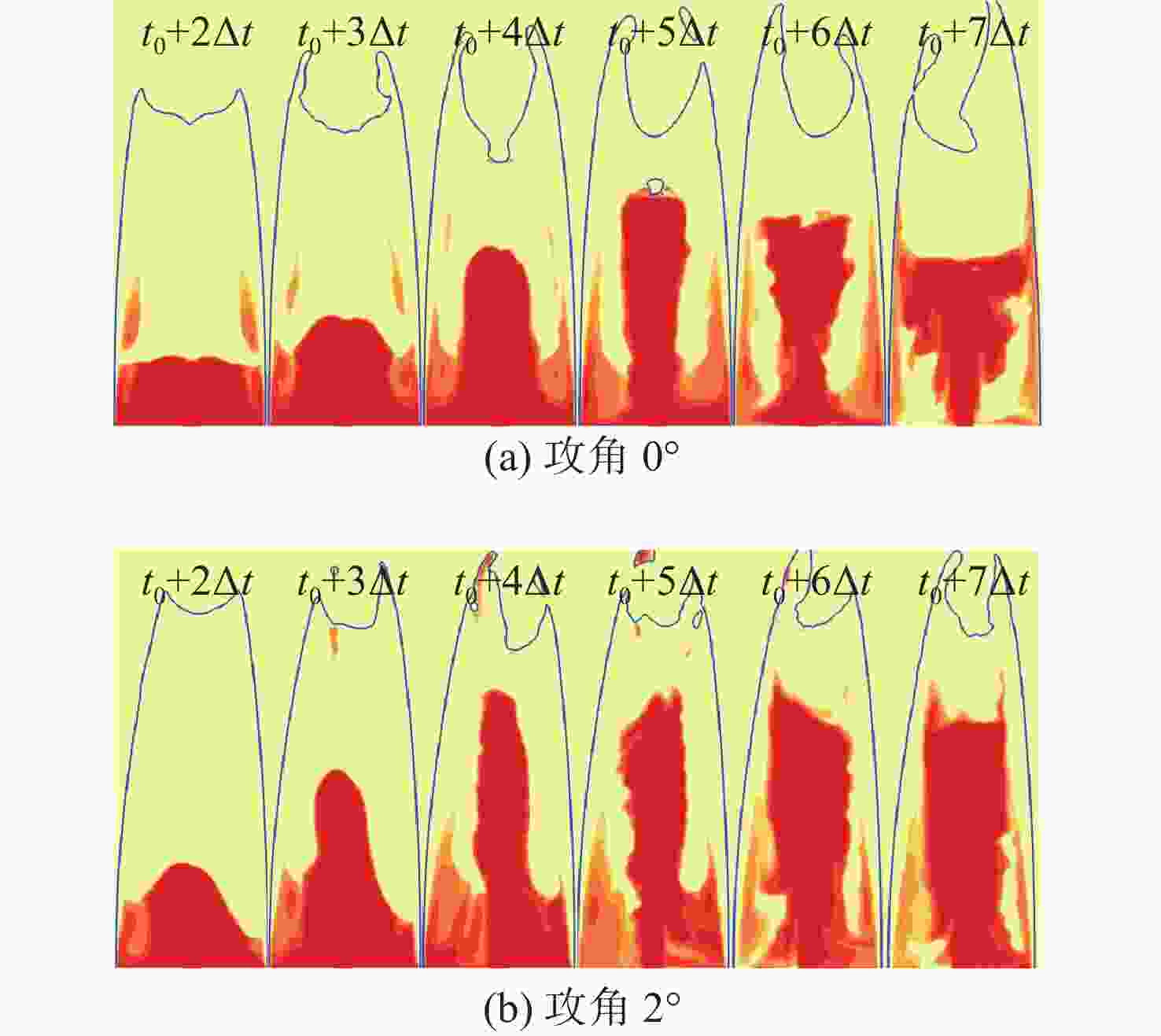
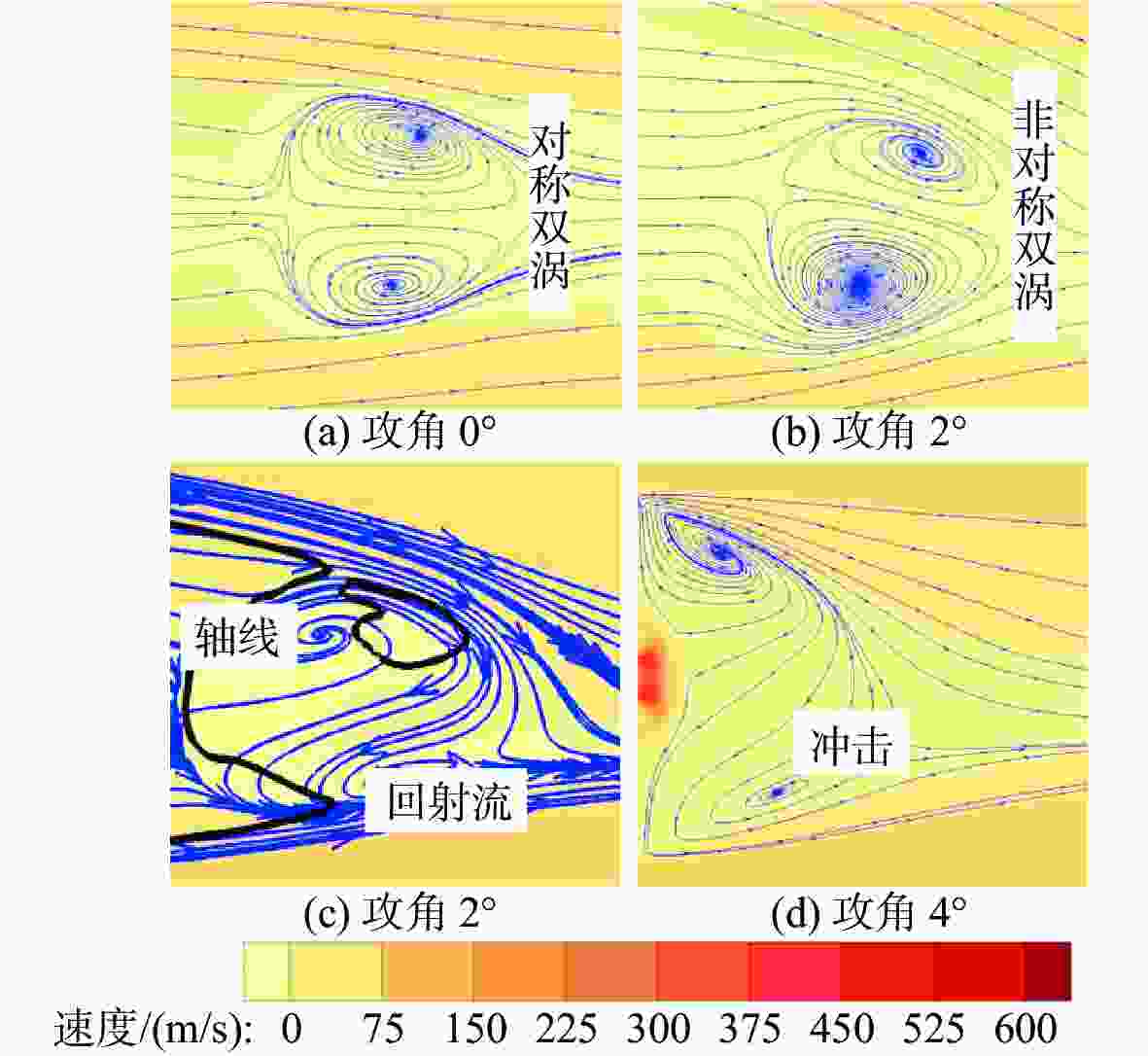
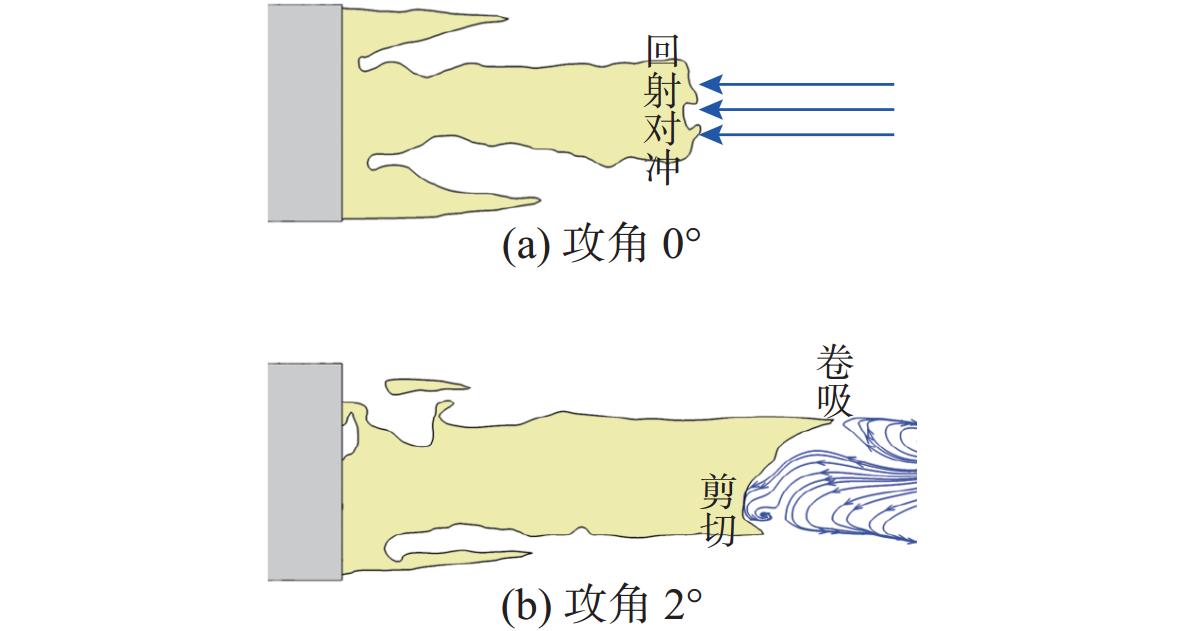
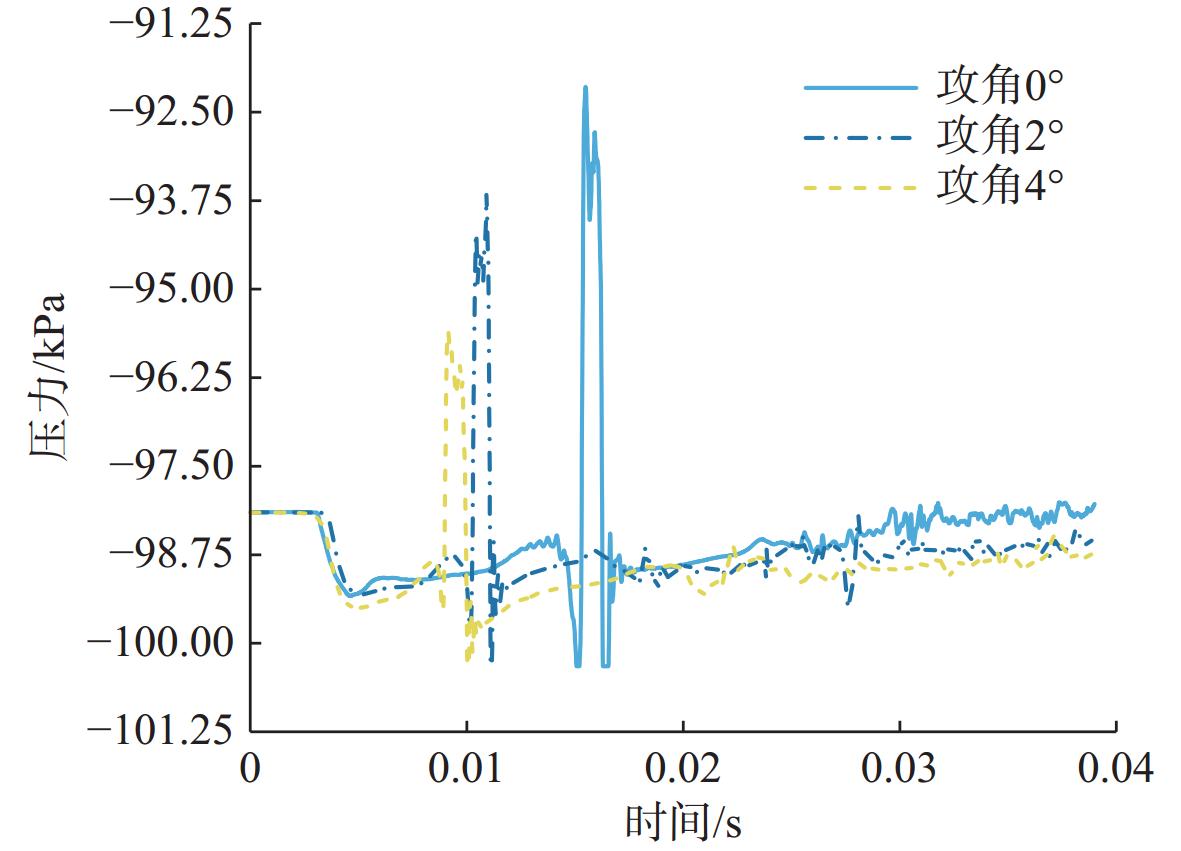
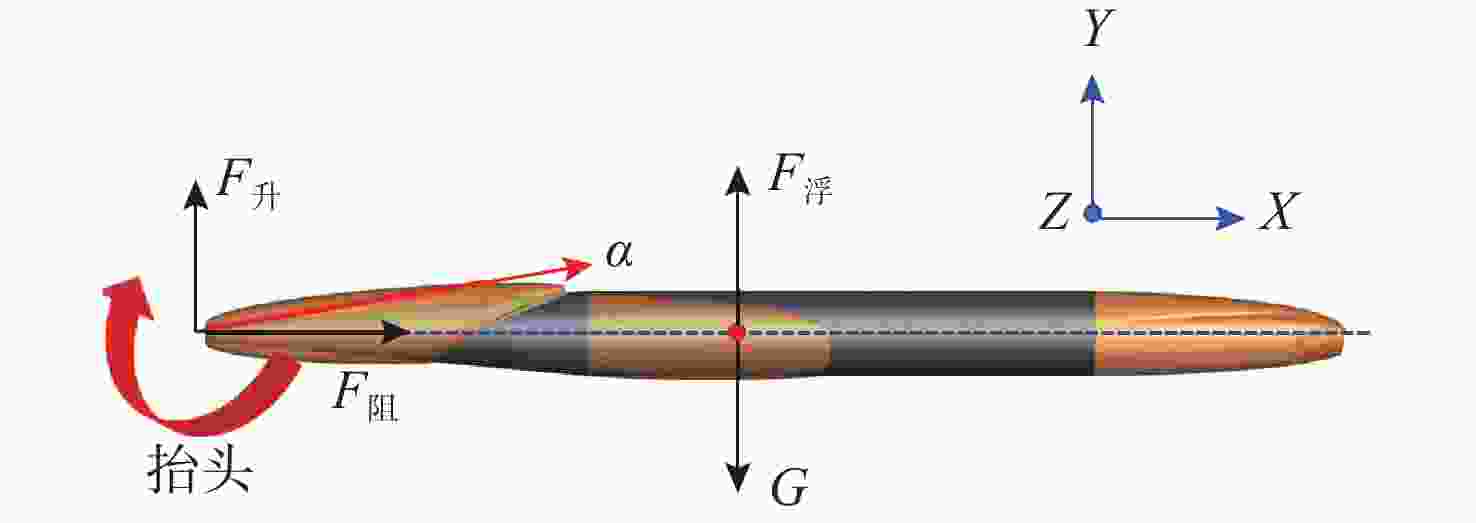
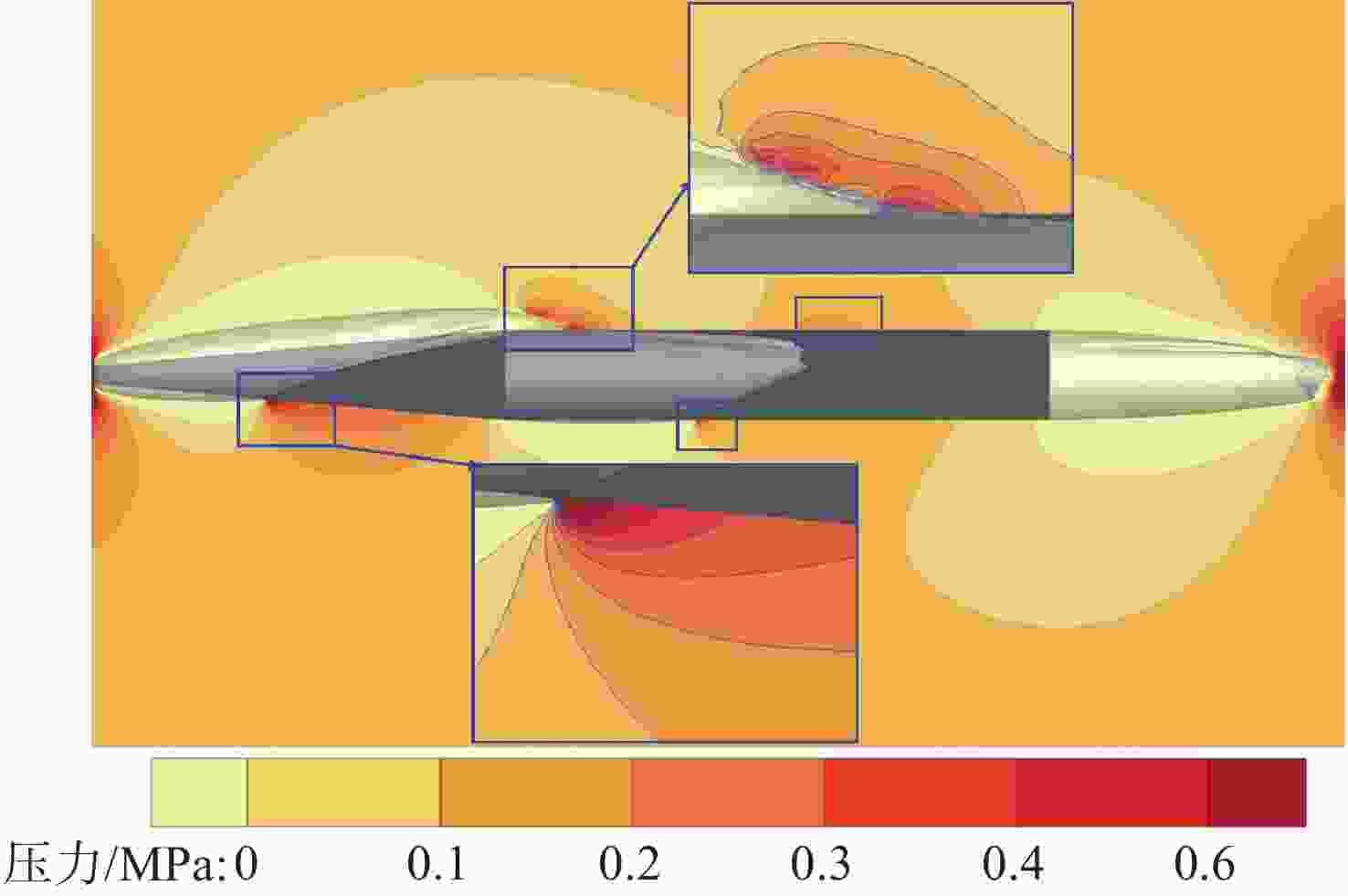
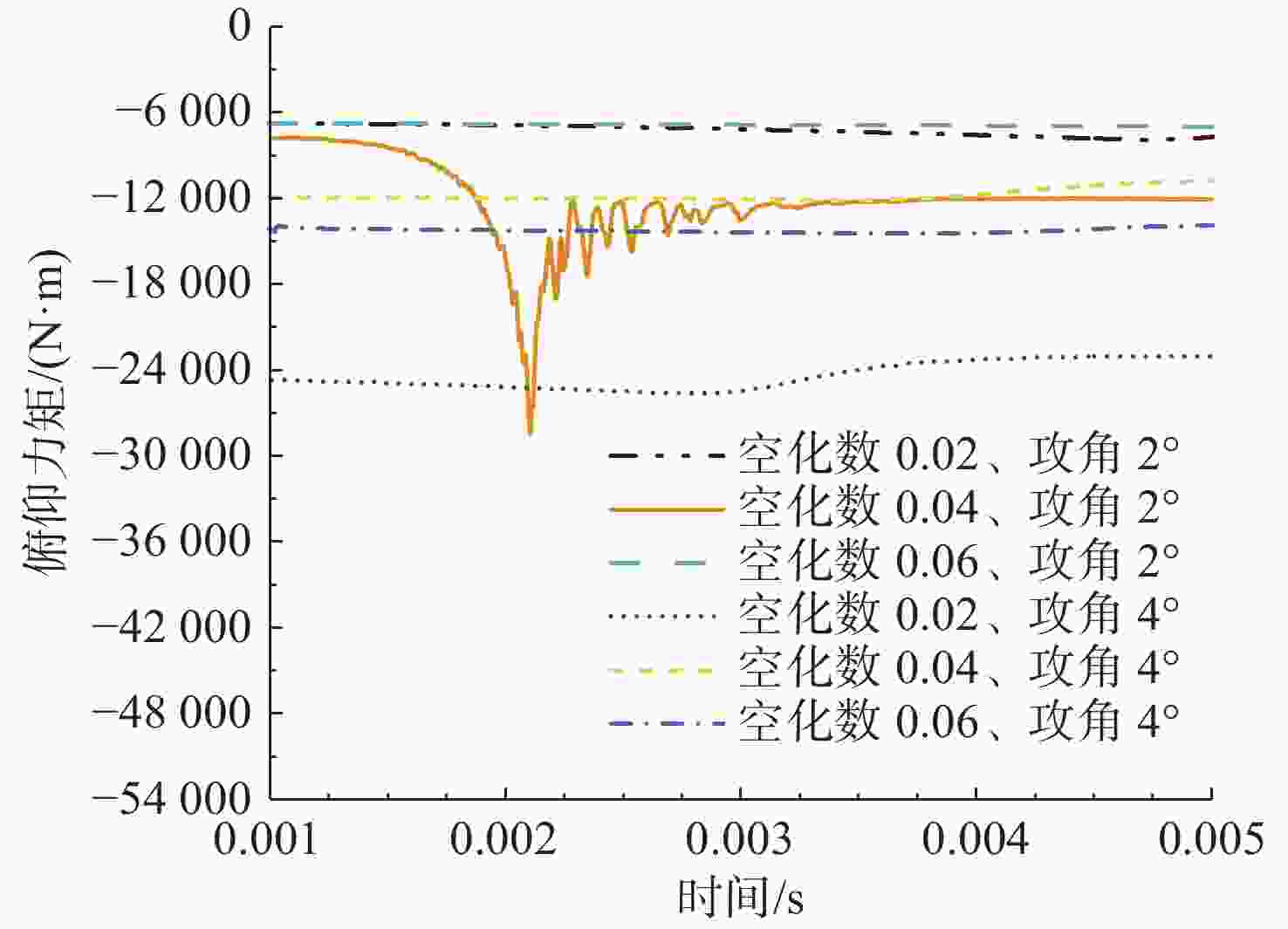
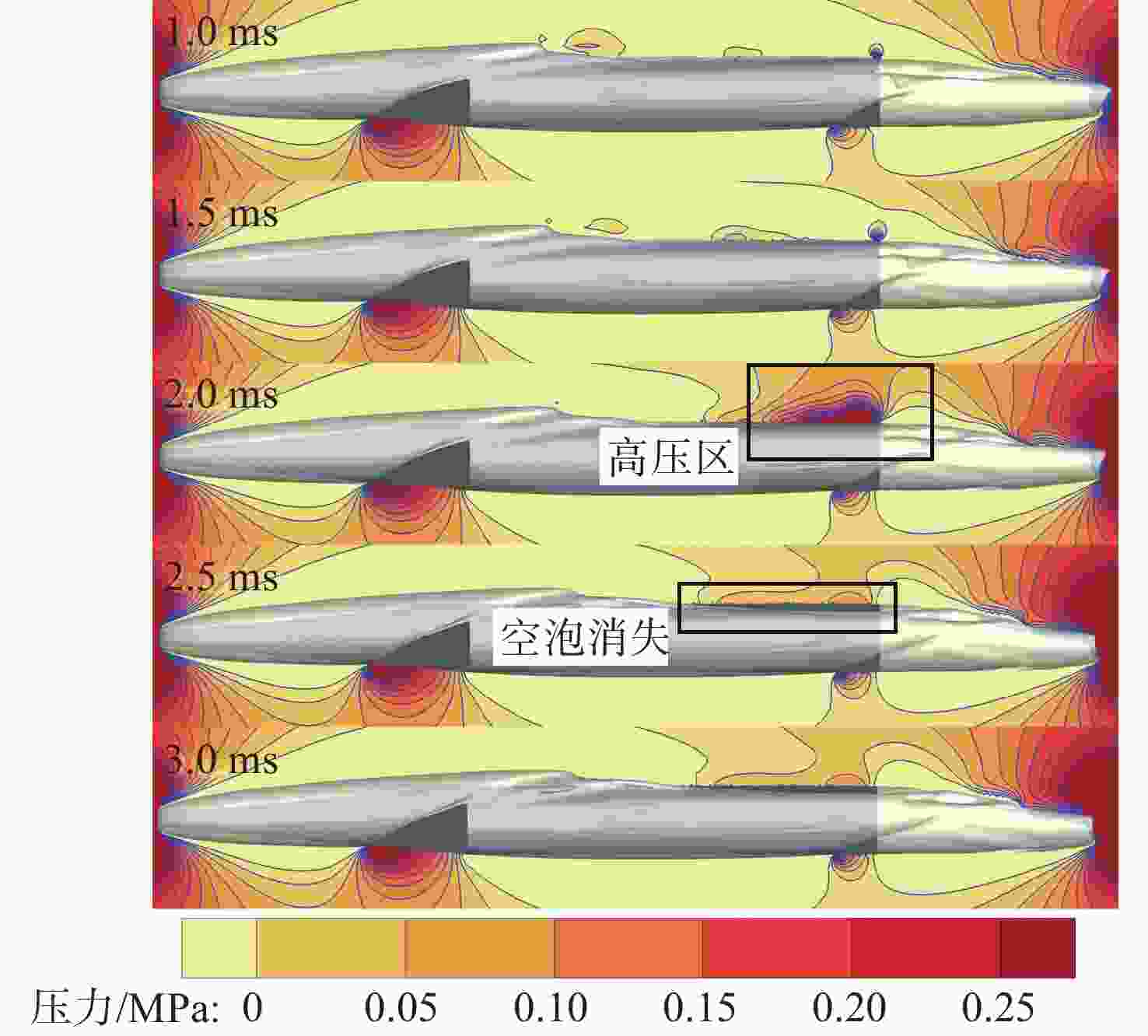
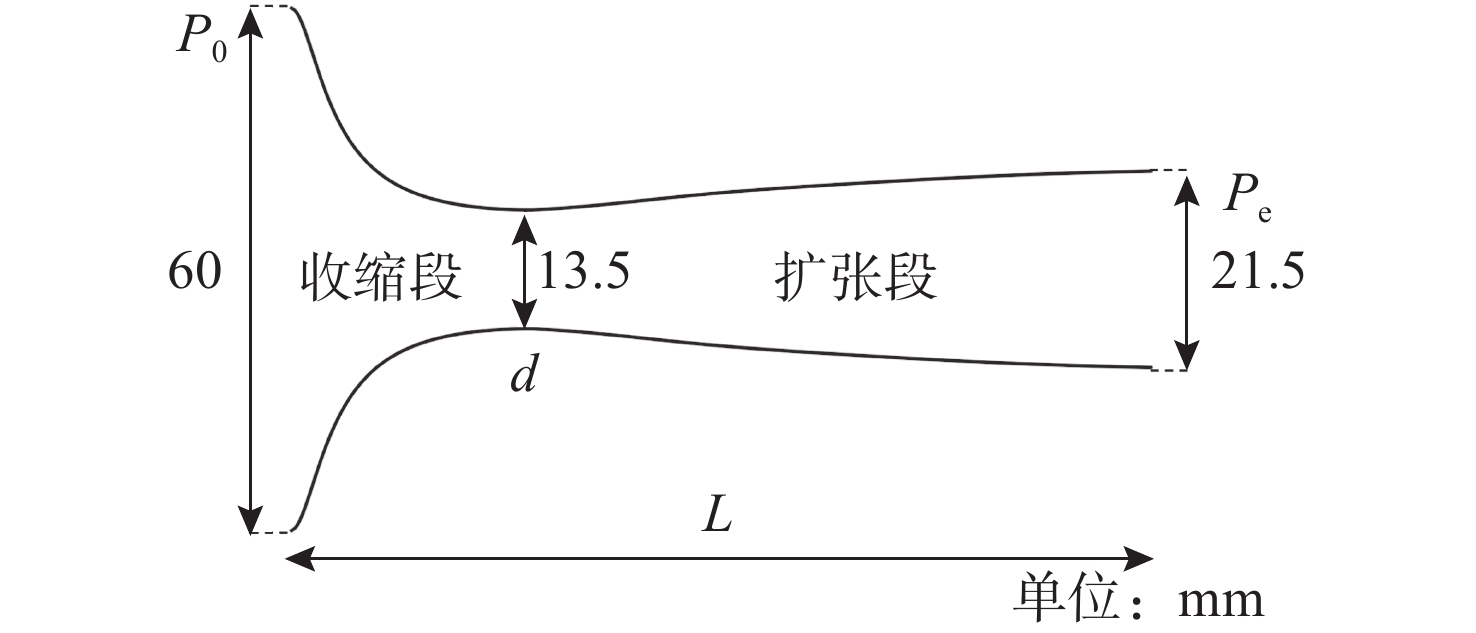
摘要: 为揭示自然空化尾空泡内超声速流场的演化规律与空泡内部的流场结构, 文中基于限体积法流体体积多相流模型, 对自然空化尾空泡内超声速射流流场展开仿真研究, 对比了不同空化数和来流攻角下的空泡内部流场参数分布, 得出如下结论: 自然空化尾空泡在超声速射流入射后, 空泡形态较稳定, 其演化主要集中在空泡尾部闭合处; 空泡内超声速射流流场发展主要受回射流影响, 无来流攻角时受回射流冲击, 射流轴向发展受抑, 轴向射流出现“回缩”现象, 有来流攻角时, 回射流位置发生偏移, 其剪切卷吸作用占主导, 射流轴向发展迅速; 航行器姿态的稳定性主要受来流冲击和表面高压区分布的影响, 空化数较小时, 增大来流攻角可大幅度增加航行器俯仰力矩。Abstract: In order to reveal the evolution law of the supersonic flow field in the natural cavitating tail cavity and the flow field structure in the cavity, this paper simulated the flow field of the supersonic jet in the natural cavitating tail cavity based on the volume of fluid (VOF) multiphase flow model. The paper compared the distribution of the flow field parameters in the cavity under different cavitation number and different angles of attack of incident flow, and drew the following conclusions: The cavity shape of the natural cavitating tail cavity is relatively stable after the incident flow of the supersonic jet, and its evolution is mainly concentrated in the closure of the cavity tail. The development of the flow field of the supersonic jet in the cavity is mainly affected by the re-entrant jet. When there is no angle of attack of incident flow, the flow field is impacted by the re-entrant jet, and the axial development of the jet is suppressed. The axial jet appears retracted phenomenon. When there is an angle of attack of the incident flow, the position of the re-entrant jet has shifted, and the shear and suction effect is dominant. The axial development of the jet is rapid, and the stability of the attitude of the vehicle is mainly affected by the impact of the incident flow and the distribution of the surface high-pressure area. When the cavitation number is small, increasing the angle of attack of the incident flow can greatly increase the pitching moment of the vehicle.
-
Key words:
- natural cavitation /
- supersonic jet /
- tail cavity /
- flow field
-
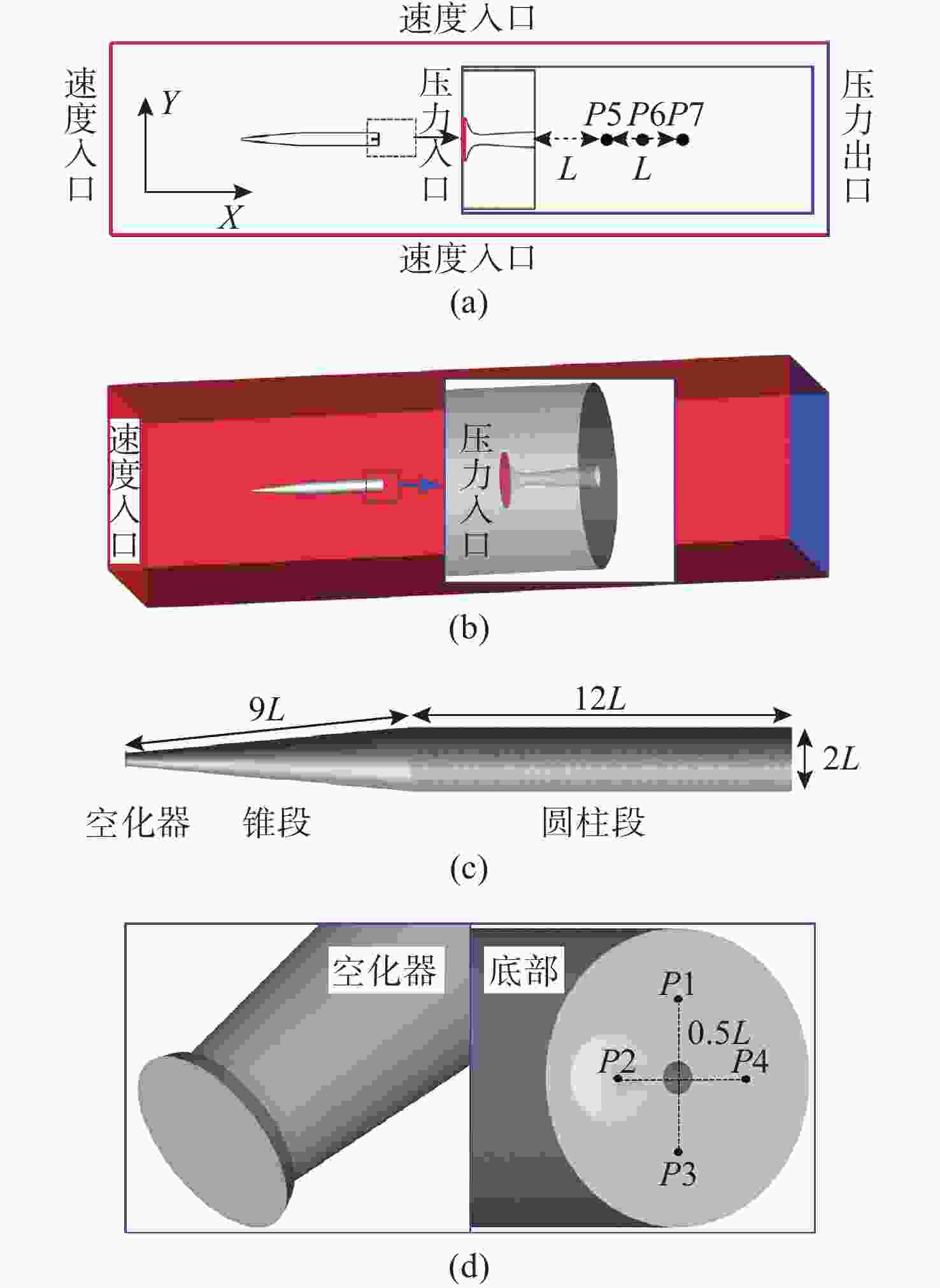
表 1 参数列表
Table 1. List of parameters
工况 空化数 来流攻角/(°) 0 0.06 0 1 0.06 2 2 0.06 4 3 0.04 0 4 0.04 2 5 0.04 4 6 0.02 0 7 0.02 2 8 0.02 4 -
[1] 刘喜燕, 袁绪龙, 罗凯, 等. 带尾裙跨介质航行体高速斜入水实验研究[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(11): 108-120. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0509Liu Xiyan, Yuan Xulong, Luo Kai, et al. Experimental study on high-velocity oblique water entry of a trans-media vehicle with tail-skirt[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(11): 108-120. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0509 [2] 赵小宇, 向敏, 张为华, 等. 超音速尾流作用下通气空泡稳定性及闭合位置数值研究[J]. 力学学报, 2021, 53(12): 3298-3309. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-346Zhao Xiaoyu, Xiang Min, Zhang Weihua, et al. Numerical study on the stability and closure position of ventailated cavity with a supersonic tail jet[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2021, 53(12): 3298-3309. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-346 [3] 许海雨, 罗凯, 黄闯, 等. 通气超空化对水下火箭发动机性能影响[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2021, 53(6): 41-47.Xu Haiyu, Luo Kai, Huang Chuang, et al. Influence of ventilated supercavitation on underwater rocket engine[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021, 53(6): 41-47. [4] Kinzel P M, Krane H M, Kirschner N I, et al. A numerical assessment of the interaction of a supercavitating flow with a gas jet[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2017, 136304-313. [5] 张春, 王宝寿. 水下航行体超声速射流与尾空泡耦合作用初期的流场特性[J]. 兵工学报, 2022, 43(7): 1685-1694.Zhang Chun, Wang Baoshou. Flow field characteristics of the early-stage coupling interaction between supersonic jet and tail cavity of underwater vehicles[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(7): 1685-1694. [6] 陈玮琪. 闭合在可压气体射流上的空泡数学模型[J]. 船舶力学, 2022, 26(12): 1737-1748. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2022.12.001Chen Weiqi. Mathematical model of cavity closure on a compressible gas jet[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2022, 26(12): 1737-1748. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2022.12.001 [7] 党建军, 刘统军, 胥银. 尾部喷流对定常超空泡形态影响的数值研究[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2007, 15(6): 50-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1948.2007.06.013Dang Jianjun, Liu Tongjun, Xu Yin. Numerical simulation of influence of tail jet on steady supercavitation configuration[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2007, 15(6): 50-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1948.2007.06.013 [8] 胡勇, 陈鑫, 鲁传敬, 等. 水下航行体尾喷燃气与通气超空泡相互作用的研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展A辑, 2008, 23(4): 438-445.Hu Yong, Chen Xin, Lu Chuanjing, et al. Study on the interaction between ventilated cavitating flow and exhausted gas of an underwater vehicle[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2008, 23(4): 438-445. [9] 舒畅, 宫兆新, 刘桦. 自然超空泡与尾喷流相互作用的数值模拟[J]. 力学季刊, 2023, 44(1): 15-30.Shu Chang, Gong Zhaoxin, Liu Ye. Numerical simulation of interaction between natural supercavitationand base jet[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2023, 44(1): 15-30. [10] 赵小宇, 向敏, 刘波, 等. 通气空泡与超音速尾喷流耦合作用实验研究[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2021, 43(5): 53-60. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202105006 [11] 裴譞, 张宇文, 孟生, 等. 超空泡航行器尾喷管实验研究[J]. 应用力学学报, 2010, 27(3): 584-588, 650. [12] 陈学军, 王瑞, 祁晓斌, 等. 燃气尾喷对水下航行体通气空泡形态及表面压力的影响[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2023, 46(4): 521-527. doi: 10.7673/j.issn.1006-2793.2023.04.05 [13] 许昊, 王聪, 陆宏志, 等. 水下超声速气体射流诱导尾空泡实验研究[J]. 物理学报, 2018, 67(1): 191-204. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.20171617 [14] Moeny J M, Krane H M, Kirschner N I, et al. Jet-supercavity interaction: Insights from experiments[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2015, 656(1): 012162. [15] Hunter C A. Experimental investigation of separated nozzle flows[J]. Journal of Propulsion & Power, 2004, 20(3): 527-532. [16] Hrubes J D. High-speed imaging of supercavitating underwater projectiles[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2001, 30(1): 57-64. doi: 10.1007/s003480000135 -





 下载:
下载: