Target Tracking Algorithm for Underwater Acoustic Sensor Networks under DoS Attack
-
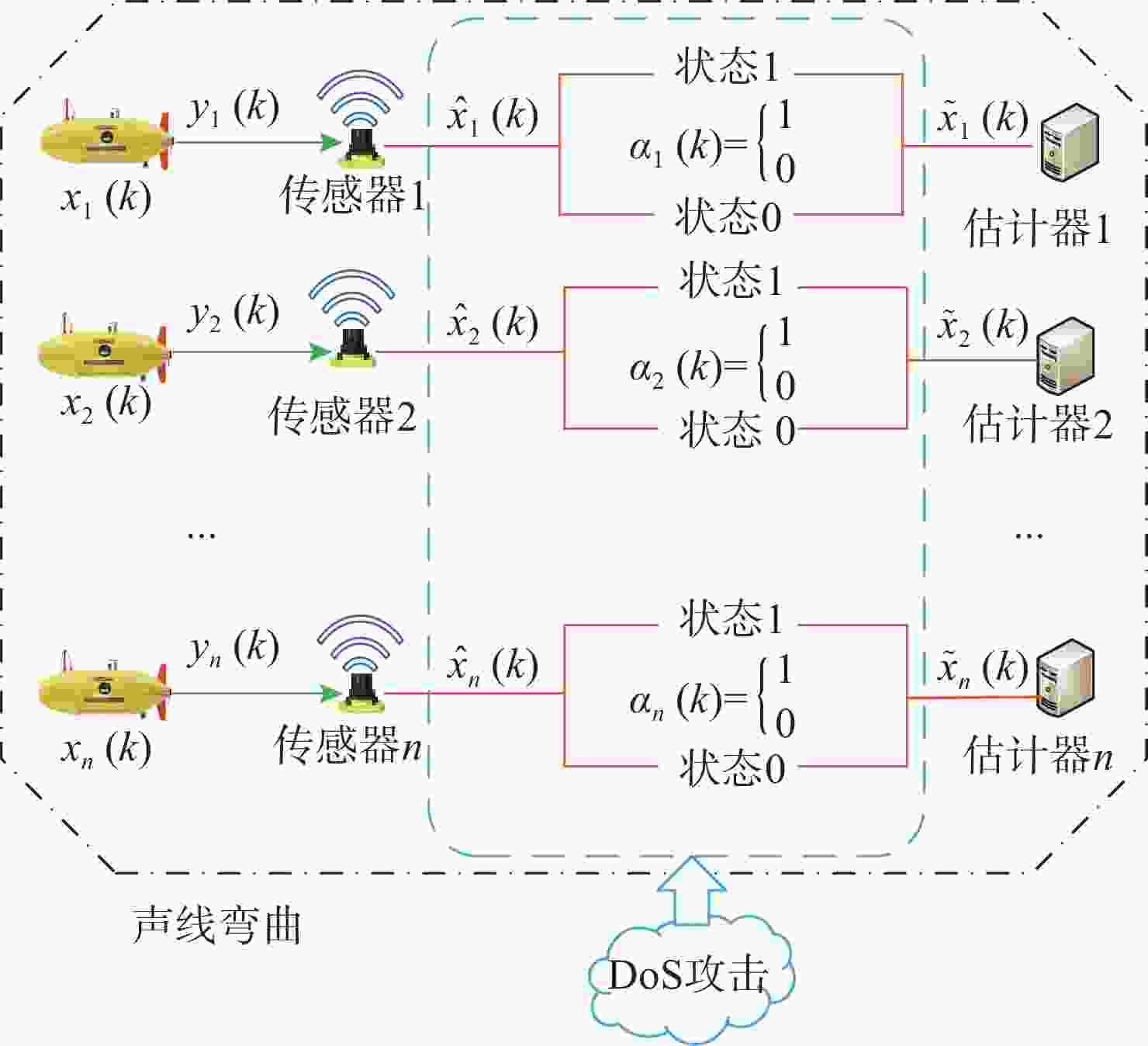
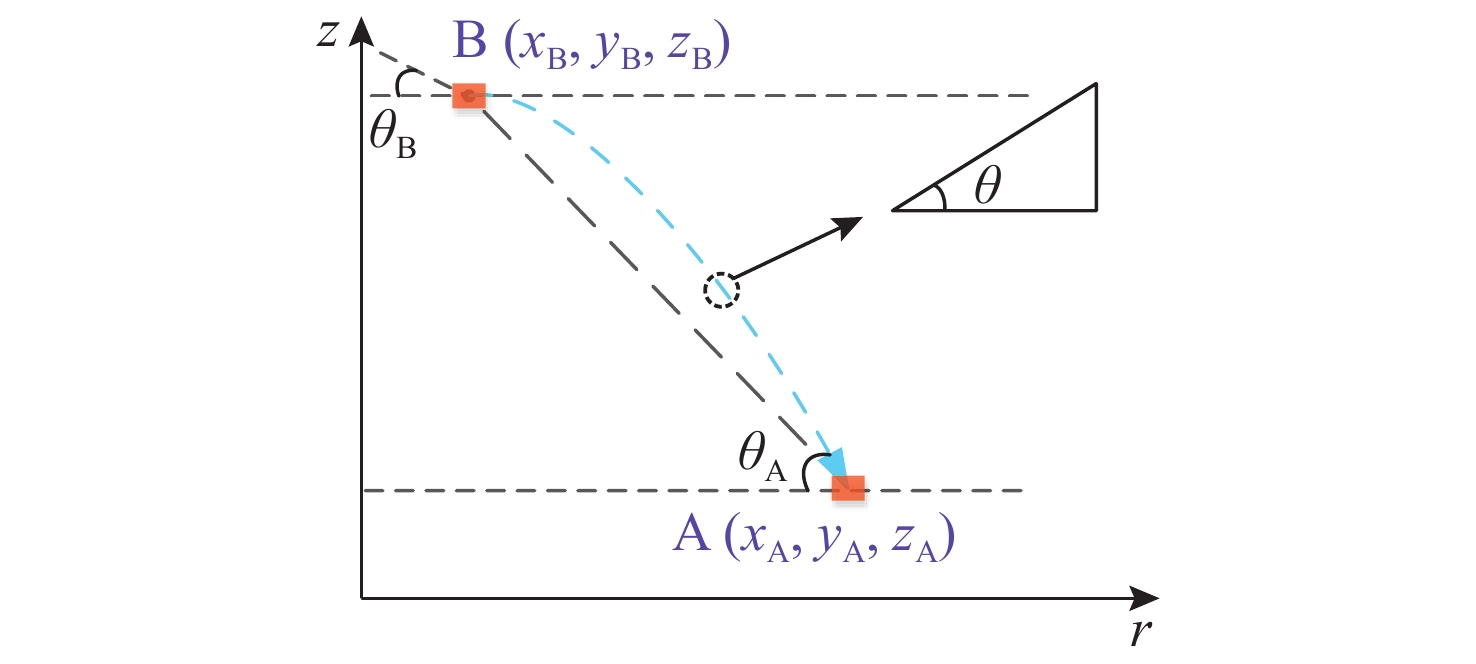
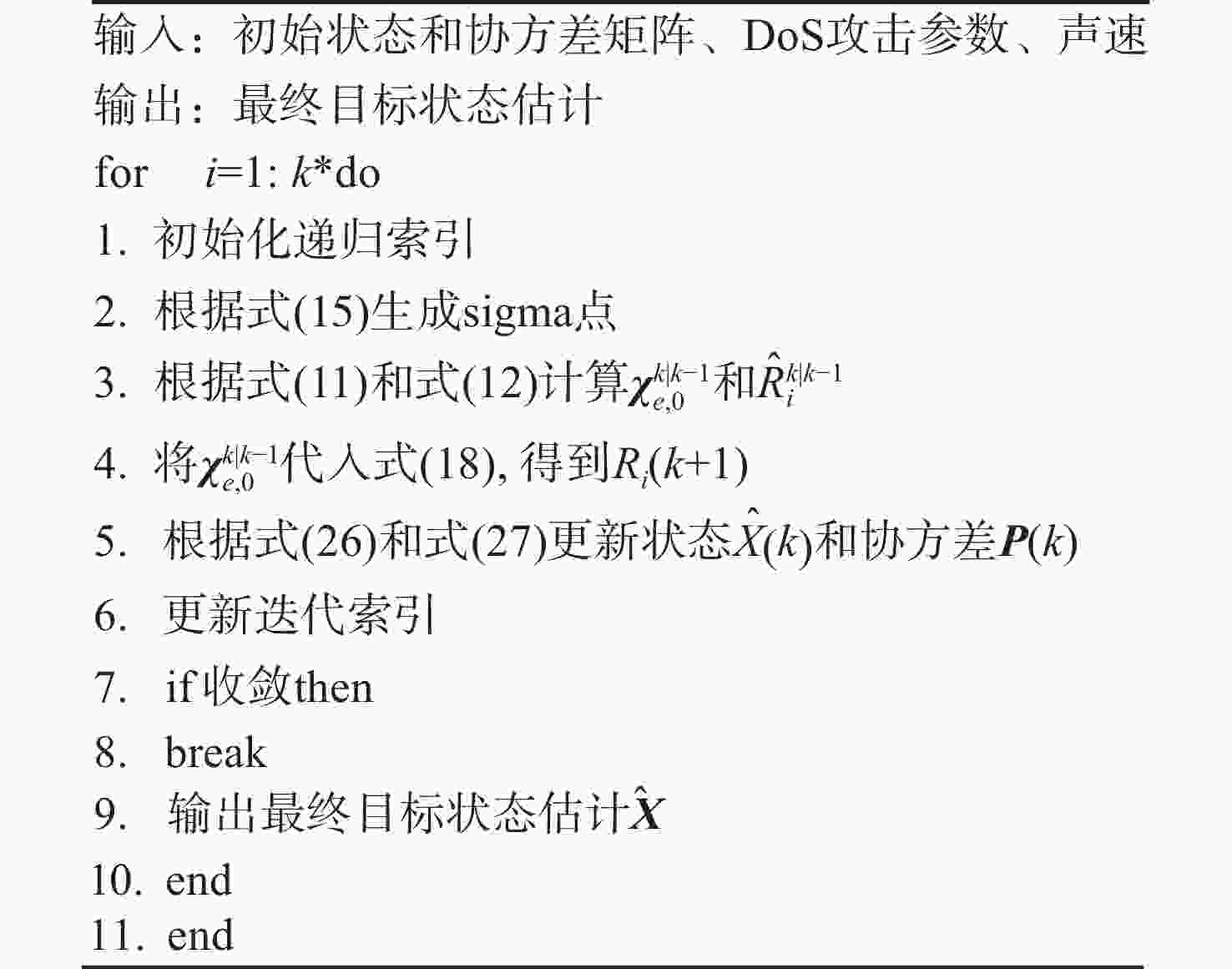
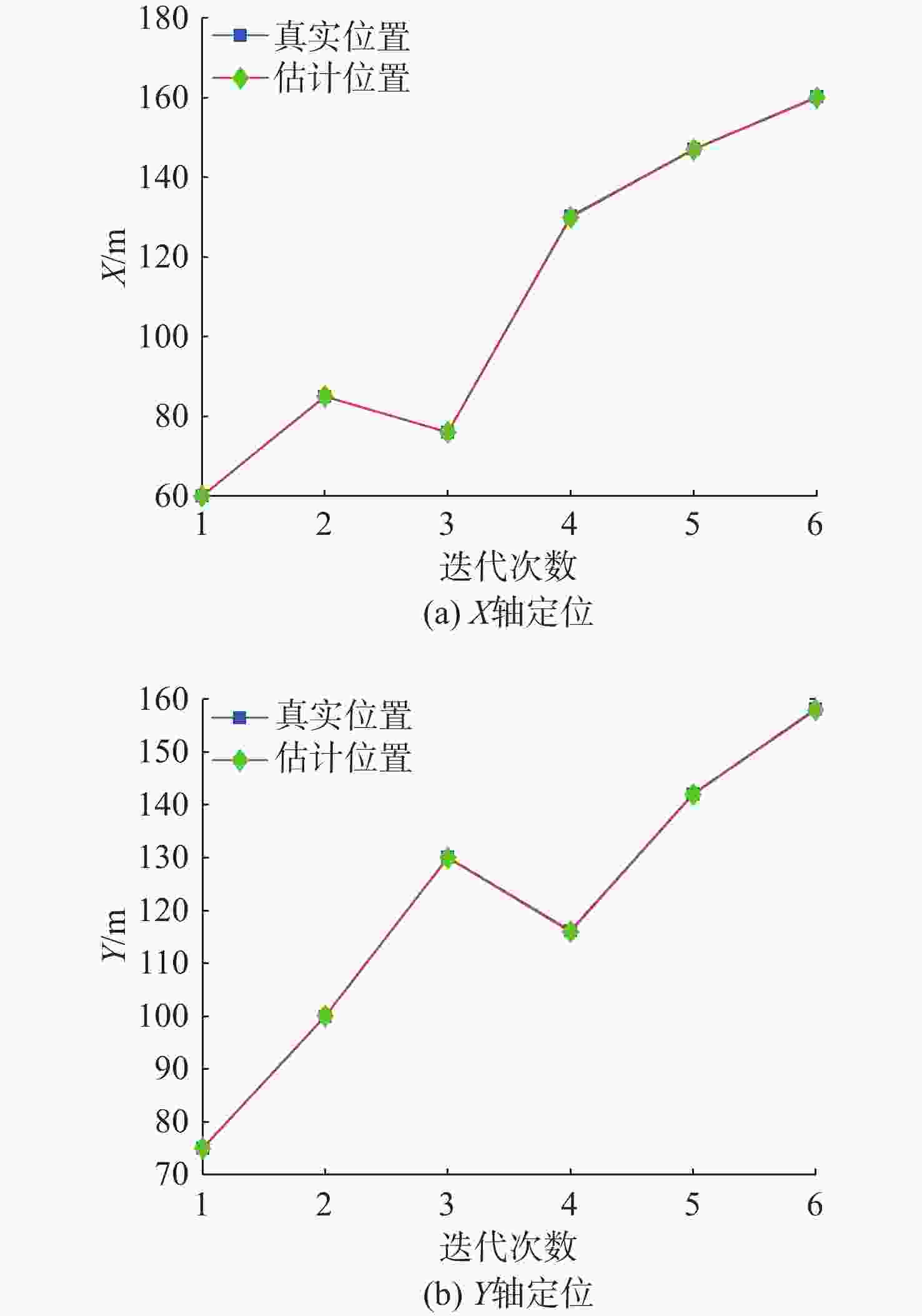
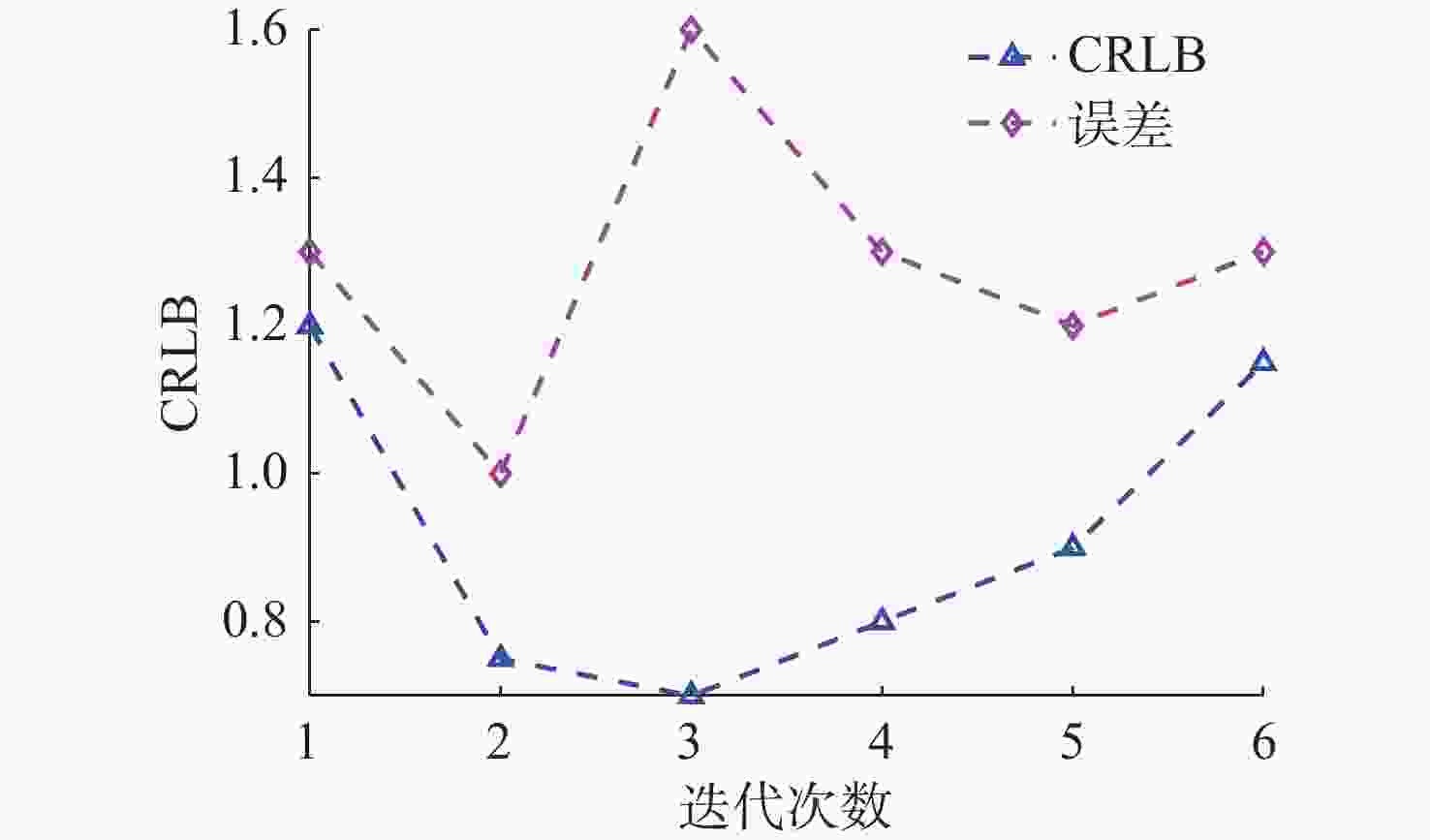
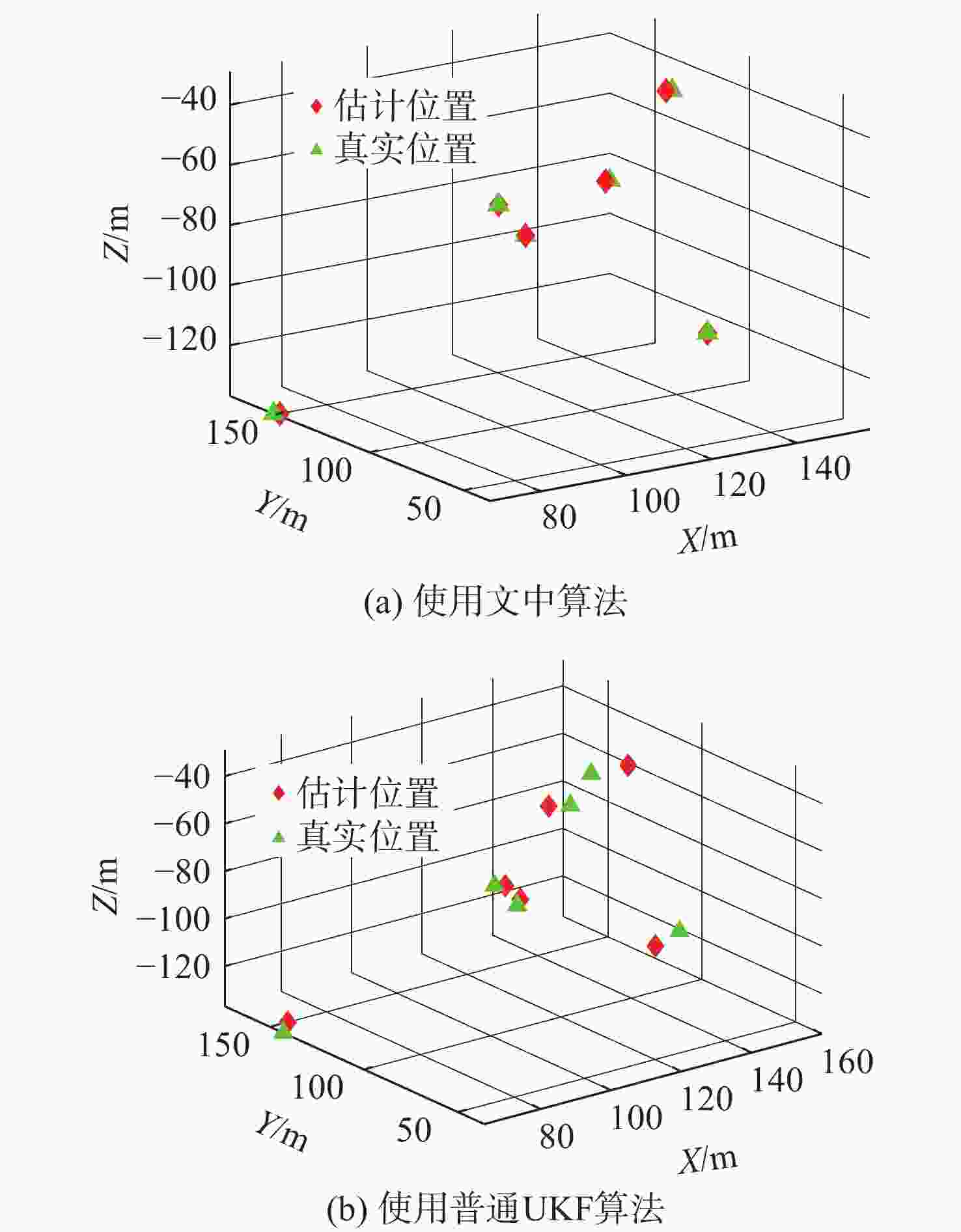
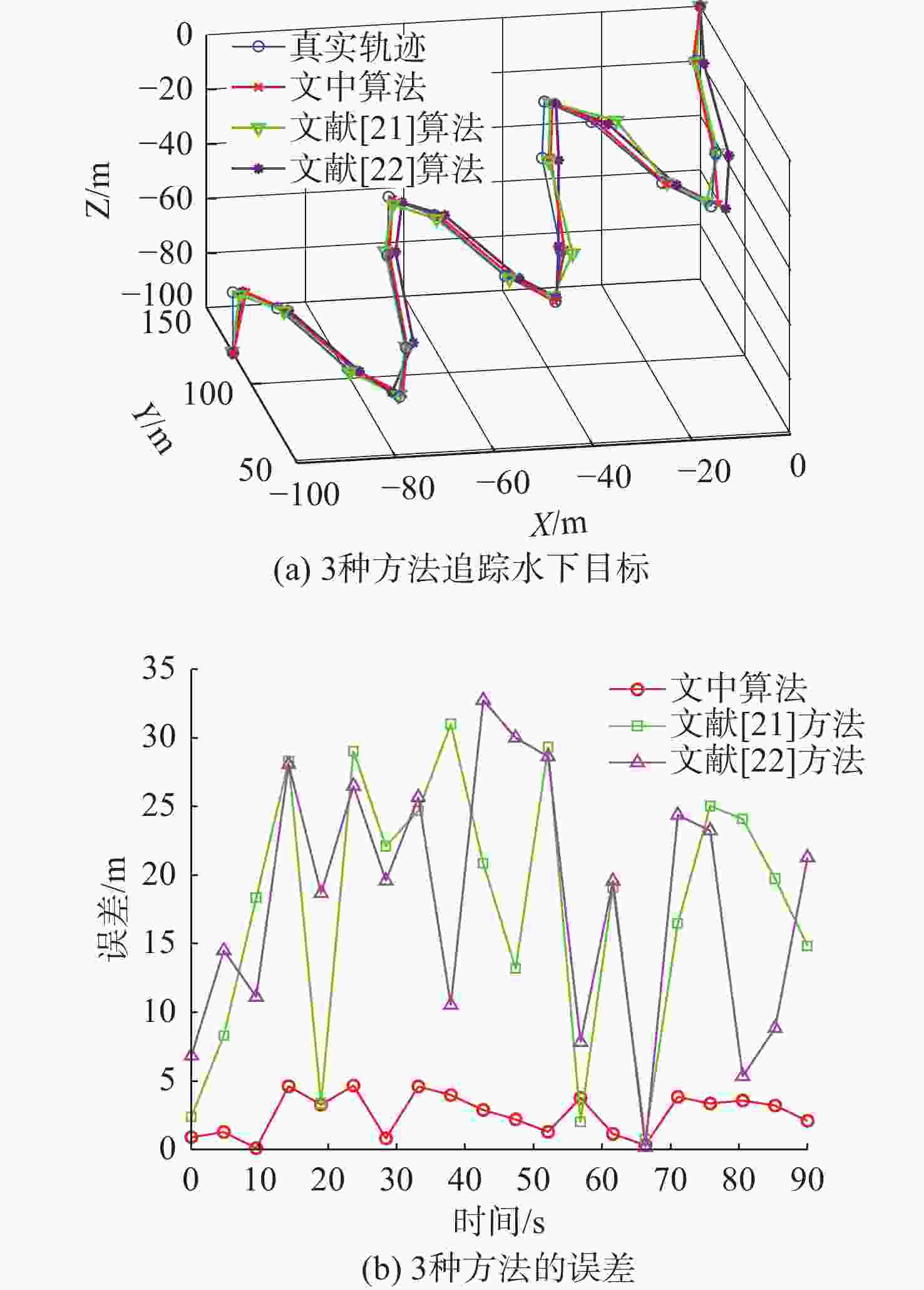
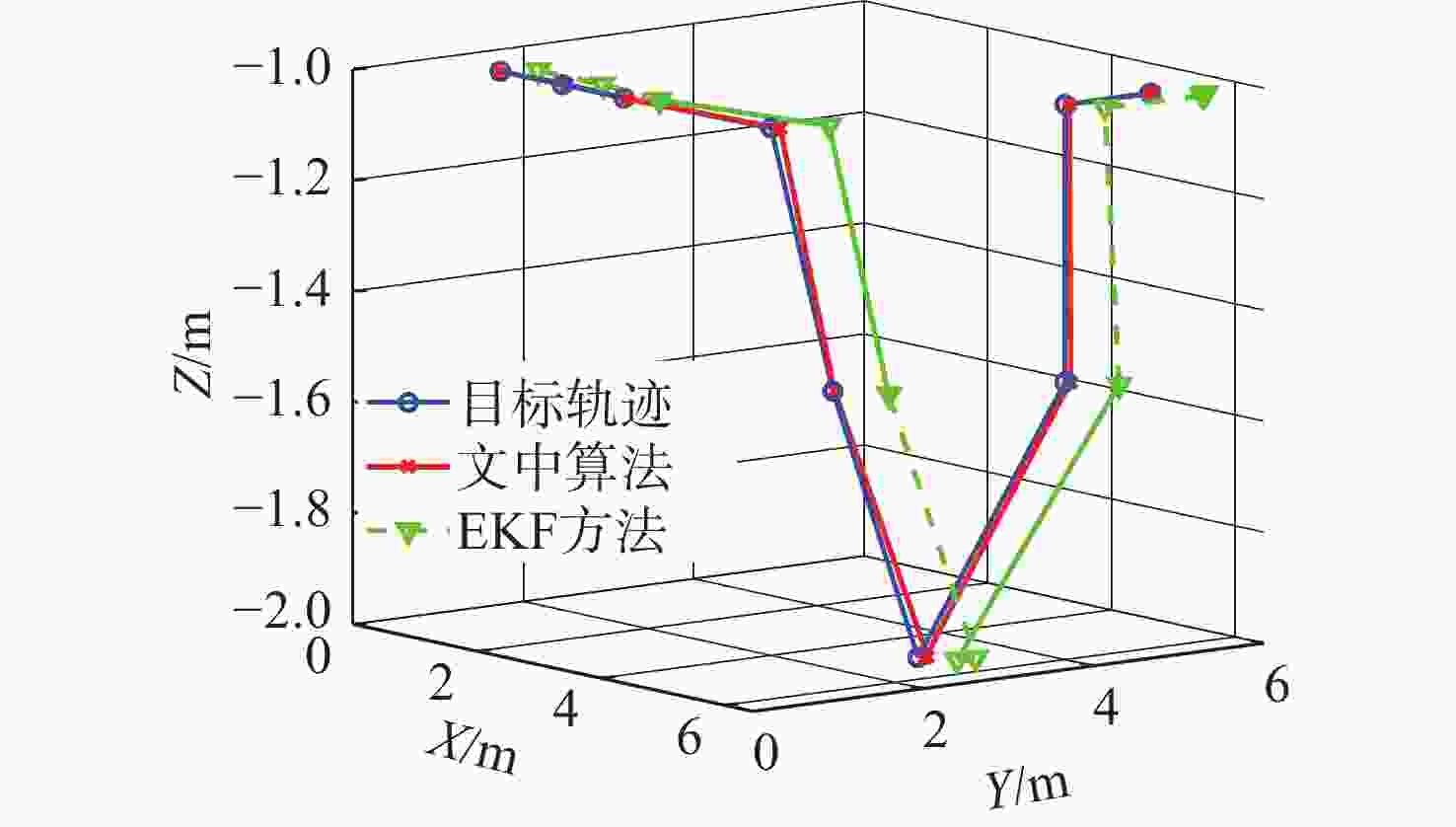
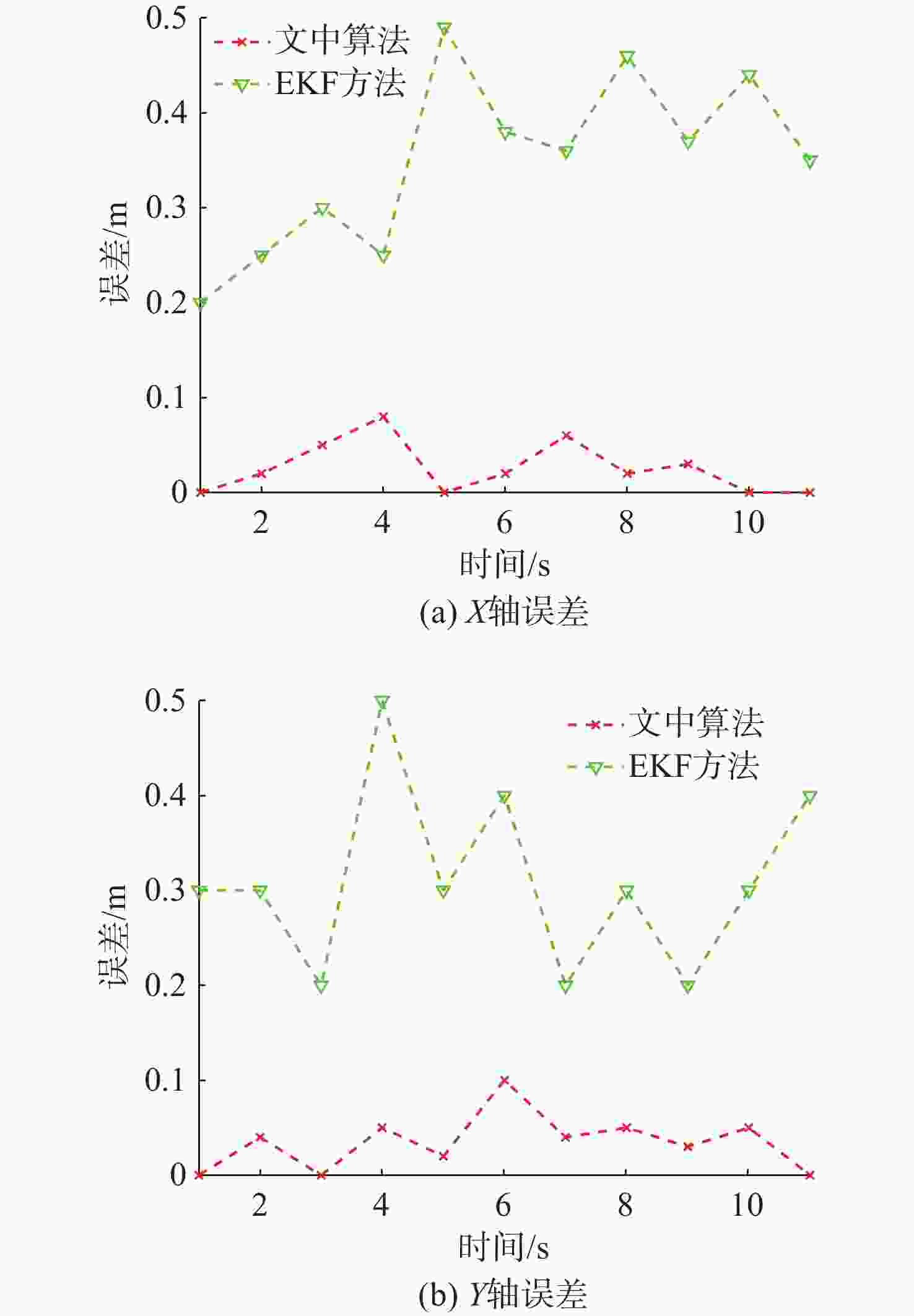
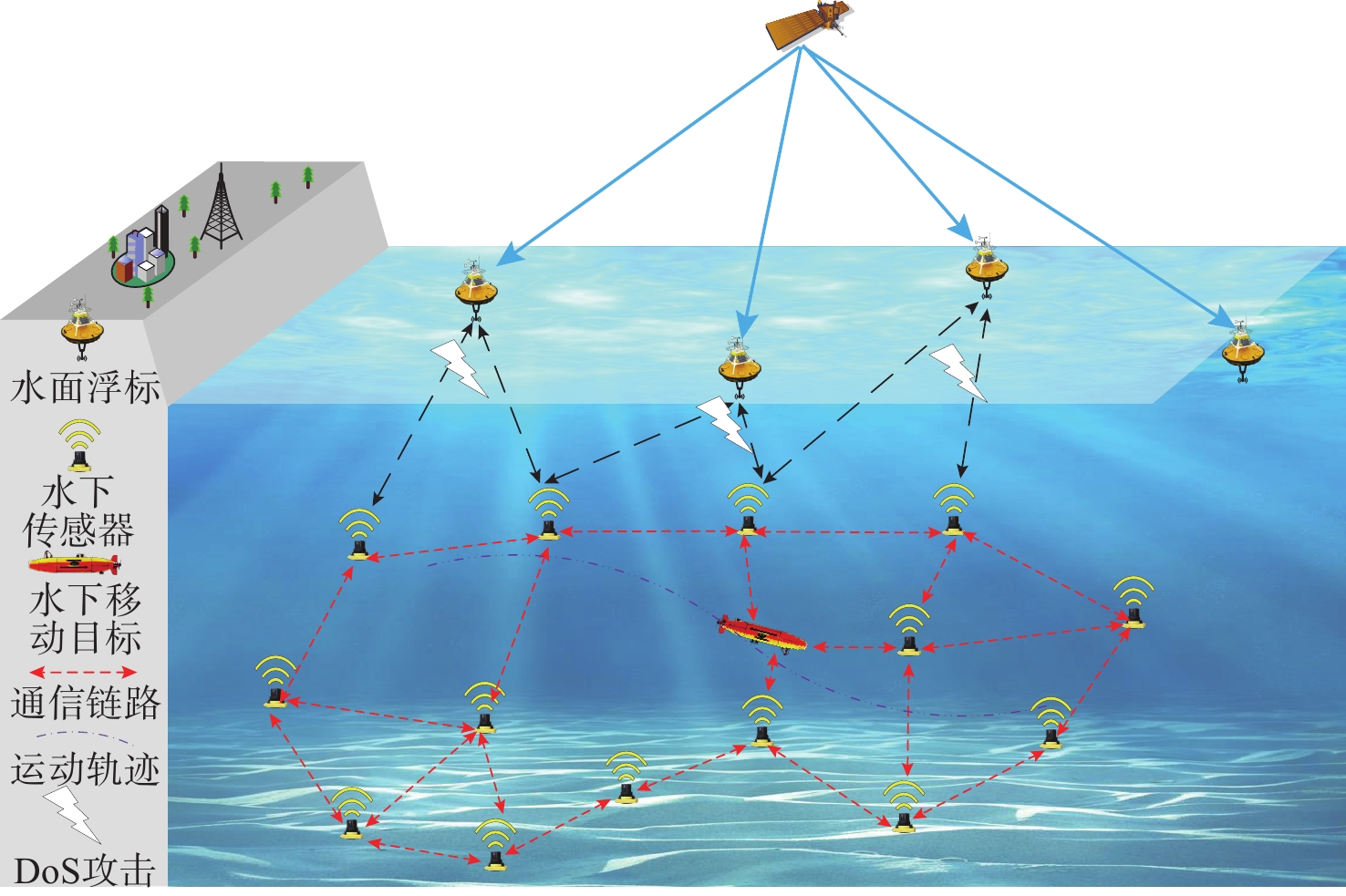
摘要: 考虑水下拒绝服务(DoS)攻击和声线分层效应的影响, 研究了基于水声传感器网络(UASN)的目标追踪问题。首先考虑由水下传感器、水面浮标和水下目标组成的UASN架构。基于此, 构造了水下目标运动模型和水下Dos攻击模型, 提出了一种改进的一致性无迹卡尔曼滤波(UKF)水下目标追踪算法。进一步, 证明了追踪算法的收敛性, 推导了算法的克拉美罗下界。仿真和实验结果表明, 文中算法可以在水下环境有效进行目标追踪, 基于一致性UKF的算法提高了跟踪精度。Abstract: By considering the effect of underwater denial of service(DoS) attack and sound line stratification, the problem of target tracking based on an underwater acoustic sensor network(UASN) was studied in this paper. Firstly, a UASN architecture consisting of underwater sensors, surface buoys, and underwater targets was developed. Then, the underwater target movement model and the underwater DoS attack model were constructed, and an improved consensus-based unscented Kalman filter(UKF) underwater target tracking algorithm was proposed. Finally, the Cramer-Rao lower bound of the algorithm was derived, and the effectiveness of the algorithm was proved. Simulation and experiments show that the proposed algorithm can track the target effectively in an underwater environment, and the consensus-based UKF algorithm improves tracking accuracy.
-
表 1 文中方法与已有研究的对比
Table 1. Comparison of the proposed method and the other existing literatures’
表 2 仿真参数列表
Table 2. Parameters of simulation
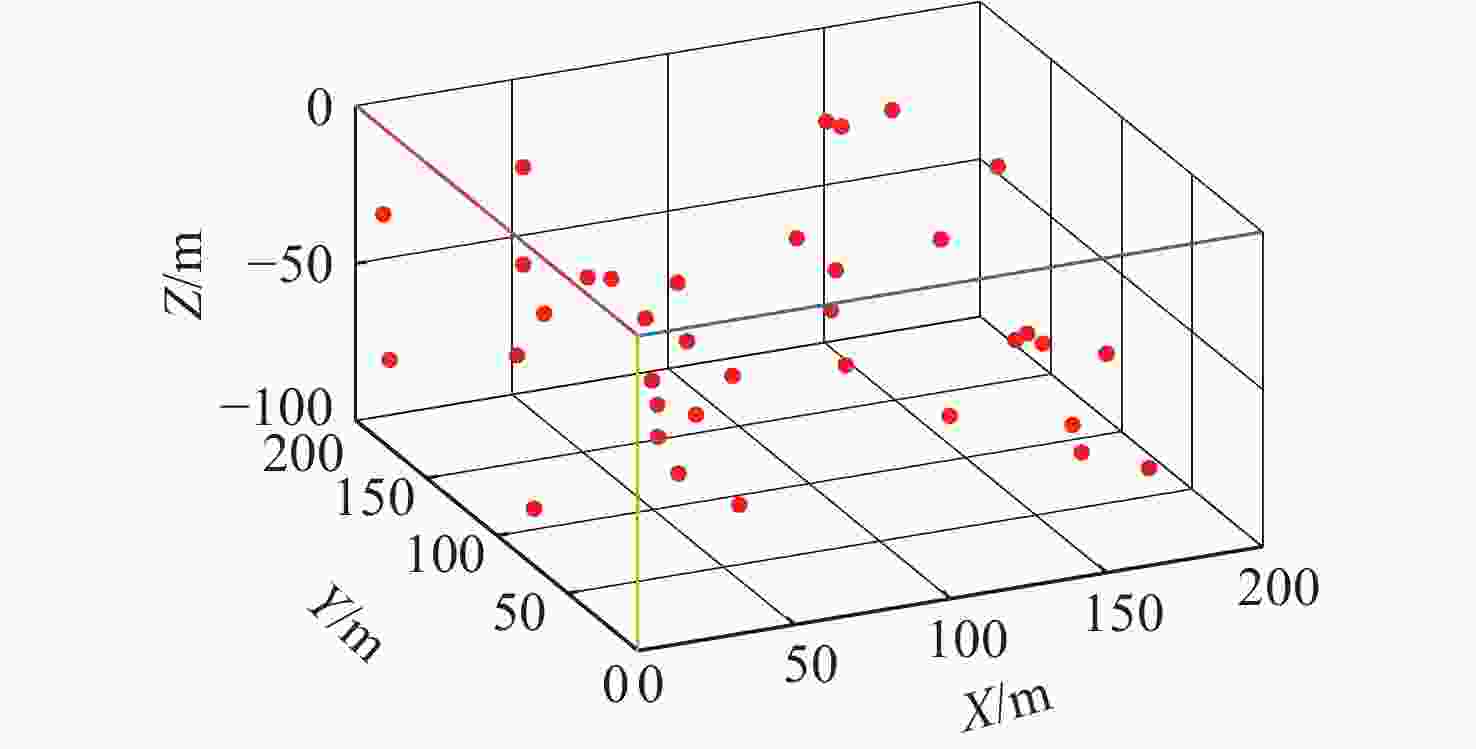
名称 数值 初始位置 [0 65 −50 5 5 0] 实验水域/m3 200×200×100 攻击参数 {1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0} 频率/Hz 21 000~27 000 通信速率/(bit/s) 300 循环次数 90 -
[1] GOLA K K, ARYA S. Underwater acoustic sensor networks: Taxonomy on applications, architectures, localization methods, deployment techniques, routing techniques, and threats: A systematic review[J]. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 2023, 35(23): 1-37. [2] ELIYEH M, RAZE J, MOHAMMAD J D, et al. A robust method for underwater wireless sensor joint localization and synchronization[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2017, 137: 276-286. [3] 孙海信, 何崇林, 王俊峰. 水下无线传感器网络抗恶意干扰技术应用及研究进展[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(1): 128-142. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2022-0090 [4] WEN L, YU S, ZHAO Y, et al. Event-based secure consensus of multiple AUVs under DoS attacks[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2022, 107(3): 2407-2419. doi: 10.1007/s11071-021-07113-8 [5] AMJAD A, MOHAMMAD A K, ABDULLCH A, et al. Securing low-power blockchain-enabled IoT devices against energy depletion attack[J]. ACM Transactions on Internet Technology, 2023, 23(3): 1-17. [6] GOPE P, LEE J, QUEK T Q S. Resilience of DoS attacks in designing anonymous user authentication protocol for wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors journal, 2016, 17(2): 498-503. [7] JISA D, CIZA T. Efficient DoS flood attack detection using dynamic thresholding on flow-based network traffic[J]. Computers & Security, 2019, 82: 284-295. [8] OLAKANMI O O, DADA A. Wireless sensor networks (WSNs): Security and privacy issues and solutions[J]. Wireless mesh networks-security, architectures and protocols, 2020, 13: 1-16. [9] BOUBICHE D E, ATHMANI S, BOUBICHE S, et al. Cybersecurity issues in wireless sensor networks: Current challenges and solutions[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2021, 117: 177-213. doi: 10.1007/s11277-020-07213-5 [10] GEBREYESUS G G. Localization and detection of multiple attacks in wireless sensor networks using artificial neural network[EB/OL]. (2023-01-10)[2023-12-23]. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1155/2023/2744706. [11] CREMERS C, RASMUSSEN K B, SCHMIDT B, et al. Distance hijacking attacks on distance bounding protocols[C]//2012 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. California, America: IEEE, 2012: 113-127. [12] DJURAEV S, CHOI J G, SOHN K S, et al. Channel hopping scheme to mitigate jamming attacks in wireless LANs[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2017, 2017(1): 1-12. doi: 10.1186/s13638-016-0795-x [13] TAN Z, JAMDAGNI A, HE X, et al. A system for denial-of-service attack detection based on multivariate correlation analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2013, 25(2): 447-456. [14] YAN J, MENG Y, LUO X, et al. To hide private position information in localization for internet of underwater things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(18): 14338-54. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3068298 [15] OLFATI S, SHAMMA J. Consensus filters for sensor networks and distributed sensor fusion[C]//IEEE Conference on Decision & Control. Seville, Spain: IEEE, 2005: 6698-703. [16] 闫敬, 陈天明, 关新平, 等. 自主水下航行器协同控制研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(1): 108-120. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2022-0096 [17] DAI P, YU W, WANG H, et al. Distributed reinforcement learning for cyber-physical system with multiple remote state estimation under DoS attacker[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2020, 7(4): 3212-22. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2020.3018871 [18] JULIER S J, UHLMANN J K. New extension of the Kalman filter to nonlinear systems[J]. Signal Processing, Sensor Fusion, and Target Recognition VI, 1997, 3068: 182-193. doi: 10.1117/12.280797 [19] YAN J, ZHAO H, LUO X, et al. Asynchronous localization of underwater target using consensus-based unscented Kalman filtering[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2019, 45(4): 1466-1481. [20] LEFEBVRE T, BRUYNINCKX H, DE SCHULLER J. Comment on“a new method for the nonlinear transformation of means and covariances in filters and estimators”[with authors’ reply][J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2002, 47(8): 1406-1409. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2002.800742 [21] YU Y, LIANG Y. Multisensor-multitarget tracking based on belief propagation against false data injection attacks and denial of service attacks[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2022, 126: 1-12. [22] LIU B, TANGY X, THARMARASA R, et al. Underwater target tracking in uncertain multipath ocean environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(6): 4899-4915. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3003703 -




 下载:
下载: