Flow Field and Motion Characteristics of Trans-Medium Submersible during Take-off and Landing on Water Surface
-
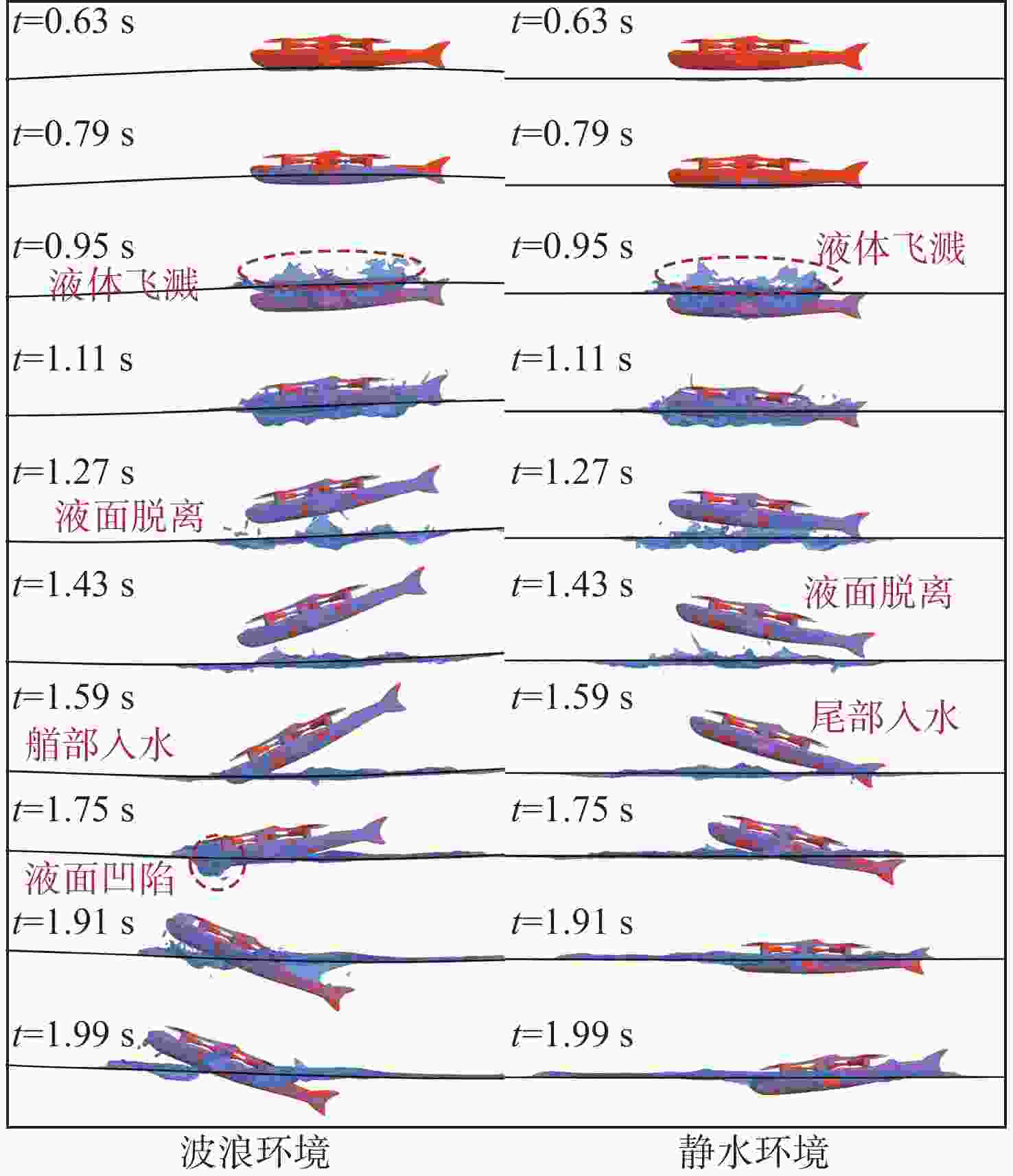
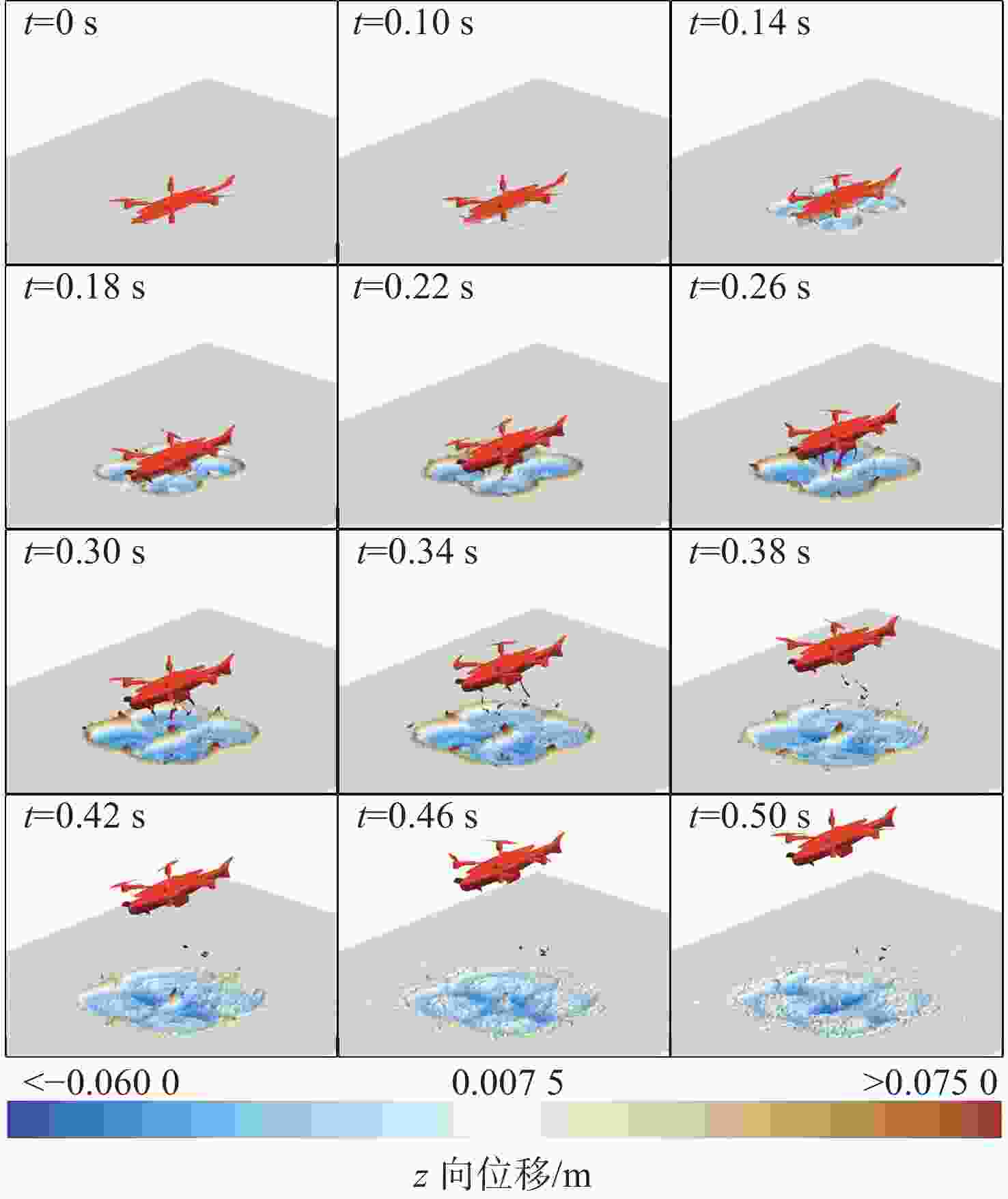
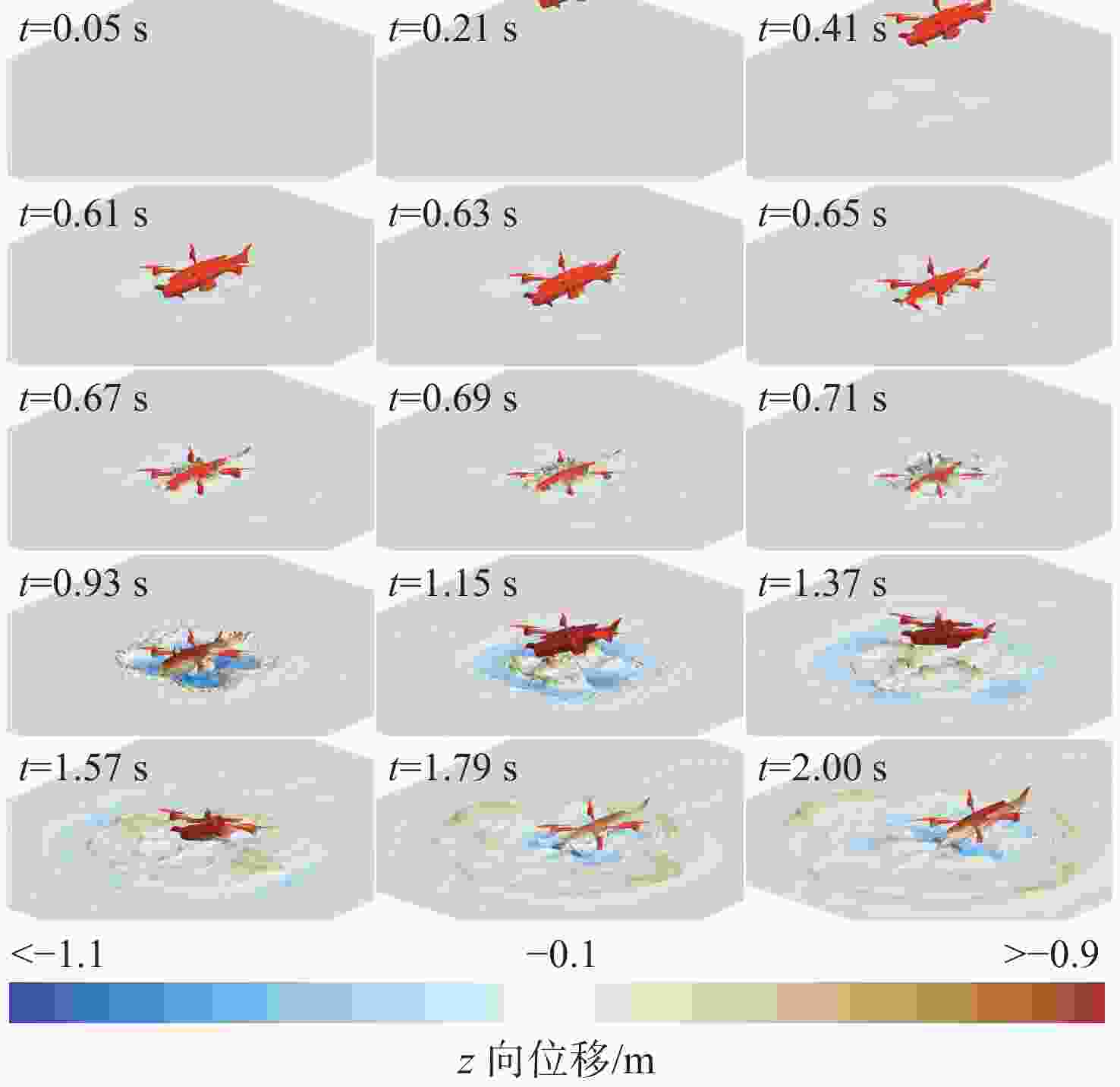
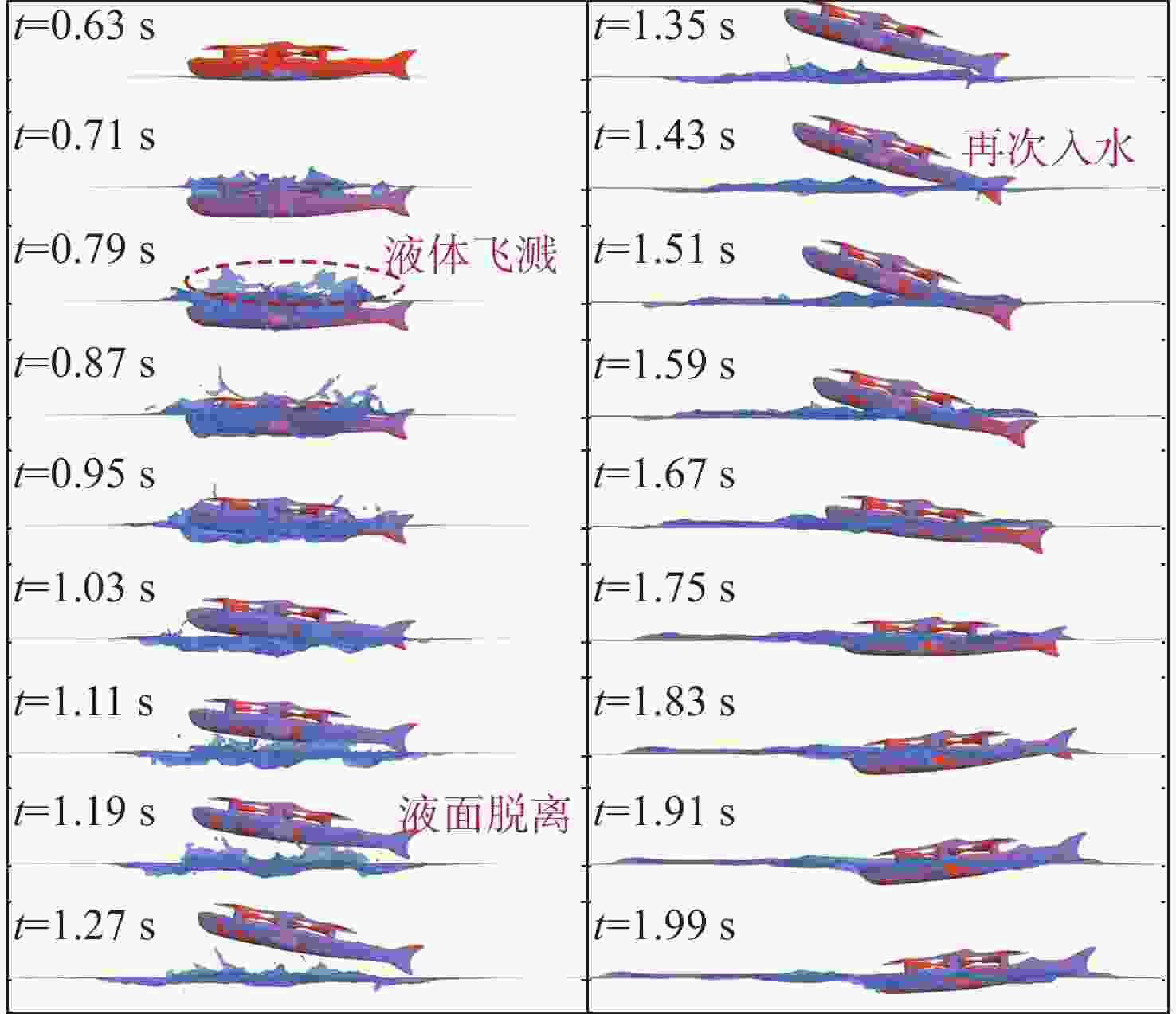
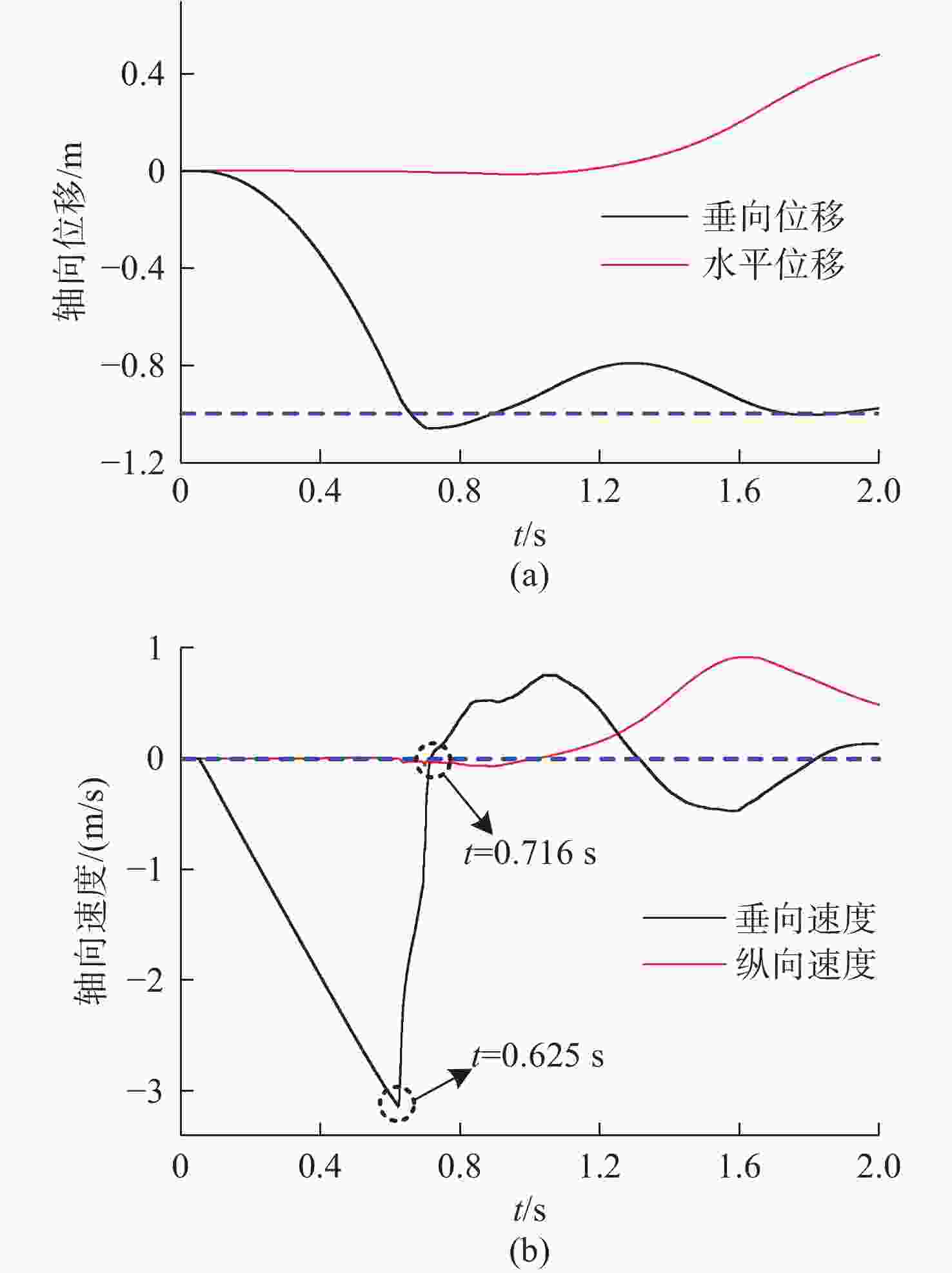
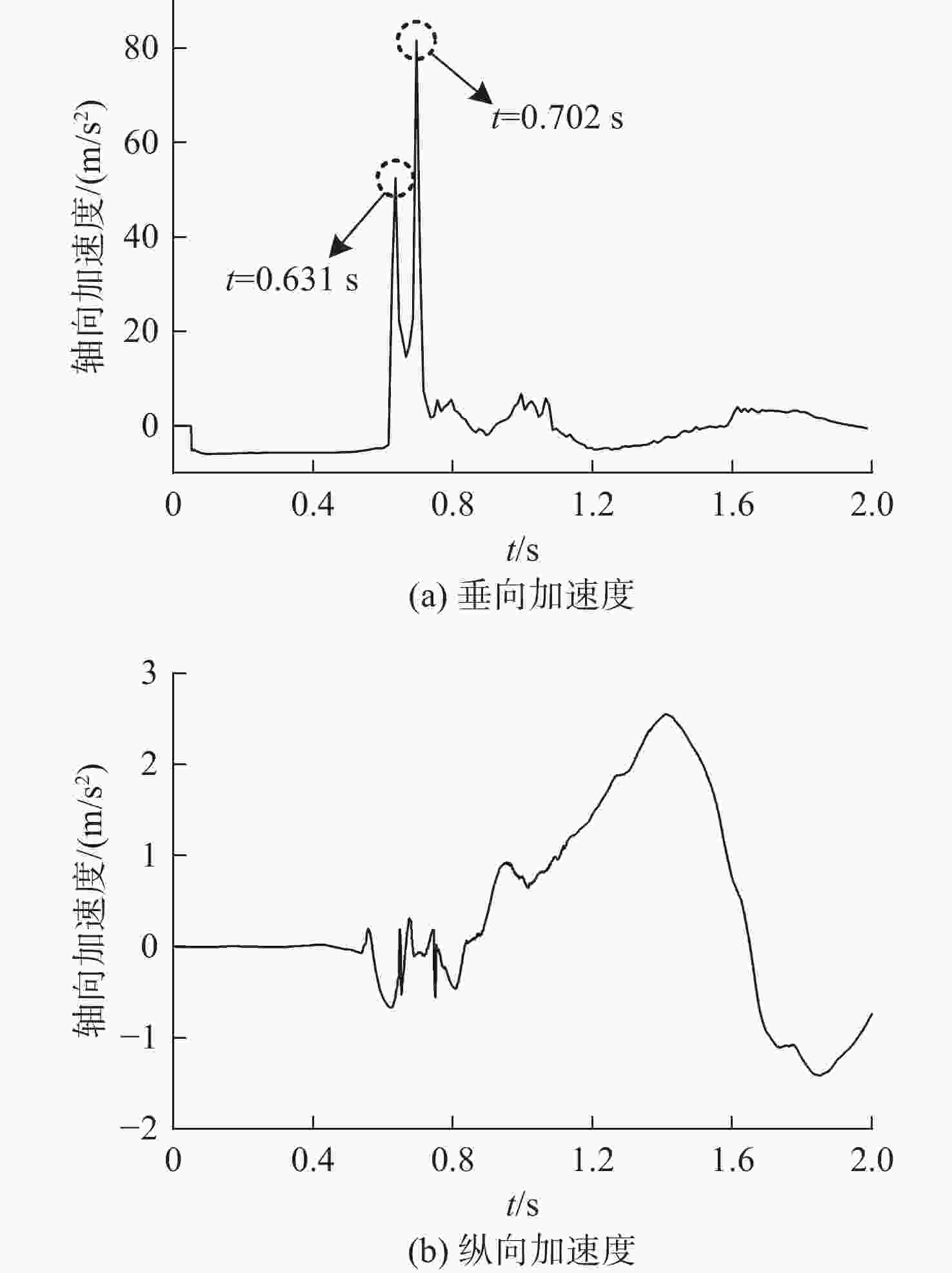
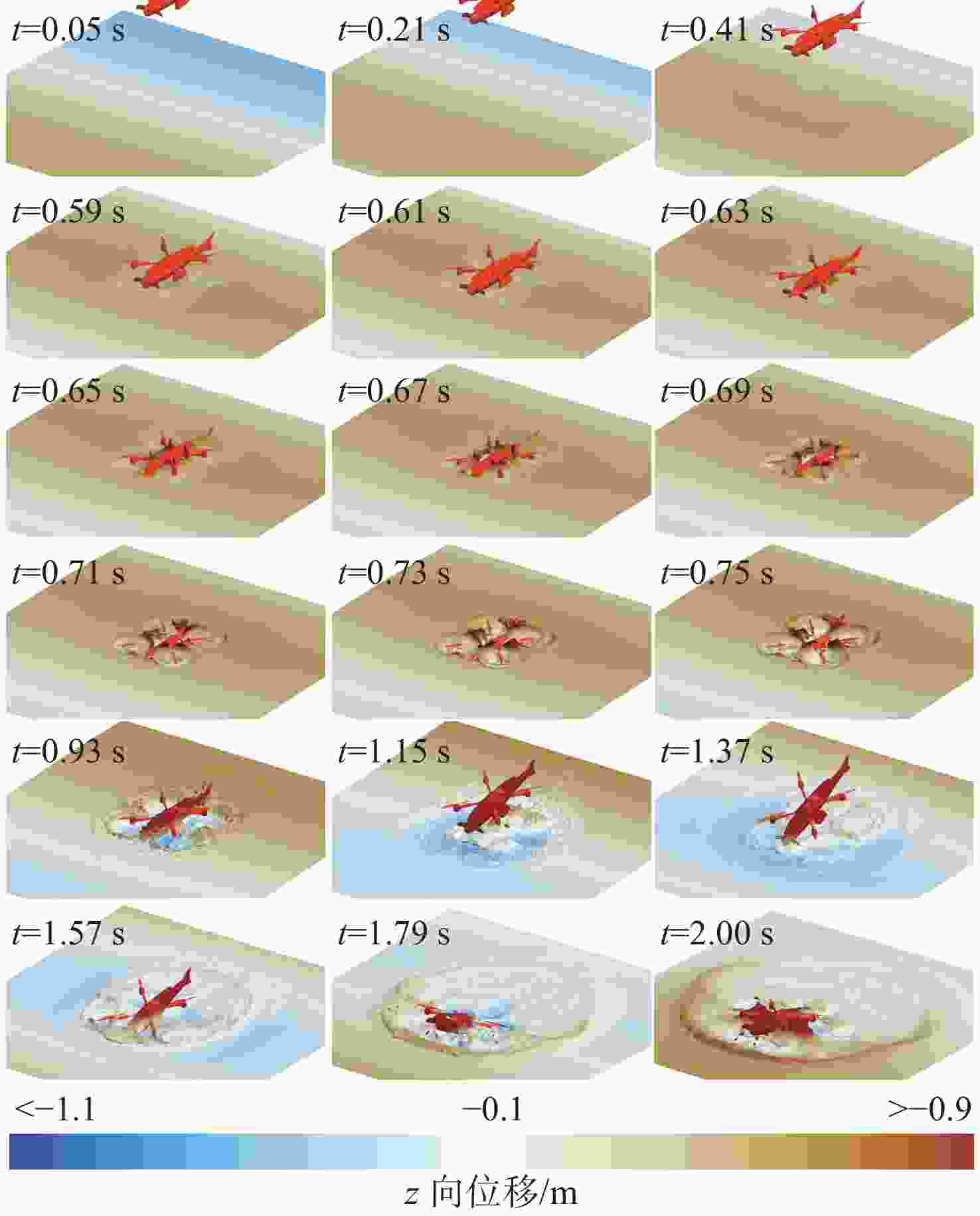
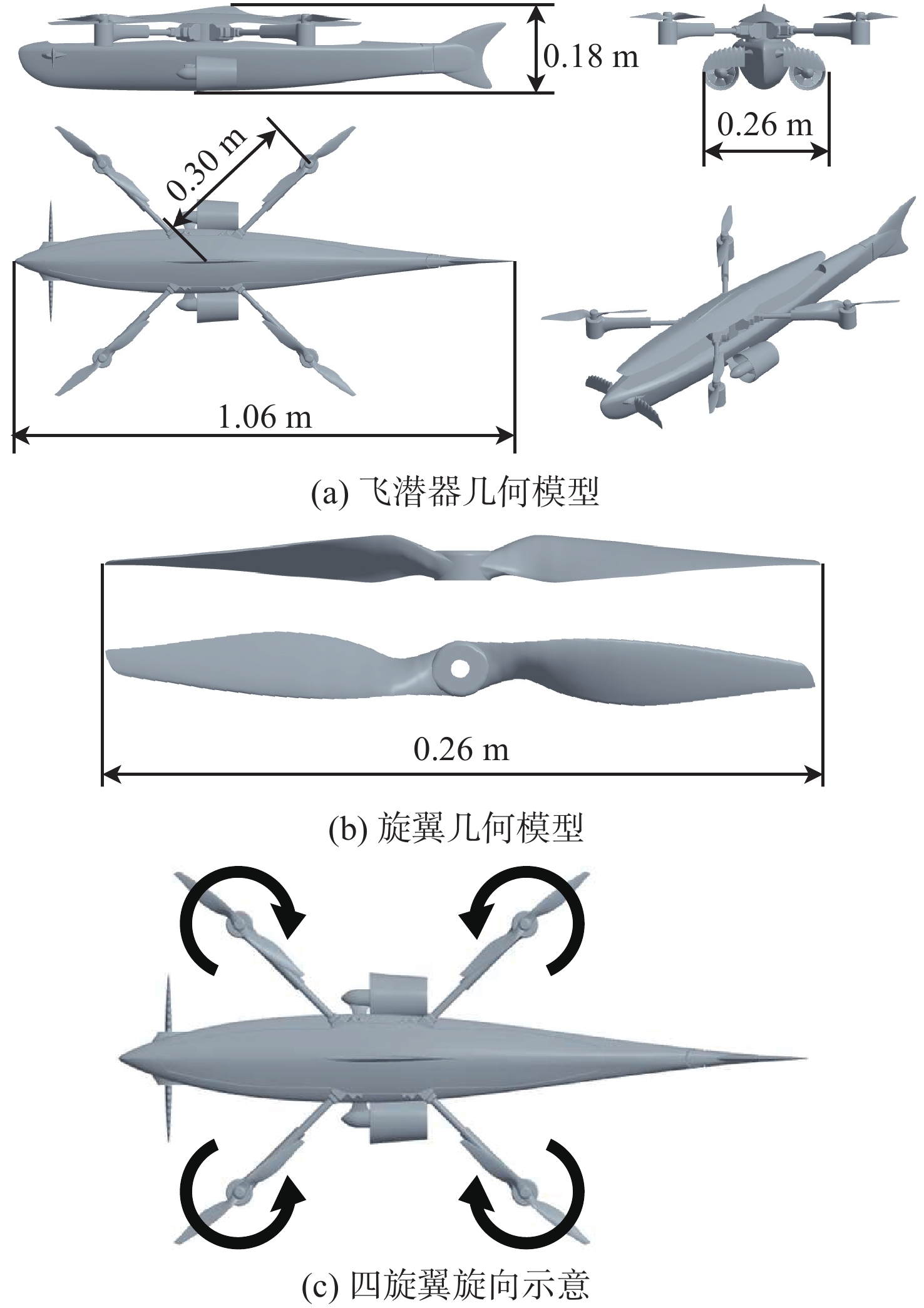
摘要: 为探究跨介质飞潜器水面起降过程流场结构演变及自身运动特性, 基于计算流体动力学数值仿真技术, 耦合流体体积多相流模型、剪切应力传输 k-ω 湍流模型、Schnerr-Sauer空化模型以及Stokes 5阶非线性波理论, 构建了飞潜器水面起降的数值计算方法。分别对静水环境下飞潜器水面起飞过程、有/无波浪环境下飞潜器水面降落过程进行数值仿真, 分析了各过程飞潜器动力学响应、载荷变化情况以及自由液面流场演化过程。结果表明: 在整个静水环境下水面起飞过程中飞潜器均能保持稳定的姿态, 其周围流场结构及自由液面演化均具有强对称性; 在水面降落过程中, 飞潜器及导管底部受到较大的反向砰击力, 导致飞潜器姿态出现一定程度的振荡, 在经过多次衰减波动后能够快速恢复平稳状态;而波浪的存在会加大触水时刻飞潜器所受到的砰击载荷, 加剧飞潜器姿态的振荡, 延后姿态最终恢复平稳时间。Abstract: In order to explore the evolution of the flow field structure and motion characteristics of the trans-medium submersible during the take-off and landing on water surface, the volume of fluid(VOF) multiphase flow model, the shear stress transfer(SST) k-ω turbulence model, the Schnerr-Sauer cavitation model, and the Stokes fifth-order nonlinear wave theory were coupled to construct a numerical calculation method for the submersible during take-off and landing on water surface based on the numerical simulation technology of computational fluid dynamic(CFD). The take-off of the submersible on water surface in the static water environment, as well as its landing on water surface in the presence or absence of the wave was numerically simulated. The dynamic response, load change of the submersible, and the evolution of the flow field on free liquid surface in each process were analyzed. The results show that the submersible can maintain a stable attitude during the whole take-off process on water surface in a static water environment, and the flow field structure and free liquid surface evolution around it have strong symmetry. In the process of landing on water surface, the bottom of the submersible and the fairing are subjected to a large reverse attack force, making the submersible fluctuate to a certain extent, but it can quickly restore the steady state after several attenuation fluctuations. The existence of the wave will increase the attack load applied to the submersible at the moment of touching the water, aggravate the attitude fluctuation of the submersible, and delay the final recovery time of the attitude.
-
Key words:
- trans-medium submersible /
- take-off and landing on water surface /
- dynamic /
- attack load
-
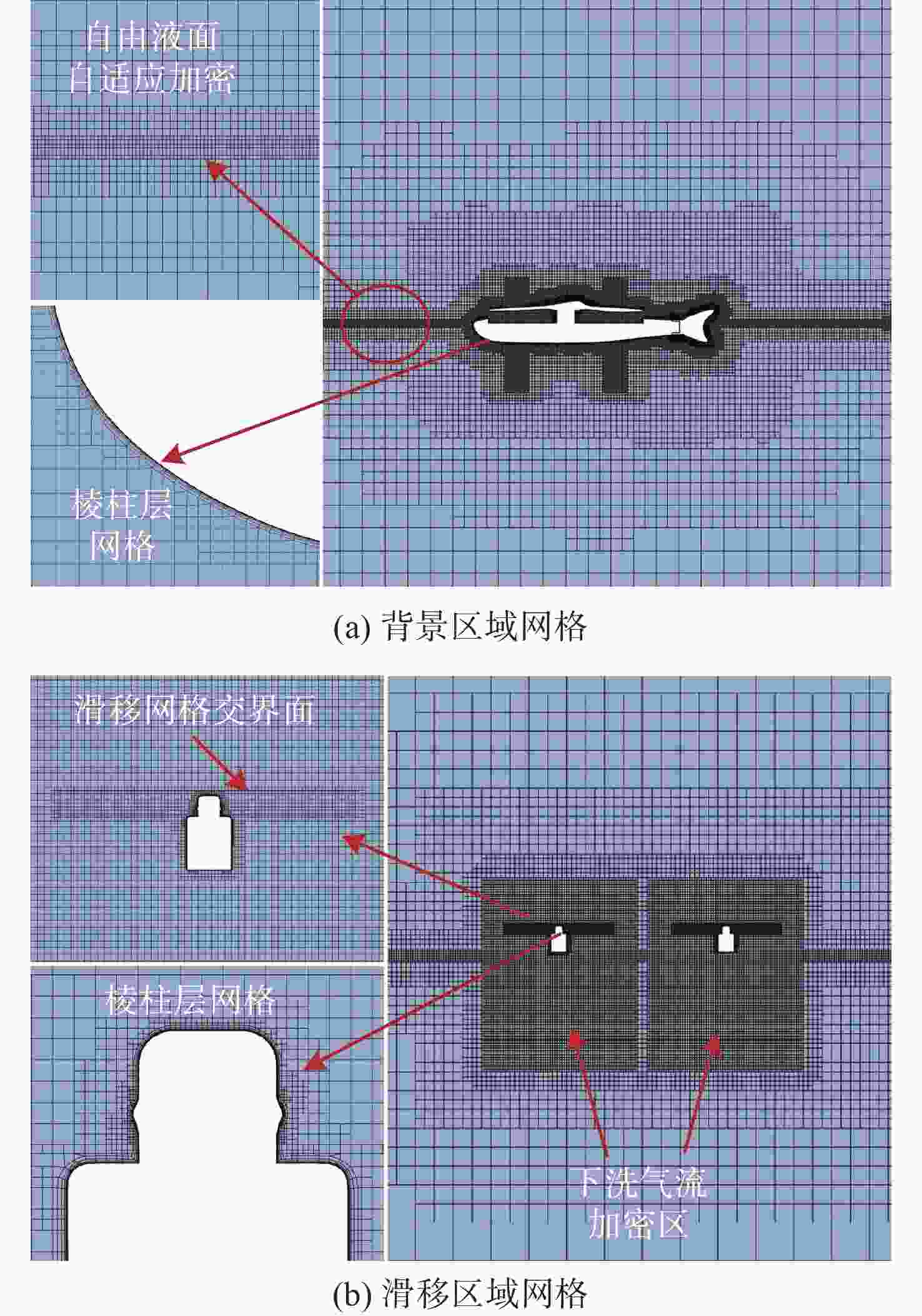
表 1 不同网格分辨率设置及网格划分结果
Table 1. Different grid resolution settings and results of grid division
网格分辨率 基础网格尺寸/mm 网格数量 粗糙 14.0 195万 中等 10.0 349万 良好 7.5 609万 表 2 不同网格分辨率入水位移计算误差
Table 2. Calculation error of water-entry displacement with different grid resolution
t/s 计算误差/% 粗糙分辨率 中等分辨率 良好分辨率 0.038 1 7.47 7.29 7.09 0.087 4 3.80 3.53 3.27 0.151 2 2.64 2.31 2.04 0.222 6 3.99 3.60 3.32 0.296 7 4.61 4.20 3.93 -
[1] Yang X, Wang T, Liang J, et al. Survey on the novel hybrid aquatic–aerial amphibious aircraft: Aquatic unmanned aerial vehicle(AquaUAV)[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2015, 74: 131-151. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2014.12.005 [2] Hong Y, Wang B, Liu H. Numerical study of hydrodynamic loads at early stage of vertical high-speed water entry of an axisymmetric blunt body[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2019, 31(10): 102105. doi: 10.1063/1.5121283 [3] Song Z J, Duan W Y, Xu G D, et al. Experimental and numerical study of the water entry of projectiles at high oblique entry speed[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 211: 107574. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107574 [4] Chen J, Xiao T, Wu B, et al. Numerical study of wave effect on water entry of a three-dimensional symmetric wedge[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 250: 110800. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.110800 [5] Liu Z, Shi Y, Wu K, et al. Experimental study on load characteristics of vehicle during high-speed water entry[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 288: 116052. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.116052 [6] Zhao C, Wang Q, Lu H, et al. Vertical water entry of a hydrophobic sphere into waves: Numerical computations and experiments[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2023, 35(7): 073324. [7] Li Z, Hu H, Wang C, et al. Hydrodynamics and stability of oblique water entry in waves[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 292: 116506. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.116506 [8] 王一伟, 黄晨光, 杜特专, 等. 航行体垂直出水载荷与空泡溃灭机理分析[J]. 力学学报, 2012, 44(1): 39-48. [9] Hu J, Xu B, Feng J, et al. Research on water-exit and take-off process for morphing unmanned submersible aerial vehicle[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 2017, 31: 202-209. doi: 10.1007/s13344-017-0024-3 [10] 李鹏程. 航行体出水过程主承力舱段结构动力稳定性与优化设计研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2018. [11] 谭骏怡, 胡俊华, 陈国明, 等. 水空跨介质航行器斜出水过程数值仿真[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2019, 14(6): 104-121.Tan Junyi, Hu Junhua, Chen Guoming, et al. Numerical simulation of oblique water-exit process of trans-media aerial underwater vehicle[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2019, 14(6): 104-121. [12] Huang J, Liang J, Wang T, et al. Numerical analysis of the body, webbed-feet, and wings during cormorant’s take off[C]//2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics(ROBIO). Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: IEEE, 2018: 94-99. [13] 云忠, 温猛, 罗自荣, 等. 仿翠鸟水空跨介质航行器设计与入水分析[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2020, 54(2): 407-415.Yun Zhong, Wen Meng, Luo Zirong, et al. Design and plunge-diving analysis of underwater-aerial transmedia vehicle of bionic kingfisher[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering Science), 2020, 54(2): 407-415. [14] Hou T G, Yang X B, Wang T M, et al. Locomotor transition: How squid jet from water to air[J]. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2020, 15(3): 036014. [15] 赵英杰. 小型无人跨介质航行器结构设计及动力学特性分析与仿真[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2021. [16] 史崇镔. 跨介质结构物出入水多相流体动力学特性研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2021. [17] 张硕, 张树新, 代季鹏. 小型跨介质无人机快速水空过渡设计与试验[J]. 飞行力学, 2021, 39(5): 77-81, 94.Zhang Shuo, Zhang Shuxin, Dai Jipeng. Design and experiments of water-to-air rapid transitions for a small cross-medium UAV[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2021, 39(5): 77-81, 94. [18] Lu D, Xiong C, Zhou H, et al. Design, fabrication, and characterization of a multimodal hybrid aerial underwater vehicle[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 219: 108324. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.108324 [19] Lyu C, Lu D, Xiong C, et al. Toward a gliding hybrid aerial underwater vehicle: Design, fabrication, and experiments[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2022, 39(5): 543-556. doi: 10.1002/rob.22063 [20] Wei Z, Teng Y, Meng X, et al. Lifting-principle-based design and implementation of fixed-wing unmanned aerial-underwater vehicle[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2022, 39(6): 694-711. doi: 10.1002/rob.22071 [21] Steelant J, Dick E. Modeling of laminar-turbulent transition for high freestream turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2001, 123(1): 22-30. doi: 10.1115/1.1340623 [22] Plesset M. The dynamics of cavitation bubbles[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1949, 16: 277-282. doi: 10.1115/1.4009975 [23] Fenton J D. A fifth-order stokes theory for steady waves[J]. Journal of Waterway Port Coastal and Ocean Engineering, 1985, 111(2): 216-234. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(1985)111:2(216) [24] Kim J W, O’Sullivan J, Read A. Ringing analysis of a vertical cylinder by Euler overlay method[C]//ASME 2012 31st International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering. [S.l.]: American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2012: 855-866. [25] Brandt J B. Small-scale propeller performance at low speeds[D]. Champaign County, Illinois: University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2005. [26] Gong K, Shao S, Liu H, et al. Two-phase SPH simulation of fluid-structure interactions[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2016, 65: 155-179. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2016.05.012 [27] 陈程, 施文奎, 沈雁鸣, 等. 楔形体底升角对入水多相界面演化作用研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展A辑, 2023, 38(5): 663-668.Chen Cheng, Shi Wenkui, Shen Yanming, et al. Study on effect of dead-rise angle on evolution of multiphase interface in wedge water entry problems[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2023, 38(5): 663-668. [28] Chen B, Ning D, Liu C, et al. Wave energy extraction by horizontal floating cylinders perpendicular to wave propagation[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2016, 121: 112-122. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2016.05.016 -





 下载:
下载: