Numerical Calculation of Water Exit Process of Supercavitating Vehicles under Different Sailing Conditions
-
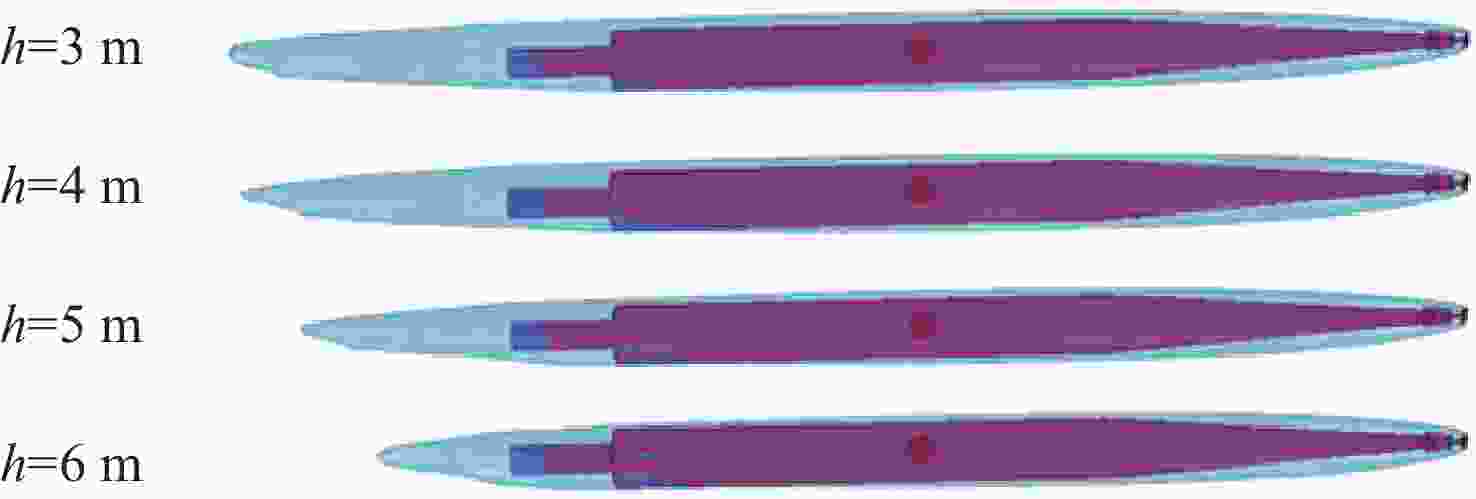
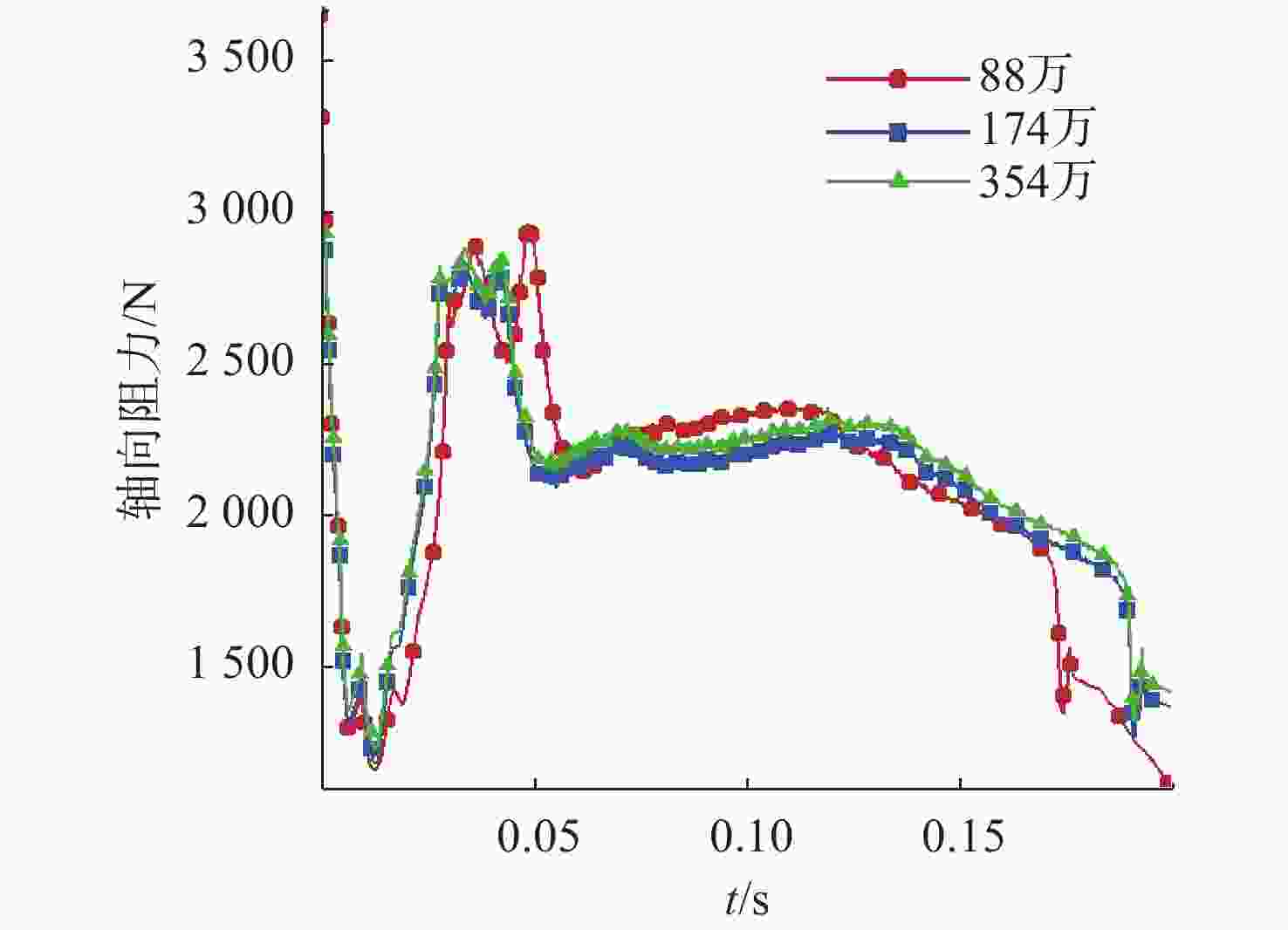
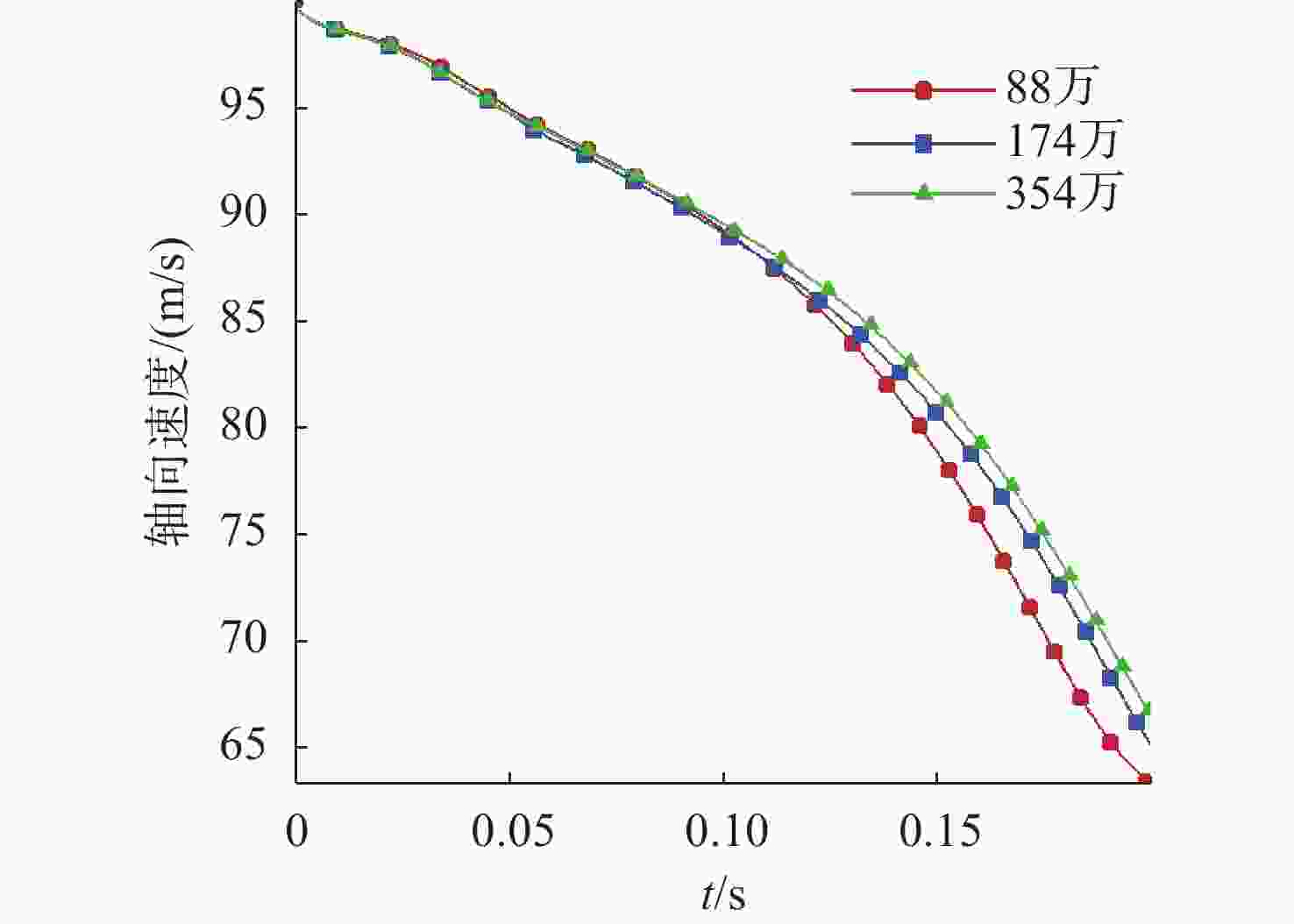
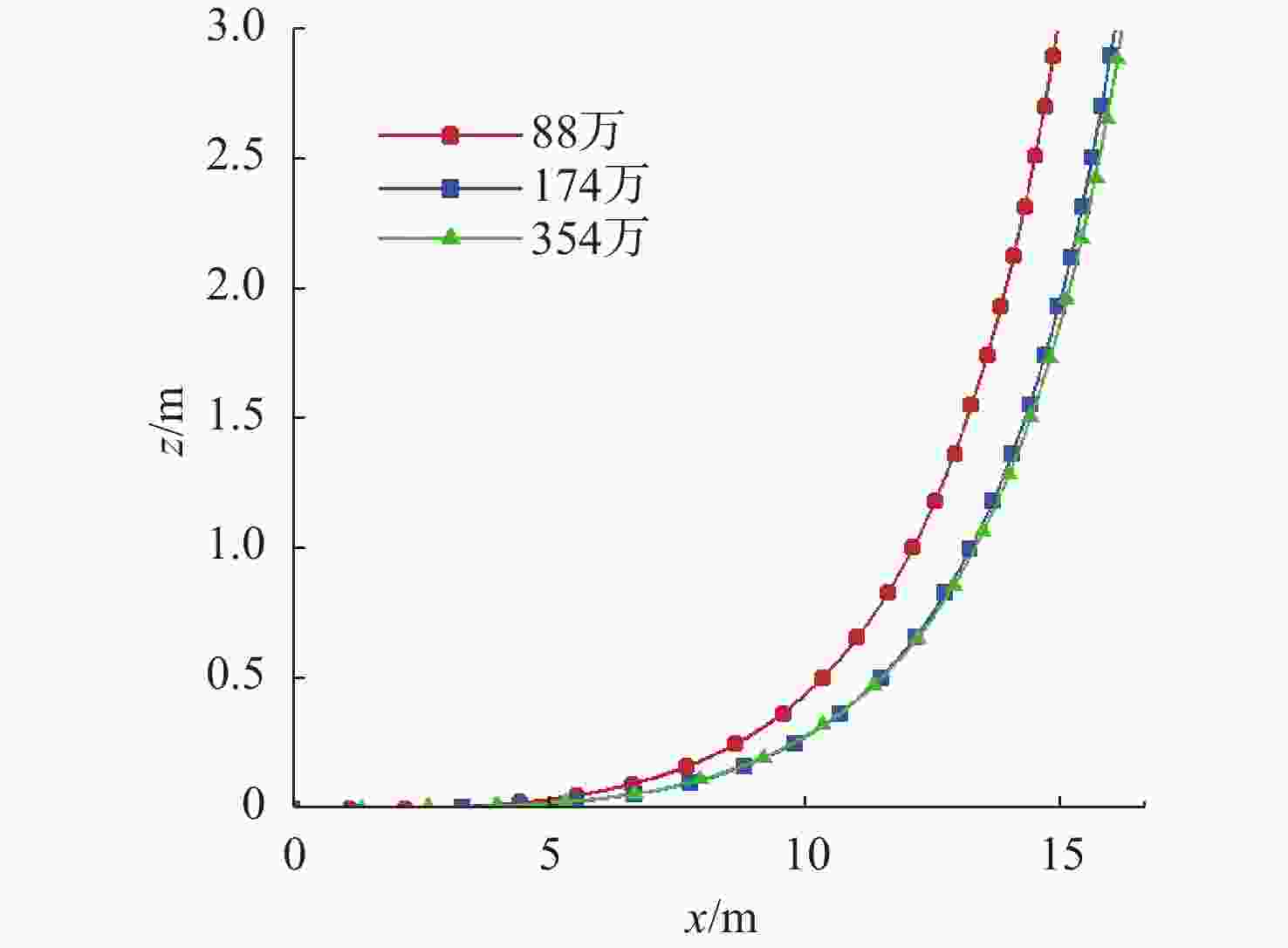
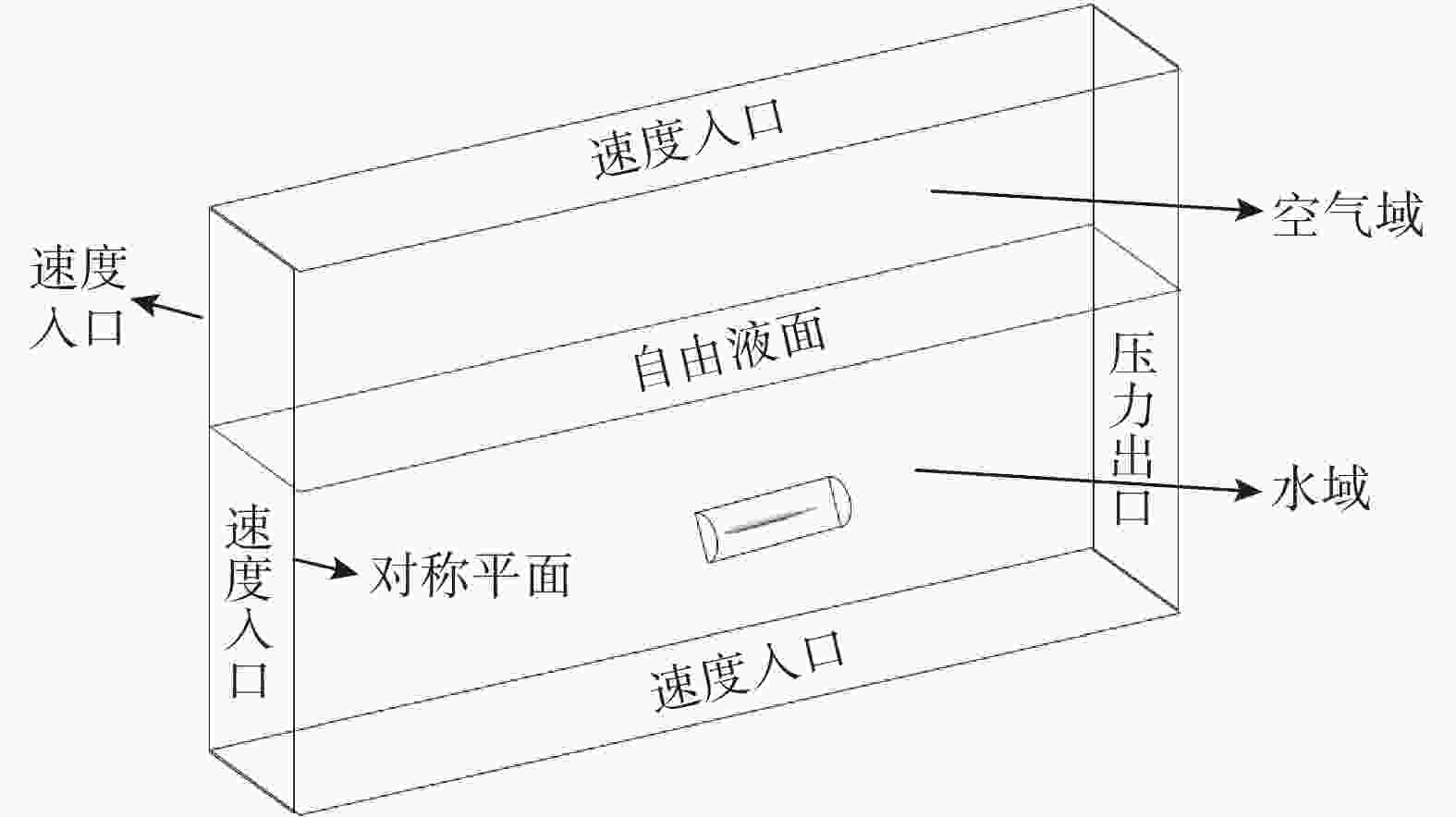
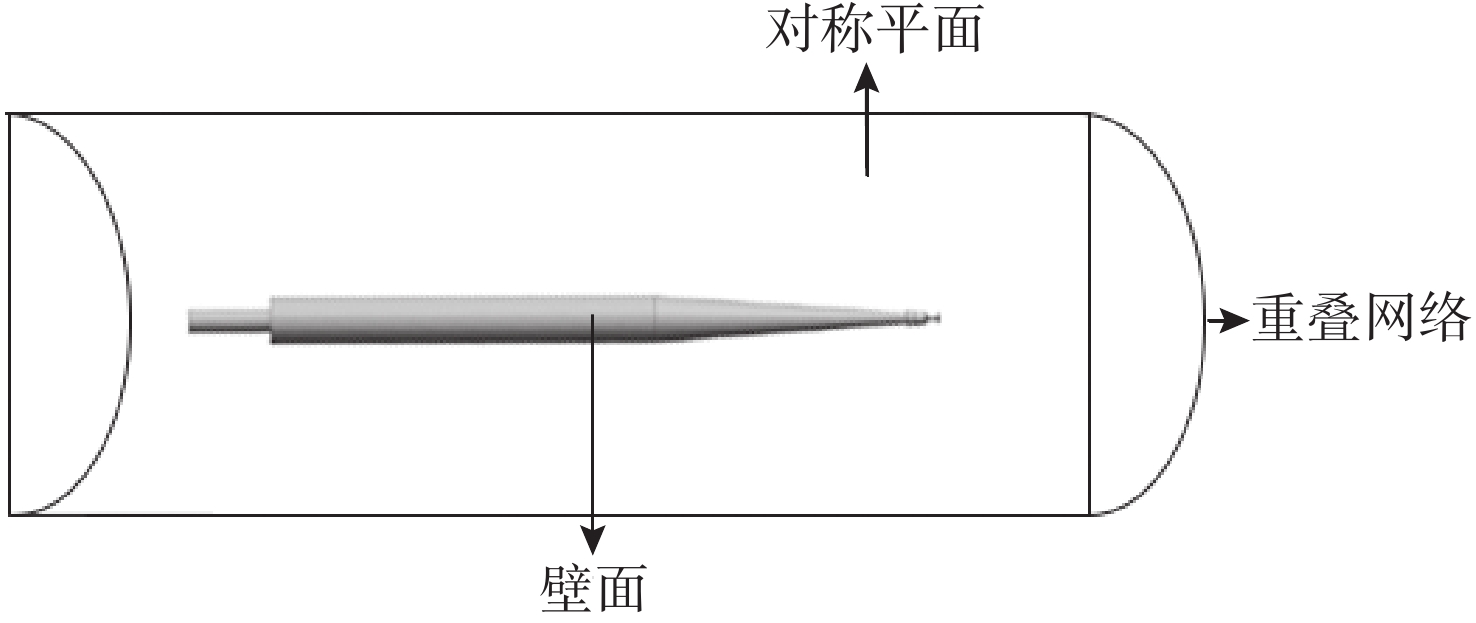
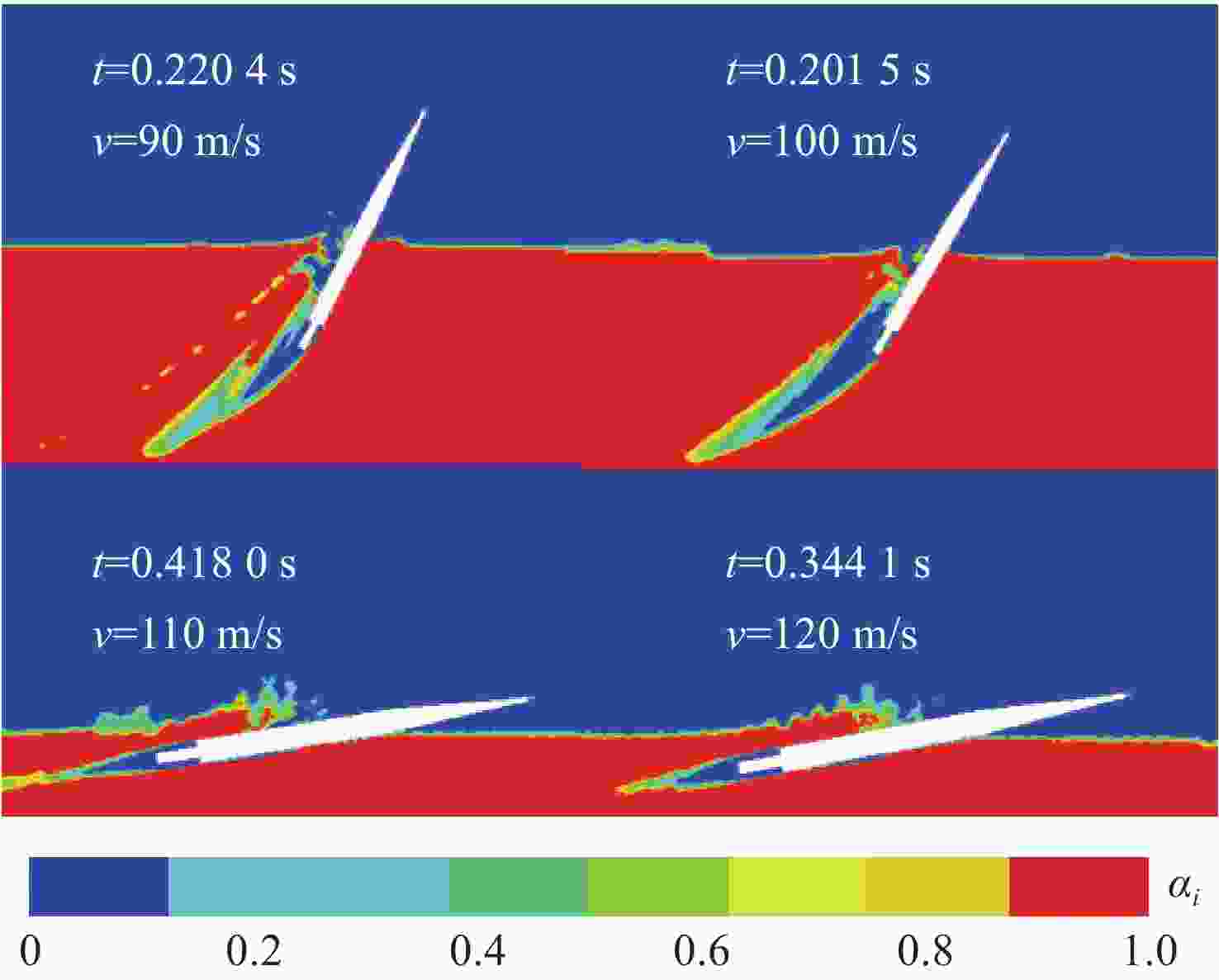
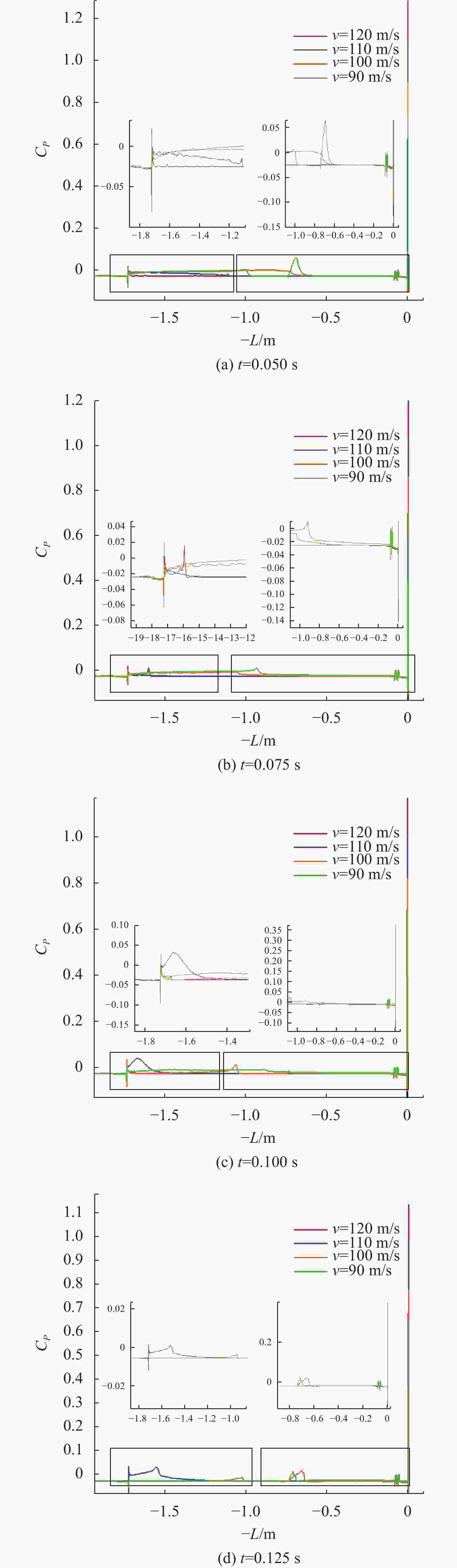
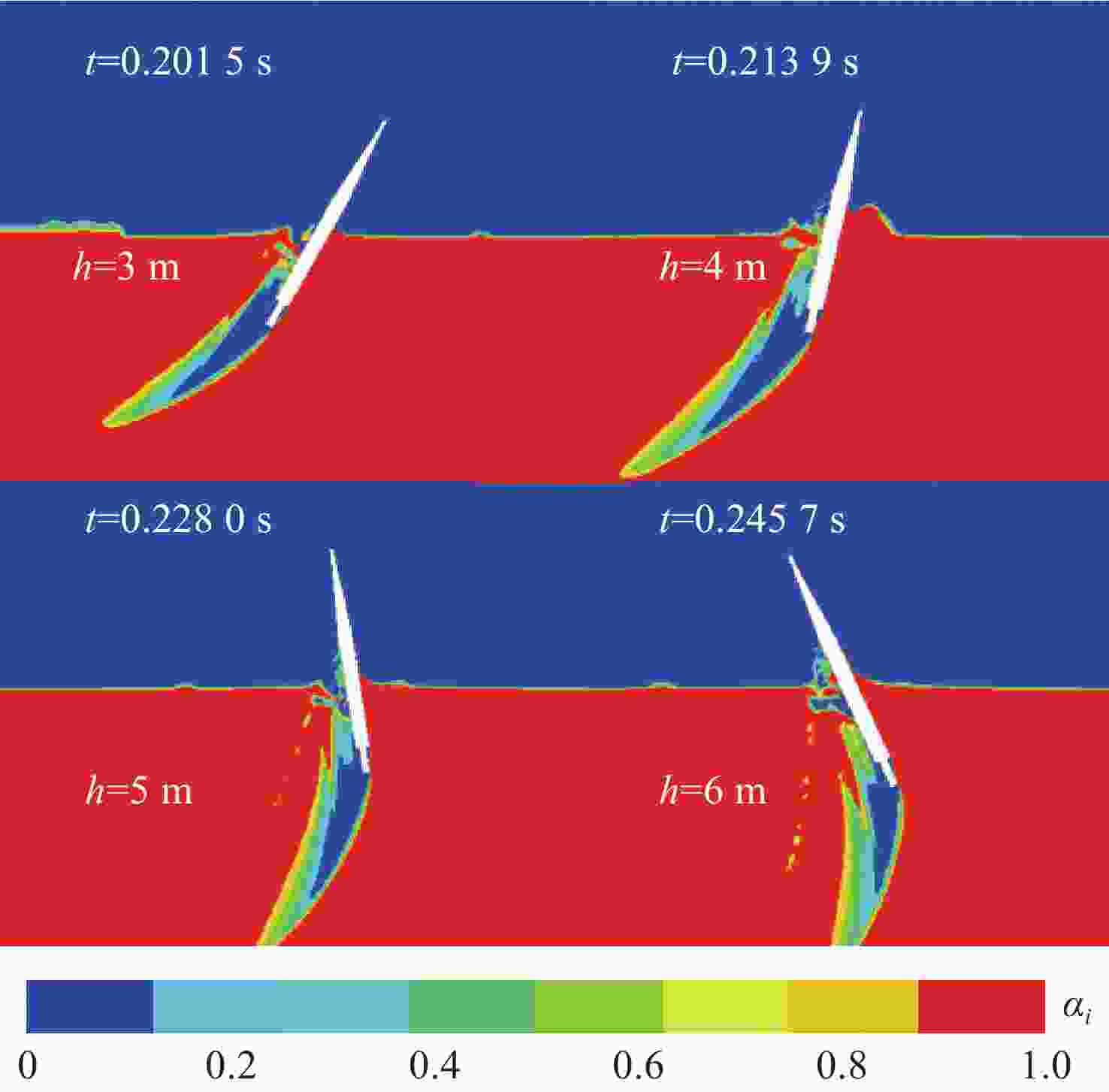
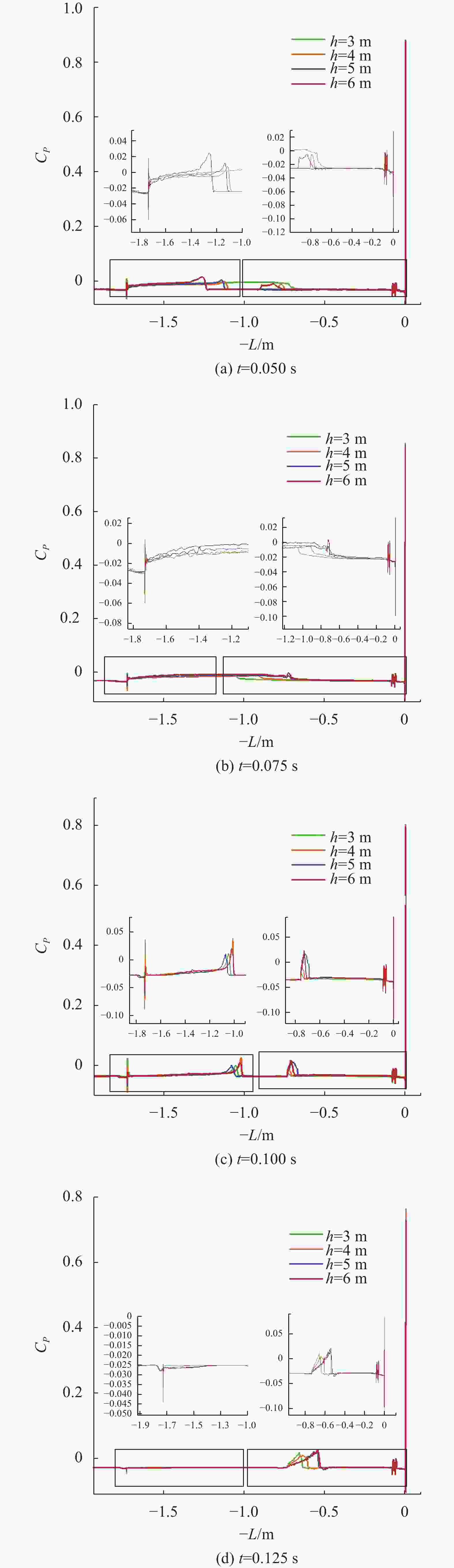
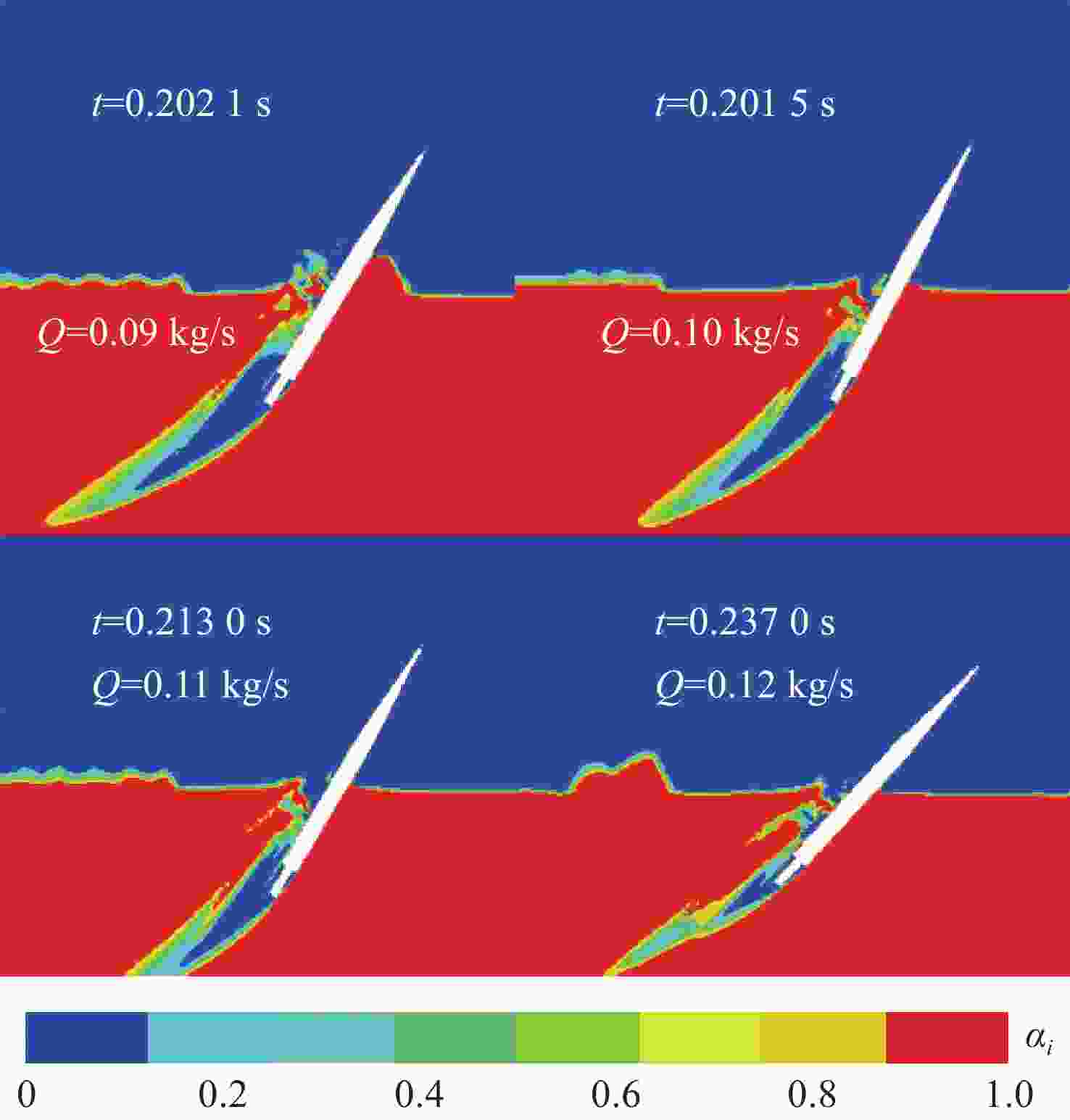
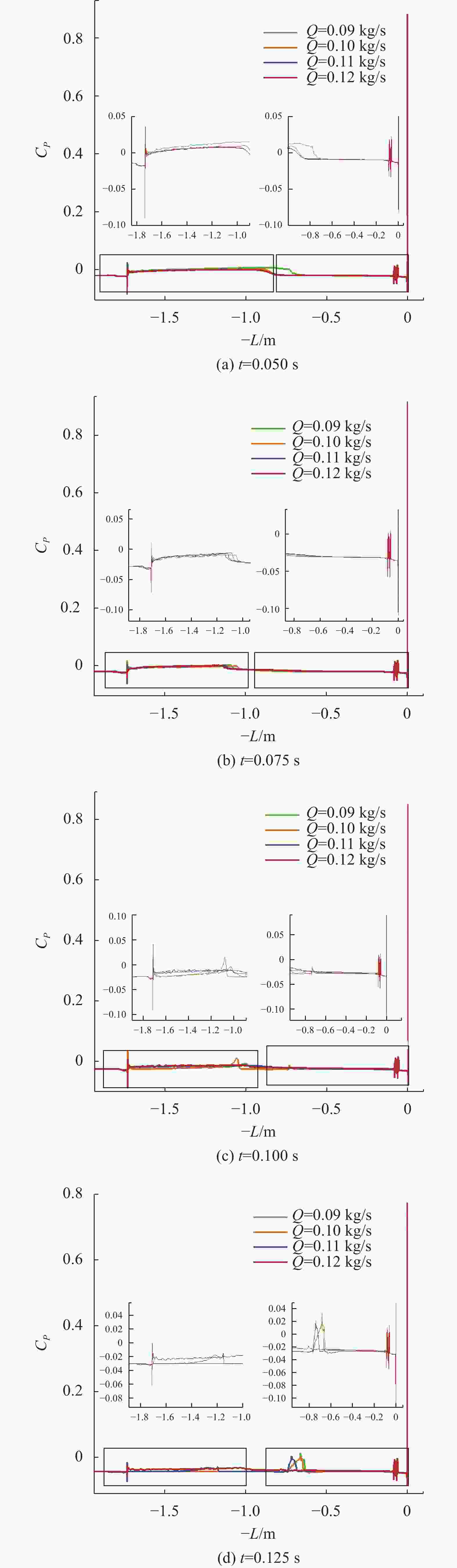
摘要: 航行器出水过程极其复杂, 伴随着多相流、空化、相变及湍流不稳定性, 其所受作用力呈现强的非定常、非线性。国内外对航行器带空泡出水问题的研究, 多为航行器垂直或者倾斜出水, 关注点往往为航行器运动轨迹及姿态, 对超空泡航行器出水过程研究较少。文中基于STAR-CCM+软件, 采用重叠网格技术进行网格划分, 使用流体体积(VOF)多相流模型捕捉气液交界面, Schnerr-Sauer模型描述航行器周围的空化过程, 建立了航行器出水过程的数值计算模型。对航行器在不同航行条件(初始速度、初始水深、通气量)下的出水过程进行仿真计算, 得到了不同工况下的流场和空泡演化规律, 分析了超空泡航行器的流体动力特性与运动特性。仿真结果表明, 不同初始运动速度的航行器, 其水下运动呈现出2种不同的模式。不同水深下, 初始空化数不同, 在较深的水域航行器周围空泡更容易破裂, 加大通气量可有效改善空泡形态。Abstract: The water exit process of vehicles is very complicated, accompanied by multiphase flow, cavitation, phase transition, and turbulence instability, and the applied force is highly unsteady and nonlinear. At present, studies on the water exit problem of the vehicle with cavitation focus on the vertical or oblique water exit, emphasizing the trajectory and attitude of the vehicle. There are few studies on the water exit process of the supercavitating vehicle. In this paper, based on STAR-CCM+ software, overlapping grid technology was used for meshing, and the volume of fluid(VOF) model was used to capture the gas-liquid interface. The Schnerr-Sauer model described the cavitation process around the vehicle, and a numerical calculation model of the water exit process of the vehicle was established. The water exit process of the vehicle under different sailing conditions(initial velocity, initial water depth, and ventilation) was simulated and calculated, and the flow field and cavity evolution laws under different conditions were obtained. The hydrodynamic and kinematic characteristics of the supercavitating vehicle were analyzed. The simulation results show that the underwater motion of the vehicle with different initial velocities presents two different modes. Under different water depths, the initial cavity number is different. Cavity around the vehicle is more likely to rupture in deeper waters. The cavity morphology can be improved effectively by increasing the ventilation.
-
Key words:
- supercavitating vehicle /
- water exit /
- overlapping grid
-
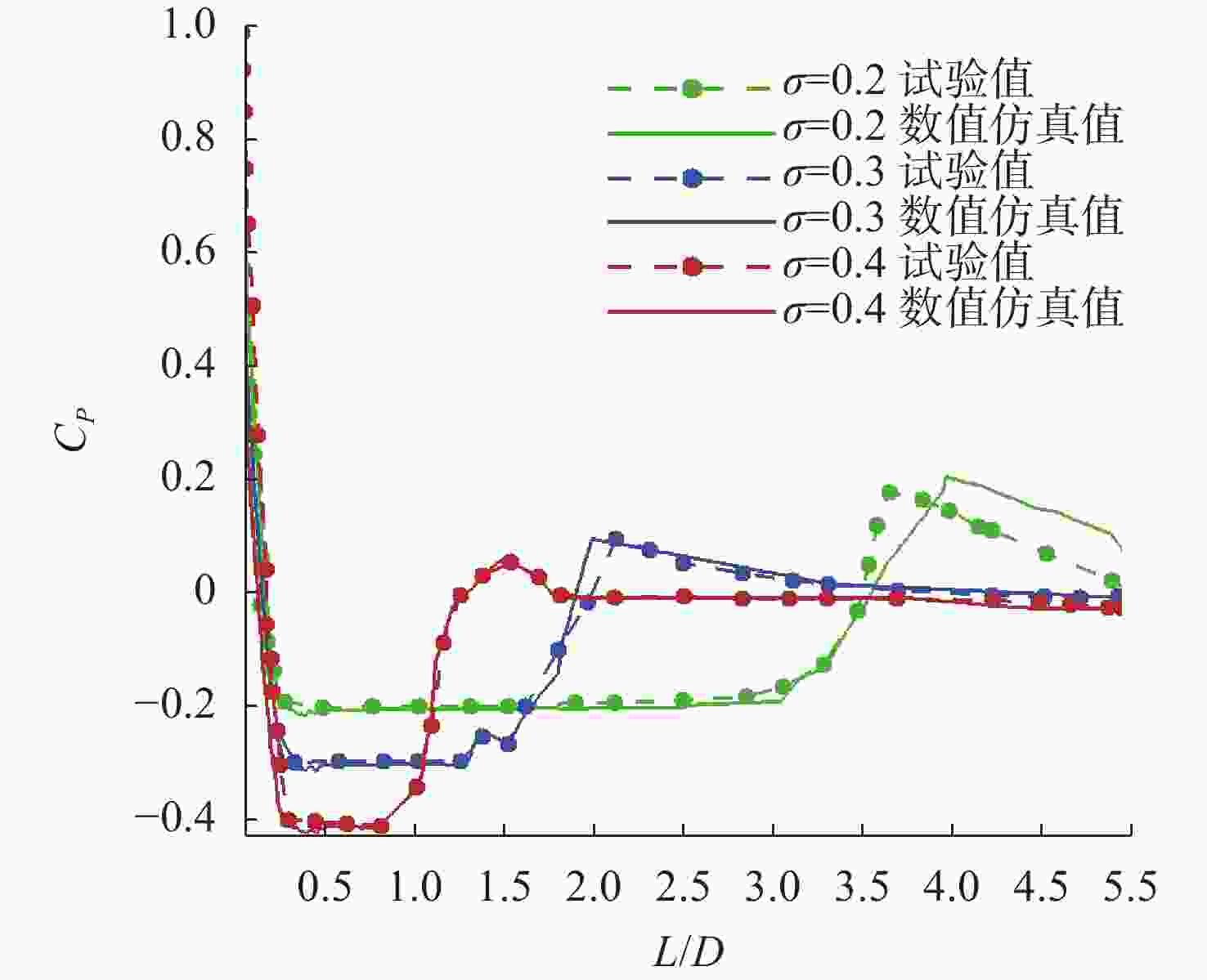
表 1 经验公式与仿真结果对比
Table 1. Comparison between empirical formula results and simulation results
参数 经验公式 仿真结果 误差/% 最大空泡半径/m 0.086 735 0.083 226 4.01 最大空泡长度/m 2.170 000 2.277 730 4.73 -
[1] Franc J P, Michel J M. Unsteady attached cavitation on an oscillatin hydrofoil[J]. Fluid Mech, 1988, 193(1): 171-189. [2] Von Karman T. The impact on seaplane floats during landing[R]. Washington, DC: National Advisory Committee on Aeronautics, 1929: 1-8. [3] Robertson J M. Hydroballistic calculations of the rise and water exit of buoyant bodies[M]. Columbus: Defense Technical Information Center, 1959. [4] Moran J P. The vertical water-exit and entry of slender symmetric bodies[J]. Journal of the Aerospace Sciences, 1961, 28(10): 803-812. doi: 10.2514/8.9194 [5] Greenhow M, Lin W M. Non-linear free surface effects: experiments and theory[R]. MIT: Department of Ocean Engineering, 1983: 83-119. [6] Greenhow M. Water-entry and exit of a horizontal circular cylinder[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 1988, 10(4): 191-198. doi: 10.1016/S0141-1187(88)80003-8 [7] Greenhow M, Moyo S. Water entry and exit of horizontal circular cylinders[J]. Philosophical Transactions-Royal Society. Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1997, 355(1724): 551-563. doi: 10.1098/rsta.1997.0024 [8] Nguyen V T, Ha C T, Park W G. Multiphase flow simulation of water-entry and exit of axisymmetric bodies [C]//Proceedings of the ASME 2013. San Diego, California, USA: ASME, 2013. [9] 李杰, 鲁传敬, 傅惠萍. 细长回转体出水过程的数值模拟[C]//第二十届全国水动力学研讨会文集. 上海: 海洋出版社, 2007: 294-299. [10] 鲁传敬,李杰. 水下航行体出水空泡溃灭过程及其特性研究[C]//第十一届全国水动力学学术会议暨第二十四届全国水动力学研讨会并周培源诞辰110周年纪念大会文集(上册).上海: 海洋出版社, 2012: 54-67. [11] 刘杰 . 航行体出水过程通气空化流场特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014. [12] 袭祥发. 超空泡导弹潜射出水过程流固耦合数值研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2022. [13] 田建辉, 胡晨明. 高速弹体出水过程数值模拟[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2023, 44(12): 73-78, 176. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2023.12.010 [14] Hirt C W, Nichols B D. Volume of fluid(VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1981, 39(1): 201-225. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(81)90145-5 [15] Shih T H, Liou W W, Shabbir A, et al. A new kepsilon eddy viscosity model for high: Reynolds number turbulent flows[J]. Computers Fluids, 1995, 24(3): 227-238. doi: 10.1016/0045-7930(94)00032-T [16] Sauer J, Schnerr G H. Development of a new cavitation model based on bubble dynamics[J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2001, 81(S3): 561-562. doi: 10.1002/zamm.20010811559 [17] 尤天庆, 张嘉钟, 王聪, 等. 航行体出水过程头部流场载荷特性分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2011, 37(5): 610-614. [18] Savchenko Y N, Vlasenko Y D, Semenenko V N. Experimental studies of high-speed cavitated flows[J]. International Journal of Fluid Mechanics Research, 1999, 26(3): 365-374. doi: 10.1615/InterJFluidMechRes.v26.i3.80 -





 下载:
下载: