Underwater Target Recognition Based on Dynamic Ensemble of Random Forest
-
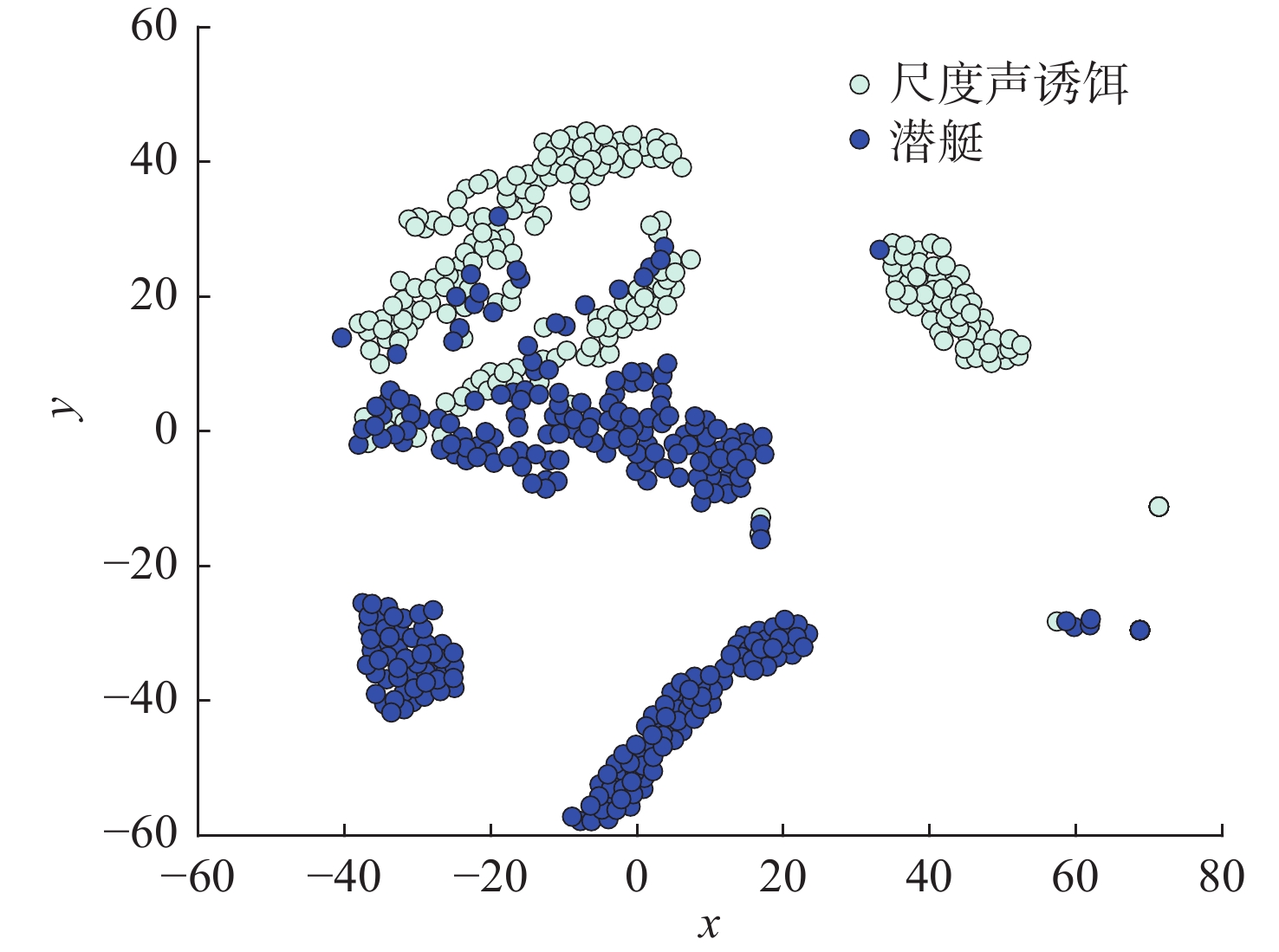
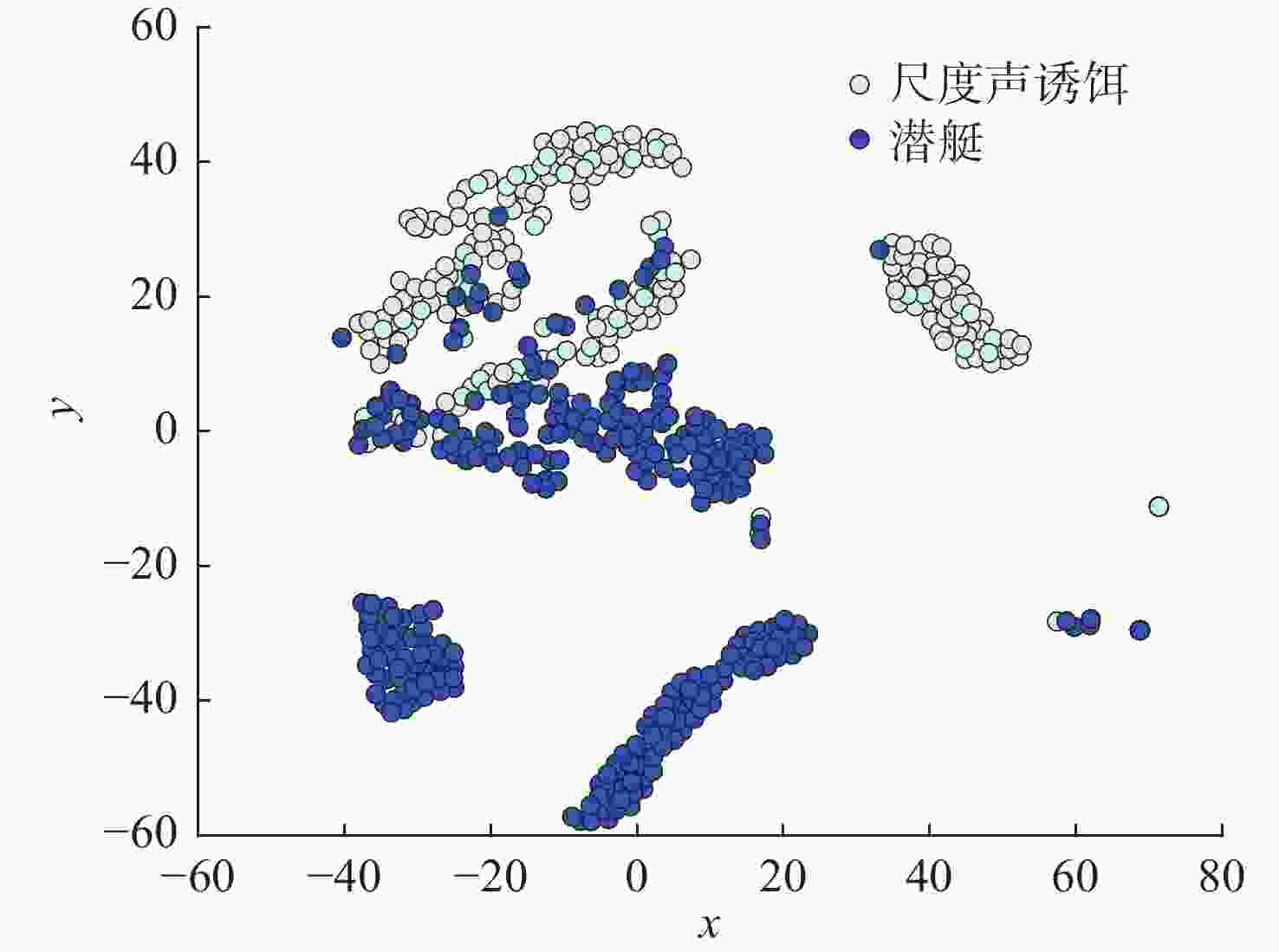
摘要: 正确识别目标是水下声自导武器攻击敌方目标的关键。文中提出一种基于动态选择集成技术的水下声自导武器实时目标识别方法。利用水下声自导武器主动宽带探测波形照射下目标不同的反射特性, 从目标宽带相关检测输出提取了能量分布和空间分布统计特征, 并构建了基于随机森林的动态选择集成模型, 利用海试数据集进行训练与测试。仿真分析表明, 文中所提出的动态集成模型识别效果优于其他分类算法, 可以较好地应用于水下声自导武器目标识别中。Abstract: Accurate recognition of the target is the key to attacking enemy for underwater acoustic homing weapon. A real-time target recognition method for underwater acoustic homing weapon was proposed based on dynamic ensemble selection technology. The statistical features of energy distribution and spatial distribution were extracted from the output of target wideband correlation detection by using the different reflection characteristics of the target irradiated by the active wideband detection waveform of the underwater acoustic homing weapon. In addition, a dynamic ensemble model based on a random forest was constructed, and it was trained and tested on the marine dataset. The simulation analysis shows that the dynamic ensemble model proposed in this paper has better recognition effects than other classification models and can be applied to target recognition by underwater acoustic homing weapon.
-
表 1 二分类混淆矩阵
Table 1. Two-class confusion matrix
真实情况 预测结果 正例 反例 正例 NTP NFN 反例 NFP NTN 表 2 不同算法ROC曲线下面积值
Table 2. The area under the curve of different algorithms
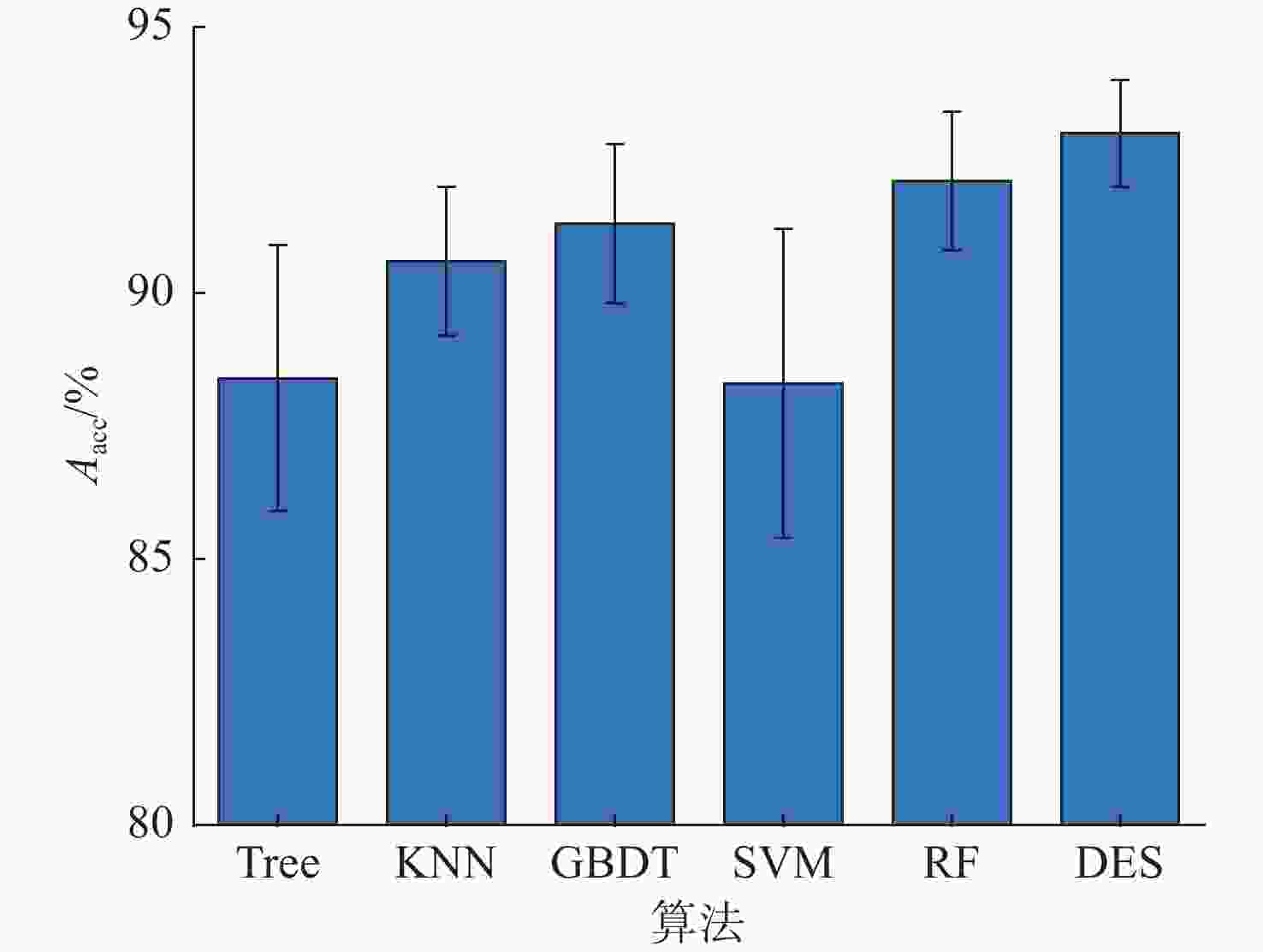
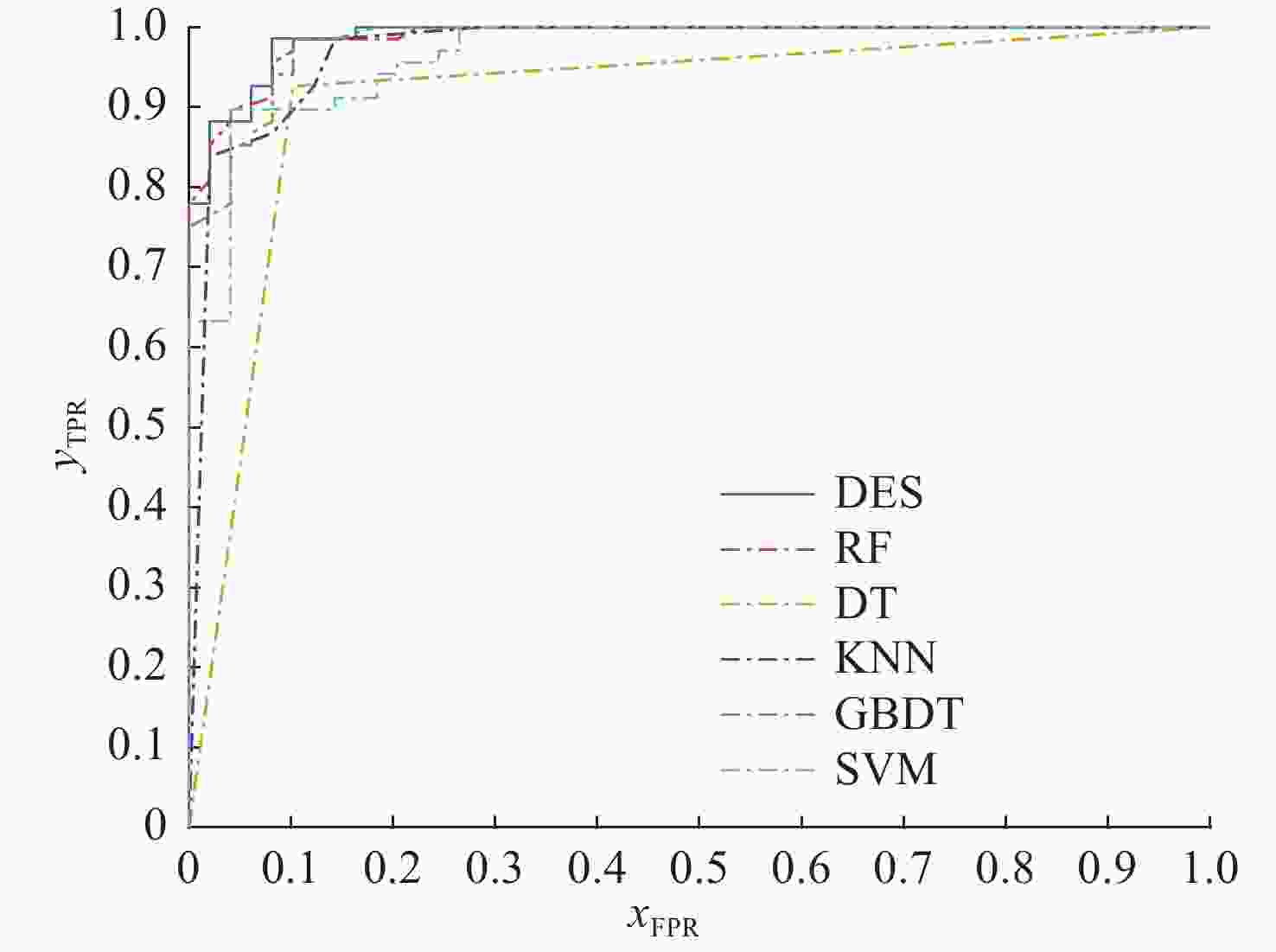
算法 均值 标准差 DT 0.881 0.030 KNN 0.970 0.030 GBDT 0.975 0.008 SVM 0.965 0.015 RF 0.964 0.010 DES 0.976 0.007 表 3 不同算法的精确率和召回率
Table 3. The precision rate and recall rate for different algorithms
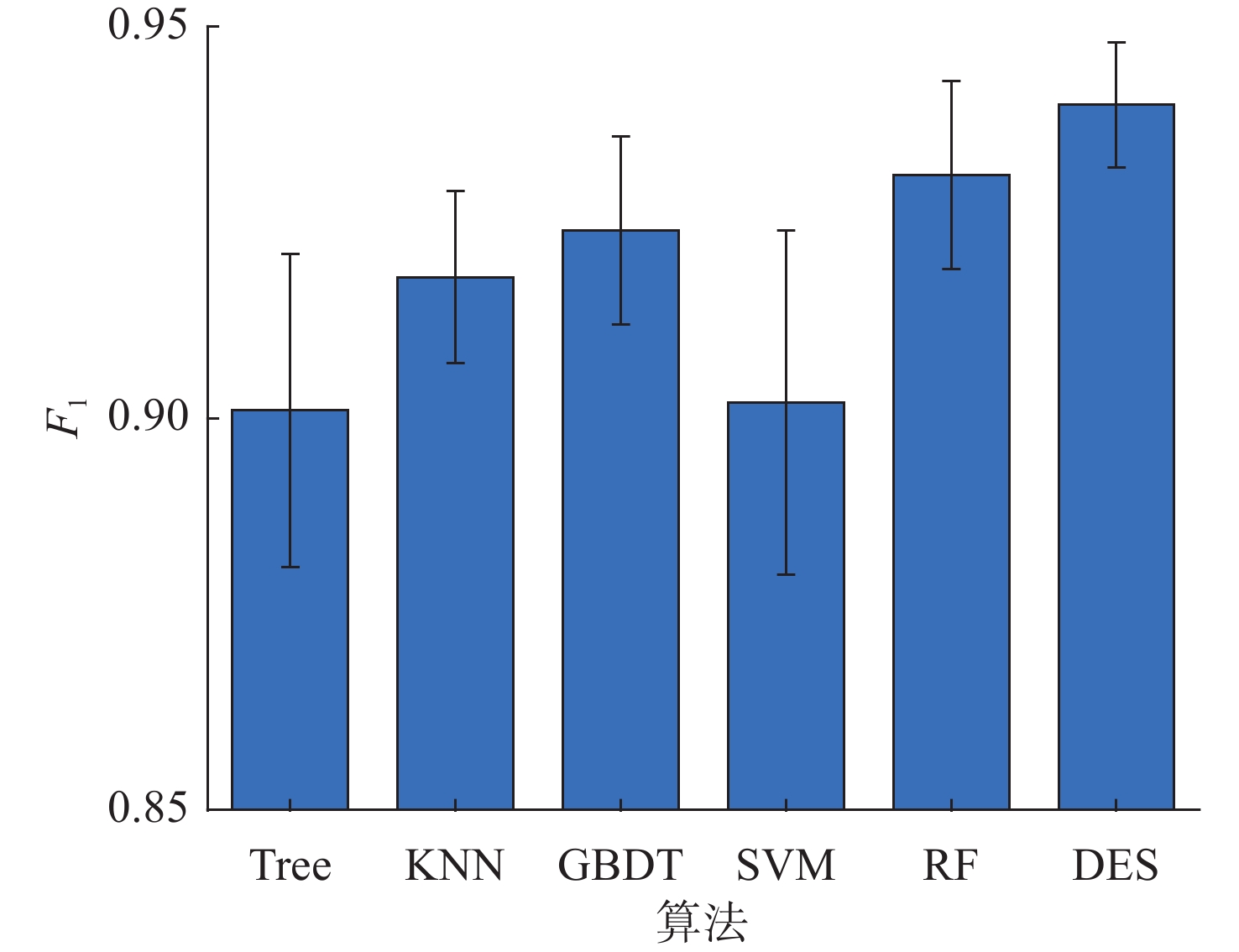
算法 精确率 召回率 DT 0.892±0.040 0.912±0.016 KNN 0.930±0.038 0.909±0.025 GBDT 0.935±0.029 0.915±0.019 SVM 0.875±0.040 0.932±0.020 RF 0.938±0.029 0.926±0.016 DES 0.937±0.027 0.944±0.019 -
[1] 周德善, 李志舜, 朱邦元. 鱼雷自导技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2009. [2] 蒋兴舟. 鱼雷制导设计原理[M]. 武汉: 海军工程大学, 2001. [3] 何心怡, 高贺, 陈菁, 等. 鱼雷真假目标识别技术现状与展望[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2016, 24(1): 23-27.He Xinyi, Gao He, Chen Jing, et al. Current situation and prospect on torpedo's true/false target identification technologies[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2016, 24(1): 23-27. [4] 王明洲, 郝重阳, 黄晓文. 基于相关法方位分析的水下主动目标尺度识别研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2003, 21(3): 317-320.Wang Mingzhou, Hao Chongyang, Huang Xiaowen. On underwater target dimension recognition based on bearings analysis of signal correlation feature[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2003, 21(3): 317-320. [5] 刘朝晖, 付战平, 王明洲. 基于方位走向法和互谱法的水中目标识别[J]. 兵工学报, 2006, 27(5): 932-935.Liu Zhaohui, Fu Zhanping, Wang Mingzhou. Underwater target identification based on the methods of bearing and cross-spectrum[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2006, 27(5): 932-935. [6] 石敏, 陈立纲, 蒋兴舟, 等. 具有亮点和方位延展特征的线列阵声诱饵研究[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2005, 17(1): 58-62.Shi Min, Chen Ligang, Jiang Xingzhou, et al. On linear array acoustic bait with light spot and azimuth-range extensi on feature[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2005, 17(1): 58-62. [7] 樊书宏, 王英民, 岳玲, 等. 基于拖曳长线阵的水下目标模拟系统[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2012, 24(5): 1083-1087.Fan Shuhong, Wang Yingmin, Yue Ling, et al. Underwater target simulation system based on towed long line array[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2012, 24(5): 1083-1087. [8] 徐枫, 严冰, 王海陆, 等. 水下声自导武器垂直目标亮点高分辨算法仿真与实验研究[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2009, 17(6): 35-40.Xu Feng, Yan Bing, Wang Hailu, et al. Simulation and experimental study high-resolution method for torpedo vertical highlights[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2009, 17(6): 35-40. [9] Meng Q, Yang S, Piao S. The classification of underwater acoustic target signals based on wave structure and support vector machine[J]. J. Acoust. Soc. Am, 2014, 136: 2265. [10] Chen C, Fu J. Recognition method of underwater target radiated noise based on convolutional neural network[J]. Acoust. Technol, 2019, 38: 424. [11] Li C, Huang Z Q, Xu J, et al. Underwater target classification using deep learning[C]//Oceans 2018. Charleston, US: IEEE, 2018. [12] Lee S, Seo I, Seok J, et al. Active sonar target classification with power-normalized cepstral coefficients and convolutional neural network[J]. Appl. Sci, 2020, 10: 8450. [13] Kamal S, Chandran C S, Supriya M H. Passive sonar automated target classifier for shallow waters using end-to-end learnable deep convolutional LSTMs[J]. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 24: 860-871. [14] Feng S, Zhu X. A transformer-based deep learning network for underwater acoustic target recognition[J]. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett, 2022, 19: 1-5. [15] Deng J, Yang X, Liu L, et al. Real-time underwater acoustic homing weapon target recognition based on stacking technique of ensemble learning[J]. J. Mar. Sci. Eng, 2023, 11: 2305. doi: 10.3390/jmse11122305 [16] King I, Yang H Q. Ensemble learning for imbalanced-commerce transaction anomaly classification[J]. Neural Information Processing, 2009, 58(63): 866-874. [17] Baumgartner D, Serpen G. Performance of global-local hybrid ensemble versus boosting bagging ensembles[J]. International Journal of Hybrid Intelligent Systems, 2012, 10(32): 25-37. [18] Azizi N, Farahn N, Ennajia A. New dynamic classifiers selection approach for handwritten recognition[C]//Proc of the 22nd International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2012: 189-196. [19] Gao Y, Ji G, Yang Z, et al. A dynamic adaboost algorithm with adaptive changes of loss function[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C: Applications and Reviews, 2012, 42(6): 1828-1839. -




 下载:
下载: