A Simplified Modeling Method of UVMS Dynamics Based on Quasi-Lagrange Equation
-
摘要: 作为一种具有强非线性、强耦合、时变、冗余且高维度的复杂系统, 水下机器人-机械臂系统(UVMS)的建模、运动控制和稳定性研究都具有较大的难度。在动力学建模中, 对于自由度较高的复杂UVMS, 采用传统拉格朗日方程建模, 需要对广义坐标向量和其导数分别进行求导和求偏导操作, 会面临符号求导计算量大、建模效率低等问题。因此, 文中基于类拉格朗日方法提出一种适用于6+n自由度UVMS的动力学简化建模方法, 以减少符号化公式推导的运算量, 提高建模效率与结果的准确性。最后结合BlueROV水下机器人与Reach Alpha水下机械臂的实物参数对所建立的模型进行了数值仿真, 实验结果验证了UVMS的复杂耦合性。基于文中方法建立的动力学模型具有明确、清晰的方程形式, 能够为控制算法研究与耦合力优化提供有力支撑, 为动力学参数设计与轨迹规划研究提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 水下机器人-机械臂系统 /
- 类拉格朗日方程 /
- 简化建模
Abstract: As a kind of complex system with strong nonlinearity, strong coupling, time variance, redundancy, and high dimension, the modeling, motion control, and stability analysis of an underwater vehicle-manipulator system(UVMS) are very challenging. In dynamics modeling, the traditional Lagrange equation is often used to model the complex UVMS with high degrees of freedom, which requires the operation of derivation and partial derivation of the generalized coordinates and their derivatives and will face the problems of a large amount of calculation and low modeling efficiency. Therefore, this paper proposed a simplified dynamics modeling method for UVMS with 6+n degree-of-freedom based on the quasi-Lagrange equation, which could reduce the amount of calculation in the symbolic formula derivation and improve the modeling efficiency and the accuracy of the results. Finally, the numerical simulation of a UVMS model was carried out with the physical parameters of the underwater vehicle BlueROV and the underwater manipulator Reach Alpha, and the simulation results verified the complex coupling of the UVMS. The dynamics model based on the proposed method had a clear equation form, which not only provided strong support for the study of control algorithms and the optimization of coupling forces but also a basis for the design of dynamics parameters and the study of trajectory planning. -
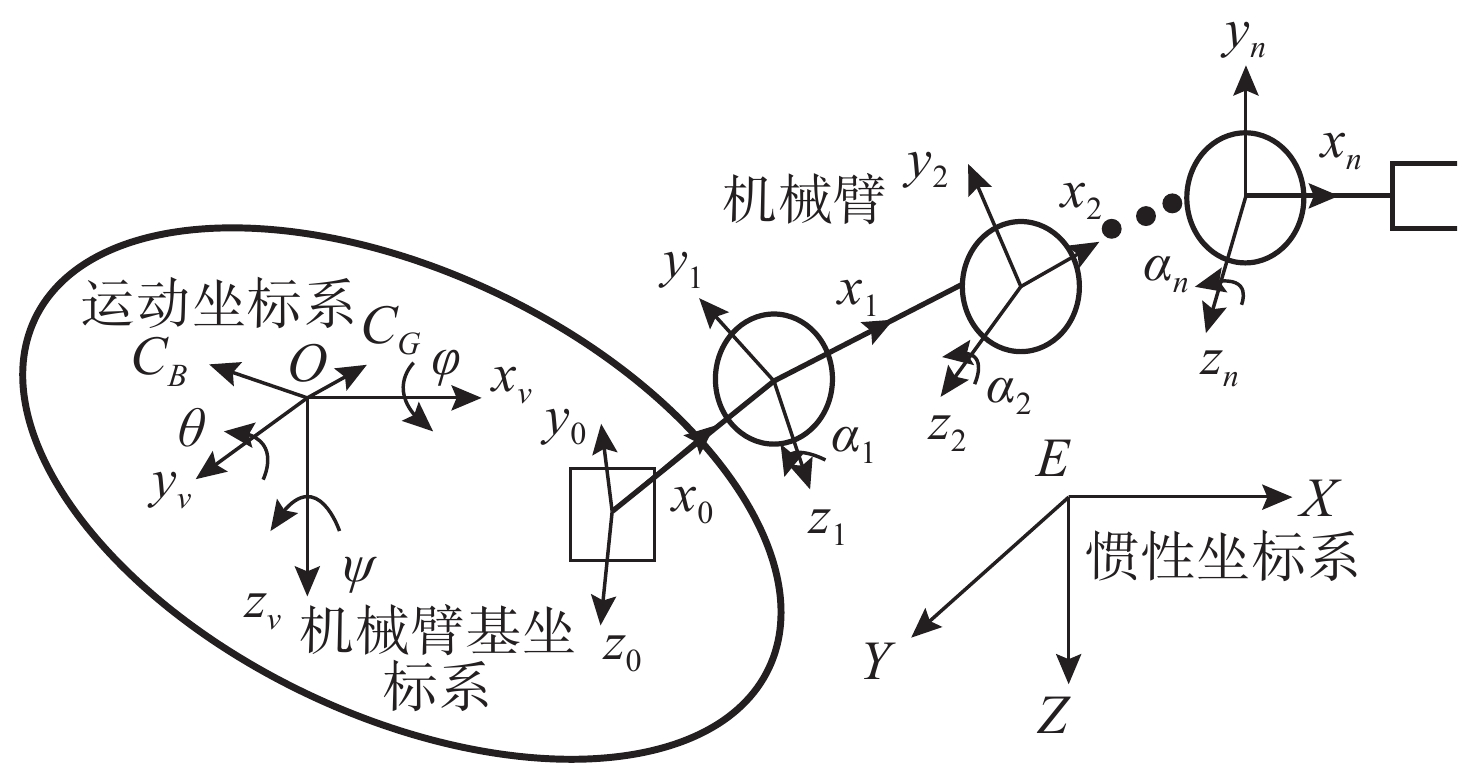
表 1 UVMS相关符号说明
Table 1. Description of symbols related to the UVMS
位置/姿态角/关节变量
(平动/转动)线速度/角速度/
关节速度力/力矩/
关节力(矩)x u X y v Y z w Z $\phi $ p K $\theta $ q M $\psi $ r N $ {\alpha _1} $ $ {\dot \alpha _1} $ ${Q_1}$ $ {\alpha _2} $ $ {\dot \alpha _2} $ ${Q_2}$ ··· ··· ··· $ {\alpha _n} $ $ {\dot \alpha _n} $ ${Q_n}$ -
[1] 杨波, 刘烨瑶, 廖佳伟. 载人潜水器——面向深海科考和海洋资源开发利用的“国之重器”[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2021, 36(5): 622-631.YANG B, LIU Y Y, LIAO J W. Manned submersible——the most important weapon of the country for deep-sea scientific research and marine resources development and utilization[J]. Proceedings of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021, 36(5): 622-631. [2] ZHANG H, ZHANG S, WANG Y, et al. Subsea pipeline leak inspection by autonomous underwater vehicle[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2021, 107: 102321. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2020.102321 [3] 王涛. 水下机器人ROV在石油行业的维修技术研究[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2023, 43(19): 184-186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2023.19.059WANG T. Research on maintenance technology of ROV in petroleum industry[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Standards and Quality, 2023, 43(19): 184-186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2023.19.059 [4] LI B, WANG Y, ZHU K, et al. Structure design and control research of a novel underwater cable-driven manipulator for autonomous underwater vehicles[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part M: Journal of Engineering for the Maritime Environment, 2020, 234(1): 170-180. doi: 10.1177/1475090219851948 [5] GAO L, SONG Y, GAO J, et al. Dynamic modeling and simulation an underwater vehicle manipulator system[C]//2022 IEEE 9th International Conference on Underwater System Technology: Theory and Applications(USYS). Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: IEEE, 2022: 1-6. [6] XIONG X, XIANG X, WANG Z, et al. On dynamic coupling effects of underwater vehicle-dual-manipulator system[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 258: 111699. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.111699 [7] SHAH U H, KARKOUB M, KERIMOGLU D, et al. Dynamic analysis of the UVMS: Effect of disturbances, coupling, and joint-flexibility on end-effector positioning[J]. Robotica, 2021, 39(11): 1952-1980. doi: 10.1017/S0263574721000072 [8] TARN T J, SHOULTS G A, YANG S P. A dynamic model of an underwater vehicle with a robotic manipulator using Kane's method[J]. Autonomous Robots, 1996, 3(2-3): 269-283. doi: 10.1007/BF00141159 [9] HAN H, WEI Y, YE X, et al. Modeling and fuzzy decoupling control of an underwater vehicle-manipulator system[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 18962-83. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2968063 [10] ZHU Q, SHANG H Q, LU X, et al. Adaptive sliding mode tracking control of underwater vehicle-manipulator systems considering dynamic disturbance[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 291: 116300. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.116300 [11] SARKAR N, PODDER T K. Coordinated motion planning and control of autonomous underwater vehicle-manipulator systems subject to drag optimization[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2001, 26(2): 228-239. doi: 10.1109/48.922789 [12] MEIROVITCH L. Methods of analytical dynamics[M]. New York: Courier Corporation, 2010. [13] FOSSEN T I. Guidance and control of ocean vehicles[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 1994. [14] CRAIG J J. 机器人学导论[M]. 3版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2006. [15] MARAIS W J, WILLIAMS S B, PIZARRO O. Go with the flow: Energy minimising periodic trajectories for UVMS[C]//2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation(ICRA). Philadelphia, PA, USA: IEEE, 2022. -





 下载:
下载: